Submitted:
12 October 2024
Posted:
14 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biocomposite Preparation
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Measurement of Body Weight and Composition, Energy Intake, Absorption, and Digestibility
2.4. Estimating Energy Expenditure Using the Energy-Balance Method
2.5. Blood Glucose and Serum Lipid Profile
2.6. Measurement of Dietary, Fecal, and Hepatic Lipids and Fecal Bile Acids
2.7. Measurement of Hepatic Gene Expression
2.8. Hepatic Histopathological Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
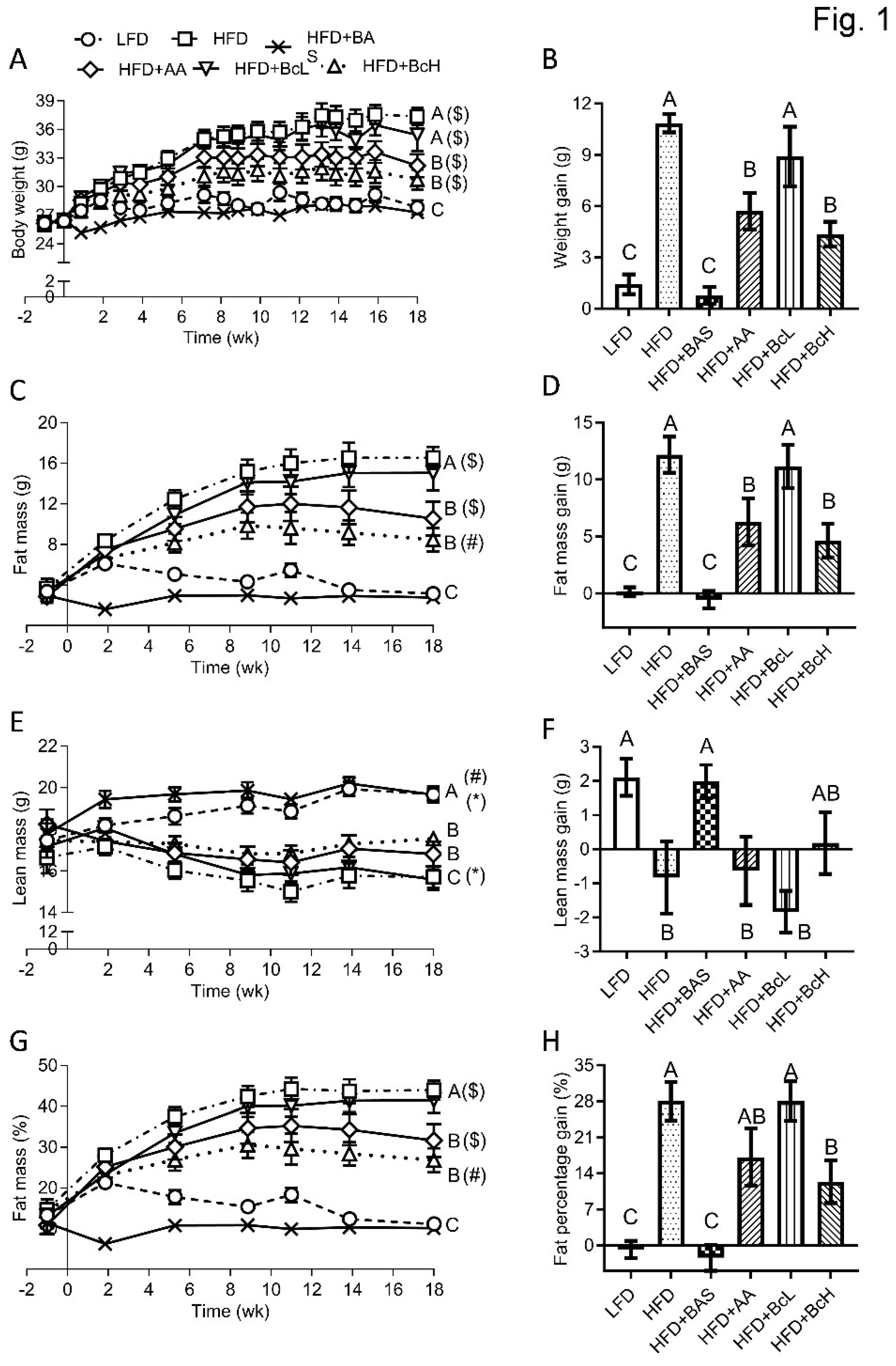
3.1. Biocomposite Supplementation Decreases HFD-Induced Fat Gain and Prevents Lean-Mass Loss
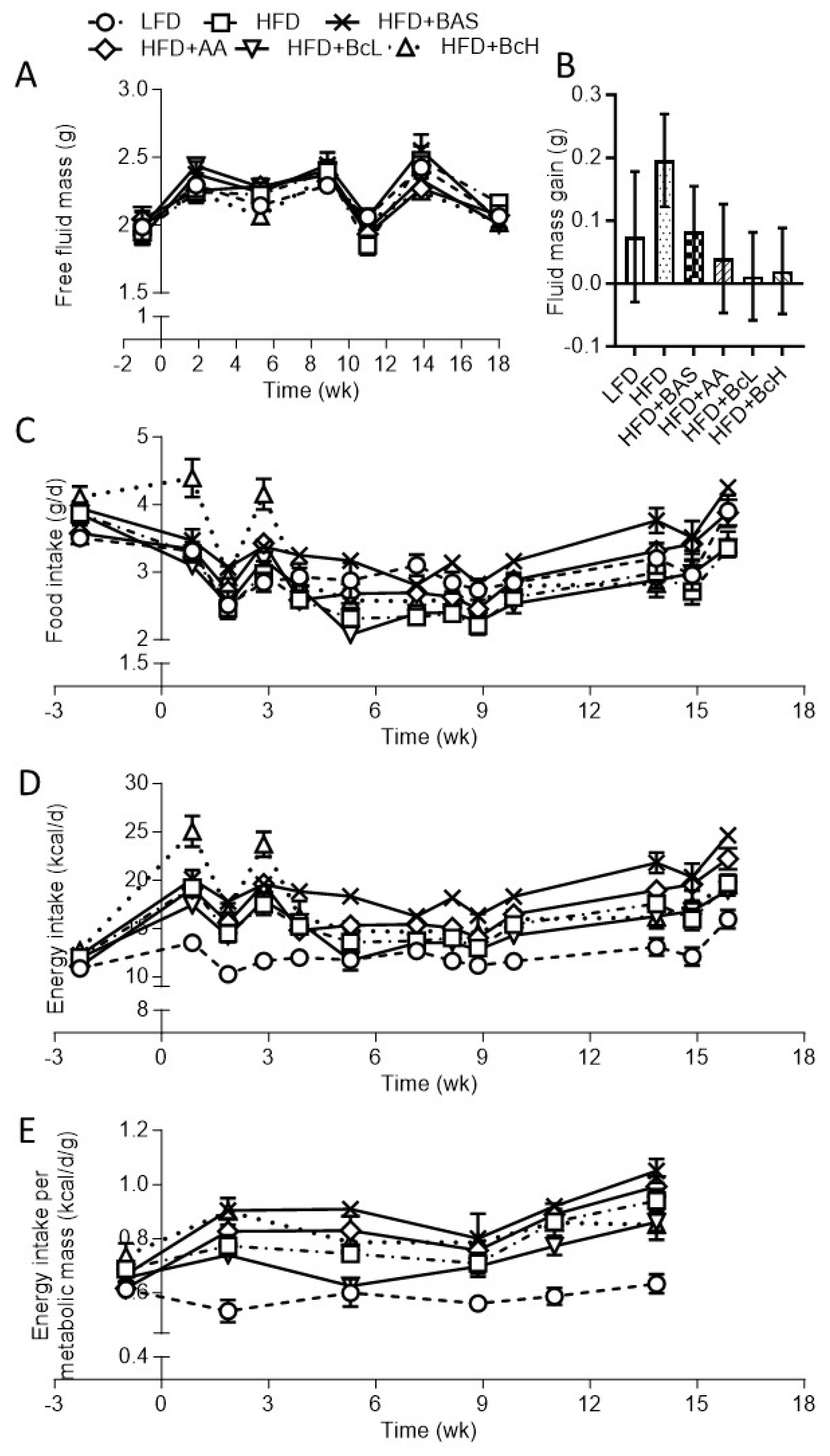
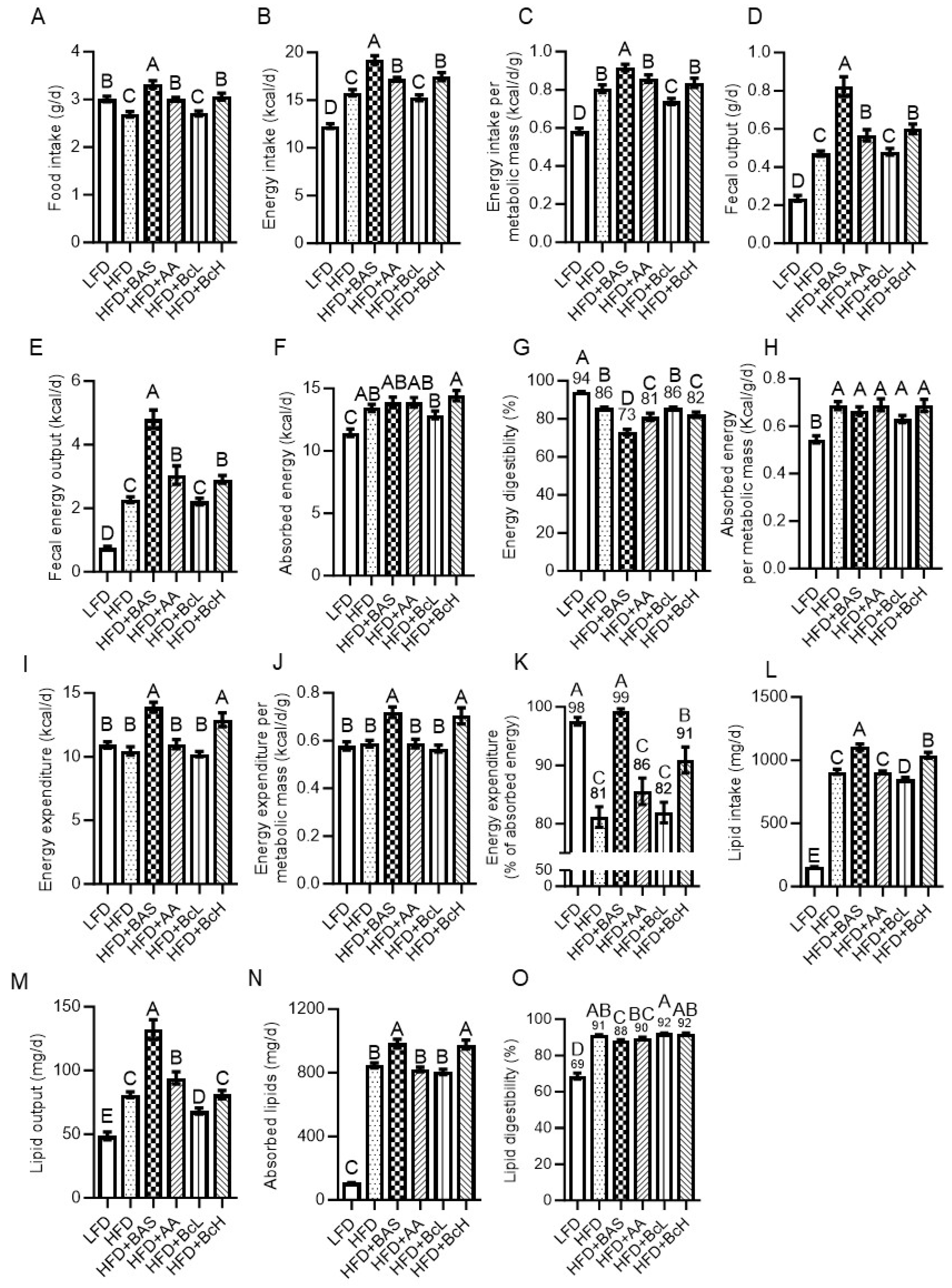
3.2. Biocomposite-Induced DIO Attenuation is Not Due to Reduced Energy Intake or Absorption
3.3. DIO Attenuation is Related to Higher Energy Expenditure, as Calculated by the Energy-Balance Method
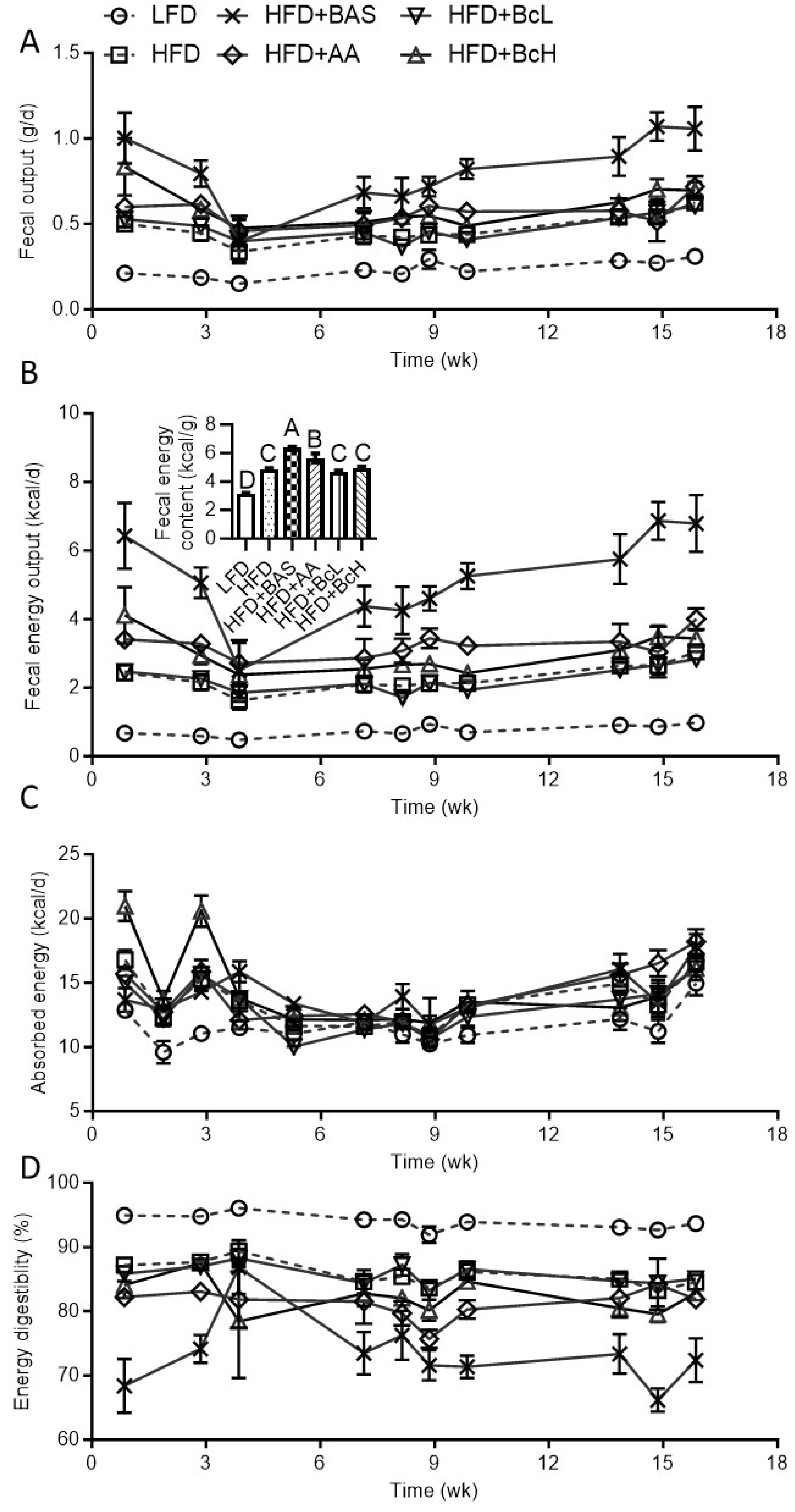
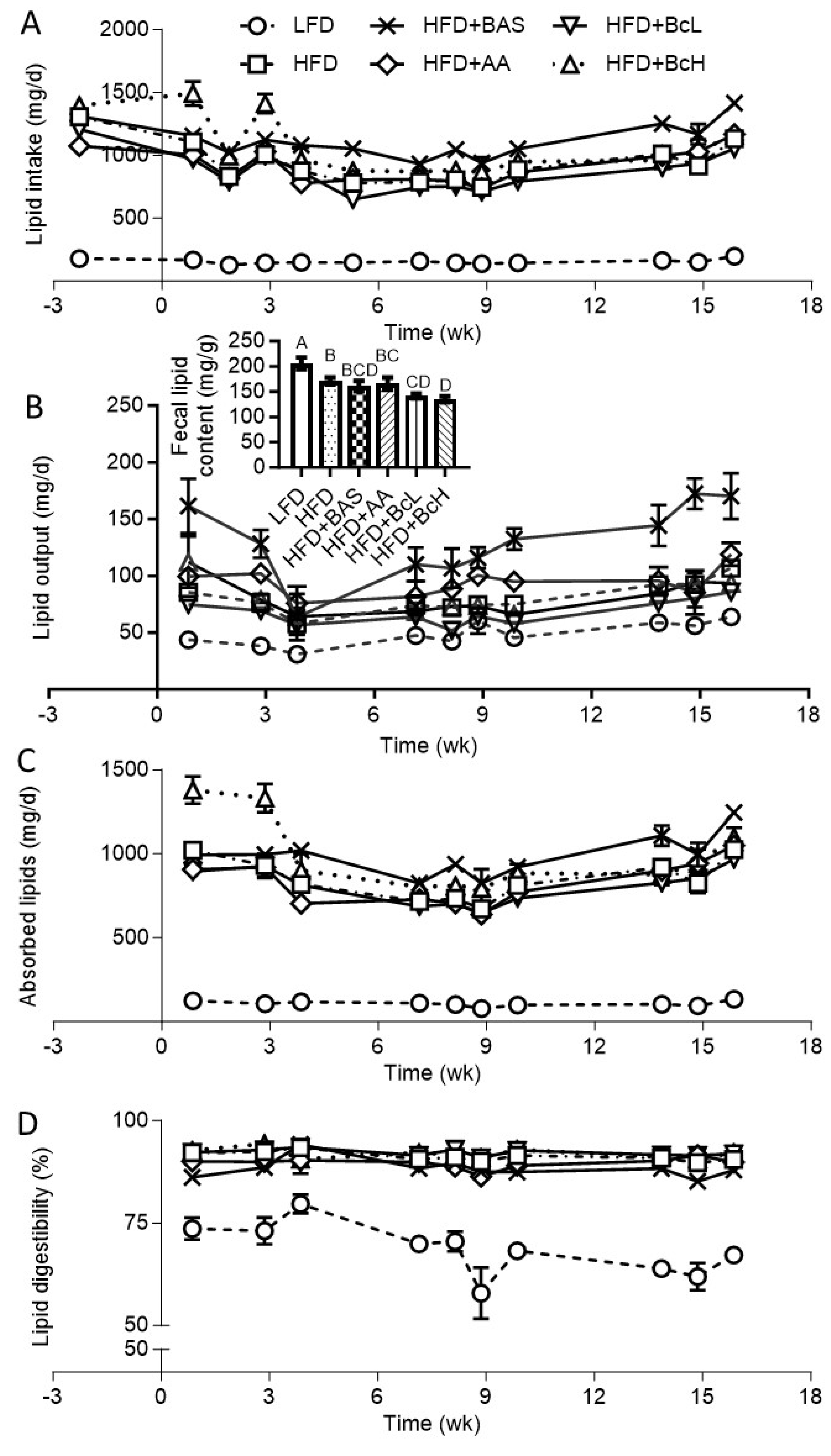
3.4. DIO Attenuation by Biocomposite Supplementation is Not Due to Attenuated Lipid Digestibility
3.5. Biocomposite Supplementation Does Not Affect the HFD-Induced Increment in Bile Salt Extraction Rate
3.6. Biocomposite Supplementation Attenuates HFD-Induced Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Related Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Noubiap JJ, Nansseu JR, Lontchi-Yimagou E, Nkeck JR, Nyaga UF, Ngouo AT, et al. Geographic distribution of metabolic syndrome and its components in the general adult population: A meta-analysis of global data from 28 million individuals. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Diabetes Res Clin Pract; 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tak YJ, Lee SY. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Anti-Obesity Treatment: Where Do We Stand? Curr Obes Rep. Nature Publishing Group; 2021. p. 14–30.
- Pilitsi E, Farr OM, Polyzos SA, Perakakis N, Nolen-Doerr E, Papathanasiou AE, et al. Pharmacotherapy of obesity: Available medications and drugs under investigation. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental. 2019;92:170–92. [CrossRef]
- Armitage J. The safety of statins in clinical practice. Lancet. 2007;370:1781–90. [CrossRef]
- Seidah NG, Prat A. The Multifaceted Biology of PCSK9. Endocrine Reviews. 2022;43:558–82. [CrossRef]
- Alder M, Bavishi A, Zumpf K, Peterson J, Stone NJ. A Meta-Analysis Assessing Additional LDL-C Reduction from Addition of a Bile Acid Sequestrant to Statin Therapy. American Journal of Medicine. 2020;133:1322–7. [CrossRef]
- Mantovani A, Dalbeni A. Treatments for nafld: State of art. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. Int J Mol Sci; 2021. p. 1–27.
- Mendrick DL, Diehl AM, Topor LS, Dietert RR, Will Y, La Merrill MA, et al. Metabolic syndrome and associated diseases: From the bench to the clinic. Toxicological Sciences. 2018;162:36–42. [CrossRef]
- Mazidi M, Rezaie P, Karimi E, Kengne AP. The effects of bile acid sequestrants on lipid profile and blood glucose concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. International Journal of Cardiology. Elsevier Ireland Ltd; 2017. p. 850–7. [CrossRef]
- Zhu A, Chen J, Wu P, Luo M, Zeng Y, Liu Y, et al. Cationic polystyrene resolves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, obesity, and metabolic disorders by promoting eubiosis of gut microbiota and decreasing endotoxemia. Diabetes. American Diabetes Association Inc.; 2017. p. 2137–43. [CrossRef]
- Zhou K, Xia W, Zhang C, (Lucy) Yu L. In vitro binding of bile acids and triglycerides by selected chitosan preparations and their physico-chemical properties. LWT. 2006;39:1087–92. [CrossRef]
- Sumiyoshi M, Kimura Y. Low molecular weight chitosan inhibits obesity induced by feeding a high-fat diet long-term in mice. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2010;58:201–7. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Liu J, Li L, Xia W. Dietary chitosan improves hypercholesterolemia in rats fed high-fat diets. Nutrition Research. 2008;28:383–90. [CrossRef]
- Bahijri SM, Alsheikh L, Ajabnoor G, Borai A. Effect of supplementation with chitosan on weight, cardiometabolic, and other risk indices in wistar rats fed normal and high-fat/high-cholesterol diets ad libitum. Nutr Metab Insights. 2017;10.
- Fukada Y, Kimura K, Ayaki Y. Effect of chitosan feeding on intestinal bile acid metabolism in rats. Lipids. 1991;26:395–9. [CrossRef]
- van Bennekum AM, Nguyen D V., Schulthess G, Hauser H, Phillips MC. Mechanisms of cholesterol-lowering effects of dietary insoluble fibres: relationships with intestinal and hepatic cholesterol parameters. British Journal of Nutrition. 2005;94:331–7. [CrossRef]
- Ni Mhurchu C, Poppitt SD, McGill AT, Leahy FE, Bennett DA, Lin RB, et al. The effect of the dietary supplement, Chitosan, on body weight: A randomised controlled trial in 250 overweight and obese adults. Int J Obes. 2004;28:1149–56.
- Bessell E, Maunder A, Lauche R, Adams J, Sainsbury A, Fuller NR. Efficacy of dietary supplements containing isolated organic compounds for weight loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. Int J Obes. Int J Obes (Lond); 2021. p. 1631–43. [CrossRef]
- Yuan Q, Shah J, Hein S, Misra RDK. Controlled and extended drug release behavior of chitosan-based nanoparticle carrier. Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6:1140–8. [CrossRef]
- Katti KS, Katti DR, Dash R. Synthesis and characterization of a novel chitosan/montmorillonite/ hydroxyapatite nanocomposite for bone tissue engineering. Biomedical Materials. 2008;3. [CrossRef]
- Sivak O, Darlington J, Gershkovich P, Constantinides PP, Wasan KM. Protonated nanostructured aluminosilicate (NSAS) reduces plasma cholesterol concentrations and atherosclerotic lesions in apolipoprotein E deficient mice fed a high cholesterol and high fat diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2009;8:30. [CrossRef]
- Gershkovich P, Darlington J, Sivak O, Constantinides PP, Wasan KM. Inhibition of intestinal absorption of cholesterol by surface-modified nanostructured aluminosilicate compounds. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:2390–400. [CrossRef]
- Gershkovich P, Sivak O, Contreras-Whitney S, Darlington JW, Wasan KM. Assessment of cholesterol absorption inhibitors nanostructured aluminosilicate and cholestyramine using in vitro lipolysis model. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101:291–300. [CrossRef]
- Xu P, Dai S, Wang J, Zhang J, Liu J, Wang F, et al. Preventive obesity agent montmorillonite adsorbs dietary lipids and enhances lipid excretion from the digestive tract. Sci Rep. 2016;6. [CrossRef]
- Xu P, Hong F, Wang J, Cong Y, Dai S, Wang S, et al. Microbiome Remodeling via the Montmorillonite Adsorption-Excretion Axis Prevents Obesity-related Metabolic Disorders. EBioMedicine. 2017;16:251–61. [CrossRef]
- Robinson A, Johnson NM, Strey A, Taylor JF, Marroquin-Cardona A, Mitchell NJ, et al. Calcium montmorillonite clay reduces urinary biomarkers of fumonisin B1 exposure in rats and humans. Food Additives and Contaminants - Part A Chemistry, Analysis, Control, Exposure and Risk Assessment. 2012;29:809–18. [CrossRef]
- Afriyie-Gyawu E, Wang Z, Ankrah NA, Xu L, Johnson NM, Tang L, et al. NovaSil clay does not affect the concentrations of vitamins A and E and nutrient minerals in serum samples from Ghanaians at high risk for aflatoxicosis. Food Additives and Contaminants - Part A Chemistry, Analysis, Control, Exposure and Risk Assessment. 2008;25:872–84. [CrossRef]
- Wang JS, Luo H, Billam M, Wang Z, Guan H, Tang L, et al. Short-term safety evaluation of processed calcium montmorillonite clay (NovaSil) in humans. Food Additives and Contaminants. 2005;22:270–9. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell NJ, Kumi J, Aleser M, Elmore SE, Rychlik KA, Zychowski KE, et al. Short-term safety and efficacy of calcium montmorillonite clay (UPSN) in children. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 2014;91:777–85. [CrossRef]
- Gutman R, Rauch M, Neuman A, Khamaisi H, Jonas-Levi A, Konovalova Y, et al. Sepiolite Clay Attenuates the Development of Hypercholesterolemia and Obesity in Mice Fed a High-Fat High-Cholesterol Diet. J Med Food. 2020;23:289–96. [CrossRef]
- Zadaka-Amir D, Bleiman N, Mishael YG. Sepiolite as an effective natural porous adsorbent for surface oil-spill. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials. 2013;169:153–9. [CrossRef]
- Shaltiel-Harpaz L, Kreimer T, Dudai N, Kaspi R, Ben-Yakir D, Rytwo G. Sepiolite- rosemary oil combination as an environmentally oriented insecticide. Applied Clay Science. 2023;234:106838. [CrossRef]
- Aranda P, Darder M, Wicklein B, Rytwo G, Ruiz-Hitzky E. Clay-Organic Interfaces for Design of Functional Hybrid Materials. Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Interfaces. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA; 2017. p. 1–84.
- Rytwo G, Sitruk A, Lavi R, Khamaisi H, Gutman R. De-emulsification of oil emulsions by clays and biocomposites. 8th Mid-European Clay Conference. 2016.
- Darder M, Colilla M, Ruiz-Hitzky E. Biopolymer-clay nanocomposites based on chitosan intercalated in montmorillonite. Chemistry of Materials. 2003;15:3774–80. [CrossRef]
- An J-H, Dultz S. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and As(V) on chitosan-montmorillonite; selectivity and pH dependence. Clays and Clay Minerals. 2008;56:549–57. [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara S, Yamauchi T, Oshima Y, Tsukamoto Y, Kadowaki T. Acetic acid activates hepatic AMPK and reduces hyperglycemia in diabetic KK-A(y) mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;344:597–604. [CrossRef]
- Kondo T, Kishi M, Fushimi T, Kaga T. Acetic acid upregulates the expression of genes for fatty acid oxidation enzymes in liver to suppress body fat accumulation. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:5982–6. [CrossRef]
- Fushimi T, Suruga K, Oshima Y, Fukiharu M, Tsukamoto Y, Goda T. Dietary acetic acid reduces serum cholesterol and triacylglycerols in rats fed a cholesterol-rich diet. British Journal of Nutrition. 2006;95:916–24. [CrossRef]
- Beh BK, Mohamad NE, Yeap SK, Ky H, Boo SY, Chua JYH, et al. Anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory effects of synthetic acetic acid vinegar and Nipa vinegar on high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Scientific Reports 2017 7:1. 2017;7:1–9. [CrossRef]
- Jalili M, Nazari M, Magkos F. Fermented Foods in the Management of Obesity: Mechanisms of Action and Future Challenges. Int J Mol Sci. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute; 2023. p. 2665. [CrossRef]
- Hattori M, Kondo T, Kishi M, Yamagami K. A single oral administration of acetic acid increased energy expenditure in C57BL/6J mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;74:2158–9. [CrossRef]
- Oh I, Baek EJ, Lee DH, Choi YH, Bae IY. Anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory effects of ginseng vinegar in high-fat diet fed mice. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2019;28:1829–36. [CrossRef]
- Rytwo G, Lavi R, Rytwo Y, Monchase H, Dultz S, König TN. Clarification of olive mill and winery wastewater by means of clay-polymer nanocomposites. Science of the Total Environment. 2013;442:134–42. [CrossRef]
- Rytwo G, Lavi R, Konovalova Y, Gutman R. Adsorption of olive oil on clay minerals and nanocomposites. 51st Annual Meeting of the Clay Mineral Society. College Station, Texas, USA: The Clay Minerals Society; 2014. p. 199.
- Rytwo G, Sitruk A, Lavi R, Khamaisi H, Gutman R. De-emulsification of oil emulsions by clays and biocomposites. 8th Mid-European Clay Conference. 2016.
- Watanabe M, Morimoto K, Houten SM, Kaneko-Iwasaki N, Sugizaki T, Horai Y, et al. Bile Acid Binding Resin Improves Metabolic Control through the Induction of Energy Expenditure. PLoS One. 2012;7:e38286. [CrossRef]
- Heidker RM, Caiozzi GC, Ricketts ML. Grape seed procyanidins and cholestyramine differentially alter bile acid and cholesterol homeostatic gene expression in mouse intestine and liver. PLoS One. 2016;11. [CrossRef]
- Maugeais C, Annema W, Blum D, Mary JL, Tietge UJF. rHDL administration increases reverse cholesterol transport in mice, but is not additive on top of ezetimibe or cholestyramine treatment. Atherosclerosis. 2013;229:94–101. [CrossRef]
- Efsa, Aquilina G, Bach A, Bampidis V, Bastos MDL, Flachowsky G, et al. Scientific Opinion on the safety and efficacy of a preparation of bentonite-and sepiolite (Toxfin® Dry) as feed additive for all species. EFSA Journal. 2013;11:1–21.
- Gutman R, Rytwo G. Acicular clays and bio-composites based thereon for use in treatment of metabolic syndrome and related disorders. US; 2017.
- Gutman R, Choshniak I, Kronfeld-Schor N, Gutman, Choshniak I, Kronfeld-Schor N. Defending body mass during food restriction in Acomys russatus: A desert rodent that does not store food. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006;290. [CrossRef]
- Steckler R, Tamir S, Gutman R. Mice held at an environmental photic cycle oscillating at their tau-like period length do not show the high-fat diet-induced obesity that develops under the 24-hour photic cycle. Chronobiol Int. 2021;1–15. [CrossRef]
- Tschöp MH, Speakman JR, Arch JRS, Auwerx J, Brüning JC, Chan L, et al. A guide to analysis of mouse energy metabolism. Nat Methods. 2012;9:57–63.
- Ravussin Y, Gutman R, Diano S, Shanabrough M, Borok E, Sarman B, et al. Effects of chronic weight perturbation on energy homeostasis and brain structure in mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;300:1352–62. [CrossRef]
- Ravussin Y, Gutman R, Leduc CA, Leibel RL. Estimating energy expenditure in mice using an energy balance technique. Int J Obes. 2013;37. [CrossRef]
- Ravussin Y, Gutman R, Leduc CA, Leibel RL. Erratum: Estimating energy expenditure in mice using an energy balance technique (International Journal of Obesity (2013) 37 (473) DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2012.147). Int J Obes. 2013;37. [CrossRef]
- Pullar JD, Webster AJF. The energy cost of fat and protein deposition in the rat. British Journal of Nutrition. 1977/05/01. 1977;37:355–63. [CrossRef]
- Schulz LO, Alger S, Harper I, Wilmore JH, Ravussin E. Energy expenditure of elite female runners measured by respiratory chamber and doubly labeled water. J Appl Physiol. 1992/01/01. 1992;72:23–8. [CrossRef]
- Hara A, Radin NS. Lipid extraction of tissues with a low-toxicity solvent. Anal Biochem. 1978;90:420–6. [CrossRef]
- Perwaiz S, Tuchweber B, Mignault D, Gilat T, Yousef IM. Determination of bile acids in biological fluids by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 2001;42:114–9. [CrossRef]
- Batta AK, Salen G, Rapole KR, Batta M, Batta P, Alberts D, et al. Highly simplified method for gas-liquid chromatographic quantitation of bile acids and sterols in human stool. J Lipid Res. 1999;40:1148–54. [CrossRef]
- Qi S, Wang C, Li C, Wang P, Liu M. Candidate genes investigation for severe nonalcoholic fatty liver disease based on bioinformatics analysis. Medicine (United States). 2017;96. [CrossRef]
- Gensure RC, Mäkitie O, Barclay C, Chan C, DePalma SR, Bastepe M, et al. A novel COL1A1 mutation in infantile cortical hyperostosis (Caffey disease) expands the spectrum of collagen-related disorders. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2005;115:1250–7.
- Jull AB, Ni Mhurchu C, Bennett DA, Dunshea-Mooij CAE, Rodgers A. Chitosan for overweight or obesity. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. John Wiley and Sons Ltd; 2008.
- Kondo T, Kishi M, Fushimi T, Ugajin S, Kaga T. Vinegar intake reduces body weight, body fat mass, and serum triglyceride levels in obese Japanese subjects. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2009;73:1837–43. [CrossRef]
- Valdes DS, So D, Gill PA, Kellow NJ. Effect of Dietary Acetic Acid Supplementation on Plasma Glucose, Lipid Profiles, and Body Mass Index in Human Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2021;121:895–914. [CrossRef]
- Petsiou EI, Mitrou PI, Raptis SA, Dimitriadis GD. Effect and mechanisms of action of vinegar on glucose metabolism, lipid profile, and body weight. Nutr Rev. 2014;72:651–61. [CrossRef]
- Zecharia D, Rauch M, Sharabi-Nov A, Tamir S, Gutman R. Postnatal administration of leptin antagonist mitigates susceptibility to obesity under high-fat diet in male αMUPA mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019;317:E783–93. [CrossRef]
- Biddinger SB, Almind K, Miyazaki M, Kokkotou E, Ntambi JM, Kahn CR. Effects of Diet and Genetic Background on Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-1c, Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1, and the Development of the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes. 2005;54:1314–23. [CrossRef]
- Podrini C, Cambridge EL, Lelliott CJ, Carragher DM, Estabel J, Gerdin A-K, et al. High-fat feeding rapidly induces obesity and lipid derangements in C57BL/6N mice. Mamm Genome. 2013;24:240–51. [CrossRef]
- Guo J, Jou W, Gavrilova O, Hall KD. Persistent diet-induced obesity in male C57BL/6 mice resulting from temporary obesigenic diets. PLoS One. 2009/04/30. 2009;4:e5370. [CrossRef]
- Williams LM, Campbell FM, Drew JE, Koch C, Hoggard N, Rees WD, et al. The development of diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance in C57Bl/6 mice on a high-fat diet consists of distinct phases. PLoS One. 2014;9:e106159. [CrossRef]
- Fraulob JC, Ogg-Diamantino R, Fernandes-Santos C, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA. A mouse model of metabolic syndrome: Insulin resistance, fatty liver and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Pancreas Disease (NAFPD) in C57BL/6 mice fed a high fat diet. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010;46:212–23. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Wu H, Liu Y, Yang L. High fat diet induced obesity model using four strains of mice: kunming, c57bl/6, balb/c and icr. Exp Anim. 2020;69:326–35. [CrossRef]
- Murphy EF, Cotter PD, Healy S, Marques TM, O’Sullivan O, Fouhy F, et al. Composition and energy harvesting capacity of the gut microbiota: Relationship to diet, obesity and time in mouse models. Gut. 2010;59:1635–42. [CrossRef]
- Park S, Zhang T, Yue Y, Wu X. Effects of Bile Acid Modulation by Dietary Fat, Cholecystectomy, and Bile Acid Sequestrant on Energy, Glucose, and Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:5935. [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto Y, Irie J, Iwabu K, Tagawa H, Itoh A, Kato M, et al. Bile acid binding resin prevents fat accumulation through intestinal microbiota in high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Metabolism. 2017;71:1–6. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi M, Ikegami H, Fujisawa T, Nojima K, Kawabata Y, Noso S, et al. Prevention and treatment of obesity, insulin resistance, and diabetes by bile acid-binding resin. Diabetes. 2007;56:239–47.
- Li X, Wang L, Li Y, Ho Y, Yang D, Chen Y, et al. Polysorbates as novel lipid-modulating candidates for reducing serum total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels in hyperlipidemic C57BL/6J mice and rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;660:468–75. [CrossRef]
- Nishida S, Horinouchi A, Higashimura Y, Akahori R, Matsumoto K. Cholestyramine, a bile acid sequestrant, increases cecal short chain fatty acids and intestinal immunoglobulin A in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020;43:565–8. [CrossRef]
- Binyamin D, Werbner N, Nuriel-Ohayon M, Uzan A, Mor H, Abbas A, et al. The aging mouse microbiome has obesogenic characteristics. Genome Med. 2020;12. [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb A, Egger L, Alminger M, Alvito P, Assunção R, Ballance S, et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat Protoc. 2019;14:991–1014. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Wang L, Cheng Y, Xia Z, Liao Y, Cao J. Efficacy of orlistat in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Rep. Spandidos Publications; 2018. p. 90–6. [CrossRef]

|
Diets (g/kg of ingredients) | |||||||
| Ingredient | Manufacturer, catalog no. | Humidity (%)1 | LFD | HFD | HFD+ּBAS2 | HFD+AA3 | HFD+BcL4 | HFD+BcH4 |
| Casein | Frutarom, 9500682599 | 7.5 | 210 | 265 | 265 | 265 | 265 | 265 |
| L-Cysteine | MP Biomedicals, 210144490 | <0.1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Maltodextrin | Zhucheng Dongxiao Biotec. | 4.6 | 465 | 160 | 160 | 160 | 160 | 160 |
| Cornstarch | Galam | 7.8 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sucrose | Sugat, 290000211503 | <0.1 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Beef fat | Local slaughterhouse | 7.3 | 20 | 310 | 310 | 310 | 310 | 310 |
| Soybean oil | Supersal, 2900024317 | <0.1 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Cellulose | MP Biomedicals, 0219149991 | 5.9 | 37.25 | 65.6 | 65.6 | 65.6 | 65.6 | 65.6 |
| Mineral mix | MP Biomedicals, 0296040002 | 0.3 | 35 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 |
| Calcium phosphate | Sigma, c7263 | 0.1 | 2 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 3.4 |
| Vitamin mix | MP Biomedicals, 0296040201 | 0.8 | 15 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 |
| Choline bitartrate | MP Biomedicals, 0210138483 | 0.1 | 2.75 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Total ingredients (g) | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | ||
| Supplemented compounds, on top (g) | Humidity (%) | LFD | HFD | HFD + ּBAS | HFD + AA | HFD + BcL | HFD + BcH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholestyramine (2% w/w) | 7 | 201 | ||||||
| Acetic acid, 1 N (3% w/w) | 94.0 | 4802 | ||||||
| Biocomposite3 (0.8% w/w) | 98.3 | 803 | ||||||
| Biocomposite3 (5% w/w) | 90.0 | 4803 | ||||||
| Added water | 540 | 80 | 80 | |||||
| Total weight (g) | 1540 | 1080 | 1100 | 1480 | 1080 | 1480 | ||
| Selected nutritional information | ||||||||
| Humidity in diet (%)4 | 20.8 | 11.5 | 8.7 | 14.1 | 11.2 | 11.1 | ||
| Carbohydrates (%, w/w)5 | 65.8 | 28.9 | 28.4 | 28.9 | 28.7 | 27.7 | ||
| Protein (%, w/w)5 | 20.7 | 26.3 | 25.8 | 25.6 | 26.1 | 25.1 | ||
| Fat (%, w/w)5 | 4.1 | 33.5 | 32.9 | 32.6 | 33.3 | 31.9 | ||
| Carbohydrates (% of MEI)6,7 | 69.5 | 22.1 | 22.1 | 21.8 | 22.1 | 21.9 | ||
| Protein (% of MEI)6,7 | 21.2 | 20.1 | 20.1 | 19.9 | 20.1 | 19.9 | ||
| Fat (% of MEI)6,7 | 9.3 | 57.8 | 57.8 | 58.2 | 57.8 | 58.2 | ||
| Metabolizable energy (kcal/g)7 | 3.9 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 5.0 | ||
| Combustible energy (kcal/g; mean ± SE)8 | 4.1±0.25 | 5.9±0.1 | 5.8±0.03 | 5.7±0.04 | 5.6±0.08 | 5.7±0.06 | ||
| Lipids (%)9 | 5.1±0.04 | 33.8±0.1 | 33.3±0.1 | 30.1±0.1 | 31.3±0.1 | 34.0±0.2 | ||
| Gene | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| Col1a1 | GCTCCTCTTAGGGGCCACT | CCACGTCTCACCATTGGGG |
| Gapdh | GGTCTACATGTTCCAGTA | CCCATTTGATGTTAGTGG |
| Parameter | Time point | LFD | HFD | HFD+ּBAS1 | HFD+AA2 | HFD+BcL3 | HFD+BcH3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Baseline | 130.3±5.0 | 130±5.5 | 129.8±7.9 | 137.8±6.7 | 135.8±3.5 | 130.8±3.7 |
| End | 144.2±4.1BC | 173.8±7.6A$ | 135.6±2.7C | 155.7±5.8AB* | 166±6.3A$ | 159.4±7AB$ | |
| Tri | Baseline | 72.9±3.7 | 80.1±3.7 | 68.9±1.1 | 72.1±3.3 | 72.3±4.8 | 77.1±2.6 |
| End | 75.6±3.0A | 69.7±2.9AB* | 46.8±4.0C$ | 68.7±4.1AB | 68±4.4AB | 62.2±4.2B# | |
| Total Cholesterol |
Baseline | 162.2±5.4 | 137.8±10.4 | 167.9±5.4 | 164.1±12.9 | 153.3±6 | 139.0±5.6 |
| End | 147.7±20.5 | 182.0±21.2# | 158.0±8.4 | 180.2±15.1 | 193±13# | 174.6±7.8# | |
| HDL Cholesterol |
Baseline | 104.9±3.3 | 92.9±7.7 | 104.5±3.4 | 100.9±5.4 | 102±2.6 | 96.4±2.6 |
| End | 85.2±9.0B* | 116.6±12.6A* | 105.2±4.6A | 117.3±8.5A* | 129±8.6A* | 109±5.7AB | |
| LDL Cholesterol |
Baseline | 41.3±2.5 | 28.8±2.7 | 49.4±3.6 | 36.0±3.7 | 36.6±4.6 | 29.7±2.6 |
| End | 33.5±5.4 | 51.4±9.2$ | 43.3±3.9 | 42.4±6.4 | 50±10.8 | 53.6±6.9$ | |
| VLDL Cholesterol |
Baseline | 14.7±0.8 | 15.9±0.8 | 13.8±0.2 | 14.1±0.7 | 13.6±0.6 | 15.3±0.6 |
| End | 15.0±0.7A | 13.9±0.6AB* | 9.2±0.8C$ | 13.8±0.8AB | 14±1AB | 12.3±0.8B# |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





