1. Introduction
As one of Earth's most abundant biological resources, wood holds tremendous potential for providing green energy and supporting a sustainable future [
1]. Due to its
unique beauty, durability, and natural feel, wood has long been used in interior furnishings and is even referred to as the "most human-friendly material" [
2]. However, as resources become increasingly scarce and environmental awareness grows, the high cost of natural wood has led many consumers and designers to turn to artificial boards. Although artificial boards offer advantages in terms of price and sustainability, they are often perceived as cheap and lacking in texture [
3,
4]. This perceptual difference extends beyond functional comparisons to include the impact of material properties on consumers’ emotions and psychology. [
5]
Wood can be classified as softwood or hardwood based on the species and texture. Softwoods, typically from coniferous trees such as pine and cedar, are lighter and have lower density. These trees generally grow faster and are more abundant, making them easier and cheaper to harvest in large quantities. Conversely, hardwoods come from deciduous trees like oak, walnut, and cherry, which are usually denser and more esthetically pleasing, thus commanding higher prices [
6]. Hardwood species often have long growth cycles, taking decades or even centuries to mature, which makes them scarcer and, consequently, more expensive.
Despite the relative scarcity of wood resources in China, there has been a strong demand for wooden furniture in the Chinese market. This is due not only to solid wood furniture's durability and esthetic appeal, but also to the cultural connection with wooden furniture in Chinese tradition. To meet market demand and address the issue of limited wood resources, artificial boards have gradually emerged in the home furnishings market. Artificial boards typically comprise sustainable materials such as particleboard and medium-density fiberboard (MDF). These boards come from fast-growing, low-cost trees like poplar, eucalyptus, and pine. By processing these fast-growing woods into chips or fibers and then shaping them under high temperature and pressure, these wood-based board products exhibit excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and stability [
7].
Due to these excellent properties and the fact they are composed of sustainable raw materials, artificial boards have garnered significant attention in the fields of materials, engineering, and environmental science [
8,
9,
10]. However, the market price and acceptance of artificial boards are generally lower than those of natural wood. For example, artificial boards are often made from wood chips or fibers, resulting in an irregular surface texture that contrasts sharply with the more uniform grain of natural wood. People prefer wood with regular grain patterns, making artificial board inferior and therefore cheap [
3]. In recent years, researchers have sought to improve the raw material form of artificial boards, altering their mechanical properties and creating different visual effects [
11,
12]. For instance, oriented-strand board (OSB) has a distinct wood chip form and relatively uniform orientation, creating a unique natural and rugged esthetic [
13], and is often used in decorations. For interior furniture, manufacturers apply wood grain-like decorative veneers to artificial board surfaces to make them more closely resemble natural wood [
14]. This approach can mitigate some of the negative perceptions of artificial boards, and decorative veneers have gained wide acceptance. Current research on decorative veneers for artificial boards primarily focuses on the effects of impregnation resins on decorative paper and the performance of veneered artificial boards [
15,
16,
17,
18].
While veneers can mimic the look of various kinds of wood, they can feel and look monotonous compared to real natural wood. In addition, the repetitive nature of veneer patterns can make the decorative effect less unique than that of natural wood. Engaging in a deep understanding of the evaluative differences between natural wood and veneered artificial boards is particularly important as material processing technology and esthetic preferences evolve.
Scholars have noted that, beyond functional differences, the perception of material properties is a key factor influencing consumer evaluations [
5]. The market success of new materials depends not only on their functionality but also on the sensations they evoke. The appreciation of a product partly stems from its material characteristics, which define its appearance and elicit emotional responses that influence purchasing behavior [
19]. Recent studies indicate that the appeal of materials is determined by their semantic, expressive, sensory, and emotional attributes, which are considered crucial components of purchasing decisions [
20]. As such, the sensory, expressive, and emotional dimensions of materials are becoming important factors affecting their practical applications.
Researchers have engaged in extensive discussions and conducted many experiments on the relationship between materials and human evaluations, focusing primarily on the psychological (subjective) and physiological levels. This article explores research methods for investigating these two levels and provides examples of their combined use.
For the psychological level, researchers employ psychological scales and surveys as powerful tools to investigate the relationship between materials and participants. These instruments, designed to capture participants' subjective emotional responses, play a pivotal role in understanding how materials influence subjective evaluations [
21,
22,
23,
24].
For example, the SAM scale, designed by Professors Bradley and Lang from the Center for Emotion and Attention at the University of Florida, is an emotion self-assessment rating system used to measure emotional responses. The SAM scale is based on the PAD (pleasure, arousal, dominance) emotional dimension model [
25]. SAM employs a series of images to represent varying levels of each dimension, allowing participants to select the image that best represents their emotional state. Initially, SAM was used in human–computer interaction evaluations and was later adapted to a paper-and-pencil version for group and cluster screening.
Mainstream emotion theories posit that human emotions comprise two opposing dimensions: positive affect and negative affect [
26]. The former includes emotional experiences such as enthusiasm, alertness, and liveliness, while the latter includes experiences such as distress, numbness, and quietness [
27]. The PANAS scale, developed by Watson and colleagues in 1988, is the most widely used tool for measuring these two dimensions of affect worldwide [
28].
The SAM and PANAS scales differ in both their measurement dimensions and methodologies. Specifically, in terms of measurement dimensions, the SAM scale evaluates emotions through three dimensions, pleasure, arousal, and dominance, although some researchers simplify it to focus on just pleasure and arousal [
19]. In contrast, the PANAS scale assesses emotions using two dimensions: positive affect and negative affect. The SAM scale employs a pictorial self-assessment method that emphasizes immediate emotional responses. Participants choose the images that best represent their current emotional state. The PANAS scale, on the other hand, uses a questionnaire format where participants rate specific emotion-related words, emphasizing their emotional state over a specific period. By combining these two scales, researchers can capture participants’ immediate emotional reactions and overall emotional states within a defined timeframe, thus providing a more comprehensive emotional profile. The pictorial assessment of the SAM scale can capture subtle, instantaneous changes in emotion, while the lexical scoring of the PANAS scale offers a detailed description of emotional experiences. Together, they complement each other, enhancing the precision and reliability of the measurements.
Despite the potential for self-reports to introduce subjective bias (Participants may adjust their responses based on social or organizational expectations to meet others' expectations of them or to avoid negative evaluations), these methods provide crucial preliminary data and a theoretical foundation for understanding the emotional impact of materials.
On the physiological level, researchers reveal the impact of materials on people’s emotions by recording and analyzing physiological indicators [
29,
30]. Variations in physiological signals often accompany human emotional changes. Compared to facial expressions or vocal signals, physiological signals more accurately reflect actual emotional states because facial and vocal representations are less nuanced and can be easily disguised [
31]. Thus, physiological signals are crucial inputs in affective computing. In the context of material emotion measurement, researchers have identified electroencephalography (EEG) and electrodermal activity (EDA) as essential sources of information on people’s emotional states [
32,
33,
34,
35].
Hwang et al. noted that EEG holds inherent advantages in measuring emotions [
36]. EEG directly detects brainwaves, or neural activity, from the central nervous system, whereas other responses (such as EDA, heart rate, and blood volume pulse) originate from peripheral nervous system activity. The central nervous system is linked to various aspects of emotion (e.g., unpleasant, or pleasant, relaxed or excited). In contrast, peripheral nervous system activity only relates to arousal and relaxation. Therefore, EEG can provide richer information about emotional states than other methods [
37,
38].
EDA significantly aids in emotion recognition. It is one of the most sensitive emotional feedback mechanisms, originating from the autonomic activation of sweat glands in the skin. EDA is closely related to emotions, arousal, and attention, making it one of the most widely used indicators of physiological response [
39]. Due to its high stability, ease of measurement, and high sensitivity, EDA is considered one of the most influential and sensitive physiological parameters for reflecting changes in sympathetic nervous system arousal. It is a reliable indicator for evaluating physiological arousal, cognitive load, effort, emotional response, and stress capacity.
Some researchers combine subjective evaluations with physiological measurements to obtain more comprehensive and objective emotional data [
40]. The combined approach of assessing subjective emotions using emotional scales while simultaneously recording physiological data captures both participants' subjective emotional experiences and their physiological reactions, providing a more holistic emotional dataset. Through dual measurement, researchers can more accurately assess the impact of materials on people’s emotions, reducing the potential bias of a single-method approach. This methodology offers new perspectives on the complex relationship between materials and emotions and reveals new directions for future research on materials and their applications.
Combining psychological (subjective) assessments with physiological measurements to provide more comprehensive and objective data on emotional responses to materials has numerous advantages; Individual biases or social expectations may influence subjective assessments, while physiological measurements provide unconscious, non-verbal response data. Their combined use can correct or supplement biases in subjective reports and improve the accuracy of research. In addition, physiological measurements can capture instantaneous and dynamic changes in emotions, while subjective assessments usually reflect overall or retrospective emotions. Their combined use allows for a more fine-grained analysis of emotional responses. However, such studies still need to be conducted for wood. Supplementing research in this area can help us better understand how the characteristics of wood materials influence emotions.
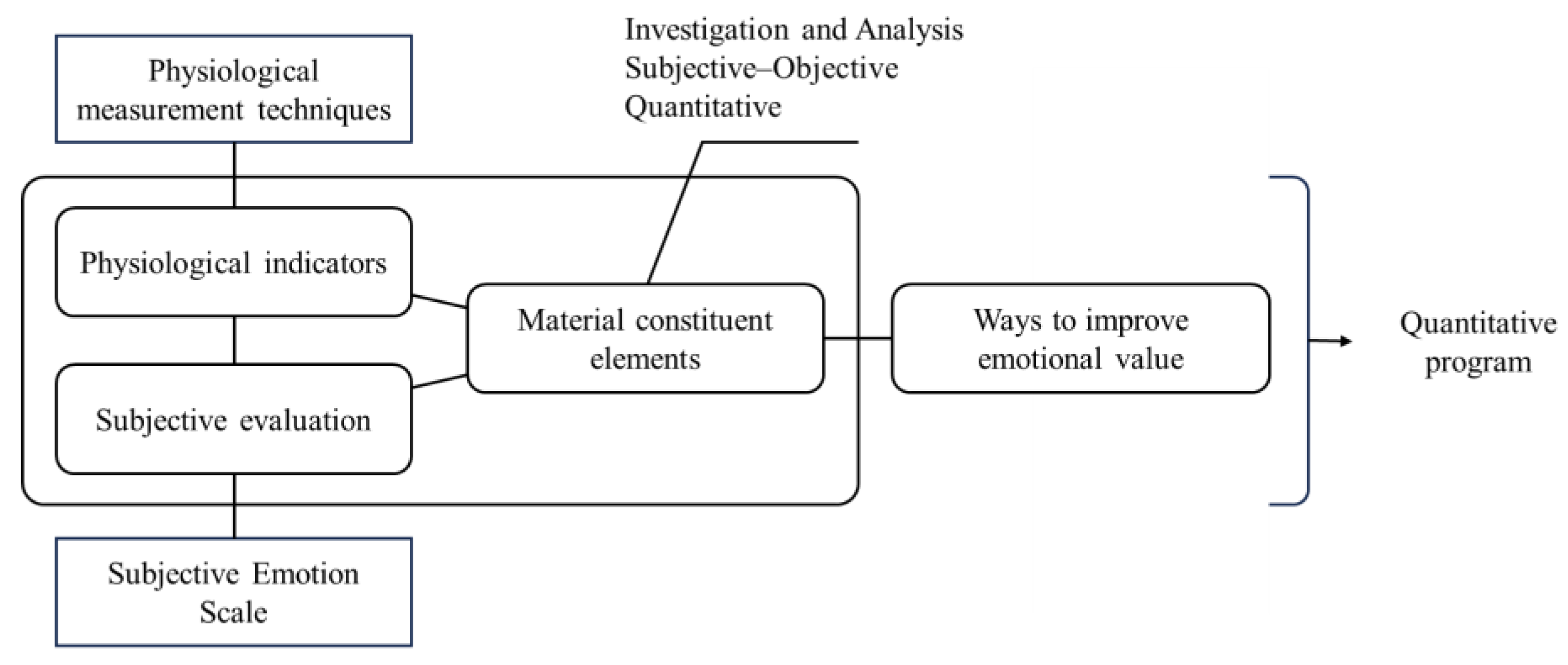
This research innovates by establishing a methodology to support the development of emotion-driven innovation in wood materials (
Figure 1). By integrating research methods for studying both psychological and physiological levels, we conducted a comprehensive and multi-faceted analysis of the relationship between material characteristics and participants' emotions. We utilized emotional experience questionnaires to capture participants' subjective emotional responses while recording their physiological reactions using wearable physiological measurement devices, ensuring data synchronization and integration. We accounted for individual differences and strictly controlled the experimental environment. Our use of advanced data analysis techniques, coupled with our adherence to rigorous ethical standards, ensures the robustness of our results and provides new theoretical foundations and practical guidance for the design and application of wood materials.
The objectives of this study, listed below, are significant, as they will contribute to establishing a deeper understanding of people’s emotional responses to materials, a field that has not been extensively explored.
Analyze the relationship between subjective evaluations and physiological indicators: By quantitatively and qualitatively assessing participants' emotional responses when interacting with different materials, we aim to better understand the interplay between their individual emotional states and physiological reactions. This analysis will provide valuable insights into the complexity of emotional experiences.
Analyze differences in the subjective and physiological indicators of emotional responses to natural wood and artificial boards: We will compare the performance of these two types of materials from visual and tactile points of view to understand their impact on participants' emotions. Natural wood, with its natural texture and feel, may evoke more positive emotional responses, whereas artificial boards, due to their synthetic characteristics, might elicit different emotional experiences. Through this comparison, we can more comprehensively assess the potential emotional impact of different materials.
Analyze the impact of sample composition elements on subjective evaluations and physiological indicators: Through comprehensive sample analysis, we aim to identify critical factors influencing participants' emotional responses, thus providing a theoretical basis for further research on wood materials.
Through this study, we aim to quantitatively reveal the differences in emotional responses to natural wood and artificial boards. By identifying key elements within the materials’ composition that affect participants' emotional responses, we hope to significantly enrich our understanding of the relationship between emotions and materials, inspiring further research in this area.
2. Materials and Methods
This study involved showing participants different samples of natural wood and artificial boards and recording their physiological and subjective emotional responses to viewing each sample.
2.1. Participants
We referred to the sample sizes used in related studies from the past two years to choose the number of participants for our study [
40,
41,
42]. Ultimately, we recruited a total of 24 university students. However, due to equipment malfunction (Some electrodes fell off during EEG data monitoring.) and abnormal participant data (Outliers caused by signal interference) during the experiment, the final valid sample size was 20 (including 15 undergraduates and 5 postgraduates, 10 males and 10 females) aged 18 to 25. All participants had normal or corrected-to-normal vision, no tactile impairment or history of neurological disorders, and normal olfactory function. To ensure the accuracy of data collection, we required all participants to abstain from drinking alcohol and coffee and staying up late within the 24 hours before the experiment. Each participant was informed about the procedures required for the experiment and provided written consent. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and received approval from the Research Ethics Committee of Shantou University.
2.2. Experimental Sample Selection and Classification
The experimental samples included ten wood-based materials, including both natural wood and artificial boards (7 natural and 3 artificial). Specifically, the natural wood samples selected were ash, elm, red oak, black walnut, white oak, pine, and cherry. The artificial boards consisted of three veneer-faced panels imitating North American black walnut, using particleboard as the base and different types of veneers for decoration, labeled Veneer A, Veneer B, and Veneer C. In this experiment, we deliberately selected materials with hues similar to those of the experimental samples. Color has been proven to be an important indicator that affects people's preference for wood [
23]. This study hopes to analyze how other wood components with the same tones affect people's evaluation of it. We set the sample size based on Harumi et al.'s study on wood tactile properties [
43], with each of the ten samples cut to a size of 30x30 cm and a thickness of 2 cm.
We collaborated with material suppliers and faculty members with wood research backgrounds to analyze the selected samples' constituent elements. Through extensive discussions with experts, we identified the categories that most strongly influence the sensory impact of materials in the visual and tactile dimensions: tactile sensation, texture, and brightness. The tactile dimension corresponds to the sense of touch; we classified the materials into three tactile categories: smooth, grainy, and rough. Texture and brightness primarily correspond to the sense of vision. For texture, we categorized the materials into three types based on the fineness and arrangement of the grain: fine texture, coarse texture, and mixed texture. Regarding brightness, we divided the materials into two categories: bright and dull.
The classification results of the experimental samples for this study are shown in
Table 1.
2.3. Subjective Emotion Evaluation Items
To enhance the accuracy and reliability of the subjective emotion measurement, we adopted a combined approach using two emotional assessment scales, as referenced in existing research [
40]. These scales were the Self-Assessment Manikin (SAM) and the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS).
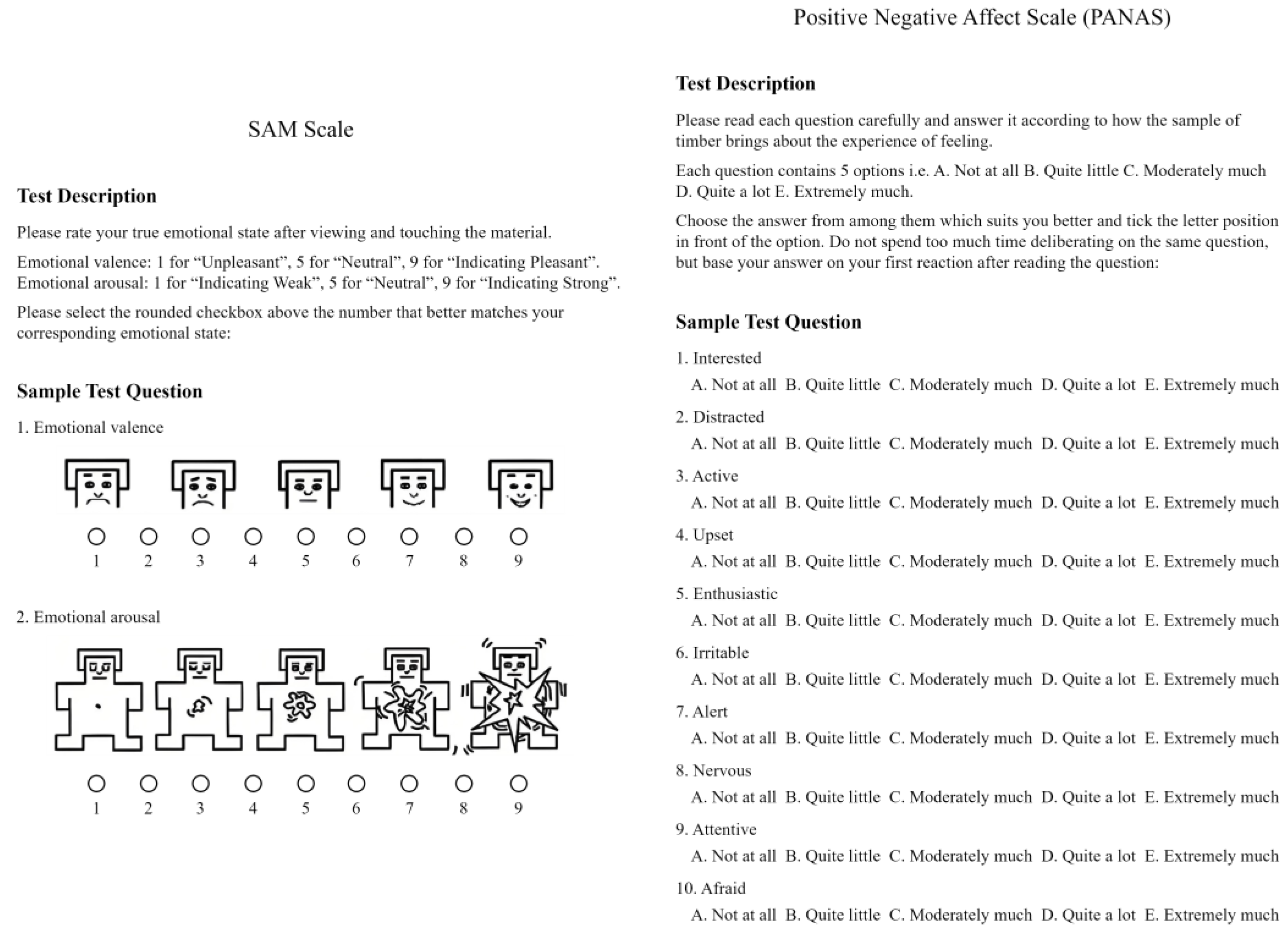
Figure 2 illustrates the use of these scales in this experiment. We present the SAM scale in image form. For the valence assessment on a 9-point grid, one end displays a happy face, while the other shows a sad face (with 9 indicating pleasant, 5 neutral, and 1 unpleasant). For the arousal assessment, the 9-point grid features an explosion image at one end and a simple dot at the other, indicating the intensity of emotional feeling (with 9 indicating strong and 1 indicating weak).
This study used the abbreviated version of the PANAS scale, which consists of 10 items. Research by Carla and colleagues indicates that the results of the 20-item PANAS scale and the 10-item short form are broadly consistent [
44]. We administered the PANAS scale in a written questionnaire format. We divided the items into two groups: positive affectivity (PA) and negative affectivity (NA). Each item offered five response options, ranging from "very slightly or not at all" to "extremely", scored from 1 to 5.
2.4. Physiological Emotion Measurement
Regarding EEG data, the theory of frontal EEG asymmetry has been effectively used to understand various emotional states [
45]. This theory suggests that left frontal activity is associated with approach behaviors and positive emotions, while right frontal activity is linked to withdrawal behaviors and negative emotions. Based on this theory, researchers have developed methods to calculate emotions using EEG data [
36,
46,
47]. Specifically, in terms of power, features such as power spectral density (PSD) have been widely used to classify emotional valence and arousal levels based on their correlation with the alpha (8-13 Hz) and beta (13-30 Hz) frequency ranges.
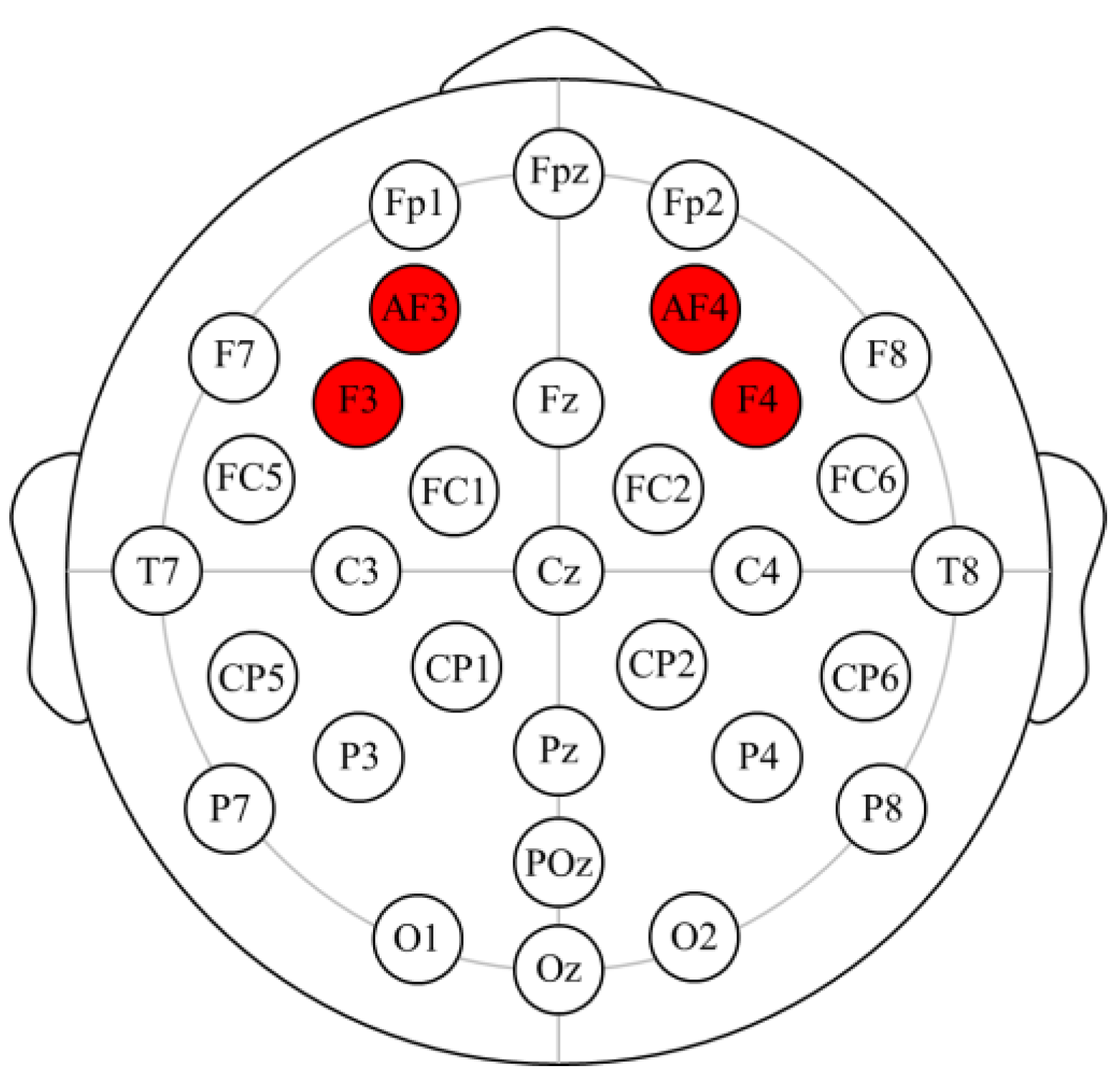
Regarding the electrodes used for emotion analysis, researchers commonly extract power in the alpha and beta bands from the AF3, F3, F4, and AF4 electrodes [
47]. They calculate emotional valence by comparing the power in the alpha and beta bands between the F3 and F4 electrodes (Formula 1). To measure emotional arousal, they use Formula 2, which calculates the ratio of the sum of beta band power to the sum of alpha band power from the AF3, F3, F4, and AF4 electrodes. Similarly, this study employs Formulas 1 and 2 to calculate EEG valence and arousal.
Regarding EDA data, the skin conductance level (SCL) is the most used indicator of EDA. Applying a small constant voltage across two points on the skin makes it possible to measure the skin's ability to conduct electricity. Since the nervous system regulates EDA, the SCL is linearly correlated with arousal levels. Changes in the SCL can reflect emotional experiences over time (as emotions like happiness and sadness can lead to a higher SCL) [
48]. In human–computer interaction, SCL is often used to study psychological load and emotional states. For instance, during the brief period when a user is about to score a goal in a computer game and immediately afterward, the user's SCL response peaks, indicating a high level of emotional excitement [
48]. The mean SCL can also reflect the participant’s overall skin conductance level, with higher mean values potentially indicating higher physiological arousal or prolonged stress levels [
49]. The skin conductance response (SCR) is an extremely sensitive indicator of emotional arousal. It is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system and manifests through the activation of sweat glands. Typically, changes in skin conductance (i.e., the difference between experimental values and baseline values) indicate the degree of somatic physiological activation [
50]. The SCL part of the EDA complex represents the slower aspect of the EDA signal (subtle changes occur within tens of seconds to minutes), while the SCR part indicates more rapid changes (these data peaks occur 1-5 seconds after a specific time). Both are crucial arousal dimensions and are believed to depend on distinct neurological mechanisms [
51].
2.5. Physiological Data Collection Equipment
This experiment used the ErgoLAB Human–Machine-Environment Synchronization Platform V3.0 (ErgoLAB 3.0) from Kingfar International Inc. It can simultaneously record subjective scale ratings, questionnaire and behavioral experiment paradigm results, and objective multi-channel data, including eye movements, electroencephalograms (EEGs), physiological signals, functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), biomechanics, human–computer interactions, spatiotemporal trajectory, physical environment measurements, etc.
The platform also includes analysis modules for heart rate variability (HRV), electroencephalograms (EEGs), electrodermal activity (EDA), electromyograms (EMGs), behavior coding, motion capture, eye tracking, and spatial–temporal behaviors, as well as interaction behavior and sequence analysis. Meanwhile, it enables custom editing and design under various research conditions, including laboratory, virtual reality, mobile device-based testing, and real-world environments.
In this experiment, we used the design module of ErgoLAB 3.0, EDA and PPG sensors from a wearable physiological recording system (Kingfar International Inc.), and a 16-channel semi-dry EEG system (Kingfar International Inc.). The data were processed with ErgoLAB 3.0 data analysis modules, and the statistical tests were conducted with SPSS.
2.6. Experimental Process
The experiment assistant guides participants into the laboratory and seats them in the preparation area. First, participants are given a personal information form to fill out, which includes the following: basic information, including age, name, and gender; physical condition information, including physical health, mental health, vision status, and dominant hand (right or left); and an informed consent signature. Participants fill out the form, sign it, and return it upon completion. Next, the experiment assistant explains the procedure and requirements of the experiment in detail.
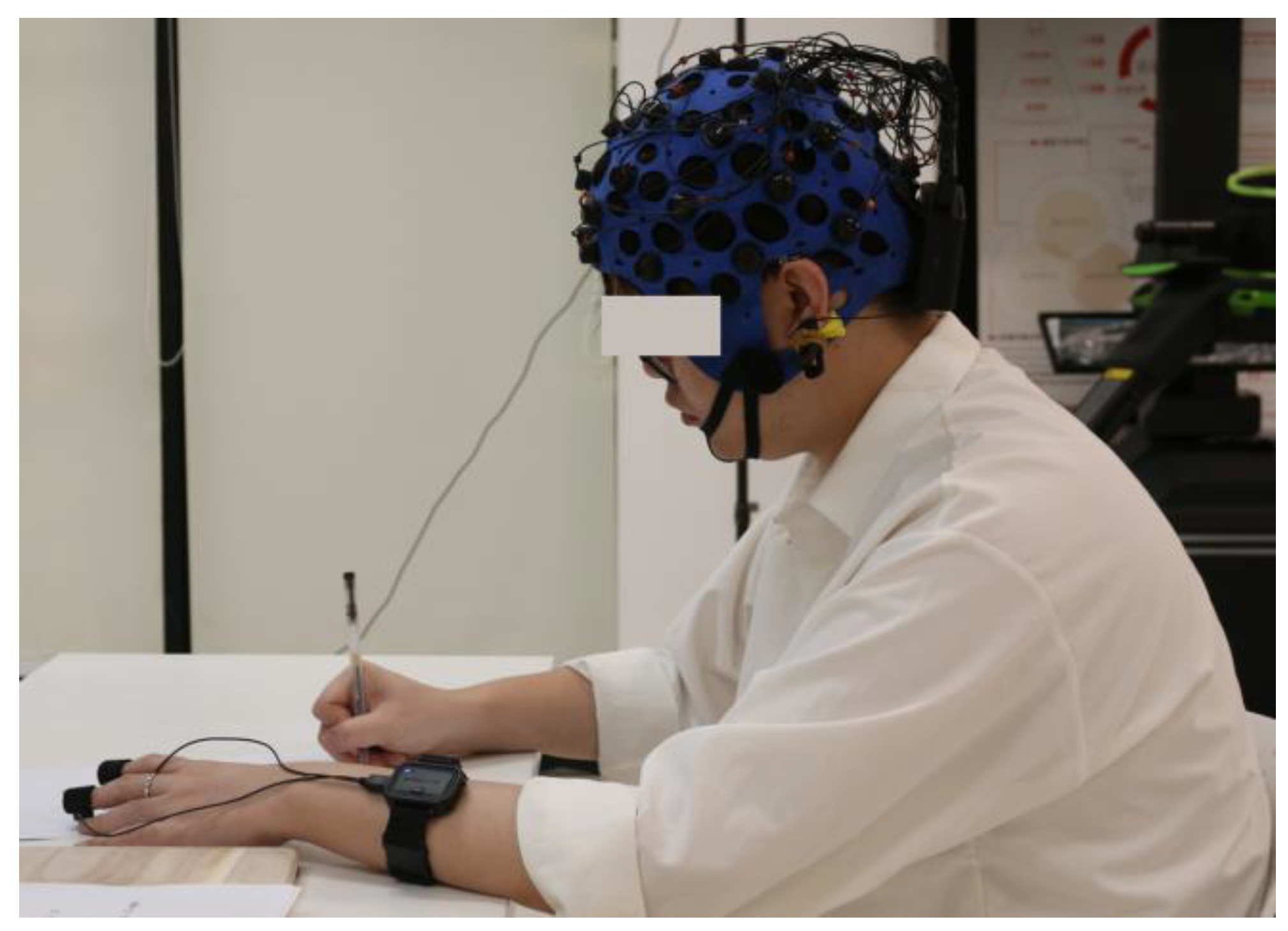
The assistant then equips the participant with the data collection devices (
Figure 3). For the EEG setup, participants should wear their hair down, remove any hair clips and left-ear earrings, and wear the EEG device, which is adjusted until a stable EEG signal is achieved. For the EDA setup, the EDA device is placed on the non-dominant hand, and the signal is adjusted until it is stable. Once all the equipment is adjusted correctly, the formal experiment begins.
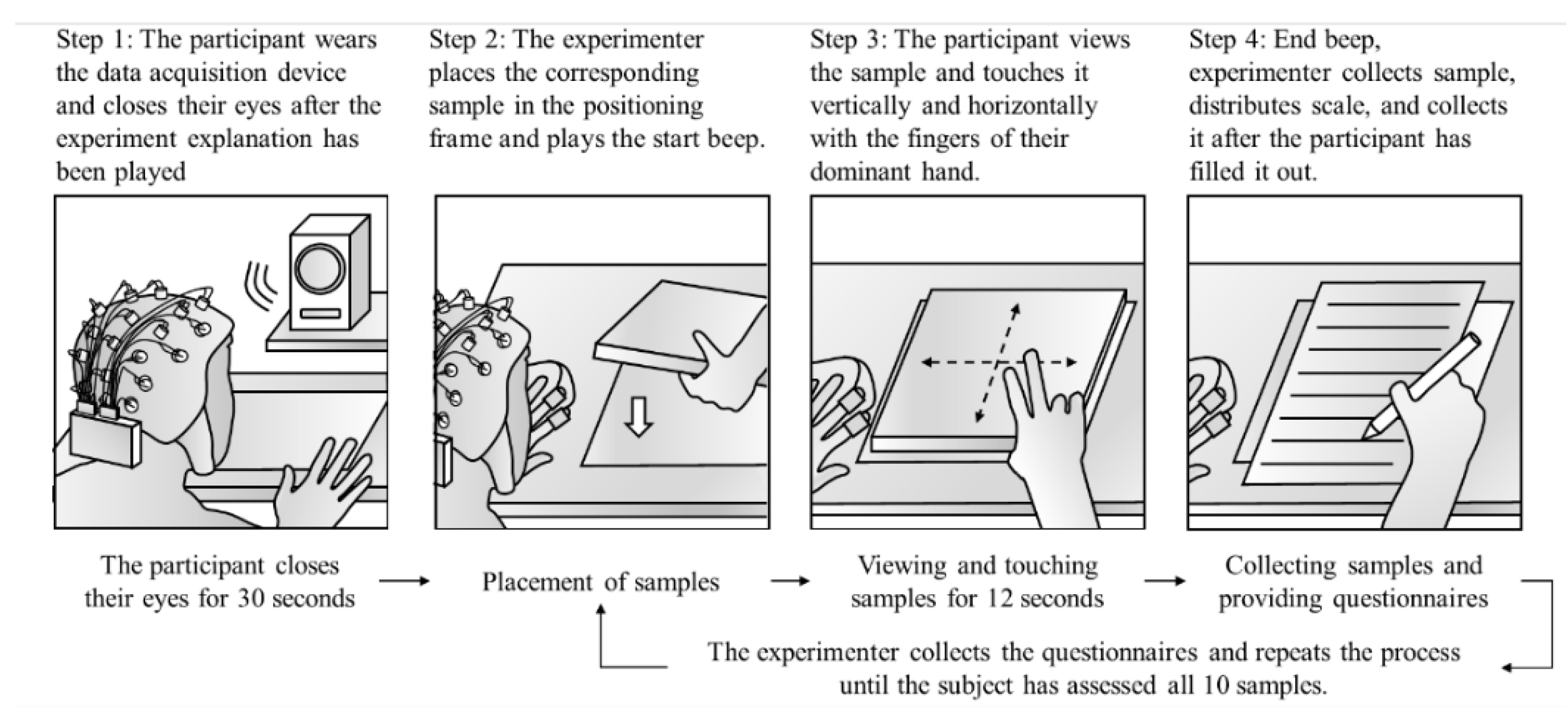
The formal experimental procedure is illustrated in
Figure 4. During the experiment, to ensure consistency, the participant is guided entirely by pre-recorded voice prompts. The experiment assistant is responsible for changing the experimental materials (boards), controlling the playback of prompts, monitoring and recording physiological signals, and distributing and collecting the subjective scales.
The assistant activates the camera and computer recording switches to ensure adequate data recording, positioning the camera lens to capture the computer's time bar. This setup facilitates the later division of time segments and the calculation of any time discrepancies. The assistant plays a voice prompt to explain the experimental procedure again and instructs the participant to close their eyes and rest for 30 seconds. This step prevents excessive tension or excitement that might inflate the baseline physiological data.
After the rest period, participants open their eyes and begin evaluating the experimental samples. First, the experiment assistant places Sample 1 in the positioning frame in front of the participant. A prompt is played to signal the start of the viewing and touching phase; this prompt constitutes a "ding" sound, which indicates the start and end of this phase. The viewing and touching phase last 12 seconds, during which the participant visually examines the sample with their eyes and uses the fingertips of their dominant hand to touch the sample's surface horizontally and vertically until the 12 seconds have elapsed.
Upon the conclusion of the viewing and touching phase, the assistant retrieves Sample 1, distributes the subjective evaluation scales, and plays a voice prompt instructing the participant to fill out the scales based on their subjective experience of Sample 1. After the participant has completed the scales, the assistant collects them and places Sample 2 in the positioning frame. The experiment proceeds in the same manner for Samples 2 to 10, with the assistant guiding the participant through the same procedure for each sample until all 10 samples have been tested. The formal experimental phase lasts approximately 15 minutes. To ensure that participants have no subjective bias regarding the experimental samples, the names and sources of the materials (including whether they are artificial boards or natural wood) are not disclosed during the experiment.
2.7. Data Extraction and Analysis
For subjective data extraction, we utilized the SAM scale to record the valence and arousal levels during the experiment. The participants’ valence and arousal scores for each sample were entered into a table, and the average valence and arousal levels for each sample were calculated. Additionally, we used the PANAS scale to sum the scores from the five positive and five negative affectivity items, obtaining a total score. These established scales added scientific rigor to our research.
We reviewed the video recordings for the physiological data extraction to exclude unusable data (such as equipment power failure or external disturbances affecting participants). We then segmented the usable data, identifying the time markers for each segment. The video recordings were imported into editing software to compare the computer-recorded time with the camera's recording time. This resulted in 11 segments for each participant (one 30-second baseline segment and ten 12-second experimental segments). Using the ErgoLAB 3.0 data analysis modules (Kingfar International Inc.), we processed and extracted the physiological data for the 20 participants in the "Record Playback" module. This involved segmenting the data according to the identified time markers, ensuring precise analysis of each participant's physiological responses during the experiment.
The EEG data collected during the experiments were preprocessed in data playback using ErgoLAB 3.0 data analysis modules. This software was employed to filter out data from subjects with dislodged or incomplete recordings (using four electrodes in this study). We removed noise artifacts recorded during the experiment, and we extracted the average power data for the alpha (8-13Hz) and beta (13-30Hz) bands from each subject at electrode positions AF3, AF4, F3, and F4 (as shown in
Figure 5). The software automatically converted these average power data to decibels (dB). The preprocessing steps were as follows: for α wave extraction, a high-pass filter at 8Hz, a low-pass filter at 13Hz, and a notch filter at 50Hz were applied; for β wave extraction, a high-pass filter at 13Hz, a low-pass filter at 30Hz, and a notch filter at 50Hz were employed. After filtering, electrode amplitude data showing excessively high voltage values were deemed unusable and excluded, and the remaining viable recordings were used in the following analysis phase.
Ultimately, for each of the 20 subjects, we extracted the average power (in dB) data for alpha (F3, F4, AF3, AF4) and beta (F3, F4, AF3, AF4) waves (totaling 8 values) obtained for the 10 different materials, resulting in a total of 1600 data points. Using Formulas 1 and 2, we calculated each subject's EEG emotional valence and EEG arousal when presented with each material.
In the data playback process, we first used ErgoLAB 3.0 data analysis modules to filter and exclude disconnected or incomplete records (specifically for SCL and SCR) for the collected EDA data. We then extracted the average SCL and SCR values (unit, μS) for each of the 20 subjects when presented with the 10 different materials, as well as the baseline SCL and SCR values during the 30-second resting state. By subtracting the baseline data from the raw data, we obtained 400 data points. These data were obtained to help assess the arousal levels elicited by the materials.
After the experiment, we obtained three different sets of data: categorical data from the experimental samples (including material source, tactile sensation, texture, and brightness) as well as subjective evaluation data (using the SAM and PANAS scales) and physiological data (EEG and EDA data) from the subjects. To analyze the impact of the material samples on the participants’ emotions, we used SPSS Statistics Version 19.0 for statistical analysis. First, we conducted a correlation analysis to explore the relationships between the subjects' subjective and physiological data. Subsequently, using the source of the experimental samples as a grouping variable, we analyzed whether there were differences in the subjective and physiological data between the natural wood and artificial board materials. Finally, we performed one-way ANOVA and independent samples t-tests, using sample composition as a factor and subjective and physiological data as dependent variables, to investigate the impact of sample differences on the subjects' subjective and physiological evaluations.
5. Conclusions
This study provides a new perspective on the emotional effects of wood materials by analyzing the impact of solid wood and artificial boards on consumers’ emotions. A combined approach of subjective evaluation and physiological measurement techniques was employed. We used SAM and PANAS for the subjective evaluation, and the physiological measurements primarily involved recording participants' EEG and EDA signals. Additionally, we calculated valence and arousal based on EEG data using specific formulas. We systematically evaluated different materials' subjective and physiological effects on participants' emotions from both visual and tactile dimensions. Through statistical analysis of the data, we obtained several important findings that are significant for understanding the mechanisms by which materials influence emotions and for guiding material design and selection.
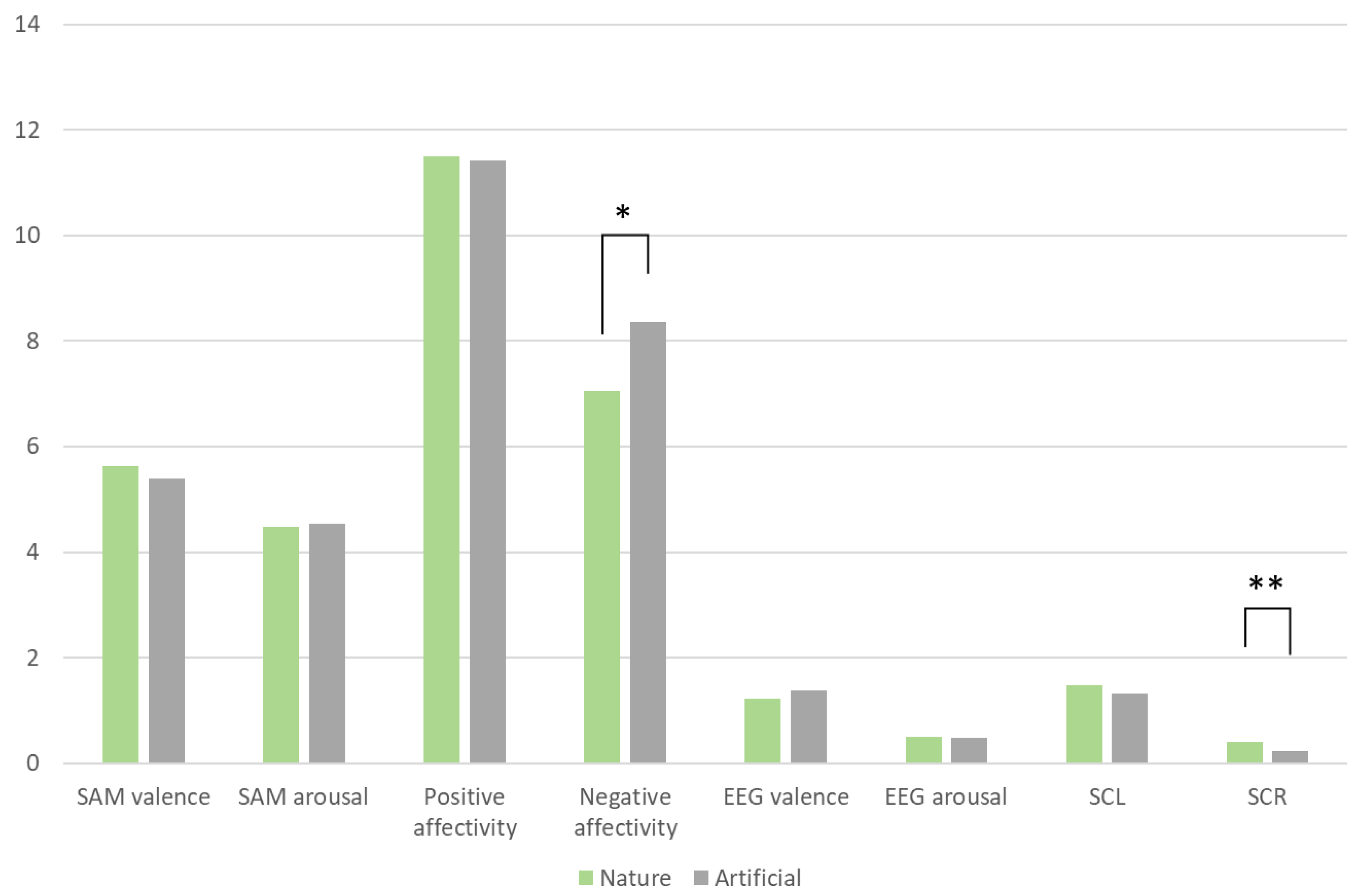
Firstly, this study found significant correlations between specific subjective and physiological data. For example, a positive correlation exists between subjective and physiological arousal and SCR. Additionally, PA and NA positively correlate with physiological arousal. This result indicates consistency between the level of arousal participants subjectively experience and their physiological responses. However, the relationship between subjective and physiological measures of valence is more complex; in this experiment, no significant relationship was observed between subjective and physiological valence. From the positive correlations between some subjective and objective data, we can conclude that, although changing the composition of materials does not directly enhance overall subjective and physiological evaluations, increasing participants' arousal levels regarding the material can indirectly improve these evaluations.
Secondly, independent samples t-tests conducted on the sources of the experimental samples revealed significant differences between natural wood and artificial boards in terms of subjective NA and SCR. Artificial boards tend to elicit higher negative emotions, whereas natural materials can evoke a more robust arousal response in participants.
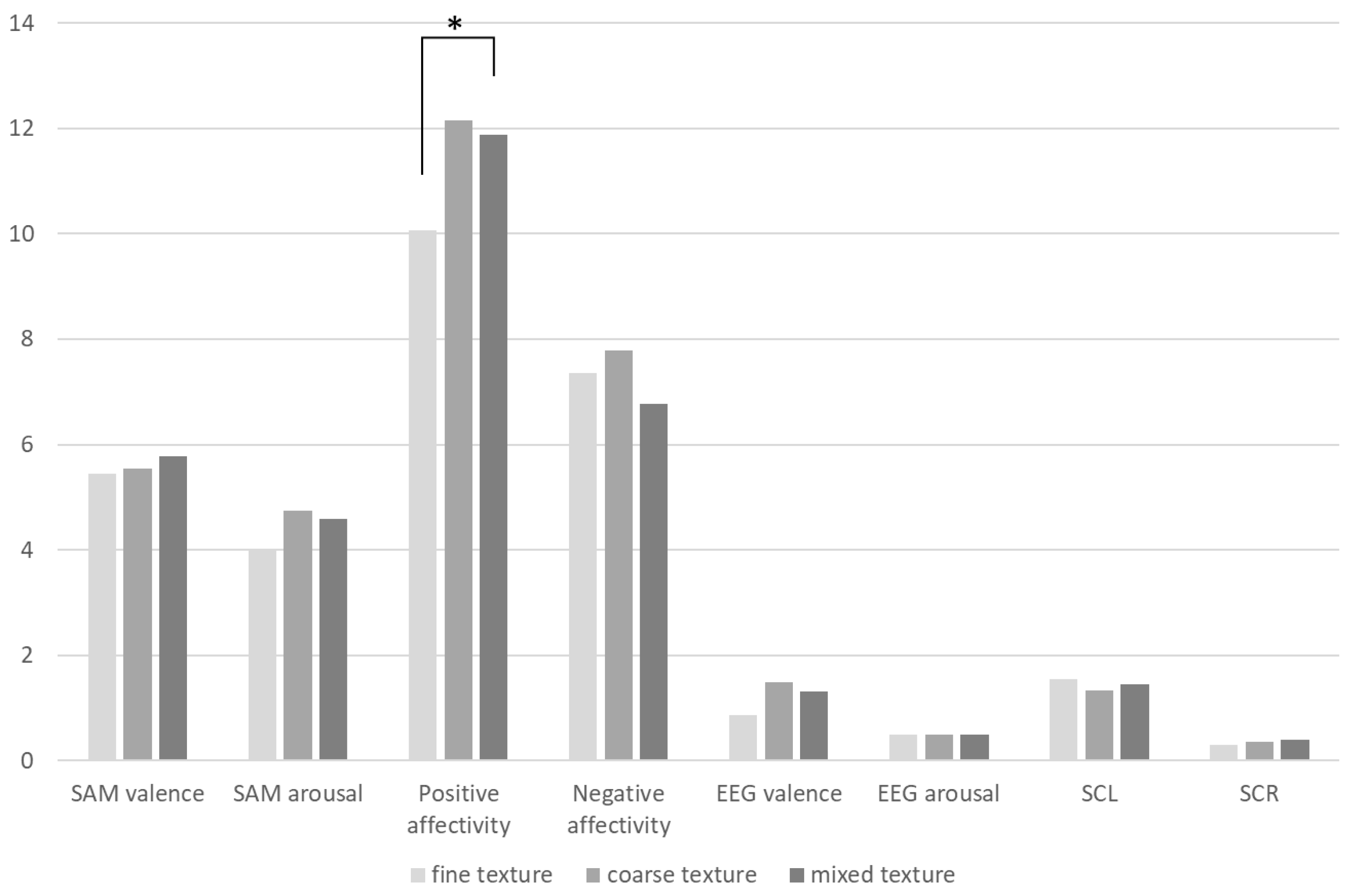
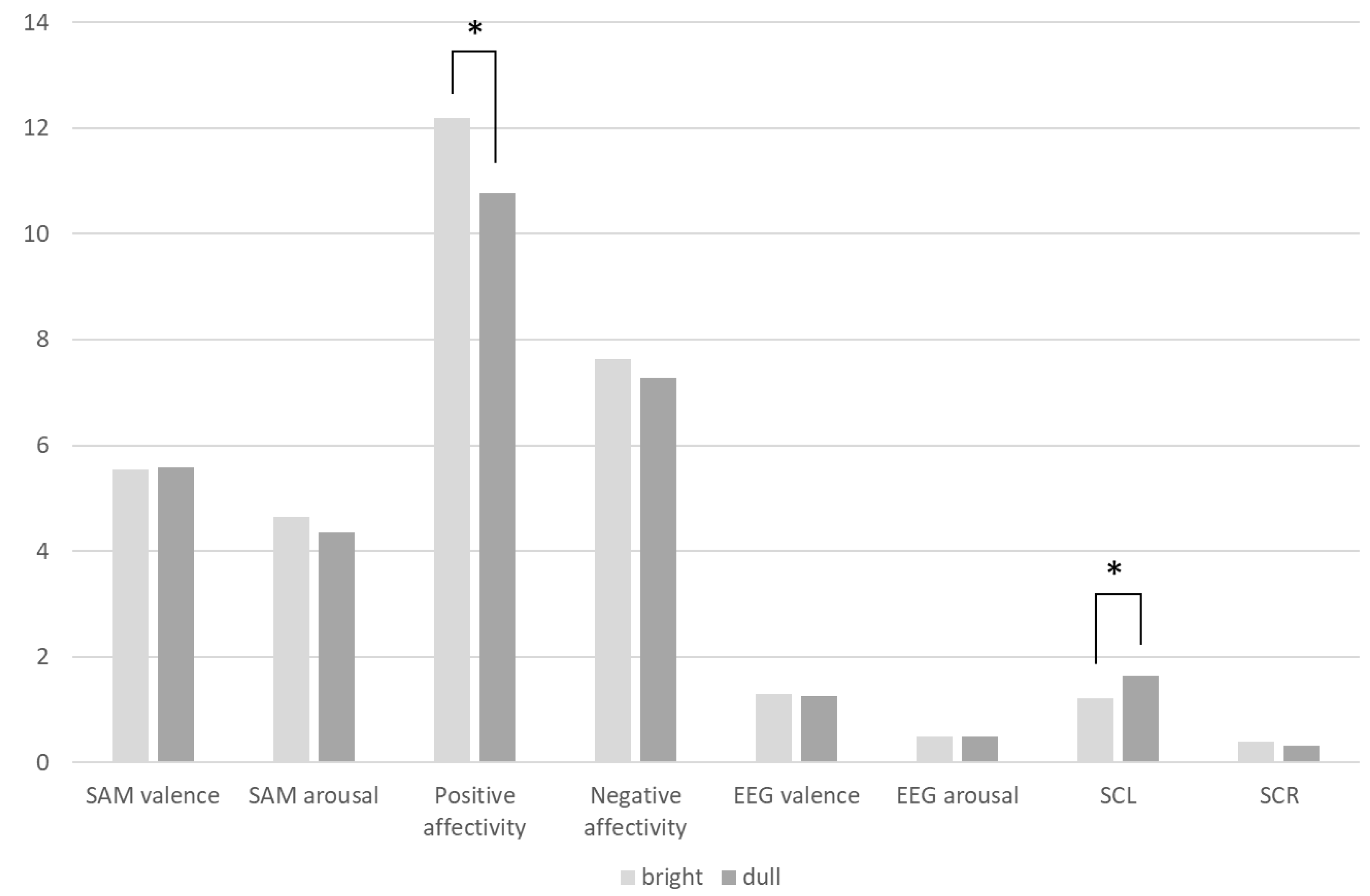
Finally, using the composition elements of the experimental samples as grouping variables, we tested for differences in subjective and objective data across different elements. We found significant differences in PA based on the tactile qualities of the samples; samples with more intense tactile sensations were more effective at eliciting positive emotions from participants. Additionally, there were significant differences in SAM arousal and PA concerning the texture of the samples. Coarser textures, due to their higher visual recognizability, led to greater emotional arousal, thereby generating positive emotions. In contrast, finer textures, which are less recognizable, tended to induce cognitive stress in participants, resulting in lower evaluations. The brightness of the samples also showed significant differences in PA and SCL; brighter samples were more effective in stimulating positive emotions, while dull samples were more likely to cause cognitive stress.
This experiment showed that the samples' tactile sensation, texture, and brightness primarily affected subjective positive emotions, subjective arousal, and SCL and SCR values. In contrast, their impact on pleasurable emotions (SAM and EEG valence) was relatively minor. This suggests that the visual and tactile characteristics of the materials primarily influenced participants' subjective and psychological arousal levels rather than directly affecting their sense of pleasure. Therefore, we can conclude that while altering the composition of materials may not directly enhance subjective and physiological valence, increasing participants' arousal levels or reducing the pressure levels indicated by skin conductance can indirectly improve these evaluations.
Although this study has revealed some significant findings, many unanswered questions still require further exploration. Future research could focus on the following areas:
Exploration of other sensory dimensions—smell and sound: In addition to visual and tactile sensations, smell and sound may also significantly influence emotions. Future research could investigate how these sensory dimensions impact the emotional effects of materials.
Other types of sustainable materials—bio-based materials: With increasing environmental awareness, bio-based materials are becoming more widespread. Future studies could explore their emotional impact to provide scientific support for their promotion.
Studies on different user groups— demographic differences: Users of different ages, genders, and cultural backgrounds may react differently to materials. Future research could segment the market by demographic to better understand the emotional needs of different user groups, offering more personalized design solutions.
By addressing these areas, future research could further enhance our understanding of how materials affect emotions, leading to more informed material choices and improved user experiences.
The conclusions of this study have practical applications in several areas. Firstly, regarding the design and promotion of wood materials, particularly artificial boards, this research provides scientific evidence that enhancing the visual characteristics of materials can improve consumers' emotional experiences, thereby increasing the market competitiveness of products. Secondly, our findings suggest that, in fields such as interior design and furniture manufacturing, paying attention to the visual characteristics of materials, such as color and texture, can effectively elevate users' emotional arousal, enhancing their overall experience.
Overall, this study reveals the different impacts of solid wood and artificial boards on people’s emotions through multidimensional analysis, offering valuable theoretical and practical references. Future research could further explore the emotional effects of other sensory dimensions, such as smell and sound, to improve our understanding of the complex relationship between materials and emotions.