Submitted:
16 October 2024
Posted:
17 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
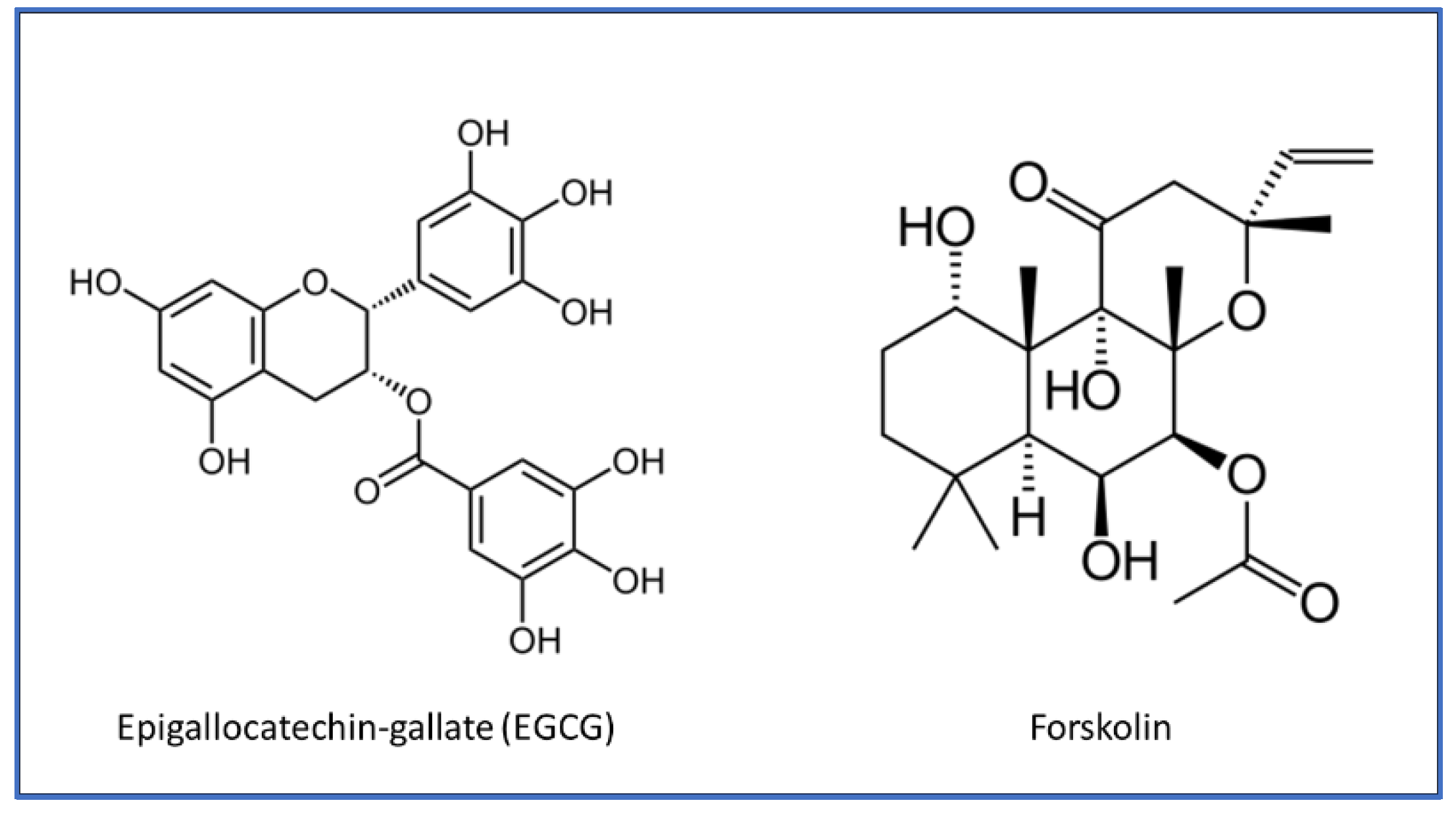
2. EGCG Biochemical Properties and Health Effects
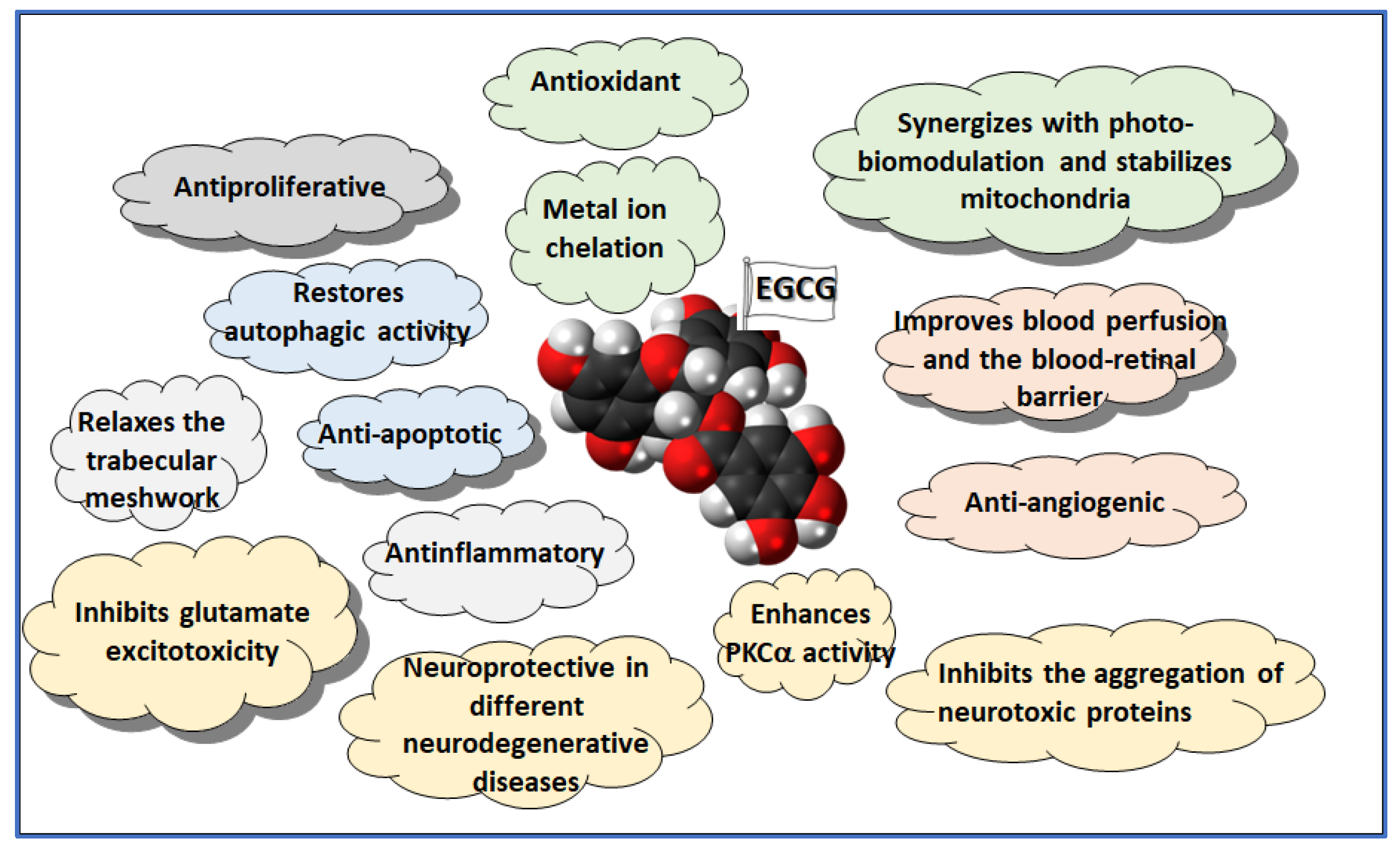
2.1. Antioxidant
2.2. Neuroprotection
2.3. Antitumoral
2.4. Metabolism and Weight Management
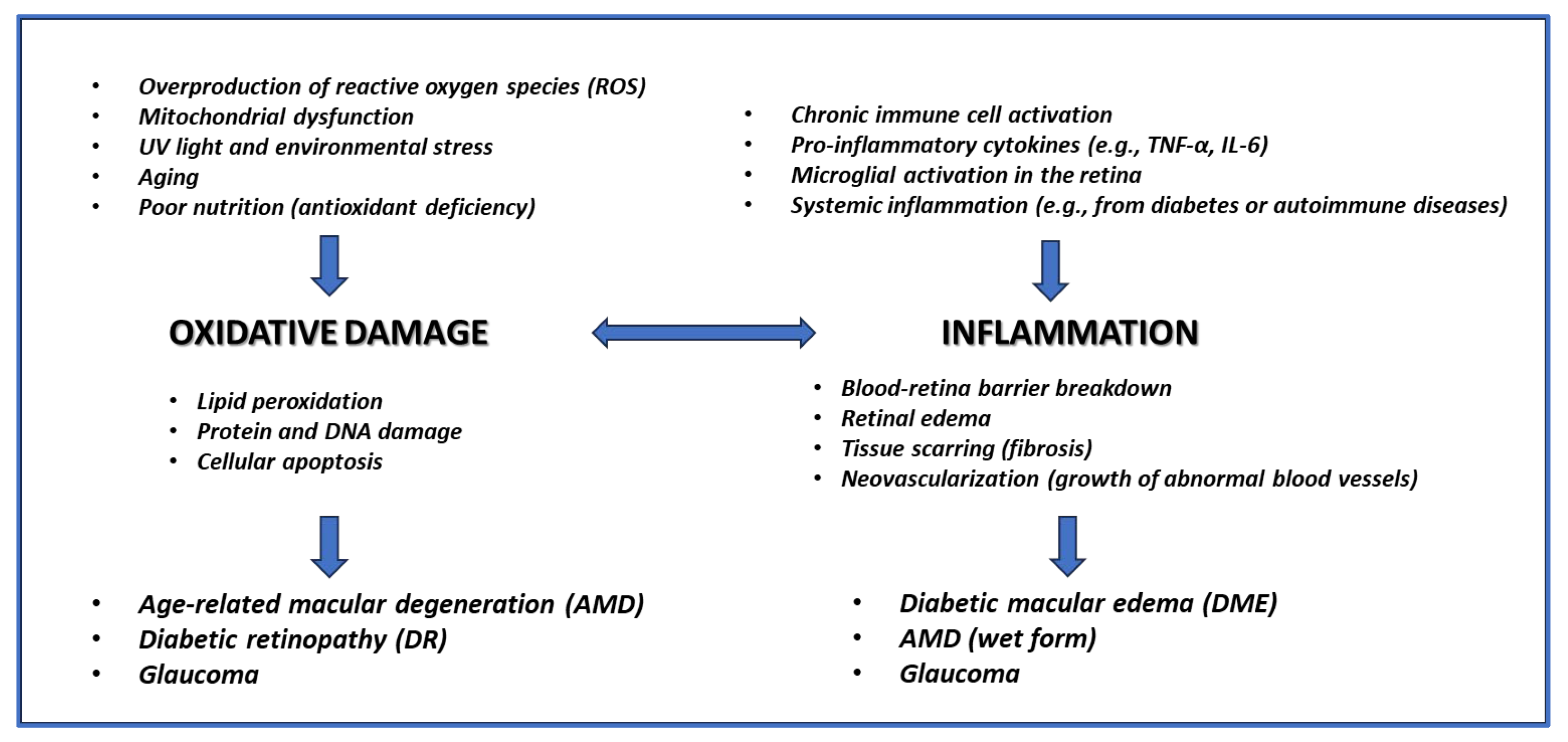
3. EGCG Efficacy on Retinal Diseases
3.1. Mitochondrial Dysfunction
3.2. Oxidative Damage
3.3. Glutamate Excitotoxicity
3.4. Inflammation
3.5. Angiogenesis
3.6. Fibrosis
3.7. Neuroprotection
3.8. Autophagy
3.9. AGEs
3.10. Trabecular Meshwork
3.11. Clinical Evidence
4. Forskolin Biochemical Properties and Health Effects
4.1. Metabolism and Weight Management
4.2. Cardiovascular Health
4.3. Respiratory Disorders
4.4. Diabetes
4.5. Neuroprotection
4.6. Antinflamatory
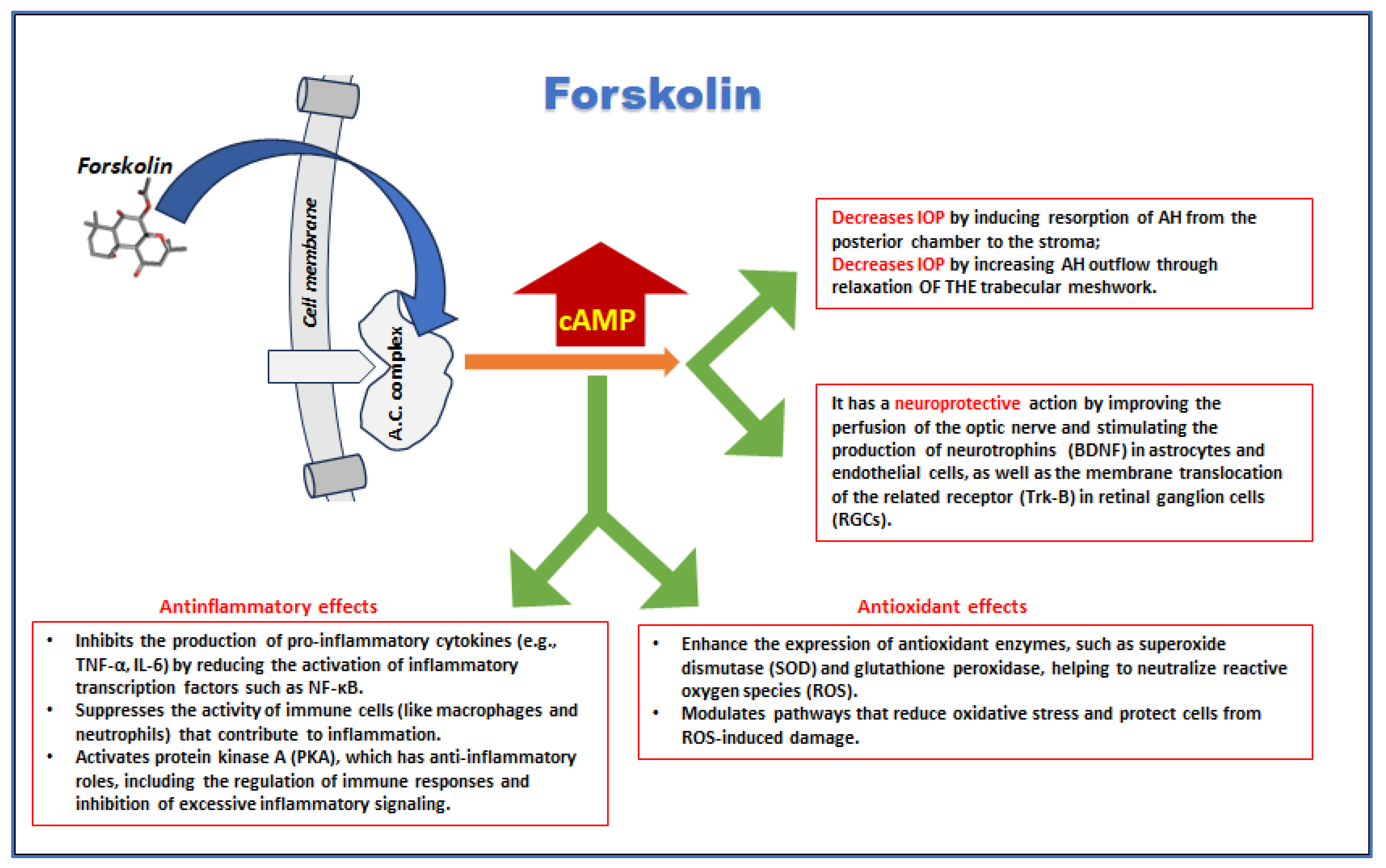
5. Forskolin Efficacy on Retinal Diseases
5.1. IOP
5.2. Neuroprotection
5.3. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
5.4. Blood Perfusion and Angiogenesis
5.5. Glucose Metabolism
6. Predicted Cooperative Effects of EGCG and Forskolin
7. Formulation Issues
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, A. , Ahsan, H. Biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in ophthalmic disorders. J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2020, 41, 257–271, Epub 2020 Feb 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm EW, Buonfiglio F, Voigt AM, Bachmann P, Safi T, Pfeiffer N, Gericke, A. Oxidative stress in the eye and its role in the pathophysiology of ocular diseases. Redox Biol. 2023, 68, 102967, Epub 2023 Nov 18. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta N, Ang LC, Noël de Tilly L, Bidaisee L, Yücel YH. Human glaucoma and neural degeneration in intracranial optic nerve, lateral geniculate nucleus, and visual cortex. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006, 90, 674–8, Epub 2006 Feb 7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudouin C, Kolko M, Melik-Parsadaniantz, S. , Messmer EM. Inflammation in Glaucoma: From the back to the front of the eye, and beyond. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021, 83, 100916, Epub 2020 Oct 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadeja RN, Martin PM. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Retinal Degeneration. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021, 10, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuolo J, Bulotta RM, Oppedisano F, Bosco F, Scarano F, Nucera S, Guarnieri L, Ruga S, Macri R, Caminiti R, Musolino V, Gliozzi M, Carresi C, Cardamone A, Coppoletta A, Nicita M, Carnevali A, Scorcia V, Mollace, V. Potential Properties of Natural Nutraceuticals and Antioxidants in Age-Related Eye Disorders. Life (Basel). 2022, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lawler T, Liu Y, Christensen K, Vajaranant TS, Mares, J. Dietary Antioxidants, Macular Pigment, and Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration: A Review of the Evidence. Nutrients. 2019, 11, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kushwah N, Bora K, Maurya M, Pavlovich MC, Chen, J. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 12, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Williams M, Hogg RE, Chakravarthy, U. Antioxidants and diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2013, 13, 481–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She C, Shang F, Cui M, Yang, X. , Liu, N. Association between dietary antioxidants and risk for diabetic retinopathy in a Chinese population. Eye (Lond). 2021, 35, 1977–1984, Epub 2020 Oct 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C. , Wu, X. Curcumin Protects Trabecular Meshwork Cells From Oxidative Stress. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016, 57, 4327–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourtas T, Birke MT, Kruse FE, Welge-Lüssen UC, Birke, K. Preventive effects of omega-3 and omega-6 Fatty acids on peroxide mediated oxidative stress responses in primary human trabecular meshwork cells. PLoS One, 2012; 7, e31340, Epub 2012 Feb 3. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrenson JG, Evans JR. Omega 3 fatty acids for preventing or slowing the progression of age-related macular degeneration. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015, 2015, CD010015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fathima S, Prokopiou E, Georgiou, T. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Anti-Oxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects in Diabetic Retinopathy: A Narrative Review. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023, 28, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegrini D, Raimondi R, Borgia A, Sorrentino T, Montesano G, Tsoutsanis P, Cancian G, Verma Y, De Rosa FP, Romano MR. Curcumin in Retinal Diseases: A Comprehensive Review from Bench to Bedside. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li J, Du L, He JN, Chu KO, Guo CL, Wong MOM, Pang CP, Chu WK. Anti-inflammatory Effects of GTE in Eye Diseases. Front Nutr. 2021, 8, 753955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wagh VD, Patil PN, Surana SJ, Wagh KV. Forskolin: upcoming antiglaucoma molecule. J Postgrad Med. 2012, 58, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokra, D. , Joskova, M., Mokry, J. Therapeutic Effects of Green Tea Polyphenol (‒)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in Relation to Molecular Pathways Controlling Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 24, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim SR, Seong KJ, Kim WJ, Jung JY. Epigallocatechin Gallate Protects against Hypoxia-Induced Inflammation in Microglia via NF-κB Suppression and Nrf-2/HO-1 Activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oliveira MR, Nabavi SF, Daglia M, Rastrelli L, Nabavi SM. Epigallocatechin gallate and mitochondria. A story of life and death. Pharmacol Res. 2016, 104, 70–85, Epub 2015 Dec 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalani E, Brunetti K, Del Quondam, S. , Cervia, D. Targeting Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress to Prevent the Neurodegeneration of Retinal Ganglion Cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 12, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Payne A, Nahashon S, Taka E, Adinew GM, Soliman KFA. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG): New Therapeutic Perspectives for Neuroprotection, Aging, and Neuroinflammation for the Modern Age. Biomolecules. 2022, 12, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Afzal O, Dalhat MH, Altamimi ASA, Rasool R, Alzarea SI, Almalki WH, Murtaza BN, Iftikhar S, Nadeem S, Nadeem MS, Kazmi, I. Green Tea Catechins Attenuate Neurodegenerative Diseases and Cognitive Deficits. Molecules. 2022, 27, 7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rodriguez SK, Guo W, Liu L, Band MA, Paulson EK, Meydani, M. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor angiogenic signaling by disrupting the formation of a receptor complex. Int J Cancer. 2006, 118, 1635–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong H, Mathur PS, Greene GL. Green tea catechins inhibit angiogenesis through suppression of STAT3 activation. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009, 117, 505–15, Epub 2008 Sep 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe H, Suzuki T, Ohishi T, Isemura, M. , Nakamura, Y., Unno, K. Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Matrix Metalloproteinases in Terms of Its Anticancer Activity. Molecules. 2023, 28, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aggarwal V, Tuli HS, Tania M, Srivastava S, Ritzer EE, Pandey A, Aggarwal D, Barwal TS, Jain A, Kaur G, Sak K, Varol M, Bishayee, A. Molecular mechanisms of action of epigallocatechin gallate in cancer: Recent trends and advancement. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022, 80, 256–275, Epub 2020 May 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh BN, Shankar, S. , Srivastava RK. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1807–21, Epub 2011 Jul 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib WH, Awajan D, Alqudah A, Alsawwaf R, Althunibat R, Abu AlRoos M, Al Safadi A, Abu Asab S, Hadi RW, Al Kury LT. Targeting Cancer Hallmarks with Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG): Mechanistic Basis and Therapeutic Targets. Molecules. 2024, 29, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li F, Qasim S, Li D, Dou QP. Updated review on green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate as a cancer epigenetic regulator. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022, 83, 335–352, Epub 2021 Jan 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín V, Burgos V, Pérez R, Maria DA, Pardi, P. , Paz, C. The Potential Role of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in Breast Cancer Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kumar M, Verma S, Rawat S, Dhatwalia SK. Exploring integrative approaches: EGCG’s potential in combating prostate cancer. WCRJ, 2744. [CrossRef]
- Sehgal A, Bhat AM, Dogra D, Rawat, S. , Dhatwalia SK. EGCG: The antioxidant powerhouse in lung cancer management and chemotherapy enhancement. Advances in Redox Research, 2023, 9, 100085. [CrossRef]
- Luo KW, Xia J, Cheng BH, Gao HC, Fu LW, Luo XL. Tea polyphenol EGCG inhibited colorectal-cancer-cell proliferation and migration via downregulation of STAT3. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2020, 9, 59–70. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang J, Xie Y, Feng Y, Zhang L, Huang X, Shen X, Luo, X. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate induces apoptosis in B lymphoma cells via caspase-dependent pathway and Bcl-2 family protein modulation. Int J Oncol. 2015, 46, 1507–15, Epub 2015 Feb 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Via FI, Shiraishi RN, Santos I, Ferro KP, Salazar-Terreros MJ, Franchi Junior GC, Rego EM, Saad STO, Torello CO. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis and differentiation in leukaemia by targeting reactive oxygen species and PIN1. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 9103. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hodgson AB, Randell RK, Jeukendrup AE. The effect of green tea extract on fat oxidation at rest and during exercise: evidence of efficacy and proposed mechanisms. Adv Nutr. 2013, 4, 129–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li F, Gao C, Yan P, Zhang M, Wang Y, Hu Y, Wu X, Wang, X. , Sheng, J. EGCG Reduces Obesity and White Adipose Tissue Gain Partly Through AMPK Activation in Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gosselin, C. , Haman, F. Effects of green tea extracts on non-shivering thermogenesis during mild cold exposure in young men. Br J Nutr. 2013, 110, 282–8, Epub 2012 Dec 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katada S, Yanagimoto A, Matsui Y, Hibi M, Osaki N, Kobayashi, S. , Katsuragi, Y. Effect of tea catechins with caffeine on energy expenditure in middle-aged men and women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Eur J Nutr. 2020, 59, 1163–1170, Epub 2019 May 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose M, Lambert JD, Ju J, Reuhl KR, Shapses SA, Yang CS. The major green tea polyphenol, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, inhibits obesity, metabolic syndrome, and fatty liver disease in high-fat-fed mice. J Nutr. 2008, 138, 1677–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- James, A. , Wang, K., Wang, Y. Therapeutic Activity of Green Tea Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Metabolic Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases: The Current Updates. Nutrients. 2023, 15, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Choi C, Song HD, Son Y, Cho YK, Ahn SY, Jung YS, Yoon YC, Kwon SW, Lee YH. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Visceral Adiposity Partly through the Regulation of Beclin1-Dependent Autophagy in White Adipose Tissues. Nutrients. 2020, 12, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Song WY, Aihara Y, Hashimoto T, Kanazawa, K. , Mizuno, M. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces secretion of anorexigenic gut hormones. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015, 57, 164–9, Epub 2015 Sep 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li H, Kek HC, Lim J, Gelling RW, Han, W. Green tea (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate counteracts daytime overeating induced by high-fat diet in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016, 60, 2565–2575, Epub 2016 Sep 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes RC, Araújo VA, Giglio BM, Marini ACB, Mota JF, Teixeira KS, Monteiro PA, Lira FS, Pimentel GD. Acute Epigallocatechin 3 Gallate (EGCG) Supplementation Delays Gastric Emptying in Healthy Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study. Nutrients. 2018, 10, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma SB, Zhang R, Miao S, Gao B, Lu Y, Hui S, Li L, Shi XP, Wen AD. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2017, 15, 3803–3809, Epub 2017 Apr 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu X, Yang M, He Y, Wang F, Kong Y, Ling TJ, Zhang, J. EGCG-derived polymeric oxidation products enhance insulin sensitivity in db/db mice. Redox Biol. 2022, 51, 102259, Epub 2022 Feb 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legeay S, Rodier M, Fillon L, Faure, S. , Clere, N. Epigallocatechin Gallate: A Review of Its Beneficial Properties to Prevent Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2015, 7, 5443–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sae-Tan S, Grove KA, Kennett MJ, Lambert JD. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate increases the expression of genes related to fat oxidation in the skeletal muscle of high fat-fed mice. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 111–6, Epub 2011 Jan 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söhle J, Knott A, Holtzmann U, Siegner R, Grönniger E, Schepky A, Gallinat S, Wenck H, Stäb F, Winnefeld, M. White Tea extract induces lipolytic activity and inhibits adipogenesis in human subcutaneous (pre)-adipocytes. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2009, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu MZ, Zhou F, Ouyang J, Wang QY, Li YL, Wu JL, Huang JA, Liu ZH. Combined use of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and caffeine in low doses exhibits marked anti-obesity synergy through regulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4105–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nainu F, Frediansyah A, Mamada SS, Permana AD, Salampe M, Chandran D, Emran TB, Simal-Gandara, J. Natural products targeting inflammation-related metabolic disorders: A comprehensive review. Heliyon. 2023, 9, e16919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ng TK, Chu KO, Wang CC, Pang CP. Green Tea Catechins as Therapeutic Antioxidants for Glaucoma Treatment. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 12, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boroughani M, Tahmasbi Z, Heidari MM, Johari M, Hashempur MH, Heydari, M. Potential therapeutic effects of green tea (Camellia sinensis) in eye diseases, a review. Heliyon. 2024, 10, e28829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, B. , Osborne NN. Oxidative-induced retinal degeneration is attenuated by epigallocatechin gallate. Brain Res. 2006, 1124, 176–87, Epub 2006 Nov 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eells, JT. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Aging Retina. Biology (Basel). 2019, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Geneva, II. Photobiomodulation for the treatment of retinal diseases: a review. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016, 9, 145–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Siqueira, RC. Photobiomodulation Using Light-Emitting Diode (LED) for Treatment of Retinal Diseases. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024, 18, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang CX, Lou Y, Chi J, Bao XL, Fan, B. , Li GY. Considerations for the Use of Photobiomodulation in the Treatment of Retinal Diseases. Biomolecules. 2022, 12, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Valter K, Tedford SE, Eells JT, Tedford CE. Photobiomodulation use in ophthalmology - an overview of translational research from bench to bedside. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024, 4, 1388602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sommer AP, Zhu, D. Green tea and red light--a powerful duo in skin rejuvenation. Photomed Laser Surg. 2009, 27, 969–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer AP, Bieschke J, Friedrich RP, Zhu D, Wanker EE, Fecht HJ, Mereles D, Hunstein, W. 670 nm laser light and EGCG complementarily reduce amyloid-β aggregates in human neuroblastoma cells: basis for treatment of Alzheimer's disease? Photomed Laser Surg. 2012, 30, 54–60, Epub 2011 Oct 26. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang B, Safa R, Rusciano D, Osborne NN. Epigallocatechin gallate, an active ingredient from green tea, attenuates damaging influences to the retina caused by ischemia/reperfusion. Brain Res. 2007, 1159, 40–53, Epub 2007 May 26. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang B, Rusciano D, Osborne NN. Orally administered epigallocatechin gallate attenuates retinal neuronal death in vivo and light-induced apoptosis in vitro. Brain Res. 2008, 1198, 141–52, Epub 2007 Dec 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du J, Wang Y, Tu Y, Guo Y, Sun X, Xu X, Liu X, Wang L, Qin, X. , Zhu, M., Song, E. A prodrug of epigallocatechin-3-gallate alleviates high glucose-induced pro-angiogenic factor production by inhibiting the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome axis in retinal Müller cells. Exp Eye Res. 2020, 196, 108065, Epub 2020 May 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel SA, Avramovich-Tirosh Y, Reznichenko L, Zheng H, Weinreb O, Amit T, Youdim MB. Multifunctional activities of green tea catechins in neuroprotection. Modulation of cell survival genes, iron-dependent oxidative stress and PKC signaling pathway. Neurosignals. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan CM, Huang JH, Lin HH, Chiang HS, Chen BH, Hong JY, Hung CF. Protective effects of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate on UVA-induced damage in ARPE19 cells. Mol Vis. 2008, 14, 2528–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boccuni, I. , Fairless, R. Retinal Glutamate Neurotransmission: From Physiology to Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Retinal Ganglion Cell Degeneration. Life (Basel). 2022, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen F, Jiang L, Shen C, Wan H, Xu L, Wang N, Jonas JB. Neuroprotective effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced excitotoxicity in the adult rat retina. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012, 90, e609–e615, Epub 2012 Sep 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L. , Chen, F., Wang, N. Neuroprotective Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate against N-methyl-D-aspartate Induced Excitotoxicity in Rat Retina. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2012, 53, 6574. [Google Scholar]
- Ellwardt, E. , Zipp, F. Molecular mechanisms linking neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in MS. Exp Neurol. 2014; 262 Pt A:8-17, Epub 2014 Feb 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R. , Reddy PH. Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iovino L, Tremblay ME, Civiero, L. Glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in Parkinson's disease: The role of glial cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2020, 144, 151–164, Epub 2020 Aug 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spalloni A, Nutini M, Longone, P. Role of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors complex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013, 1832, 312–22, Epub 2012 Nov 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu Q, Langley M, Kanthasamy AG, Reddy MB. Epigallocatechin Gallate Has a Neurorescue Effect in a Mouse Model of Parkinson Disease. J Nutr. 2017, 147, 1926–1931, Epub 2017 Aug 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang S, Zhang Y, Botchway BOA, Wang, X., Huang, M., Liu, X. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Oxidative Stress Through the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway to Improve Alzheimer Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2024; Epub ahead of print. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh SH, Lee SM, Kim HY, Lee KY, Lee YJ, Kim HT, Kim J, Kim MH, Hwang MS, Song C, Yang KW, Lee KW, Kim SH, Kim OH. The effect of epigallocatechin gallate on suppressing disease progression of ALS model mice. Neurosci Lett. 2006, 395, 103–7, Epub 2005 Dec 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuldesz AC, Tudor R, Nandarge PS, Elagez A, Cornea A, Ion R, Bratosin, F. , Prodan, M., Simu, M. The Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Nutritional Supplementation in the Management of Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Nutrients. 2024, 16, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang WH, Chen, Y. , Gao LM, Cao YN. Neuroprotective role of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in acute glaucoma via the nuclear factor-κB signalling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2021, 22, 1235, Epub 2021 Aug 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu J, Tu Y, Wang Y, Xu X, Sun X, Xie L, Zhao Q, Guo Y, Gu Y, Du J, Du S, Zhu, M. , Song, E. Prodrug of epigallocatechin-3-gallate alleviates choroidal neovascularization via down-regulating HIF-1α/VEGF/VEGFR2 pathway and M1 type macrophage/microglia polarization. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020, 121, Epub 2019 Nov 25. 109606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao G, Chen M, Song Q, Liu Y, Xie L, Han Y, Liu Z, Ji, Y. , Jiang, Q. EGCG protects against UVB-induced apoptosis via oxidative stress and the JNK1/c-Jun pathway in ARPE19 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2012, 5, 54–9, Epub 2011 Sep 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L. , Zhang ZK, Liang, S. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects retinal vascular endothelial cells from high glucose stress in vitro via the MAPK/ERK-VEGF pathway. Genet Mol Res. 2016; 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasiak J, Chojnacki J, Szczepanska J, Fila M, Chojnacki C, Kaarniranta, K. , Pawlowska, E. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate, an Active Green Tea Component to Support Anti-VEGFA Therapy in Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nutrients. 2023, 15, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee HS, Jun JH, Jung EH, Koo BA, Kim YS. Epigalloccatechin-3-gallate inhibits ocular neovascularization and vascular permeability in human retinal pigment epithelial and human retinal microvascular endothelial cells via suppression of MMP-9 and VEGF activation. Molecules. 2014, 19, 12150–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shankar S, Chen Q, Srivastava RK. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathways act synergistically to enhance antiangiogenic effects of EGCG through activation of FOXO transcription factor. J Mol Signal. 2008, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, Z. , Zhang, D. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits eNOS Uncoupling and Alleviates High Glucose-Induced Dysfunction and Apoptosis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells by PI3K/AKT/eNOS Pathway. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. Erratum in: Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020, 13, 2751. 10.2147/DMSO.S274564. 2020, 13, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva KC, Rosales MA, Hamassaki DE, Saito KC, Faria AM, Ribeiro PA, Faria JB, Faria JM. Green tea is neuroprotective in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013, 54, 1325–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin HL, Qin YJ, Zhang YL, Zhang YQ, Chen YL, Niu YY, Pang CP, Chu WK, Zhang HY. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits myofibroblast transformation of human Tenon's fibroblasts. Exp Eye Res. 2020, 197, 108119, Epub 2020 Jun 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan CM, Huang JH, Chiang HS, Wu WB, Lin HH, Hong JY, Hung CF. Effects of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate on RPE cell migration and adhesion. Mol Vis. 2010, 16, 586–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen C, Chen L, Jiang L, Lai TY. Neuroprotective effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in a mouse model of chronic glaucoma. Neurosci Lett. 2015, 600, 132–6, Epub 2015 Jun 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng PH, Chiou LF, Chao HM, Lin S, Chen CF, Liu JH, Ko ML. Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on rat retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve axotomy. Exp Eye Res. 2010, 90, 528–34, Epub 2010 Jan 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang F, Zhuang P, Feng X, Liu P, Liu D, Huang H, Li L, Chen W, Liu L, Sun Y, Jiang H, Ye J, Hu, Y. NMNAT2 is downregulated in glaucomatous RGCs, and RGC-specific gene therapy rescues neurodegeneration and visual function. Mol Ther. 2022, 30, 1421–1431, Epub 2022 Jan 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribble JR, Jöe M, Varricchio C, Otmani A, Canovai A, Habchi B, Daskalakis E, Chaleckis R, Loreto A, Gilley J, Wheelock CE, Jóhannesson G, Wong RCB, Coleman MP, Brancale A, Williams PA. NMNAT2 is a druggable target to drive neuronal NAD production. Nat Commun. Erratum in: Nat Commun. 2024, 15, 8143. 10.1038/s41467-024-52439-7. 2024, 15, 6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li CP, Yao J, Tao ZF, Li XM, Jiang, Q. , Yan, B. Epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) regulates autophagy in human retinal pigment epithelial cells: a potential role for reducing UVB light-induced retinal damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013, 438, 739–45, Epub 2013 Jul 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang YL, Zhang YQ, Lin HL, Qin YJ, Zeng J, Chen YL, Niu YY, Pang CP, Chu WK, Zhang HY. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate increases autophagic activity attenuating TGF-β1-induced transformation of human Tenon's fibroblasts. Exp Eye Res. 2021, 204, 108447, Epub 2021 Jan 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang L, Sun X, Zhu M, Du J, Xu J, Qin X, Xu X, Song, E. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate stimulates autophagy and reduces apoptosis levels in retinal Müller cells under high-glucose conditions. Exp Cell Res. 2019, 380, 149–158, Epub 2019 Apr 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, C. , Sang, S. , Ahmedna, M. In vitro and in vivo inhibition of aldose reductase and advanced glycation end products by phloretin, epigallocatechin 3-gallate and [6]-gingerol. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 502–513, Epub 2016 Sep 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasetti RB, Maddineni P, Millar JC, Clark AF, Zode GS. Increased synthesis and deposition of extracellular matrix proteins leads to endoplasmic reticulum stress in the trabecular meshwork. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou L, He JN, Du L, Ho BM, Ng DS, Chan PP, Tham CC, Pang CP, Chu WK. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Protects Trabecular Meshwork Cells from Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 7435754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Falsini B, Marangoni D, Salgarello T, Stifano G, Montrone L, Di Landro S, Guccione L, Balestrazzi E, Colotto, A. Effect of epigallocatechin-gallate on inner retinal function in ocular hypertension and glaucoma: a short-term study by pattern electroretinogram. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009, 247, 1223–33, Epub 2009 Mar 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasiunas, K. , Galgauskas, S. Green tea-a new perspective of glaucoma prevention. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022, 15, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Salehi B, Staniak M, Czopek K, Stępień A, Dua K, Wadhwa R, Kumar Chellappan D, Sytar O, Brestic M, Ganesh Bhat, N., et al. The Therapeutic Potential of the Labdane Diterpenoid Forskolin. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9, 4089. [CrossRef]
- Pullaiah, T. (2022). Pharmacology of Coleus forskohlii and Forskolin. In: Forskolin. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, RJ. Stimulation of cAMP accumulation and lipolysis in hamster adipocytes with forskolin. Am J Physiol. C: Pt 1), 1984; 246(1 Pt 1):C63-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead A, Krause FN, Moran A, MacCannell ADV, Scragg JL, McNally BD, Boateng E, Murfitt SA, Virtue S, Wright J, Garnham J, Davies GR, Dodgson J, Schneider JE, Murray AJ, Church C, Vidal-Puig A, Witte KK, Griffin JL, Roberts LD. Brown and beige adipose tissue regulate systemic metabolism through a metabolite interorgan signaling axis. Nat Commun. 2021, 12, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Loftus HL, Astell KJ, Mathai ML, Su XQ. Coleus forskohlii Extract Supplementation in Conjunction with a Hypocaloric Diet Reduces the Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Overweight and Obese Subjects: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2015, 7, 9508–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Godard MP, Johnson BA, Richmond SR. Body composition and hormonal adaptations associated with forskolin consumption in overweight and obese men. Obes Res. 2005, 13, 1335–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlepper M, Thormann J, Mitrovic, V. Cardiovascular effects of forskolin and phosphodiesterase-III inhibitors. Basic Res Cardiol. 1989; 84, Suppl 1, 197–212. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann G, Felix S, Sattelberger, U. , Klein, G. Cardiovascular effects of forskolin (HL 362) in patients with idiopathic congestive cardiomyopathy--a comparative study with dobutamine and sodium nitroprusside. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Sánchez R, Trujillo X, Trujillo-Hernández B, Vásquez C, Huerta M, Elizalde, A. Forskolin versus sodium cromoglycate for prevention of asthma attacks: a single-blinded clinical trial. J Int Med Res. 2006, 34, 200–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma C, Zou L, Xia Y, Tu Y, Xue D, Yang Y, Liu D, Liu, Y. , Wu, H., Dan, H., You, P. Extracts of Coleus forskohlii relieves cough and asthma symptoms via modulating inflammation and the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 9648–9655, Epub 2018 Dec 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran QTN, Wong WSF, Chai CLL. Labdane diterpenoids as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Pharmacol Res. 2017, 124, 43–63, Epub 2017 Jul 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Silva M, Trujillo X, Trujillo-Hernández B, Sánchez-Pastor E, Urzúa Z, Mancilla E, Huerta, M. Effect of chronic administration of forskolin on glycemia and oxidative stress in rats with and without experimental diabetes. Int J Med Sci. 2014, 11, 448–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen JY, Peng SY, Cheng YH, Lee IT, Yu YH. Effect of Forskolin on Body Weight, Glucose Metabolism and Adipocyte Size of Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Animals (Basel). 2021, 11, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Salzillo A, Ragone A, Spina A, Naviglio, S. , Sapio, L. Forskolin affects proliferation, migration and Paclitaxel-mediated cytotoxicity in non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines via adenylyl cyclase/cAMP axis. Eur J Cell Biol. 2023, 102, 151292, Epub 2023 Jan 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapio L, Gallo M, Illiano M, Chiosi E, Naviglio D, Spina A, Naviglio, S. The Natural cAMP Elevating Compound Forskolin in Cancer Therapy: Is It Time? J Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 922–927, Epub 2016 Nov 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Franke A, Kaplan MR, Pfrieger FW, Barres BA. Characterization of the signaling interactions that promote the survival and growth of developing retinal ganglion cells in culture. Neuron. 1995, 15, 805–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz SS, Theofilopoulos S, Jauniaux E, Stern GM, Bradford HF. The differentiation potential of human fetal neuronal progenitor cells in vitro. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2004, 153, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo H, Yoo M, Han D, Cho Y, Joung, I. , Kwon YK. Upregulation of TrkB by forskolin facilitated survival of MSC and functional recovery of memory deficient model rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013, 431, 796–801, Epub 2013 Jan 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas NJ, Johnson-Kerner B, Roybon L, Kim YA, Garcia-Diaz A, Wichterle H, Henderson CE. Neurotrophic requirements of human motor neurons defined using amplified and purified stem cell-derived cultures. PLoS One. Erratum in: PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0119195. 10.1371/journal.pone.0119195. 2014, 9, e110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan B, Harini L, Krishnakumar V, Kannan VR, Sundar K, Kathiresan, T. Insights on the involvement of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate in ER stress-mediated apoptosis in age-related macular degeneration. Apoptosis. 2017, 22, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owona BA, Zug C, Schluesener HJ, Zhang ZY. Protective Effects of Forskolin on Behavioral Deficits and Neuropathological Changes in a Mouse Model of Cerebral Amyloidosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2016, 75, 618–27, Epub 2016 May 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi M, Alshammari A, Kaur G, Kalra S, Mehan S, Suri M, Chhabra S, Kumar N, Alanazi WA, Alshanwani AR, Al-Ghamdi AH, Narula AS, Kalfin, R. Effect of Natural Adenylcyclase/cAMP/CREB Signalling Activator Forskolin against Intra-Striatal 6-OHDA-Lesioned Parkinson's Rats: Preventing Mitochondrial, Motor and Histopathological Defects. Molecules. 2022, 27, 7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vetrugno M, Uva MG, Russo V, Iester M, Ciancaglini M, Brusini P, Centofanti M, Rossetti LM. Oral administration of forskolin and rutin contributes to intraocular pressure control in primary open angle glaucoma patients under maximum tolerated medical therapy. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2012, 28, 536–41, Epub 2012 Jun 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprioli J, Sears M, Bausher L, Gregory, D. , Mead, A. Forskolin lowers intraocular pressure by reducing aqueous inflow. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984, 25, 268–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen X, Koga T, Park BC, SundarRaj, N. , Yue BYJT. Rho GTPase and cAMP/protein kinase A signaling mediates myocilin-induced alterations in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283, 603–612, Epub 2007 Nov 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor T, Mehan S, Suri M, Sharma N, Kumar N, Narula AS, Alshammari A, Alasmari AF, Alharbi M, Assiri MA, Kalfin, R. Forskolin, an Adenylcyclase/cAMP/CREB Signaling Activator Restoring Myelin-Associated Oligodendrocyte Destruction in Experimental Ethidium Bromide Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Cells. 2022, 11, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wagh V, Kalpana, Inamdar B, Samanta, M. 2009. The effect of forskolin ophthalmic inserts on intraocular pressure in rabbit eyes. Int. J. Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sci.
- Shim MS, Kim KY, Ju WK. Role of cyclic AMP in the eye with glaucoma. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Russo R, Adornetto A, Cavaliere F, Varano GP, Rusciano D, Morrone LA, Corasaniti MT, Bagetta, G. , Nucci, C. Intravitreal injection of forskolin, homotaurine, and L-carnosine affords neuroprotection to retinal ganglion cells following retinal ischemic injury. Mol Vis. 2015, 21, 718–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Juric DM, Loncar, D., Carman-Krzan, M. Noradrenergic stimulation of BDNF synthesis in astrocytes: mediation via alpha1- and beta1/beta2-adrenergic receptors. Neurochem Int. 2008; 52, 297–306, Epub 2007 Jul 4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahashi T, Fujimura H, Altar CA, Li J, Kambayashi J, Tandon NN, Sun, B. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett. 2000, 470, 113–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Franke A, Wilkinson GA, Kruttgen A, Hu M, Munro E, Hanson MG Jr, Reichardt LF, Barres BA. Depolarization and cAMP elevation rapidly recruit TrkB to the plasma membrane of CNS neurons. Neuron. 1998, 21, 681–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caprioli, J. , Sears, M. Forskolin lowers intraocular pressure in rabbits, monkeys, and man. Lancet. 1983, 1, 958–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed M, Nagabhushanam K, Natarajan S, Vaidyanathan P, Kumar SK. A Double-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Forskolin Eye Drops 1% in the Treatment of Open Angle Glaucoma – A Comparative Study. J Clin Trials. 2014; 4, 184. [CrossRef]
- Rusciano D, Pezzino S, Mutolo MG, Giannotti R, Librando A, Pescosolido, N. Neuroprotection in Glaucoma: Old and New Promising Treatments. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2017, 2017, 4320408, Epub 2017 Oct 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisto D, Lavermicocca N, Errico D, Rusciano D (2013) Oral Administration of Forskolin and Rutin Contributes to Reduce Intraocular Pressure and Improve PERG (Pattern Electroretinogram) Amplitude in Glaucomatous Patients. JSM Biotechnol Bioeng 2, 1036.
- Watanabe M, Tokita Y, Kato M, Fukuda, Y. Intravitreal injections of neurotrophic factors and forskolin enhance survival and axonal regeneration of axotomized beta ganglion cells in cat retina. Neuroscience. 2003; 116, 733–742. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locri F, Cammalleri M, Dal Monte M, Rusciano D, Bagnoli, P. Protective Efficacy of a Dietary Supplement Based on Forskolin, Homotaurine, Spearmint Extract, and Group B Vitamins in a Mouse Model of Optic Nerve Injury. Nutrients. 2019, 11, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cammalleri M, Dal Monte M, Amato R, Bagnoli P, Rusciano, D. A Dietary Combination of Forskolin with Homotaurine, Spearmint and B Vitamins Protects Injured Retinal Ganglion Cells in a Rodent Model of Hypertensive Glaucoma. Nutrients. 2020, 12, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tavares LP, Negreiros-Lima GL, Lima KM, E Silva PMR, Pinho V, Teixeira MM, Sousa LP. Blame the signaling: Role of cAMP for the resolution of inflammation. Pharmacol Res. 2020, 159, 105030, Epub 2020 Jun 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh V, Deepika G, Bantal V, Beedu SR, Rupula, K. Evaluation of Anti-inflammatory and Anti-nociceptive Potentials of Andrographolide and Forskolin: In vivo Studies. Journal of Biologically Active Products from Nature. 2018; 8, 326–334. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. , Eklund KK. Insights image for Forskolin attenuates the NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL-1β secretion in human macrophages. Pediatr Res. 2019; 86, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu L, Jiang Y, Steinle JJ. Forskolin eye drops improve retinal damage from ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Vis. P: ;27, 365-369. PMCID, 2021; 27, 365–369. [PubMed]
- Neto, M. , Lunardi, C., Rodrigues, G. and Bendhack, L. (2011) Vasodilatation induced by forskolin involves cyclic GMP production. Journal of Biophysical Chemistry, 2, 373-379. [CrossRef]
- Nedvetsky PI, Zhao X, Mathivet T, Aspalter IM, Stanchi F, Metzger RJ, Mostov KE, Gerhardt, H. cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) regulates angiogenesis by modulating tip cell behavior in a Notch-independent manner. Development. 2016, 143, 3582–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu L, Jiang Y, Steinle JJ. Forskolin regulates retinal endothelial cell permeability through TLR4 actions in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021; 476, 4487–4492. [CrossRef]
- Xue Y, Sun R, Zheng W, Yang, L. , An, R. Forskolin promotes vasculogenic mimicry and invasion via Notch-1-activated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in syncytiolization of trophoblast cells in choriocarcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2020, 56, 1129–1139, Epub 2020 Feb 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You ZP, Xiong B, Zhang YL, Shi L and Shi, K. Forskolin attenuates retinal inflammation in diabetic mice. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 17, 2321–2326. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S. , Kesarla, R., Omri, A. Formulation strategies to improve the bioavailability of poorly absorbed drugs with special emphasis on self-emulsifying systems. ISRN Pharm. 2013, 2013, 848043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen G, Kang W, Li W, Chen, S. , Gao, Y. Oral delivery of protein and peptide drugs: from non-specific formulation approaches to intestinal cell targeting strategies. Theranostics. 2022, 12, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi M, Shi YL, Li XM, Yang R, Cai ZY, Li QS, Ma SC, Ye JH, Lu JL, Liang YR, Zheng XQ. Food-grade Encapsulation Systems for (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate. Molecules. 2018, 23, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zagury, Y. , Kazir, M., Livney YD. Improved antioxidant activity, bioaccessibility and bioavailability of EGCG by delivery in β-lactoglobulin particles. Journal of Functional Foods. 2019, 52, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameta RK, Soni, K. , Bhattarai, A. Recent Advances in Improving the Bioavailability of Hydrophobic/Lipophilic Drugs and Their Delivery via Self-Emulsifying Formulations. Colloids and Interfaces. 2023, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangueiro JF, Andreani T, Fernandes L, Garcia ML, Egea MA, Silva AM, Souto EB. Physicochemical characterization of epigallocatechin gallate lipid nanoparticles (EGCG-LNs) for ocular instillation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014, 123, 452–60, Epub 2014 Sep 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




