Submitted:
10 October 2024
Posted:
11 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Type I Interferon Signaling Activation by DNA-Binding PSMs
2.1.1. PSM Influence on Reporter mCherry Expression Driven by IFN-Sensitive Response Element
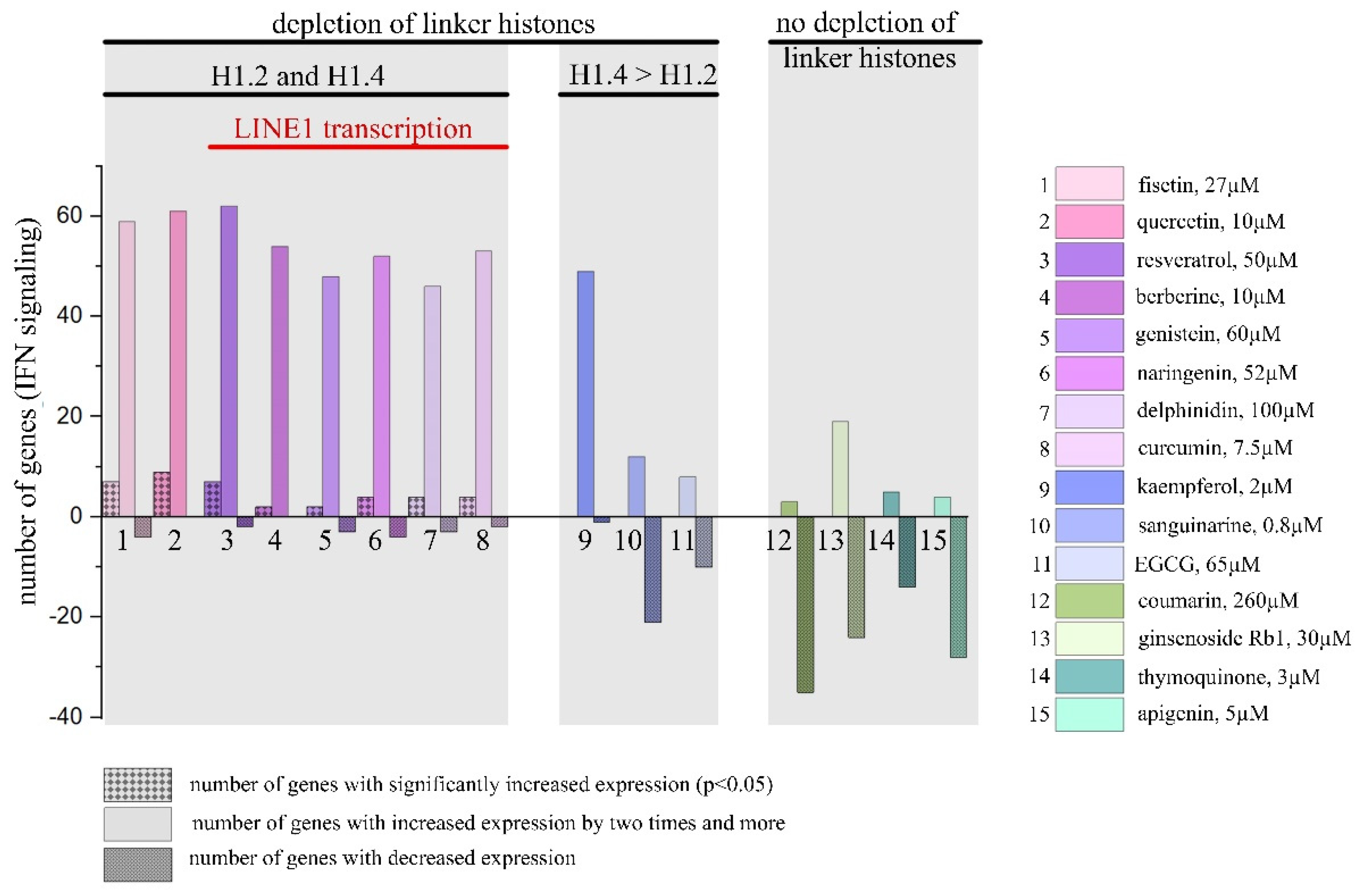
2.1.2. Influence of PSMs on the Expression Pattern of IFN-Responsive Genes
2.2. Induction of LINE1 Expression by Some PSMs
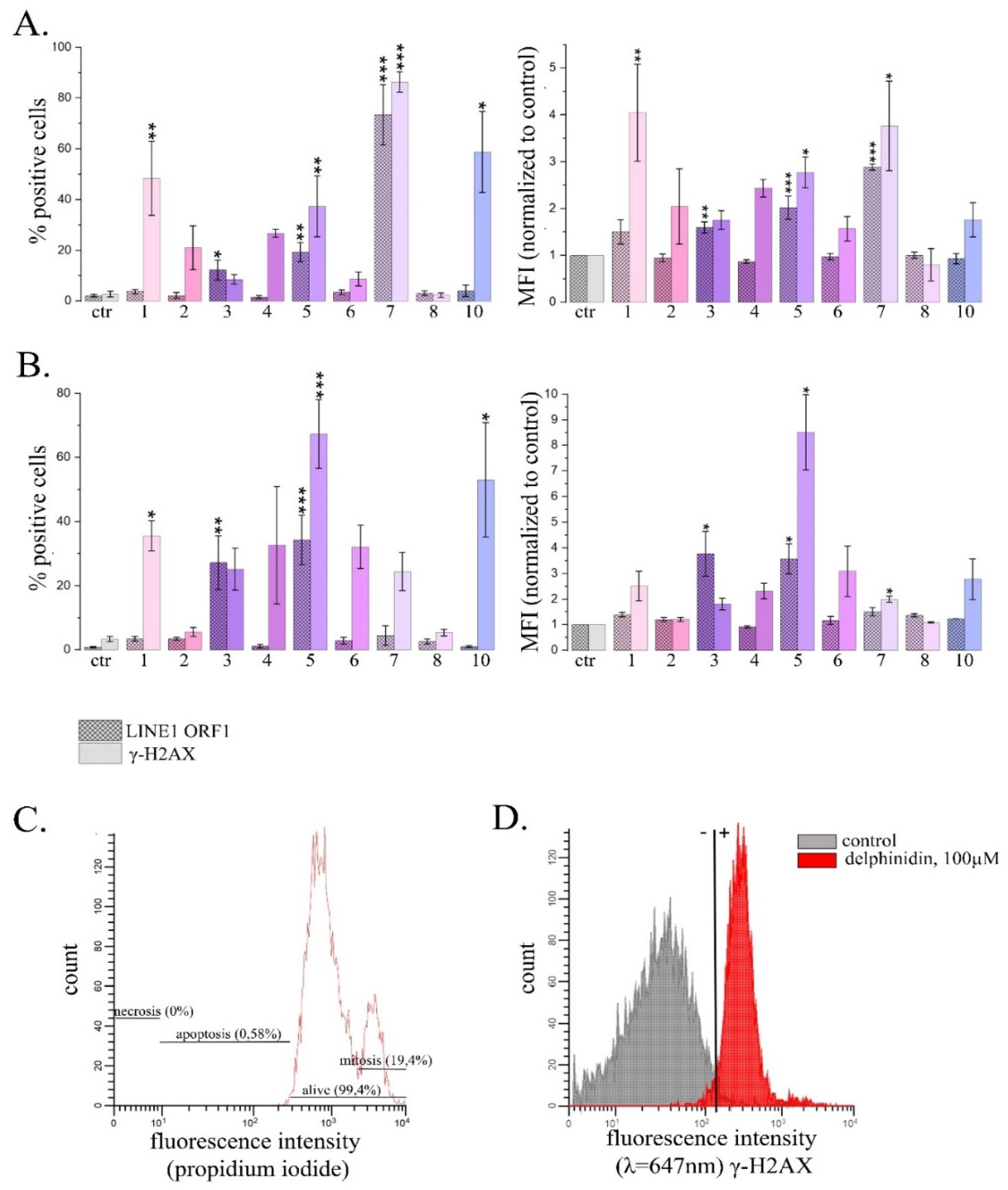
2.2.1. Quantitative Estimation of LINE1 Expression Level in HeLa Cells Treated with PSMs
2.2.2. Analysis of the Amount of ORF1 LINE1 and γ-H2AX Proteins by Flow Cytometry in HeLa Cells Treated with PSM.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Plant Secondary Metabolites
4.3. Other Chemicals and Reagents
4.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction for Analysis of Expression of LINE1 and PSM-Induced Interferon Signaling
4.5. Analysis of ISRE-mCherry Reporter Activation in HeLa-TI-ISRE-mCherry Cells by Flow Cytometry
4.6. Analysis of PSM Induced LINE1 Activation by Immunofluorescent Antibody Staining and Flow Cytometry
4.7. Annexin-FITC/Propidium Iodide Double Staining
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, S. Effect of genistein on in vitro and in vivo models of cancer. The Journal of Nutrition. 1995. 125, 3 Suppl, 777S-783S. [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, A. Cancer prevention and treatment with resveratrol: from rodent studies to clinical trials. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.). 2009. 409–418. [CrossRef]
- Kisková, T., Ekmekcioglu, C., Garajová, M. et al. A combination of resveratrol and melatonin exerts chemopreventive effects in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced rat mammary carcinogenesis. European journal of cancer prevention: the official journal of the European Cancer Prevention Organisation (ECP). 2012. 21, 2, 163–170. [CrossRef]
- Whitsett, T. G. and Lamartiniere, C. A. Genistein and resveratrol: mammary cancer chemoprevention and mechanisms of action in the rat. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy. 2006. 6, 12, 1699–1706. [CrossRef]
- Fantini, M., Benvenuto, M., Masuelli, L. et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Antitumoral Effects of Combinations of Polyphenols, or Polyphenols and Anticancer Drugs: Perspectives on Cancer Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015. 16, 5, 9236–9282. [CrossRef]
- Jantan, I., Ahmad, W. and Bukhari, S. N. A. Plant-derived immunomodulators: an insight on their preclinical evaluation and clinical trials. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2015. 6, 655. [CrossRef]
- Pezzuto, J. M. Resveratrol: Twenty Years of Growth, Development and Controversy. Biomolecules & Therapeutics. 2019. 27, 1, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Russo, M., Russo, G. L., Daglia, M. et al. Understanding genistein in cancer: The “good” and the “bad” effects: A review. Food Chemistry. 2016. 196, 589–600. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X., Gao, Q.-Y., Zou, T.-H. et al. Berberine versus placebo for the prevention of recurrence of colorectal adenoma: a multicentre, double-blinded, randomised controlled study. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2020. 5, 3, 267–275. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R., Williams, M., Sharma, H. et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial evaluating the effect of a polyphenol-rich whole food supplement on PSA progression in men with prostate cancer—the UK NCRN Pomi-T study. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases. 2014. 17, 2, 180–186. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., Gordon, R., Li, W. et al. Genistein treatment duration effects biomarkers of cell motility in human prostate. PLOS ONE. 2019. 14, 3, e0214078. [CrossRef]
- Britton, R. G. Kovoor, C. and Brown, K. Direct molecular targets of resveratrol: identifying key interactions to unlock complex mechanisms: Direct molecular targets of resveratrol. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2015. 1348, 1, 124–133. [CrossRef]
- Khan, F., Niaz, K., Maqbool, F. et al. Molecular Targets Underlying the Anticancer Effects of Quercetin: An Update. Nutrients. 2016. 8, 9, 529. [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, G. P. Zafar, S. F. and El-Rayes, B. F. Pleiotropic effects of genistein in metabolic, inflammatory, and malignant diseases. Nutrition Reviews. 2013. 71, 8, 562–572. [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M. I., Naqvi, S. T. Q. and Muhammad, S. A. Curcumin: a Polyphenol with Molecular Targets for Cancer Control. Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP. 2016. 17, 6, 2735–2739.
- N’soukpoé-Kossi, C. N., Bourassa, P., Mandeville, J. S. et al. Structural modeling for DNA binding to antioxidants resveratrol, genistein and curcumin. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology. 2015. 151, 69–75. [CrossRef]
- Kanakis, C. D., Tarantilis, P. A., Polissiou, M. G. and Tajmir-Riahi, H.-A. Interaction of Antioxidant Flavonoids with tRNA: Intercalation or External Binding and Comparison with Flavonoid-DNA Adducts. DNA and Cell Biology. 2006. 25, 2, 116–123. [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, S. Hashemi, M., Rajabi, M. and Tajmir-Riahi, H. A. DNA Adducts with Antioxidant Flavonoids: Morin, Apigenin, and Naringin. DNA and Cell Biology. 2008. 27, 8, 433–442. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. Chakraborty, S., Sengupta, P. K. and Bhowmik, S. Exploring the Interactions of the Dietary Plant Flavonoids Fisetin and Naringenin with G-Quadruplex and Duplex DNA, Showing Contrasting Binding Behavior: Spectroscopic and Molecular Modeling Approaches. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B. 2016. 120, 34, 8942–8952. [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Murillo, R. and Cheatham, T. E. Computational DNA binding studies of (–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics. 2018. 36, 13, 3311–3323. [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S. Kukreti, S. and Kaushik, M. Designing a two-stage colorimetric sensing strategy based on citrate reduced gold nanoparticles: Sequential detection of Sanguinarine (anticancer drug) and visual sensing of DNA. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy. 2021. 246, 119039. [CrossRef]
- Basu, A. and Kumar, G. S. Biophysical studies on curcumin–deoxyribonucleic acid interaction: Spectroscopic and calorimetric approach. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2013. 62, 257–264. [CrossRef]
- Pandya, N. Khan, E., Jain, N. et al. Curcumin analogs exhibit anti-cancer activity by selectively targeting G-quadruplex forming c-myc promoter sequence. Biochimie. 2021. 180, 205–221. [CrossRef]
- Mikutis, G., Karaköse, H., Jaiswal, R. et al. Phenolic promiscuity in the cell nucleus--epigallocatechingallate (EGCG) and theaflavin-3,3′-digallate from green and black tea bind to model cell nuclear structures including histone proteins, double stranded DNA and telomeric quadruplex DNA. Food & Function. 2013. 4, 2, 328–337. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S., Chakraborty, S., Chorell, E. et al. Importance of the hydroxyl substituents in the B–ring of plant flavonols on their preferential binding interactions with VEGF G–quadruplex DNA: Multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2018. 118, 629–639. [CrossRef]
- Dickerhoff, J., Brundridge, N., McLuckey, S. A. and Yang, D. Berberine Molecular Recognition of the Parallel MYC G-Quadruplex in Solution. Journal of medicinal chemistry. 2021. 64, 21, 16205–16212. [CrossRef]
- Jarosova, P., Paroulek, P., Rajecky, M. et al. Naturally occurring quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids selectively stabilize G-quadruplexes. Physical chemistry chemical physics: PCCP. 2018. 20, 33, 21772–21782. [CrossRef]
- Tawani, A. Mishra, S. K. and Kumar, A. Structural insight for the recognition of G-quadruplex structure at human c-myc promoter sequence by flavonoid Quercetin. Scientific Reports. 2017. 7, 3600. [CrossRef]
- Salem, A. A., El Haty, I. A., Abdou, I. M. and Mu, Y. Interaction of human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA with thymoquinone: A possible mechanism for thymoquinone anticancer effect. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)—General Subjects. 2015. 1850, 2, 329–342. [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, O., Antonova, I., Zenkov, R. et al. Anticancer Plant Secondary Metabolites Induce Linker Histone Depletion from Chromatin. Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, 2024, 29(7). [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Bouldstridge, A., Bustillos, A., Bonet-Costa, C. et al. Histone H1 depletion triggers an interferon response in cancer cells via activation of heterochromatic repeats. Nucleic Acids Research. 2017. 45, 20, 11622. [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Pena M, Serna-Pujol N, Jordan A. Genomic profiling of six human somatic histone H1 variants denotes that H1X accumulates at recently incorporated transposable elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 28;52(4):1793-1813. [CrossRef]
- Healton, S. E., Pinto, H. D., Mishra, L. N. et al. H1 linker histones silence repetitive elements by promoting both histone H3K9 methylation and chromatin compaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020. 117(25):14251-14258. [CrossRef]
- Leonova, K., Safina, A., Nesher, E., Sandlesh, P. et al. TRAIN (Transcription of Repeats Activates INterferon) in response to chromatin destabilization induced by small molecules in mammalian cells. Elife. 2018. 7:e30842. [CrossRef]
- Stilp, A. C., Scherer, M., König, P., Fürstberger, A. et al. The chromatin remodeling protein ATRX positively regulates IRF3-dependent type I interferon production and interferon-induced gene expression. PLoS Pathog. 2022. 18(8):e1010748. [CrossRef]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005. 5(5):375-86. [CrossRef]
- Petrova, L., Bunz, F. Interferons in Colorectal Cancer Pathogenesis and Therapy. Dis Res. 2024. 4(1):31-39. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F. and Gong, Z. The Beneficial Roles of SIRT1 in Neuroinflammation-Related Diseases. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2020. 6782872. [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A., Nicosia, N., Fumia, A. et al. Resveratrol and Immune Cells: A Link to Improve Human Health. Molecules. 2022. 27, 2, 424. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J., Zeng, Q., Wu, Z. et al. Berberine inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and proinflammatory macrophage M1 polarization to accelerate peripheral nerve regeneration. Neurotherapeutics. 2024. 21, 4, e00347. [CrossRef]
- Warowicka, A., Nawrot, R. and Goździcka-Józefiak, A. Antiviral activity of berberine. Archives of Virology. 2020. 165, 9, 1935–1945. [CrossRef]
- Lani, R., Teoh, B.-T., Sam, S.-S. et al. Fisetin Modulates Toll-like Receptor-Mediated Innate Antiviral Response in Chikungunya Virus-Infected Hepatocellular Carcinoma Huh7 Cells. Immuno. 2022. 2, 4, 703–719. [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H., Saeki, A., Hasebe, A. et al. Naringenin suppresses Toll-like receptor 2-mediated inflammatory responses through inhibition of receptor clustering on lipid rafts. Food Science & Nutrition. 2020. 9, 2, 963–972. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J., Shi, H., Song, K. et al. Naringenin Improves Innate Immune Suppression after PRRSV Infection by Reactivating the RIG-I-MAVS Signaling Pathway, Promoting the Production of IFN-I. Viruses. 2023. 15, 11, 2172. [CrossRef]
- Sunthamala, N., Suebsamran, C., Khruaphet, N. et al. Sanguinarine and Chelidonine Synergistically Induce Endosomal Toll-like Receptor and M1-Associated Mediators Expression. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology. 2020. 14(4):2351-2361. [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, S. and Helen, A. Quercetin modulates toll-like receptor-mediated protein kinase signaling pathways in oxLDL-challenged human PBMCs and regulates TLR-activated atherosclerotic inflammation in hypercholesterolemic rats. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2016. 423, 1–2, 53–65. [CrossRef]
- De Cecco, M., Ito, T., Petrashen, A. P., Elias, A.E. et al. L1 drives IFN in senescent cells and promotes age-associated inflammation. Nature. 2019. 566(7742):73-78. [CrossRef]
- Zenkov, R. G., Kirsanov, K. I., Ogloblina, A. M., Vlasova, O. A. et al. Effects of G-Quadruplex-Binding Plant Secondary Metabolites on c-MYC Expression. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. 23(16):9209. [CrossRef]
- Amarante-Mendes, G. P., Adjemian, S., Branco, L. M. et al. Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Host Cell Death Molecular Machinery. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 2379. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F., Gong, Z. The Beneficial Roles of SIRT1 in Neuroinflammation-Related Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. 2020:6782872. [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, A. M. Paul Ehrlich’s passion: the origins of his receptor immunology. Cell Immunol. 1999. 194(2):213-21. [CrossRef]
- Matzinger, P. Tolerance, danger, and the extended family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994. 12:991-1045. [CrossRef]
- Matzinger, P. The danger model: a renewed sense of self. Science. 2002. 296(5566):301-5. [CrossRef]
- Ancona, G., Alagna, L., Alteri, C. et al. Gut and airway microbiota dysbiosis and their role in COVID-19 and long-COVID. Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1080043. [CrossRef]
- Stetson, D. B., Medzhitov, R. Type I interferons in host defense. Immunity. 2006. 25(3):373-81. [CrossRef]
- Seo, D. J., Choi, C. Inhibitory mechanism of five natural flavonoids against murine norovirus. Phytomedicine. 2017 Jul. 30:59-66. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. J., Lin, H. J., Chen, T.H. et al. Polygonum cuspidatum and its active components inhibit replication of the influenza virus through toll-like receptor 9-induced interferon beta expression. PLoS One. 2015. 6;10(2):e0117602. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. H., Weeratunga, P., Kim, M. S. et al. Inhibitory effects of an aqueous extract from Cortex Phellodendri on the growth and replication of broad-spectrum of viruses in vitro and in vivo. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. 16:265. [CrossRef]
- Fast, D. J., Stern, N. P., Chuang, J. et al. Flavanones common to citrus fruits activate the interferon-stimulated response element by stimulating expression of IRF7. Journal of Food Bioactives. 2019. 8. [CrossRef]
- Akash, S., Bayil, I., Rahman, Md A. et al. Target specific inhibition of West Nile virus envelope glycoprotein and methyltransferase using phytocompounds: an in silico strategy leveraging molecular docking and dynamics simulation. Front. Microbiol. 2023. 14. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, T. R., Balka, K. R., Ambrose, R. L et al. Genistein Targets STING-Driven Antiviral Responses. mBio. 2022. 13(4):e0206422. [CrossRef]
- LeCher, J. C, Diep, N., Krug, P. W., Hilliard, J. K. Genistein Has Antiviral Activity against Herpes B Virus and Acts Synergistically with Antiviral Treatments to Reduce Effective Dose. Viruses. 2019. 11(6):499. [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N., Son, Y. J., Cho, J. Y. Thymoquinone Suppresses IRF-3-Mediated Expression of Type I Interferons via Suppression of TBK1. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. 19(5):1355. [CrossRef]
- Lee, M. H., Seo, D. J., Kang, J. H. et al. Expression of antiviral cytokines in Crandell-Reese feline kidney cells pretreated with Korean red ginseng extract or ginsenosides. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. 70:19-25. [CrossRef]
- Li, S., Yang, L. J., Wang, P. et al. Dietary apigenin potentiates the inhibitory effect of interferon-α on cancer cell viability through inhibition of 26S proteasome-mediated interferon receptor degradation. Food Nutr Res. 2016. 60:31288. [CrossRef]
- Volkman, H. E., Stetson, D. B. The enemy within: endogenous retroelements and autoimmune disease. Nat Immunol. 2014. 15(5):415-22. [CrossRef]
- Molagoda, I. M. N., Athapaththu, A. M. G. K, Choi, Y. H. et al. Fisetin Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome by Suppressing TLR4/MD2-Mediated Mitochondrial ROS Production. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. 10(8):1215. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K., Yang, J., Xue, G. et al. Fisetin Ameliorates the Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endometritis. J Inflamm Res. 2021. 14:2963-2978. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X., Shen, H., Liu, Y. et al. Fisetin attenuates periodontitis through FGFR1/TLR4/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. 95:107505. [CrossRef]
- Lani, R., Teoh, B.-T., Sam, S.-S. et al. Fisetin Modulates Toll-like Receptor-Mediated Innate Antiviral Response in Chikungunya Virus-Infected Hepatocellular Carcinoma Huh7 Cells. Immuno. 2022. 2: 703-719. [CrossRef]
- Domiciano, T. P., Wakita, D., Jones, H.D. et al. Quercetin Inhibits Inflammasome Activation by Interfering with ASC Oligomerization and Prevents Interleukin-1 Mediated Mouse Vasculitis. Sci Rep. 2017. 7:41539. [CrossRef]
- Alattar, A., Alshaman, R., Althobaiti, Y. S. et al. Quercetin Alleviated Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis and Modulated the mTOR/P70S6/P6/eIF4E/4EBP1 Pathway in Ischemic Stroke. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. 16(8):1182. [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, L. Influence of Resveratrol on the Immune Response. Nutrients. 2019. 11(5):946. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., Bellot, G. L., Iskandar, K. et al. Resveratrol attenuates TLR-4 mediated inflammation and elicits therapeutic potential in models of sepsis. Sci Rep. 2020. 10(1):18837. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J. W., Lee, H. H., Han, M. H. et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of genistein via suppression of the toll-like receptor 4-mediated signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia. Chem Biol Interact. 2014. 212:30-9. [CrossRef]
- Bae, C. H., Jeon, B. S., Choi, Y. S. et al. Delphinidin Inhibits LPS-Induced MUC8 and MUC5B Expression Through Toll-like Receptor 4-Mediated ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2014. 7(3):198-204. [CrossRef]
- Shen, X. Y., Liu, X. P., Song, C. K. et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals alcohol dehydrogenase 1C and secreted phosphoprotein 1 for prognostic biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 2019. 234(12):22311-22320. [CrossRef]
- Chang, S., Li, X., Zheng, Y. et al. Kaempferol exerts a neuroprotective effect to reduce neuropathic pain through TLR4/NF-ĸB signaling pathway. Phytother Res. 2022. 36(4):1678-1691. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y. Y., Liu, Y., Hu, Z. F. et al. Sanguinarine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-induced Inflammation and Apoptosis by Inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in H9c2 Cardiomyocytes. Curr Med Sci. 2018. 38(2):204-211. [CrossRef]
- Sunthamala, N., Suebsamran, C., Khruaphet, N. et al. Sanguinarine and Chelidonine synergistically induce endosomal toll-like receptor and M1-associated mediators expression. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020. 14, 2351–2361. [CrossRef]
- Bao, S., Cao, Y., Zhou, H. et al. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) activity via 67 kDa laminin receptor (67LR) in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. 63(10):2811-9. [CrossRef]
- Kim, A., Lee, C. S. Apigenin reduces the Toll-like receptor-4-dependent activation of NF-κB by suppressing the Akt, mTOR, JNK, and p38-MAPK. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018. 391(3):271-283. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B., Zhang, S., Amin, N. et al. Thymoquinone regulates microglial M1/M2 polarization after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via the TLR4 signaling pathway. Neurotoxicology. 2024. 101:54-67. [CrossRef]
- Gao, H., Kang, N., Hu, C. et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in vivo by modulating toll-like receptor 4 dimerization and NF-kB/MAPKs signaling pathways. Phytomedicine. 2020. 69:153197. [CrossRef]
- Rostom, B., Karaky, R., Kassab, I., Sylla-Iyarreta Veitía, M. Coumarins derivatives and inflammation: Review of their effects on the inflammatory signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. 922:174867. [CrossRef]
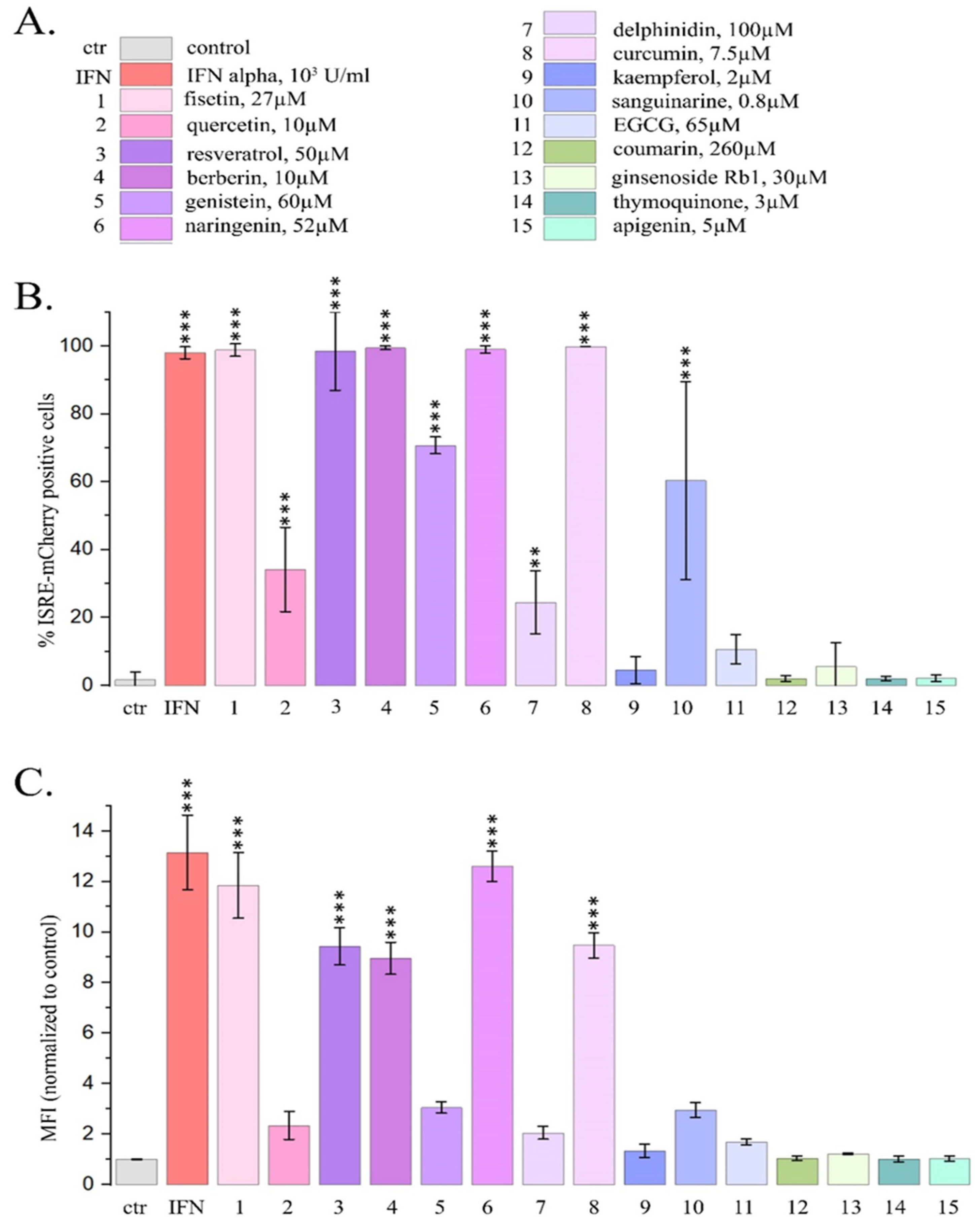
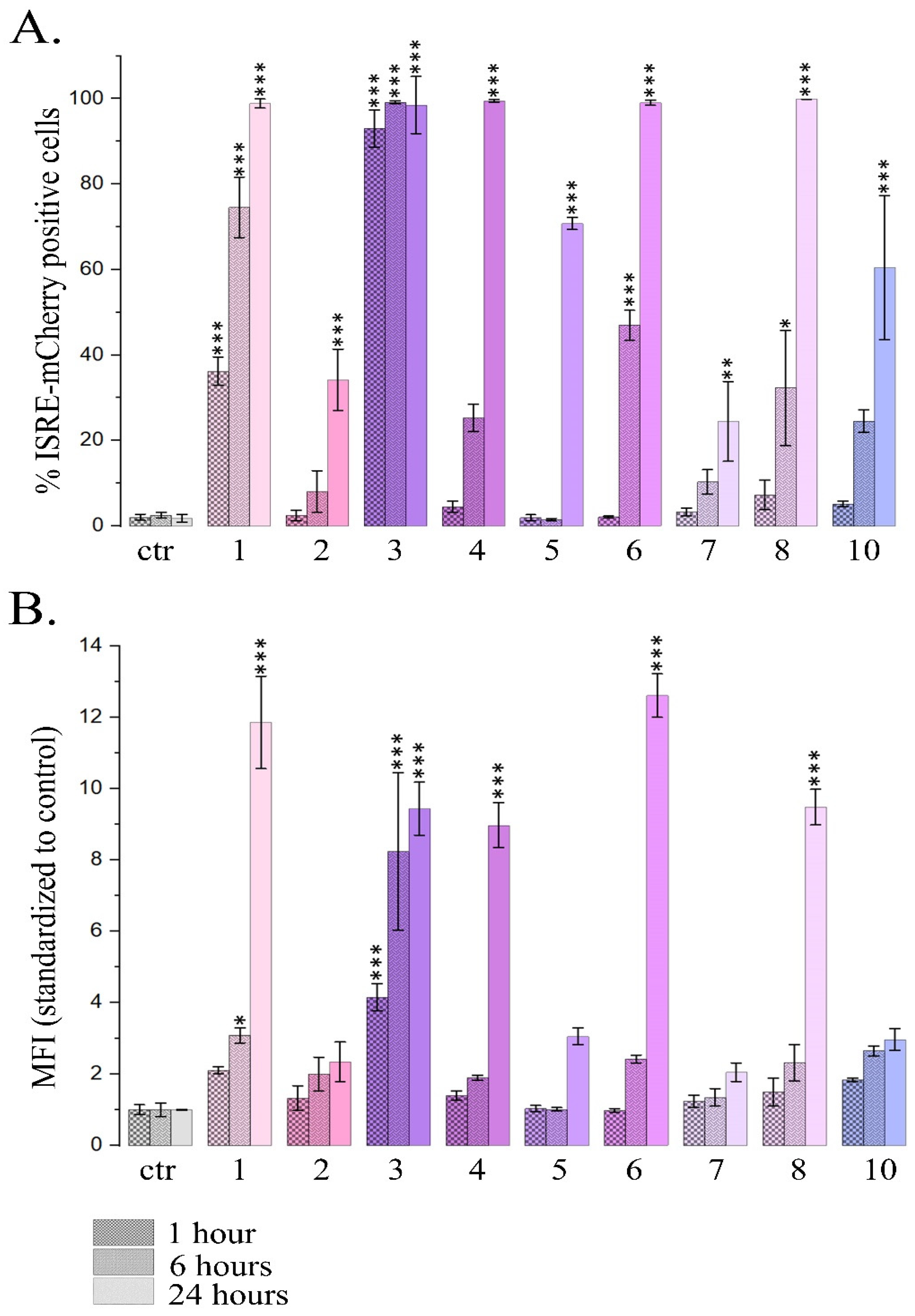
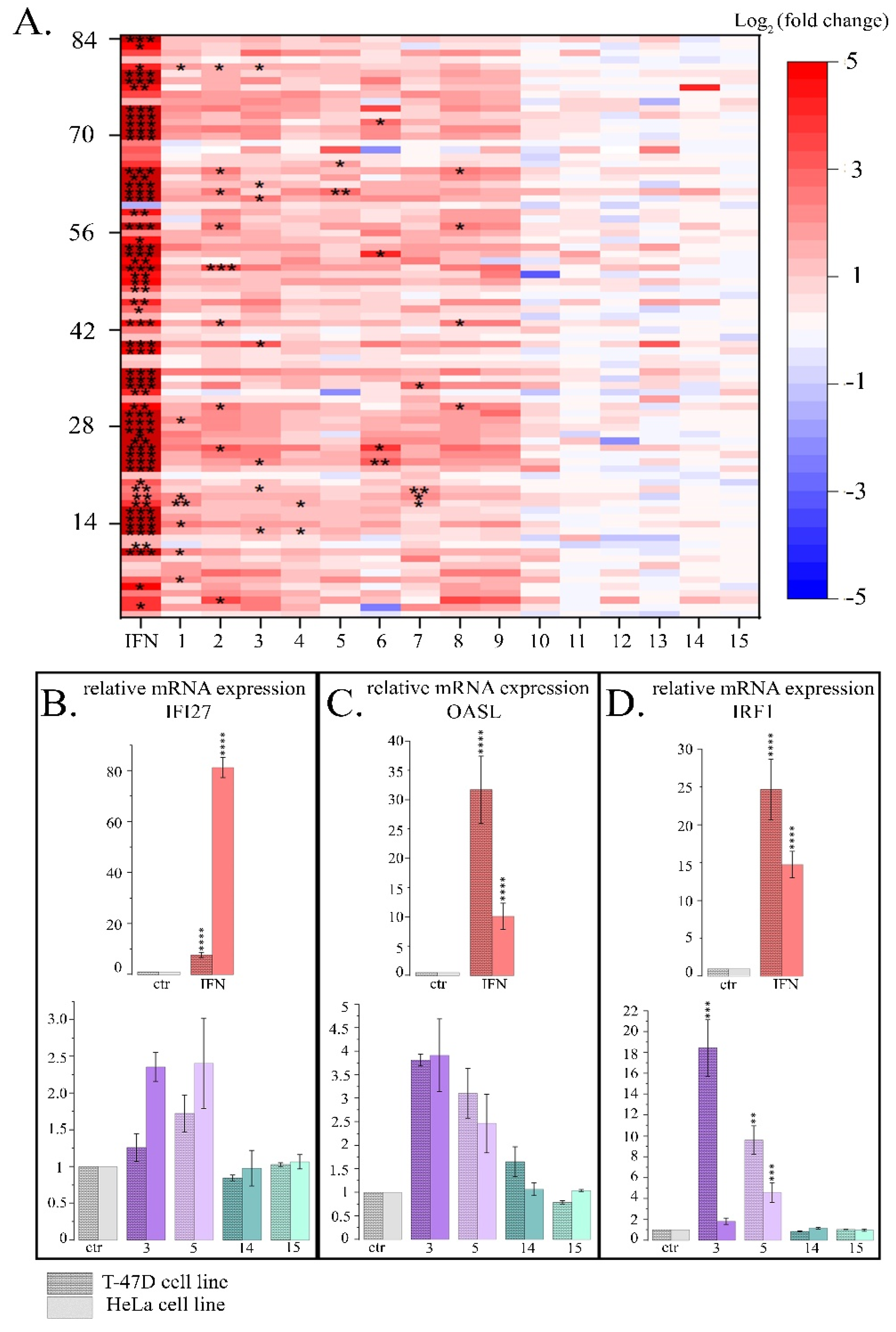
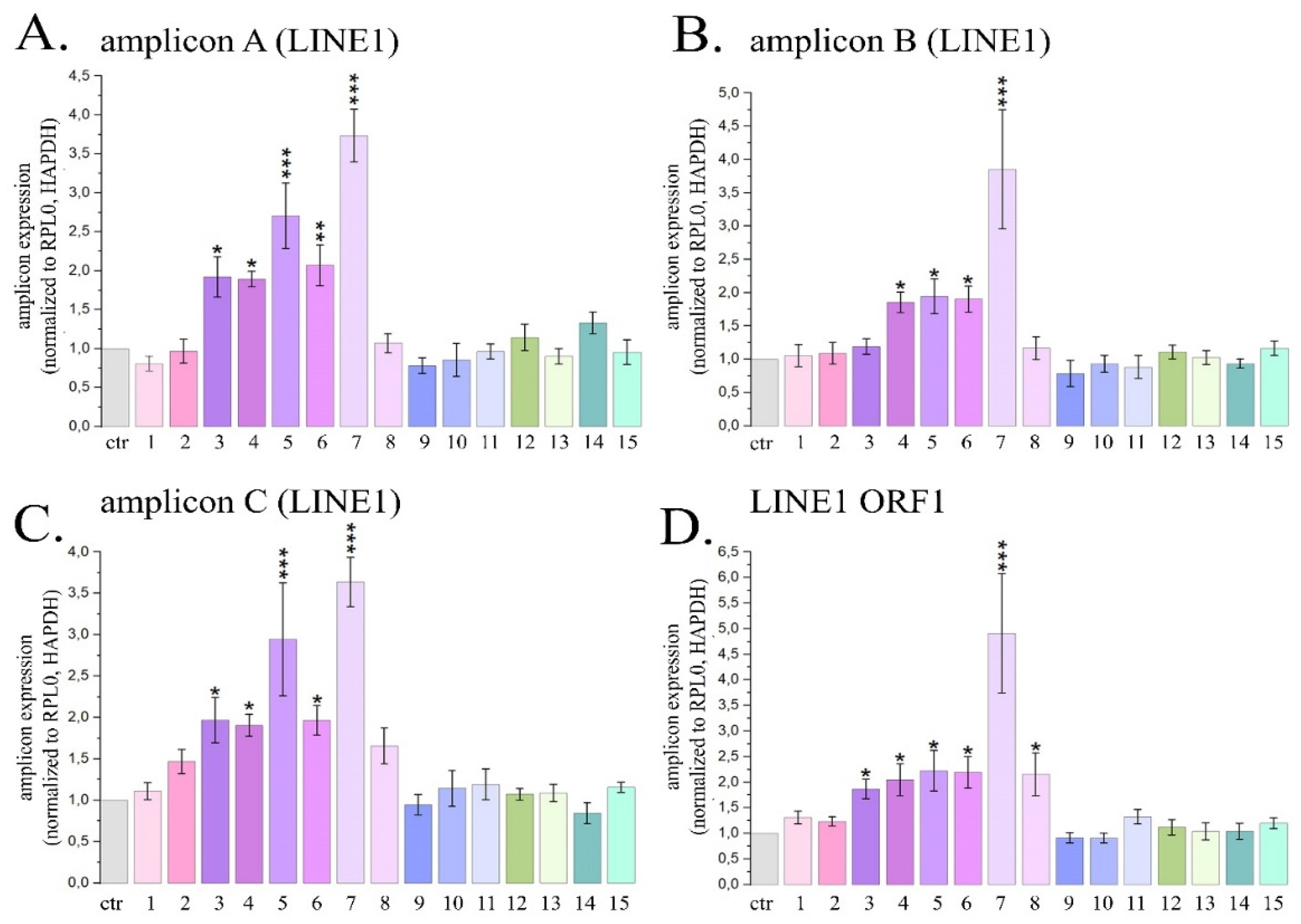
| Type of gene products | Gene products | Number of genes |
|---|---|---|
| IFNs(21) | IFN-α; IFN-β; receptor ligands | 5 genes |
| IFN-γ; receptor ligands | 1 genes | |
| Hematopoietin & IFN class (D200-domain) cytokine receptor ligands | 10 genes | |
| Other IFN related genes | 5 | |
| IFN receptors(37) | IFN-α and IFN-β receptors | 2 |
| IFN-γ receptors | 2 | |
| Hematopoietin, IFN class (D200-domain) receptors | 28 | |
| IFN regulatory factors (9) | 9 | |
| IFN-responsive genes(23) | Response to virus | 13* |
| Transcriptional regulation | 2* | |
| Other IFN responsive genes | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





