Submitted:
14 October 2024
Posted:
16 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
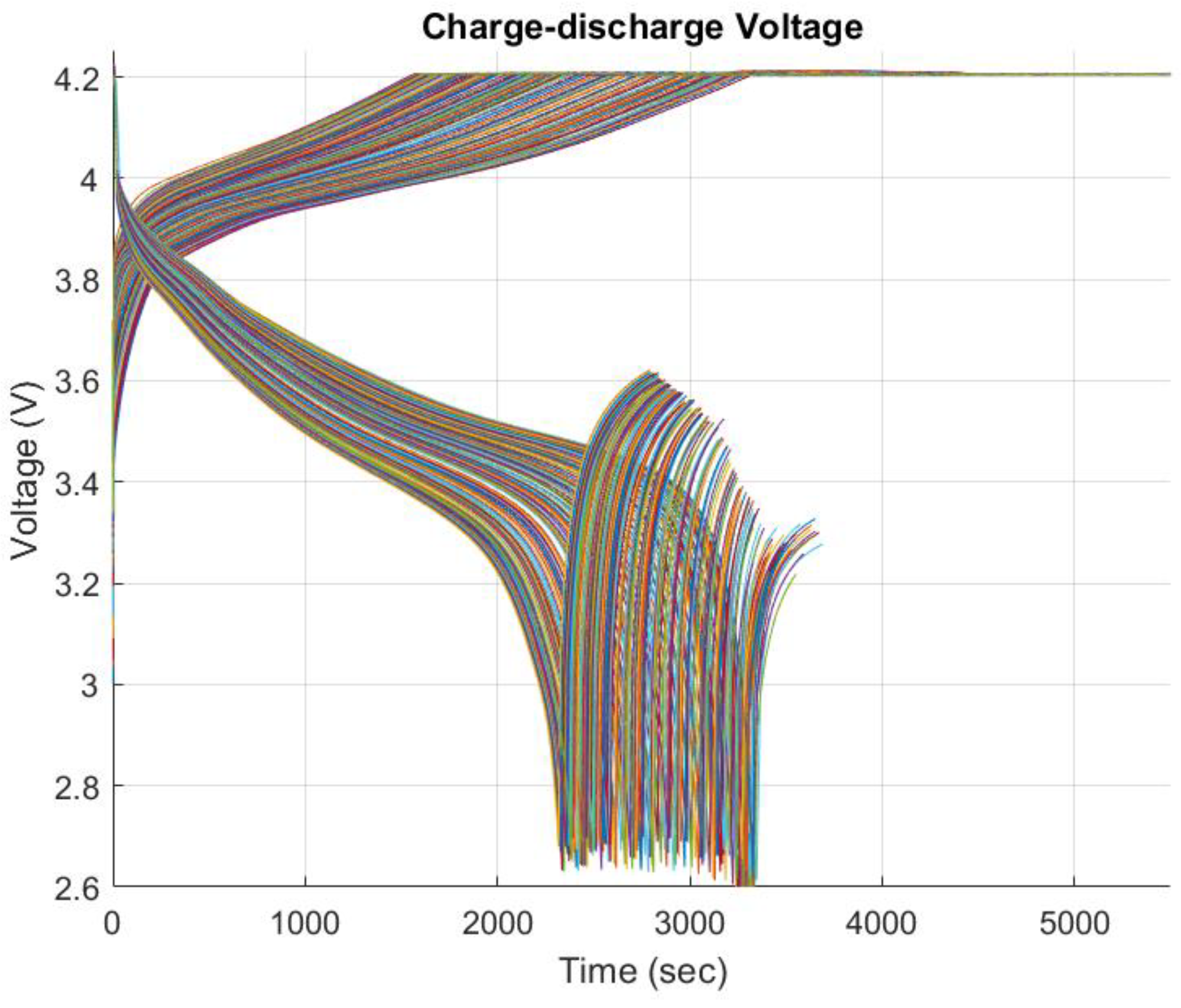
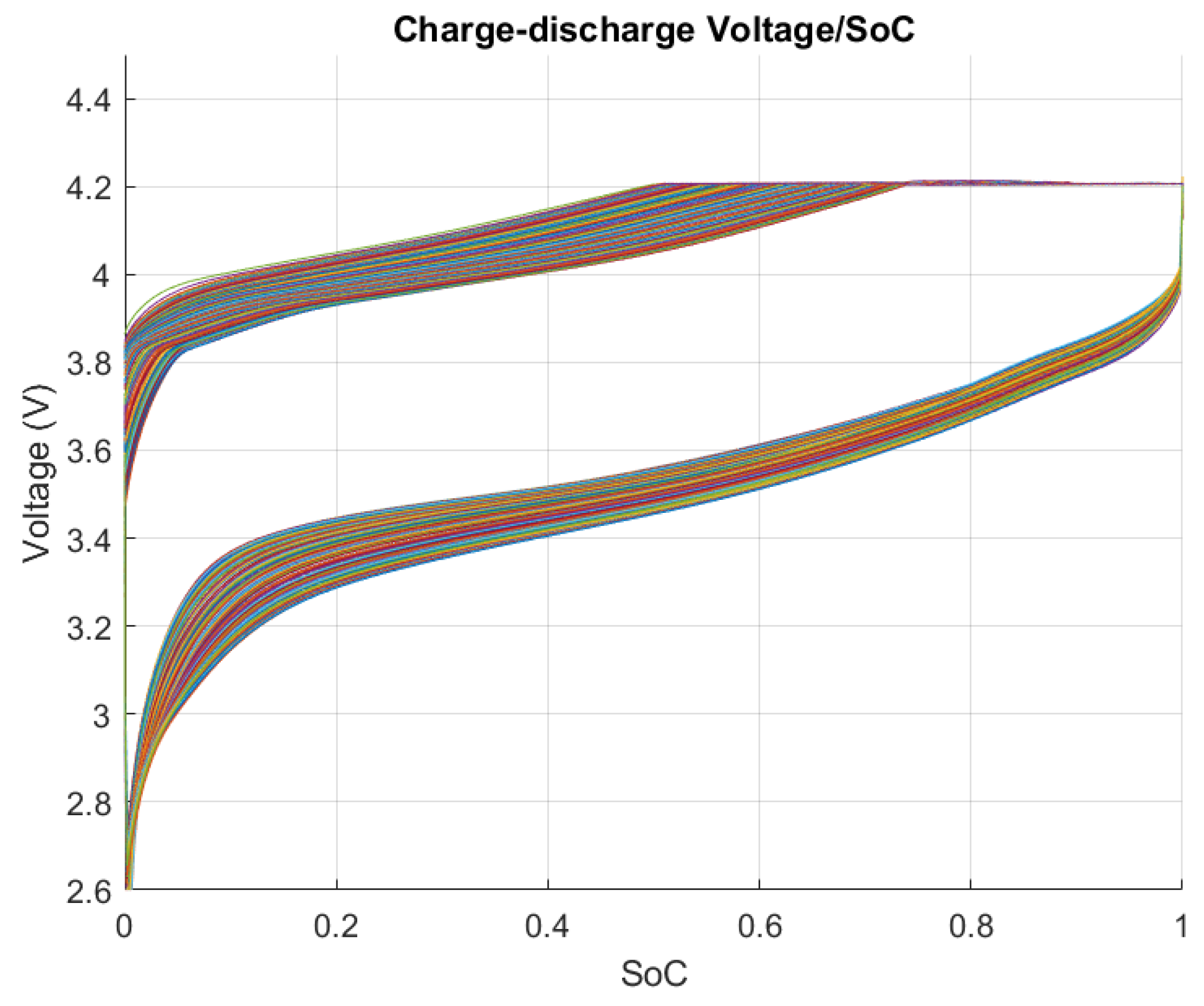
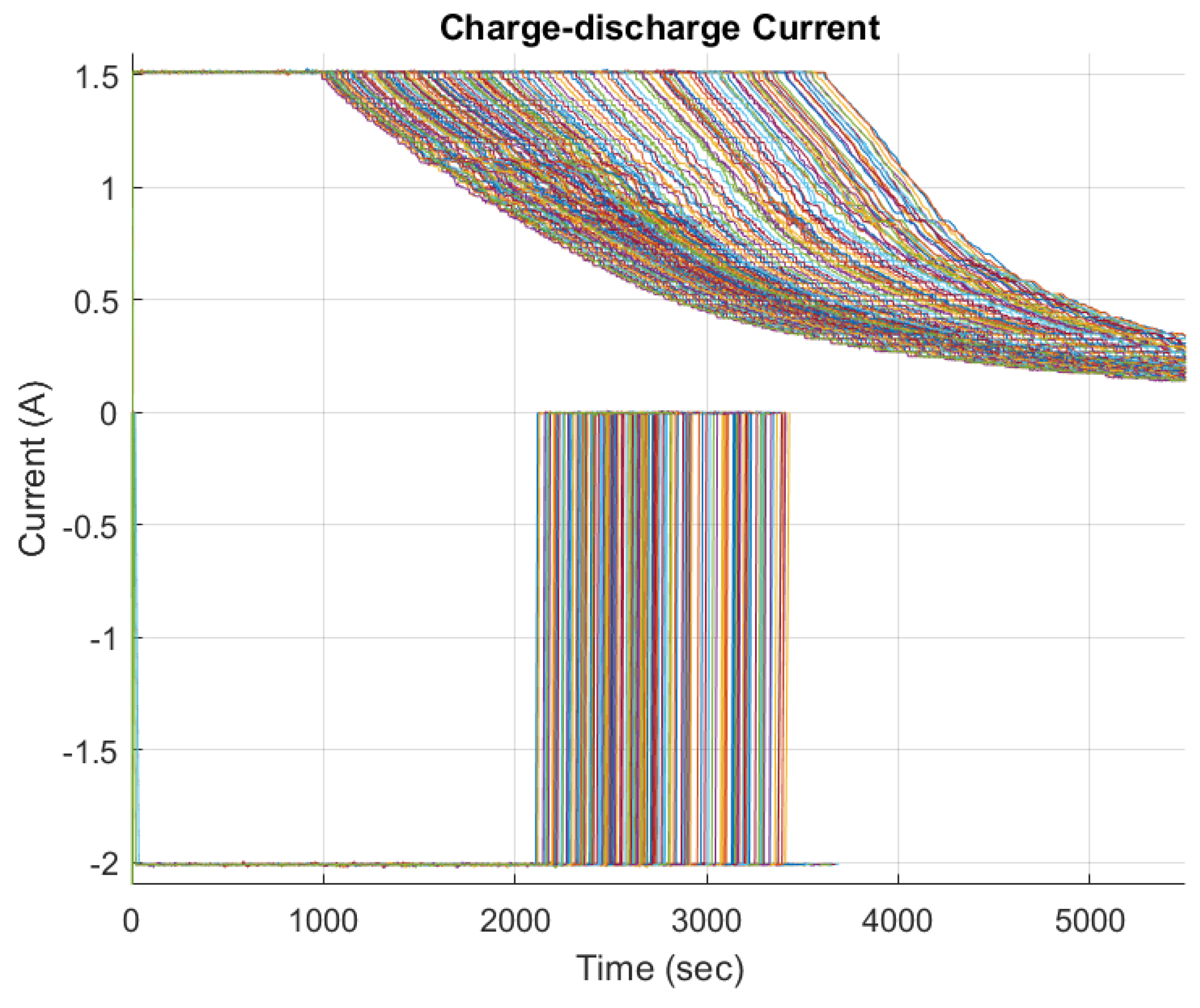
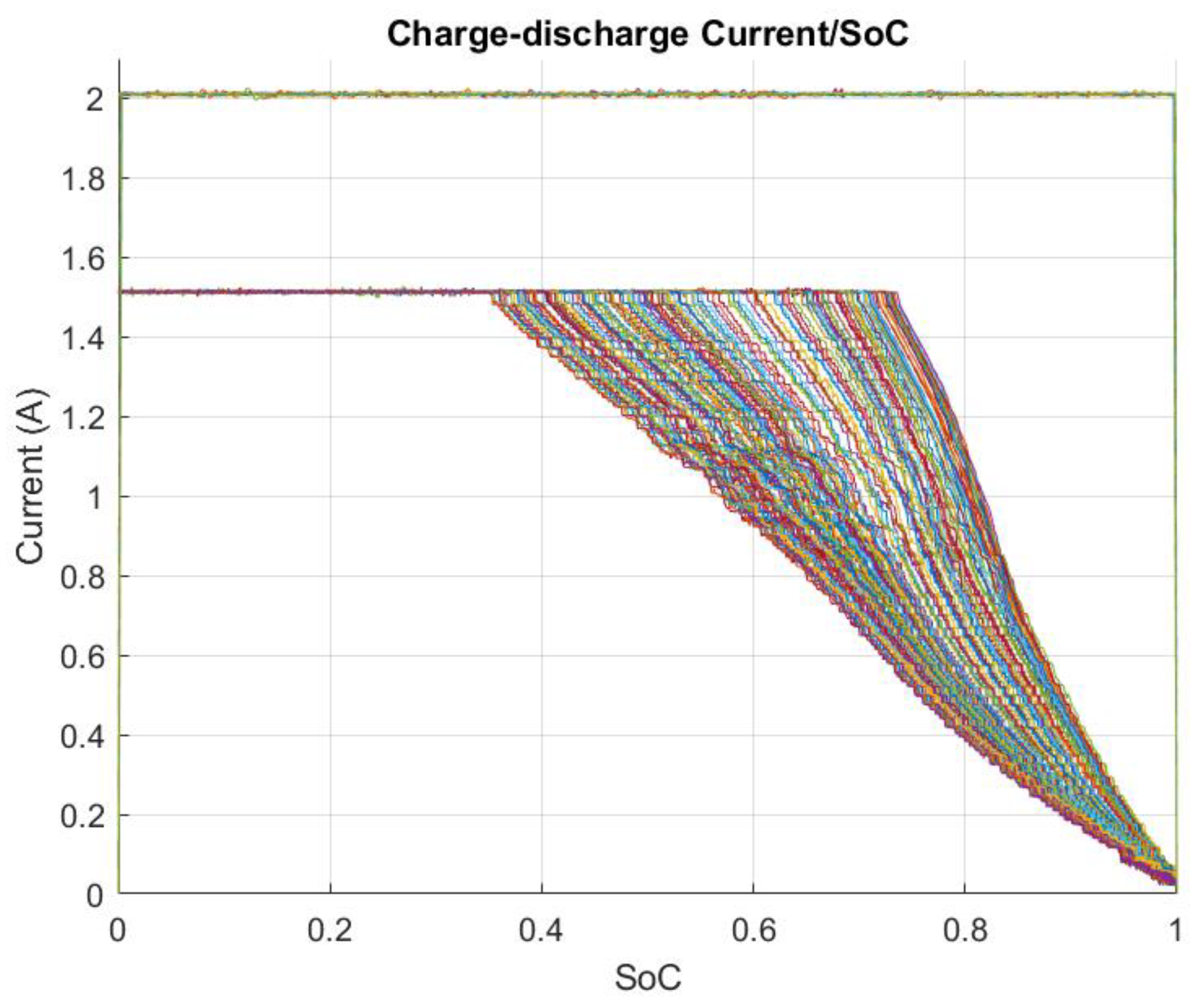
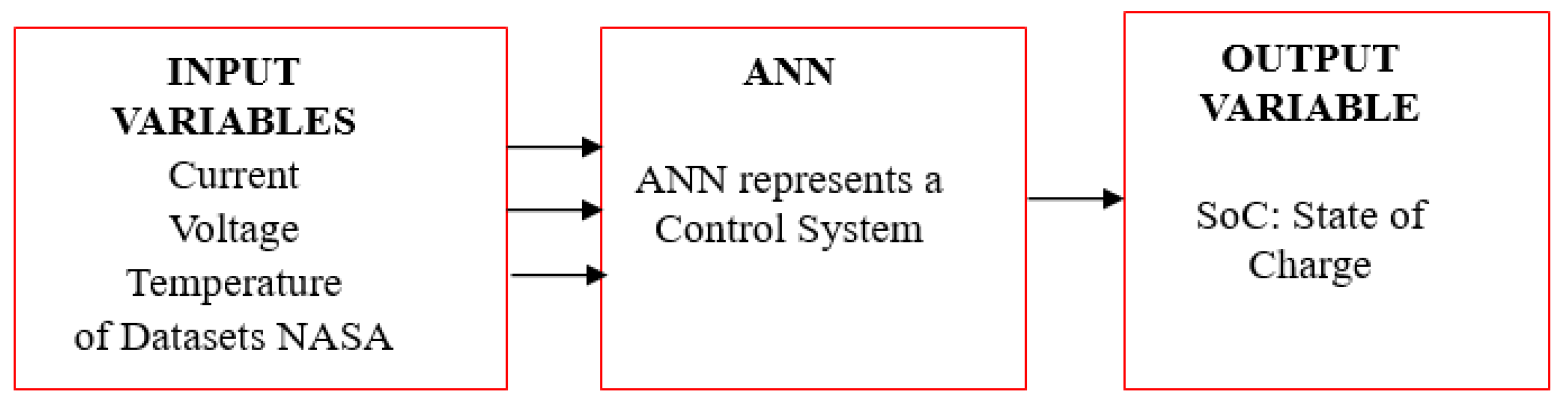
2. Data Acquisition Nasa Prognostics Center Of Excellence Dataset
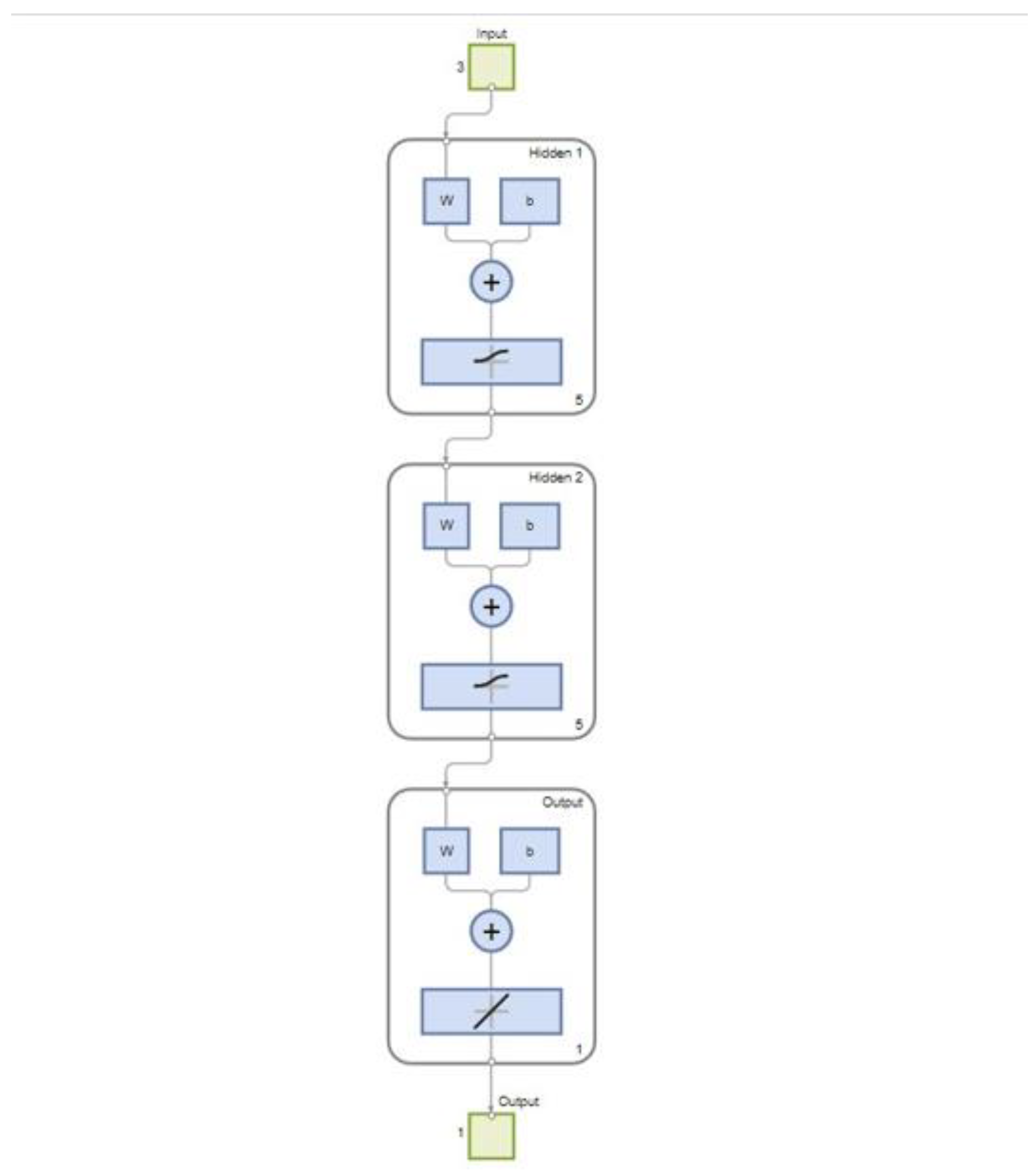
3. Described The FFFBPN Model Development And The Architecture Of The Model
3.1. Parameters Considered for the Realization of the Model
3.2. Data Normalization
- SoC(t): State of Charge;
- I(t): Current at time (t);
- Cbat: Battery capacity;
- t0: Initial time (s);
- tn: Final time (s).
- wij: Weight between neurons (i) and (j)
- : Learning rate
- : Error
3.3. Method For FFBPN Model Improvement
4. Suggested Feed-Forward Back Propagation Network (FFBPN).
4.1. Direct Model or Single Output Model
4.2. Training and Test Data
4.3. Training Algorithm
4.4. Hidden Layers in Prediction
4.5. Using for Battery Health Prediction
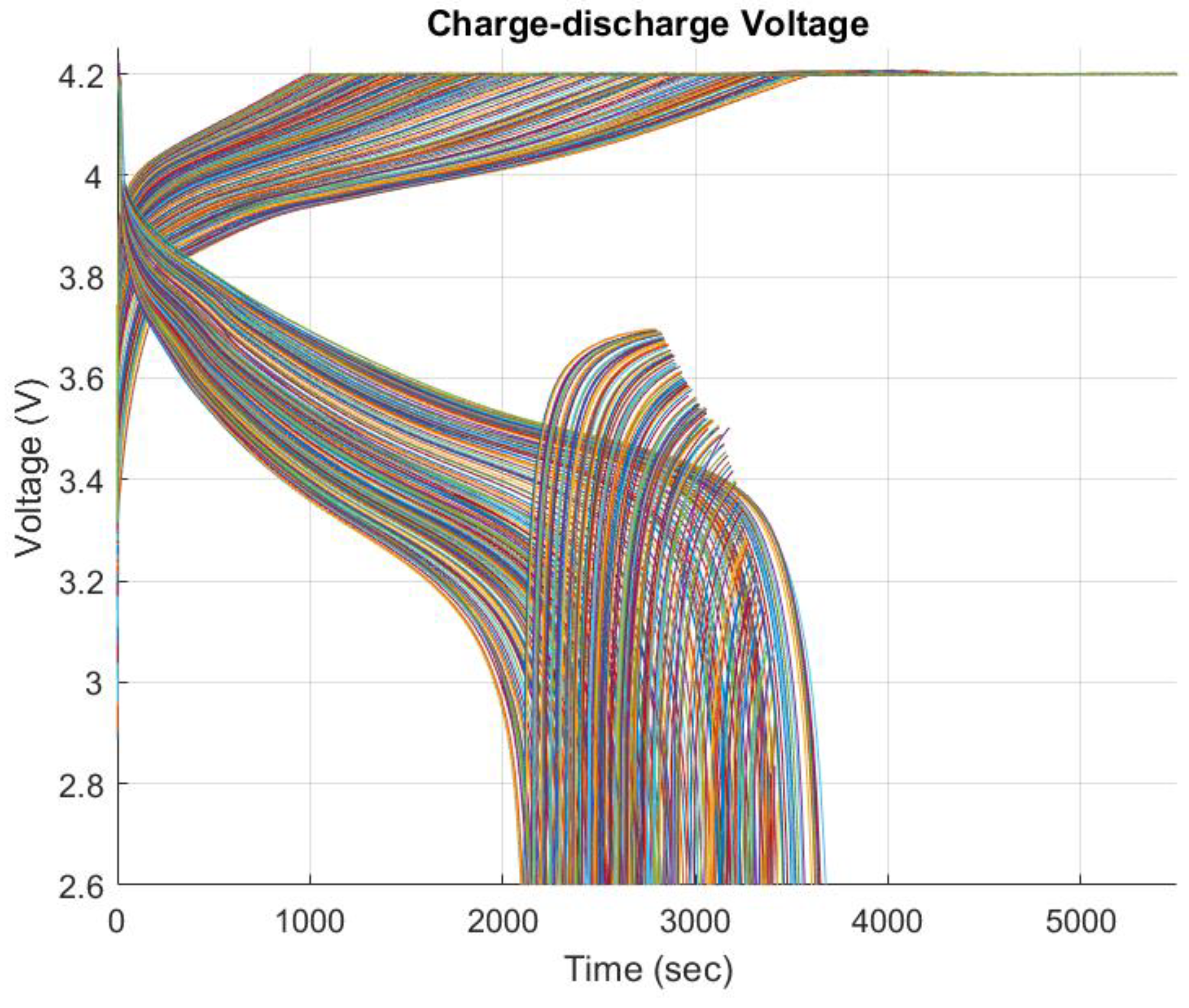
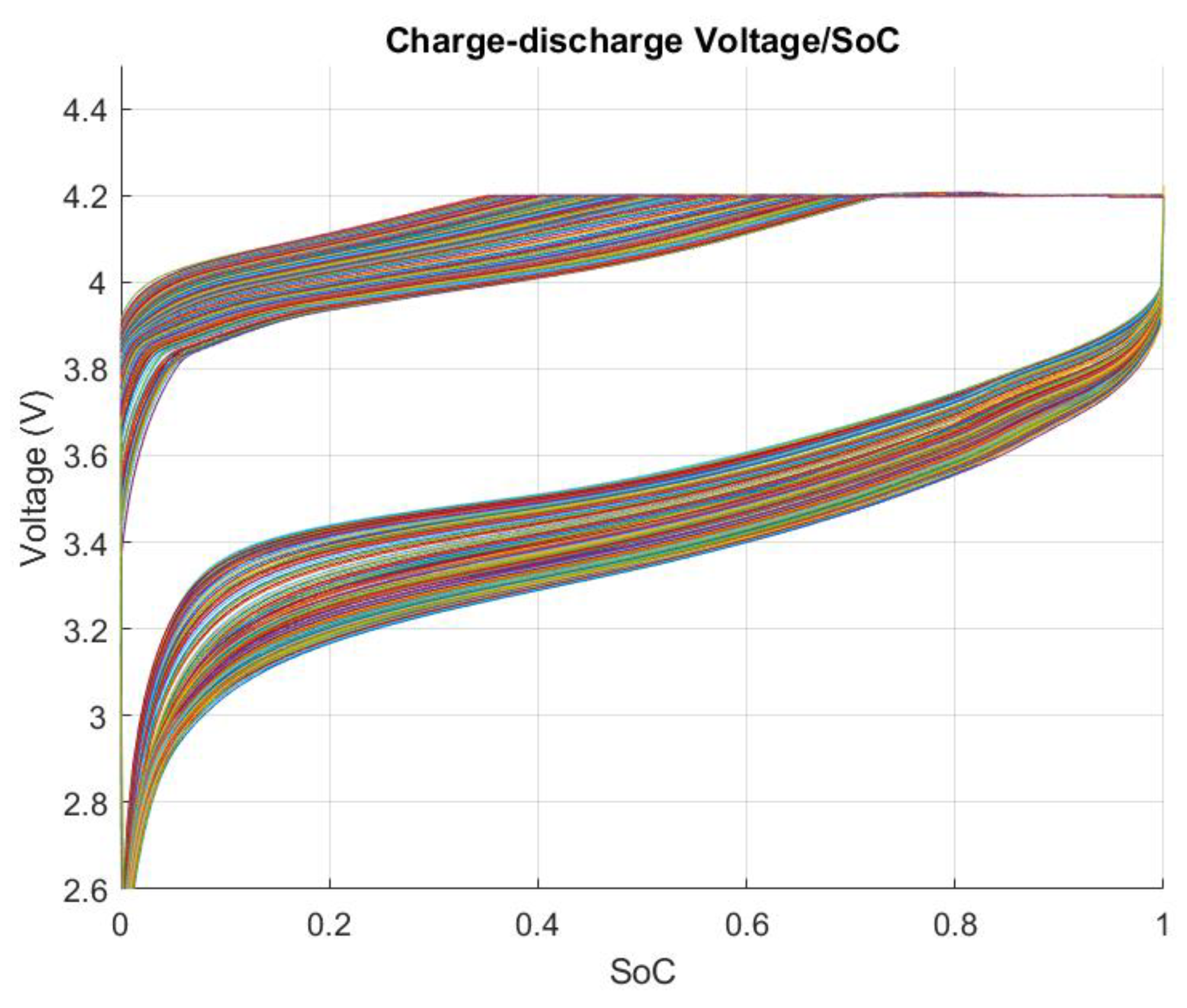
5. Results and discussions
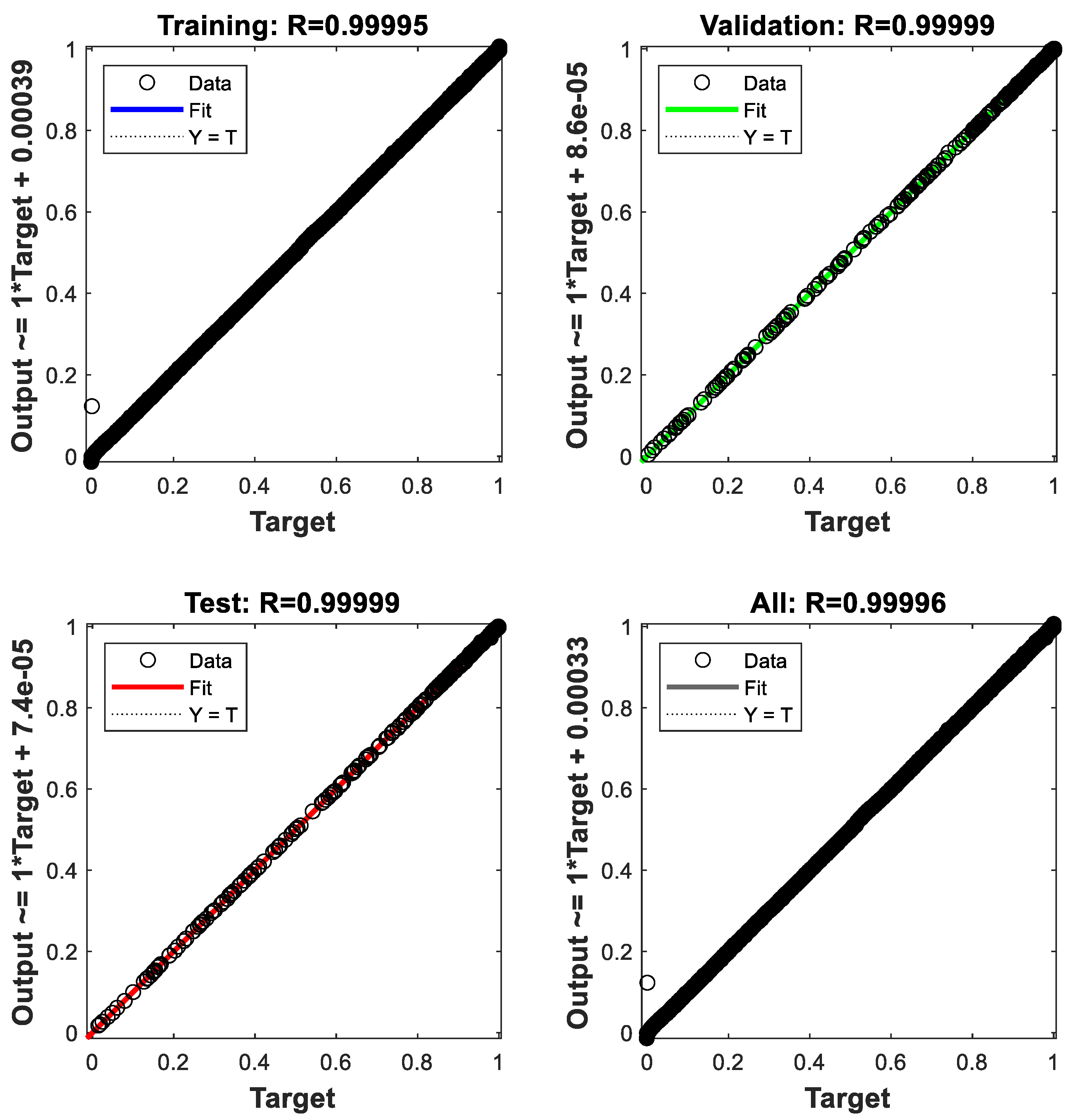
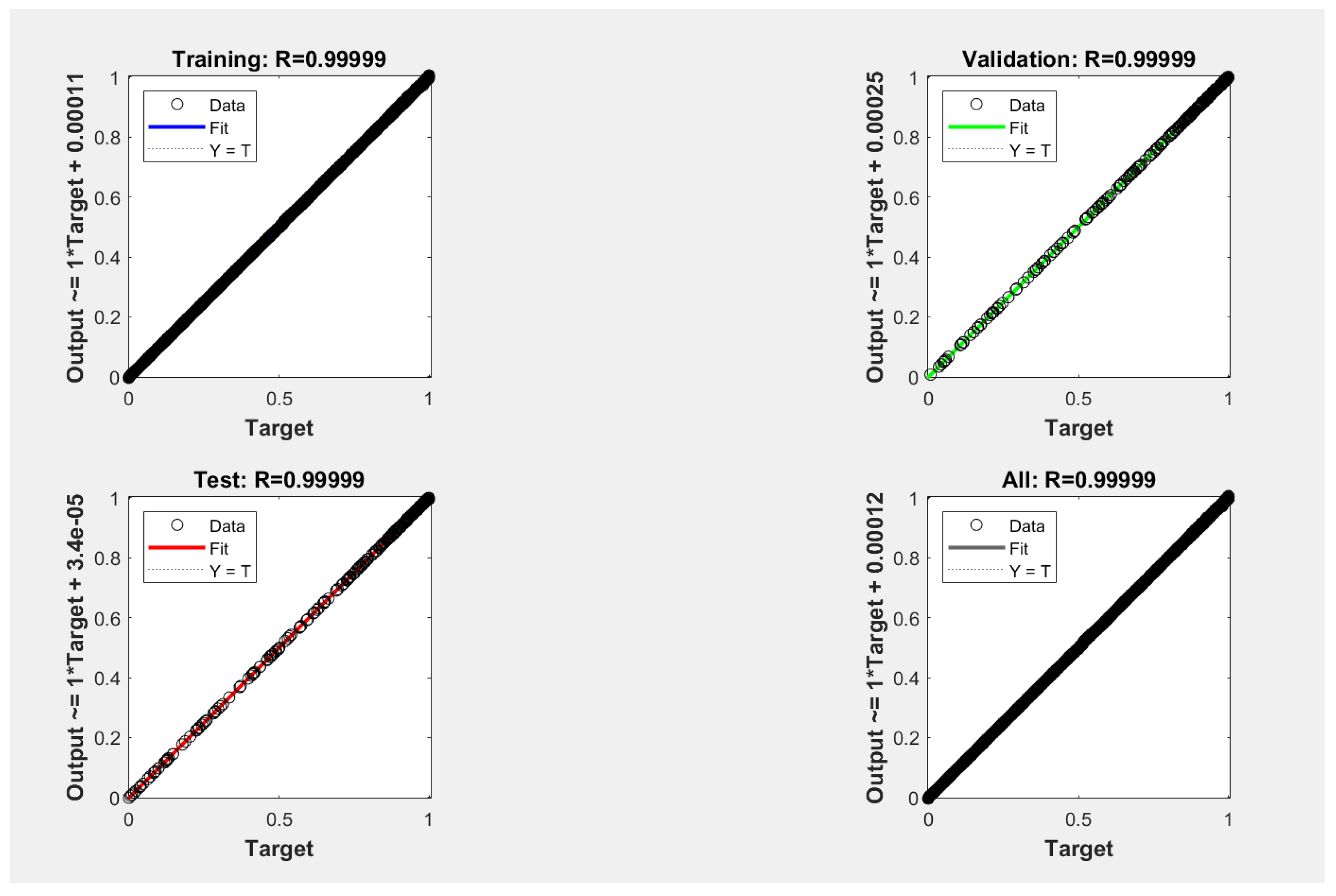
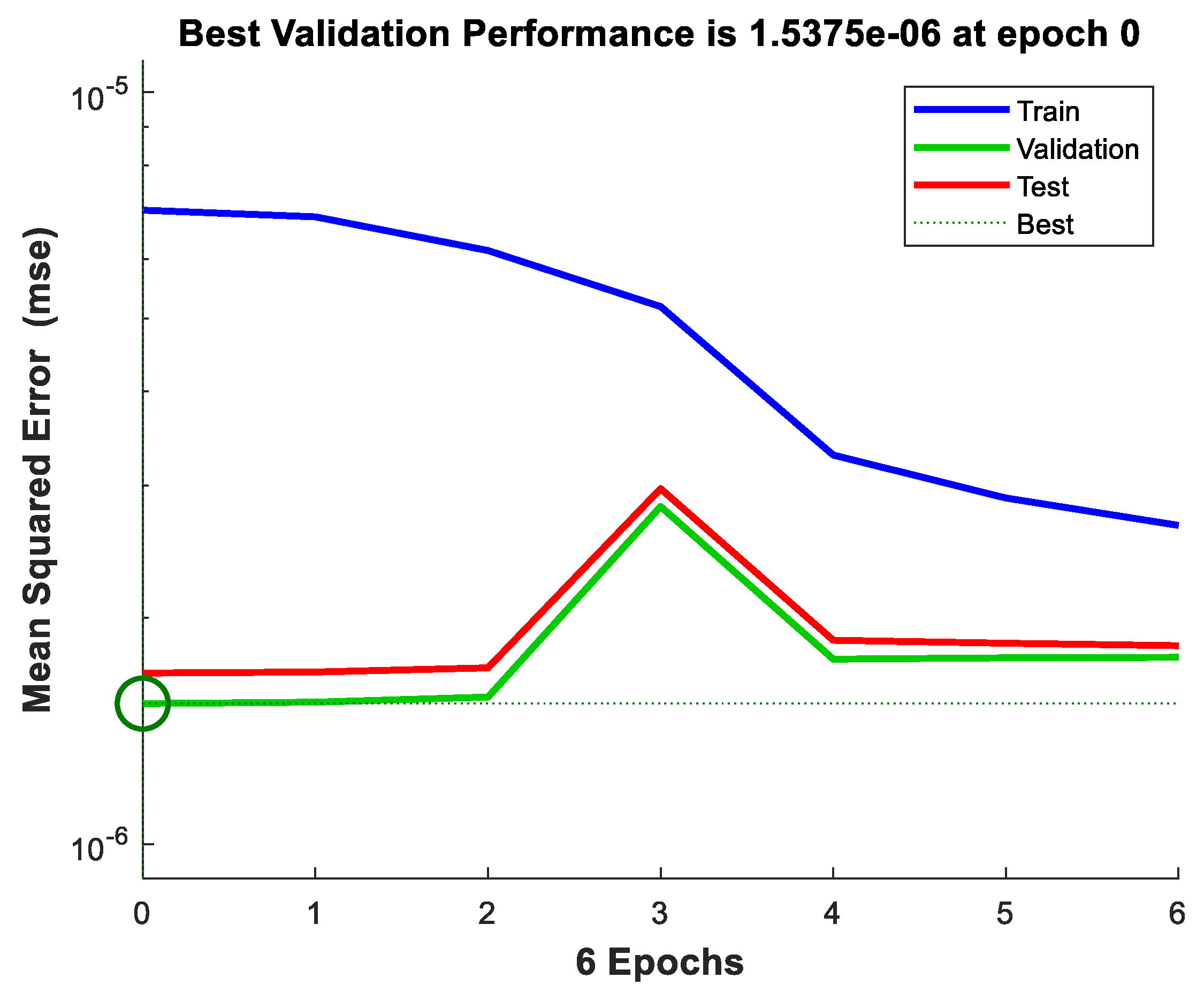
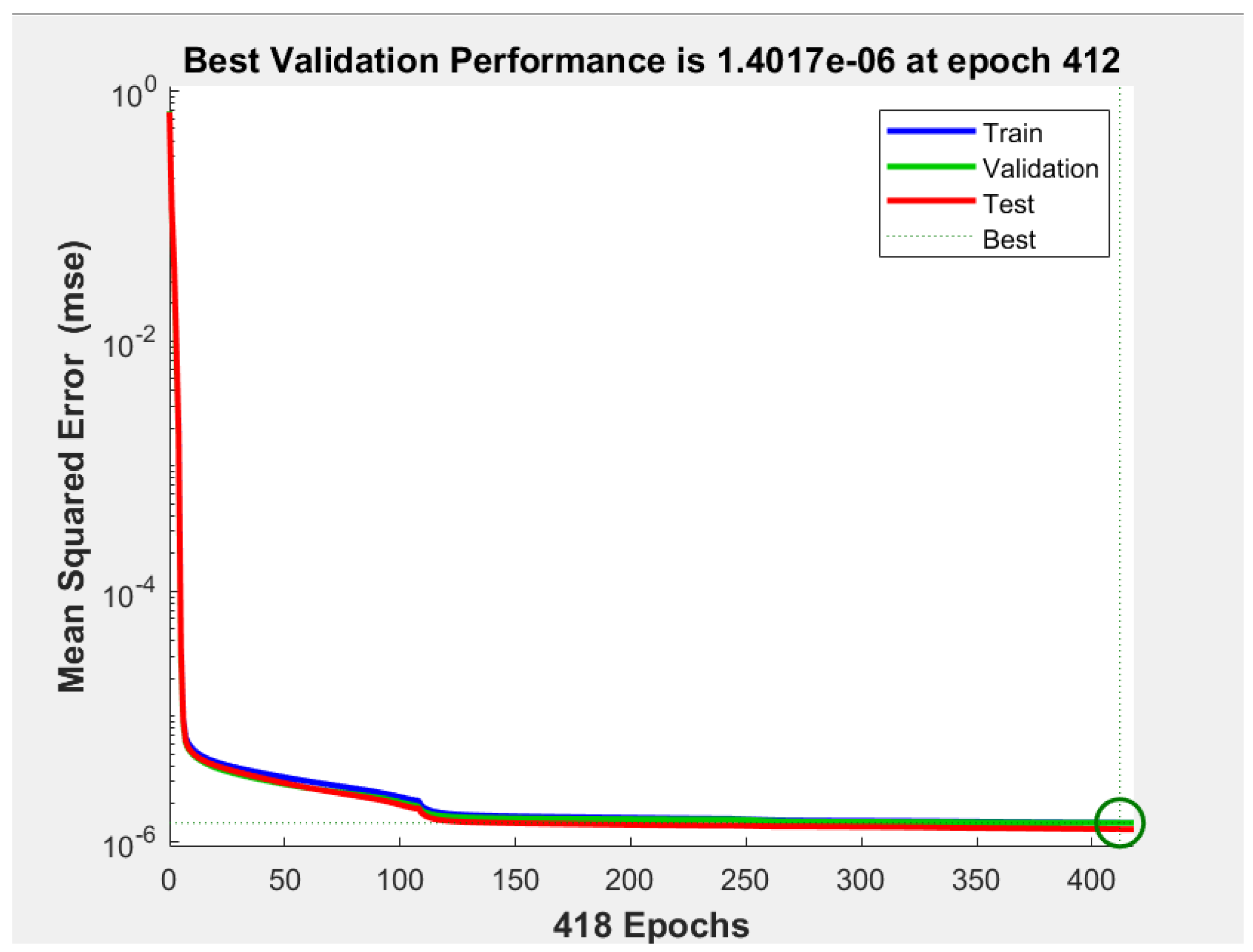
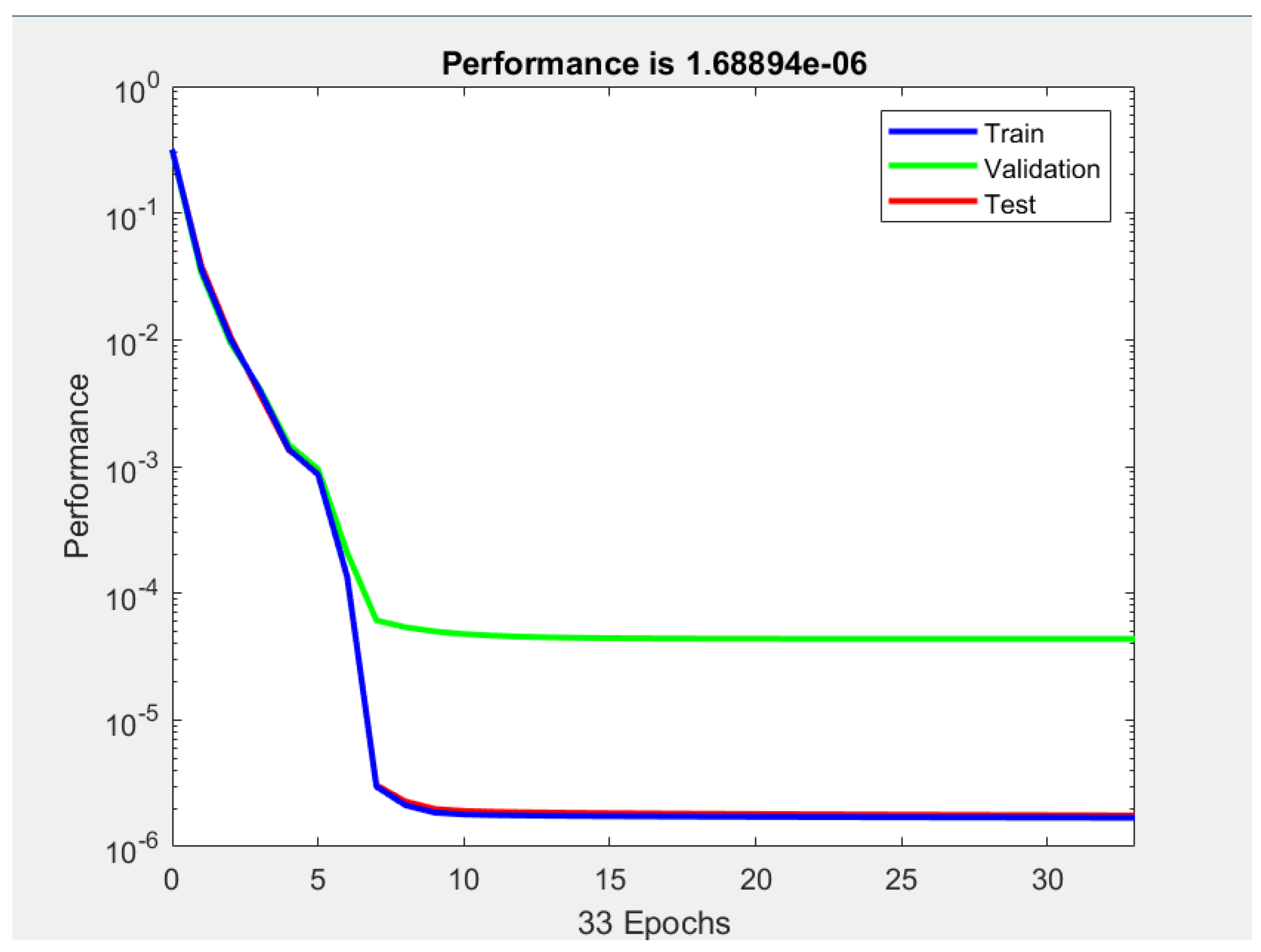
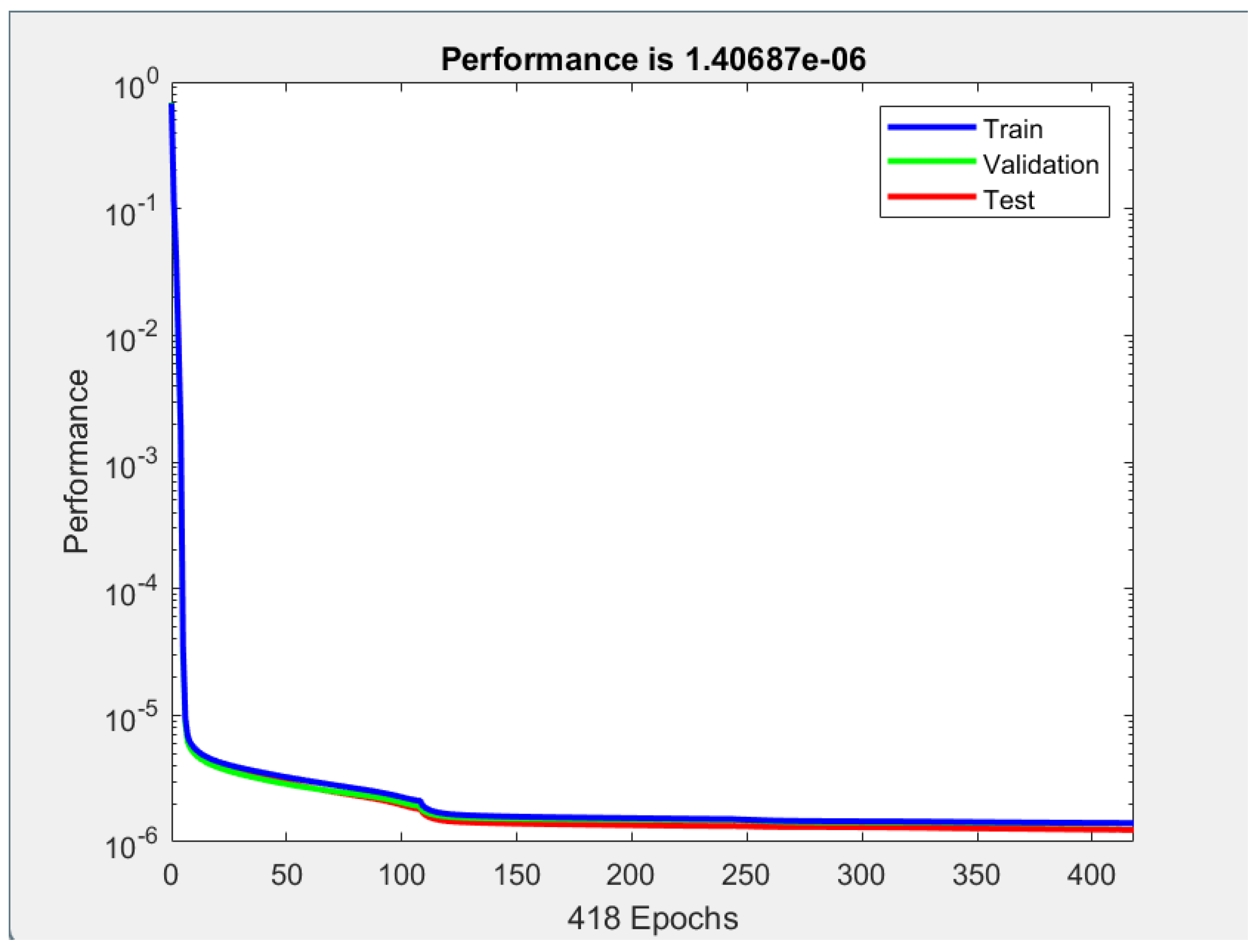
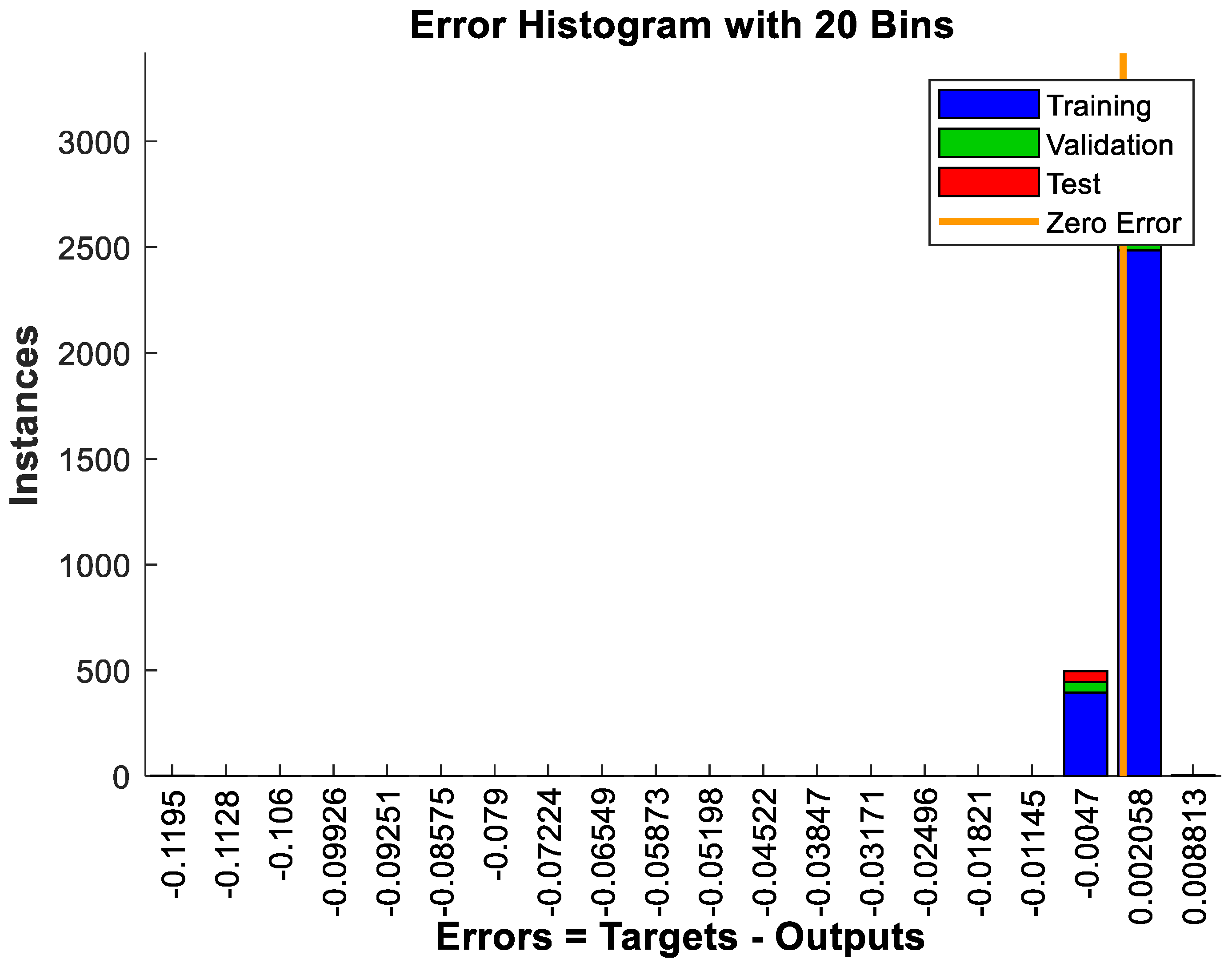
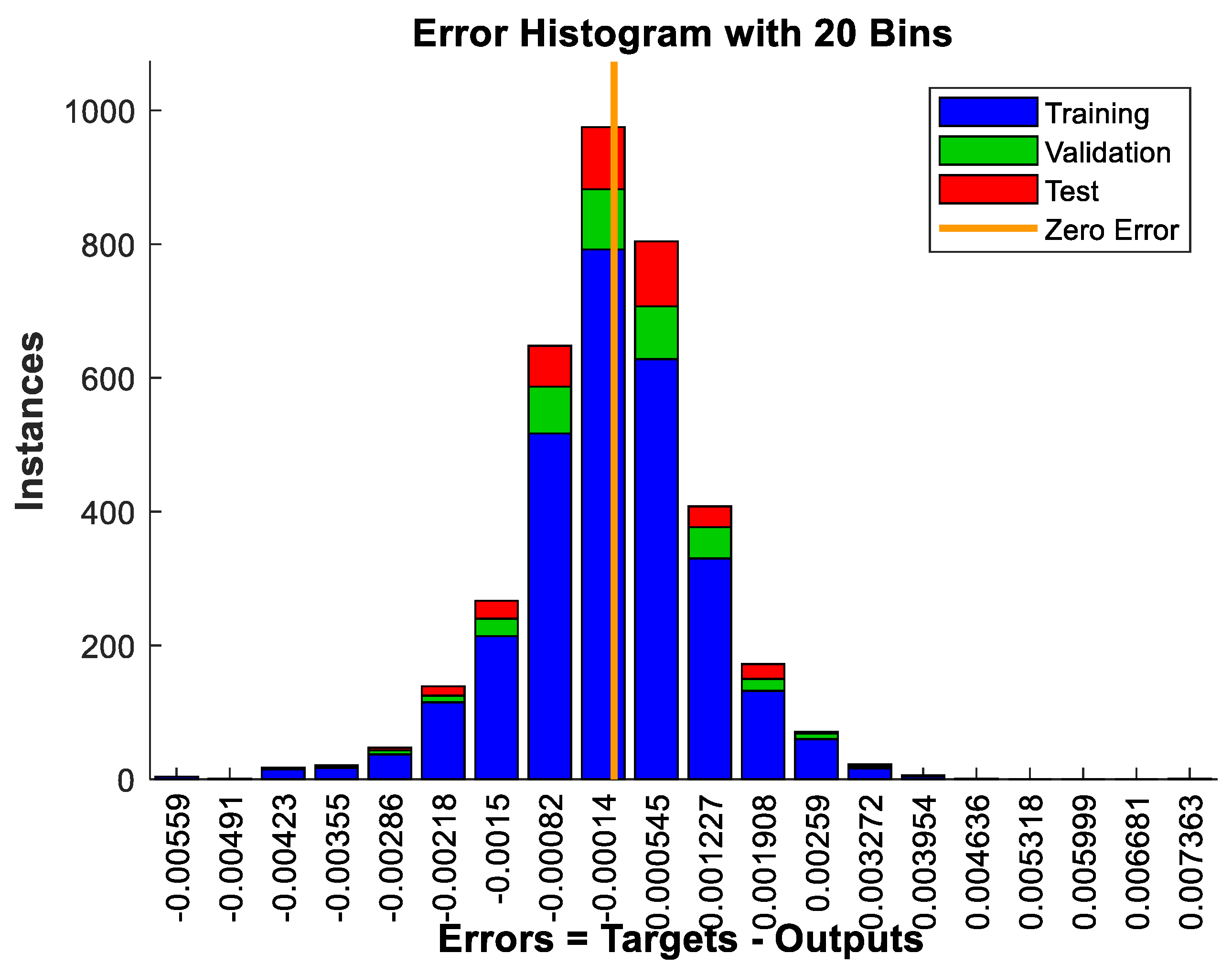
5.1. FFBPN Model Training and FFBPN Model Testing
|
Evaluation of MSE Mean Squared Error |
Dataset NASA PCoE Research Center | Dataset NASA PCoE Research Center |
| MSE | Battery B0005 | Battery B0006 |
| MSE | 5.8991e-06 | 1.3928e-06 |
5.2. Evaluation Criteria- Root Mean Squared Error
- =actual value;
- =predicted value.
|
Evaluation of RMSE Root Mean Squared Error |
Dataset NASA PCoE Research Center | Dataset NASA PCoE Research Center |
| RMSE | Battery B0005 | Battery B0006 |
| RMSE | 0.0024 | 0.0012 |
5.3. Remaining Useful Life Calculation Results
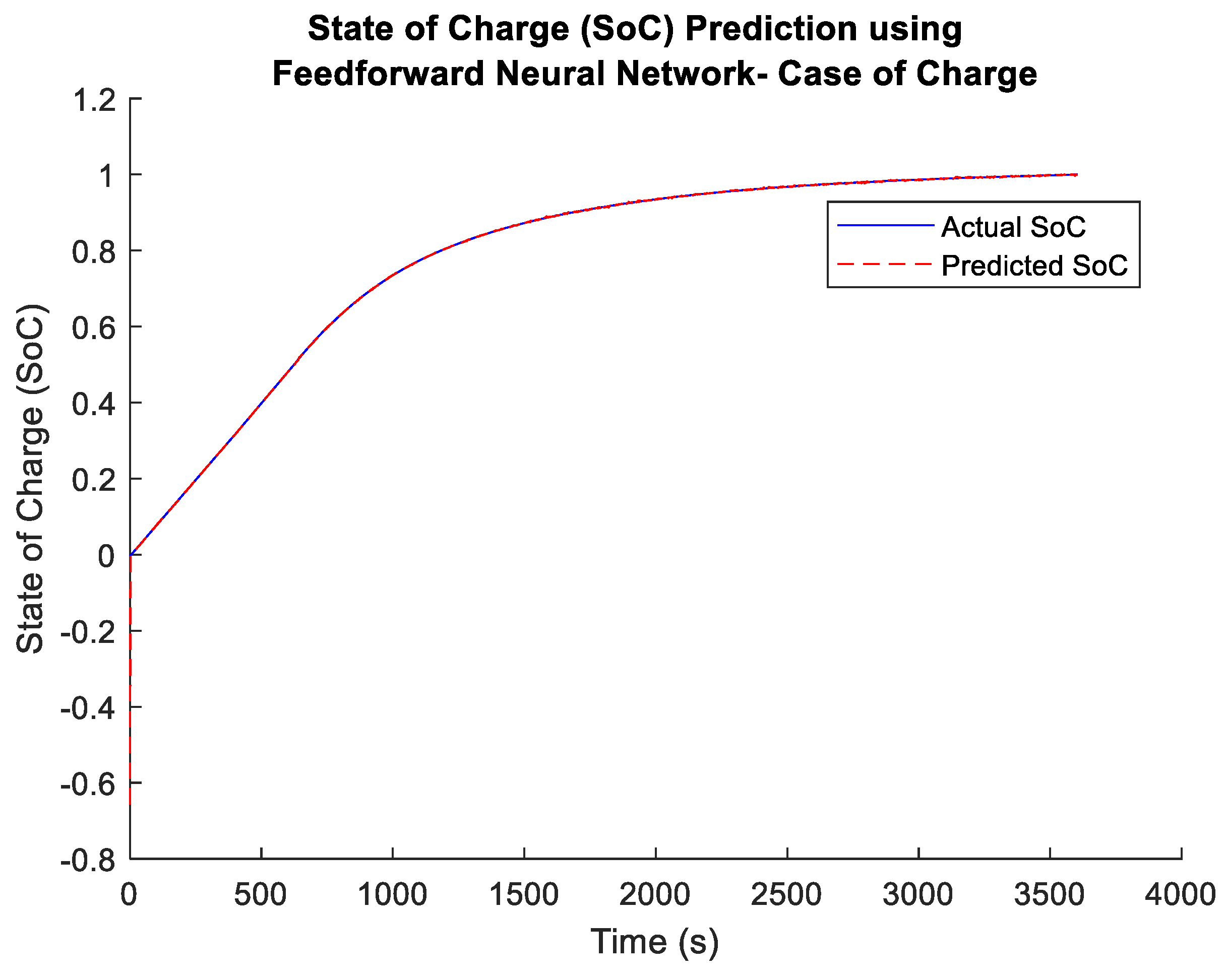
- xi= Actual SOC State of Charge for battery B0005;
- xp= Predicted SOC State of Charge for battery B0005.
6. Conclusion
References
- Cervellieri A., A lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction method with the incremental capacity analysis based on a new algorithm, ISSN 1112-5209, Journal of Electrical System, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Cervellieri A., An incremental capacity analysis for a lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction method based on a new algorithm, AJSE-ASEAN Journal of Science and Engineering, 2024.
- Cervellieri A. A new algorithm for ICA/DVA utilized for a SOC and RUL prediction method of lithium-ion batteries, AJSE-ASEAN Journal of Science and Engineering, 2024.
- Cervellieri A. Literature review of lithium-ions batteries for SOH analysis and their transformative role within sectoral innovation systems, AJSE-ASEAN Journal of Science and Engineering, 2024.
- Cervellieri A. A critical review of lithium-ion batteries cycling process from a safety testing prospective, AJSE-ASEAN Journal of Science and Engineering, 2024.
- Damiano, Alfonso & Gatto, Gianluca & Marongiu, I. & Porru, Mario & Serpi, Alessandro. (2014). Vehicle-to-Grid Technology: State-of-the-Art and Future Scenarios. Journal of Energy and Power Engineering. 8. 152-165. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Ruifeng & Peng, Shuaikang & Chang, Tai & Lee, Kwang. (2023). Annotated Survey on the Research Progress within Vehicle-to-Grid Techniques Based on CiteSpace Statistical Result. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 14. 303. [CrossRef]
- Escoto, M.; Guerrero, A.; Ghorbani, E.; Juan, A.A. Optimization Challenges in Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Systems and Artificial Intelligence Solving Methods. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5211. [CrossRef]
- Bortotti, M.F.; Rigolin, P.; Udaeta, M.E.M.; Grimoni, J.A.B. Comprehensive Energy Analysis of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Integration with the Power Grid: A Systemic Approach Incorporating Integrated Resource Planning Methodology. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11119. [CrossRef]
- Shin, GS., Kim, HY., Mahseredjian, J. et al. Smart Vehicle-to-Grid Operation of Power System based on EV User Behavior. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 19, 2941–2952 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S., Behera, S., Mekapati, S., Choudhury, N.B.D. (2024). Rapid EV Market Expansion Due to V2G Technology: A Review on V2G Grid Load Balancing and Control. In: Mahajan, V., Chowdhury, A., Singh, S.N., Shahidehpour, M. (eds) Emerging Technologies in Electrical Engineering for Reliable Green Intelligence. ICSTACE 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1117. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Yu, X.; Guo, Z.; Qian, T.; Li, Y. Online EVs Vehicle-to-Grid Scheduling Coordinated with Multi-Energy Microgrids: A Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Approach. Energies 2024, 17, 2491. [CrossRef]
- Trinandana G.A., Pratama A.W., Prasetyono E., Anggriawan D.O. Real time state of charge estimation for lead acid battery using artificial neural network 2020 International Seminar on Intelligent Technology and its Applications, ISITIA, IEEE (2020), pp. 363-368. [CrossRef]
- How D.N., Hannan M.A., Lipu M.S.H., Sahari K.S., Ker P.J., Muttaqi K.M. State-of-charge estimation of li-ion battery in electric vehicles: A deep neural network approach IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 56 (5) (2020), pp. 5565-5574. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez A.D., Garcia F.S., Naranjo J.E., Anaya J.J., Jimenez F. Modeling the driving behavior of electric vehicles using smartphones and neural networks IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag., 6 (3) (2014), pp. 44-53. [CrossRef]
- Modi S., Bhattacharya J., Basak P. Estimation of energy consumption of electric vehicles using deep convolutional neural network to reduce driver’s range anxiety ISA Trans., 98 (2020), pp. 454-47. [CrossRef]
- Steinbaach L., Altinsoy M.E. Prediction of annoyance evaluations of electric vehicle noise by using artificial neural networks Appl. Acoust., 145 (2019), pp. 149-158. [CrossRef]
- Hussein A.A. Capacity fade estimation in electric vehicle li-ion batteries using artificial neural networks IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 51 (3) (2014), pp. 2321-2330. [CrossRef]
- Tian Z., Qian C., Gu B., Yang L., Liu F. Electric vehicle air conditioning system performance prediction based on artificial neural network Appl. Therm. Eng., 89 (2015), pp. 101-114. [CrossRef]
- Hussein, Ala. (2015). Capacity Fade Estimation in Electric Vehicles Li-ion Batteries using Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications. 51. 2321-2330. [CrossRef]
- Ansari S., Ayob A., Hossain Lipu M.S., Hussain A., Saad M.H.M. Multi-channel profile based artificial neural network approach for remaining useful life prediction of electric vehicle lithium-ion batteries Energies, 14 (22) (2021), p. 7521. [CrossRef]
- Guo Y., Zhao Z., Huang L., SoC Estimation of Lithium Battery Based on Improved BP Neural Network, Energy Procedia, Volume 105, 2017, Pages 4153-4158, ISSN 1876-6102. [CrossRef]
- Zhao F., Li Y., Wang X., Bai L., Liu T. Lithium-ion batteries state of charge prediction of electric vehicles using RNNs-CNNs neural networks IEEE Access, 8 (2020), pp. 98168-98180. [CrossRef]
- Nie Z., Farzaneh H. Real-time dynamic predictive cruise control for enhancing eco-driving of electric vehicles, considering traffic constraints and signal phase and timing (SPaT) information, using artificial-neural-network-based energy consumption model Energy, 241 (2022), Article 122888. [CrossRef]
- Narasimhulu N., Krishnam Naidu R.S.R., Falkowski-Gilski P., Divakarachari P.B., Roy U. Energy management for PV powered hybrid storage system in electric vehicles using artificial neural network and aquila optimizer algorithm Energies, 15 (22) (2022), p. 8540. [CrossRef]
- Hong J., Wang Z., Chen W., Wang L.Y., Qu C. Online joint-prediction of multi-forward-step battery SOC using LSTM neural networks and multiple linear regression for real-world electric vehicles J. Energy Storage, 30 (2020), Article 101459. [CrossRef]
- Charkhgard M., Farrokhi M. State-of-charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries using neural networks and EKF IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 57 (12) (2010), pp. 4178-4187. [CrossRef]
- Zheng L., Hou Y., Zhang T., Pan X. Performance prediction of fuel cells using long short-term memory recurrent neural network Int. J. Energy Res., 45 (6) (2021), pp. 9141-9161. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z.H., Hendrick, Horng G.J., Wu H.T., Jong G.J. A prediction method for voltage and lifetime of lead–acid battery by using machine learning Energy Explor. Exploit., 38 (1) (2020), pp. 310-329. [CrossRef]
- Bukola Peter Adedeji, Golam Kabir, A feedforward deep neural network for predicting the state-of-charge of lithium-ion battery in electric vehicles, Decision Analytics Journal, Volume 8, 2023, 100255, ISSN 2772-6622. [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, B. (2023). A feedforward deep neural network for predicting the state-of-charge of lithium-ion battery in electric vehicles. Decision Analytics Journal. 8. 100255. [CrossRef]
- Shaik, N. & Pedapati, S. Rao & Taqvi, Syed Ali A. & Othman, A. & Abd D., Faizul A.. (2020). A Feed-Forward Back Propagation Neural Network Approach to Predict the Life Condition of Crude Oil Pipeline. Processes. 8. [CrossRef]
- Makhambet Sarbayev, Ming Yang, Haiqing Wang, Risk assessment of process systems by mapping fault tree into artificial neural network, Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, Volume 60. [CrossRef]
- 2019, Pages 203-212, ISSN 0950-4230. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




