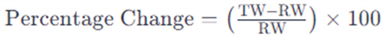1. Introduction
Direct discharge of wastewater into the environment from communities and industries is not recommended. Severe environmental and public health issues may result from it if treatment is not received. As a result, it ought to go toward wastewater treatment facilities, whose job it is to discharge clean water that satisfies regulations while also collecting pollutants present in wastewater in remaining form. This is achieved through a combination of physicochemical and biological processes (Lam et al., 2015; Slomp, 2012).
Hungary aims to build sewage treatment systems and facilities, comprising works for removing the liquid waste expand and modernize current wastewater collection and treatment; boost the recycling process and treatment of sludge (Balazs et al., 2013; Pistocchi et al., 2020.; Wastewater Treatment, n.d.). Conservation and protection of water bodies require the treatment of wastewater treatment of various sources and the improvement of the purification efficiency of treatment technologies and processes, the development of wastewater treatment has a key-question since the organisms always react to changed or modified environmental conditions, it is essential to consider how the intervention helps the improvement of purification processes (Pistocchi et al., n.d.; Takman et al., 2023). Furthermore, the Hungarian government activities to promise the transportation of sufficient liquid waste (via on-road routes), treatment, and advancement of utilization in settlements or portions of settlements in extremely vulnerable areas devoid of a sewer system, where professional, individual wastewater disposal is unsustainable. Beside with improving and growing sludge treatment and utilization, Hungary also wants to decrease the amount of municipal liquid waste produced. Following EU agreement, smaller-scale treatment facilities are required to produce treated water with a higher quality of discharge. Changes in practical employments or fluctuating economic considerations can primarily be related to these causes (OECD Environmental Performance Reviews: Hungary 2018, 2018).
The direct discharge of wastewater into the natural environment disturbs the aquatic equilibrium in transforming the acceptor medium into sewers. This pollution can go as far as the disappearance of all life. To do this, it is necessary to purify and eliminate wastewater a maximum of waste, before discharging into the environment, so that their impact on the water quality, aquatic environment as low as possible (Khan et al., 2017; Said Hamaidi et al., n.d.). Purification consists in eliminating the largest organic or mineral debris, eliminating different densities of water such as sand grains and mineral particles, as well as eliminating residual pollution that could pose a downstream problem (pathogens, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc.), this is carried out in wastewater treatment plants that include treatment facilities and devices for treating the sludge produced (Benfréha Benyelles et al., 2022; Kalloum et al., 2011; Muela et al., 2011) There are many processes and approaches for evaluating the efficiency of specific wastewater treatment plants. There are many municipal wastewater treatment plants in European society, but many do not function properly. For example, in a study in Spain, after examining eight small wastewater treatment plants, it was concluded that 50% of them were defective, while 25% were good enough and 25% were functioning properly (Colmenarejo et al., 2006). According to another study, of the 71 small municipal wastewater treatment plants examined in Greece, only 55% worked, 21% worked well, 51% worked adequately and 28% worked incorrectly (Tsagarakis et al., 2001). Changes in the ecological status can be recognized using individual biological and physico-chemical parameters or using indicators. An indicator is defined as “a feature of the environment that, when measured, quantifies the magnitude of the stress, the habitat characteristics, the degree of exposure to the stressor, or the degree of ecological response to the stress’’ (Arregui et al., 2013; Baharvand , Mansouri Daneshvar, 2019)
Directive 91/271/EEC of May 21, 1991, on community wastewater treatment, reports obligatory standards in a clear manner. In order to protect the situation from the adverse effects of sewage discharge, it is essential to monitor treatment plants, receiving waters, and the disposal of sludge. Discharges from certain sectors of biodegradable industrial waste water that do not enter urban waste water treatment plants before discharge to receiving waters should be subject to suitable requirements.
Table 1.
International Discharge Standards.
Table 1.
International Discharge Standards.
| Parameters |
Units |
Standards used |
| pH |
- |
6,5-8,5 |
| BOD5 |
Mg/l |
<30 |
| COD |
Mg/l |
<90 |
| TSS |
Mg/l |
<20 |
| NH4+ |
Mg/l |
<0.5 |
| NO2 |
Mg/l |
1 |
| NO3 |
Mg/l |
<1 |
| P2O5 |
Mg/l |
<2 |
| Temperature |
°C |
<30 |
| Color |
- |
Colorless |
| Odor |
- |
Odorless |
Growing population and development needs in the world highlight the need for increased reuse of treated wastewater. However, treated wastewater contains a large number of pathogens that require proper treatment before reuse. Standard Plate Counts (SPC) were used to get an idea of the total microbial concentration in different wastewater treatment plant effluents, counting total coliforms (TC), fecal coliforms (FC) and coliphages (CPg) due to their importance in wastewater treatment than traditional significant pollution indicators(Elmeddahi et al., 2016; Makuwa et al., 2020; Saleem et al., 2000)
The purpose of our experiments was to measure all the relevant parameters (Total Chemical Physical Analysis, Heterotrophic Plate Counts) and confirm whether the 14 plants in Hungary were operating effectively. We also wanted to make sure that the plants were meeting the standards set by the EU wastewater treatment directive. The heterotrophic plate count is simply an extra parameter used to further elucidate the plants' efficiency (Muela et al., 2011; Ugoh et al., 2013); in the end, we compare our findings following the computation of the average removal efficiency (ARE) and Depend on the hypothesis by performing statistical analysis using R software.
2. Material and Method
In any wastewater treatment plant it is necessary to carry out analysis of the raw wastewater (the inlet) and the treated water (the outlet) in order to determine the different physicochemical and bacteriological parameters making it possible to evaluate the level of pollution in each treatment plant and the efficiency of eliminating pollution to give a good appreciation of the purification performance of the WWTP. Our samples were taken from the effluents of 14 treatment plants in Hungary in December 2019. We analyzed the following parameters: Ammonia-N (NH3-N) , Nitrate-N ( NO3-N) , Nitrite-N ( NO2-N) , TOTAL P-CONTENT, Total N (mg/l), Kjeldahl-nitrogen (organic N + ammonia-N) , Total inorganic N , Total suspended solids, Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD₅) , Chemical oxygen demand (COD) , Heterotrophic total plate count ( HPC).
2.1. Areas Studied
The current work was carried out in December 2019 in northeastern Hungary where most of the targeted treatment plants are located; they are subjected to treat raw wastewater for 26,000 residents that live around this plain area. The yield loading of treated wastewater is 598000 m
3 as total capacity, but it is not found per plants, only three plants were found, while other were not, they marked as nd (not detected) on the
Table 2.
2.2. Sampling Processes
Collecting the samples were performed in the field at the level of those treatment plants (concern the effluents and influents wastewater), a certain volume is taken. It is usually done 8 times a day to ultimately get the final sample to be analyzed and using plastic and glass bottles (1.5 litres) before and after treatment, in case of the discharging channel , they sampled only once with the same tools. The samples must be analyzed within a maximum of 24 hours in order to avoid any change in the concentrations of the sample (Tavazzi et al., 2023). Thus, they should be stored at a temperature of 4°C after they are transported to the lab.
2.3. Laboratory Methods
After getting the samples from target waste water treatment plant, measurements of different physic-chemical parameters were performed in Debrecen testing laboratory ( Tiszamenti Regional waterworks) which is known as one of the most significant water utility facilities in Hungary, it strives to achieve consumer satisfaction, taking into account environmental and economic considerations. At the level of this laboratory, in the beginning, we started to look at the most important parameters that are obliged to be measured and that could determine the efficiency and operation of wastewater treatment plants (6 Wastewater Parameters and Dealing with Discharge Limits - Alumichem.Com, n.d.; Understanding Wastewater Parameters and Standards, n.d.; Hejabi et al., 2021) . It is based on standards methods, we have identified the required parameters that have to be measured with advanced machines and new instruments in the laboratory.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Paired t-tests were performed for our statistical analysis to evaluate the wastewater treatment process’s effectiveness in lowering different water quality parameters. A comparison of the main pollutants' concentrations in 14 sewage treatment plants' treated wastewater (TW) and raw wastewater (RW). Nitrate-N, Nitrite-N, Kjeldahl-nitrogen, Total Inorganic Nitrogen, Ammonia-N, and Total Phosphorus were among the parameters examined.
Another calculation, along with yardsticks, is used generally by governments and health associations, among others, to assess the adequacy of effluents from the WWTP in light of the guidelines' parameters and the current environmental conditions (Aniyikaiye et al., 2019). Efficiency was calculated for only four of the most important parameters: BOD, COD, Total-P, and Total-N. To calculate the reduction efficiencies of different parameters, we used the following equation:
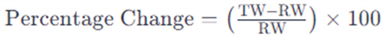
3. Results and Discussion
In this section, as we have studied on fourteen (14) sewage treatment plants, analyses were performed on the inflow and outflow. We have obtained the physic-chemical results (
Table 3) and the microbiological parameter (HPC). The mean values and percentage reductions taking into account all the parameters were calculated (
Table 4). They are put on tables and are represented in graphs.
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters
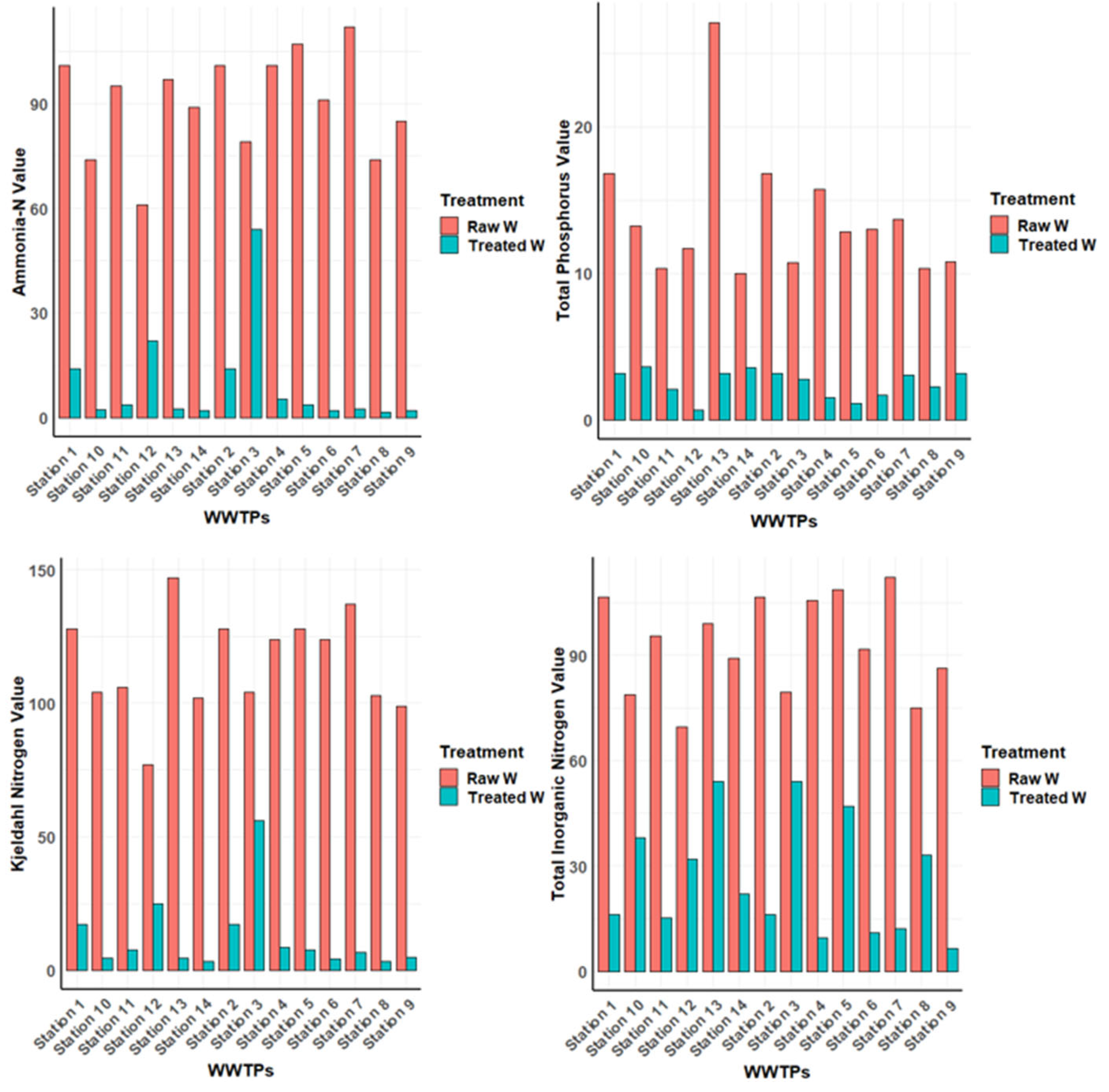
Ammonia-N: With an average reduction efficiency of 81.08%, the wastewater treatment process showed a noteworthy decrease in the concentration of ammonia-nitrogen view (
Figure 1). The removal of ammonia, a significant nitrogenous pollutant, by the treatment plant is demonstrated by this great decrease.
Total Phosphorus: There was a noteworthy decrease in total phosphorus levels (
Figure 1), with an average reduction efficiency of 11-25%. The overall efficiency of nutrient removal was enhanced by the treatment process's effective mitigation of phosphorus concentrations.
Kjeldahl-nitrogen: which expresses nitrogen from both organic and ammonia sources, showed a significant decrease (
Figure 1) with an average efficiency of 102.87%. The treatment plant was able to handle complex nitrogen compounds with remarkable efficacy.
Total Inorganic Nitrogen: The treatment process significantly reduced Total Inorganic Nitrogen concentrations, with a mean reduction efficiency of 67.1% this outcome underscores the plant's ability to target various inorganic nitrogen species.
Total N Concentration: the total N concentration significantly decreased after wastewater treatment. The significant post-treatment decrease in Total N levels is further supported by the 95 percent confidence interval (74.76, 102.91), with a mean reduction efficiency of 88.84% (t = 13.632, p<0.001).
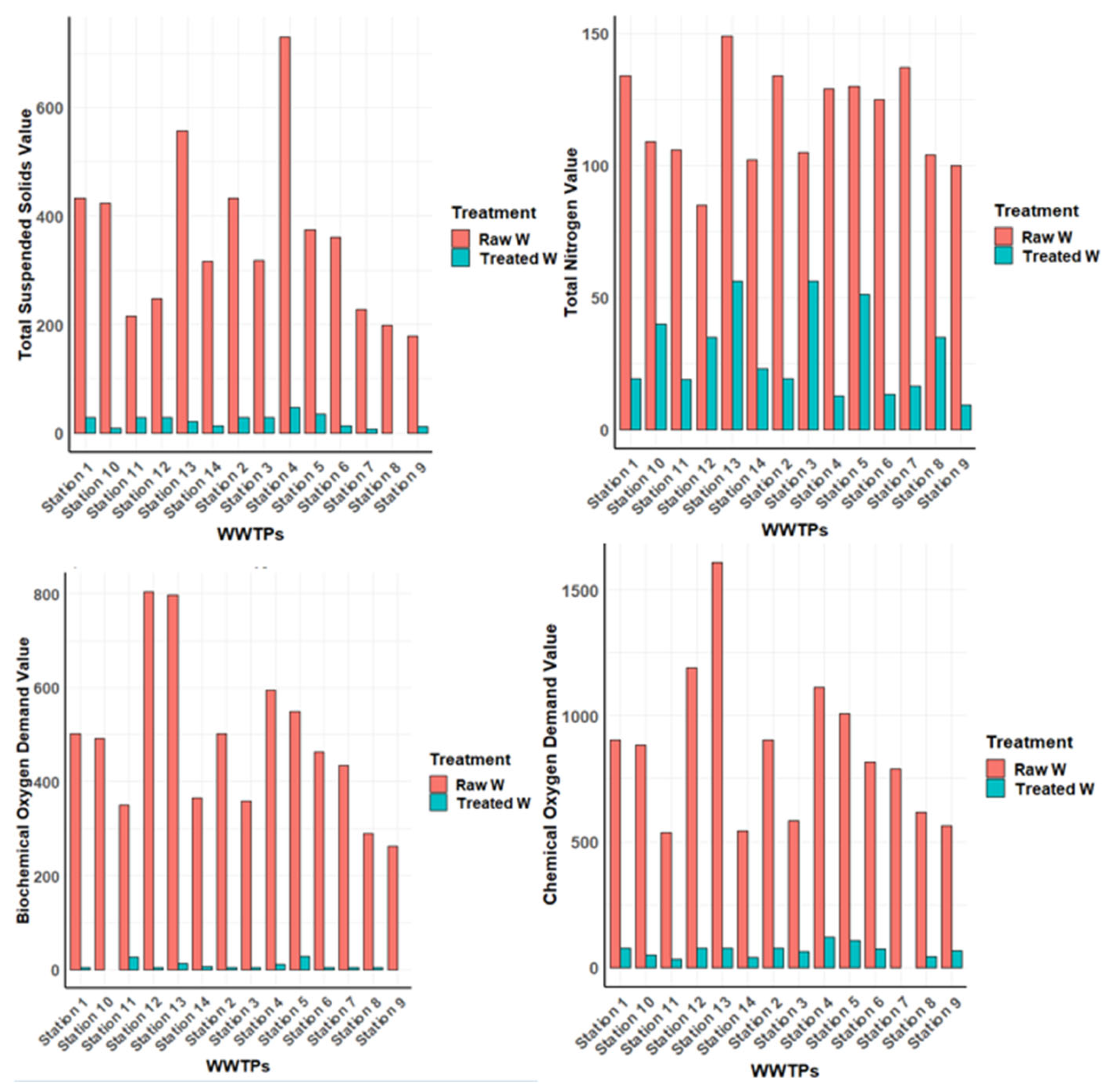
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD): The removal of organic pollutants was evident in the wastewater treatment process as there was a noteworthy decrease in Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD). The water quality has significantly improved, as evidenced by the mean reduction efficiency of 474.5% (t = 10.802, p<0.001) and a 95% confidence interval of 379.60, 569.40, this is consistent with the findings of a study conducted to assess the satisfaction of wastewater treatment plants at different levels of treatment units using the activated sludge process(Sundara Kumar et al., 2010)
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD): A noteworthy decrease was observed in Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), with a mean reduction efficiency of 794.14 % (t = 10.244, p<0.001). The plant's successful removal of oxidizable substances is highlighted by the 95 percent confidence interval (626.66, 961.62), which highlights the significant decrease in COD levels following treatment.
Total suspended solids (TSS), total nitrogen (Total N), total phosphorus (Total P), and organic matter (COD, BOD5) were found to have considerably diminished in the effluent during treatment. These results confirm the usefulness of these indicators for treatment monitoring and are also compatible with the results of other researchers, for instance one study highlights the importance of eliminating organic matter (van Gijn et al., 2021), and another study was conducted to evaluate the microbiological and physiochemical parameters as markers of satisfaction with the wastewater treatment plant (Howard et al., 2004). Further evidence of the usefulness of these indicators in evaluating the effectiveness of water treatment processes is the decrease in total dissolved solids, turbidity, phosphates and nitrates in wastewater and the use of surrogate organisms as indicators (Maguvu et al., 2020).
Figure 1.
NH3, TP, TIN, and TKN Reduction in Wastewater Treatment Process: percentages of removal prior and after purification.
Figure 1.
NH3, TP, TIN, and TKN Reduction in Wastewater Treatment Process: percentages of removal prior and after purification.
Figure 2.
COD, BOD, TSS, and TN Reduction in Wastewater Treatment Process Percentages of Removal Prior and After Purification.
Figure 2.
COD, BOD, TSS, and TN Reduction in Wastewater Treatment Process Percentages of Removal Prior and After Purification.
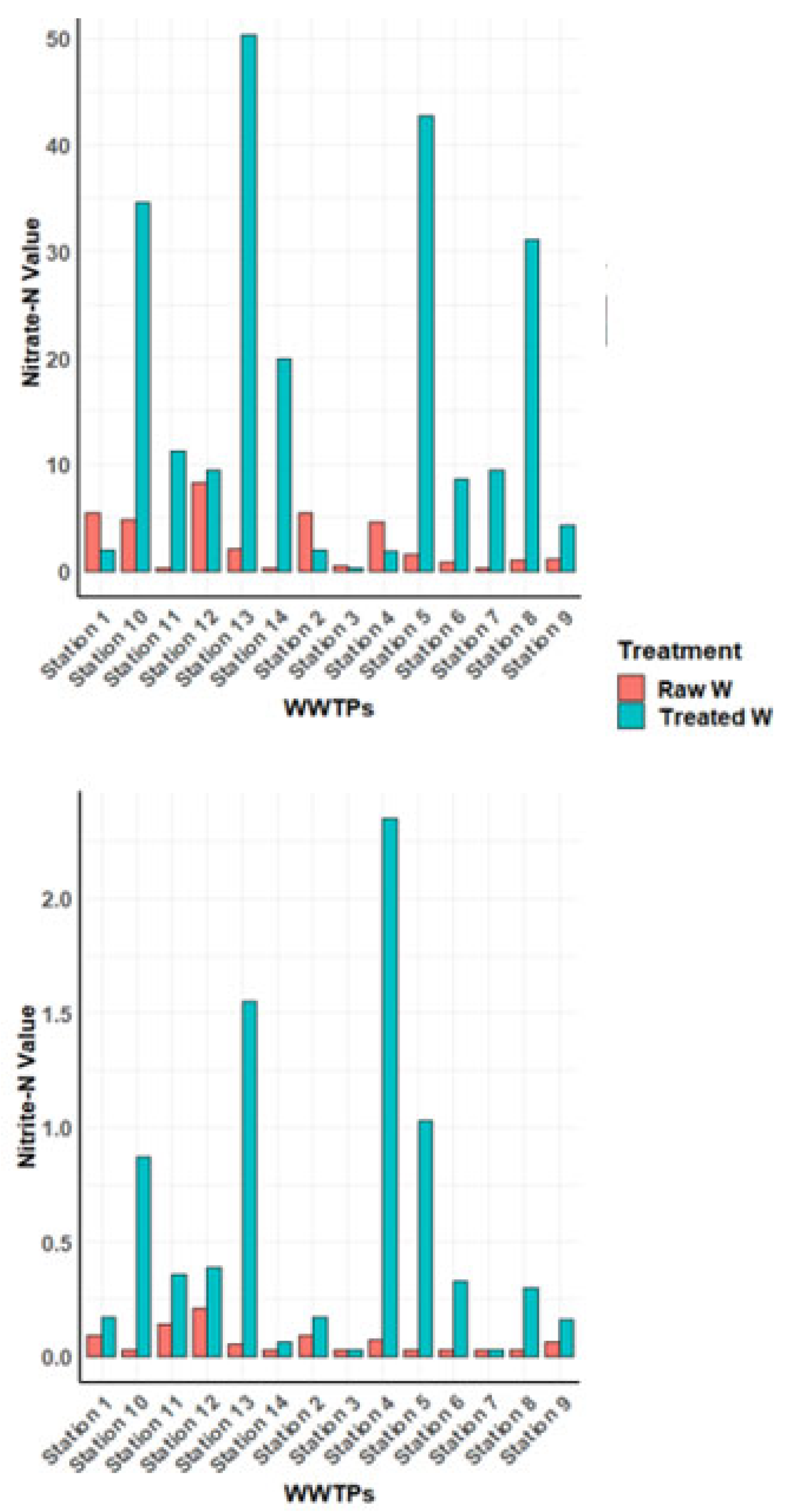
3.2. Nitrite-N and Nitrate-N Results
It is possible that the treatment procedure had little effect on nitrate levels because nitrate-N concentrations did not significantly change after treatment (P=0.2619). Following treatment, there was no discernible change in nitrite-N concentrations (p=0.9613), suggesting a strong level of treatment effectiveness for this dimension.
In this section, the results of nitrate-N concentration were explained. As we found, it was ineffective in reducing this pollutant in almost all treatment plants due to the obvious differences between inflows and outflows. This concentration difference was either reduced or mostly increased in the subsequent waters.
We only have three wastewater treatment plants that manage to remove the nitrate, but not as much as shown in
Table 5 and
Figure 3 which concerned the
first,
third and
fourth treatment plants respectively, when the concentrations were 5.49 mg/l, 0.54 mg/l, 4.59 mg/l. l in the raw water and were reduced to 2 mg/l, 0.23 mg/l and 1.88 mg/l, respectively.
The contents of the treated water in the other WWTPs that we are monitoring increased significantly in comparison to the raw wastewater in most of them; the highest one was 50.3 mg/l, whereas the lowest one was 2.02 mg/l in the thirteenth plant. Some WWTPs were not significantly increased, we notice only slightly increased in treated water.
The presence of nitrogenous compounds in the effluent, such as thickener and nitrocellulose resin, may be the cause of the high nitrate content when the effluent is discharged into a receiving watershed (Aniyikaiye et al., 2019), which can subsequently lead to eutrophication due to nutrient loading. Aquatic ecosystems may be adversely affected by this, which can ultimately result in oxygen depletion in water bodies (Singh and Kumar, 2017).
Nitrites-N concentration results have been clarified. At the level of all the treatment plants the values of Nitrates content are higher in treated water the values of the raw water, most often slight increase only in seventh plant when we have got a constant value <0.03 mg/l in both inflow and outflow.
The highest amount was 2.35mg/l in fourth plant despite in the effluent was very low concentration 0.07mg/l, however it was significantly increased during treatment.
The representation graphically shows that as following:
In general, this noticeable increase of nitrate and nitrite in our results is mainly due to the oxidation of nitrogen through the nitrification process (Galloway, 2003), as this is obvious as mentioned above. Denitrification does not appear to have occurred properly and may have resulted in higher levels in the wastewater. In the case of phosphate, the results can be explained by the discharge of industrial and domestic wastewater, which is rich in phosphate detergents and provides about 3 g of phosphorus per person per day (van Puijenbroek et al., 2018). In this section, the average reduction efficiency percentages of all studied wastewater treatment plants are given, taking into account BOD, COD, TSS, TP and TN. We only adopted the parameters according to the EU directive, which depend on the same parameters.
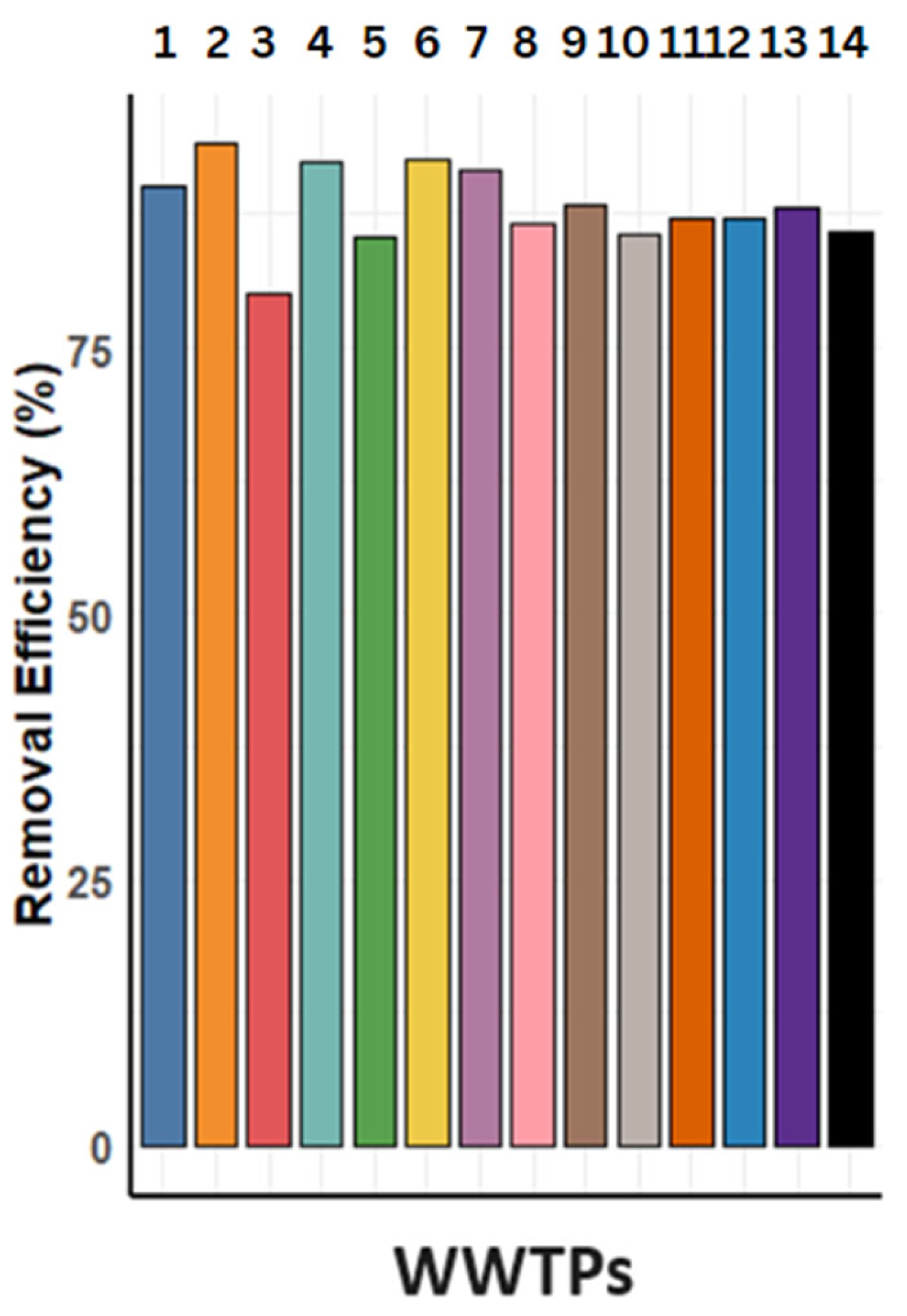
According to our results, we find that only four plants are highly effective in reducing all parameters, including BOD, COD, TSS, TP and TN, and meet the wastewater discharge standards required by the EU Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive (EU Water Law, n.d.). These plants are the first, second, and fourth sewage treatment plants achieved their goals and reduced connections by 90.23%, 94.19%, and 92.26% respectively. As previously mentioned, all wastewater treatment plants significantly and effectively remove BOD, COD and TSS. As for TN and TP, the removal efficiency varies from plant to plant. Some of them almost manage to eliminate TP while significantly removing the other pollutants. The wastewater treatment plant affected the seventh, ninth and eleventh plants at 77.81%, 70.82% and 79.80% while the directive says it should be removed at 80%. However, their efficiency is 91.64%, 88.47% and 87.01% respectively, where we can assume that their performances are acceptable. The fifth, twelfth and thirteenth sewage treatment plants do not achieve the goal of TN removal while they have significantly removed the other pollutants. Their efficiency is 85.44%, 87.03% and 88.01% respectively. The third, eighth, tenth and fourteenth sewage treatment plants fail to remove both TP and TN as shown in the previous results. Their reduction percentages were 79.94%, 86.53%, 85.67% and 85.73% respectively.
Ultimately all the plants have been classified per their performances based on all the physicochemical parameters
Table 7.
Based on the
Figure 4, we note that most systems in most cases give good results that meet European standards.
3.3. Microbiological Parameter HPC (Heterotrophic Place Count)
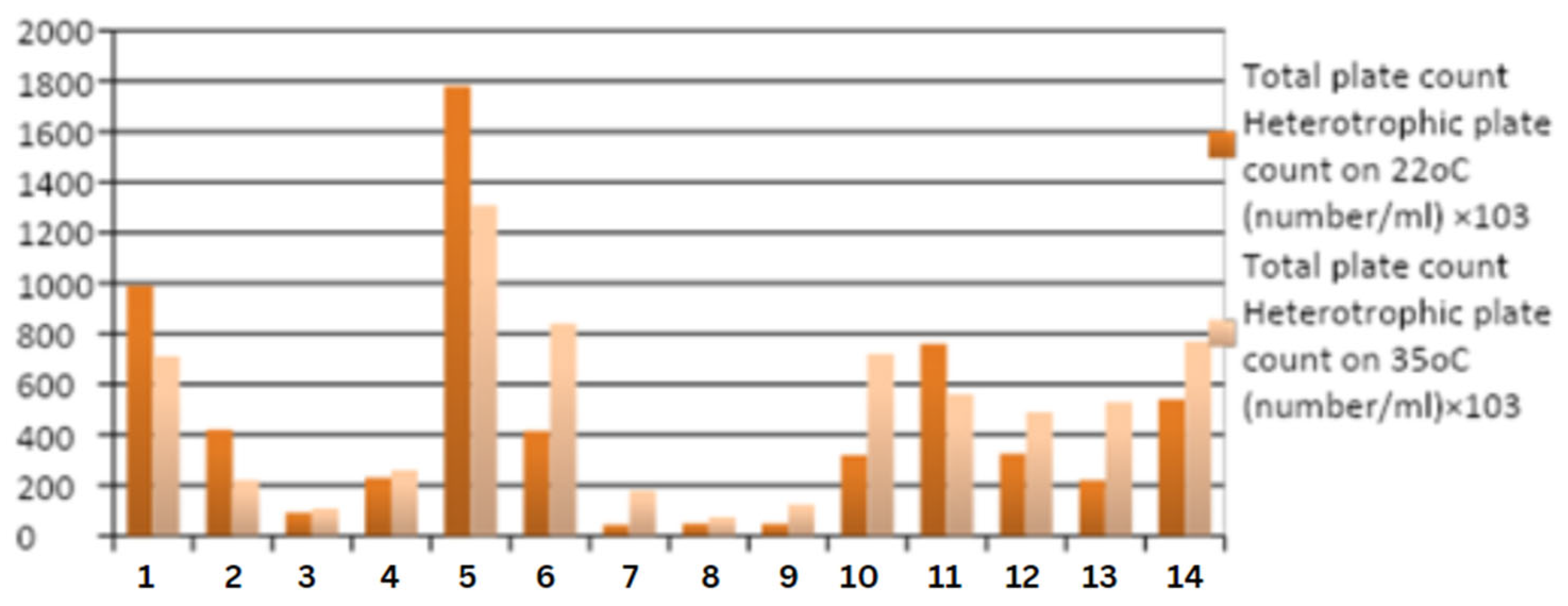
The
Figure 5 obtained shows that only four (4) wastewater treatment plants recorded logical values where the number of heterotrophic plates heated to 22°C is higher than the heterotrophic number heated to 35°C.
The planned sewage treatment plants are first, second, fifth and tenth works. While the other sewage treatment plants recorded exactly the opposite, the graphic shows that the number of heterotrophic germs at 35 °C is higher than the number heated at 22 °C. The highest value was reached in the fifth plant with 1780,000 CFU and this was reduced to 1310,000 CFU, where we can observe that the difference between heating to 22 °C and 35 °C is very significant. The lowest value was 44,000 CFU in the seventh plant and was increased to 180,000 CFU, where the difference is not so significant at 22 °C and 35 °C. We found a significant difference in colony numbers between the two temperatures at most wastewater treatment plants. However, further heating treatment is required, which could be 45°C, to examine more bacteria and also identify organisms such as molds, yeasts and fungi. This is not our aim in this article. Additionally, we found that the incubation temperature used to assess contamination was between 22°C and 35°C.
Furthermore, the coincident resemblance observed in heterotrophic plate count and physicochemical results, for example the sewage plants classified as excellent removal efficiency in physic-chemical parameters showed satisfied values in both heating treatment except number sixth plant, however we noticed the colonies number has been decreased in first and second plant, as well as we noticed no significant difference in the fourth, seventh and ninth plant. Similar findings have been reported by a number of studies there as well. One study, for instance, examined the relationship between water quality parameters and heterotrophic bacteria (HPC) levels in water distribution systems. The investigation found that HPC counts might be helpful in determining the water quality of systems that distribute drinking water (Carter et al., 2000)
An additional research endeavor examined the correlation between heterotrophic bacteria and water quality parameters within a drinking water distribution system. The objective of this investigation was to ascertain the factors that account for the spatiotemporal distribution of heterotrophic bacteria and to develop a model of their establishment within the system (Francisque et al., 2009).
Generally speaking, almost all the treatment plants which recorded illogical values by increased the number, it can be explained that these colonies are multiplied and propagated as they have the ability to adapt in high temperature (Heterotrophic Plate Count (HPC) Testing - Phoslab Environmental Laboratories Phoslab Environmental Laboratories, n.d.). From the other hand, these bacteria present in the rejected water confirm that the disinfection process did not work properly. In fact, it is assumed that there is no significant difference after second-time heating at 35 ° C or the number supposed to be reduced. The results obtained after performing the heating treatment on 22 ° C is expected decent or in another word the disinfection is not too bad and hence, we can say it requires detoxification and good disinfection because it is inadequate to adopt the strict rules of HPC requirements(Hallas, Monis, 2015; Pavlov et al., 2004).
4. Conclusions
Our analysis is subjected to different sewage treatment depended on the familiar physicochemical parameters and heterotrophic plate count which are accurate indicators of effluent quality. In fact, The experimental data obtained reveals that all the wastewater treatment systems showed almost similar values in organic matter removal efficiencies (COD, BOD5), and even total suspended solid (TSS) which were significantly eliminated and showed an important reduction over treatment in the effluent, thus confirming the value of these indicators for the control of treatment.
TP and TN removal efficiencies were inadequate and showed different values in all the WWTPs, some of them managed to remove them and the concentration in the effluents highly decreased to the extent that discharging it into natural water bodies with confidence and undoubted, included 1,2,4,6. Most of them did not; in case of TP, the reduction percentages varied between (70.83% - 79.80%), despite these rates did not meet the required values of the official journal of the European communities but they are relatively close to the requirements. Expect of the last treatment plant where the removal efficiency was only 64.2%. In the case on TN, only the last plant had reduction percentage was a bit closed to the required values of the EU directive which was 77.45%, as for the other plants were ineffective vary between (46.66%-66.34%).
In the case of Nitrates-N and Nitrites-N, the efficiency could not be quantified due to the results showed an increased level in outflows. The microbiological removal efficiency rates of our study considered well enough because did not show an important reduction over the treatment. The idea concluded that there are close similarities and correspondence between physic-chemical and total plate count results in the studied treatment plants. The majority of the physicochemical parameters investigated in the research did not exceed the recommended levels for discharge into the environment, indicating that nearly all of the WWTPs studied in Hungary are efficient and provide good purification performance due to their ability to afford good effluent treatment procedures and in control.
Additionally, the research greatly demonstrated compliance to various regulatory standards. Despite that, some recommendations should be suggested and shall apply:
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs): AOPs are used to treat wastewater by eliminating organic compounds, micropollutants, and other contaminants that may not be effectively removed by conventional methods. These include ozone, hydrogen peroxide, and ultraviolet (UV) combined with hydrogen peroxide. The goal is to purify the wastewater and make it suitable for residential use (Kaur et al., 2017; Zahmatkesh et al., 2022).
Membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Wastewater can be treated more effectively and compactly when biological treatment and membrane separation are combined (Zahmatkesh et al., 2022).
Microscreening: This method offers an affordable water treatment option by eliminating suspended solids from wastewater (Advanced Wastewater Treatment Methods (Complete List) - EngineeringCivil.Org, n.d.).
Ultrafiltration: When combined with the activated sludge process, ultrafiltration effectively eliminates toxic materials, suspended solids, and dissolved solids from wastewater (Advanced Wastewater Treatment Methods (Complete List) - EngineeringCivil.Org, n.d.; Zahmatkesh et al., 2022).
Advanced carbon adsorption: Wastewater is treated with activated carbon adsorption to eliminate organic pollutants, hazardous materials, and persistent organic pollutants (Advanced Wastewater Treatment Methods (Complete List) - EngineeringCivil.Org, n.d.).
Phosphorus and nitrogen elimination: Phosphorus and nitrogen, which are necessary nutrients for the growth of algae and can cause eutrophication, are taken out of wastewater by chemical precipitation and clarification, as well as chemical coagulation and clarification (Advanced Wastewater Treatment Methods (Complete List) - EngineeringCivil.Org, n.d.).
By investigating these recommendations, sewage treatment plants could be operated more effectively and controlling the discharge of effluents into ecosystems and hence the water bodies will not be contaminated and protected from eutrophication phenomena and in the aquatic life, the living organisms will not be disturbed, the public health and environment will be protected.
References
- 6 wastewater parameters and dealing with discharge limits - alumichem.com. (n.d.). Retrieved December 20, 2023, from https://alumichem.com/6-wastewater-parameters-and-dealing-with-discharge-limits/.
- Advanced Wastewater Treatment Methods - EngineeringCivil.org. (n.d.). Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://engineeringcivil.org/articles/advanced-wastewater-treatment-methods-complete-list/.
- ANIYIKAIYE, T. E., OLUSEYI, T., ODIYO, J. O., EDOKPAYI, J. N. (2019). Physico-Chemical Analysis of Wastewater Discharge from Selected Paint Industries in Lagos, Nigeria. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, Vol. 16. Issue 7. [CrossRef]
- ARREGUI, L., LIÉBANA, R., CALVO, P., PÉREZ-UZ, B., SALVADÓ, H., SERRANO, S. (2013). Bioindication in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. In Handbook of Wastewater Treatment: Biological Methods, Technology and Environmental Impact pp. 277–291.
- BAHARVAND, S., MANSOURI DANESHVAR, M. R. (2019). Impact assessment of treating wastewater on the physiochemical variables of environment: a case of Kermanshah wastewater treatment plant in Iran. Environmental Systems Research, Vol.8, Issue 1. [CrossRef]
- BALAZS, M., MR, D., GAYER, J., GABOR, M., MR, G., KOVACS, R. (2013). The Hungarian Water and Sanitation Industry in the 21st century, Hungarian investment and trade agency, Budapest water summit, 19 p. WWW.HITA.HU.
- BENFRÉHA BENYELLES, M., BELGHARBI ALLAM, A., MOKRANI, S., TIR TOUIL MEDDAH, A., MOUSSA-BOUDJEMÂA, B. (2022). Microbiological aspects of the aeration tanks of an activated sludge treatment plant in dysfunction: Consequences on its treatment performance. Lebanese Science Journal, Vol. 23, Issue 1, pp. 17–32. [CrossRef]
- CARTER, J. T., RICE, E. W., BUCHBERGER, S. G., LEE, Y. (2000). Relationships between levels of heterotrophic bacteria and water quality parameters in a drinking water distribution system. Water Research, Vol.34, Issue 5, pp.1495–1502. [CrossRef]
- COLMENAREJO, M. F., RUBIO, A., SÁNCHEZ, E., VICENTE, J., GARCÍA, M. G., BORJA, R. (2006). Evaluation of municipal wastewater treatment plants with different technologies at Las Rozas, Madrid (Spain). Journal of Environmental Management, Vol. 81, Issue 4, pp 399–404. [CrossRef]
- ELMEDDAHI, Y., MAHMOUDI, H., ISSAADI, A., GOOSEN, M. F. A. (2016). Analysis of treated wastewater and feasibility for reuse in irrigation: a case study from Chlef, Algeria. Desalination and Water Treatment, Vol. 57, Issue 12, pp.5222–5231. [CrossRef]
- EU WATER LAW. (n.d.). Retrieved December 20, 2023, from https://www.era-comm.eu/EU_water_law/part_4/index.html.
- FRANCISQUE, A., RODRIGUEZ, M. J., MIRANDA-MORENO, L. F., SADIQ, R., PROULX, F. (2009). Modeling of heterotrophic bacteria counts in a water distribution system. Water Research, Vol. 43, Issue 4, pp.1075–1087. [CrossRef]
- GALLOWAY, J. N. (2003). The Global Nitrogen Cycle. Treatise on Geochemistry, Vol. 8–9, pp. 557–583. [CrossRef]
- HALLAS, G., MONIS, P. (2015). Evaluation of heterotrophic plate and chromogenic agar colony counting in water quality laboratories. MethodsX, Vol. 2, pp. 415-422. [CrossRef]
- HEJABI, N., SAGHEBIAN, S. M., AALAMI, M. T., NOURANI, V. (2021). Evaluation of the effluent quality parameters of wastewater treatment plant based on uncertainty analysis and post-processing approaches (case study). Water Science and Technology, Vol.83, Issue 7, pp. 1633–1648. [CrossRef]
- Heterotrophic Plate Count (HPC) Testing - Phoslab Environmental Laboratories Phoslab Environmental Laboratories. (n.d.). Retrieved December 20, 2023, from https://www.phoslab.com/environmental-services/hpc/.
- HOWARD, I., ESPIGARES, E., LARDELLI, P., MARTÍN, J. L., ESPIGARES, M. (2004). Evaluation of microbiological and physicochemical indicators for wastewater treatment. Environmental Toxicology, Vol.19, Issue 3, pp. 241–249. [CrossRef]
- KALLOUM, S., BOUABDESSALEM, H., TOUZI, A., IDDOU, A., OUALI, M. S. (2011). Biogas production from the sludge of the municipal wastewater treatment plant of Adrar city (southwest of Algeria). Biomass and Bioenergy, Vol. 35, Issue 7, pp. 2554–2560. [CrossRef]
- KAUR, J., PUNIA, S., KUMAR, K. (2017). Need for the advanced technologies for wastewater treatment. Advances in Environmental Biotechnology, pp. 39–52. [CrossRef]
- KHAN, S. A., ATTA, T., REHMAN, U., NASIR, A., AFTAB, S., HAFEEZ, A. (2017). Assessment of Waste Water Treatment Plant Efficiency through Physico-Chemical Analysis: A Case Study of I-9 Waste Water Treatment Plant, Islamabad, Pakistan. In Int.J.Econ.Environ.Geol Vol. 8, Issue 4. www.econ-environ-geol.org.
- LAM, S., NGUYEN-VIET, H., TUYET-HANH, T. T., NGUYEN-MAI, H., HARPER, S. (2015). Evidence for Public Health Risks of Wastewater and Excreta Management Practices in Southeast Asia: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, Vol. 12, Issue 10, Article number 12863. [CrossRef]
- MAGUVU, T. E., BEZUIDENHOUT, C. C., KRITZINGER, R., TSHOLO, K., PLAATJIE, M., MOLALE-TOM, L. G., MIENIE, C. M., COERTZE, R. D. (2020). Combining physicochemical properties and microbiome data to evaluate the water quality of South African drinking water production plants. PLoS ONE, Vol. 15, Issue 8. [CrossRef]
- MAKUWA, S. MAKUWA, S., TLOU, M., FOSSO-KANKEU, E., GREEN, E. (2020). Evaluation of fecal coliform prevalence and physicochemical indicators in the effluent from a wastewater treatment plant in the north-west province, south Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, Vol.17, Issue 17, pp. 1–13. [CrossRef]
- MUELA, A., ORRUÑO, M., ALONSO, M. L., PAZOS, M., ARANA, I., ALONSO, R. M., JIMÉNEZ, R. M., GARAIZABAL, I., MAGUREGUI, M. I., BARCINA, I. (2011). Microbiological parameters as an additional tool to improve wastewater treatment plant monitoring. Ecological Indicators, Vol. 11, Issue 2, pp. 431–437. [CrossRef]
- OECD (2018) Environmental Performance Reviews: Hungary, 208 p. (also available in French). [CrossRef]
- PAVLOV, D., DE WET, C. M. E., GRABOW, W. O. K., EHLERS, M. M. (2004). Potentially pathogenic features of heterotrophic plate count bacteria isolated from treated and untreated drinking water. International Journal of Food Microbiology, Vol. 92, Issue 3, pp. 275–287. [CrossRef]
- PISTOCCHI, A., HUSEMANN, J., MASI, F., NANU, C., EUROPÄISCHE KOMMISSION GEMEINSAME FORSCHUNGSSTELLE. (2020). Wastewater treatment in the Danube region: opportunities and challenges lessons learnt from a “synthesis centres” exercise, the European commission’s science and knowledge service, Joint Research Center, 84 p.
- SAID HAMAIDI, M., HAMAIDI-CHERGUI, F., ERRAHMANI, M. B., LAMROUSSI, A., BENMIRA, H. (n.d.). EFFICIENCY OF INDICATOR BACTERIA REMOVAL IN A WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT (ALGIERS, ALGERIA). http://www.limnology.ro/water2014/proceedings.html.
- SALEEM, M., BUKHARI, A. A., AL-MALACK, M. H. (2000). Removal efficiencies of indicator micro-organisms in the Al-Khobar wastewater treatment plant. Environmental Engineering Science, Vol.17, Issue 4, pp. 227–232. [CrossRef]
- SINGH, U. K., KUMAR, B. (2017). Pathways of heavy metals contamination and associated human health risk in Ajay River basin, India. Chemosphere, Vol.174, pp.183–199. [CrossRef]
- SLOMP, C. P. (2012). Phosphorus Cycling in the Estuarine and Coastal Zones: Sources, Sinks, and Transformations. Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science, Vol.5, pp. 201–229. [CrossRef]
- SUNDARA KUMAR, * K, SUNDARA KUMAR, P., BABU, M. J. R. (2010). Performance evaluation of Waste water treatment plant. In International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 2, Issue 12.
- TAKMAN, M., SVAHN, O., PAUL, C., CIMBRITZ, M., BLOMQVIST, S., STRUCKMANN POULSEN, J., LUND NIELSEN, J., DAVIDSSON, Å. (2023). Assessing the potential of a membrane bioreactor and granular activated carbon process for wastewater reuse – A full-scale WWTP operated over one year in Scania, Sweden. Science of the Total Environment, Vol. 895, Article number: 165185. [CrossRef]
- TAVAZZI, S., CACCIATORI, C., COMERO, S., FATTA-KASSINOS, D., KARAOLIA, P., IAKOVIDES, I. C., LOUTSIOU, P., GUTIERREZ-AGUIRRE, I., LENGAR, Z., BAJDE, I., TENSON, T., KISAND, V., LAAS, P., PANKSEP, K., TAMMERT, H., MARIANI, G., SKEJO, H., GAWLIK, B. M. (2023). Short-term stability of wastewater samples for storage and shipment in the context of the EU Sewage Sentinel System for SARS-CoV-2. In Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Vol. 11, Issue 2. Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- TSAGARAKIS, K. P., MARA, D. D., HORAN, N. J., ANGELAKIS, A. N. (2001). Institutional status and structure of wastewater quality management in Greece. Water Policy, Vol. 3, Issue 1, pp.81–99. [CrossRef]
- UGOH, S. C., NNEJI, L. M., ATOYEBI, B. A. (2013). Bacteriological and Physico-Chemical Assessment of Wastewater from Wupa Wastewater Treatment Plant. Abuja. World Rural Observ, Vol. 5, Issue 11, pp. 74–79. http://www.sciencepub.net/ruralhttp://www.sciencepub.net/rural74.
- Understanding wastewater parameters and standards. (n.d.). Retrieved December 20, 2023, from https://www.1h2o3.com/en/learn/wastewater-parameters/.
- VAN GIJN, K., CHEN, Y. L., VAN OUDHEUSDEN, B., GONG, S., DE WILT, H. A., RIJNAARTS, H. H. M., LANGENHOFF, A. A. M. (2021). Optimizing biological effluent organic matter removal for subsequent micropollutant removal. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, Vol. 9, Issue 5, article number 106247. [CrossRef]
- VAN PUIJENBROEK, P. J. T. M., BEUSEN, A. H. W., BOUWMAN, A. F. (2018). Datasets of the phosphorus content in laundry and dishwasher detergents. Data in Brief, Vol. 21, pp. 2284–2289. [CrossRef]
- Wastewater Treatment. (n.d.). Retrieved December 19, 2023, from https://www.fcsm.hu/en/services/wastewater-treatment/wastewater-treatment.
- ZAHMATKESH, S., KLEMEŠ, J. J., BOKHARI, A., WANG, C., SILLANPAA, M., AMESHO, K. T. T., VITHANAGE, M. (2022). Various advanced wastewater treatment methods to remove microplastics and prevent transmission of SARS-CoV-2 to airborne microplastics. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, Vol. 20, Issue 2, pp. 2229–2246. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).