Submitted:
17 October 2024
Posted:
18 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Target
2.2. Ligands
2.3. Molecular Docking
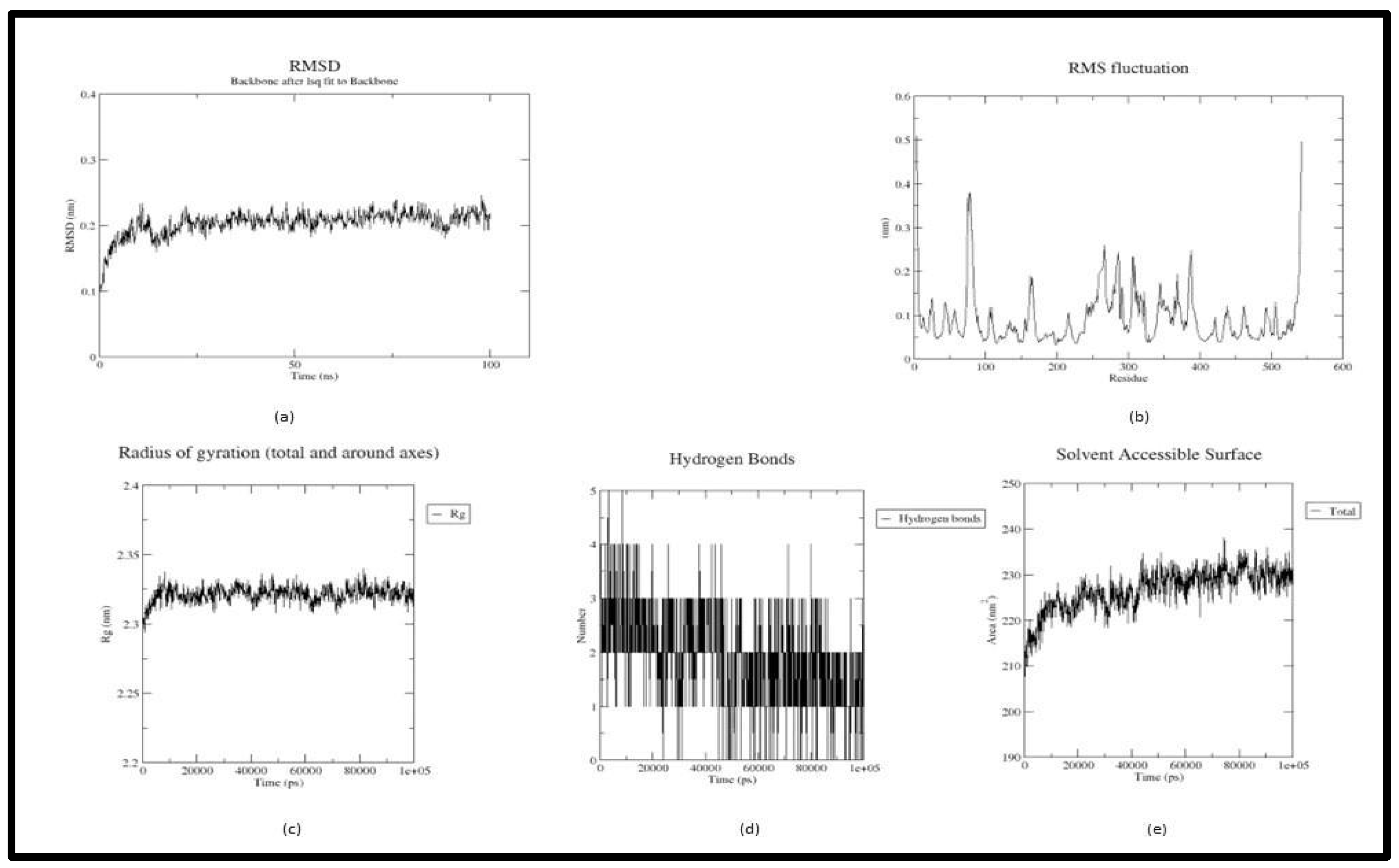
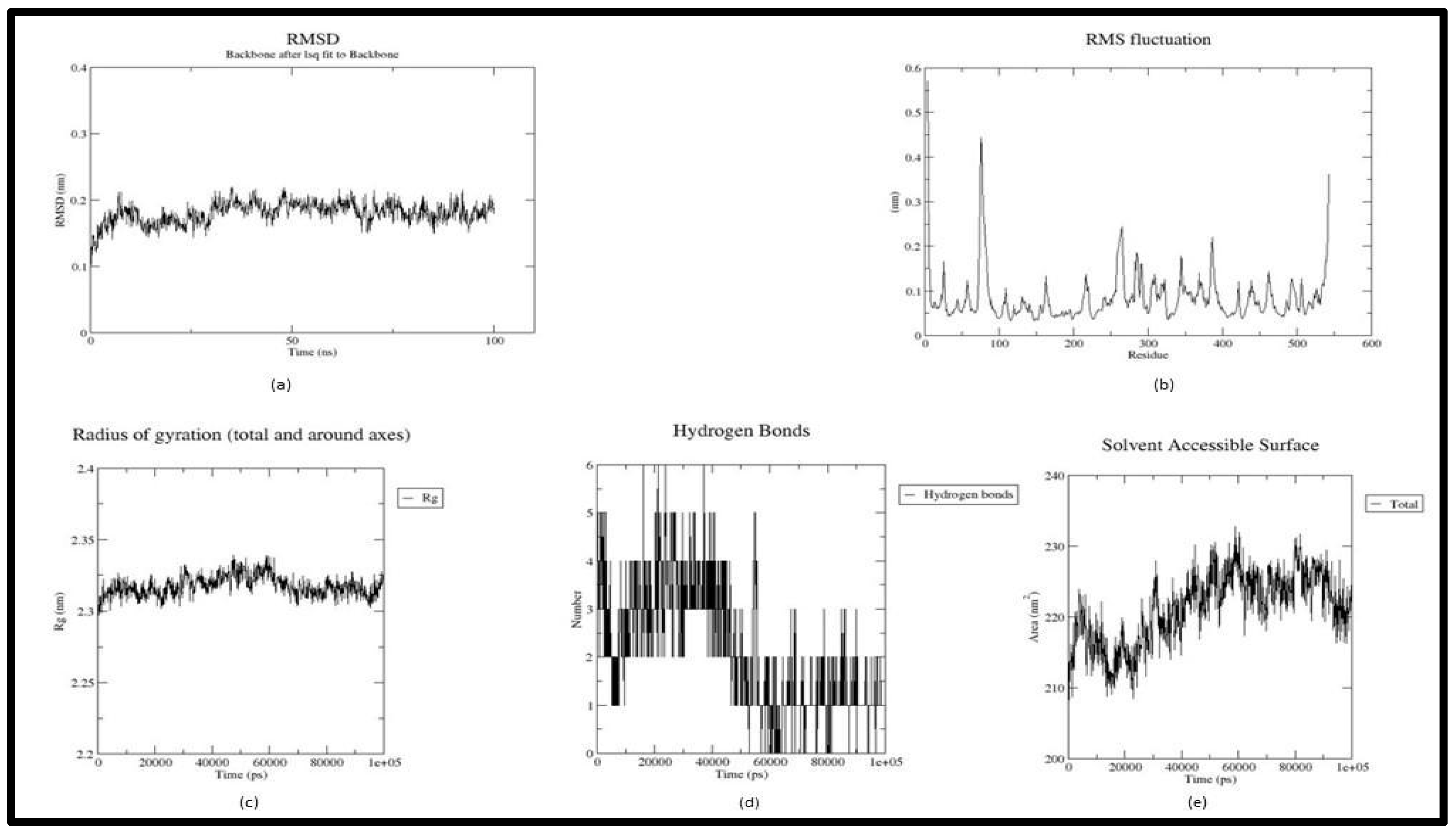
2.4 Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.4.1. MMPBSA
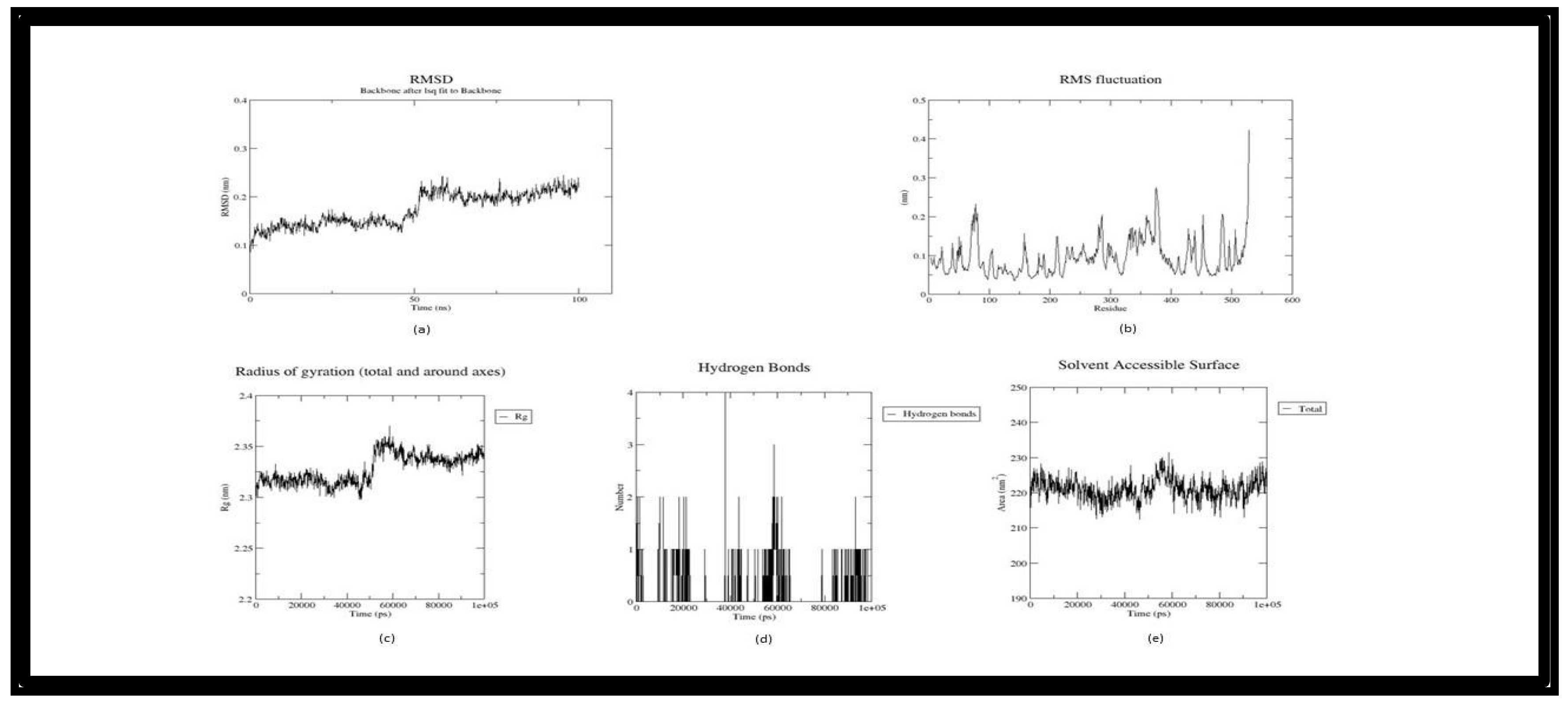
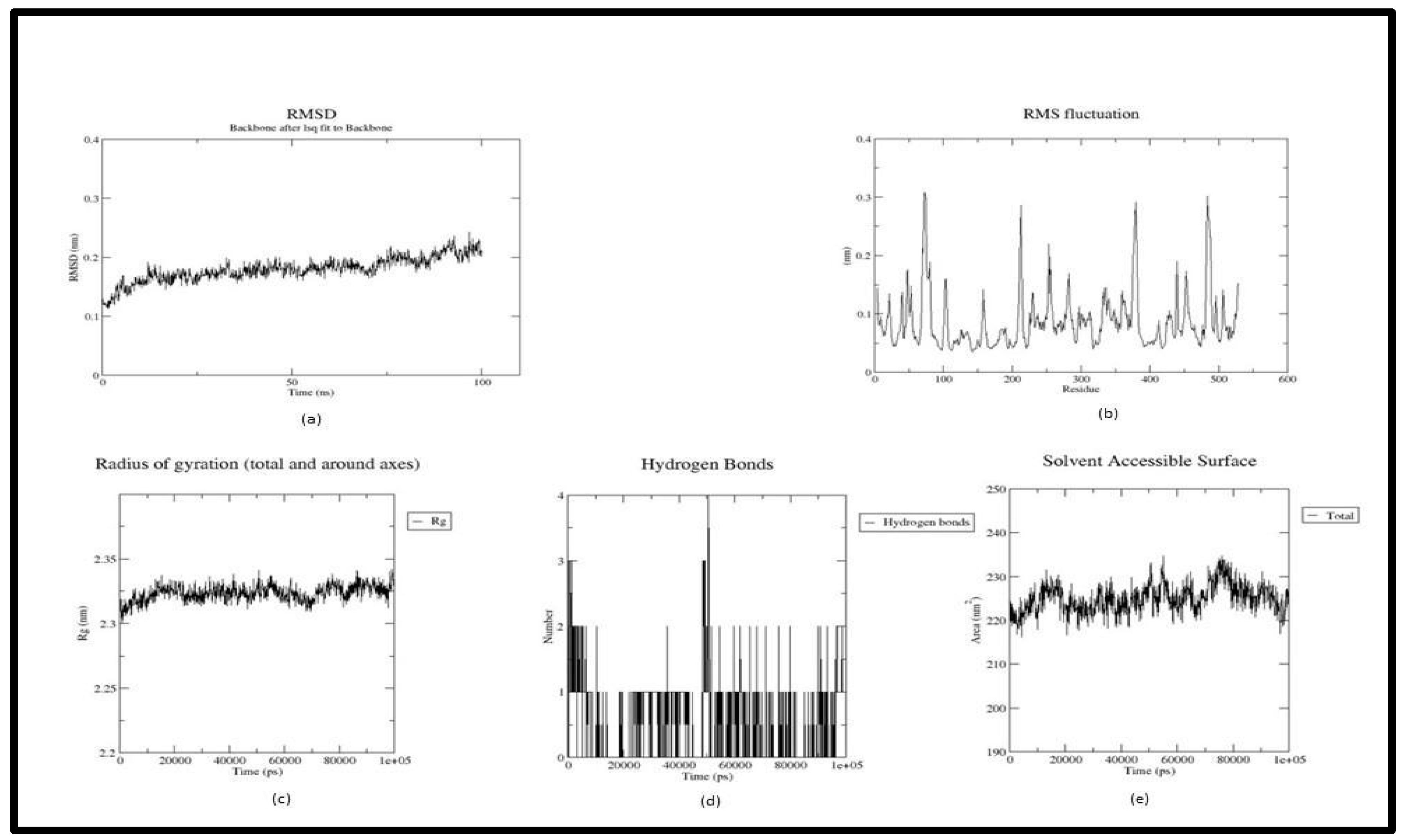
3. Result and Discussion
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Availability of Data and Material
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Inter
References
- Al-Karmalawy, A. A., Dahab, M. A., Metwaly, A. M., Elhady, S. S., Elkaeed, E. B., Eissa, I. H., & Darwish, K. M. (2021). Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulation Revealed the Potential Inhibitory Activity of ACEIs Against SARS-CoV-2 Targeting the hACE2 Receptor. Frontiers in Chemistry, 9. [CrossRef]
- Luana Severo Alves, Valdir Cechinel Filho, Pires, R., & Furtado-Alle, L. (2022). BChE inhibitors from marine organisms – A review. 367, 110136–110136. [CrossRef]
- Arunima, C., Julia, J. and Prasobh, G. (2021) ‘A review on role of ginkgo biloba in treating alzheimer’s disease’.
- Balestrino, R. and Schapira, A.H. V (2020) ‘Parkinson disease’, European journal of neurology, 27(1), pp. 27–42.
- de Barros Viana, M. et al. (2022) ‘Cannabis sativa and Cannabidiol: A Therapeutic Strategy for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases?’, Medical Cannabis and Cannabinoids, 5(1), pp. 207–219. [CrossRef]
- Basheer, A. et al. (2022) ‘Use of Bacopa monnieri in the Treatment of Dementia Due to Alzheimer Disease: Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials’, Interactive journal of medical research, 11(2), p. e38542. [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, K.P. et al. (2020) ‘Insilico method for prediction of maximum binding affinity and ligand—protein interaction studies on Alzheimer’s disease’, Int J Res Granthaalayah, 8(11), pp. 362–370.
- Bauer, P., Hess, B. and Lindahl, E. (2022) ‘GROMACS 2022 manual’.
- Baumard, J. et al. (2021) ‘Physical understanding in neurodegenerative diseases’, Cognitive Neuropsychology, 38(7–8), pp. 490–514.
- Benson, N.C. and Daggett, V. (2012) ‘A comparison of multiscale methods for the analysis of molecular dynamics simulations’, The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 116(29), pp. 8722–8731. [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z. and Karaman, R. (2020) ‘Comprehensive review on Alzheimer’s disease: causes and treatment’, Molecules, 25(24), p. 5789. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. and Pan, W. (2014) ‘The treatment strategies for neurodegenerative diseases by integrative medicine’, Integrative Medicine International, 1(4), pp. 223–225. [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J. et al. (2013) ‘Structures of human acetylcholinesterase bound to dihydrotanshinone I and territrem B show peripheral site flexibility’, ACS medicinal chemistry letters, 4(11), pp. 1091–1096. [CrossRef]
- Emamzadeh, F.N. and Surguchov, A. (2018) ‘Parkinson’s disease: biomarkers, treatment, and risk factors. Front Neurosci 12: 612’.
- Geourjon, C. and Deleage, G. (1995) ‘SOPMA: significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments’, Bioinformatics, 11(6), pp. 681–684. [CrossRef]
- Gu, X. and Wang, X. (2021) ‘An overview of recent analysis and detection of acetylcholine’, Analytical Biochemistry, 632, p. 114381. [CrossRef]
- H Ferreira-Vieira, T. et al. (2016) ‘Alzheimer’s disease: targeting the cholinergic system’, Current neuropharmacology, 14(1), pp. 101–115.
- Ha, Z.Y., Mathew, S. and Yeong, K.Y. (2020) ‘Butyrylcholinesterase: a multifaceted pharmacological target and tool’, Current Protein and Peptide Science, 21(1), pp. 99–109. [CrossRef]
- Hyman, B.T. et al. (1989) ‘Alzheimer’s disease’, Annual review of public health, 10(1), pp. 115–140.
- Johansson, M.U. et al. (2012) ‘Defining and searching for structural motifs using DeepView/Swiss-PdbViewer’, BMC bioinformatics, 13(1), pp. 1–11.
- Kandiah, N. et al. (2017) ‘Rivastigmine: the advantages of dual inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase and its role in subcortical vascular dementia and Parkinson’s disease dementia’, Clinical interventions in aging, 12, p. 697. [CrossRef]
- Khare, N., Maheshwari, S.K. and Jha, A.K. (2021) ‘Screening and identification of secondary metabolites in the bark of Bauhinia variegata to treat Alzheimer’s disease by using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations’, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 39(16), pp. 5988–5998.
- Kim, S. et al. (2021) ‘PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces’, Nucleic Acids Research, 49(D1), pp. D1388–D1395. [CrossRef]
- Kuboyama, T., Tohda, C. and Komatsu, K. (2014) ‘Effects of Ashwagandha (roots of Withania somnifera) on neurodegenerative diseases’, Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 37(6), pp. 892–897. [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A. (2001) ‘PDBsum: summaries and analyses of PDB structures’, Nucleic acids research, 29(1), pp. 221–222.
- Marcos-Rabal, P. et al. (2021) ‘Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Multidisciplinary Approach’, Current Pharmaceutical Design, 27(30), pp. 3305–3336.
- Murugesan, V. et al. (2022) ‘Phytonutrients in Neurological Disorders’, in Role of Nutrients in Neurological Disorders. Springer, pp. 3–15.
- Nicolet, Y. et al. (2003) ‘Crystal structure of human butyrylcholinesterase and of its complexes with substrate and products’, Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(42), pp. 41141–41147. [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M. et al. (2011) ‘Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox’, Journal of cheminformatics, 3(1), pp. 1–14.
- Pagano, G. et al. (2015) ‘Cholinesterase inhibitors for Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis’, Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 86(7), pp. 767–773. [CrossRef]
- Pirolli, D. et al. (2014) ‘Insights from molecular dynamics simulations: structural basis for the V567D mutation-induced instability of zebrafish alpha-dystroglycan and comparison with the murine model’, PLoS One, 9(7), p. e103866. [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Pérez, W.A., Yépes-Pérez, A.F. and Martínez-Pabón, M.C. (2019) ‘Molecular docking and in silico studies of the physicochemical properties of potential inhibitors for the phosphotransferase system of Streptococcus mutans’, Archives of Oral Biology, 98, pp. 164–175. [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, W. et al. (2012) ‘Relaxation estimation of RMSD in molecular dynamics immunosimulations’, Computational and mathematical methods in medicine, 2012. [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.S. et al. (2019) ‘3-Acyltetramic acids as a novel class of inhibitors for human kallikreins 5 and 7’, Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 29(9), pp. 1094–1098.
- Tanaka, N. and Kashiwada, Y. (2021) ‘Phytochemical studies on traditional herbal medicines based on the ethnopharmacological information obtained by field studies’, Journal of natural medicines, 75(4), pp. 762–783. [CrossRef]
- Trott, O. and Olson, A.J. (2010) ‘AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading’, Journal of computational chemistry, 31(2), pp. 455–461.
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S. et al. (2021) ‘gmx_MMPBSA: A New Tool to Perform End-State Free Energy Calculations with GROMACS’, Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 17(10), pp. 6281–6291. Available at: . [CrossRef]
- Vanessa, V. V and Mah, S.H. (2021) ‘Xanthone: Potential Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment’, Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry, 21(17), pp. 2507–2529. [CrossRef]
| PDB_ID | T- PI | Al | Mol. Weight |
No. of amino acids |
GV |
II |
Half Life | Extinction Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mammalian | Yeast | E-coli | Cysteines | Cys reduced | |||||||
| 4EY6 | 5.83 | 84.00 | 59390.46 | 542 | -0.110 | 40.07 | 30 hours | >20 hours | >10 hours | 100185 |
99810 |
| 1P0I | 7.22 | 77.60 | 59653.87 | 529 | -0.275 | 38.32 | 1 hours | 30 min | >10 hours | 104195 | 103820 |
| PDB _ID | Alpha helix percent |
Beta turn Percent |
Random Coil |
Extended strand |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4EY6 | 29.11% | 4.73% | 48.02% | 18.15% |
| 1P0I | 28.04% | 5.35% | 48.15% | 18.45% |
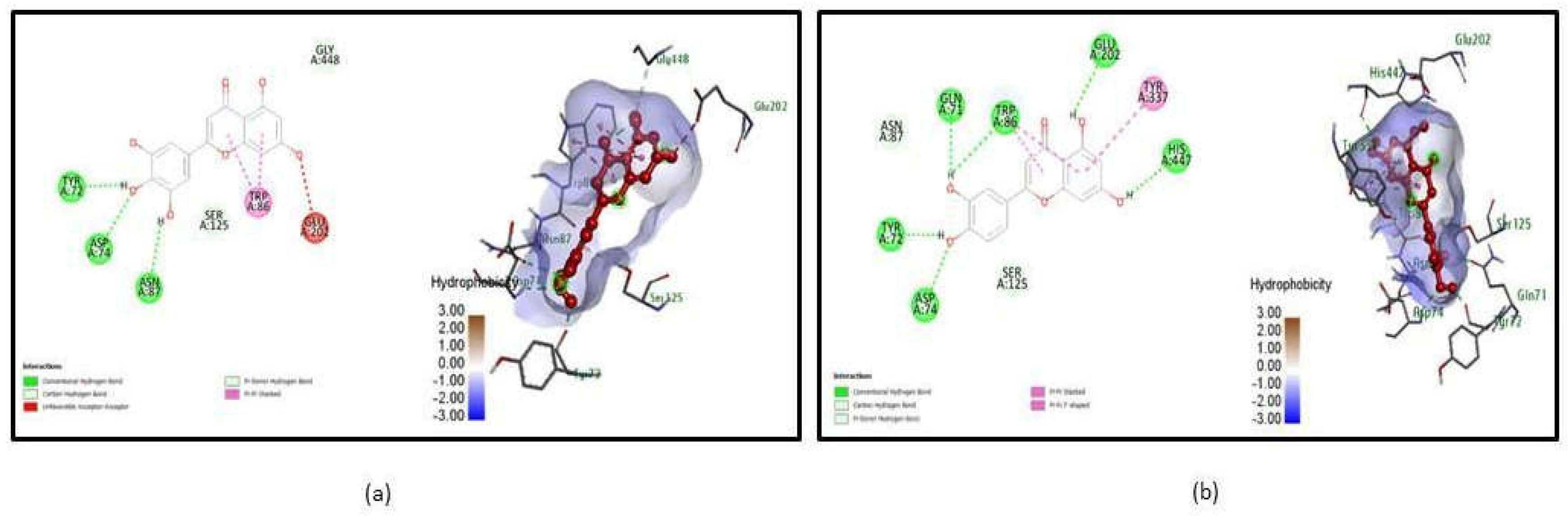
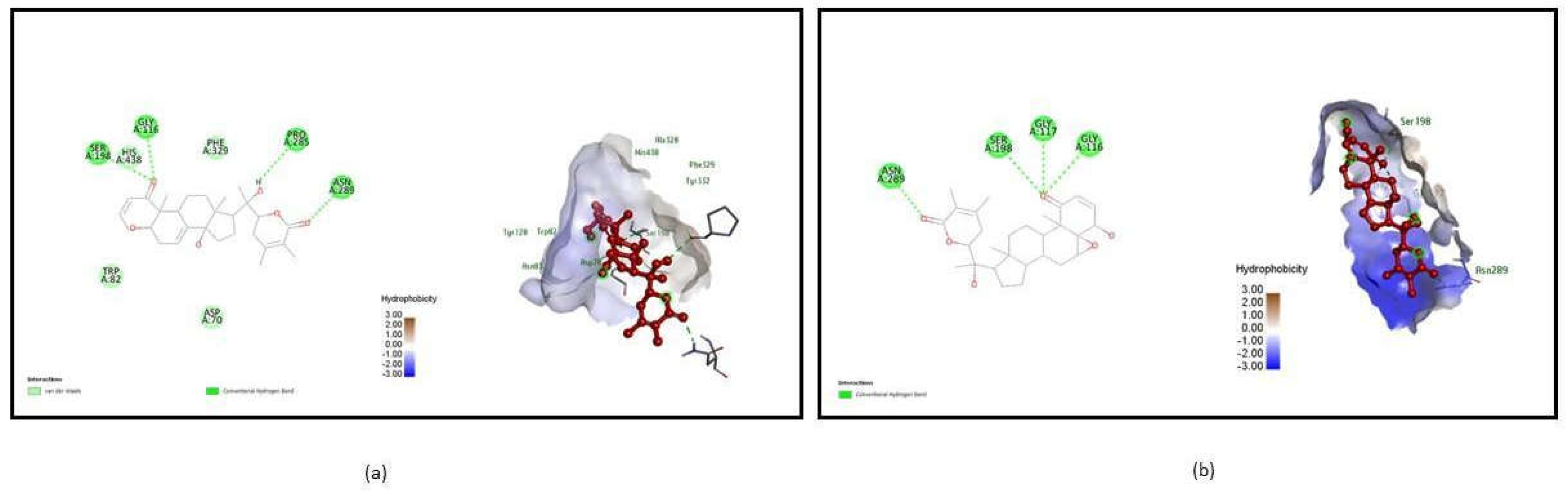
| Target | Ligand_Name | H-Bond Interaction |
No. of H-Bonds | Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) |
H-bond interaction after MD Simulation | Binding energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4EY6 | Tricetin | TYR 72, ASP 74, ASN 87 | 3 | -10.9 | ASP 74 | -8.49 |
| 4EY6 |
Luteolin | GLN 71, TRP 86, GLU 202, HIS 447, TYR 72, ASP 74 | 6 | -10.6 | TYR 341, HIS 447 |
-9.85 |
| 1P0I | Withasomniferol C | SER 198, GLY 116, PRO 285, ASN 289 | 4 | -11 | TRP 231 | -25.26 |
| 1P0I |
Withanolide | ASN 289, SER 198, GLY 117, GLY 116 | 4 | -11 | TYR 332 | -24.1 |
| Ligand_Name | MW | H-Bond Donor | H-Bond Acceptor | Log P | MR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tricetin | 302.24 | 5 | 7 | 1.33 | 78.04 |
| Luteolin | 286.24 | 4 | 6 | 1.86 | 76.01 |
| Withasomniferol C | 470.6 | 3 | 6 | 3.49 | 129.28 |
| Withanolide | 470.6 | 2 | 6 | 3.78 | 127.53 |
| Property | Model Name | Tricetin | Luteolin | Withasomniferol C | Withanolide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbtion | Water solubility | -3.028 | -3.094 | -5.269 | -5.127 |
| Caco2 permeability | -0.272 | 0.096 | 0.769 | 0.831 | |
| Intestinal absorption (human) | 78.366 | 81.13 | 97.917 | 99.2 | |
| Skin Permeability | -2.735 | -2.735 | -3.764 | -3.267 | |
| P-glycoprotein substrate | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| P-glycoprotein I inhibitor | No | No | No | Yes | |
| P-glycoprotein II inhibitor | No | No | No | Yes | |
| Distribution | VDss (human) | 0.932 | 1.153 | 0.142 | -0.048 |
| Fraction unbound (human) | 0.208 | 0.168 | 0.23 | 0.093 | |
| BBB permeability | -1.38 | -0.907 | -0.774 | -0.315 | |
| CNS permeability | -3.557 | -2.251 | -3.008 | -2.696 | |
| Metabolilsm | CYP2D6 substrate | No | No | No | No |
| CYP3A4 substrate | No | No | Yes | Yes | |
| CYP1A2 inhibitior | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| CYP2C19 inhibitior | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP2C9 inhibitior | No | Yes | No | No | |
| CYP2D6 inhibitior | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP3A4 inhibitior | No | No | No | No | |
| Excretion | Total Clearance | 0.513 | 0.495 | 0.43 | 0.347 |
| Renal OCT2 substrate | No | No | No | No | |
| Toxicity | AMES toxicity | No | No | No | No |
| Max. tolerated dose (human) | 0.545 | 0.499 | -0.722 | -0.867 | |
| hERG I inhibitor | No | No | No | No | |
| hERG II inhibitor | No | No | No | No | |
| Hepatotoxicity | No | No | No | No | |
| Skin Sensitisation | No | No | No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




