Submitted:
16 October 2024
Posted:
18 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
1. Materials and Methods
Ethical statement
1.1. Study Population
1.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
1.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
1.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
1.3. Methods
1.3.1. Control Group: Conventional Nursing Care
1.3.2. Observation Group: Bimodal Collaborative Nursing Model
1.4. Observational Metrics
1.4.1. Postoperative Recovery
1.4.2. Psychological Status
1.4.3. Quality of Life
1.5. Data Analysis
2. Results
2.1. Basic Information
2.2. Comparison of Postoperative Recovery between the Two Groups
2.3. Comparison of Psychological Status between the Two Groups
2.4. Comparison of Quality of Life between the Two Groups
3. Discuss
References
- Wang, S.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Liao, C.-H.; Fu, C.-Y.; Ouyang, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-T.; Hsu, J.-T.; Yeh, T.-S.; Yeh, C.-N. Surgical outcome evaluation of perforated gastric cancer: from the aspects of both acute care surgery and surgical oncology. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaguchi, Y.; Inaba, T.; Kumata, Y.; Horikawa, M.; Kiyokawa, T.; Fukushima, R. Two cases of early recurrence after transabdominal preperitoneal inguinal hernia repair. Asian J. Endosc. Surg. 2018, 11, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakil, A.; Aparicio, K.; Barta, E.; Munez, K. Inguinal Hernias: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 102, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stahlman, S.; Fan, M. Incidence of inguinal hernia and repair procedures and rate of subsequent pain diagnoses, active component service members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2010-2019. Msmr 2020, 27, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, A.J.; Campbell, S. Inguinal Hernia Repair in Older Persons. J. Am. Med Dir. Assoc. 2022, 23, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, E.; Zetner, D.; Andresen, K.; Rosenberg, J. Imaging modalities for inguinal hernia diagnosis: a systematic review. Hernia 2020, 24, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.T.; Schwarz, J.L.; Roggin, K.K. Surgical considerations and outcomes of minimally invasive approaches for gastric cancer resection. Cancer 2022, 128, 3910–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.H.; Wright, A.S. Controversies in Inguinal Hernia. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2021, 101, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrena, J.; Mattila, A.; Böhm, J.; Jantunen, I.; Kellokumpu, I. Surgical care quality and oncologic outcome after D2 gastrectomy for gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 13294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Kumar, A.; Reljic, T.; Blonski, W. Is inguinal hernia associated with an increased risk of colon cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2022, 37, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, C.; Lai, D.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L. Safety and effectiveness of inguinal hernia repair in patients with liver cirrhosis: a retrospective study and literature review. Hernia 2019, 24, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, M.D.; Graham, P.J.; Bathe, O.F. Quality of life: A critical outcome for all surgical treatments of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akelma, F.K.; Altınsoy, S.; Arslan, M.T.; Ergil, J. Effect of favorite music on postoperative anxiety and pain. Der Anaesthesist 2020, 69, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goksoy, B.; Yilmaz, G.; Azamat, I.; Ozata, I.; Duman, K. Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair—TAPP versus TEP: Results of 301 Consecutive Patients. Surg. Technol. Online 2021, 39, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, S.G.; Öberg, S.; Rosenberg, J. Treatment of longstanding groin pain: a systematic review. Hernia 2019, 23, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, K.K.; Shrestha, R.; Gc, S.; Maharjan, S.; Shrestha, A.; Neupane, A. Hernia among Patients Admitted to the Department of Surgery of a Tertiary Care Centre: A Descriptive Cross-sectional Study. J. Nepal Med Assoc. 2023, 61, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.H.; Kim, J.; Chao, J. Perioperative chemotherapy for resectable gastric cancer: MAGIC and beyond. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7343–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Greenberg, J.A.; Xu, Y.; Shada, A.L.; Funk, L.M.; Lidor, A.O. Phone follow-up after inguinal hernia repair. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 35, 5159–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndsen, M.R. Gudbjartsson, and F.H. Berndsen, [Inguinal hernia - review]. Laeknabladid 2019, 105, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Ding, Z.; Qiang, H. Analysis on Influencing Factors of Recurrence after Indirect Inguinal Hernia Laparoscopic Surgery. J. Heal. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2978745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, N.; Kerawala, A. QUALITY OF LIFE AFTER INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR. Pol. J. Surg. 2021, 93, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köckerling, F.; Maneck, M.; Günster, C.; Adolf, D.; Hukauf, M. Comparing routine administrative data with registry data for assessing quality of hospital care in patients with inguinal hernia. Hernia 2020, 24, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencivenga, M.; Palla, I.; Scorsone, L.; Bortolami, A.; Mengardo, V.; Pavarana, M.; Turchetti, G.; de Manzoni, G. Clinical pathways in gastric cancer care. Updat. Surg. 2018, 70, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enodien, B.; Moser, D.; Kessler, F.; Taha-Mehlitz, S.; Frey, D.M.; Taha, A. Cost and Quality Comparison of Hernia Surgery in Stationary, Day-Patient and Outpatient Care. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Control group(n=30) | Observation group(n=30) | t/x2 | P | ||
| Gender | Male | 28 | 29 | 0.351 | 0.554 |
| Female | 2 | 1 | |||
| Age(year) | - | 19-53 | 20-54 | - | - |
| Average | 40.38±3.74 | 39.42±4.02 | 0.958 | 0.342 | |
| BMI(kg/m2) | - | 17.9-28.6 | 18.3-29.2 | - | - |
| Average | 23.7±1.4 | 24.2±1.6 | 1.288 | 0.203 | |
| Indirect inguinal hernia(case) | Left side | 10 | 9 | 0.077 | 0.781 |
| Right side |
20 | 21 | |||
| Gastric cancer course(year) | - | 2-8 | 1-7 | - | - |
| Average | 6.02±0.73 | 5.87±0.62 | 0.858 | 0.394 | |
| Group | Case | Time to First Flatus(h) | Time to First Bowel Movement(h) | Time to First Ambulation(h) | Time to First Oral Intake(h) | Length of Hospital Stay(d) |
| Observation group | 30 | 16.54±1.62 | 19.87±0.61 | 12.66±0.54 | 21.05±0.34 | 8.54±0.23 |
| Control group | 30 | 20.97±1.74 | 22.55±0.57 | 16.97±0.63 | 24.04±0.51 | 10.63±0.72 |
| t | 10.206 | 17.582 | 28.450 | 26.718 | 15.145 | |
| P | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 |
| Group | Case | Anxiety | Depression | ||
| Before intervention | After intervention | Before intervention | After intervention | ||
| Observation group | 30 | 52.34±6.32 | 34.23±4.12 | 54.65±4.28 | 31.64±3.24 |
| Control group | 30 | 53.36±5.29 | 41.67±3.28 | 53.93±5.76 | 46.68±3.87 |
| t | 0.678 | 7.738 | 0.550 | 16.321 | |
| P | 0.500 | <0.001 | 0.584 | <0.001 | |
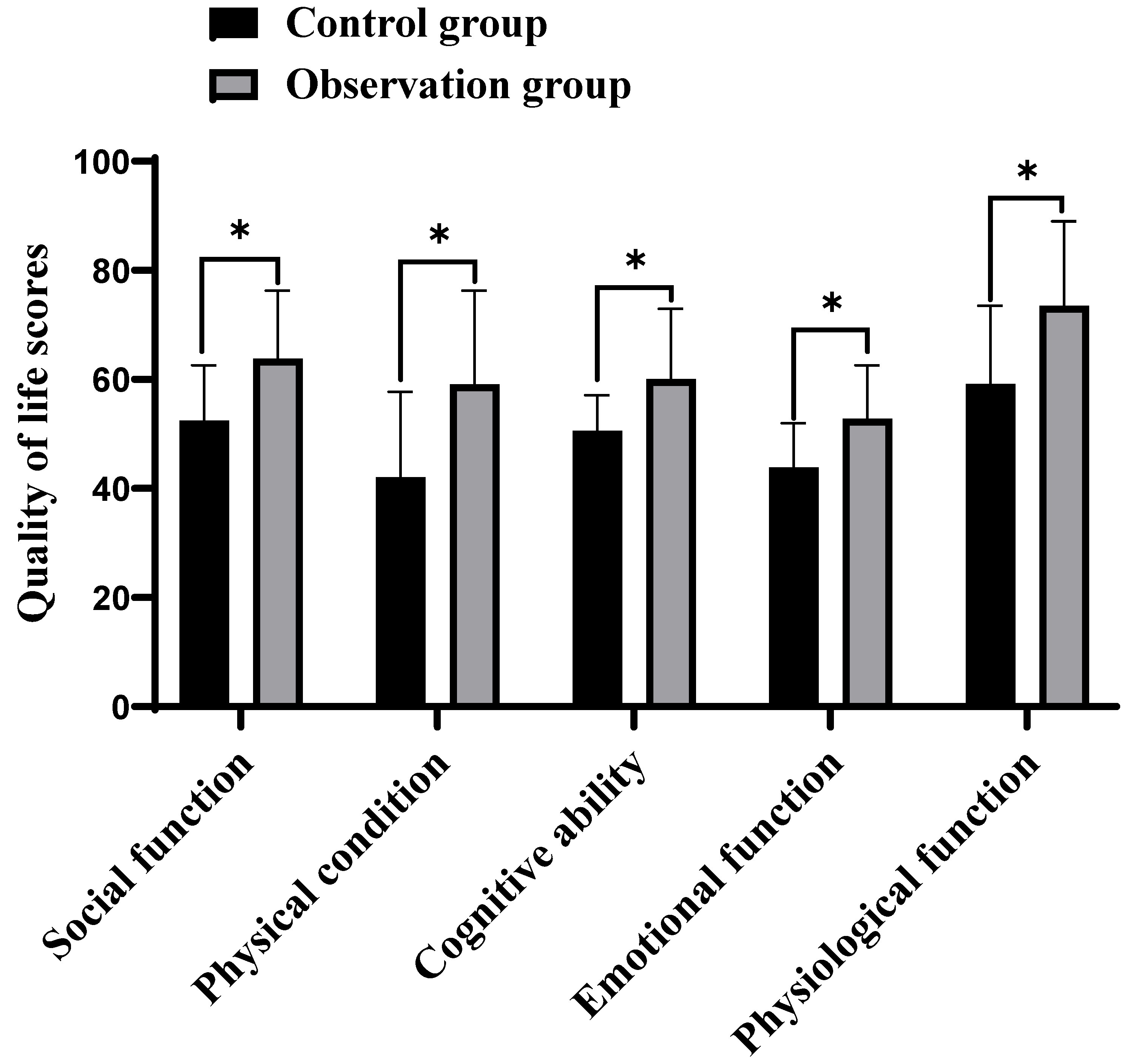
| Observation group(n=30) | Control group(n=30) | t | P | |
| Social function | 63.84±12.47 | 52.48±10.11 | 3.876 | <0.001 |
| Physical condition | 59.15±17.14 | 42.05±15.69 | 4.031 | <0.001 |
| Cognitive ability | 60.13±12.85 | 50.58±6.57 | 3.624 | <0.001 |
| Emotional function | 52.84±9.74 | 43.85±8.14 | 3.879 | <0.001 |
| Physiological function | 73.48±15.48 | 59.19±14.34 | 3.709 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




