Submitted:
16 October 2024
Posted:
17 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
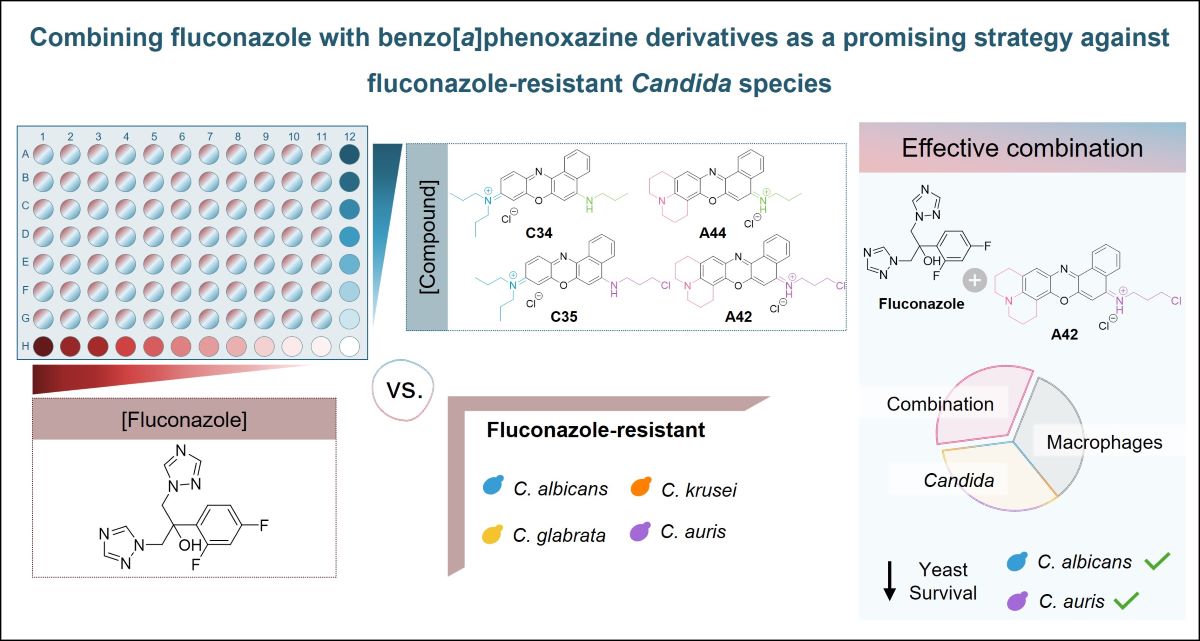
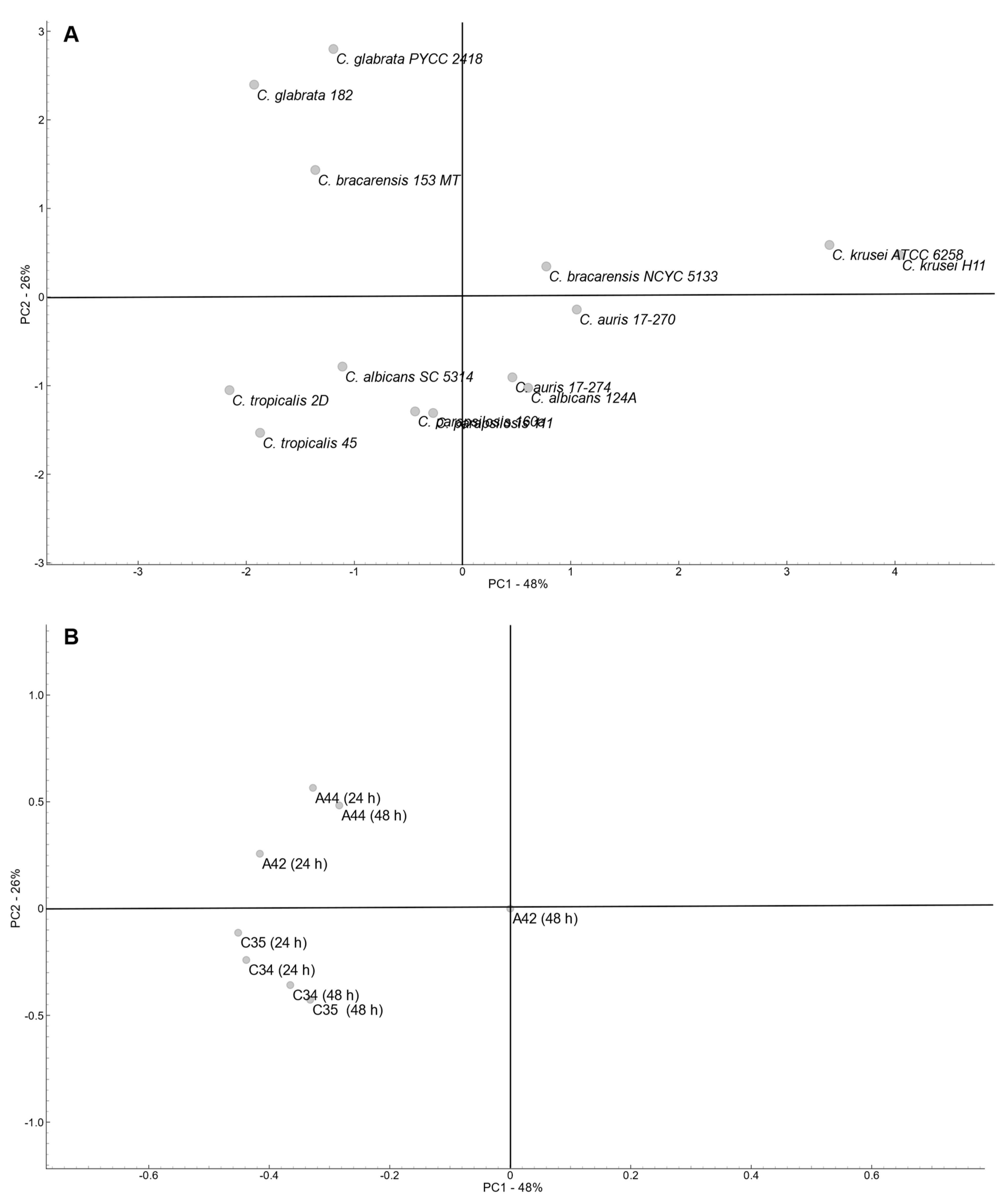
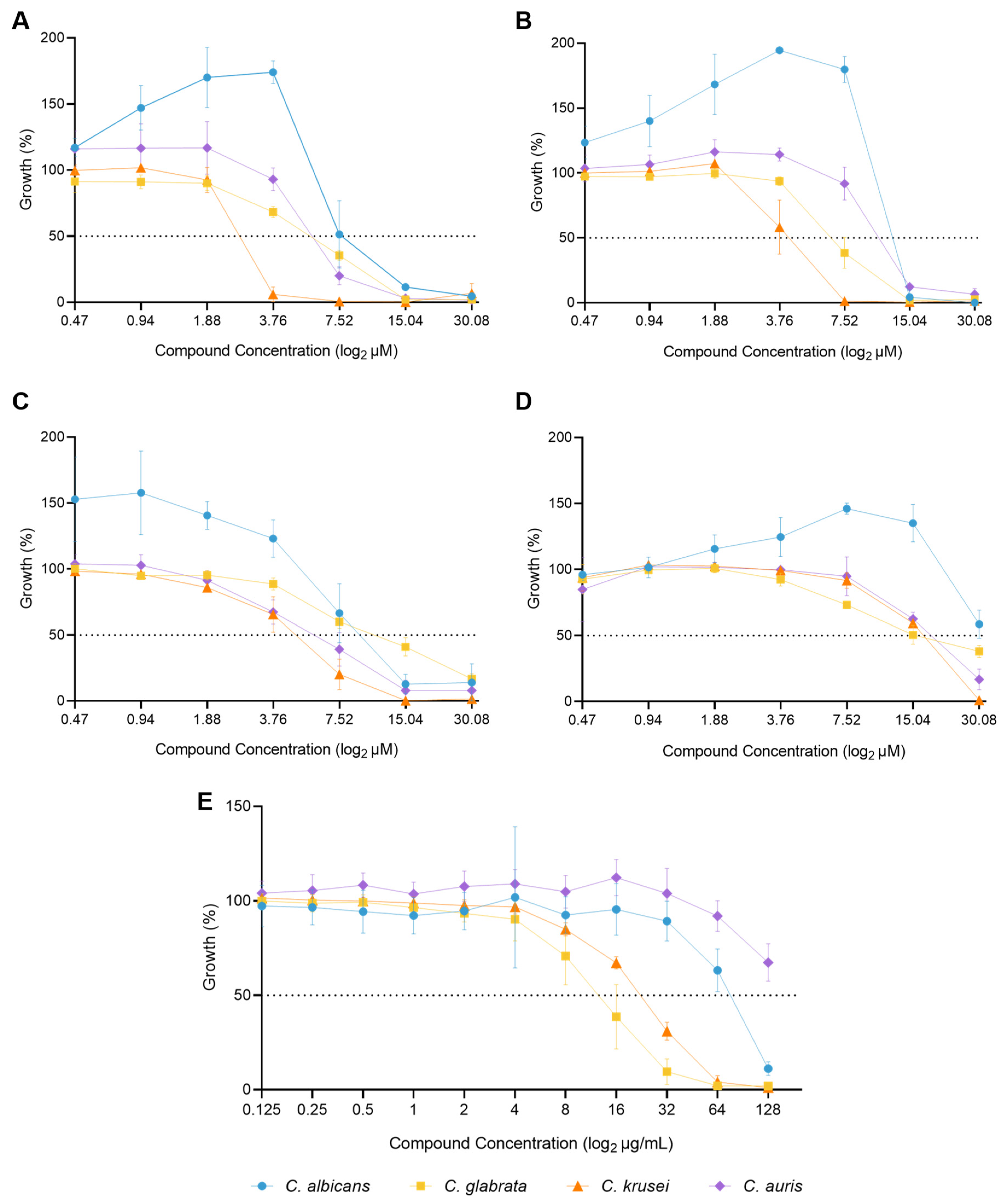
2.1. Antifungal Activity of Benzo[a]phenoxazine Derivatives
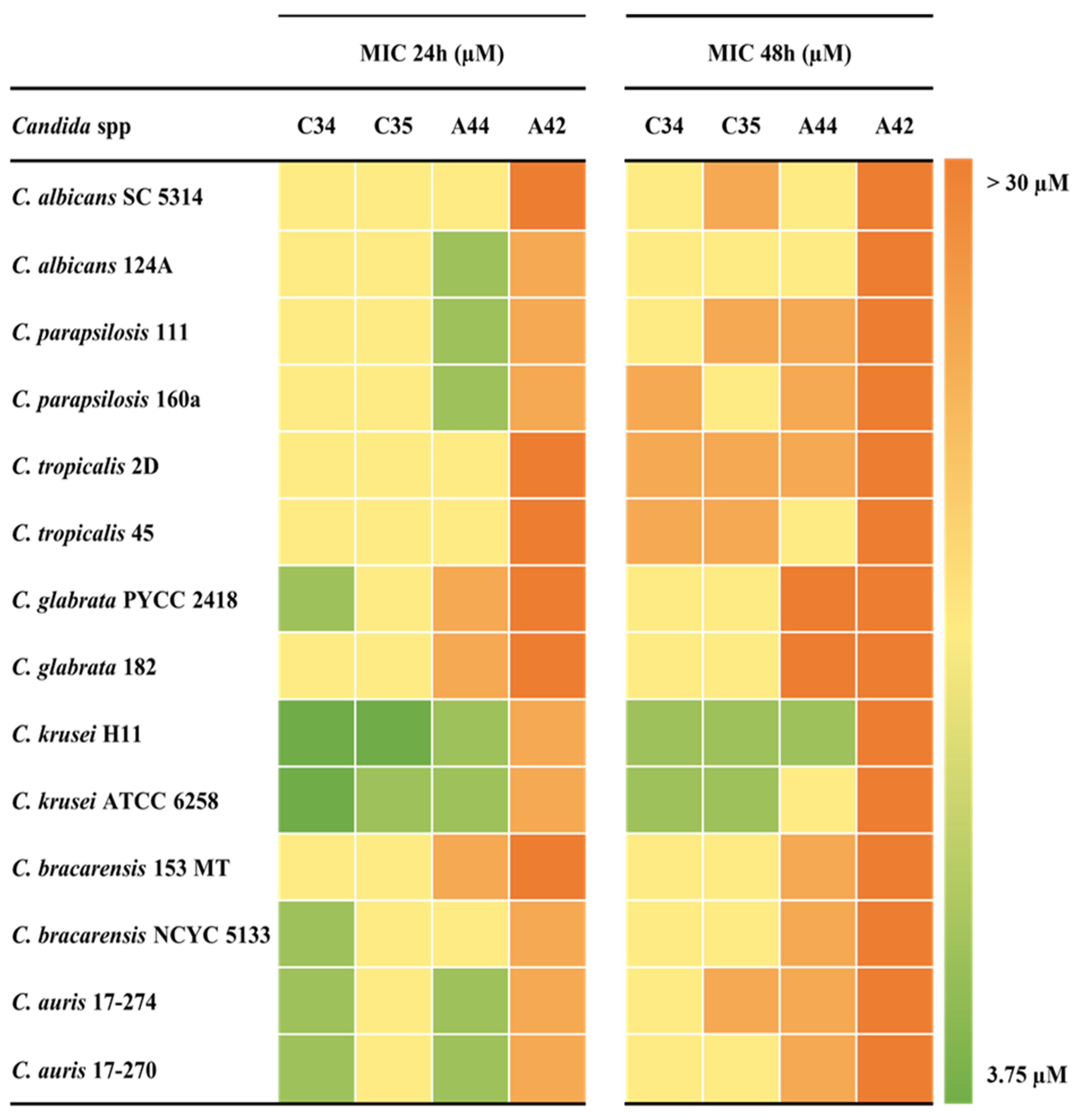
2.2. In Vitro Antifungal Activity of Fluconazole and Benzo[a]phenoxazine Derivatives
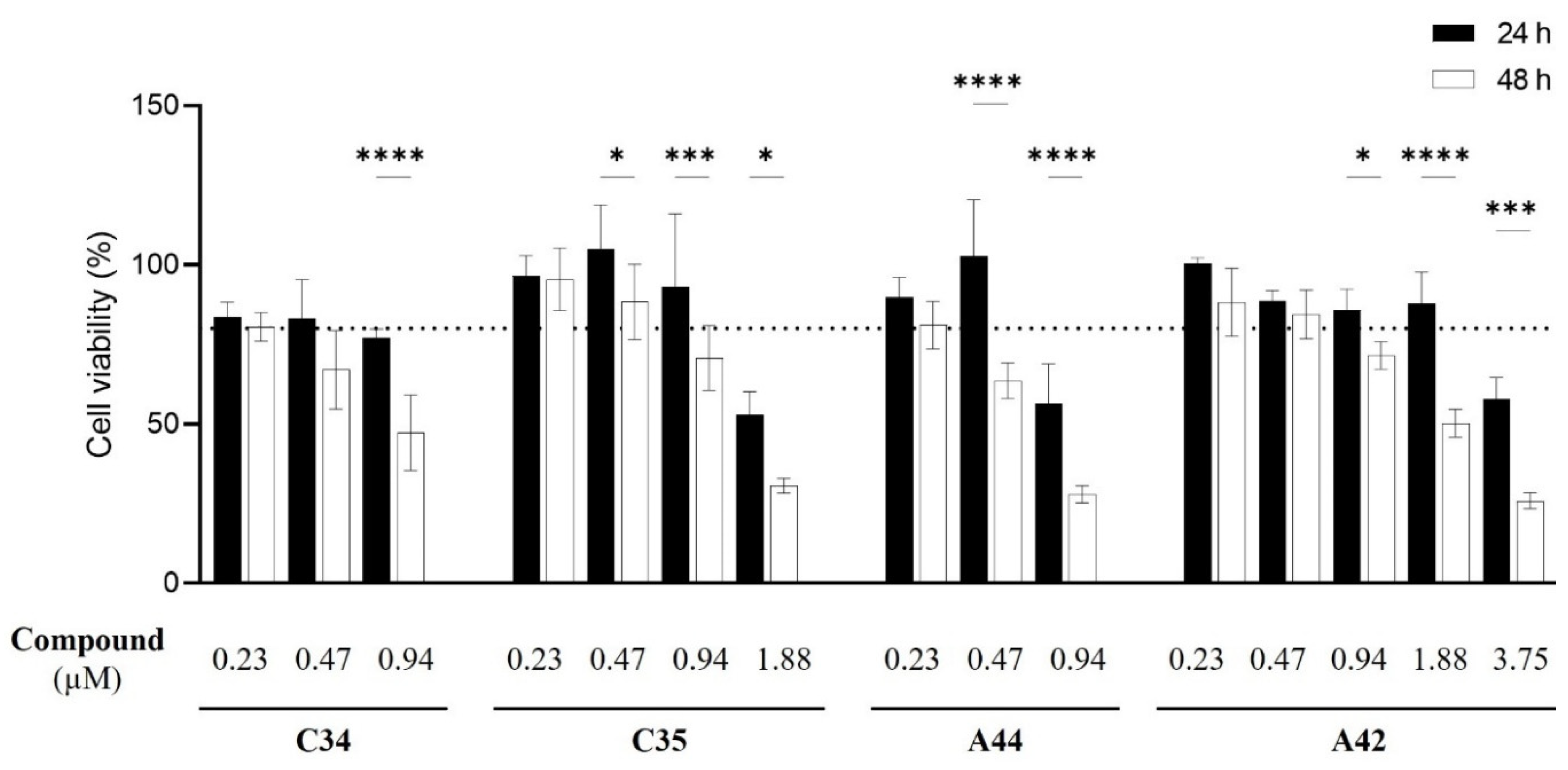
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assays
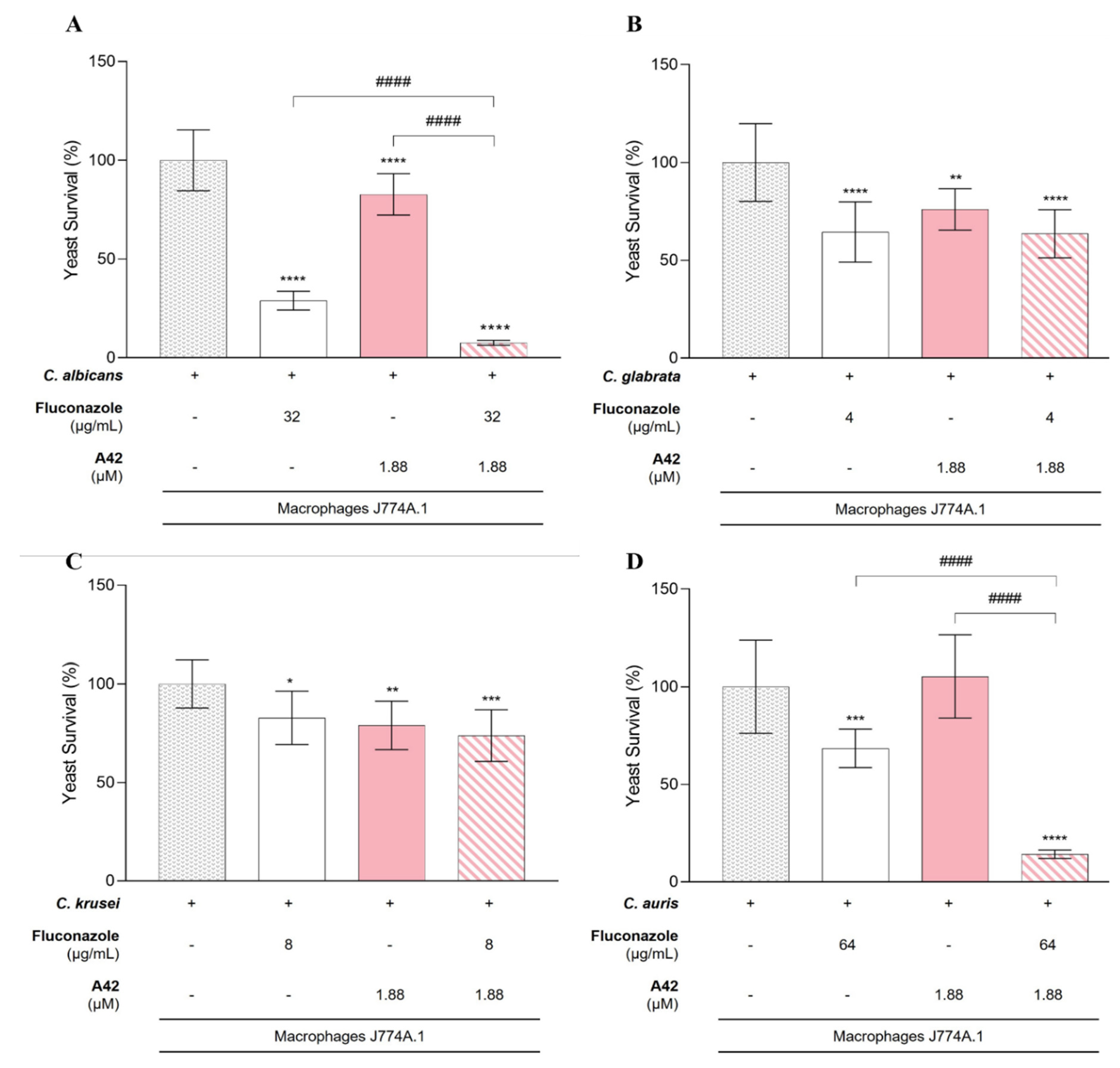
2.4. Macrophage Yeast Killing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fungal Strains and Cell Lines
4.2. Drugs and Medium
4.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Assays
4.4. Checkerboard Assays – Microplate Preparation
4.4.1. Analysis of Results
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.6. Macrophage Yeast Killing
4.7. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow EWL, Pang LM, Wang Y (2021) From jekyll to hyde: The yeast–hyphal transition of Candida albicans. Pathogens 10:859. [CrossRef]
- Rosenbach A, Dignard D, Pierce J V., et al. (2010) Adaptations of Candida albicans for growth in the mammalian intestinal tract. Eukaryot Cell 9:1075–1086. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Dantas A, Lee KK, Raziunaite I, et al. (2016) Cell biology of Candida albicans–host interactions. Curr Opin Microbiol 34:111–118. [CrossRef]
- Denning DW (2024) Global incidence and mortality of severe fungal disease. Lancet Infect Dis 24:e428–e438. [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gaviria M, Ramírez-Sotelo U, Mora-Montes HM (2023) Non-albicans Candida Species: Immune Response, Evasion Mechanisms, and New Plant-Derived Alternative Therapies. Journal of Fungi 9:. [CrossRef]
- Logan C, Martin-Loeches I, Bicanic T (2020) Invasive candidiasis in critical care: challenges and future directions. Intensive Care Med 46:2001–2014. [CrossRef]
- Friedman DZP, Schwartz IS (2019) Emerging fungal infections: New patients, new patterns, and new pathogens. Journal of Fungi 5:. [CrossRef]
- 2022; 8. World Health Organization (2022) WHO fungal priority pathogens list to guide research, development and public health action.
- Gómez-Gaviria M, Mora-Montes HM (2020) Current aspects in the biology, pathogeny, and treatment of Candida krusei, a neglected fungal pathogen. Infect Drug Resist 13:1673–1689. [CrossRef]
- Pristov KE, Ghannoum MA (2019) Resistance of Candida to azoles and echinocandins worldwide. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 25:792–798. [CrossRef]
- Leitão MIPS, Raju BR, Cerqueira NMFSA, et al. (2020) Benzo[a]phenoxazinium chlorides: Synthesis, antifungal activity, in silico studies and evaluation as fluorescent probes. Bioorg Chem 98:. [CrossRef]
- Martinez V, Henary M (2016) Nile Red and Nile Blue: Applications and syntheses of structural analogues. Chem Eur J 22:13764–13782. [CrossRef]
- Leitão MIPS, Raju BR, Naik S, et al. (2016) Synthesis and photophysical studies of new benzo[a]phenoxazinium chlorides as potential antifungal agents. Tetrahedron Lett 57:3936–3941. [CrossRef]
- Frade VHJ, Sousa MJ, Moura JCVP, Gonçalves MST (2008) Synthesis of naphtho [2,3-a]phenoxazinium chlorides: Structure-activity relationships of these heterocycles and benzo[a]phenoxazinium chlorides as new antimicrobials. Bioorg Med Chem 16:3274–3282. [CrossRef]
- Raju BR, Leitão MIPS, Sousa MJ, et al. (2020) New NIR dyes based on quinolizino[1,9-hi]phenoxazin-6-iminium chlorides: synthesis, photophysics and antifungal activity. Dyes and Pigments 173:. [CrossRef]
- Farmakiotis D, Kontoyiannis DP (2017) Epidemiology of antifungal resistance in human pathogenic yeasts: current viewpoint and practical recommendations for management. Int J Antimicrob Agents 50:318–324. [CrossRef]
- Arastehfar A, Lass-Flörl C, Garcia-Rubio R, et al. (2020) The quiet and underappreciated rise of drug-resistant invasive fungal pathogens. Journal of Fungi 6:1–34. [CrossRef]
- Arendrup MC, Patterson TF (2017) Multidrug-resistant Candida: Epidemiology, molecular mechanisms, and treatment. Journal of Infectious Diseases 216:S445–S451. [CrossRef]
- Fioriti S, Brescini L, Pallotta F, et al. (2022) Antifungal Combinations against Candida Species: From Bench to Bedside. Journal of Fungi 8:. [CrossRef]
- Carmo A, Rocha M, Pereirinha P, et al. (2023) Antifungals: From Pharmacokinetics to Clinical Practice. Antibiotics 12:. [CrossRef]
- Caballero U, Kim S, Eraso E, et al. (2021) In vitro synergistic interactions of isavuconazole and echinocandins against Candida auris. Antibiotics 10:. [CrossRef]
- Kane A, Dinh H, Campbell L, et al. (2024) Spectrum of activity and mechanisms of azole–bisphosphonate synergy in pathogenic Candida. Microbiol Spectr 12:. [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque IKP, de Santana DL, de Assis Graciano dos Santos F, et al. (2024) Novel aza-bicyclic 2-isoxazoline acylhydrazone hybrids and their synergistic potential with fluconazole against a drug-resistant Candida albicans strain. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology 55:1811–1816. [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Cadena K, Dias M, Costa-Barbosa A, et al. (2021) Development and Characterization of Monoolein-Based Liposomes of Carvacrol, Cinnamaldehyde, Citral, or Thymol with Anti-Candida Activities. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 65:e01628-20.
- Gutierrez-Gongora D, Woods M, Prosser RS, Geddes-McAlister J (2024) Natural compounds from freshwater mussels disrupt fungal virulence determinants and influence fluconazole susceptibility in the presence of macrophages in Cryptococcus neoformans. Microbiol Spectr 12:e02841-23. [CrossRef]
- Lu H, Shrivastava M, Whiteway M, Jiang Y (2021) Candida albicans targets that potentially synergize with fluconazole. Crit Rev Microbiol 47:323–337. [CrossRef]
- Berman J, Krysan DJ (2020) Drug resistance and tolerance in fungi. Nat Rev Microbiol 18:319–331. [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto AT, Sharma C, Rogers PD (2020) Molecular and genetic basis of azole antifungal resistance in the opportunistic pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 75:257–270. [CrossRef]
- Ivnitski-Steele I, Holmes AR, Lamping E, et al. (2009) Identification of Nile red as a fluorescent substrate of the Candida albicans ATP-binding cassette transporters Cdr1p and Cdr2p and the major facilitator superfamily transporter Mdr1p. Anal Biochem 394:87–91. [CrossRef]
- Bidaud AL, Djenontin E, Botterel F, et al. (2020) Colistin interacts synergistically with echinocandins against Candida auris. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55:. [CrossRef]
- Bidaud AL, Botterel F, Chowdhary A, Dannaouia E (2019) In Vitro Antifungal Combination of Flucytosine with Amphotericin B, Voriconazole, or Micafungin against Candida auris Shows No Antagonism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63:. [CrossRef]
- Bidaud AL, Schwarz P, Herbreteau G, Dannaoui E (2021) Techniques for the assessment of in vitro and in vivo antifungal combinations. Journal of Fungi 7:1–16. [CrossRef]
- Schwarz P, Nikolskiy I, Bidaud AL, et al. (2022) In Vitro Synergy of Isavuconazole Combined With Colistin Against Common Candida Species. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:. [CrossRef]
- Di Veroli GY, Fornari C, Wang D, et al. (2016) Combenefit: An interactive platform for the analysis and visualization of drug combinations. Bioinformatics 32:2866–2868. [CrossRef]
- Sabino R, Sampaio P, Carneiro C, et al. (2011) Isolates from hospital environments are the most virulent of the Candida parapsilosis complex. BMC Microbiol 11:. [CrossRef]
- Madesh M, Balasubramanian KA (1997) A microtiter plate assay for superoxide using MTT reduction method. Indian journal of biochemistry and biophysics 34:535–539.
- Carneiro C, Correia A, Collins T, et al. (2015) DODAB:monoolein liposomes containing Candida albicans cell wall surface proteins: A novel adjuvant and delivery system. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 89:190–200. [CrossRef]
- McKenzie CGJ, Koser U, Lewis LE, et al. (2010) Contribution of Candida albicans cell wall components to recognition by and escape from murine macrophages. Infect Immun 78:1650–1658. [CrossRef]
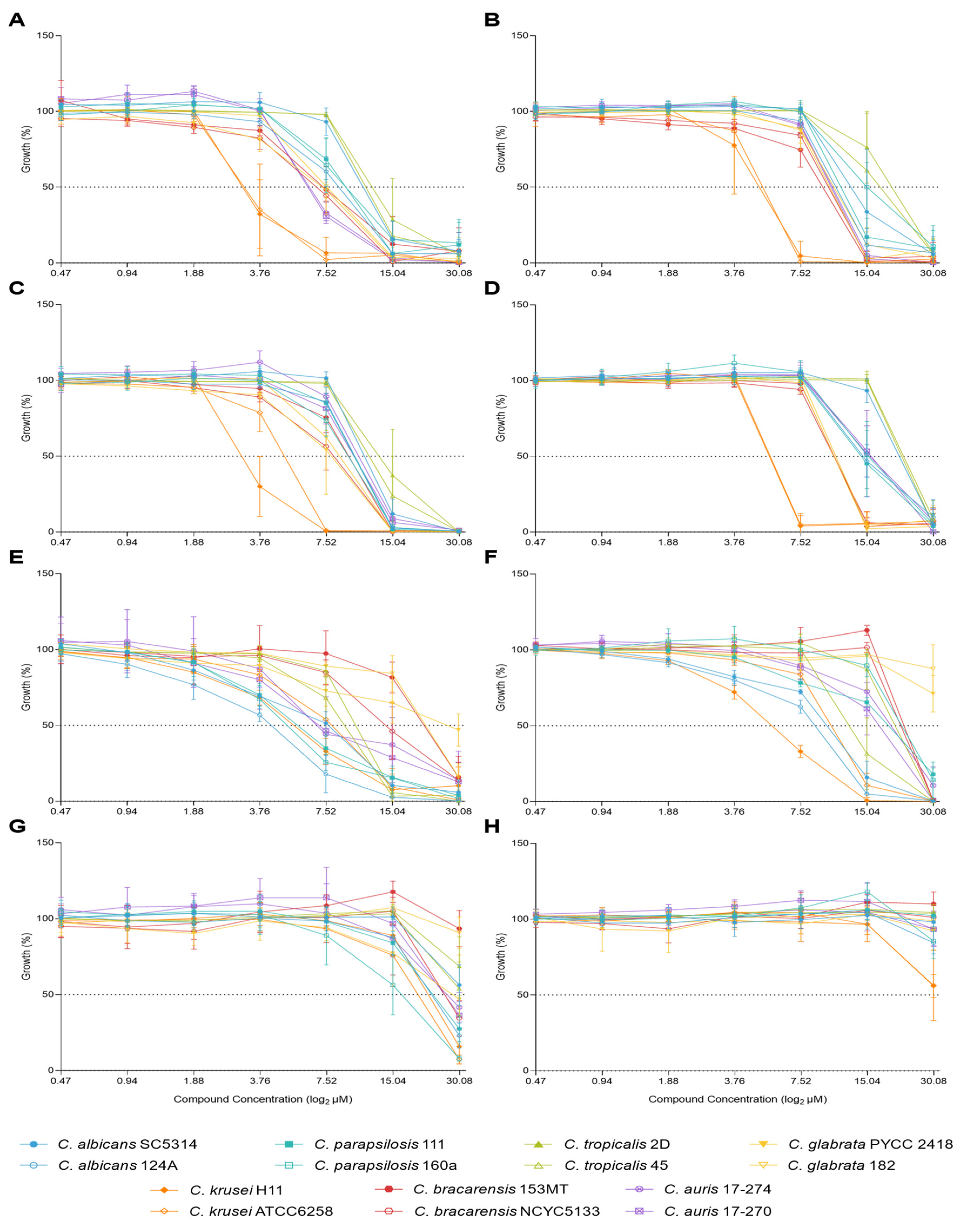
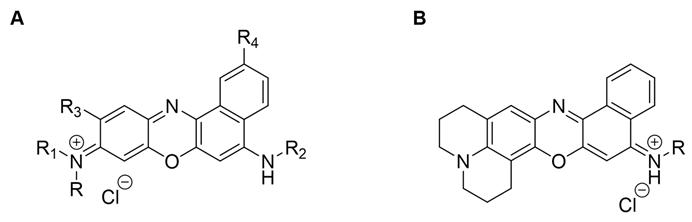 | ||||||||
| Core Structure | Compound | R | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | MIC (µM) | Ref |
| A | C34 | (CH2)2CH3 | (CH2)2CH3 | (CH2)2CH3 | H | H | 1.56 |
As 7 [13] |
| A | C35 | (CH2)2CH3 | (CH2)2CH3 | (CH2)3Cl | H | H | 6.25 | As C35 / 6 [11] |
| B | A44 | (CH2)2CH3 | - | - | - | - | 6.25 | As 4c [15] |
| B | A42 | (CH2)3Cl | - | - | - | - | 0.78 | As 4d [15] |
| MIC 24h (µM) | MIC 48h (µM) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | C34 | C35 | A44 | A42 | C34 | C35 | A44 | A42 | ||
| Mode | 15 | 15 | 7.5 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 30 | >30 | ||
| Range MIC | 3.75 – 15 | 3.75 – 15 | 7.5 – 30 | 30 - >30 | 7.5 – 30 | 7.5 – 30 | 7.5 - >30 | >30 | ||
| MIC GM | 10.1 | 12.9 | 12.3 | 40.4 | 15.8 | 17.4 | 24.6 | 60.0 | ||
| MIC of Drugs Alone | MIC of the Drugs in Combination | Lowest FICI for the Combination | Interpretation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Flu (µg/mL) | C34 (µM) |
Flu (µg/mL) | C34 (µM) |
||||||
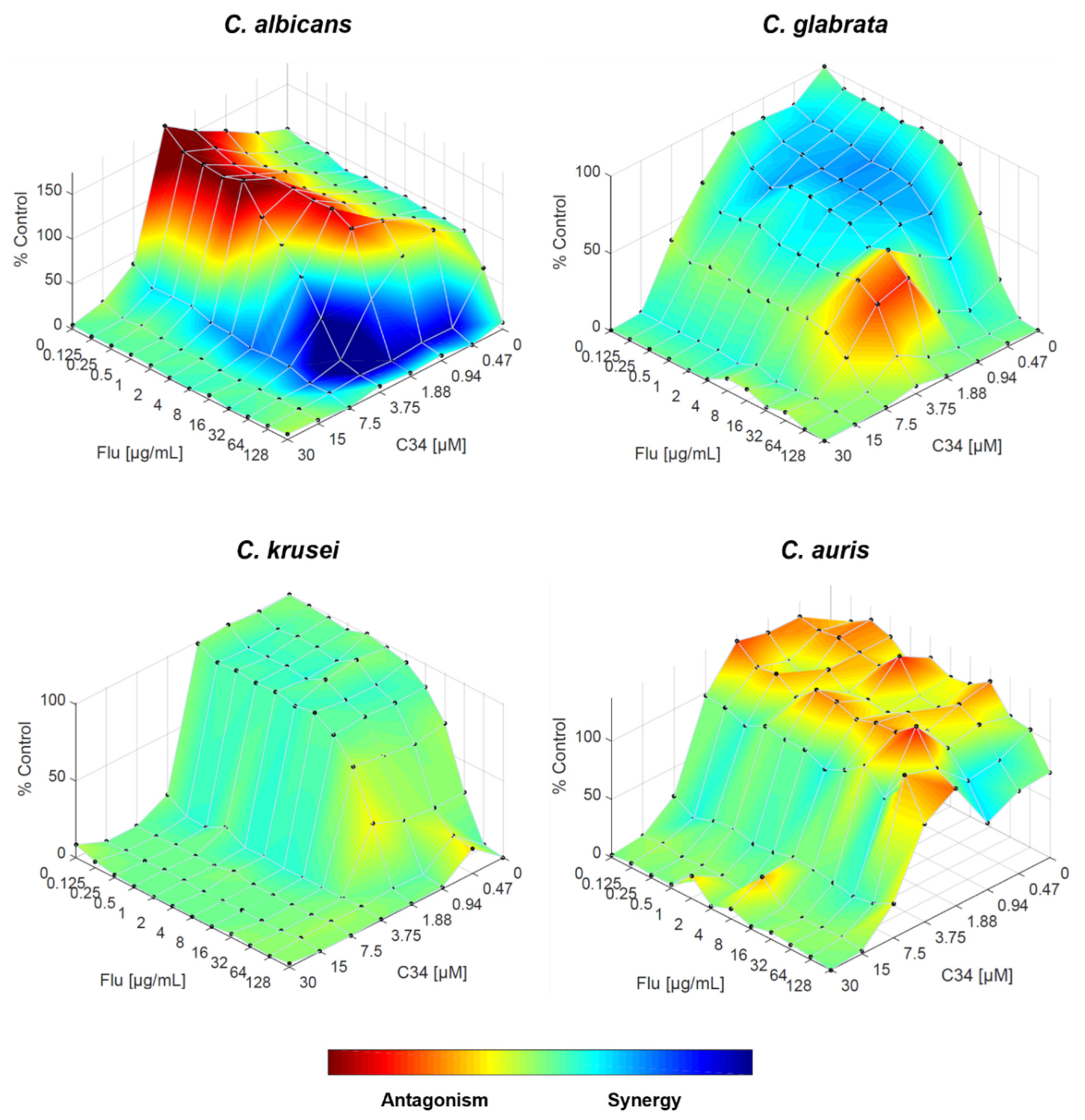
| C. albicans | 128 | 7.5 | 64 | 0.47 | 0.56 | IND | ||||
| C. glabrata | 16 | 7.5 | 64 | 1.88 | 4.25 | ANT | ||||
| C. krusei | 32 | 3.75 | 0.125 | 3.75 | 1 | IND | ||||
| C. auris | >128 | 7.5 | 0.125 | 7.5 | 1 | IND | ||||
| MIC of Drugs Alone | MIC of the Drugs in Combination | Lowest FICI for the Combination | Interpretation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Flu (µg/mL) | C35 (µM) |
Flu (µg/mL) | C35 (µM) |
||||||
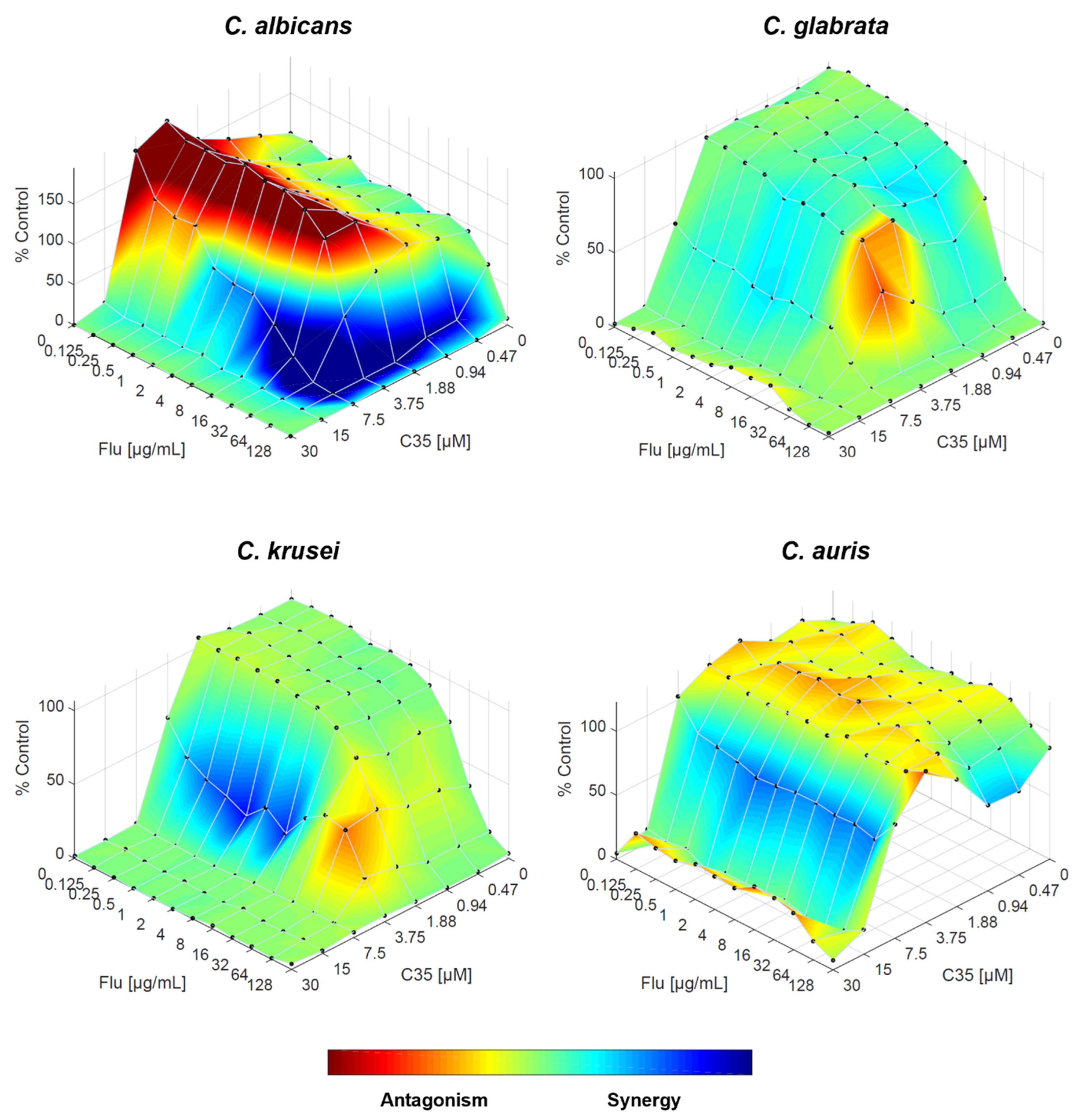
| C. albicans | 128 | 15 | 64 | 0.47 | 0.53 | IND | ||||
| C. glabrata | 16 | 7.5 | 8 | 0.47 | 0.56 | IND | ||||
| C. krusei | 32 | 7.5 | 0.125 | 3.75 | 0.50 | SYN | ||||
| C. auris | >128 | 15 | 0.125 | 15 | 1 | IND | ||||
| MIC of Drugs Alone | MIC of the Drugs in Combination | Lowest FICI for the Combination | Interpretation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Flu (µg/mL) | A44 (µM) |
Flu (µg/mL) | A44 (µM) |
||||||
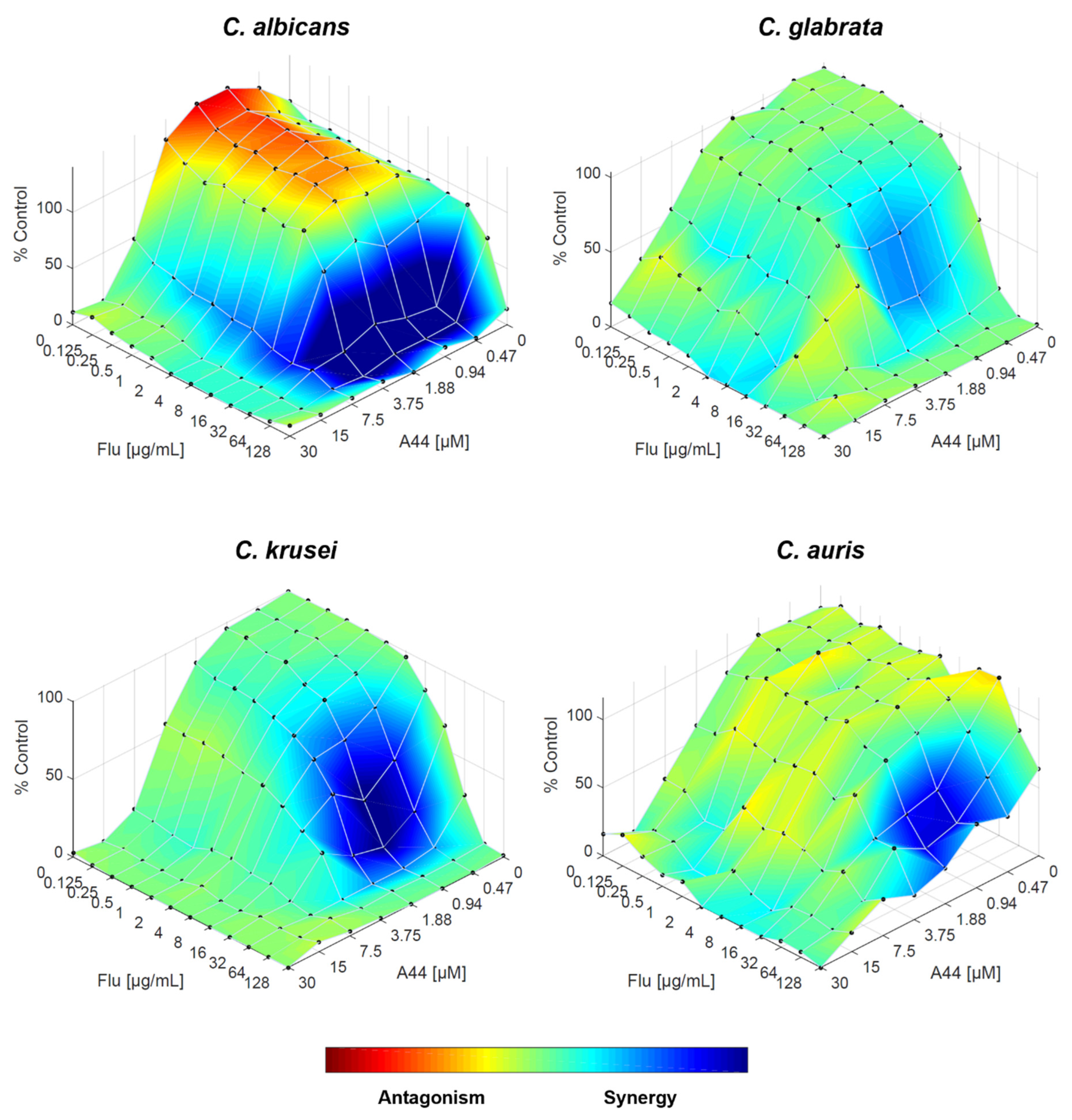
| C. albicans | 128 | 7.5 | 32 | 0.47 | 0.31 | SYN | ||||
| C. glabrata | 16 | 15 | 8 | 0.47 | 0.53 | IND | ||||
| C. krusei | 32 | 7.5 | 8 | 0.94 | 0.38 | SYN | ||||
| C. auris | >128 | 15 | 64 | 1.88 | 0.38 | SYN | ||||
| MIC of Drugs Alone | MIC of the Drugs in Combination | Lowest FICI for the Combination | Interpretation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Flu (µg/mL) | A42 (µM) |
Flu (µg/mL) | A42 (µM) |
||||||
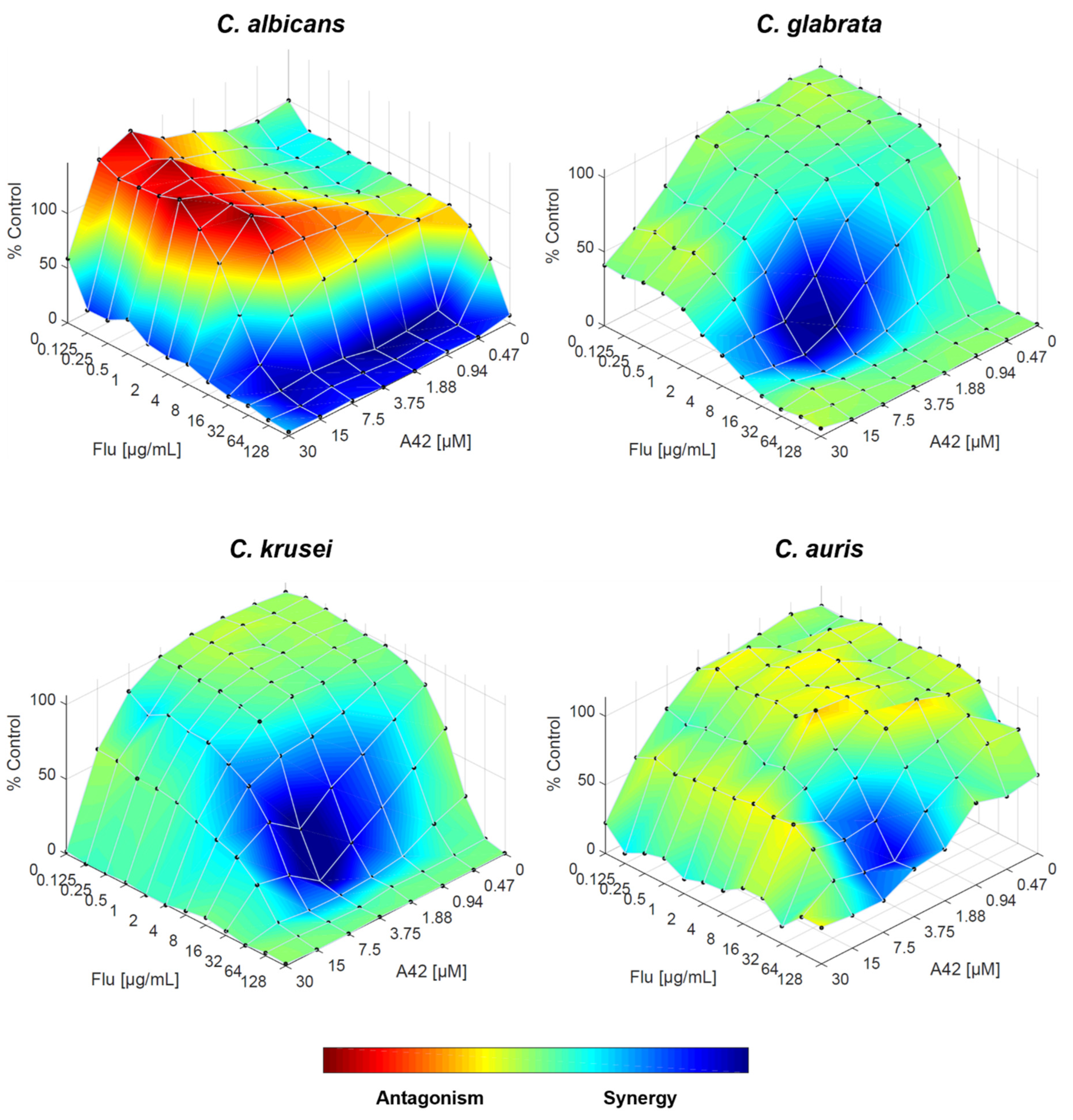
| C. albicans | 128 | >30 | 32 | 0.47 | 0.26 | SYN | ||||
| C. glabrata | 16 | 30 | 4 | 3.75 | 0.38 | SYN | ||||
| C. krusei | 32 | 30 | 8 | 1.88 | 0.31 | SYN | ||||
| C. auris | >128 | 30 | 64 | 3.75 | 0.31 | SYN | ||||
| Fluconazole (µg/mL) |
A42 (µM) |
Growth Inhibition (%) | Combination Improvement over Fluconazole (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | MIC | Tested | MIC | Tested | Flu | A42 | Combination | ||||
| C. albicans | 128 | 32 | >30 | 1.88 | 71% | 17% | 92% | 21% | |||
| C. glabrata | 16 | 4 | 30 | 1.88 | 36% | 24% | 36% | 0% | |||
| C. krusei | 32 | 8 | 30 | 1.88 | 17% | 21% | 26% | 9% | |||
| C. auris | >128 | 64 | 30 | 1.88 | 32% | 0% | 86% | 54% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





