1. Introduction
Earth is often referred to as the "blue planet" because about 71% of its surface is covered by salt water, primarily in oceans and seas. However, less than 5% of the Earth’s water is freshwater, most of which is in ice caps, glaciers, groundwater aquifers, and lakes [
1]. Lakes are crucial resource for life Earth, providing essential ecosystem services to human populations [
2]. Aside from few remote lakes, they have historically been vital for human settlements, supplying food, water for domestic and industrial use [
3], and offering economic benefits in transportation, recreational activities, irrigation, and agriculture [
4]. Even in remote, pristine areas like high mountains or Arctic regions, lakes are exposed to increasing contamination through passive or active long-range transport of various inorganic and organic contaminants [
5,
6,
7]. Additionally, lakes continuously receive significant amounts of materials from their watersheds [
8], leading to plastic pollution that impacts sediment, water column and biota [
9,
10,
11]. Besides natural processes of eutrophication, nutrient discharges enhanced by human activity present another major challenge for environmental sustainability and lake management [
12]. Human activities have had such a significant impact that it is now crucial to take action to protect freshwater ecosystems, by enhancing their resilience to various pressures, preventing any further loss of biodiversity and improving sustainability [
13,
14,
15].
In this context, habitat restoration has been identified globally as a sustainable and effective solution at worldwide level [
16,
17]. Restoration programs mainly focus on improving communities of foundational organisms that can better structure habitats and support biodiversity. Numerous examples from marine ecosystems highlight projects aimed at restoring coral reefs in tropical areas [
18,
19,
20] and
Posidonia oceanica in the Mediterranean Sea [
21,
22,
23], both fundamental habitats for marine ecosystems and human uses. For lacustrine ecosystems, restoration efforts have mainly addressed the growing issue of eutrophication, particularly through biomanipulation strategies that involve removing certain species of fish to control zooplankton density [
24,
25], and to a lesser extent, introducing submerged macrophytes [
26,
27,
28].
Lake Como, the deepest lake in Italy, provides substantial ecosystem services, including drinking water, recreational uses, industrial uses and irrigation. However, its location in a heavily industrialized area, means it is subject to pollution from watershed activities and even from melting glaciers [
29,
30]; the lake also receives water inflows from rivers and various Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTP) that struggle to effectively reduce contaminants from urban and industrial sources [
31]. Due to the inefficiency of current water treatment practices, despite the current water treatment implementations, many pollutants continue to enter the ecosystem and accumulate in edible fish species, including
Alosa agone [
32,
33,
34]. In conclusion, various human impacts, such as plastic pollution, climate change and urbanization have led to a significant reduction in biodiversity and a decline in key freshwater ecosystems that provide essential services. Urgent action is required to address the challenges and protect these crucial environments.
This study aims to maximize and ensure the autonomous repopulation of the littoral zone in a specific area of Lake Como using both traditional and innovative techniques. These include utilizing artificial biodegradable substrates for the implantation of submerged macrophytes, which play an important role in increasing littoral biodiversity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Lake Como, recognized for its stunning landscapes and rich history, is indeed one of the most remarkable alpine oligomictic lakes in Europe. Its unique geological formations, shaped by significant Messinian River erosion, contribute to its impressive depth and steep underwater topography. Oligomictic lakes are characterized by minimal mixing, which is evident in Lake Como's thermal stratification during the warmer months.
In summer, the lake's water layers form distinct thermal layers, with warmer water on top and colder water below, leading to different ecological conditions in various depths. The phenomenon of isothermy, where the entire body of water reaches a uniform temperature, typically occurs at the end of winter when surface temperatures drop, and mixing can occur. This process can affect the distribution of nutrients and oxygen levels throughout the lake.
The limited submerged areas within depths of 1.5 to 10 meters suggest that the lake's surface area is primarily composed of deeper water, which can heavily influence the biodiversity, and habitats present in the lake. These conditions make Lake Como not only a vital ecological region but also a popular destination for tourism and outdoor activities, such as boating, hiking, and enjoying the natural scenery. The interplay of its geological history, hydrodynamics, and climatic conditions contributes to making Lake Como a unique ecological and recreational gem in Italy.
To maximize the effectiveness of the intervention, the chosen area is the coastal environment located between a depth of 1.5 and 8 m. In this specific zone, habitats offer greater complexity and are favourable due to the presence of light, higher temperatures, and high biodiversity. Additionally, the restoration process at this depth is relatively simple, as decompression stops of divers are not required. These stops would increase the duration and complexity of diving, as well as the costs for respiratory mixtures containing helium or other diluents to lower oxygen concentration. Conversely, it is possible to use oxygen-enriched mixtures and nitrogen-depleted mixtures, which allow for longer dive times at shallow depths with limited costs. The underwater campaign was conducted using either air or nitrox up to 32%.
2.2. Target Species
For this study, the target species is
Vallisneria spiralis, a submerged plant species originating from Asia but native in the area of Lake Como [
35]. The choice of using this species is based on two main reasons: first, it is commonly found in meso- to eutrophic water habitats [
36], where it forms dense stands due to its stoloniferous growth habits [
37]; second, it is widely considered as an ecological engineering species for aquatic ecosystem restoration [
38]. As the other submerged macrophytes, this species depends on sediments for nutrient uptake, since the available nutrients have higher concentrations in pore water than in water column [
39]. The presence of this plant implies a strong impact on the surrounding environment promoting the shift of large amount of oxygen to roots to allow their respiration; this phenomenon creates oxic conditions around roots and influences several redox-sensitive biogeochemical processes at bottom sediment level [
39,
40].
2.3. Mesocosm Experiment
Vallisneria spiralis was taken directly from the coastal environment of Lake Como in the surrounding areas selected for replanting. The choice was made considering that resident populations may have the best adaptive characteristics for rooting. The number of individuals was kept as low as possible in order to minimise the impact of the collection on relict populations. The removed specimens were taken, preferring stolons during the detachment, and therefore had little chance of survival.
Laboratory conditions selected for the growth and reproduction of Vallisneria spiralis were considering the autoecology of the target species. Two tanks were equipped with thermostatic heaters set at 26°C, which is the maximum temperature recorded in summer at depth up to 10 meters. Therefore, this is the highest temperature to which individuals of Vallisneria spiralis have adapted to live in the coastal areas of Lake Como. The tanks were also equipped with LED lights with a 6000K full spectrum growing light. As a first approach, the light has been kept constant always at maximum power, but this condition favoured the uncontrolled development of algae. The illumination period was then reduced to 12 hours, and the conditions improved, but algae was still present. Therefore, six hours of light and six hours of alternating darkness were set. The short period of light inhibits the development of filamentous microalgae while allowing the phanerogams a good growth. The tanks were fitted with ceramic filter rings and sponges to prevent the build-up of organic matter and to counteract Chlorophyceae blooms. Despite these precautions, one tank has still experienced blooms, possibly due to the delayed asexual reproduction of plants caused by lower nutrient levels or its closeness to natural light. To stimulate Vallisneria spiralis growth, CO2 was injected into the tank at a concentration of six bubbles per minute for every 180 L of water. The phenomenon of pearling occurred, where oxygen released by plants forms visible bubbles on their leaves, however the growth rates remained relatively similar.
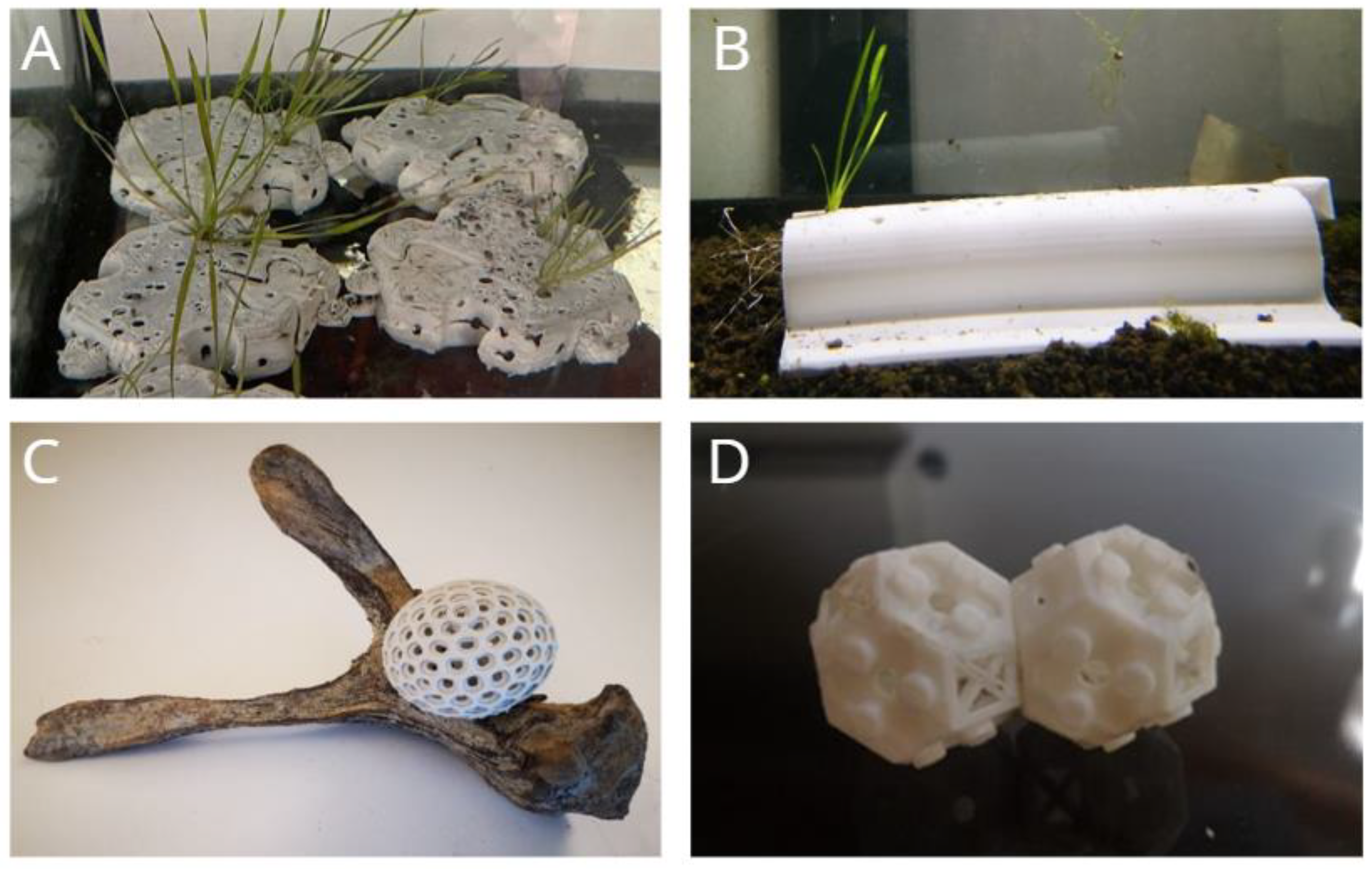
Biodegradable substrates were developed to establish suitable planting environments in each tank to promote the modular rooting of macrophytes. The substrates were designed, shaped, and 3D printed using computer graphics and a combination of polylactide (PLA) and natural composite materials found on-site. The goal was to minimize alteration of natural compositions while ensuring a functional structure for agamic rooting and reproduction in the environment. The 3D models were continuously modified to improve effectiveness, with alterations made to roughness, number of cavities, dimensions, and planting techniques. Four different substrates were produced to facilitate the rooting of aquatic plants in varying coastal environments:
- (1)
PATCH type: A hydrodynamic geometric module designed to be placed over sandy sediment or inside muddy ground. It features a reduced thickness and shape that provides resistance to waves, able to withstand water turbulence up to a depth of 10 m (
Figure 1A).
- (2)
LINEAR PATCH type: a substrate designed to facilitate the growth of plants in a linear formation, promoting rapid expansion in flat and uniform environments. This substrate is specifically intended to combat the spread of invasive species, like
Egeria densa (
Figure 1B).
- (3)
BRANCH or BOULDER type: an ovoid object useful to occupy the space between rocky blocks or submerged branches, equipped with a point of attachment to the bottom by screw (or dowel) passing through. The geometric shape allows a storage of a large amount of nutrient reserve and therefore ensures greater autonomy in environments with little organic soil available for engraftment (
Figure 1C).
- (4)
BLOCK type: a modular object that can be used to create any structure by combining small blocks. It has been specifically designed to be used in mixed environments where other objects may not be suitable (
Figure 1D).
All four types of substrates have been designed with a primarily clustered arrangement to promote recolonization with diffuse patches. This approach was selected to increase intervention efficiency by reducing the need for multiple underwater interventions and facilitating natural recolonization between clusters. Most substrates were modular, allowing for the creation of a continuous surface. This flexibility enables on-site adjustment of patch size to maximize functionality for root processes and recolonization. The starting substrate was enhanced with Osmocote fertilizer (Osmocote Exact Tablet 8-9M;
https://icl-growingsolutions.com) at a concentration proportional to the recommended dosage for aquatic plants in order to improve the rooting phase. However, it was found that the dosage was slightly undersized and was corrected in the second moment. Additionally, a support fertilizer has been developed using compounds derived from the target ecosystem of Lake Como. This fertilizer was placed within the substrate and calibrated to provide nutrients for approximately one year. The substrate's morphology also allows for the addition of extra nutrients if needed, even after implantation in the environment through underwater intervention.
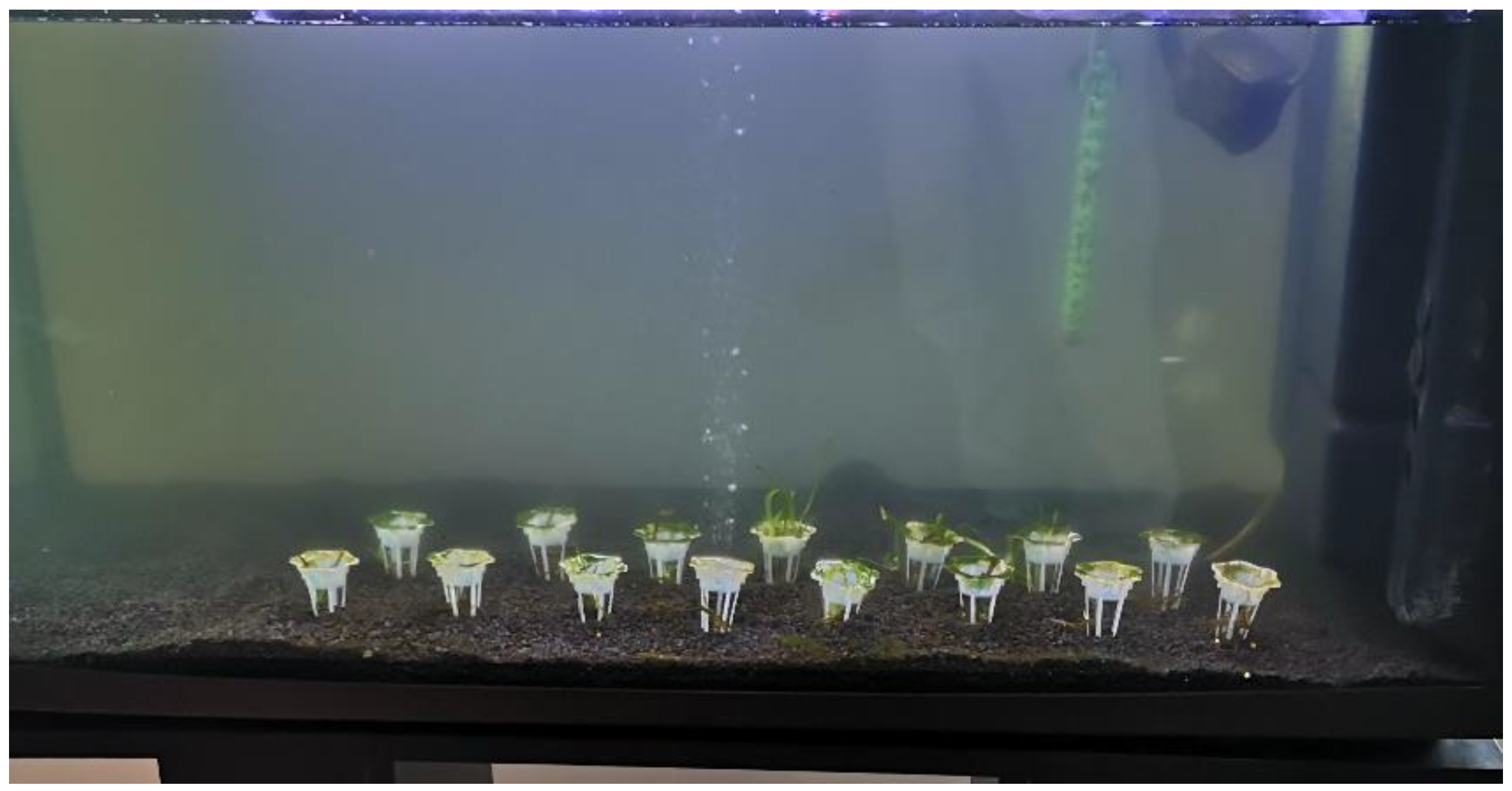
The tanks were set up in February and March 2021, with 12 specimens of
Vallisneria spiralis, from the lake. It was decided to proceed by selecting small adventitious individuals in order to easily insert their root systems into the artificial substrate, ensuring proper development, growth of the initial individual, and colonization of the bottom by subsequent specimens reproduced via stolons (
Figure 2).
After the rooting phase, which took two weeks, the growth of the stoloniferous and foliar apparatus was measured. After 11 months it was necessary to renew the Osmocote content in order to renew reproduction.
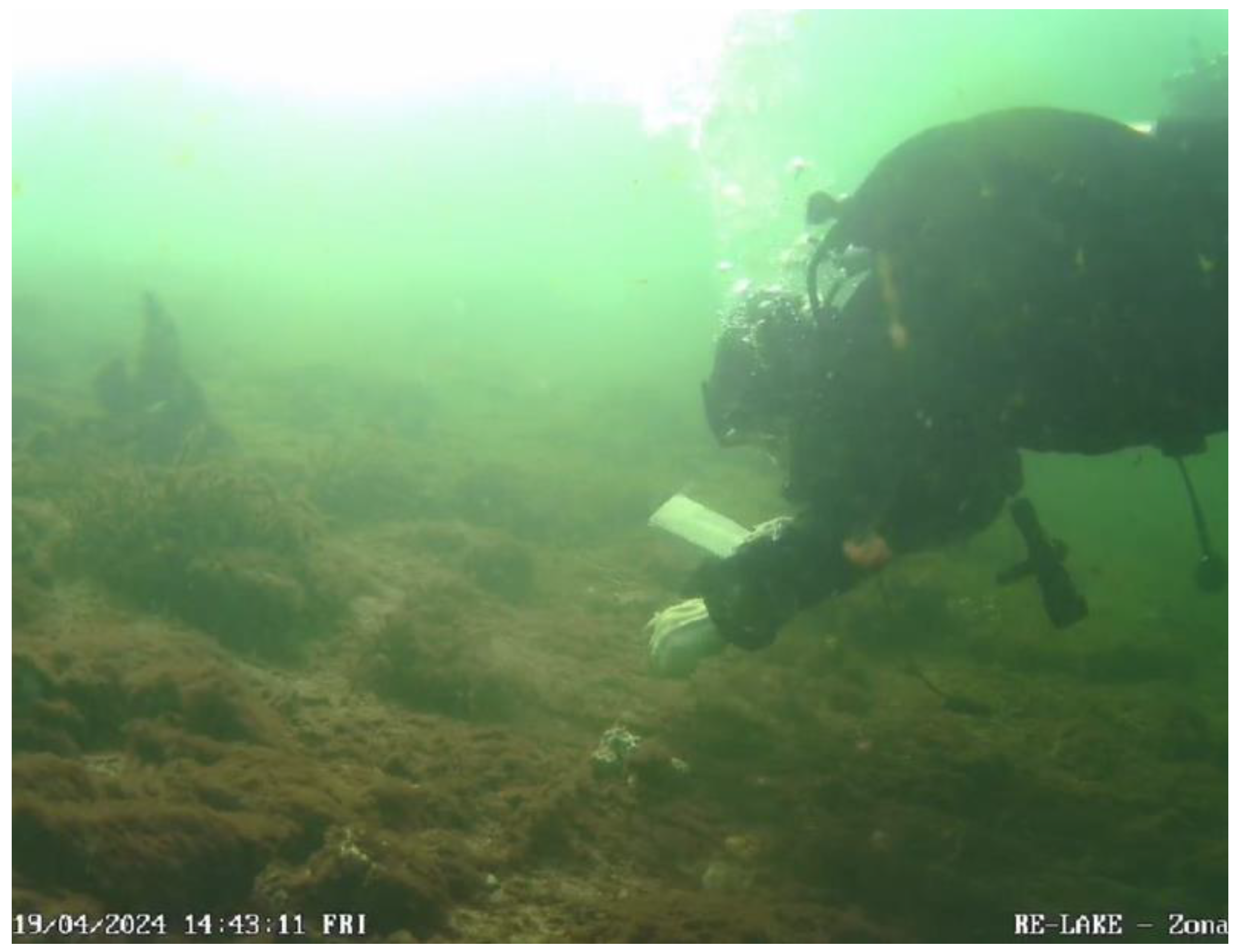
Once fully growth, three
Vallisneria spiralis specimens were implanted into each substrate and placed in a separate tank. In November 2023, an underwater webcam was installed to monitor the first 15 m2 littoral area at a weekly basis, and
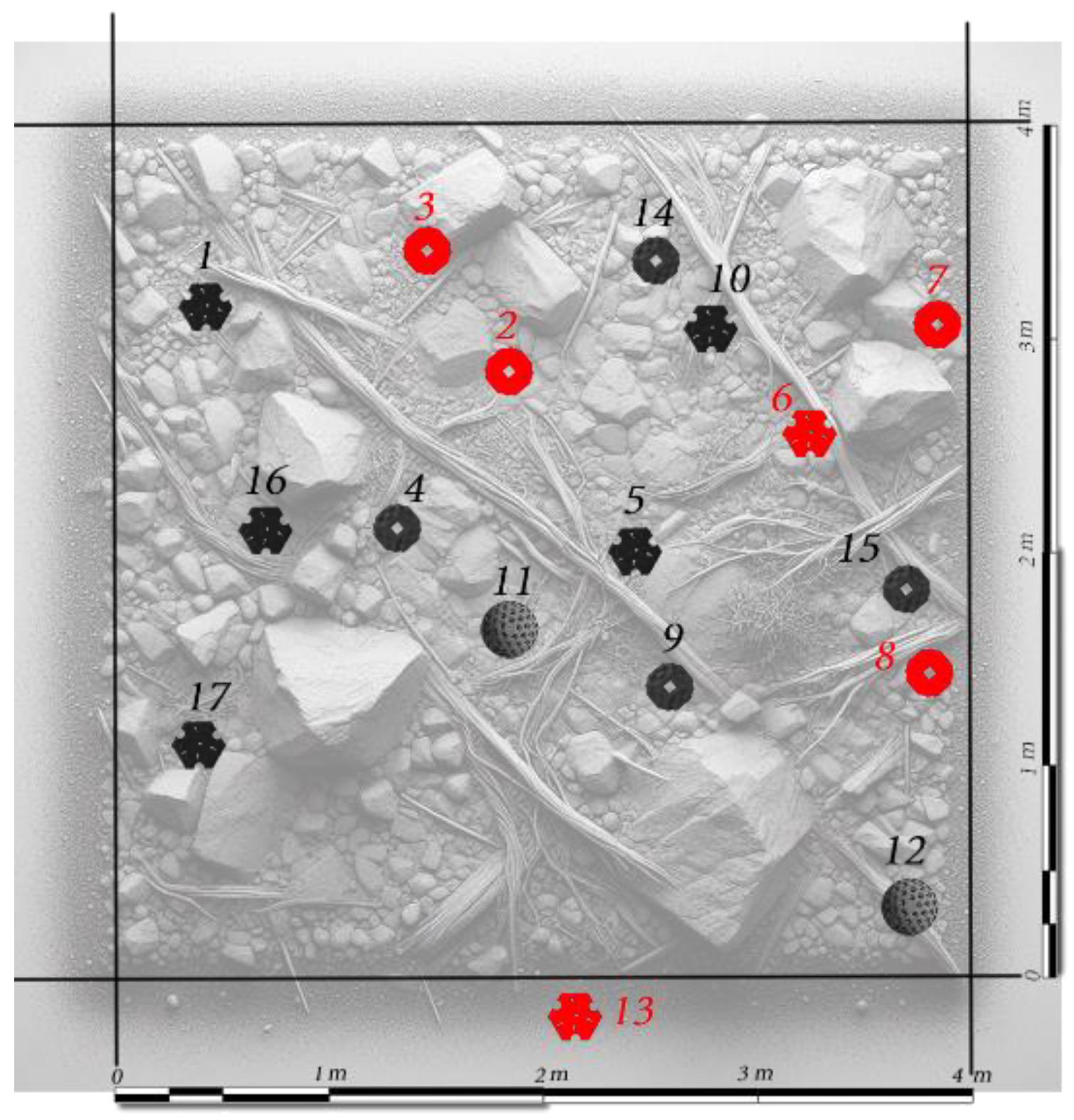
Vallisneria spiralis specimens were implanted in Lake Como. A second implantation survey was carried out in February 2024. The installation (
Figure 3) was carried out for 7 patch-type, 3 branch-type and 8 block-type supports were settled (N = 18). The patch-type supports were installed manually and attached to the substrate using a metal clamp. Two branch supports were positioned by sinking them halfway into the sandy substrate where it was loose or fixed between rock blocks to prevent displacement by currents or turbulent movement. One was removed by water turbulence, so it was immediately reinserted into the environment after the detachment. The plants remained vital despite the slippage.
Later, 8 additional block type supports were added through remote implantation using an underwater drone. They were initially positioned using a robotic arm and then fixed in a subsequent phase with a clamp. This type proved to be the most unstable, resulting in the highest percentage of detachment due to the time elapsed between the initial placement and the second manual attachment with metal clamps. Besides virtual check using the underwater webcam, a comprehensive monitoring survey in the field was carried out in March 2024. The survival rate was quantified with a final check on April 2024 through underwater survey immersion, ROV video recording, and webcam observation positioned in front of the intervention area.
3. Results
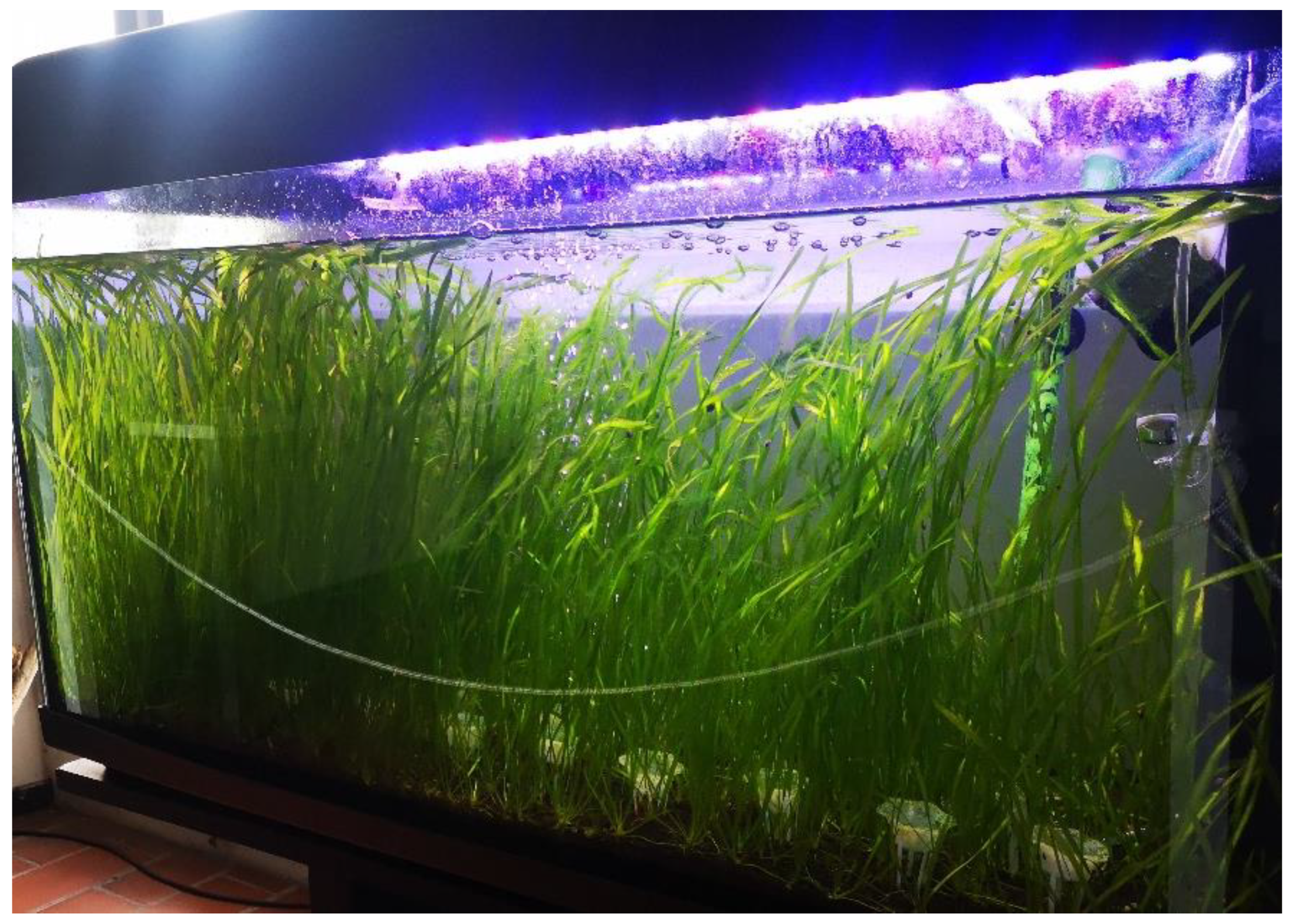
Laboratory conditions set in tanks for
Vallisneria spiralis appeared to be optimal as the growth of the stoloniferous and foliar apparatus reached peaks of 4 mm/day until the tank space was filled (
Figure 4).
From the initial number of specimens (N = 12), the tank counted 400
Vallisneria spiralis individuals after 4 months and more than 700 specimens before the installation phase. Regarding the field experiment, of the 18 tutors introduced into the environment, 4 block tutors (
Figure 5) were unsuccessful plantings since they were deployed during scientific outreach and citizen science activities via ROV without the opportunity of immediate manual bottom fixation. Without considering those 4, 12 out of 14 remained viable (85.7%), and only 2 detached from the bottom. Thus, the main cause of
Vallisneria spiralis death is solely linked to the detachment of the artificial substrate from the bottom and the subsequent sliding.
Currently, a second installation and monitoring process is taking place on a larger area (400 m2) to further define the effectiveness of the restoration process of submerged prairies of phanerogams on a more ecologically functional scale.
4. Discussion
At present, while
Vallisneria spiralis is well known as an ecological engineering species for aquatic ecosystem restoration [
38], there is a lack of reviews concerning effective restoration projects of
Vallisneria spiralis populations in the environment, especially when dealing with biodegradable matrices as substrates. Only a few restoration campaigns, without including biodegradable matrices, were carried out using
V. americana, another species of the same genus
Vallisneria [
41,
42]. Therefore, the results of this study are the first regarding a restoration project using this species combined with biodegradable substrates. According to literature, only three works [
43,
44,
45] have examined the use of these materials in restoration programs with marine seagrass. Balestri et al. [
43] work is the most similar to this research system: both are based on the use of biodegradable polymers. But, instead of polylactide (PLA) polymer, they created biodegradable substrates applying Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV). However, PLA fibres used for this experiment are considered more resistant to biodegradation in comparison with PHBV fibres [
46]. With regards to species used in restoration programs, different seagrasses were previously used:
Cymodocea nodosa and
Zostera noltei [
43],
Halodule wrightii [
44] and
Amphibolis [
45]. All the studies mentioned came to the conclusion that the application of sediment-filled biodegradable tubes or bio-container recorded a significant acceleration in the seagrass recovery and restoration. Moreover, Balestri et al. [
43] specified that bio-containers degraded after about three years, a period long enough to obtain well-developed plants in nurseries.
In conclusion, this is the first project aimed at implementing the restoration of Vallisneria spiralis in a freshwater environment, including the coastal area of Lake Como. This initiative seeks to preserve biodiversity for the environmental sustainability of the lake shores and to serve as a model for future restoration efforts. Furthermore, as preserving biodiversity is crucial for the environmental sustainability of the lake shores, other experiments are underway and will be further developed using other aquatic macrophytes such as Potamogeton and Myriophyillum spp.
Author Contributions
N. Castelnuovo: Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration. B. Villa: Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Visualization. G. Boldrocchi: Validation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. P. Iotti: Validation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. R. Bettinetti: Validation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Herdendorf, C.E. Distribution of the world’s large lakes. In Large Lakes: Ecological Structure and Function; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1990; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Downing, J.A.; Prairie, Y.T.; Cole, J.J.; Duarte, C.M.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; McDowell, W.H.; Kortelainen, P.; Caraco, N.F.; Melack, J.M.; Middelburg, J.J. The global abundance and size distribution of lakes, ponds, and impoundments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönmark, C.; Hansson, L.A. Environmental issues in lakes and ponds: current state and perspectives. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Keeler, B.; Polasky, S.; Poudel, R.; Rhude, K.; Rogers, M. Ecosystem services of Earth’s largest freshwater lakes. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 41, 101046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenset, A.; Christensen, G.N.; Carroll, J.; Zaborska, A.; Berger, U.; Herzke, D.; Gregor, D. Historical trends in persistent organic pollutants and metals recorded in sediment from Lake Ellasjøen, Bjørnøya, Norwegian Arctic. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 146, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, P.; Vilanova, R.M.; Martínez, C.; Appleby, P.; Grimalt, J.O. The historical record of atmospheric pyrolytic pollution over Europe registered in the sedimentary PAH from remote mountain lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, K.; Urrutia, R.; Barra, R.; Mariottini, M.; Treutler, H.C.; Araneda, A.; Focardi, S. Records of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments of four remote Chilean Andean lakes. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, V.; Chandra, S.; Aherne, J.; Alfonso, M.B.; Antão-Geraldes, A.M.; Attermeyer, K.; Bao, R.; et al. Plastic debris in lakes and reservoirs. Nature 2023, 619, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellasi, A.; Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Galafassi, S.; Volta, P.; Bettinetti, R. Microplastic contamination in freshwater environments: A review, focusing on interactions with sediments and benthic organisms. Environments 2020, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avignon, G.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Ricciardi, A. Microplastics in lakes and rivers: an issue of emerging significance to limnology. Environ. Rev. 2022, 30, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusaucy, J.; Gateuille, D.; Perrette, Y.; Naffrechoux, E. Microplastic pollution of worldwide lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K. Fresh water availability and its global challenge. Br. J. Multidiscip. Adv. Stud. 2023, 4, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, C.J.; Beheregaray, L.B. Recent and rapid anthropogenic habitat fragmentation increases extinction risk for freshwater biodiversity. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 2857–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudgeon, D. Prospects for sustaining freshwater biodiversity in the 21st century: linking ecosystem structure and function. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2010, 2, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Subiza, E.A.; Epele, L.B. Drivers of biodiversity loss in freshwater environments: A bibliometric analysis of the recent literature. Aquat. Conserv.: Mar. Freshwater Ecosyst. 2021, 31, 2469–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawecka, K.A.; Bascompte, J. Habitat restoration and the recovery of metacommunities. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 60, 1622–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, J.M.; Walters, L.J.; Cook, G.S. Recovering trophic structure through habitat restoration: A review. Food Webs 2020, 25, e00162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström-Einarsson, L.; Babcock, R.C.; Bayraktarov, E.; Ceccarelli, D.; Cook, N.; Ferse, S.C.; Hancock, B.; et al. Coral restoration–A systematic review of current methods, successes, failures and future directions. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0226631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’Ath, G.; Fabricius, K.E.; Sweatman, H.; Puotinen, M. The 27–year decline of coral cover on the Great Barrier Reef and its causes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2012, 109, 17995–17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. Long-term change in bioconstruction potential of Maldivian coral reefs following extreme climate anomalies. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 5629–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escandell-Westcott, A.; Riera, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, N. Posidonia oceanica restoration review: Factors affecting seedlings. J. Sea Res. 2023, 191, 102337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansini, A.; Bosch-Belmar, M.; Berlino, M.; Sarà, G.; Ceccherelli, G. Collating evidence on the restoration efforts of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: current knowledge and gaps. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacchi, M.; De Falco, G.; Simeone, S.; Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; Ferrari, M.; Bianchi, C.N. Biogeomorphology of the Mediterranean Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2017, 42, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Han, S.; et al. Nontraditional biomanipulation: A powerful ecotechnology to combat cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic freshwaters. Innovation Life 2023, 1, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurajda, P.; Adámek, Z.; Janáč, M.; Roche, K.; Mikl, L.; Rederer, L.; Zapletal, T.; Koza, V.; Špaček, J. Use of multiple fish-removal methods during biomanipulation of a drinking water reservoir–evaluation of the first four years. Fish. Res. 2016, 173, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamarna, M.Z.; Tandyrak, R. Lakes restoration approaches. Limnol. Rev. 2021, 21, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hu, W. A bibliometric analysis of lake restoration with submerged macrophytes. Water 2023, 15, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammeorg, O.; Chorus, I.; Spears, B.; Nõges, P.; Nürnberg, G.K.; Tammeorg, P.; Søndergaard, M.; et al. Sustainable lake restoration: From challenges to solutions. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2024, 11, e1689. [Google Scholar]
- Bettinetti, R.; Quadroni, S.; Galassi, S.; Bacchetta, R.; Bonardi, L.; Vailati, G. Is meltwater from Alpine glaciers a secondary DDT source for lakes? Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinetti, R.; Quadroni, S.; Boggio, E.; Galassi, S. Recent DDT and PCB contamination in the sediment and biota of the Como Bay (Lake Como, Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, S.; Zuccato, E.; Fattore, E.; Riva, F.; Terzaghi, E.; Koenig, R.; Principi, P.; Di Guardo, A. Micropollutants in Lake Como water in the context of circular economy: A snapshot of water cycle contamination in a changing pollution scenario. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrocchi, G.; Monticelli, D.; Mazzoni, M.; Spanu, D.; Bettinetti, R. Accumulation of selected trace elements in shads from three lakes: first insights from Italian pre-alpine area. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoni, M.; Boggio, E.; Manca, M.; Piscia, R.; Quadroni, S.; Bellasi, A.; Bettinetti, R. Trophic transfer of persistent organic pollutants through a pelagic food web: The case of Lake Como (Northern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsecchi, S.; Babut, M.; Mazzoni, M.; Pascariello, S.; Ferrario, C.; De Felice, B.; Bettinetti, R.; Veyrand, B.; Marchand, P.; Polesello, S. Per-- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in fish from European lakes: Current contamination status, sources, and perspectives for monitoring. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 658–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portal to the Flora of Italy. Vallisneria spiralis L. FlorItaly Database. Available online: https://floritaly.plantdata.it/index.php?procedure=taxon_page&tipo=all&id=6693 (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Bolpagni, R.; Laini, A.; Soana, E.; Tomaselli, M.; Nascimbene, J. Growth performance of Vallisneria spiralis under oligotrophic conditions supports its potential invasiveness in mid--elevation freshwaters. Weed Res. 2015, 55, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.P.; Mort, M.E. Vallisneria (Hydrocharitaceae): novel species, taxonomic revisions, and hybridization. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 188, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, L. Identification of the spectral characteristics of submerged plant Vallisneria spiralis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racchetti, E.; Bartoli, M.; Ribaudo, C.; Longhi, D.; Brito, L.E.Q.; Naldi, M.; Iacumin, P.; Viaroli, P. Short-term changes in pore water chemistry in river sediments during the early colonization by Vallisneria spiralis. Hydrobiologia 2010, 652, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, M.; Benelli, S.; Bartoli, M. Vallisneria spiralis promotes P and Fe retention via radial oxygen loss in contaminated sediments. Water 2023, 15, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloesser, D.W.; Manny, B.A. Restoration of wildcelery, Vallisneria americana Michx., in the lower Detroit River of the Lake Huron-Lake Erie corridor. J. Great Lakes Res. 2007, 33 (Suppl. 1), 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanski, E.M. Culturing Vallisneria americana for restoration efforts; Univ. North Texas, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Balestri, E.; Vallerini, F.; Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Menicagli, V.; Vannini, C.; Lardicci, C. Use of bio-containers from seagrass wrack with nursery planting to improve the eco-sustainability of coastal habitat restoration. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 251, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenworthy, W.J.; Hall, M.O.; Hammerstrom, K.K.; Merello, M.; Schwartzschild, A. Restoration of tropical seagrass beds using wild bird fertilization and sediment regrading. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 112, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wear, R.J.; Tanner, J.E.; Hoare, S.L. Facilitating recruitment of Amphibolis as a novel approach to seagrass rehabilitation in hydrodynamically active waters. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2010, 61, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, A.; Feijoo, P.; de Llanos, R.; Carbonetto, B.; González-Torres, P.; Tena-Medialdea, J.; García-March, J.R.; Gámez-Pérez, J.; Cabedo, L. Microbiological Characterization of the Biofilms Colonizing Bioplastics in Natural Marine Conditions: A Comparison Between PHBV and PLA. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).