Submitted:
17 October 2024
Posted:
18 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modification of GO with NC
2.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.4. SEM Analysis
2.5. The Particle Size of NC and GO Suspensions
2.6. Preparation of WBDFs
2.7. Drilling Fluid Properties Measurements
2.7.1. Contact Angle Measurement
2.7.2. Filtration Properties
3. Results and Discussion
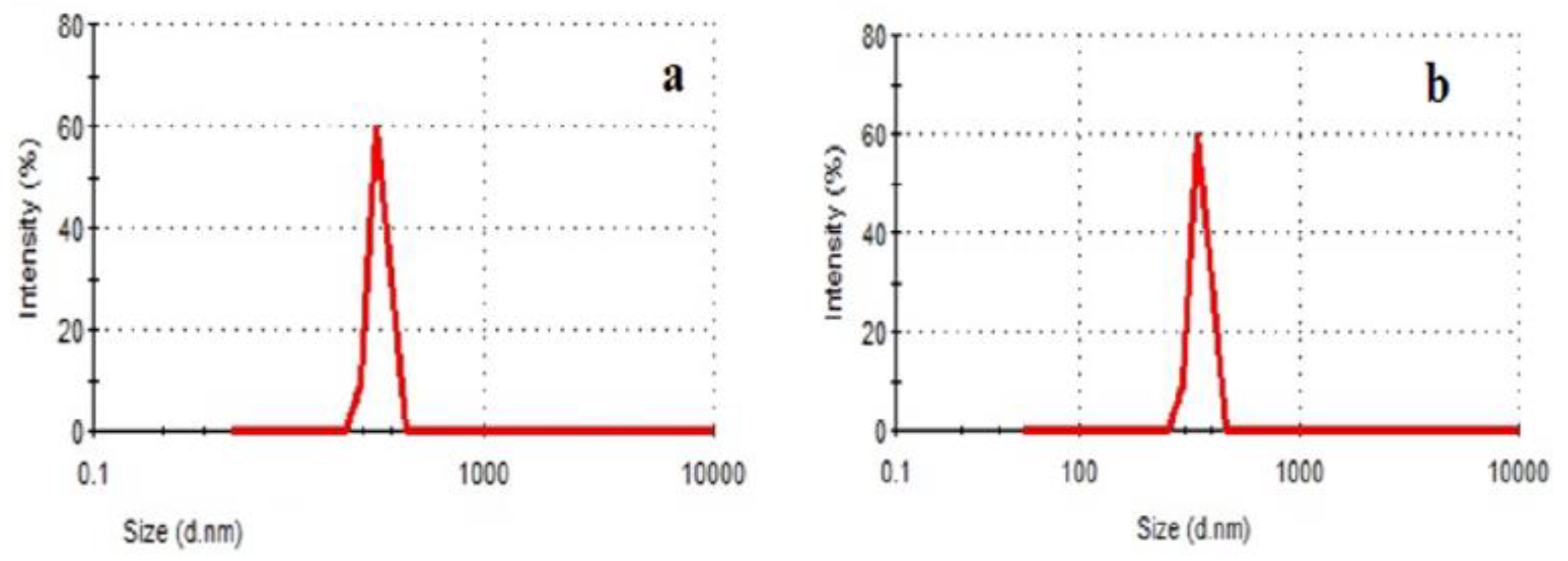
3.1. The Particle Size of NC and GO Suspensions
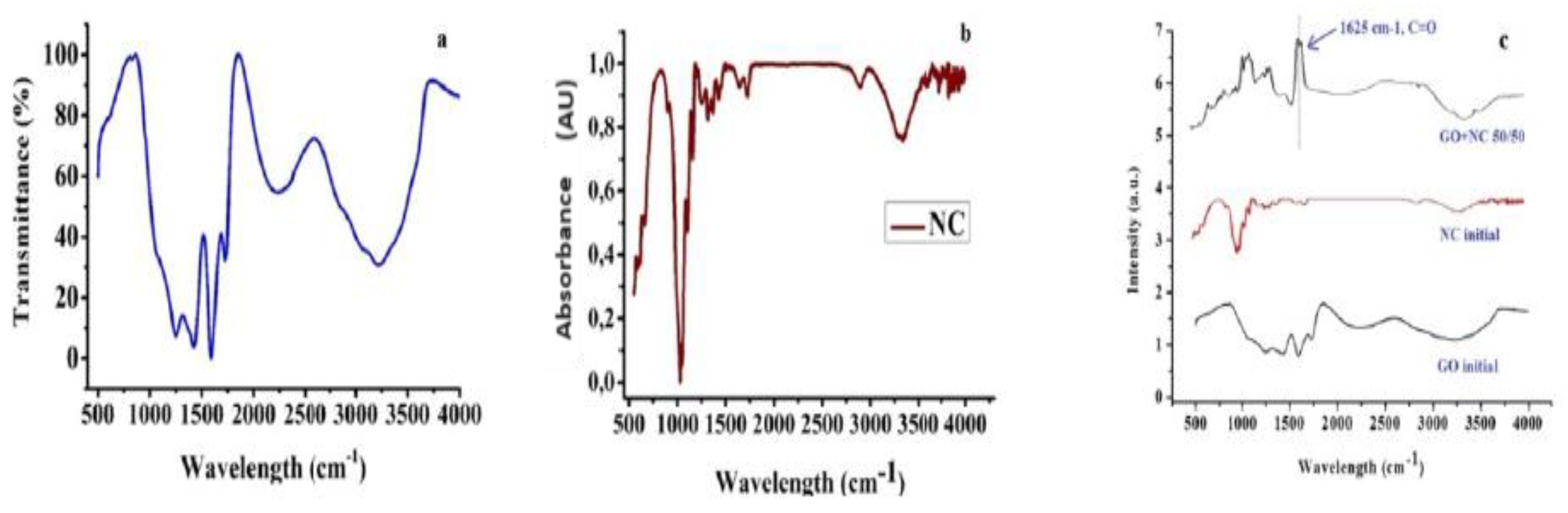
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
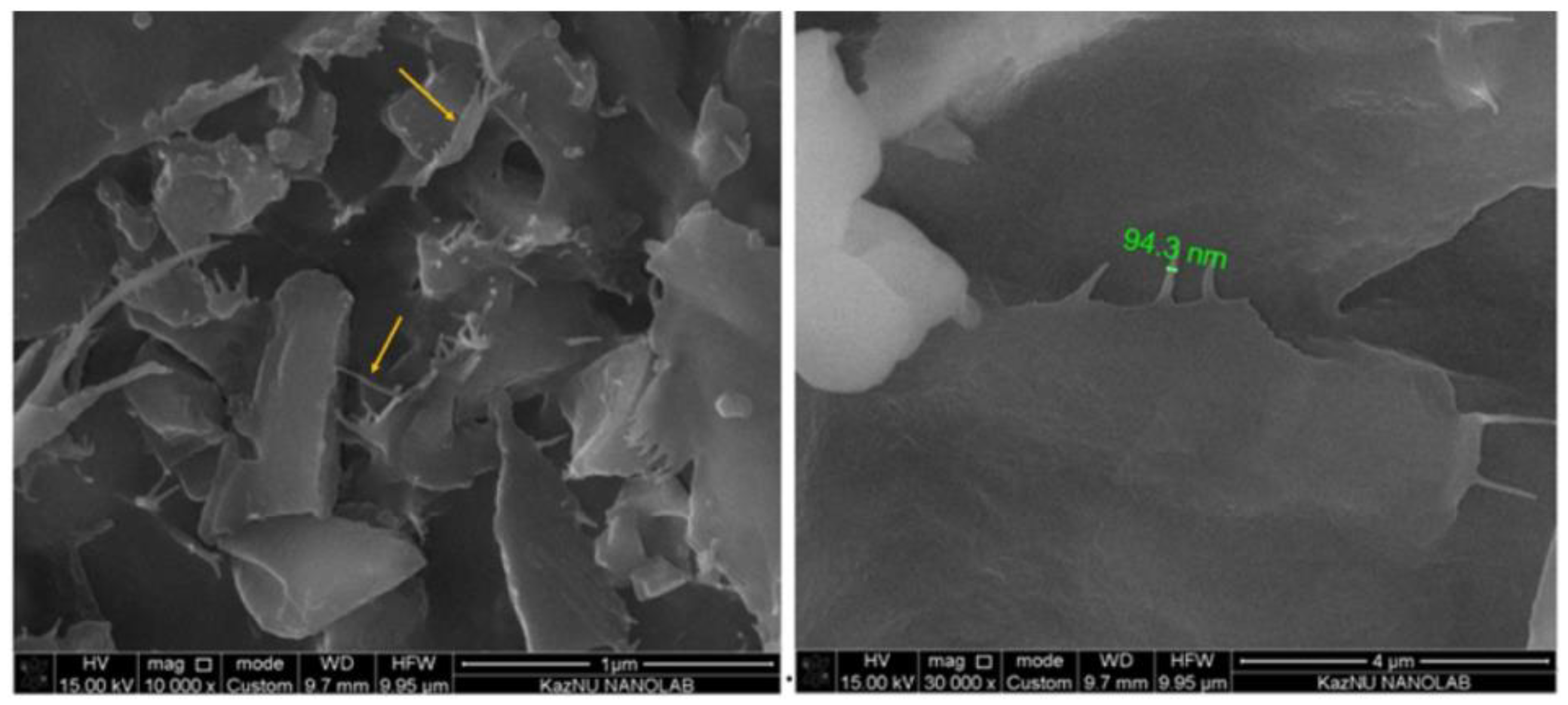
3.3. SEM Analysis
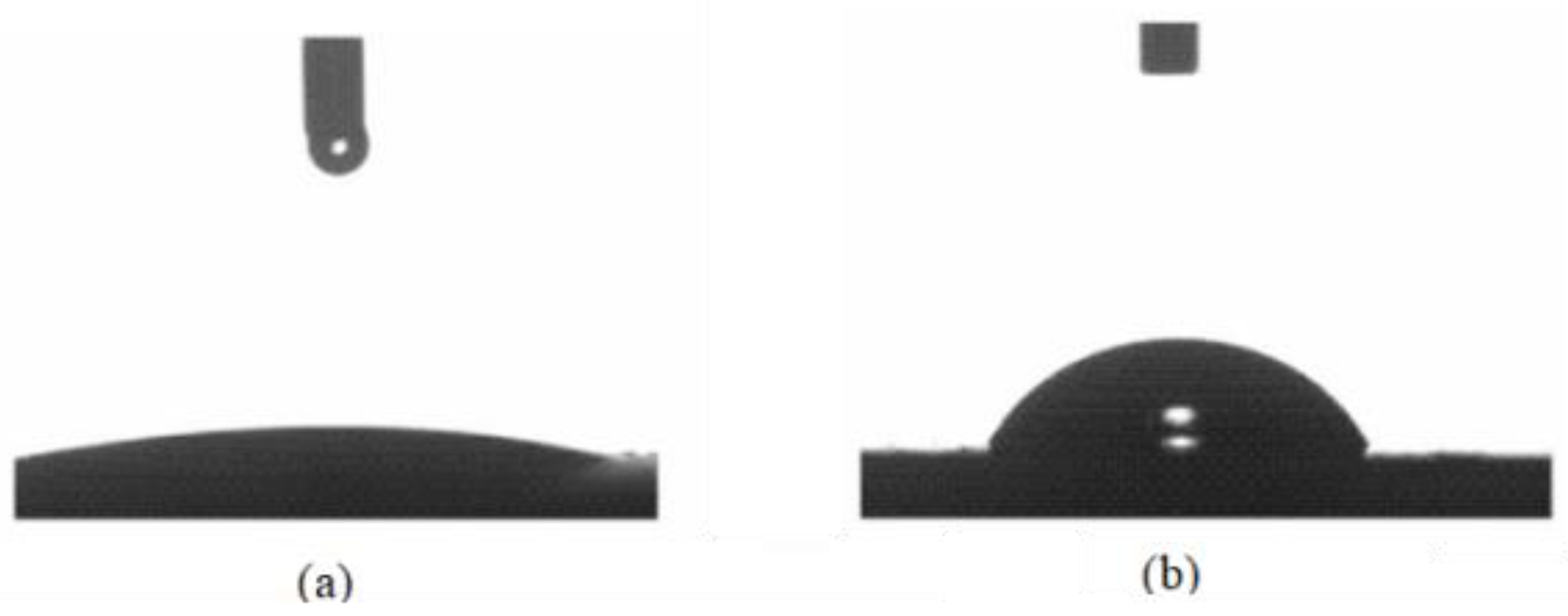
3.4. Contact Angle Measurement
3.5. Filtration Properties

3.6. Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
References
- Steiger, R., Leung, P.K., 1992. Quantitative determination of the mechanical properties of shales. SPE Paper 18024, SPE Drilling Engineering, 7(3), 181-185. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhang, Z. Qiu, W. Huang, J. Cao, X. Luo,Characterization of a novel aluminum-based shale stabilizer J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 103 (2013), pp. 36-40. [CrossRef]
- E. Van Oort. On the physical and chemical stability of shales. J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 38 (3) (2003), pp. 213-235. [CrossRef]
- C. Liang, M. Chen, Y. Jin, Y. Lu. Wellbore stability model for shale gas reservoir considering thecoupling of multi-weakness planes and porous flow. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng., 21 (2014), pp. 364-378. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhou, H. Xue, W. Guo, X. Li, A new nuclear magnetic resonance permeability model of shale of Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin, J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.), 40 (1) (2016), pp. 56-61. [CrossRef]
- S. Akhtarmanesh, M.A. Shahrabi, A. Atashnezhad. Improvement of wellbore stability in shale using nanoparticles. J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 112 (2013), pp.290-295. [CrossRef]
- R.T. Ewy, E.K. Morton. Wellbore stability performance of water base mud additives. Soc. Pet. Eng. (2008). [CrossRef]
- S. Ponmani, R. Nagarajan, J.S. Sangwai. Effect of nanofluids of CuO and ZnO in polyethylene glycol and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the thermal, electrical, and filtration-loss properties of water-based drilling fluids SPE J., 21 (02) (2016), pp. 405-415. [CrossRef]
- K.P. Hoelscher, G. De Stefano, M. Riley, S. Young, Application of nanotechnology in drilling fluids SPE International Oilfield Nanotechnology Conference and Exhibition, (June), 12–14 (2012). [CrossRef]
- M.M. Sharma, R. Zhang, M.E. Chenevert. A new family of nanoparticle-based drilling fluids. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition (2012), pp.1-13. [CrossRef]
- A.I. El-Diasty, A.M.S. Ragab. Applications of nanotechnology in the oil & gas industry: latest trends worldwide & future challenges in Egypt North Africa Technical Conference and Exhibition (2013), pp. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- J. Abdo, M.D. Haneef. Nano-enhanced drilling fluids: pioneering approach to overcome uncompromising drilling problems. J. Energy Resour. Technol., 134 (1) (2012), p. 014501. [CrossRef]
- A.H. Salih, T.A. Elshehabi, H.I. Bilgesu. Impact of nanomaterials on the rheological and filtration properties of water-based drilling fluids. SPE Eastern Regional Meeting (2016). [CrossRef]
- Anirudh Bardhan, Sushipra Varts, Deepak Kumar Prajapati, Darshan Halari, Shivanjali Sharma, Amit Saxena. Utilization of mesoporous nano-silica as high-temperature water-based drilling fluids additive: Insights into the fluid loss reduction and shale stabilization potential // Geoenergy Science and Engineering, Vol. 292, Part A, January 2024, 212436. [CrossRef]
- Anirudh Bardhan, Fahad Khan, Himanshu Kesarwani, Sushipra Vats, Shivanjali Sharma, Shailesh Kumar. Performance evaluation of novel silane coated nanoparticles as an additive for high-performance drilling fluid applications // The international Petroleum Technology Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, March 2023, Paper Number: IPTC-22878-MS. [CrossRef]
- Anirudh Bardhan, Ankit Singh, Harshwardhanam Nishanta, Shivanjali Sharma, Abhay Kumar Choubey, Shailesh Kumar. Biogenic copper oxide nanoparticles for improved lubricity and filtration control in water-based drilling mud // Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 10, 8564-8578 Publication Date: April 27, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Fabrication of a nanocomposite material via graphene oxide modification with nanocellulose Akatan, T.K. Kuanyshbekov, S.K. Kabdrakhmanova, A.A. Imasheva, A.K. Battalova, R.B. Abylkalykova, A.K. Nasyrova, Zh.E. Ibraeva. Chemical Bulletin of Kazakh National University.
- Wojtoniszaka M.X., Chena R.J., Wajdab K.A., et al. Synthesis, dispersion, and cytocompatibility of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide // Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. – 2012. – Vol.89. – P.79-85. [CrossRef]
- Tang G., Jiang Z.G., Li X., et al. Three dimensional graphene aerogels and their electrically conductive composites // Carbon. – 2014. – Vol.77. –P.592-599. [CrossRef]
- Kian L.K., Jawaid M., Ariffin H., Alothman O.Y. Isolation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from roselle fibers // International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. – 2017. – Vol.103. – P.931-940. [CrossRef]
- Haafiz M.K.M., Hassan A., Zakaria Z., Inuwa I.M. Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanowhiskers from oil palm biomass microcrystalline cellulose // Carbohydrate Polymers. – 204. – Vol.103. – P.119-125. [CrossRef]
- Szabo T., Berkesi O., Dekany I. Free-green synthesis and dynamics of reduced graphene sheets via sun light irradiation // Carbon. – 2005. – Vol.43. – P.3186-3189. [CrossRef]
- Liu P., Zhu C., Mathe A. Mechanically robust high flux graphene oxide - nanocellulose membranes for dye removal from water Journal of Hazardous Materials. – Vol.371. – P.484-493. [CrossRef]
- Laboratory evaluation and analysis of physical shale inhibition of an innovative water-based drilling fluid with nanoparticles for drilling unconventional shales SPE Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, (Sandrea 2006) (2012), pp. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- M. Riley, S. Young, E. Stamatakis, Q. Guo, L. Ji, G. De Stefano, J. Friedheim Wellbore stability in unconventional shales - the design of a nano-particle fluid SPE Oil and Gas India Conference and Exhibition (2012). [CrossRef]
- J.P. Deville, B. Fritz, M. Jarrett. Development of water-based drilling fluids customized for shale reservoirs SPE Drill. Complet., 26 (04) (2011), pp. 484-491. [CrossRef]
- M.F. Fakoya, S.N. Shah. Enhancement of filtration properties in surfactant-based and polymeric fluids by nanoparticles SPE Eastern Regional Meeting, 1–12 (2014) SPE-171029-MS. [CrossRef]
- D.V. Kosynkin, G. Ceriotti, K.C. Wilson, J.R. Lomeda, J.T. Scorsone, A.D. Patel, J.M. Tour Graphene oxide as a high-performance fluid-loss-control additive in water-based drilling fluids ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 4 (1) (2012), pp. 222-227. [CrossRef]
- A.H. Salih, H. Bilgesu. Investigation of rheological and filtration properties of water-based drilling fluids using various anionic nanoparticles SPE Western Regional Meeting (2017). [CrossRef]
- A.H. Salih, T.A. Elshehabi, H.I. Bilgesu Impact of nanomaterials on the rheological and filtration properties of water-based drilling fluids. SPE Eastern Regional Meeting (2016). [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



