Submitted:
13 October 2024
Posted:
15 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
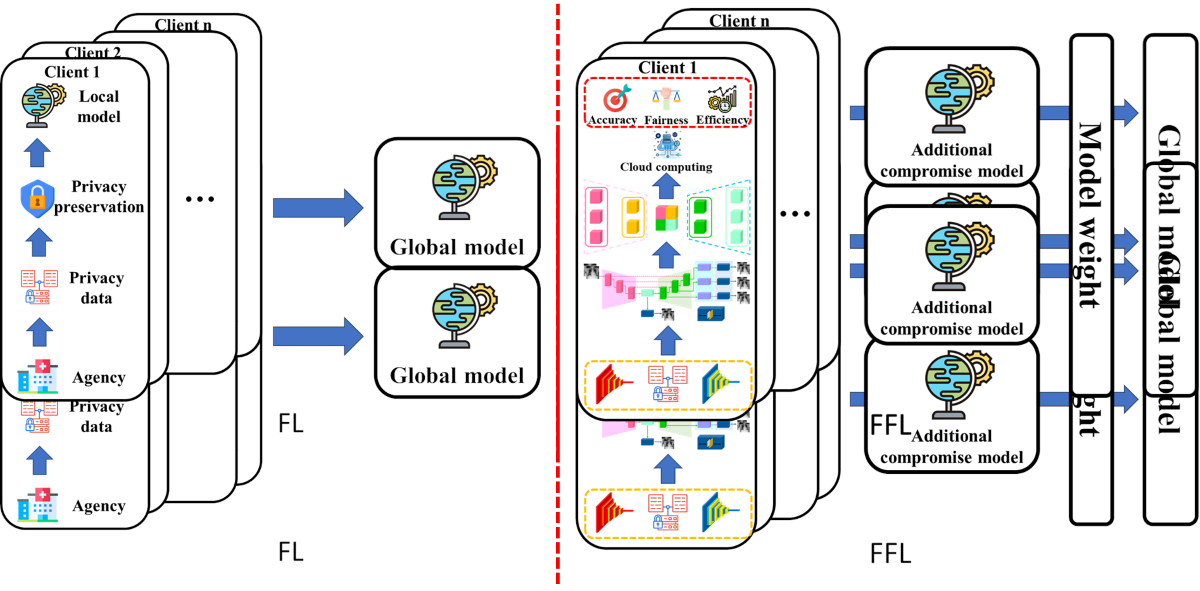
Keywords:
1. Introduction
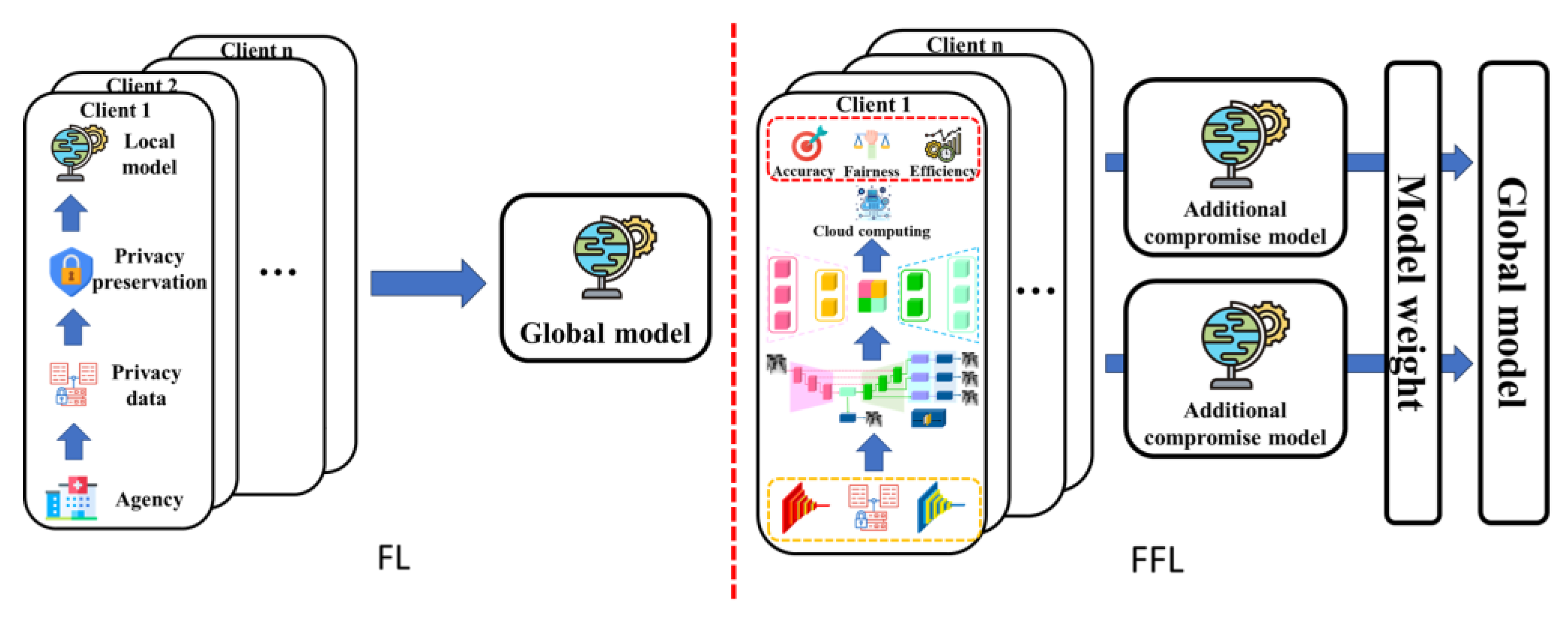
2. Methodology
2.1. Literature Review and Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
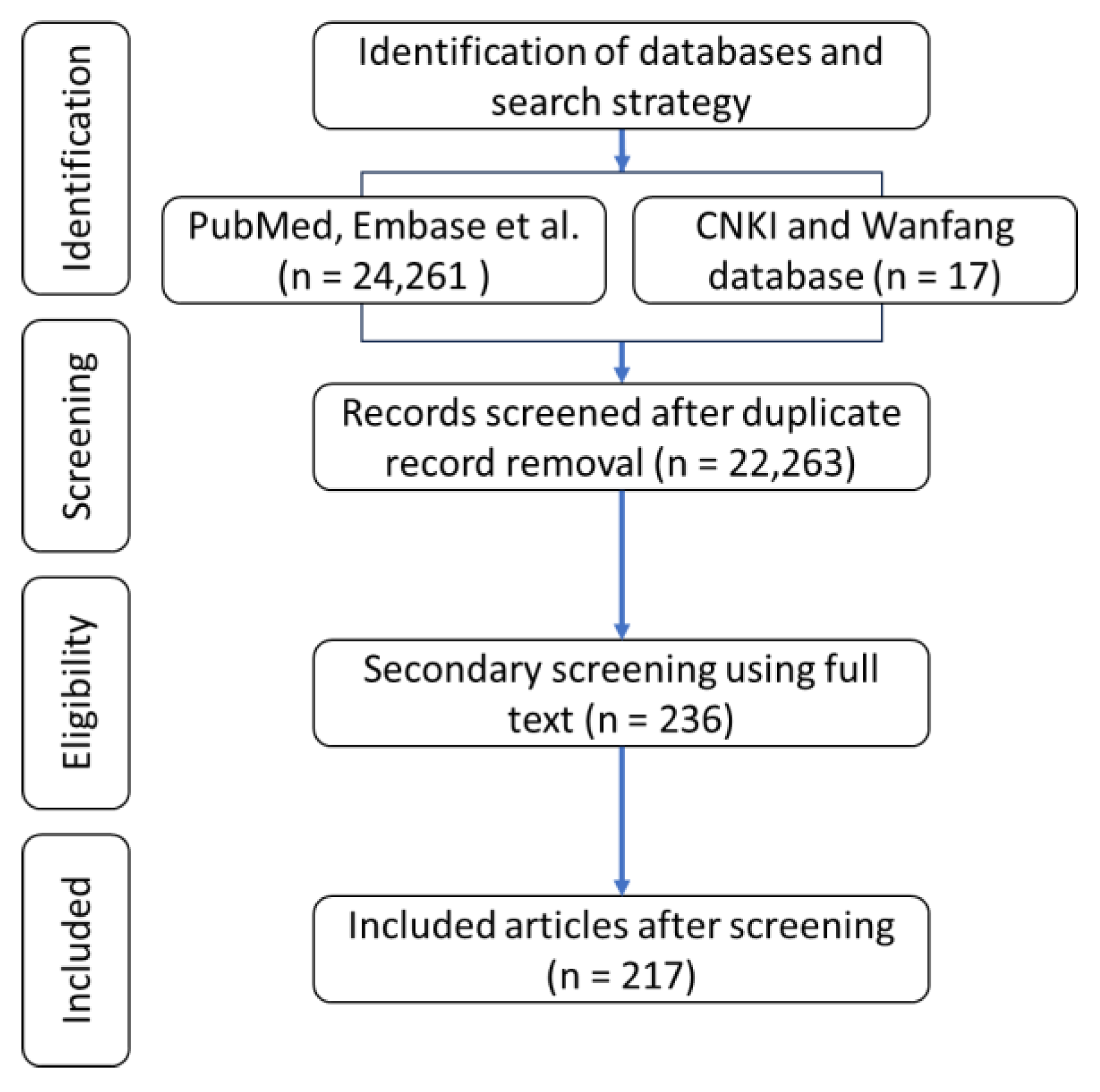
2.3. Selection of Eligible Articles
3. Causes of bias in FL and fairness in FFL
3.1. Causes of Bias in FL
3.1.1. Conventional Bias Sources
3.1.2. Sub-Sampling, Party Selection, and Dropouts
3.1.3. Data Heterogeneity
3.1.4. Conventional Bias Sources
3.1.5. Systems Heterogeneity
3.2. Fairness and Recent Trends in FFL Research
4. Bias for categorizations
4.1. Data Partition
4.1.1. Fair Horizontal Federated Learning (FHFL)
4.1.2. Fair Vertical Federated Learning (FVFL)
4.1.3. Conventional Bias Sources
4.1.4. Conventional Bias Sources
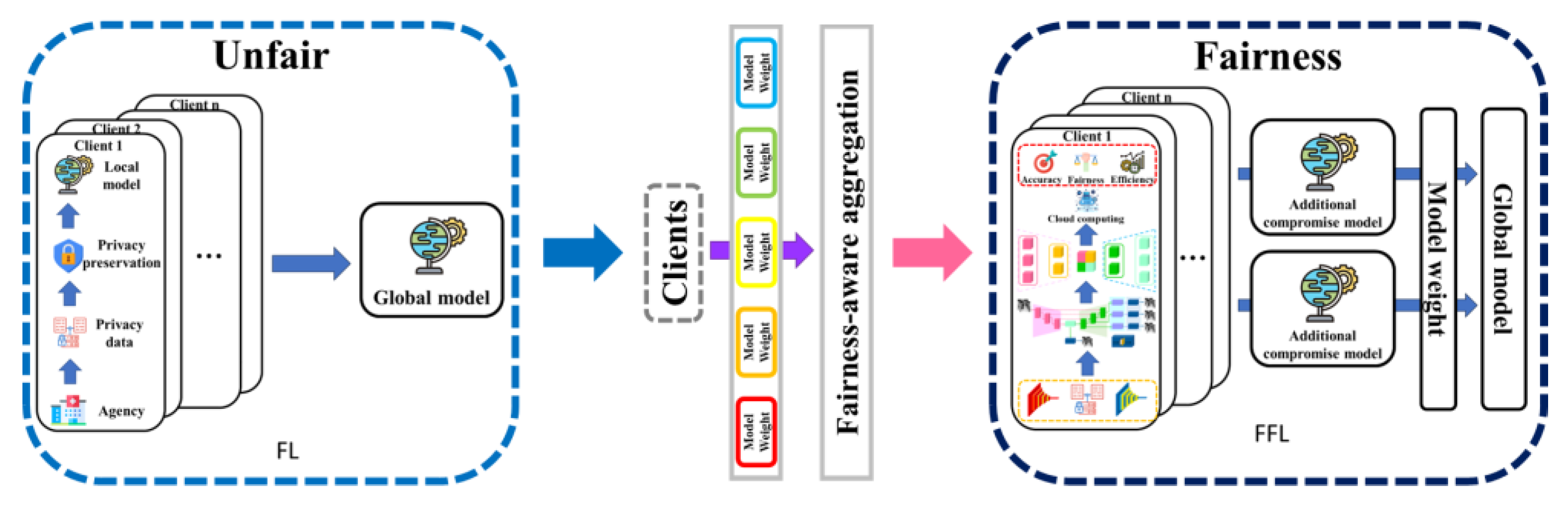
4.2. Privacy Preservation Mechanism
4.2.1. Fair Cryptographic methods
4.2.1.1. Homomorphic Encryption, HE
4.2.1.2. Secure Multi-party Computation, SMPC
4.2.1.3. Secret Sharing, SS
4.2.2. Anonymization methods
4.2.2.1. Data Masking
4.2.2.2. Data Shuffling
4.2.3. Perturbative methods
4.2.3.1. Differential Privacy, DP
4.2.3.2. Additive/Multiplicative Perturbation methods
4.2.4. Hardware-based protection
4.2.5. Hybrid Privacy Preserving Federated Learning, Hybrid PPFL
4.2.5.1. Model Aggregation
4.2.5.2. Sensitivity-based Weight Distribution
4.3. Methods for solving heterogeneity
4.3.1. Asynchronous Communication
4.3.2. Sampling
4.3.3. Fault Tolerance
4.3.4. Model Heterogeneity
5. Fairness evaluation metrics
5.1. Evaluations of fairness
5.2. FFL model
6. FFL Application in Wireless Communication
6.1. Improving Usability
6.2. Wireless Communication
7. FFL Challenge and Future work
7.1. Privacy Preservation
7.2. Communication Cost
7.3. Systems Heterogeneity
7.4. Unreliable Model Upload
7.5. Multi-Center FL (MCFL)
7.6. MMFFL Research Direction and Tasks
7.7. Reliable Client Selection
8. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. bmj 2021, 372. [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Shokri, R. Bias propagation in federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.02160 2023.
- Zawad, S.; Yan, F.; Anwar, A. Systems bias in federated learning. In Federated Learning: A Comprehensive Overview of Methods and Applications; Springer: 2022; pp. 259-278.
- Rafi, T.H.; Noor, F.A.; Hussain, T.; Chae, D.-K. Fairness and privacy preserving in federated learning: A survey. Information Fusion 2024, 105, 102198. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J. Combating client dropout in federated learning via friend model substitution. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.13222 2022.
- Sun, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J. Mimic: Combating client dropouts in federated learning by mimicking central updates. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2023. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, X.; Lin, T. FedDebias: Reducing the Local Learning Bias Improves Federated Learning on Heterogeneous Data. 2022.
- Taghiyarrenani, Z.; Nowaczyk, S.; Pashami, S. Analysis of Statistical Data Heterogeneity in Federated Fault Identification. In Proceedings of the PHM Society Asia-Pacific Conference, 2023.
- Dai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Heinecke, S.; Sun, L.; Xu, R. Tackling data heterogeneity in federated learning with class prototypes. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023; pp. 7314-7322.
- Vahidian, S.; Morafah, M.; Chen, C.; Shah, M.; Lin, B. Rethinking data heterogeneity in federated learning: Introducing a new notion and standard benchmarks. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence 2023, 5, 1386-1397. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; Dong, C.; Huang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Hou, Z.; Qiao, S.; Tan, C.W. FedDRL: Trustworthy Federated Learning Model Fusion Method Based on Staged Reinforcement Learning. Computing and Informatics 2024, 43, 1–37-31–37. [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Chiaro, D.; Guzzo, A.; Ianni, M.; Fortino, G.; Piccialli, F. Model aggregation techniques in federated learning: A comprehensive survey. Future Generation Computer Systems 2023. [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sahu, A.K.; Talwalkar, A.; Smith, V. Federated learning: Challenges, methods, and future directions. IEEE signal processing magazine 2020, 37, 50-60.
- Ye, M.; Fang, X.; Du, B.; Yuen, P.C.; Tao, D. Heterogeneous federated learning: State-of-the-art and research challenges. ACM Computing Surveys 2023, 56, 1-44. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Xin, F.; Dong, F.; Luo, J.; Wu, Z. Addressing Heterogeneity in Federated Learning with Client Selection via Submodular Optimization. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks 2024, 20, 1-32. [CrossRef]
- Djebrouni, Y.; Benarba, N.; Touat, O.; De Rosa, P.; Bouchenak, S.; Bonifati, A.; Felber, P.; Marangozova, V.; Schiavoni, V. Bias mitigation in federated learning for edge computing. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies 2024, 7, 1-35. [CrossRef]
- Ferraguig, L.; Djebrouni, Y.; Bouchenak, S.; Marangozova, V. Survey of bias mitigation in federated learning. In Proceedings of the Conférence francophone d'informatique en Parallélisme, Architecture et Système, 2021.
- Gao, Y.; Lu, G.; Gao, J.; Li, J. A High-Performance Federated Learning Aggregation Algorithm Based on Learning Rate Adjustment and Client Sampling. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4344. [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhu, T.; Zhou, W. Fair Federated Learning with Opposite GAN. Knowledge-Based Systems 2024, 287, 111420. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Hu, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, J. FedUB: Federated Learning Algorithm Based on Update Bias. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1601. [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Wu, F.; Wu, C.; Lyu, L.; Xu, T.; Liao, H.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xie, X. Fairvfl: A fair vertical federated learning framework with contrastive adversarial learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2022, 35, 7852-7865.
- Liu, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zou, T.; Pu, Y.; He, Y.; Ye, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Yang, Q. Vertical federated learning: Concepts, advances, and challenges. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2024.
- Yang, L.; Chai, D.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, K. A survey on vertical federated learning: From a layered perspective. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.01829 2023.
- Wu, Z.; Li, Q.; He, B. Practical vertical federated learning with unsupervised representation learning. IEEE Transactions on Big Data 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shuai, Z.; Kuang, K.; Wu, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Xiao, J. Unified fair federated learning for digital healthcare. Patterns 2024, 5. [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Du, X.; Lu, Z.; Chai, H. Universal adversarial backdoor attacks to fool vertical federated learning. Computers & Security 2024, 137, 103601. [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B.; Dong, Y. Practical and general backdoor attacks against vertical federated learning. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, 2023; pp. 402-417.
- Salazar, T.; Fernandes, M.; Araújo, H.; Abreu, P.H. Fair-fate: Fair federated learning with momentum. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science, 2023; pp. 524-538.
- Zhou, P.; Xu, H.; Lee, L.H.; Fang, P.; Hui, P. Are you left out? an efficient and fair federated learning for personalized profiles on wearable devices of inferior networking conditions. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies 2022, 6, 1-25.
- Zhao, Z.; Joshi, G. A dynamic reweighting strategy for fair federated learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2022; pp. 8772-8776.
- Coston, A.; Ramamurthy, K.N.; Wei, D.; Varshney, K.R.; Speakman, S.; Mustahsan, Z.; Chakraborty, S. Fair transfer learning with missing protected attributes. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2019 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, 2019; pp. 91-98.
- Fan, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Guo, S. Balanced Multi-modal Federated Learning via Cross-Modal Infiltration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.00894 2023.
- Su, C.; Yu, G.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, H. Multi-Dimensional Fair Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2024; pp. 15083-15090.
- Zhou, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Liang, W.; Kevin, I.; Wang, K.; Ma, J.; Pan, Y.; Jin, Q. Personalized federation learning with model-contrastive learning for multi-modal user modeling in human-centric metaverse. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2024. [CrossRef]
- Paillier, P. Public-key cryptosystems based on composite degree residuosity classes. In Proceedings of the International conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques, 1999; pp. 223-238.
- Fan, J.; Vercauteren, F. Somewhat practical fully homomorphic encryption. Cryptology ePrint Archive 2012.
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Flashe: Additively symmetric homomorphic encryption for cross-silo federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.00675 2021.
- Jin, W.; Yao, Y.; Han, S.; Joe-Wong, C.; Ravi, S.; Avestimehr, S.; He, C. FedML-HE: An efficient homomorphic-encryption-based privacy-preserving federated learning system. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.10837 2023.
- Volgushev, N.; Schwarzkopf, M.; Getchell, B.; Varia, M.; Lapets, A.; Bestavros, A. Conclave: secure multi-party computation on big data. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Fourteenth EuroSys Conference 2019, 2019; pp. 1-18.
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jolfaei, A.; Yu, D.; Xu, G.; Zheng, X. Privacy-preserving federated learning framework based on chained secure multiparty computing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 8, 6178-6186. [CrossRef]
- Kalapaaking, A.P.; Stephanie, V.; Khalil, I.; Atiquzzaman, M.; Yi, X.; Almashor, M. Smpc-based federated learning for 6g-enabled internet of medical things. IEEE Network 2022, 36, 182-189. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, T.; Ren, P. VFL-R: a novel framework for multi-party in vertical federated learning. Applied Intelligence 2023, 53, 12399-12415. [CrossRef]
- Mohassel, P.; Zhang, Y. Secureml: A system for scalable privacy-preserving machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE symposium on security and privacy (SP), 2017; pp. 19-38.
- Pentyala, S.; Neophytou, N.; Nascimento, A.; De Cock, M.; Farnadi, G. Privfairfl: Privacy-preserving group fairness in federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.11584 2022.
- Mugunthan, V.; Polychroniadou, A.; Byrd, D.; Balch, T.H. Smpai: Secure multi-party computation for federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the NeurIPS 2019 Workshop on Robust AI in Financial Services, 2019.
- Chen, L.; Xiao, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, M. Secure and efficient federated learning via novel multi-party computation and compressed sensing. Information Sciences 2024, 667, 120481. [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, A.; Ju, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, Q. Privacy-preserving heterogeneous federated transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE international conference on big data (Big Data), 2019; pp. 2552-2559.
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Ma, J. Privacy-preserving federated k-means for proactive caching in next generation cellular networks. Information Sciences 2020, 521, 14-31. [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, K.; Lin, X. VerifyNet: Secure and verifiable federated learning. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2019, 15, 911-926.
- Ezzeldin, Y.H.; Yan, S.; He, C.; Ferrara, E.; Avestimehr, A.S. Fairfed: Enabling group fairness in federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2023; pp. 7494-7502.
- Li, A.; Sun, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Chen, Y. Fedmask: Joint computation and communication-efficient personalized federated learning via heterogeneous masking. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, 2021; pp. 42-55.
- Setayesh, M.; Li, X.; Wong, V.W. Perfedmask: Personalized federated learning with optimized masking vectors. In Proceedings of the The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023.
- Lu, J.; Li, S.; Bao, K.; Wang, P.; Qian, Z.; Ge, S. Federated Learning with Label-Masking Distillation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2023; pp. 222-232.
- He, S.; Yan, Q.; Wu, F.; Wang, L.; Lécuyer, M.; Beschastnikh, I. Gluefl: Reconciling client sampling and model masking for bandwidth efficient federated learning. Proceedings of Machine Learning and Systems 2023, 5, 695-707.
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, H. PrivMaskFL: A private masking approach for heterogeneous federated learning in IoT. Computer Communications 2024, 214, 100-112. [CrossRef]
- Girgis, A.; Data, D.; Diggavi, S.; Kairouz, P.; Suresh, A.T. Shuffled model of differential privacy in federated learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, 2021; pp. 2521-2529.
- Liu, R.; Cao, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, R.; Yoshikawa, M. Flame: Differentially private federated learning in the shuffle model. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021; pp. 8688-8696.
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, M.; Kuang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Yu, S. A multi-shuffler framework to establish mutual confidence for secure federated learning. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2022, 20, 4230-4244. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C. DPBalance: Efficient and Fair Privacy Budget Scheduling for Federated Learning as a Service. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09715 2024.
- ur Rehman, M.H.; Dirir, A.M.; Salah, K.; Svetinovic, D. Fairfed: Cross-device fair federated learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR), 2020; pp. 1-7.
- Bhowmick, A.; Duchi, J.; Freudiger, J.; Kapoor, G.; Rogers, R. Protection against reconstruction and its applications in private federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.00984 2018.
- Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Yu, S.; Deng, H. PEFL: A privacy-enhanced federated learning scheme for big data analytics. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2019; pp. 1-6.
- Hu, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, Z.; He, B. The oarf benchmark suite: Characterization and implications for federated learning systems. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST) 2022, 13, 1-32. [CrossRef]
- McMahan, H.B.; Ramage, D.; Talwar, K.; Zhang, L. Learning differentially private recurrent language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.06963 2017.
- Geyer, R.C.; Klein, T.; Nabi, M. Differentially private federated learning: A client level perspective. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.07557 2017.
- Truex, S.; Baracaldo, N.; Anwar, A.; Steinke, T.; Ludwig, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y. A hybrid approach to privacy-preserving federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 12th ACM workshop on artificial intelligence and security, 2019; pp. 1-11.
- Ling, X.; Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, H.; Cheng, T.; Xu, G.; Li, Q. FedFDP: Federated Learning with Fairness and Differential Privacy. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16028 2024.
- Salim, S.; Moustafa, N.; Turnbull, B.; Razzak, I. Perturbation-enabled deep federated learning for preserving internet of things-based social networks. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM) 2022, 18, 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Kuang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Yu, L. From Optimization to Generalization: Fair Federated Learning against Quality Shift via Inter-Client Sharpness Matching. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.17805 2024.
- Tang, X.; Shen, M.; Li, Q.; Zhu, L.; Xue, T.; Qu, Q. Pile: Robust privacy-preserving federated learning via verifiable perturbations. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing 2023, 20, 5005-5023. [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Guo, Y.; Gong, Y. Federated learning with sparsified model perturbation: Improving accuracy under client-level differential privacy. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2023. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Ni, Z.; Xue, H.; Shao, H. Staged noise perturbation for privacy-preserving federated learning. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Computing 2024. [CrossRef]
- Chamikara, M.A.P.; Bertok, P.; Khalil, I.; Liu, D.; Camtepe, S. Privacy preserving distributed machine learning with federated learning. Computer Communications 2021, 171, 112-125. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Hou, R.; Meng, D. ShuffleFL: Gradient-preserving federated learning using trusted execution environment. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 18th ACM international conference on computing frontiers, 2021; pp. 161-168.
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Hu, J.; Chen, K. {FLASH}: Towards a high-performance hardware acceleration architecture for cross-silo federated learning. In Proceedings of the 20th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 23), 2023; pp. 1057-1079.
- Mondal, A.; More, Y.; Rooparaghunath, R.H.; Gupta, D. Poster: Flatee: Federated learning across trusted execution environments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), 2021; pp. 707-709.
- Ye, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Tang, Y.; Hu, W. EdgeFed: Optimized federated learning based on edge computing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 209191-209198. [CrossRef]
- Issa, W.; Moustafa, N.; Turnbull, B.; Choo, K.-K.R. RVE-PFL: Robust Variational Encoder-based Personalised Federated Learning against Model Inversion Attacks. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2024.
- Xu, R.; Baracaldo, N.; Zhou, Y.; Anwar, A.; Ludwig, H. Hybridalpha: An efficient approach for privacy-preserving federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 12th ACM workshop on artificial intelligence and security, 2019; pp. 13-23.
- Ma, J.; Naas, S.A.; Sigg, S.; Lyu, X. Privacy-preserving federated learning based on multi-key homomorphic encryption. International Journal of Intelligent Systems 2022, 37, 5880-5901.
- Yazdinejad, A.; Dehghantanha, A.; Srivastava, G.; Karimipour, H.; Parizi, R.M. Hybrid privacy preserving federated learning against irregular users in next-generation Internet of Things. Journal of Systems Architecture 2024, 148, 103088. [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Tang, K.; Fan, B. APPFed: A Hybrid Privacy-Preserving Framework for Federated Learning over Sensitive Data. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Machine Learning and Intelligent Systems Engineering (MLISE), 2022; pp. 389-395.
- Sánchez, P.M.S.; Celdrán, A.H.; Xie, N.; Bovet, G.; Pérez, G.M.; Stiller, B. Federatedtrust: A solution for trustworthy federated learning. Future Generation Computer Systems 2024, 152, 83-98. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gálvez, B.; Granqvist, F.; van Dalen, R.; Seigel, M. Enforcing fairness in private federated learning via the modified method of differential multipliers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.08604 2021.
- 김도형; 오경수; 이영호. HFAD: 공정한 연합학습 및 하이브리드 융합 멀티모달 산업 이상 탐지. 한국정보통신학회논문지 2024, 28, 805-814.
- Papernot, N.; Abadi, M.; Erlingsson, U.; Goodfellow, I.; Talwar, K. Semi-supervised knowledge transfer for deep learning from private training data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.05755 2016.
- Kim, D.-h.; Oh, K.; Kang, S.-h.; Lee, Y. Development of Pneumonia Patient Classification Model Using Fair Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Human Computer Interaction, 2023; pp. 153-164.
- Zhao, X.; Shen, D. FedSW: Federated learning with adaptive sample weights. Information Sciences 2024, 654, 119873. [CrossRef]
- Cellamare, M.; van Gestel, A.J.; Alradhi, H.; Martin, F.; Moncada-Torres, A. A federated generalized linear model for privacy-preserving analysis. Algorithms 2022, 15, 243. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Khalaf, O.; Algburi, S.; Selvaraj, D.; Sharif, M.S.; Elmedany, W. Federated learning with hybrid differential privacy for secure and reliable cross-IoT platform knowledge sharing. Security and Privacy 2024, 7, e374. [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Muñoz, J.P.; Jannesari, A. Federated foundation models: Privacy-preserving and collaborative learning for large models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11414 2023.
- Li, T.; Sanjabi, M.; Beirami, A.; Smith, V. Fair resource allocation in federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.10497 2019.
- Ma, J.; Tu, A.; Chen, Y.; Reddi, V.J. FedStaleWeight: Buffered Asynchronous Federated Learning with Fair Aggregation via Staleness Reweighting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.02877 2024.
- Yin, Q.; Huang, J.; Yao, H.; Zhang, L. Distribution-Free Fair Federated Learning with Small Samples. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.16158 2024.
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Tang, T.; Wang, R. Fairness-aware federated learning with unreliable links in resource-constrained Internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9, 17359-17371. [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ceyani, E.; Balasubramanian, K.; Annavaram, M.; Avestimehr, S. Spreadgnn: Decentralized multi-task federated learning for graph neural networks on molecular data. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2022; pp. 6865-6873. [CrossRef]
- Sprague, M.R.; Jalalirad, A.; Scavuzzo, M.; Capota, C.; Neun, M.; Do, L.; Kopp, M. Asynchronous federated learning for geospatial applications. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, 2018; pp. 21-28.
- Nguyen, J.; Malik, K.; Zhan, H.; Yousefpour, A.; Rabbat, M.; Malek, M.; Huba, D. Federated learning with buffered asynchronous aggregation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, 2022; pp. 3581-3607.
- Chen, Y.; Ning, Y.; Slawski, M.; Rangwala, H. Asynchronous online federated learning for edge devices with non-iid data. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), 2020; pp. 15-24.
- Baccarelli, E.; Scarpiniti, M.; Momenzadeh, A.; Ahrabi, S.S. AFAFed—Asynchronous fair adaptive federated learning for IoT stream applications. Computer Communications 2022, 195, 376-402. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H. Collaborative fairness in federated learning. Federated Learning: Privacy and Incentive 2020, 189-204.
- Yu, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Cong, M.; Weng, X.; Niyato, D.; Yang, Q. A fairness-aware incentive scheme for federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, 2020; pp. 393-399.
- Bey, R.; Goussault, R.; Grolleau, F.; Benchoufi, M.; Porcher, R. Fold-stratified cross-validation for unbiased and privacy-preserving federated learning. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2020, 27, 1244-1251. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Ma, W.; Wang, R.; Deng, S.; Wu, Y. Federated learning based on stratified sampling and regularization. Complex & Intelligent Systems 2023, 9, 2081-2099. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Fan, P.; Peng, C.; Letaief, K.B. ISFL: Federated Learning for Non-iid Data with Local Importance Sampling. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024.
- Balakrishnan, R.; Li, T.; Zhou, T.; Himayat, N.; Smith, V.; Bilmes, J. Diverse client selection for federated learning via submodular maximization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022.
- Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Lin, T.; Tang, X. Delta: Diverse client sampling for fasting federated learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 36.
- Morell, J.Á.; Alba, E. Dynamic and adaptive fault-tolerant asynchronous federated learning using volunteer edge devices. Future Generation Computer Systems 2022, 133, 53-67. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-H.; Chen, M.-R.; Zeng, G.-Q.; Weng, J.-S. BDFL: A byzantine-fault-tolerance decentralized federated learning method for autonomous vehicle. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2021, 70, 8639-8652. [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Ye, M.; Du, B. Learn from others and be yourself in heterogeneous federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022; pp. 10143-10153.
- Mendieta, M.; Yang, T.; Wang, P.; Lee, M.; Ding, Z.; Chen, C. Local learning matters: Rethinking data heterogeneity in federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022; pp. 8397-8406.
- Alam, S.; Liu, L.; Yan, M.; Zhang, M. Fedrolex: Model-heterogeneous federated learning with rolling sub-model extraction. Advances in neural information processing systems 2022, 35, 29677-29690.
- Wang, G.; Payani, A.; Lee, M.; Kompella, R. Mitigating group bias in federated learning: Beyond local fairness. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.09931 2023.
- Li, J.; Zhu, T.; Ren, W.; Raymond, K.-K. Improve individual fairness in federated learning via adversarial training. Computers & Security 2023, 132, 103336. [CrossRef]
- Commission, P.I.P. Pseudonymization information processing guidelines. 2024, 241.
- Welfare, M.o.H.a.; Commission, P.I.P. Healthcare data utilization guideline. 2024, 126.
- Turgay, S.; İlter, İ. Perturbation methods for protecting data privacy: A review of techniques and applications. Automation and Machine Learning 2023, 4, 31-41. [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-G.; Lee, M.-U.; Lee, T.-H. Efficient Robust Design Optimization Using Statistical Moments Based on Multiplicative Decomposition Method. Transactions of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers A 2012, 36, 1109-1114. [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Pietzuch, P.; Paverd, A.; Vaswani, K. Trustworthy AI Using Confidential Federated Learning. Communications of the ACM.
- Tran, A.T.; Luong, T.D.; Pham, X.S. A Novel Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Model Based on Secure Multi-party Computation. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Integrated Uncertainty in Knowledge Modelling and Decision Making, 2023; pp. 321-333.
- Chatzikonstantinou, C.; Konstantinidis, D.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Daras, P. Federated Learning Aggregation based on Weight Distribution Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), 2023; pp. 1-6.
- Dilley, O.; Parra-Ullauri, J.M.; Hussain, R.; Simeonidou, D. Federated Fairness Analytics: Quantifying Fairness in Federated Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.08214 2024.
- Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Ye, M. Fair Federated Learning under Domain Skew with Local Consistency and Domain Diversity. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024; pp. 12077-12086.
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shan, H.; Wang, W.; Quek, T.Q. Asynchronous federated learning over wireless communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2022, 21, 6961-6978. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Mao, B.; Ma, T. Efficient and robust asynchronous federated learning with stragglers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, 2019.
- Luo, B.; Xiao, W.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Tassiulas, L. Tackling system and statistical heterogeneity for federated learning with adaptive client sampling. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2022-IEEE conference on computer communications, 2022; pp. 1739-1748.
- Xu, X.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. Safe: Synergic data filtering for federated learning in cloud-edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2022, 19, 1655-1665. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.; Shin, S.; Hwang, S.J.; Yang, E. Fedmix: Approximation of mixup under mean augmented federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.00233 2021.
- Duan, M.; Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Tan, Y.; Ren, J.; Qiao, L.; Liang, L. Astraea: Self-balancing federated learning for improving classification accuracy of mobile deep learning applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 37th international conference on computer design (ICCD), 2019; pp. 246-254.
- Jeong, E.; Oh, S.; Kim, H.; Park, J.; Bennis, M.; Kim, S.-L. Communication-efficient on-device machine learning: Federated distillation and augmentation under non-iid private data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.11479 2018.
- Hu, R.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Pei, Q.; Gong, Y. Personalized federated learning with differential privacy. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 7, 9530-9539. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, O.; Gkoulalas-Divanis, A.; Salonidis, T.; Sylla, I.; Park, Y.; Hsu, G.; Das, A. Anonymizing data for privacy-preserving federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.09096 2020.
- Li, D.; Wang, J. Fedmd: Heterogenous federated learning via model distillation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.03581 2019.
- He, C.; Annavaram, M.; Avestimehr, S. Group knowledge transfer: Federated learning of large cnns at the edge. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, 33, 14068-14080.
- Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Ding, L.; Tao, D.; Duan, L.-Y. Fine-tuning global model via data-free knowledge distillation for non-iid federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2022; pp. 10174-10183.
- Zhang, F.; Kuang, K.; Chen, L.; You, Z.; Shen, T.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, F.; Zhuang, Y. Federated unsupervised representation learning. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering 2023, 24, 1181-1193.
- Lubana, E.S.; Tang, C.I.; Kawsar, F.; Dick, R.P.; Mathur, A. Orchestra: Unsupervised federated learning via globally consistent clustering. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.11506 2022.
- Li, Q.; He, B.; Song, D. Model-contrastive federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2021; pp. 10713-10722.
- Mu, X.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, K.; Geng, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z. Fedproc: Prototypical contrastive federated learning on non-iid data. Future Generation Computer Systems 2023, 143, 93-104. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kwak, Y.; Jung, M.; Shin, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, C. Protofl: Unsupervised federated learning via prototypical distillation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023; pp. 6470-6479.
- Li, T.; Sahu, A.K.; Zaheer, M.; Sanjabi, M.; Talwalkar, A.; Smith, V. Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks. Proceedings of Machine learning and systems 2020, 2, 429-450.
- Shoham, N.; Avidor, T.; Keren, A.; Israel, N.; Benditkis, D.; Mor-Yosef, L.; Zeitak, I. Overcoming forgetting in federated learning on non-iid data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.07796 2019.
- T Dinh, C.; Tran, N.; Nguyen, J. Personalized federated learning with moreau envelopes. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, 21394-21405.
- Fallah, A.; Mokhtari, A.; Ozdaglar, A. Personalized federated learning with theoretical guarantees: A model-agnostic meta-learning approach. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, 3557-3568.
- Khodak, M.; Balcan, M.-F.F.; Talwalkar, A.S. Adaptive gradient-based meta-learning methods. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2019, 32.
- Smith, V.; Chiang, C.-K.; Sanjabi, M.; Talwalkar, A.S. Federated multi-task learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30.
- Li, T.; Hu, S.; Beirami, A.; Smith, V. Ditto: Fair and robust federated learning through personalization. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning, 2021; pp. 6357-6368.
- Lin, T.; Kong, L.; Stich, S.U.; Jaggi, M. Ensemble distillation for robust model fusion in federated learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, 2351-2363.
- Zhu, Z.; Hong, J.; Zhou, J. Data-free knowledge distillation for heterogeneous federated learning. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning, 2021; pp. 12878-12889.
- Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Wu, F. Parameterized knowledge transfer for personalized federated learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, 34, 10092-10104.
- Chen, Y.; Qin, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Gao, W. Fedhealth: A federated transfer learning framework for wearable healthcare. IEEE Intelligent Systems 2020, 35, 83-93. [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.; Hassani, H.; Mokhtari, A.; Shakkottai, S. Exploiting shared representations for personalized federated learning. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning, 2021; pp. 2089-2099.
- Shang, X.; Lu, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, H. Federated learning on heterogeneous and long-tailed data via classifier re-training with federated features. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.13399 2022.
- Liang, P.P.; Liu, T.; Ziyin, L.; Allen, N.B.; Auerbach, R.P.; Brent, D.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Morency, L.-P. Think locally, act globally: Federated learning with local and global representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.01523 2020.
- Xu, J.; Tong, X.; Huang, S.-L. Personalized federated learning with feature alignment and classifier collaboration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.11867 2023.
- Diao, E.; Ding, J.; Tarokh, V. Heterofl: Computation and communication efficient federated learning for heterogeneous clients. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.01264 2020.
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; Xu, W. Layer-wised model aggregation for personalized federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2022; pp. 10092-10101.
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, L. Cd2-pfed: Cyclic distillation-guided channel decoupling for model personalization in federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022; pp. 10041-10050.
- Wang, H.; Kaplan, Z.; Niu, D.; Li, B. Optimizing federated learning on non-iid data with reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE conference on computer communications, 2020; pp. 1698-1707.
- Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Qian, H. Federated learning with class imbalance reduction. In Proceedings of the 2021 29th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), 2021; pp. 2174-2178.
- Li, L.; Duan, M.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, A.; Chen, X.; Tan, Y.; Wang, C. FedSAE: A novel self-adaptive federated learning framework in heterogeneous systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2021; pp. 1-10.
- Nishio, T.; Yonetani, R. Client selection for federated learning with heterogeneous resources in mobile edge. In Proceedings of the ICC 2019-2019 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), 2019; pp. 1-7.
- Briggs, C.; Fan, Z.; Andras, P. Federated learning with hierarchical clustering of local updates to improve training on non-IID data. In Proceedings of the 2020 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN), 2020; pp. 1-9.
- Long, G.; Xie, M.; Shen, T.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J. Multi-center federated learning: clients clustering for better personalization. World Wide Web 2023, 26, 481-500. [CrossRef]
- Sattler, F.; Müller, K.-R.; Samek, W. Clustered federated learning: Model-agnostic distributed multitask optimization under privacy constraints. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems 2020, 32, 3710-3722. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Rieger, P.; De Viti, R.; Chen, H.; Brandenburg, B.B.; Yalame, H.; Möllering, H.; Fereidooni, H.; Marchal, S.; Miettinen, M. {FLAME}: Taming backdoors in federated learning. In Proceedings of the 31st USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 22), 2022; pp. 1415-1432.
- Hu, C.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Z. Decentralized federated learning: A segmented gossip approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.07782 2019.
- Kalra, S.; Wen, J.; Cresswell, J.C.; Volkovs, M.; Tizhoosh, H.R. Decentralized federated learning through proxy model sharing. Nature communications 2023, 14, 2899. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, N.; Huang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, Q. A blockchain-based decentralized federated learning framework with committee consensus. IEEE Network 2020, 35, 234-241. [CrossRef]
- Luping, W.; Wei, W.; Bo, L. CMFL: Mitigating communication overhead for federated learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 39th international conference on distributed computing systems (ICDCS), 2019; pp. 954-964.
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, R.; Cheng, M.; Yu, F.; Hsieh, C.-J. Feddm: Iterative distribution matching for communication-efficient federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023; pp. 16323-16332.
- Dai, R.; Shen, L.; He, F.; Tian, X.; Tao, D. Dispfl: Towards communication-efficient personalized federated learning via decentralized sparse training. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning, 2022; pp. 4587-4604.
- Galli, F.; Biswas, S.; Jung, K.; Cucinotta, T.; Palamidessi, C. Group privacy for personalized federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.03396 2022.
- Xia, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, X. A vertical federated learning framework for horizontally partitioned labels. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.10056 2021.
- Kim, S. Incentive design and differential privacy based federated learning: A mechanism design perspective. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 187317-187325. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Kou, Z.; Wang, D. Fairfl: A fair federated learning approach to reducing demographic bias in privacy-sensitive classification models. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), 2020; pp. 1051-1060.
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, H.; Lee, K. Improving fairness via federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.15545 2021.
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, W.; Leng, J.; Guo, M. Dubhe: Towards data unbiasedness with homomorphic encryption in federated learning client selection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 50th International Conference on Parallel Processing, 2021; pp. 1-10.
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X. Fedeba+: Towards fair and effective federated learning via entropy-based model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.12407 2023.
- Huang, J.; Xu, C.; Ji, Z.; Xiao, S.; Liu, T.; Ma, N.; Zhou, Q. [Retracted] AFLPC: An Asynchronous Federated Learning Privacy-Preserving Computing Model Applied to 5G-V2X. Security and Communication Networks 2022, 2022, 9334943.
- Passerat-Palmbach, J.; Farnan, T.; McCoy, M.; Harris, J.D.; Manion, S.T.; Flannery, H.L.; Gleim, B. Blockchain-orchestrated machine learning for privacy preserving federated learning in electronic health data. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE international conference on blockchain (Blockchain), 2020; pp. 550-555.
- Papadaki, A.; Martinez, N.; Bertran, M.; Sapiro, G.; Rodrigues, M. Federating for learning group fair models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.01999 2021.
- Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Z. Heterogeneity-aware fair federated learning. Information Sciences 2023, 619, 968-986. [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wu, Z.S.; Smith, V. Fair federated learning via bounded group loss. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Conference on Secure and Trustworthy Machine Learning (SaTML), 2024; pp. 140-160.
- Gao, L.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, W.; Xu, C.; Xu, M. Fifl: A fair incentive mechanism for federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 50th International Conference on Parallel Processing, 2021; pp. 1-10.
- Sun, L.; Lyu, L. Federated model distillation with noise-free differential privacy. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.05537 2020.
- Xie, C.; Huang, K.; Chen, P.-Y.; Li, B. Dba: Distributed backdoor attacks against federated learning. In Proceedings of the International conference on learning representations, 2019.
- Wang, H.; Sreenivasan, K.; Rajput, S.; Vishwakarma, H.; Agarwal, S.; Sohn, J.-y.; Lee, K.; Papailiopoulos, D. Attack of the tails: Yes, you really can backdoor federated learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, 33, 16070-16084.
- Xie, C.; Chen, M.; Chen, P.-Y.; Li, B. Crfl: Certifiably robust federated learning against backdoor attacks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021; pp. 11372-11382.
- Wu, D.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Gao, L. A blockchain-based multi-layer decentralized framework for robust federated learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN), 2022; pp. 1-8.
- Li, J.; Rakin, A.S.; Chen, X.; He, Z.; Fan, D.; Chakrabarti, C. Ressfl: A resistance transfer framework for defending model inversion attack in split federated learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022; pp. 10194-10202.
- Sun, J.; Li, A.; Wang, B.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Chen, Y. Soteria: Provable defense against privacy leakage in federated learning from representation perspective. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2021; pp. 9311-9319.
- Andreina, S.; Marson, G.A.; Möllering, H.; Karame, G. Baffle: Backdoor detection via feedback-based federated learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 41st International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), 2021; pp. 852-863.
- He, C.; Li, S.; So, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Vepakomma, P.; Singh, A.; Qiu, H. Fedml: A research library and benchmark for federated machine learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.13518 2020.
- Lai, F.; Dai, Y.; Singapuram, S.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Madhyastha, H.; Chowdhury, M. Fedscale: Benchmarking model and system performance of federated learning at scale. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning, 2022; pp. 11814-11827.
- Chai, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Yang, Q. Fedeval: A holistic evaluation framework for federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.09655 2020.
- Zhuang, W.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gan, X.; Yin, D.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, S.; Yi, S. Performance optimization of federated person re-identification via benchmark analysis. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2020; pp. 955-963.
- Chen, D.; Gao, D.; Kuang, W.; Li, Y.; Ding, B. pfl-bench: A comprehensive benchmark for personalized federated learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 9344-9360.
- He, C.; Balasubramanian, K.; Ceyani, E.; Yang, C.; Xie, H.; Sun, L.; He, L.; Yang, L.; Yu, P.S.; Rong, Y. Fedgraphnn: A federated learning system and benchmark for graph neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.07145 2021.
- Caldas, S.; Duddu, S.M.K.; Wu, P.; Li, T.; Konečný, J.; McMahan, H.B.; Smith, V.; Talwalkar, A. Leaf: A benchmark for federated settings. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.01097 2018.
- Luo, J.; Wu, X.; Luo, Y.; Huang, A.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q. Real-world image datasets for federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.11089 2019.
- Huang, X.; Han, L.; Li, D.; Xie, K.; Zhang, Y. A reliable and fair federated learning mechanism for mobile edge computing. Computer Networks 2023, 226, 109678. [CrossRef]
- Abdul Salam, M.; Fouad, K.M.; Elbably, D.L.; Elsayed, S.M. Federated learning model for credit card fraud detection with data balancing techniques. Neural Computing and Applications 2024, 36, 6231-6256. [CrossRef]
- Ducange, P.; Marcelloni, F.; Renda, A.; Ruffini, F. Federated Learning of XAI Models in Healthcare: A Case Study on Parkinson’s Disease. Cognitive Computation 2024, 1-26. [CrossRef]

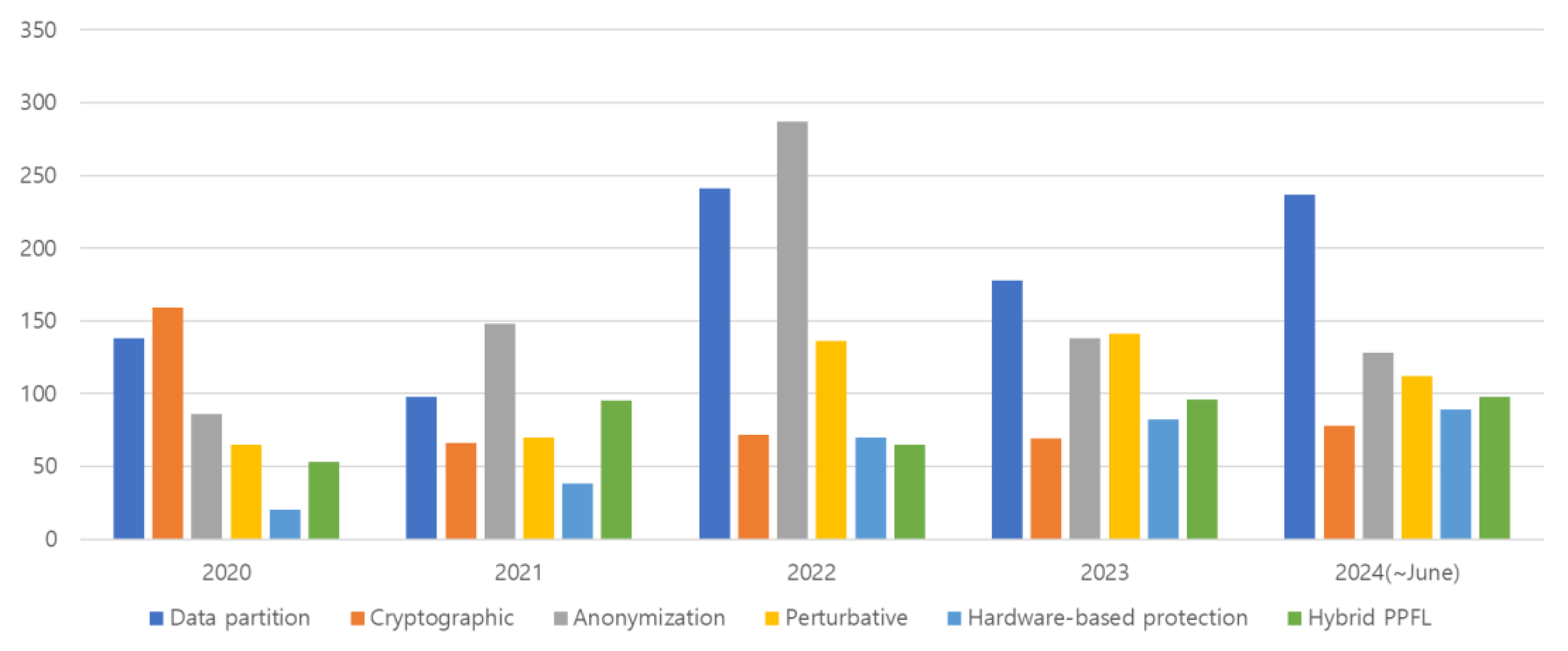
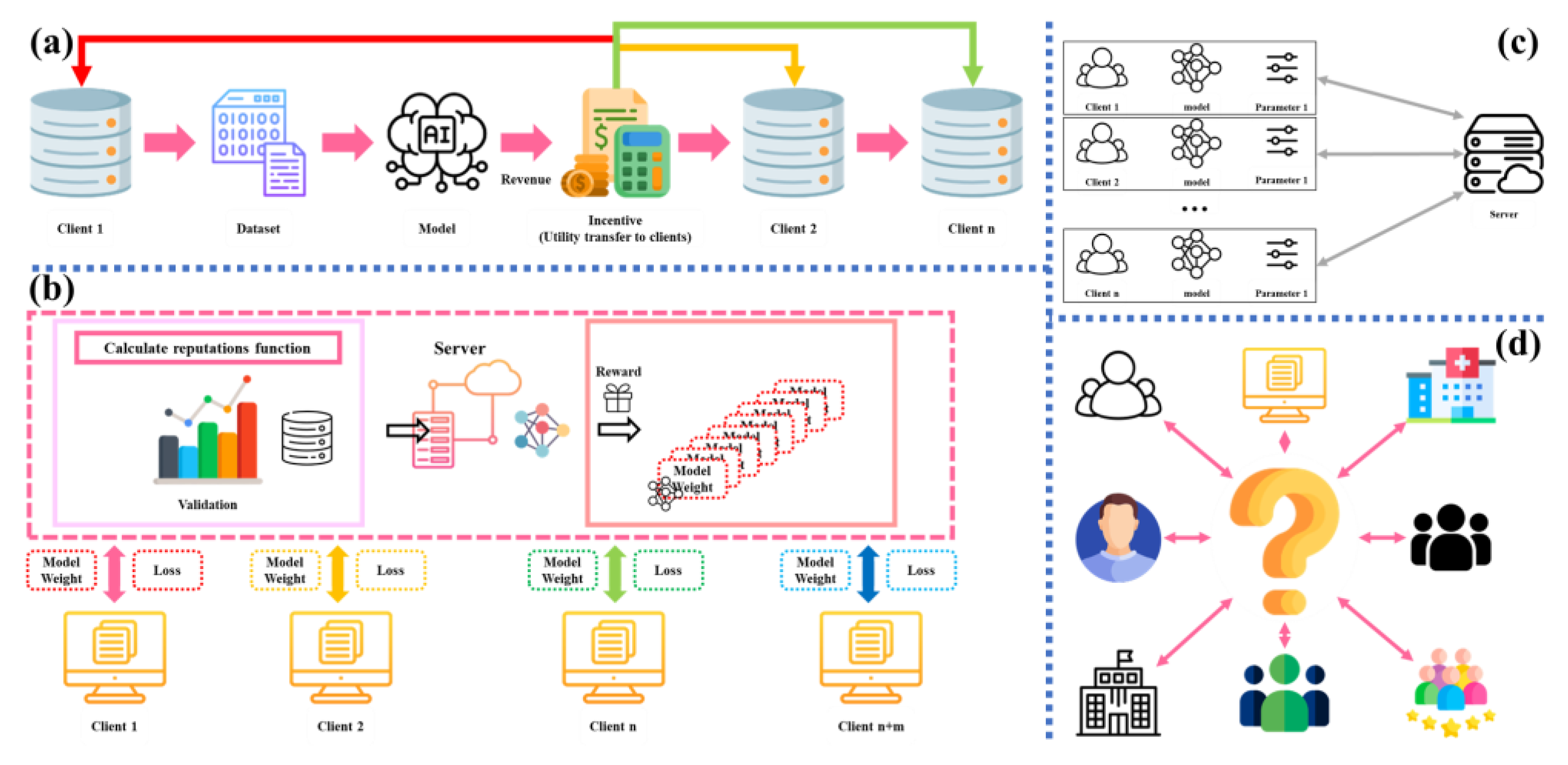
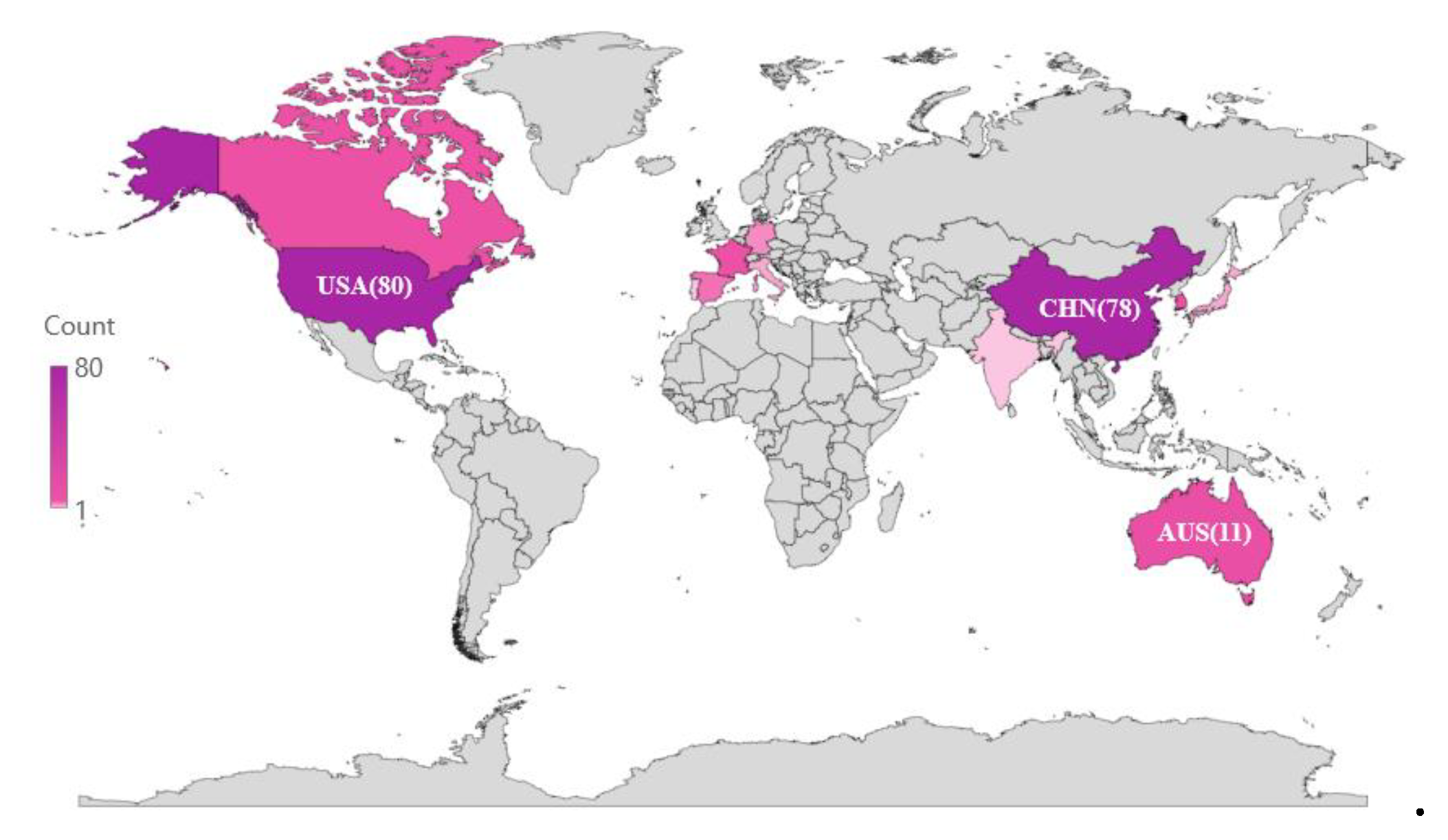
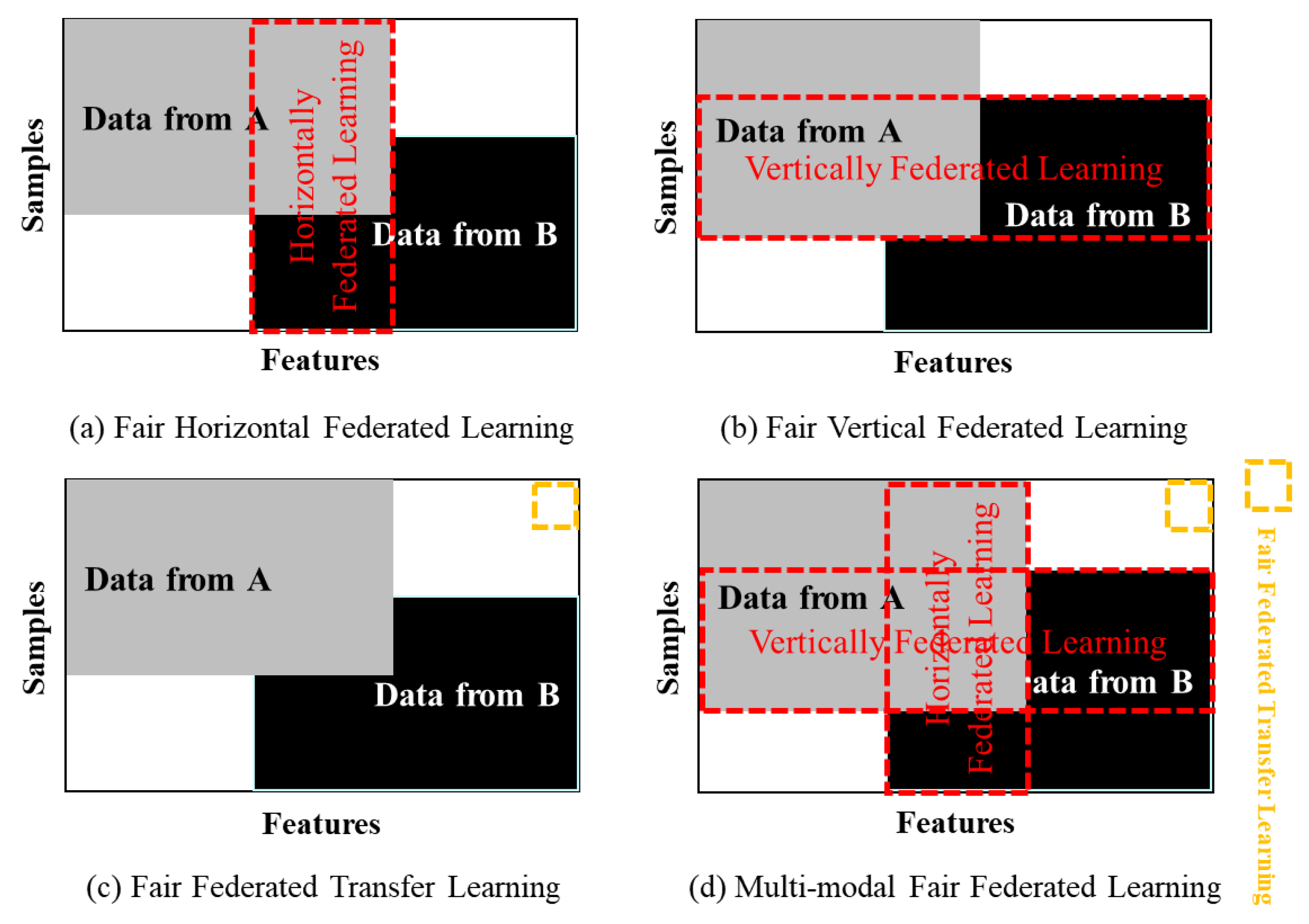
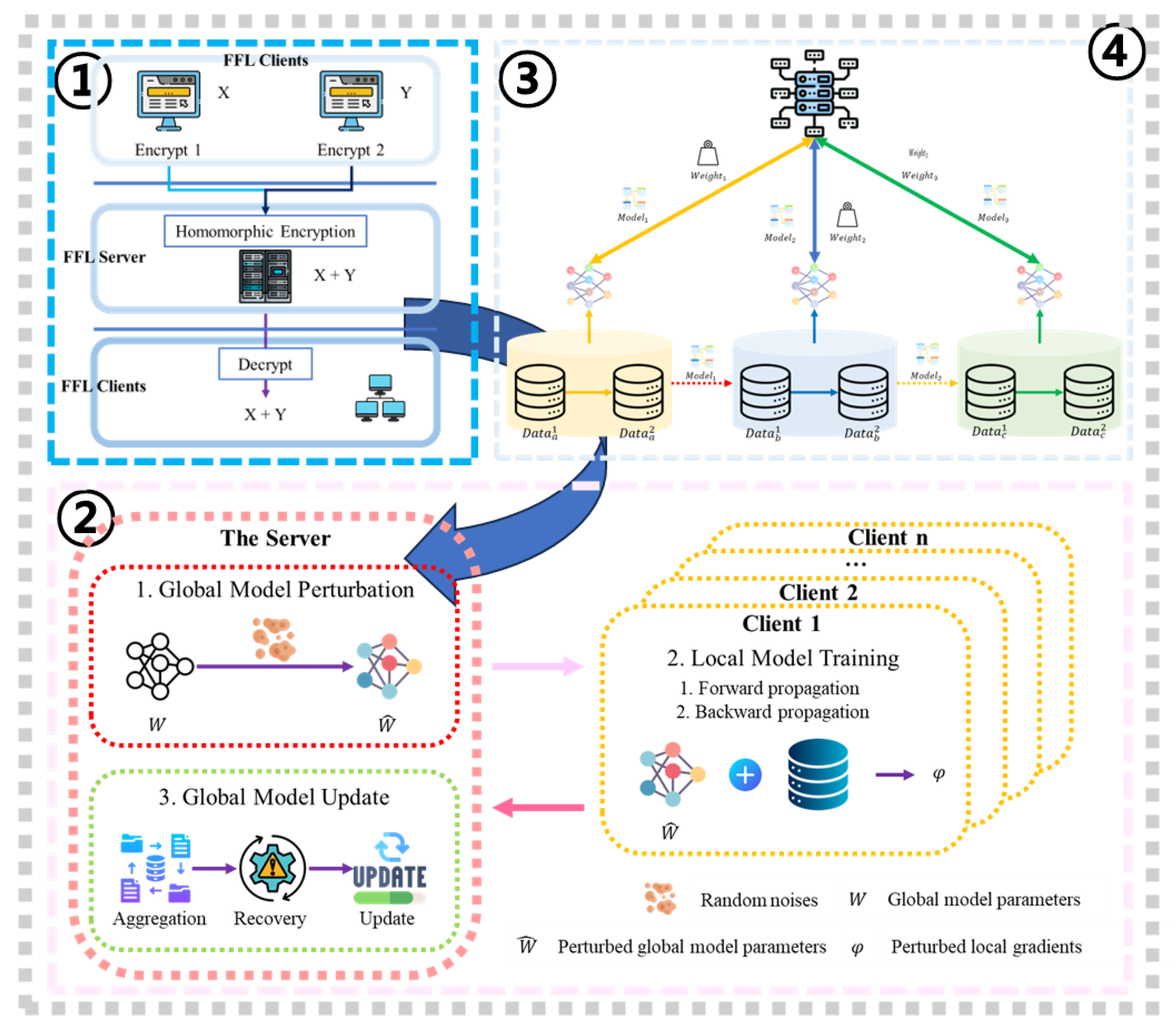
| Categorizations | Ref. | Methods | Main conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional bias sources | [2] | Bias propagation | Analyzing the bias propagation of FL on real-world datasets, we show that biased parties unintentionally covertly encode bias in a small number of model parameters, steadily increasing the global model's reliance on sensitive attributes throughout training. |
| [3] | DCFair | Focusing on the impact of bias, we explore how factors such as device interruptions, biased device data, and biased participation affect the FL process from a system perspective. We present a characterization study that empirically demonstrates how these challenges affect important performance metrics such as model error, fairness, cost, and training time, and why it is important to consider them together rather than individually, and describe a method called DCFair, a framework that comprehensively considers several important challenges of real-world FL systems. | |
| [4] | FFL | We discussed how to eradicate the source of bias and create a more fair federated learning environment. | |
| Sub-sampling, party selection and dropouts | [5] | FL-FDMS | Based on convergence analysis, we develop a novel algorithm, FL-FDMS, which discovers a client's friends (i.e., clients with similar data distributions) on the fly and uses the friends' local updates as replacements for dropout clients to reduce errors and improve convergence performance. |
| [6] | MimiC | The MimiC algorithm server modifies each received model update based on the previous update. The proposed modification to the received model update mimics a virtual central update regardless of the interrupted client. Theoretical analysis of MimiC shows that the difference between the aggregated update and the central update is reduced with an appropriate learning rate, leading to convergence. | |
| [7] | FedDebias | To address the unexplored phenomenon of biased local learning that can explain the problems caused by local updates in supervised FL, we propose FedDebias, a novel integrated algorithm that reduces the local learning bias of features and classifiers. | |
| Data heterogeneity | [8] | FL solutions | We consider the problem of fault identification and simulate various data heterogeneity scenarios, demonstrating that these settings remain challenging for popular FL algorithms and should be taken into consideration when designing a federated predictive maintenance solution. |
| [9] | FedNH | We initially showed that uniformly distributing class prototypes across the latent space and smoothly injecting class semantics into class prototypes and enforcing uniformity helped prevent prototype collapse, and that injecting class semantics improved the local model. | |
| [10] | non-IID settings | By analyzing the principal angles between subspaces in different classes of each dataset, we propose a new concept and framework for non-IID segmentation in FL settings. | |
| Fusion methodologies | [11] | FedDRL | Including malicious models in the fusion process that uses weighted average techniques for model fusion can significantly reduce the accuracy of the aggregated global model, and to address the problem of FL where the number of client samples does not determine the weight values of the model due to the heterogeneity of devices and data, we propose a reliable model fusion method based on reinforcement learning (FedDRL). |
| [12] | Aggregation method | We investigated various aggregation methods that could affect the fairness and bias of the resulting model. | |
| Systems heterogeneity | [13] | Challenges of FL | We discuss the unique characteristics and challenges of FL, provide a broad overview of current approaches, and suggest several directions for future work relevant to the broader research community. |
| [14] | HFL | We summarize the various research challenges of HFL from five aspects: statistical heterogeneity, model heterogeneity, communication heterogeneity, device heterogeneity, and additional challenges. We also review recent progress in HFL, propose a new taxonomy of existing HFL methods, and deeply analyze their advantages and disadvantages. | |
| [15] | Client selection mechanism | We propose a client selection mechanism that considers both system and statistical heterogeneity, aiming to improve the time-to-accuracy performance by offsetting the impact of system performance differences and inter-client data distribution differences on training efficiency. |
| Categorization | Methods | Algorithm | Advantage | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data partitioning | Fair horizontal federated learning (FHFL) | FFL-OppoGAN[19], FedUB[20] | Increases user sample size | Android phone model updates; logistic regression |
| Fair vertical federated learning (FVFL) | FairVFL[21], vflow[22], MOSP[23], FedOnce[24], FedUFO[25], UAB[26], BadVFL[27] | Increases feature dimension | Decision trees; neural networks | |
| Fair federated transfer learning (FFTL) | FAIR-FATE[28], FCFL[29], DRFL[30], TFCS[31] | Increases user sample size and feature dimension | Transfer learning | |
| Multimodal fair federated learning(MMFFL) | FedUFO[25], FedCMI[32], mFairFL[33], MAFL[29], PFL-MCL[34] | Enhances data security, powerful performance, accessibility, scalability, and data use | Securing multi-dimensional fairness, optimizing integrated model learning processes, metaverse applications | |
| Privacy mechanism | Homomorphic encryption (HE) | CKKS[35], FV[36], FLASHE[37], FedML-HE[38] | Users can calculate and process encrypted data | Ridge regression; federated learning |
| Secure multi-party computation (SMPC) | Obliv-C[39], chain-PPFL[40], FL rack[41], VFL-R[42], SecureML[43], PrivFairFL[44], SMPAI[45], SMPC[46] | Minimizes risk of information leakage, optimizes computation across multiple participants | Effective scaling to large networks | |
| Secret sharing (SS) | HFTL[47], PFK-means[48], VerifyNet[49], FairFed[50] | Strengthens security, elasticity, and flexibility | Distributes important information among managers or systems | |
| Data masking (DM) | FedMask[51], PerFedMask[52], FedLMD[53], GlueFL[54], PrivMaskFL[55] | Trains models without exposing local data | Develops a recommendation system based on user behavior while protecting user identity | |
| Data shuffling (DS) | CLDP-SGD[56], SS-Double[57], MSFL[58] | Resolves data imbalance and prevents overfitting | Data characteristics are evenly reflected in the model learning process | |
| Differential privacy (DP) | DPBalance[59], mFairFL[33], FFL-OppoGAN[19], FairFed[60], Local DP FL[61], PEFL[62], OARF[63], FL-LSTM[64], Client-Level DP FL[65], Hybrid FL[66], FedFDP[67], DP-DLP[68] | Protects user privacy by adding noise | Conventional machine learning; deep learning | |
| Additive perturbation methods (APM), Multiplicative perturbation methods (MPM) | FedISM[69], PILE[70], Fed-SMP[71], ANP[72], DISTPAB[73] | Maintains data usefulness while enhancing data privacy, Protects data privacy while preserving original data structure and relationships | Incorporates random noise into data with a specific distribution, Prevents exposure of personal identity or sensitive information; ensures compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR) | |
| Hardware-based protection | FFL-OppoGAN[19], FairFed[60], ShuffleFL[74], FLASH[75], FLATEE[76], EdgeFed[77] | HSM and TPM protect against hardware physical attacks | Hardware solutions often provide faster throughput than software alone | |
| Hybrid privacy-preserving federated learning (HPPFL) | RVE-PFL[78], HybridAlpha[79], xMK-CKKS[80], LEGATO[81], APPFed[82], FederatedTrust[83], PrivFairFL[44], FPFL[84], HFAD[85] | Simultaneously provides improved data privacy and model efficiency | Adapts protection techniques to different environments and requirements; improves efficiency of the entire system | |
| Model aggregation (MA) | PATE[86] | Avoids transmitting original data | Deep network federated learning; PATE method | |
| Sensitivity-based weight distribution | FFLFCN[87], FedSW[88] | Improves accuracy, efficiency, and fairness | Healthcare, finance, smart cities | |
| Applicable machine learning model | Linear models | GLM[89], FedUFO[25], HDP-FL[90], FairFed[50], FFM[91], mFairFL[33] | Concise format, easy to model | Linear regression; ridge regression |
| Tree models | q-FFL[92], FedStaleWeight[93], FAIR-FATE[28], FedFaiREE[94] | Accurate, stable, and able to map non-linear relationships | Classification trees; regression trees | |
| Neural network models | RSRA[95], SpreadGNN[96] | Exhibits learning capabilities, high robustness, and fault tolerance | Pattern recognition, intelligent control | |
| Heterogeneity resolution methods | Asynchronous communication(AC) | Asynchronous FL[97], FedBuff[98], ASO-Fed[99], AFAFed[100] | Prevents communication delay | Device heterogeneity |
| Sampling | CFFL[101], FLI[102], Fold-stratified cross-validation[103], FedSSAR[104], ISFL[105], DivFL[106], Delta[107] | Avoids simultaneous training with heterogeneous equipment | Pulling reduction with local compensation (PRLC) | |
| Fault-tolerant mechanism | FEEL[108], BDFL[109] | Prevents entire system from collapsing | Redundancy algorithm | |
| Heterogeneous model | FCCL[110], FedAlign[111], FedRolex[112] | Solves corresponding heterogeneous device | LG-FEDAVG algorithm |
| Categorization | Personal Information protection commissioner’s pseudonymous information processing guidelines[115] | Guidelines for processing pseudonymized information in the education field[115] | Guide to pseudonyms and anonymization in the financial sector[115] | Guidelines for using healthcare data[116] |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Privacy mechanism |
|||||
| Deletion technology |
Deletion, partial deletion, line-item deletion, local deletion, masking | Record deletion, column deletion, partial deletion, deletion of all identifying elements | Masking, local deletion, record deletion | Identifier: deleted or replaced with serial number Key personal information: Reduce identification by deleting or extracting some meaningful information Attribute value: Apply pseudonymization techniques for each data type, such as deletion and masking |
|
| Statistical tools | Total processing, partial processing | Sampling, total processing | Sampling, total processing | ||
| Generalization skills |
General rounding, random rounding, control rounding, top and bottom coding, local generalization, range method, problem data categorization | Rounding, general rounding, random rounding, control rounding, local generalization, top and bottom coding, attribute combination (categorization) | Rounding, top and bottom coding, combining attribute sets into a single attribute value (categorization), local generalization | ||
| Encryption technique |
Bidirectional encryption, one-way encryption, order-preserving encryption, form-preserving encryption, homomorphic encryption, polymorphic encryption | Deterministic encryption, order-preserving encryption, form-preserving encryption, homomorphic encryption, homomorphic secret distribution | Deterministic encryption, order-preserving encryption, form-preserving encryption, homomorphic encryption, homomorphic secret distribution | Some data types do not require pseudonymization (e.g., measurement value information) and pseudonymization is limited (e.g., voice data, biometric data, and genome data) | |
| Randomization technique |
Noise addition, permutation (permutation), tokenization, random number generation | Add noise, permutations, 1:1 swaps, partial sums |
Permutations, noise addition, partial totals | ||
| Other technologies | Sampling, dissection, data reproduction, homomorphic secret distribution, differential privacy | Anatomy, data reproduction | Anatomy, data reproduction | ||
| Pseudonymization technique |
No relevant technique or classification criteria available | Mapping table, counting, pseudorandom number generation, hash algorithm, bidirectional encryption, masking, scrambling, blurring, token system, polymorphic encryption | Mapping table, bidirectional encryption, one-way encryption, tokenization | ||
| Privacy protection model |
No relevant technique or classification criteria available | No relevant technique or classification criteria available | k-anonymity, l-diversity model, t-proximity model, differential privacy, protection model | ||
| Metrics | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Measure how accurately the model predicts |
| Precision | Proportion of predicted positive outcomes that are actually positive |
| Recall | Proportion of true positive cases predicted by the model as positive |
| F1-score | Represents the harmonic average of precision and recall, and expresses the balance of the two indices |
| Loss Metrics | Measures how incorrectly the model predicted during training (ex: cross-entropy loss) |
| AUROC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, measuring the classification performance of the model |
| MSE | Used in rare problems, the difference between the predicted and actual values is squared and averaged |
| MAE | An indicator that averages the absolute difference between predicted and actual values |
| Model Convergence Time | Measure the time it takes for the model to converge |
| Communication Efficiency | Measure the efficiency required for data transfer during training |
| Training time | Measure the time required to train a model |
| Model size | Size of models that need to be transferred, which affects network traffic in FFL |
| Update Frequency | How often the client sends model updates to the server |
| Resource usage | Client's CPU and memory usage during training |
| Scalability | Measures how well a system handles varying numbers of clients and data volumes |
| Data usage efficiency | Learning efficiency relative to the amount of used data |
| Client participation | Degree of involvement and impact of various clients |
| Latency | Latency between data processing and model update |
| Robustness | Models are resistant to data quality fluctuations or malicious attacks |
| Client Drift | Dispersion of trained model across clients |
| Categories | Classification | Algorithm | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data-Level | Private Data Processing | Data Preparation | Safe[127] | Detects and filters out infected data from attacked devices using clustering algorithms | |
| FedMix[128] | Perform data augmentation based on MixUp strategy | ||||
| Astraea[129] | Perform data augmentation based on global data distribution created by collecting local data distribution | ||||
| Faug[130] | Study the balance between personal information leakage and communication overhead through GAN-based data augmentation method | ||||
| Data Privacy Protection | PLDP-PFL[131] | Perform personalized differential privacy protection according to the sensitivity of personal data | |||
| A Syntactic approach for privacy in FL[132] | Use anonymization techniques to reduce the sensitivity of local personal data | ||||
| External Data Utilization | Knowledge Distillation | FedMD[133] | Leverage Federated Distillation (FD) or Co-Distillation to learn knowledge from other clients | ||
| FedGKT[134] | Through knowledge distillation, the edge knowledge of the small CNN is periodically transferred to the large server-side CNN to reduce the burden of edge learning | ||||
| FedFTG[135] | Input virtual data into global and local models for knowledge refinement | ||||
| Unsupervised Representation Learning | FedCA[136] | The FURL algorithm based on contrast loss solves the problems of data distribution inconsistency and representation inconsistency across clients | |||
| Orchestra[137] | Discussed to learn a common representation model while decentralizing and labeling private data | ||||
| MOON[138] | Modify update direction by introducing model contrast loss | ||||
| FedProc[139] | Mitigating statistical heterogeneity through prototype-based contrastive learning | ||||
| ProtoFL[140] | Extract representations from existing models trained using existing datasets, independent of individual client data | ||||
| Model-Level | Federated Optimization | Regularization | FedProx[141] | Federated optimization algorithm adding proximal flavor to FedAvg | |
| FedCurv[142] | Preventing serious forgetting when transferring jobs using the EWC algorithm | ||||
| pFedME[143] | Using the Moreau envelope function as a normalized loss function | ||||
| Meta Learning | Per-FedAvg[144] | A custom variant of the FedAvg algorithm based on the MAML formula | |||
| ARUBA[145] | Leverage online convex optimization and sequence prediction algorithms to adaptively learn direct similarity and test FL performance | ||||
| Multi-task Learning | MOCHA[146] | A system-aware optimization framework for FMTL | |||
| Ditto[147] | A scalable federated multitask learning framework with two tasks: a global goal and a local goal | ||||
| Knowledge Transfer | Knowledge Distillation | FedDF[148] | Leverage unlabeled or generated data for ensemble refinement | ||
| FedGEN[149] | Performing statistical HFL via data-free knowledge distillation method | ||||
| FedLMD[53] | Facilitates FL by recognizing different label distributions for each client | ||||
| Transfer Learning | FT-pFL[150] | Personalized knowledge transfer through knowledge coefficient matrix | |||
| Fedhealth[151] | Federated transfer learning framework applied to the medical field | ||||
| Architecture Sharing | Backbone Sharing | FedRep[152] | All clients can jointly train a global representation learning structure and then use their private data to train their own heads | ||
| CReFF[153] | Retrain by learning the associated features, similar to training a classifier on real data | ||||
| Classifier Sharing | LG-FedAvg[154] | Extract advanced features using personalized layers and use server-shared base layers for classification | |||
| FedPAC[155] | Reduce feature variance across clients by constraining each sample feature vector close to the global feature centroid of its category | ||||
| Other Part Sharing | HeteroFL[156] | Assign local models of various sizes depending on the computational and communication capabilities of each client | |||
| FedLA[157] | Utilizes a hypernetwork of servers to evaluate the importance of each client model layer and generate aggregate weights for each model layer | ||||
| CD2-pFed[158] | Dynamically separate global model parameters for personalization | ||||
| Server-Level | Client Selection | Favor[159] | A heuristic-based control framework that actively selects an optimal subset of clients to participate in the FL iterative process | ||
| CUCB[160] | Client selection algorithm to minimize class imbalance and facilitate global model convergence | ||||
| FedSAE[161] | Estimate the reliability of each device and select clients based on training loss | ||||
| FedCS[162] | Perform client selection tasks based on data resources, computer capabilities, and wireless channel conditions | ||||
| Client Clustering | FL + HC[163] | Introducing a hierarchical clustering step to separate client clusters based on the similarity of client updates to the global joint model | |||
| FeSEM[164] | Calculate the distance between local models and cluster centroids using SEM optimization | ||||
| CFL[165] | Clustering similar clients via cosine similarity between gradient updates | ||||
| FLAME[166] | Detect adversarial model updates through a clustering strategy that limits the noise scale of backdoor denoising | ||||
| Decentralized Communication | Combo[167] | After dividing the local model into model segments, randomly select some clients to send the model segments | |||
| ProxyFL[168] | Ensures that each client maintains two models: a private model for the exchange and a publicly shared proxy model | ||||
| BFLC[169] | Strengthen the security of FL by leveraging blockchain to store global models and exchange local model updates | ||||
| Future Direction | Improving Communication Efficiency | CMFL[170] | Prevents irrelevant updates from being sent to the server by measuring whether local updates are consistent with global updates | ||
| FedDM[171] | Construct some synthetic data locally on the client to have a similar distribution to the original data for the loss function | ||||
| DisPFL[172] | Adopt distributed sparse learning technology | ||||
| Federated Fairness | FedDM[84] | Modified method of differential multipliers | |||
| FPFL[173] | Improving differential multiplier MMDM to improve system fairness | ||||
| q-FedAvg[92] | Improve fairness by reducing accuracy differences in client models | ||||
| CFFL[101] | Collaborative fairness is achieved in FL by assigning models with different performance according to the contribution of each client | ||||
| FFLFCN[87] | Personal information protection in the medical field FFL | ||||
| PrivFairFL[44] | The conflict between fairness and privacy is resolved by combining FL with secure multi-party computation (SMC) and differential privacy (DP) | ||||
| CVFL[174] | To alleviate the straggler problem, we design a new optimization objective that can increase the contribution of stragglers to the trained model | ||||
| Incentive design and differential privacy based federated learning[175] | Designing a new incentive mechanism to encourage many data owners to participate in the FL process through MD and DP, considering privacy protection | ||||
| FairFL[176] | It consists of a principled deep multi-agent reinforcement learning framework and a secure information aggregation protocol that optimizes both the accuracy and fairness of the learned model while respecting the strict privacy constraints of the client | ||||
| FairVFL[21] | Learn an integrated and fair representation of samples based on distributed feature fields in a privacy-preserving manner. Specifically, each platform with fairness-insensitive features first learns a local data representation from the local features | ||||
| FedFB[177] | Modifies the FedAvg protocol to effectively mimic centralized process learning | ||||
| Dubhe[178] | To address the statistical heterogeneity problem, we propose a pluggable system-level client selection method called Dubhe. With the help of HE, clients actively participate in learning while protecting their personal information | ||||
| FedEBA+[179] | We propose FedEBA+, a new FL algorithm that enhances fairness while improving global model performance. FedEBA+ integrates a fair aggregation system that assigns higher weights to low-performing clients and a sort update method, provides theoretical convergence analysis, and demonstrates fairness | ||||
| AFLPC[180] | Reduce noise while protecting data privacy using an adaptive differential privacy mechanism. We propose a weight-based asynchronous FL aggregate update method to reasonably control the proportion of parameters submitted by users with different training speeds in the aggregate parameters, and actively update the aggregate parameters of delayed users to find the speed difference in the model. Effectively reduce negative impacts | ||||
| Blockchain-orchestrated machine learning[181] | Exploring more detailed combinations of uses along with the auditability and incentives that blockchain can allow in machine learning processes, with a focus on decentralizing or federating the learning process. Provides an advanced blockchain-orchestrated machine learning system for privacy-preserving FL in medicine based on cost-benefit analysis and a framework for new utility in the health field | ||||
| FairFed[50] | We empirically evaluate it against a common baseline for fair ML and FL, and provide a fairer model under highly heterogeneous data distributions across clients. Exploring techniques for ensuring group fairness in a FL environment and addressing potential biases that may arise during model training | ||||
| FeMinMax[182] | Formally analyzing how fairness goals differ from existing FL fairness criteria that impose similar performance across participants instead of demographic groups | ||||
| FGFL[183] | Evaluate players based on reputation and contributing factors and create a blockchain-based incentive governor for FL. Job publishers pay clients fairly to recruit efficient players, and malicious players are punished and deleted | ||||
| Bounded Group Loss[184] | We explore and extend the concept of Bounded Group Loss as a theoretically grounded approach to group fairness that offers a favorable balance over previous work between fairness and usefulness. We propose a scalable federated optimization method to optimize empirical risk under multiple group fairness constraints | ||||
| FIFL[185] | Compensate workers fairly to attract trustworthy and efficient workers and punish and eliminate malicious workers based on a dynamic, real-time worker evaluation process | ||||
| Privacy Protection | DP-FedAvg[64] | Applying a Gaussian mechanism to add user-level privacy features to FedAvg | |||
| FedMD-NFDP[186] | Adding a noise-free DP mechanism to FedMD to protect data privacy without generating noise | ||||
| Attack Robustness | Attack Methods | DBA[187] | Decompose global triggers into local triggers and inject them into multiple malicious clients | ||
| Edge-case backdoors[188] | Consider contaminating edge case samples (tail data of the data distribution) | ||||
| Defense Stratedgies | CRFL[189] | Improve robustness against backdoor attacks by clipping the model and adding soft noise | |||
| RBML-DFL[190] | Prevent central server failure or malfunction through blockchain encrypted transactions | ||||
| ResSFL[191] | We obtain a durable feature extractor that is trained by experts with the attacker's perception to initialize the client model. | ||||
| Soteria[192] | Attack defenses are performed by creating distorted data representations, which reduces the quality of the reconstructed data. | ||||
| BaFFLe[193] | The server trains a backdoor filter and randomly sends it to the client to identify and remove backdoor instances. | ||||
| Uniform Benchmark | General Federated Learning Systems | FedML[194] | A research library that supports distributed learning, mobile on-device learning, and standalone simulation learning. Provides standardized implementations of several existing FL algorithms and provides standardized benchmark settings for various datasets, including non-IID segmentation methods, number of devices, and baseline models. | ||
| FedScale[195] | A federated learning benchmark suite that provides real-world datasets covering a wide range of FL tasks, including image classification, object detection, language modeling, and speech recognition. FedScale also includes the extensible and extensible FedScale runtime to enable and standardize real-world endpoint deployments of FL. | ||||
| OARF[63] | Simulate real-world data distribution using public datasets collected from various sources. Additionally, OARF quantitatively studies preliminary relationships between various design indicators such as data partitioning and privacy protection mechanisms in FL systems. | ||||
| FedEval[196] | FL evaluation model with five metrics including accuracy, communication, time consumption, privacy, and robustness. FedEval is implemented and evaluated on two of the most widely used algorithms: FedSGD and FedAvg. | ||||
| Specific Federated Learning Systems | FedReIDBench[197] | A new benchmark for implementing FL on human ReID, including 9 different datasets and 2 federation scenarios. Specifically, the two federation scenarios are the camera federation scenario and the dataset federation scenario, which represent the standard server-client architecture and client-edge-cloud architecture, respectively. | |||
| pFL-Bench[198] | A benchmark for personalized FL, covering 12 different dataset variants including images, text, graphs, and recommendation data with integrated data partitioning and realistic heterogeneous settings. Additionally, pFL-Bench provides implementation of over 20 competitive, personalized FL criteria to aid in standardized evaluation. | ||||
| FedGraphNN[199] | A benchmark system built on a unified formulation of graph federated learning, including extensive datasets from seven fields, popular graph neural network (GNN) models and FL algorithms. | ||||
| Datasets | LEAF[200] | Contains six types of federated datasets covering a variety of fields, including image classification (FEMNIST, Synthetic Dataset), image recognition (Celeba), sentiment analysis (Sentiment140), and next character prediction (Shakespeare, Reddit). Additionally, LEAF provides two sampling methods, ‘IID’ and ‘non-IID’, to partition the dataset to different clients. | |||
| Street Dataset[201] | Introducing a federated dataset for object detection. This dataset contains over 900 images generated from 26 street cameras and 7 object categories annotated with detailed bounding boxes. Additionally, the article provides data partitioning of 5 or 20 clients, where the data distribution is non-IID and unbalanced, reflecting the characteristics of real federated learning scenarios. | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





