Submitted:
18 October 2024
Posted:
21 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Questions
- How do CRM systems influence customer acquisition?
- In what ways do CRM systems contribute to customer retention?
- What is the impact of CRM systems on customer lifetime value?
- What challenges and limitations are associated with the use of CRM systems in achieving these goals?
- What are the long-term impacts of CRM system integration on SME competitiveness in the market?
1.2. Objectives
- To assess the impact of CRM systems on the operational efficiency of SMEs.
- To examine the effects of CRM adoption on sales and revenue growth in SMEs.
- To analyze the challenges SMEs face in implementing CRM systems.
- To investigate the influence of CRM systems on decision-making and data management in SMEs.
- To explore the relationship between CRM system customization and SME business performance.
1.3. Rationale
1.4. Research Motivation
- In today’s competitive business environment, CRM systems have become essential, especially for SMEs that often have fewer resources than larger enterprises. Optimizing customer interactions and relationships is crucial for their long-term growth. However, the literature has not adequately explored the specific effects of CRM systems on SMEs, including aspects such as customer retention, sales growth, and operational efficiency.
- The aim of this systematic literature review (SLR) is to consolidate the research on CRM systems and their impact on SMEs, offering a comprehensive view of the current state of the field. This review will identify research gaps, emerging trends, and provide actionable recommendations for SMEs looking to optimize their customer interaction strategies.
1.5. Research Contribution
- An in-depth analysis of the ways in which CRM systems influence the success of SMEs in terms of customer satisfaction, sales growth, and operational effectiveness. This synthesis will clarify the conditions under which CRM systems are most beneficial to SMEs.
- Identification of gaps in the existing research, such as the challenges SMEs face during CRM implementation or the long-term consequences of CRM adoption. Highlighting these gaps will pave the way for further investigation, enriching the scholarly discourse on CRM in the SME context.
- Providing valuable insights for SME managers and decision-makers. Understanding the established advantages and potential difficulties associated with CRM systems will enable SMEs to make informed decisions regarding CRM adoption and deployment, ensuring alignment with their financial constraints and business objectives.
1.6. Research Novelty
- It provides a detailed evaluation of CRM systems' roles in customer acquisition, retention, and lifetime value, extending beyond the existing literature.
- This research aims to identify best practices for CRM implementation in SMEs and potentially develop a framework or model tailored to their specific needs. Developing such a framework would represent a novel contribution, offering SMEs practical guidance for optimizing CRM adoption and maximizing its impact on business performance. By addressing these novel aspects, this study fills critical gaps in the current literature, providing new insights and practical tools for SMEs aiming to leverage CRM systems for enhanced business performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibilty Criteria
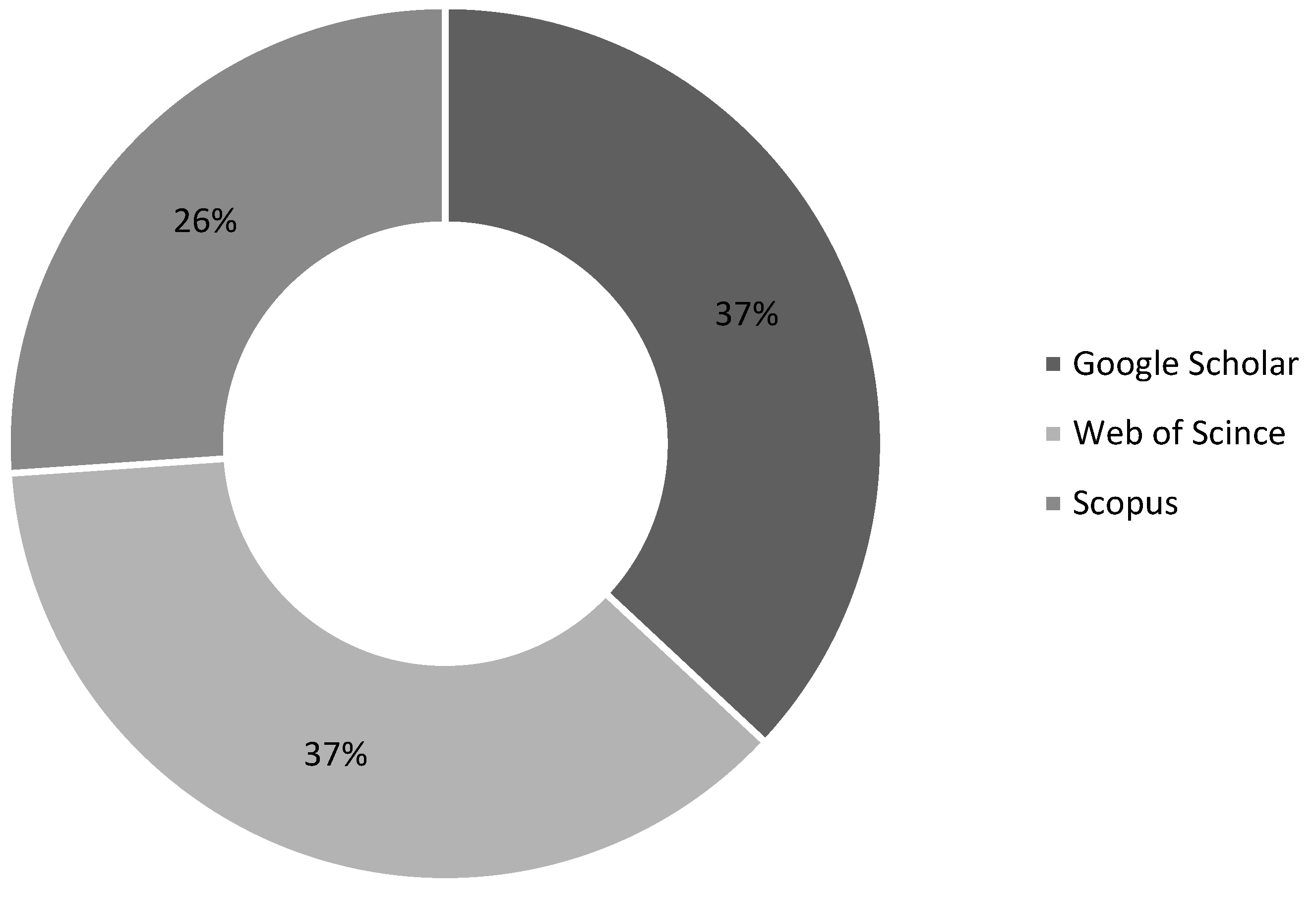
2.2. Information Sources
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Collection Process
2.6. Data Items
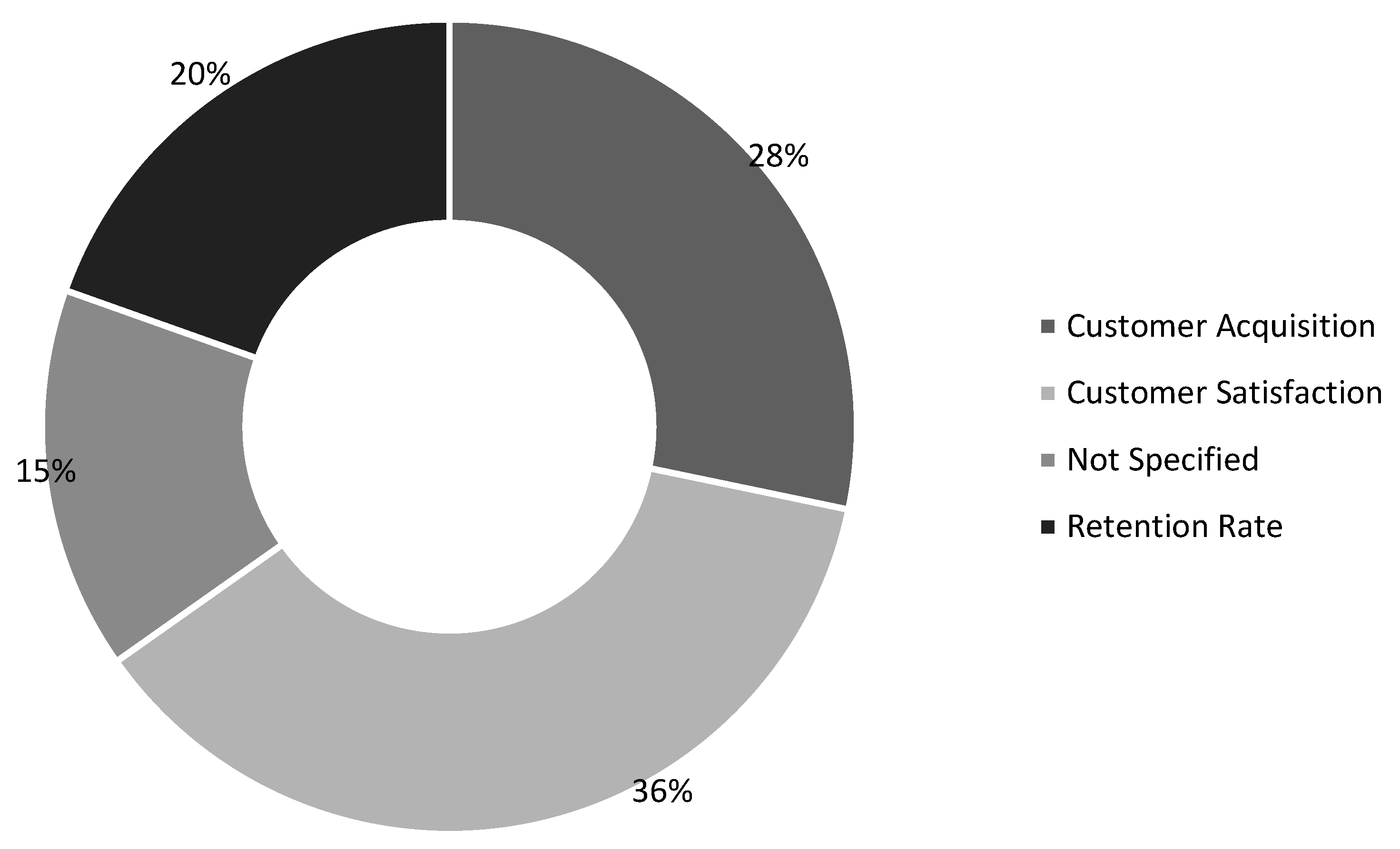
2.6.1. Outcomes
2.6.2. Data Variables
2.7. Study Risk of Bias Assessments
| Ref. | Random Sequence Generation (Selection Bias) | Allocation Concealment (Selection Bias) | Blinding of Participants and Personnel (Performance Bias) | Blinding of Outcome Assessment (Detection Bias) | Incomplete Outcome Data (Attrition Bias) | Selective Reporting (Reporting Bias) | Other Sources of Bias | Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | Low | Low | High | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Moderate |
| [2] | High | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| [3] | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [4] | Unclear | High | High | High | High | Unclear | High | High |
| [5] | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
2.8. Effect Measures
2.9. Synthesis Methods
2.10. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.11. Certainty Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Results of Study Selection
3.1.1. Identification and Screening Process
3.1.2. Final Inclusion
3.1.3. Potential Studies for Exclusion
3.1.4. PRISMA Flow Diagram
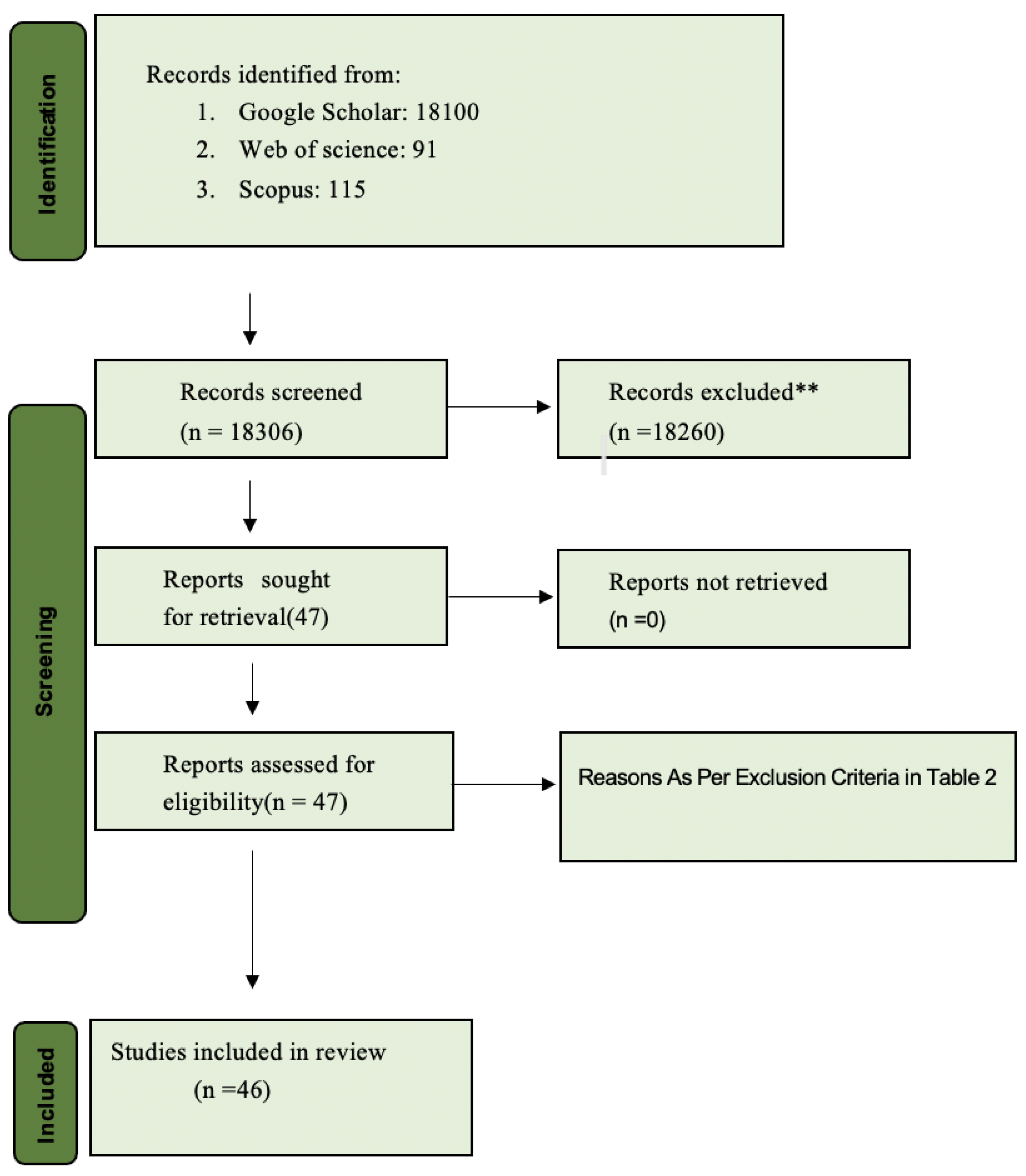
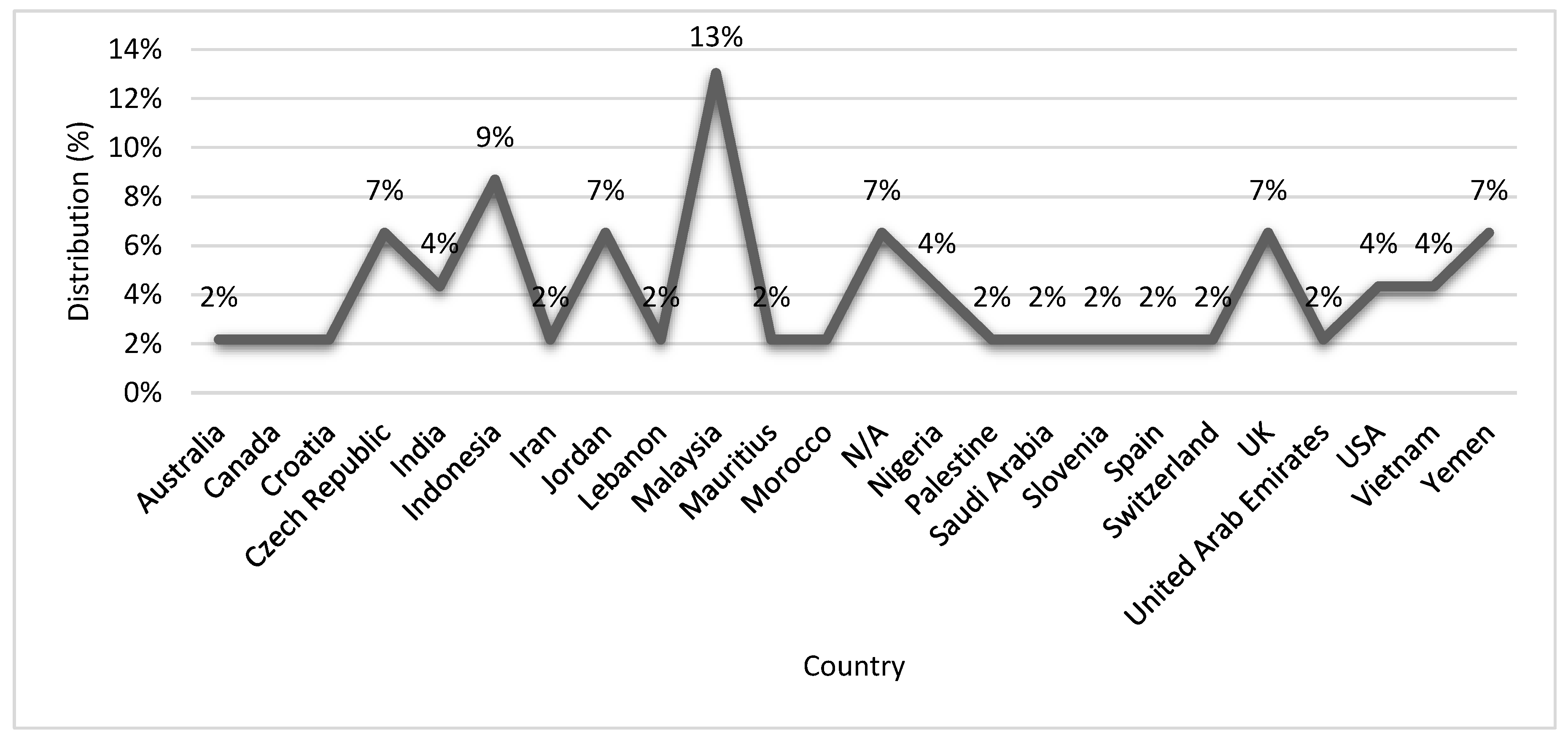
3.2. Eligible Studies Attribute
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
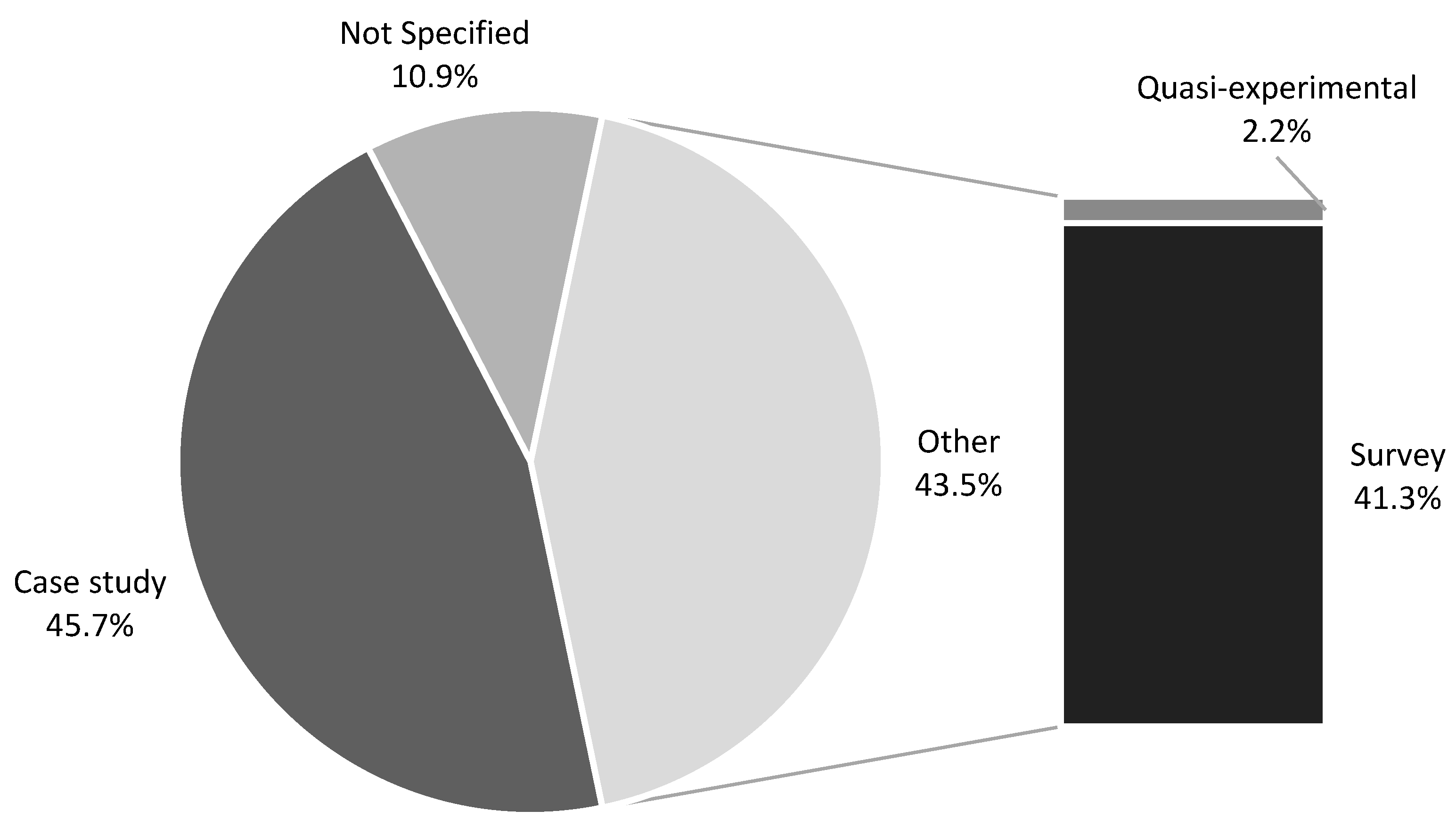
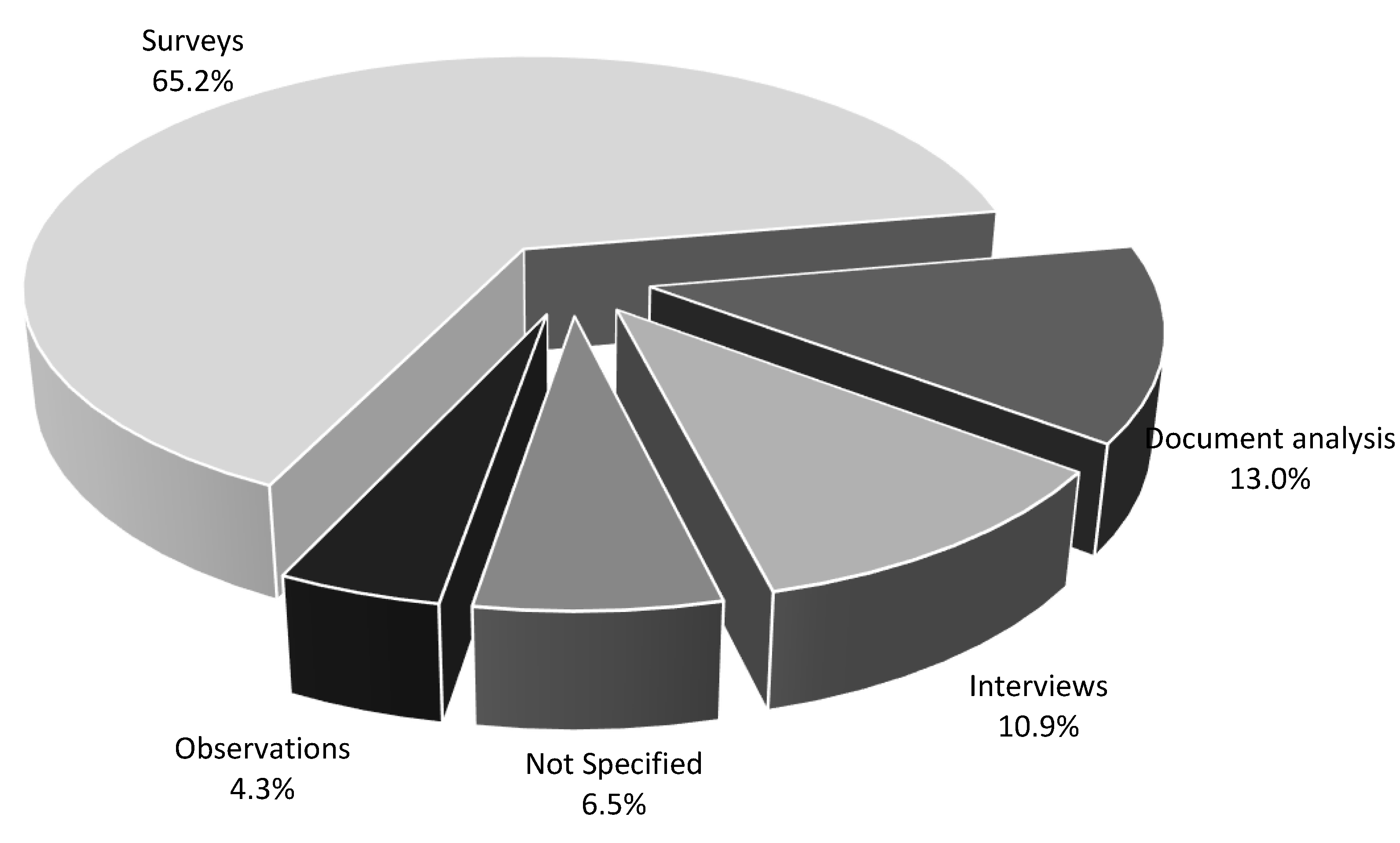
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
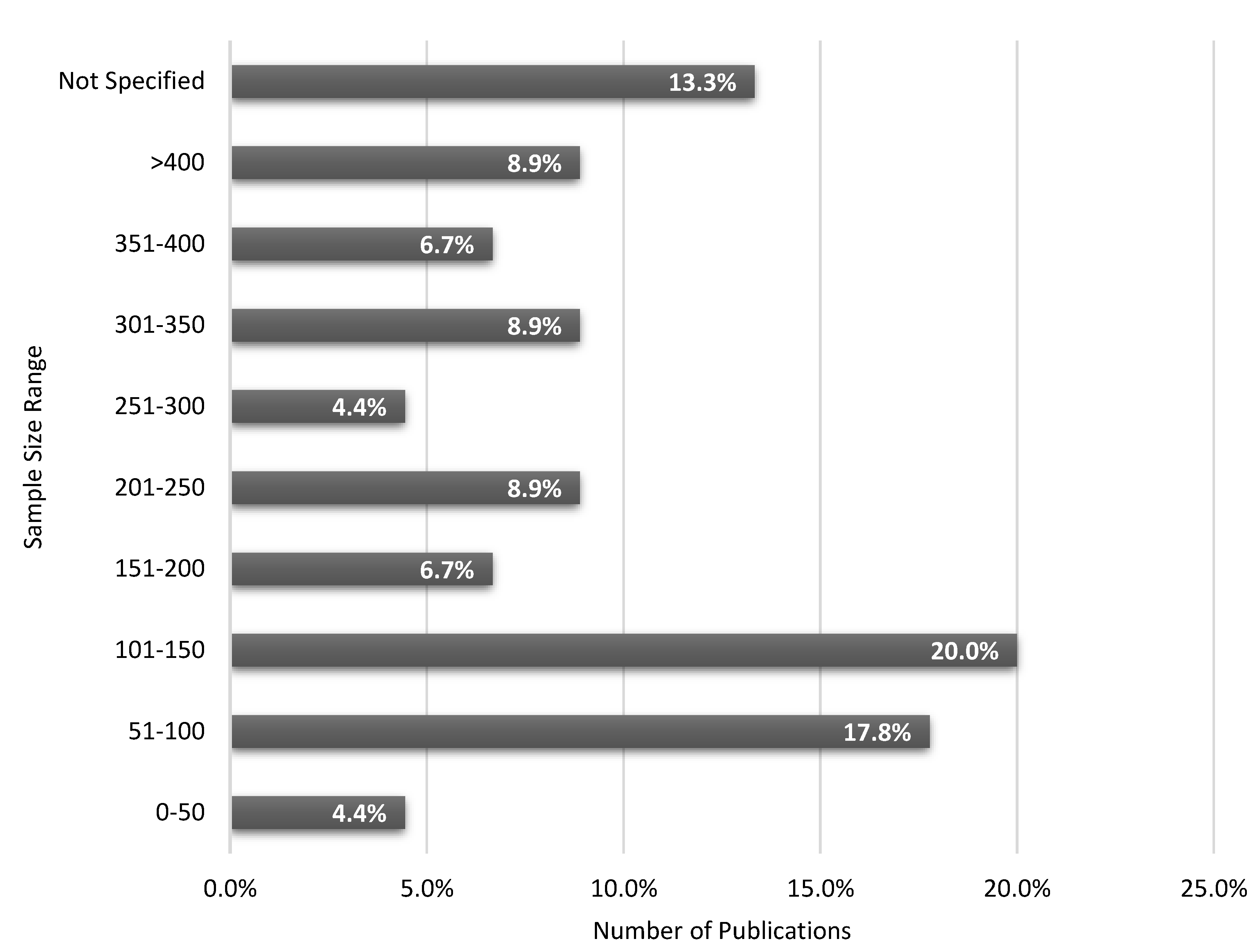
3.5. Results of Syntheses
3.6. Reporting Biases
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
4. Practical Recommendations
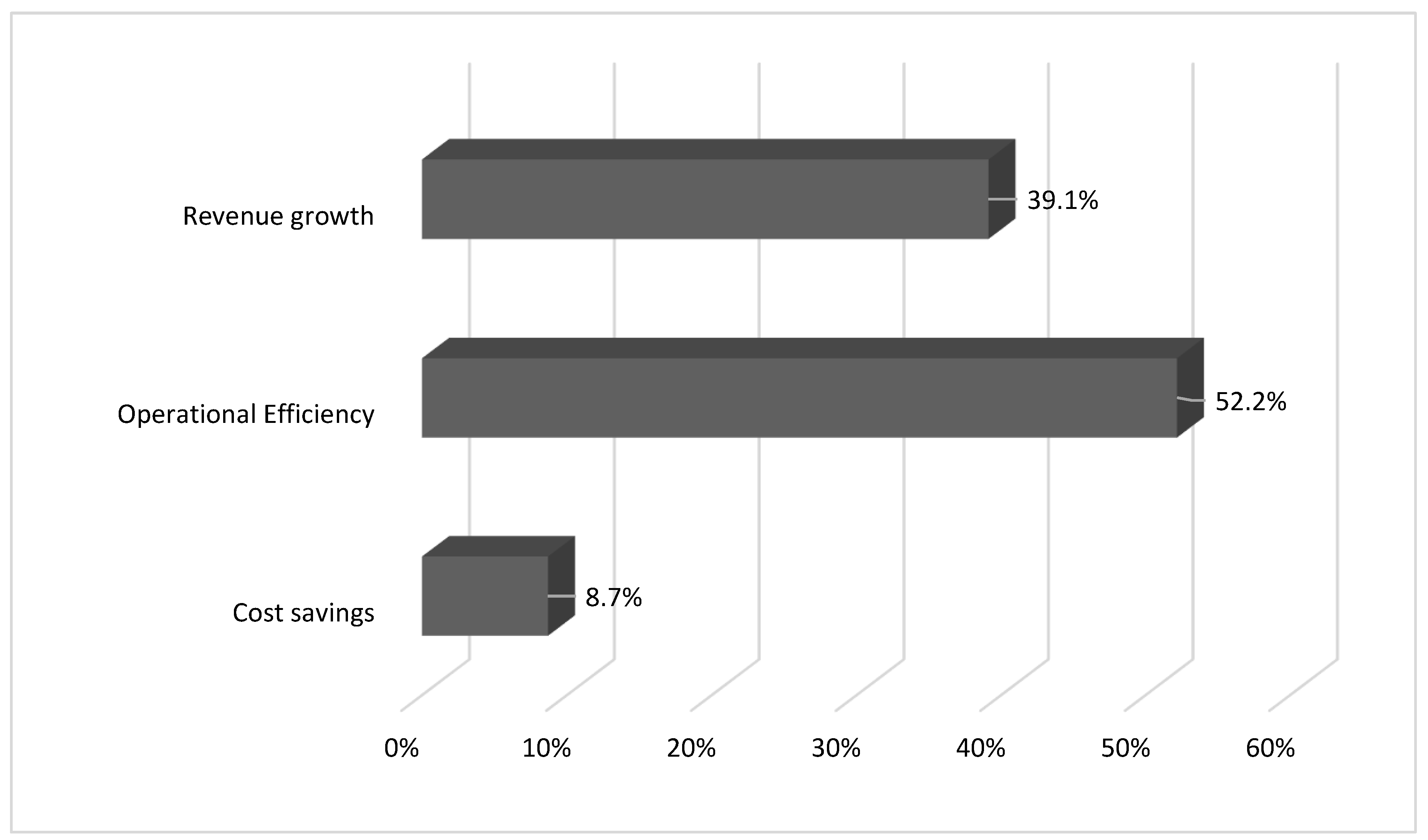
4.1. Key Findings and Strategic Implications for Business Leaders
4.2. Proposed Decision-Making Framework for Implementation
4.3. Proposed Best Practices for Successful Study Implementation
4.4. Proposed Metrics and KPIs for Measuring Performance
4.4. Proposed Roadmap for SMEs Businesses and Policy Recommendations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alshura, M. S. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Capabilities & Building a Sustainable Competitive Advantage in Mobile Phone Operators in Jordan. International Journal of Business and Management 2018, 13, 262. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v13n3p262.
- Hamida, A., Alshehhia, A., Abdullaha, A., & Mohamed, E. Key Success Factors for Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Projects within SMEs. Emirati Journal of Business, Economics and Social Studies 2022, 1. https://doi.org/10.54878/ejbess.176.
- Anees, R. T., Nordin, N. A., Anjum, T., Cavaliere, L. P. L., & Heidler, P. Evaluating the Impact of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Strategies on Customer Retention (A Study of Fast Food Chains in Pakistan). Business Management and Strategy 2020, 11, 117. https://doi.org/10.5296/bms.v11i2.17934.
- Mohammed, F., Hassan, S. B., Ahmad, R. B., & Fazea, Y. An Integrated Model for Investigating the Impact of Social CRM on Performance of SMEs in Developing Countries: Instrument Development. Journal of System and Management Sciences 2021, 11, 140–162. https://doi.org/10.33168/jsms.2021.0308.
- Soltani, Z., Zareie, B., Milani, F. S., & Navimipour, Nima Jafari. The impact of the customer relationship management on the organization performance. The Journal of High Technology Management Research 2018, 29, 2.
- Kyengo, J., Ombui, K., & Iravo, M. Determinants of customer relationship management strategies on the performance of small and medium enterprises in Westlands Nairobi City. Int. Acad. Journals 2016, 2, 1.
- Rafiki, A., Hidayat, S. E., & Abdul, A. CRM and organizational performance: A survey on telecommunication companies in Kuwait. International Journal of Organizational Analysis 2019, 27, 1.
- Al-Suraihi, Walid Abdullah, Al-Suraihi, Al-Hussain Abdullah, Ibrahim, I., Al-Tahitah, A., & Abdulrab, M. The effect of customer relationship management on consumer behavior: a case of retail industry in Malaysia. International Journal of Management and Human Science (IJMHS) 2020, 4, 3.
- Hardjono, B., & San, L. P. Customer Relationship Management Implementation and its Implication to Customer Loyalty in Hospitality Industry. Jurnal Dinamika Manajemen 2017, 8, 92–107. https://doi.org/10.15294/jdm.v8i1.10414.
- Rosalina, V., & Malik, A. Electronic customer relationship management (e-crm) modeling on micro, small & medium enterprises (MSMEs) banten. INA-Rxiv. 2017.
- Branner, K. (2020). Small–and medium-sized enterprises’ customer relationship management processes impact on firm performance moderated by entrepreneurial orientation.
- Rodriguez, M., & Honeycutt, E. D. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)“s Impact on B to B Sales Professionals” Collaboration and Sales Performance. Journal of Business-To-Business Marketing 2011, 18, 335–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/1051712x.2011.574252.
- Newby, M., Nguyen, H., & Waring, S. Understanding customer relationship management technology adoption in small and medium-sized enterprises: An empirical study in the USA. Journal of Enterprise Information Management 2014, 27, 5.
- Mohammed, A. A., Rashid, B., & Tahir, S. Customer relationship management (CRM) technology and organization performance: Is marketing capability a missing link? An empirical study in the Malaysian hotel industry. Asian Social Science 2014, 10, 9.
- Hussin, N., Shah, Campus, U., Perdana, P., & Sultan, U. Customer relationship management performance and technology impact among logistic operators in SME’s. In IBIMA Business Review.
- Baashar, Y., Alhussian, H., Patel, A., Alkawsi, G., Alzahrani, A. I., Alfarraj, O., & Hayder, G. (2020). Customer relationship management systems (CRMS) in the healthcare environment: A systematic literature review. Computer Standards & Interfaces 2021, 71, 103442. NCBI. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csi.2020.103442.
- Setyaningrum, E., Santoso, B., & Hevrizen, R. (2019). E-crm information system for tapis Lampung SMEs E-crm information system for tapis Lampung SMEs. 1338.
- Baashar, Yahia Mohamed, Mahomood, A. K., Almomani, Malek Ahmad, & Alkawsi, Gamal Abdulnaser. (2016). Customer relationship management (CRM) in healthcare organization: A review of ten years of research. IEEE, 97–102.Pratiwi, M., & Arsyah, U. I. (2021). The Effectiveness of the Concept of CRM Application for SMEs during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1933, 012026. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1933/1/012026.
- Pratiwi, M., & Arsyah, U. I. The Effectiveness of the Concept of CRM Application for SMEs during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2021, 1933, 012026. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1933/1/012026.
- Gaffar, V., Budiman, A., & Tjahjono, B. (2021). Understanding CRM Implementation in SMEs. Proceedings of the 5th Global Conference on Business, Management and Entrepreneurship (GCBME 2020). https://doi.org/10.2991/aebmr.k.210831.111.
- Ali, Rizwan, et al. “Impact of Crm Capability Dimensions on Organizational Performance.” SMART Journal of Business Management Studies, vol. 15, no. 2, 2019, p. 80, https://doi.org/10.5958/2321-2012.2019.00017.4. Accessed 20 Sept. 2020.
- Nagwan AlQershi, et al. “Explore the Dynamics of Customer Relationship Management on Organizational Performance.” INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL of MANAGEMENT & INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY, vol. 3, no. 1, 1 Mar. 2018, pp. 10–16. Accessed 20 Sept. 2024.
- Ohliati, Jenny, et al. “The Role of Social Customer Relationship Management in Improving Relationship Performance in Small Businesses.” International Journal of Innovation and Technology Management, 4 May 2022, https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219877022500341. Accessed 5 May 2022.
- . Ali, Z., Ishaya, I., & Hassan, H. (2015). The critical success factors of e-CRM implementation to small and medium enterprises.
- Valmohammadi, Changiz. “Customer Relationship Management: Innovation and Performance.” International Journal of Innovation Science, vol. 9, no. 4, 4 Dec. 2017, pp. 374–395, https://doi.org/10.1108/ijis-02-2017-0011.
- Ardyan, Elia, and Gita Sugiyarti. “The Influence of E-CRM Capability and Co-Information Sharing Activity on Product Competitiveness and Marketing Performance of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises.” International Journal of Electronic Customer Relationship Management, vol. 11, no. 2, 2018, p. 158, https://doi.org/10.1504/ijecrm.2018.090208. Accessed 3 Dec. 2020.
- Marolt, Marjeta. Social CRM Adoption and Its Influence on Customer Relationship Performance -SMEs Perspective. 1 Jan. 2018. Accessed 19 Sept. 2024.
- Galvão, Marcella Brito, et al. “Customer Loyalty Approach Based on CRM for SMEs.” Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, vol. 33, no. 5, 4 June 2018, pp. 706–716, https://doi.org/10.1108/jbim-07-2017-0166.
- Adewole, Oladejo Dauda. “Customer Relationship Management and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) Growth in South West, Nigeria.” Scholedge International Journal of Management & Development ISSN 2394-3378, vol. 5, no. 5, 6 Aug. 2018, p. 48, https://doi.org/10.19085/journal.sijmd050501. Accessed 16 Oct. 2019.
- Cheng, Colin CJ, and Eric C Shiu. “How to Enhance SMEs Customer Involvement Using Social Media: The Role of Social CRM.” International Small Business Journal: Researching Entrepreneurship, vol. 37, no. 1, 31 May 2019, pp. 22–42, https://doi.org/10.1177/0266242618774831.
- . Álvarez Jaramillo, J., Zartha Sossa, J. W., & Orozco Mendoza, G. L. Barriers to sustainability for small and medium enterprises in the framework of sustainable development—L iterature review. Business Strategy and the Environment 2019, 28, 512–524.
- Herman, Lalu Edy, et al. “Electronic Customer Relationship Management and Company Performance: Exploring the Product Innovativeness Development.” Journal of Relationship Marketing, vol. 20, no. 1, 10 June 2020, pp. 1–19, https://doi.org/10.1080/15332667.2019.1688600.
- Yasiukovich, S., & Haddara, M. Social CRM in SMEs: A systematic literature review. Procedia Computer Science 2021, 181, 535–544.
- Aldoseri, S., Al Mubarak, M., & El Hajjar, S. (2019, September). Evaluating the impact of social CRM on SMEs' performance. In International Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship (pp. 32-40). Academic Conferences International Limited.
- Marolt, M., Zimmermann, H. D., Žnidaršič, A., & Pucihar, A. Exploring social customer relationship management adoption in micro, small and medium-sized enterprises. Journal of theoretical and applied electronic commerce research 2020, 15, 38–58.
- Sofi, M. R., Bashir, I., Parry, M. A., & Dar, A. The effect of customer relationship management (CRM) dimensions on hotel customer’s satisfaction in Kashmir. International Journal of Tourism Cities 2020, 6, 601–620.
- Herman, L. E., Sulhaini, S., & Farida, N. Electronic customer relationship management and company performance: Exploring the product innovativeness development. Journal of Relationship Marketing 2021, 20, 1–19.
- Sutrisno, R., Djatnika, T., & Gunawan, A. I. (2020, December). Can SMEs capture the social media phenomenon?: CRM strategies to improve relationship performance. In International Seminar of Science and Applied Technology (ISSAT 2020) (pp. 109-116). Atlantis Press.
- Letchumannan, Rajamanal, et al. “The Impact of Social Customer Relationship Management Practices on Public Organizational Performance: Social Customer Relationship Management Effectiveness as Mediator Variable.” International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, vol. 12, no. 5, 12 May 2022, https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarbss/v12-i5/13880. Accessed 27 May 2022.
- Alshourah, S., Jodeh, I., Swiety, I., & Ismail, A. Social customer relationship management capabilities and performance: moderating social media usage among SMES Jordanian. Decision Sciences 2022, 25(S2), 1-8.
- Harrigan, P., & Miles, M. From e-CRM to s-CRM. Critical factors underpinning the social CRM activities of SMEs. Small Enterprise Research 2014, 21, 99–116. https://doi.org/10.1080/13215906.2014.11082079.
- Khodakarami, F., & Chan, Y. E. Exploring the role of customer relationship management (CRM) systems in customer knowledge creation. Information & Management 2014, 51, 27–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2013.09.001.
- Bull, C. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, intermediation and disintermediation: The case of INSG. International Journal of Information Management 2014, 30, 94–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2009.11.004.
- Harrigan, P., Ramsey, E., & Ibbotson, P. Critical factors underpinning the e-CRM activities of SMEs. Journal of Marketing Management 2014, 27(5-6), 503–529. https://doi.org/10.1080/0267257x.2010.495284.
- Siti Hajar Mohamad, Othman, N., Jabar, J., & Izaidin Abdul Majid. Customer Relationship Management Practices: The Impact on Organizational Performance in SMEs of Food Manufacturing Industry. European Journal of Business and Management 2014, 6, 35–48.
- Lawson-Body, A., & Limayem, M. The Impact of Customer Relationship Management on Customer Loyalty: The Moderating Role of Web Site Characteristics. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication 2014, 9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1083-6101.2004.tb00295.x.
- Alireza Fazlzadeh, Mostafa Kamali Tabrizi, & Kazem Mahboobi. Customer relationship management in small-medium enterprises: The case of science and technology parks of Iran. African Journal of Business Management 2014, 5, 6159–6167. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajbm10.695.
- Mohamad, S. H., Othman, N. A., Jabar, J., Majid, I. A., & Kamarudin, Mohd Fauzi. The impact of customer relationship management on small and medium enterprises performance. Journal of Technology Management and Technopreneurship (JTMT) 2014, 2, 2.
- Nguyen, T. H., & Waring, T. S. The adoption of customer relationship management (CRM) technology in SMEs: An empirical study. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development 2014, 20, 4.
- Mozaheb, A., Alamolhodaei, S. M. A., & Ardakani, M. F. Effect of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) on Performance of Small-Medium Sized Enterprises (SMEs) Using Structural Equations Model (SEM). International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences 2015, 5. https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarafms/v5-i2/1561.
- Safari, F., Safari, N., & Montazer, G. A. Customer lifetime value determination based on RFM model. Marketing Intelligence & Planning 2016, 34, 446–461. https://doi.org/10.1108/mip-03-2015-0060.
- Ahani, A., Rahim, N. Z. Ab., & Nilashi, M. Forecasting social CRM adoption in SMEs: A combined SEM-neural network method. Computers in Human Behavior 2017, 75, 560–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.05.032.
- Das, S., Mishra, M., & Mohanty, P. K. The Impact of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Practices on Customer Retention and the Mediating Effect of Customer Satisfaction. International Journal of Management Studies 2018, 5, 95. https://doi.org/10.18843/ijms/v5i1/15.
- Minh Ngo, V., Pavelkova, D., Thi Phan, Q. P., & Van Nguyen, N. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in Small and Medium Tourism Enterprises: A Dynamic Capabilities Perspective. Tourism and Hospitality Management 2018, 24, 63–86. https://doi.org/10.20867/thm.24.1.11.
- Marolt, M., Zimmermann, H.-D., & Pucihar, A. Exploratory study of Social CRM use in SMEs. Engineering Economics 2018, 29. https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.ee.29.4.20246.
- Kantorová, K., & Bachmann, P. Social Customer Relationship Management and Organizational Characteristics. Information 2018, 9, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9120306.
- Nugroho, A., Suharmanto, A., & Masugino, M. Customer relationship management implementation in the small and medium enterprise. AIP Publishing 2018, 1941, 1.
- Pohludka, M., & Štverková, H. The Best Practice of CRM Implementation for Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Administrative Sciences 2019, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci9010022.
- Roopchund, R. Exploring Social CRM for Development of SMEs in Mauritius. Journal of Enterprising Culture 2019, 27, 93–109. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218495819500043.
- Hassan, S. H., Mohamed Haniba, N. M., & Ahmad, N. H. Social customer relationship management (s-CRM) among small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Malaysia. International Journal of Ethics and Systems 2019, 35, 284–302. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijoes-11-2017-0192.
- Bukola, A. A., Abosede, A. G., & Adesola, M. A. Customer Relationship Management and Small and Medium Enterprises Performance: Pragmatic Evidence from Oyo State, Nigeria. Asian Journal of Education and Social Studies 2019, 5, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajess/2019/v5i230139.
- Josiah, U., & Nkamare, S. E. Effect of customer relationship management (CRM) on the performance of SMES on hospitality industry in cross river state. International Journal of Marketing and Communication Studies 2019, 4, 2.
- Guerola-Navarro, V., Oltra-Badenes, R., Gil-Gomez, H., & Gil-Gomez, J. A. Research model for measuring the impact of customer relationship management (CRM) on performance indicators. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja 2020, 34, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677x.2020.1836992.
- AlQershi, N. A., Mokhtar, S. S. M., & Abas, Z. B. (2020). CRM dimensions and performance of SMEs in Yemen:the moderating role of human capital. Journal of Intellectual Capital, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/jic-05-2020-0175.
- AlQershi, N., Mokhtar, S. S. M., & Abas, Z. B. Innovative CRM and Performance of SMEs: The Moderating Role of Relational Capital. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 2020, 6, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6040155.
- Salah, O. H., Yusof, Z. M., & Mohamed, H. The determinant factors for the adoption of CRM in the Palestinian SMEs: The moderating effect of firm size. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, e0243355. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0243355.
- Vu Minh Ngo, & Hieu Minh Vu. Can Customer Relationship Management Create Customer Agility and Superior Firms’ Performance? International Journal of Business and Society 2021, 22, 175–193. https://doi.org/10.33736/ijbs.3169.2021.
- Furman, E., Diamant, A., & Kristal, M. Customer Acquisition and Retention: A Fluid Approach for Staffing. Production and Operations Management 2021, 30. https://doi.org/10.1111/poms.13520.
- AlQershi, N., Mokhtar, S. S. M., & Abas, Z. The influence of structural capital on the relationship between CRM implementation and the performance of manufacturing SMEs. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management 2021, 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01417-z.
- Kaul, D. Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Customer Satisfaction and Customer Lifetime Value in Retail. Review of Professional Management- a Journal of New Delhi Institute of Management 2021, 15, 55. https://doi.org/10.20968/rpm/2017/v15/i2/163914.
- Rahmadi, A., Djunaedi, D., & Nurlaely, N. The effect of customer relationship management (CRM) and entrepreneurship orientation towards the company performance in micro small medium enterprises in kediri. Atlantis Press 2021, 65–68.
- Lamrhari, S., Ghazi, H. E., Oubrich, M., & Faker, A. E. A social CRM analytic framework for improving customer retention, acquisition, and conversion. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2022, 174, 121275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121275.
- Hanaysha, Jalal Rajeh, Al-Shaikh, M. E., & Kumar, P. An examination of customer relationship management and business sustainability in small and medium enterprises. International Journal of Customer Relationship Marketing and Management (IJCRMM) 2022, 13, 1.
- Utami, B., & Sudarmiatin, S. The impact of CRM on business or MSME performance: A literature review. Journal of Social Science 2022, 3, 3.
- Alenazi, S., & Alanazi, T. The Mediating Role of Sustainable Dynamic Capabilities in the Effect of Social Customer Relationship Management on Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Study on SMEs in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031952.
- Binsaeed, R. H., Yousaf, Z., Grigorescu, A., Chitescu, Razvan Ion, Nassani, Abdelmohsen A, & Samoila, A. Customer engagement and customer relationship management capabilities’ effects on innovation performance and customer distrust’s moderating role. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12.
- Mohanad, A., Ibrahim, O., & Khasawneh, A. M. Social customer relationship management model for small and medium enterprises: Factors and challenges. AIP Publishing 2023, 2979, 1.
- Nilashi, M., Abumalloh, Rabab Ali, Ahmadi, H., Samad, S., Alrizq, M., Abosaq, H., & Alghamdi, A. The nexus between quality of customer relationship management systems and customers’ satisfaction: Evidence from online customers’ reviews. Heliyon 2023, 9, 11.
- Nurfarida, I. N., Hermawan, A., & Restuningdiah, N. Social customer relationship management and business performance: Evidence from small and medium enterprises. Quality-Access to Success 2023, 24, 197.
- Mohammad, Hussain, S., Abdalrazzaq AlOqool, & Ali, W. (2024). Does Supply Chain Resilience Mediate the Relationship Between CRM Dimensions and Customer Satisfaction? FIIB Business Review. https://doi.org/10.1177/23197145231225570.
- Hamzeh Alhawamdeh, Mahmoud, Abdel, M., Bashar Younis Alkhawaldeh, Maher Nawasra, Aref, A., Zraqat, O., Lina Fuad Hussien, & Al-Eitan, G. N. The relationship between marketing capabilities and financial performance: the moderating role of customer relationship management in Jordanian SMES. Cogent Business & Management 2024, 11. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2023.2297458.
- Gui, G., Andreas Raharto Condrobimo, & Enggal Sriwardiningsih. (2024). Increasing Customer Loyalty in Food and Beverage MSMEs Through Social CRM. In 2024 4th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1109/iraset60544.2024.10548580.
- Mohammed, F., Ahmad, R. B., Hassan, S. B., Fazea, Y., & Alzahrani, A. I. An empirical evidence on the impact of social customer relationship management on the small and medium enterprises performance. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights 2024, 4, 2.
- Solís-Rivera, L. R., Leiva, J. C., & Mora-Esquivel, R. Profitability, Customer, Operations, And Logistics Management in MSMEs During The COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Technology Management & Innovation 2024, 19, 67–84. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0718-27242024000200067.
- Tsiu, S.; Ngobeni, M.; Mathabela, L.; Thango, B. Applications and Competitive Advantages of Data Mining and Business Intelligence in SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090940. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202409.0940.v1.
- Mkhize, A.; Mokhothu, K.; Tshikhotho, M.; Thango, B. Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090882. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202409.0882.v1.
- Kgakatsi, M.; Galeboe, O.; Molelekwa, K.; Thango, B. The Impact of Big Data on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090985. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202409.0985.v1.
- Molete, O. B.; Mokhele, S. E.; Ntombela, S. D.; Thango, B. A. The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091024. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202409.1024.v1.
- Mothapo, M.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Tracking and Measuring Social Media Activity: Key Metrics for SME Strategic Success – A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091757. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202409.1757.v1.
- Ngcobo, K.; Bhengu, S.; Mudau, A.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Enterprise Data Management: Types, Sources, and Real-Time Applications to Enhance Business Performance - A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091913. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202409.1913.v1.
- Mohlala, T. T.; Mehlwana, L. L.; Nekhavhambe, U. P.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Strategic Innovation in HRIS and AI for Enhancing Workforce Productivity in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091996. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202409.1996.v1.
- Chabalala, K.; Boyana, S.; Kolisi, L.; Thango, B. A.; Matshaka, L. Digital Technologies and Channels for Competitive Advantage in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100020. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202410.0020.v1.
- Ndzabukelwako, Z.; Mereko, O.; Sambo, T. V.; Thango, B. The Impact of Porter’s Five Forces Model on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100119. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202410.0119.v1.
- Maswanganyi, N. G.; Fumani, N. M.; Khoza, J. K.; Thango, B. A.; Matshaka, L. Evaluating the Impact of Database and Data Warehouse Technologies on Organizational Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100059. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202410.0059.v1.
- Gumede, T. T.; Chiworeka, J. M.; Magoda, A. S.; Thango, B. Building Effective Social Media Strategies for Business: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100379. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202410.0379.v1.
- Myataza, A.; Mafunga, M.; Mkhulisi, N. S.; Thango, B. A. A Systematic Review of ERP, CRM, and HRM Systems for SMEs: Managerial and Employee Support. Preprints 2024, 2024100384. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202410.0384.v1.
- Mudau, M. C.; Moshapo, L. W.; Monyela, T. M.; Thango, B. A. The Role of Manufacturing Operations in SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100539. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202410.0539.v1.
- Khanyi, M.; Xaba, S.; Mlotshwa, N.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. The Role of Data Networks and APIs in Enhancing Operational Efficiency in SME: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100848. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202410.0848.v1.
- Skosana, S.; Mlambo, S.; Madiope, T.; Thango, B. Evaluating Wireless Network Technologies (3G, 4G, 5G) and Their Infrastructure: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101331. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202410.1331.v1.
| Ref. | Cites | Year | Contribution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | 11 | 2015 | It highlights how knowledge management boosts e-CRM effectiveness in SMEs. | Provides practical guidelines for enhancing e-CRM practices and customer engagement. | Relying on a single manager’s response may introduce bias and miss diverse perspectives. |
| [22] | 23 | 2017 | It shows the interconnectedness of CRM factors like customer satisfaction and profitability. | Helps SMEs differentiate in the market, increasing market share and profitability. | A lack of customer-centric culture may cause CRM systems to fail. |
| [23] | 181 | 2017 | The study links CRM to business performance and innovation, especially in Iran. | Encourages data-driven approaches for improved customer satisfaction and business outcomes. | Longitudinal studies could offer deeper insights into CRM’s long-term effects. |
| [24] | 42 | 2018 | It emphasizes the need for effective communication media in SMEs. | Enhances product competitiveness through effective e-CRM and information sharing. | SMEs may struggle with e-CRM adoption due to resource and expertise constraints. |
| [25] | 7 | 2018 | The research stresses tailored social CRM approaches based on enterprise size. | Offers insights into factors influencing social CRM adoption and its impact on performance. | A 6% response rate limits the representativeness of the sample. |
| [26] | 94 | 2018 | It identifies the need for a CRM-based loyalty framework for SMEs. | Proposes a systematic framework for customer loyalty based on CRM. | Small sample sizes may fail to capture diverse SME experiences. |
| [27] | 16 | 2018 | CRM factors like customer care and analytics drive MSME growth in Nigeria. | Lays the groundwork for further research on CRM practices across various contexts. | Critical factors for MSME growth may be overlooked. |
| [28] | 3 | 2018 | The study ranks 21 critical success factors for CRM in MSMEs. | Promotes leveraging customer data for informed decision-making. | Self-reported data from entrepreneurs may introduce bias. |
| [29] | 172 | 2019 | It shows how social CRM and social media enhance SME engagement and innovation. | Strengthens customer relationships through Social CRM, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty. | Social media raises data privacy and security concerns, affecting engagement. |
| [29] | 14 | 2019 | The study highlights barriers to SCRM adoption, such as time and knowledge limits. | Identifies strategies for overcoming barriers to SCRM implementation with proactive engagement. | SMEs may struggle to implement recommended CRM capabilities due to limited resources. |
| [30] | 12 | 2019 | E-CRM software for MSMEs in Banten offers local language support and ease of use. | Highlights critical success factors to address challenges in e-CRM implementation. | Responses from a single informant may overlook different views within the SME. |
| [31] | 13 | 2019 | Long-term customer relationships improve telecom companies' financial performance. | Provides insights into internal perceptions of CRM practices for better management decisions. | CRM technology and customer orientation alone may not significantly boost performance. |
| [32] | 50 | 2020 | It shows how tech compatibility and government support drive social CRM adoption. | Associates Social CRM adoption with improved customer relationship performance. | Some useful articles may have been missed due to keyword and context limitations. |
| [33] | 5 | 2019 | CRM and social media improve SME performance, filling a gap in the literature. | Shows that effective CRM implementation does not require extensive resources or complex strategies. | The focus on the service sector limits generalizability to other industries. |
| [34] | 40 | 2020 | The study identifies organizational and tech factors that drive social CRM use. | Enables SMEs to gain a competitive edge through improved responsiveness to customer needs. | Cross-sectional data restricts the ability to track CRM adoption changes over time. |
| [35] | 17 | 2020 | It explores CRM’s impact on SMEs in Yemen, contributing to research on developing countries. | Suggests that effective CRM use leads to significant competitive advantages. | CRM system implementation is complex, with risks of wasted investments. |
| [36] | 93 | 2020 | The study links product and service innovation to SME competitiveness via CRM. | Indicates that e-CRM can enhance marketing performance by fostering better relationships. | Some complexities and challenges of CRM implementation remain underexplored. |
| [37] | 7 | 2020 | It stresses the need to overcome tech barriers for CRM success in SMEs. | Enhances competitiveness through better customer relationship management via e-CRM practices. | SMEs’ lack of awareness of CRM’s benefits may slow progress. |
| [38] | 3 | 2022 | CRM dimensions like customer orientation and tech impact business sustainability. | Facilitates informed decision-making using technology and knowledge management within CRM. | Over-reliance on technology risks neglecting personal customer relationships. |
| [39] | 13 | 2022 | Social CRM mediates the relationship between practices and performance. | Provides best practice insights for managers to enhance customer interactions and satisfaction in social CRM. | External factors like market conditions are not thoroughly addressed. |
| [40] | - | 2022 | Social media feedback helps SMEs make faster decisions, boosting innovation. | Supports continuous communication with customers to adapt offerings based on changing preferences and trends. | Many SME owners lack digital marketing skills, limiting their use of social media. |
| Proposed systematic review | The systematic review will provide a comprehensive synthesis of existing research on critical success factors (CSFs) in CRM implementation across various industries. | Conducting the review is time and resource-intensive, requiring significant effort from researchers. | |||
| Criteria | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Topic | Focuses on CRM systems and their impact on SMEs | Studies not related to CRM systems |
| Research Framework | Must include a clear research framework or methodology | Lacks a framework or methodology relevant to CRM |
| Language | Written in English | Published in other languages |
| Publication Period | Published between 2014 and 2024 | Outside the specified period |
| No | Online Repository | Number of results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Google scholar | 18100 |
| 2 | Web of science | 91 |
| 3 | SCOPUS | 115 |
| Total | 18306 |
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Paper ID | Numbering for the papers |
| Title | Topic used for the paper |
| Year | When was it published |
| Online Database | Where the paper is found |
| Journal Name | Name of the journal where the paper is published |
| Research Type | Type of research conducted |
| Discipline or Subject Area | Field or subject area of the research |
| Industry Context | Context of the industry in which the research is relevant |
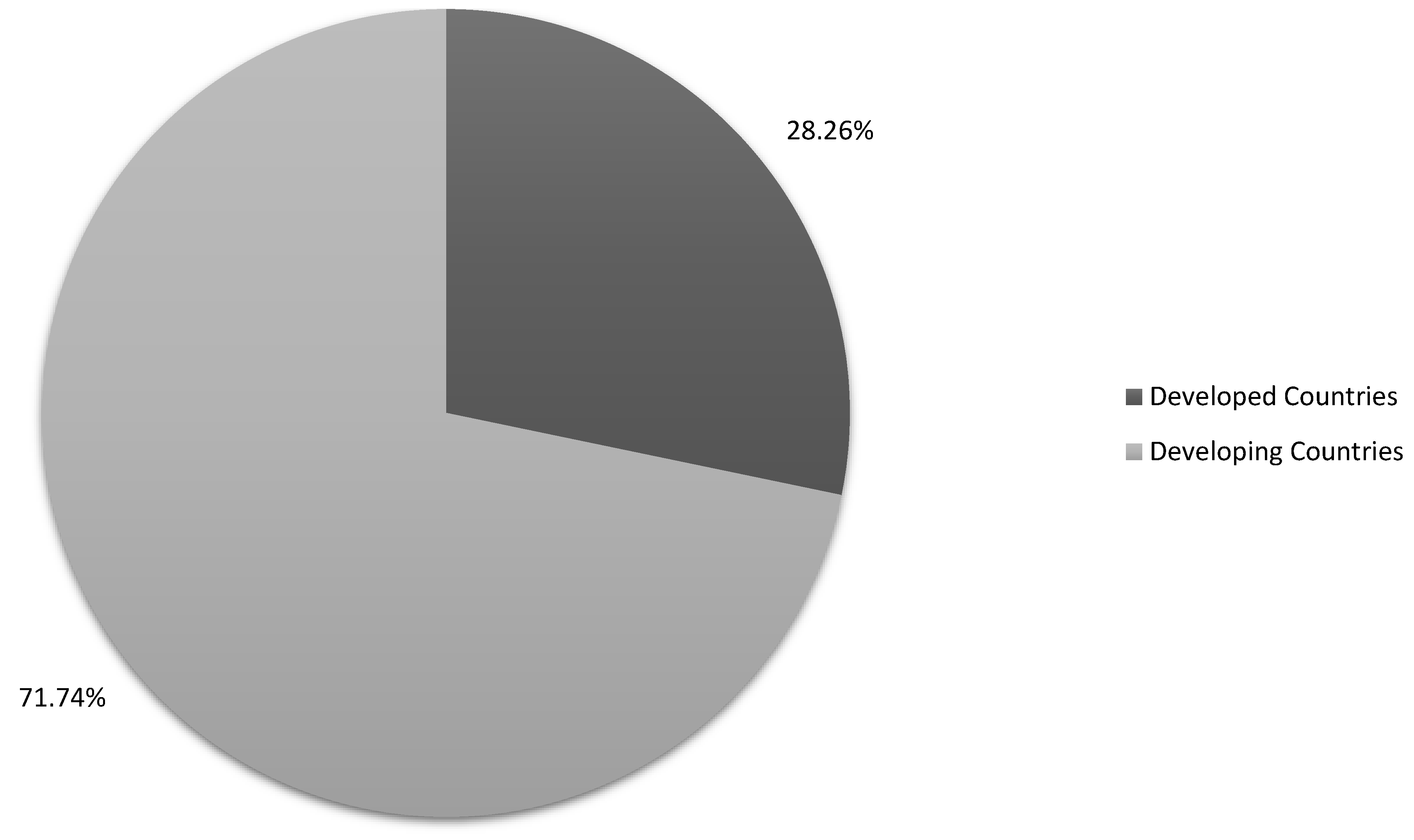
| Geographic Location | Geographic location relevant to the study |
| Economic Context | Economic conditions or factors considered in the study |
| Technology Implementation Model | Model used for implementing the technology |
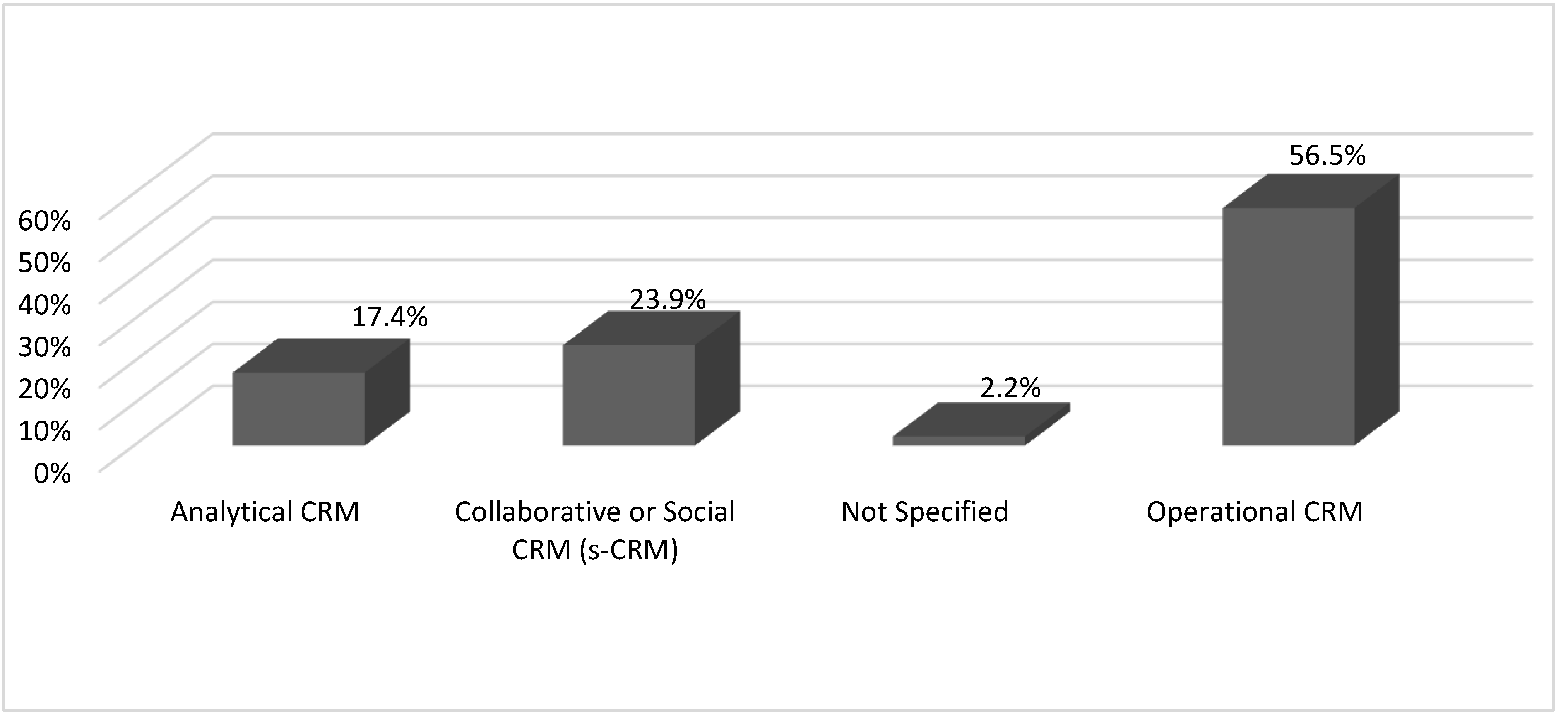
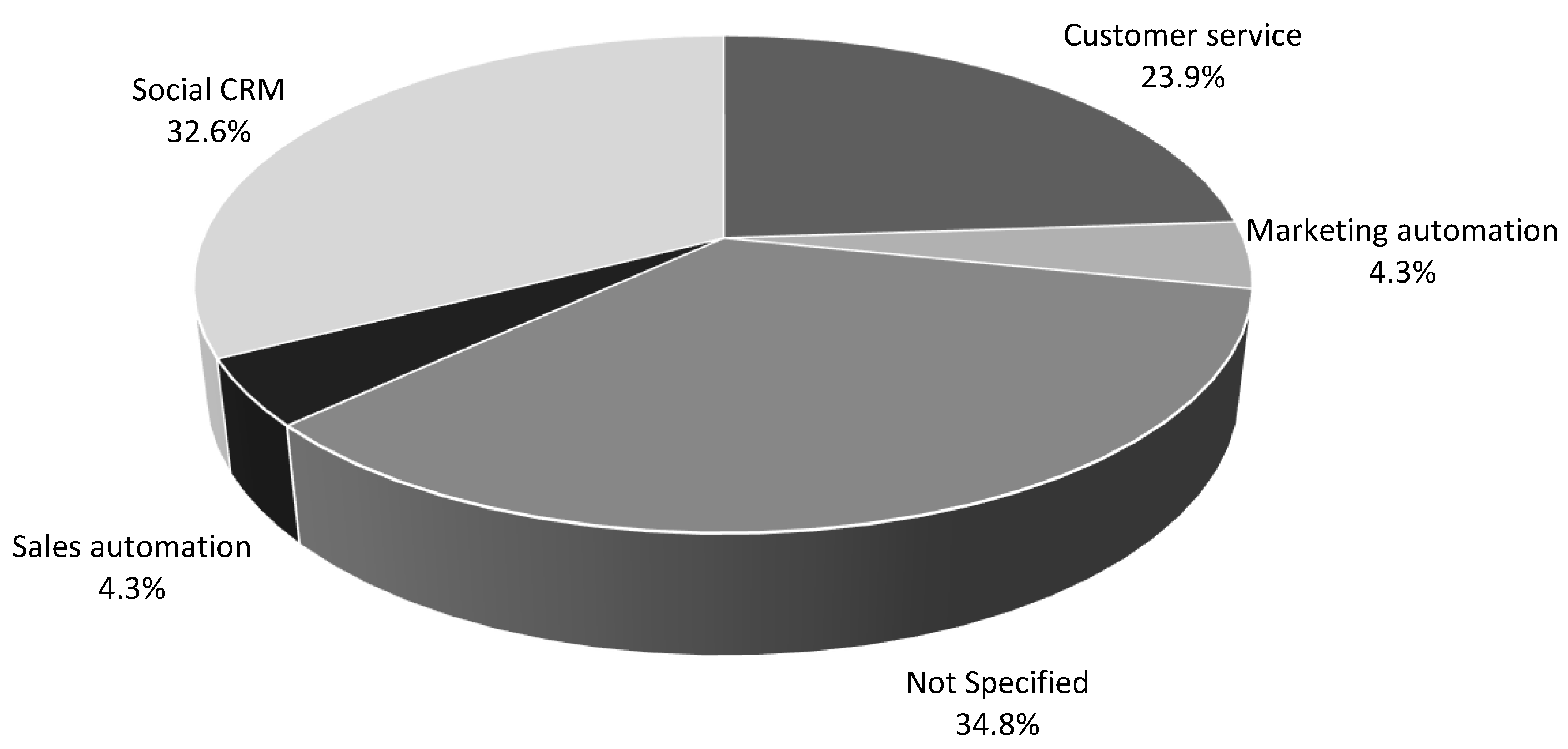
| Types of CRM Technologies | Types of CRM technologies studied |
| Technology Providers | Providers of the technologies analyzed |
| Research Design | Design of the research study |
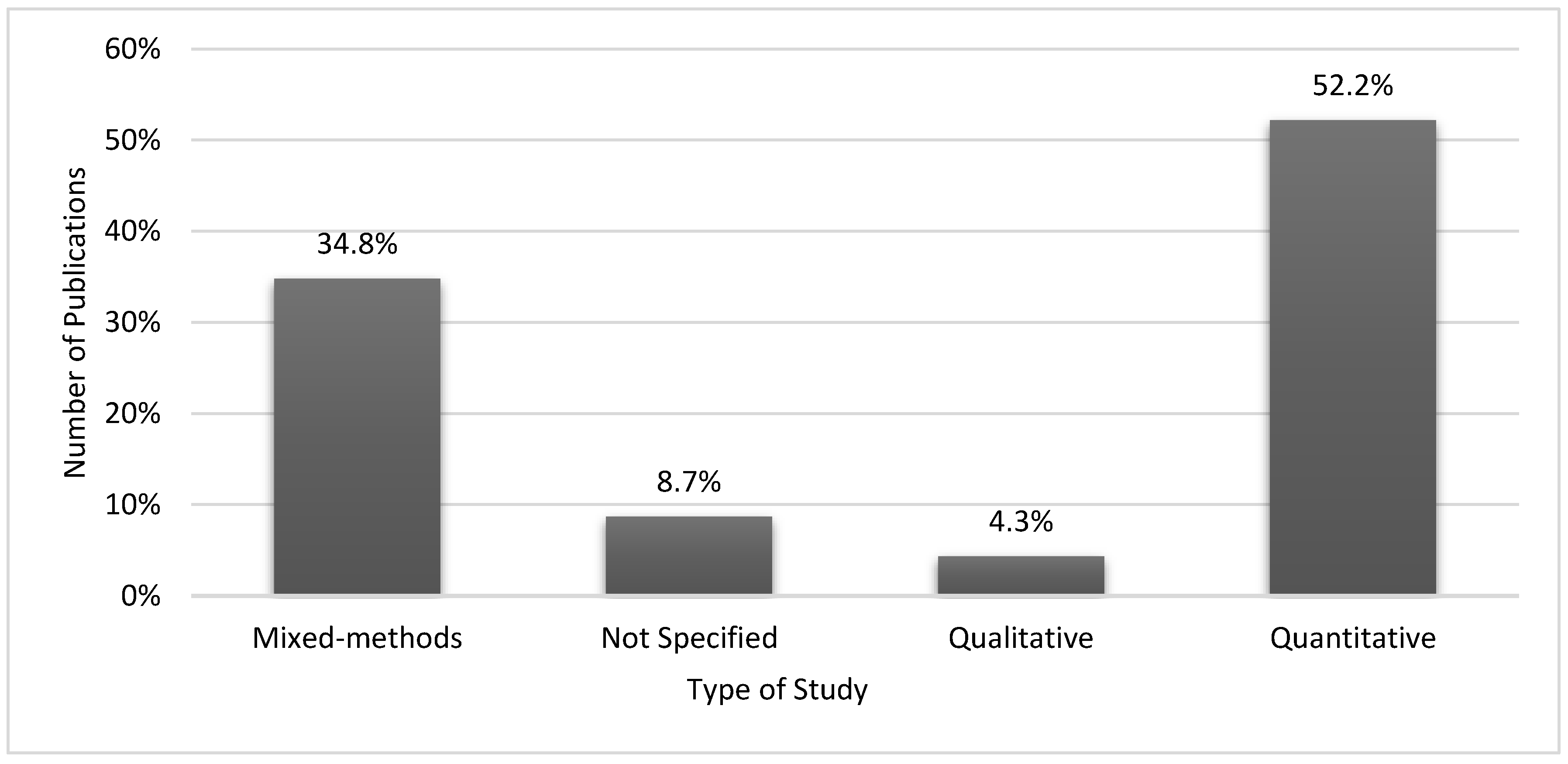
| Type of Study | Qualitative, quantitative, mixed Methods, etc. |
| Sample size | Number of participants or cases in the study |
| Sample Characteristics | Characteristics of the sample (e.g., demographics) |
| Data collection methods | Methods used to collect data |
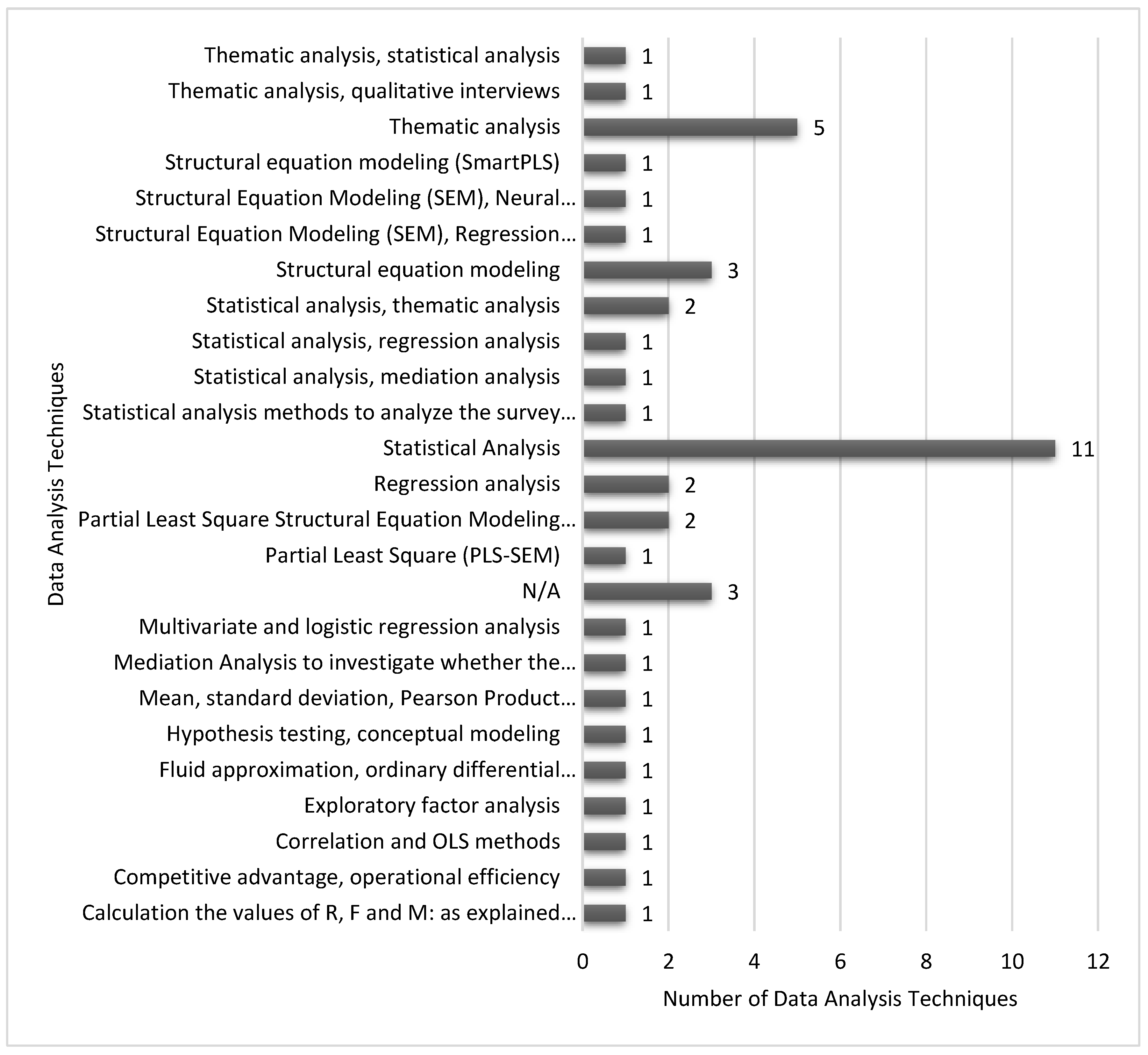
| Data Analysis Techniques | Techniques used to analyze data |
| CRM Performances Metrics | Metrics used to assess CRM performance |
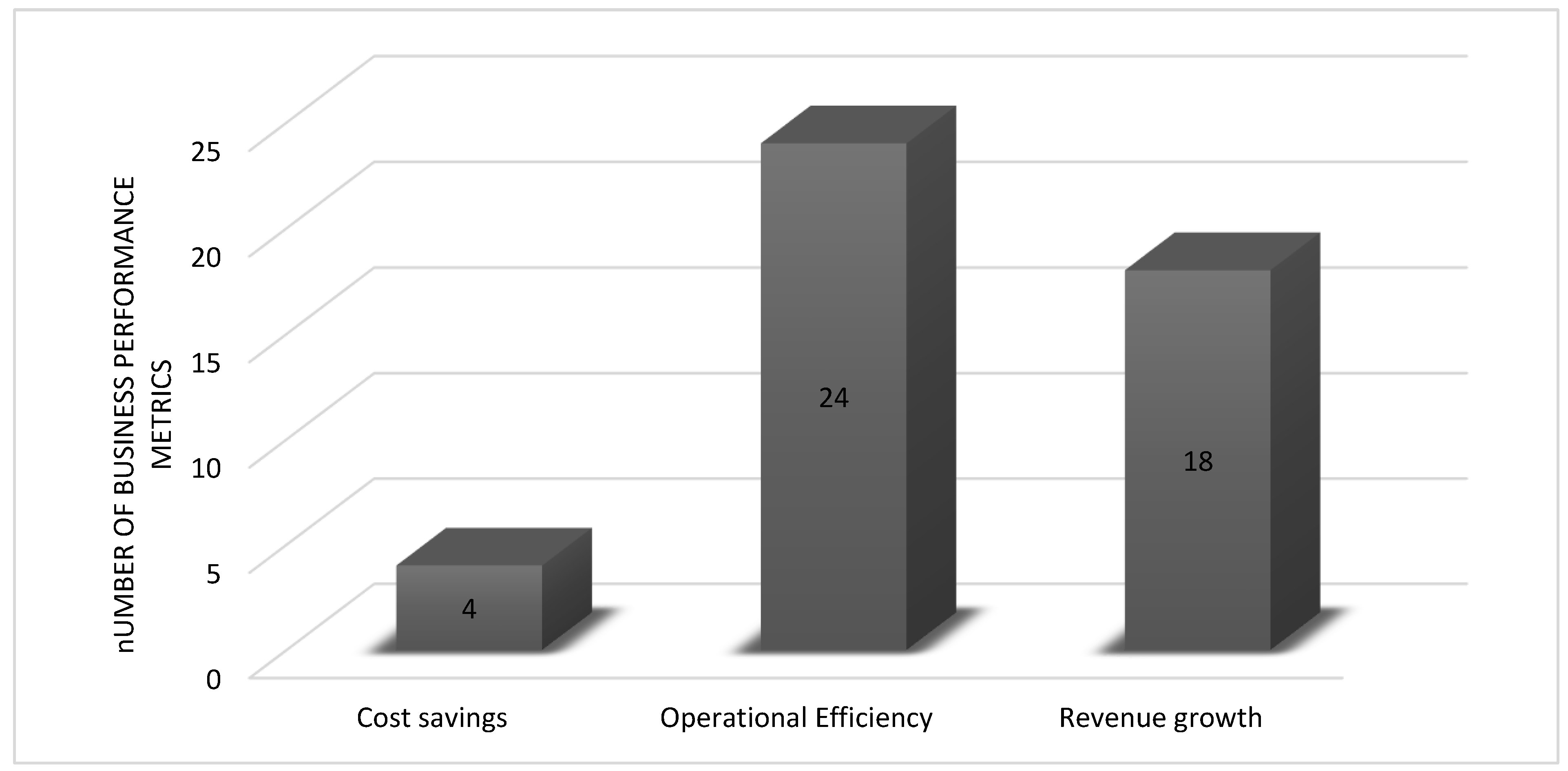
| Business Performance Metrics | Metrics used to assess overall business performance |
| Organizational Outcomes | Outcomes related to the organization |
| Long-Term Impacts | Long-term effects or impacts of the CRM technologies |
| Method Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Objective | To systematically assess the influence of CRM tool on SMEs' performance. |
| Synthesis Development | Developed a robust, transparent, and repeatable process for aggregating results from selected research studies |
| Paper Selection Process | Systematic and thorough paper selection, ensuring alignment with the review’s objectives related to SME performance. |
| Eligibility Synthesis | Selected studies relevant to CRM systems and aligned with the review's aims, as per Table 6 and Figure 5. |
| Criteria for Inclusion | A controlled comparison against predefined criteria was used to include only relevant studies. |
| Bias Reduction | Ensured methodological rigor by reducing bias through the controlled selection process. |
| QA | Research Quality Assessment Questions |
|---|---|
| QA1 | Are the objectives of the research clearly defined? |
| QA2 | Is the methodology of the research well-explained? |
| QA3 | Is the impact of CRM systems on SMEs' performance clearly analyzed? |
| QA4 | Are the methods used for data collection adequately described? |
| QA5 | Is the study's field or context clearly outlined? |
| Ref. | QA1 | QA2 | QA3 | QA5 | QA5 | Total | %Grading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [53, 55, 56, 58, 60, 62, 63, 64, 65, 68, 86] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [41, 48, 52, 77, 78, 85] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [42, 43, 50, 70, 72, 79, 84] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 4 | 80 |
| [46, 80] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 70 |
| [44, 49, 51, 54, 57, 59, 66, 67, 69, 73, 74, 75, 76, 81, 82, 83] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3 | 60 |
| [45, 61, 71] | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 2 | 40 |
| [47] | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 1.5 | 30 |
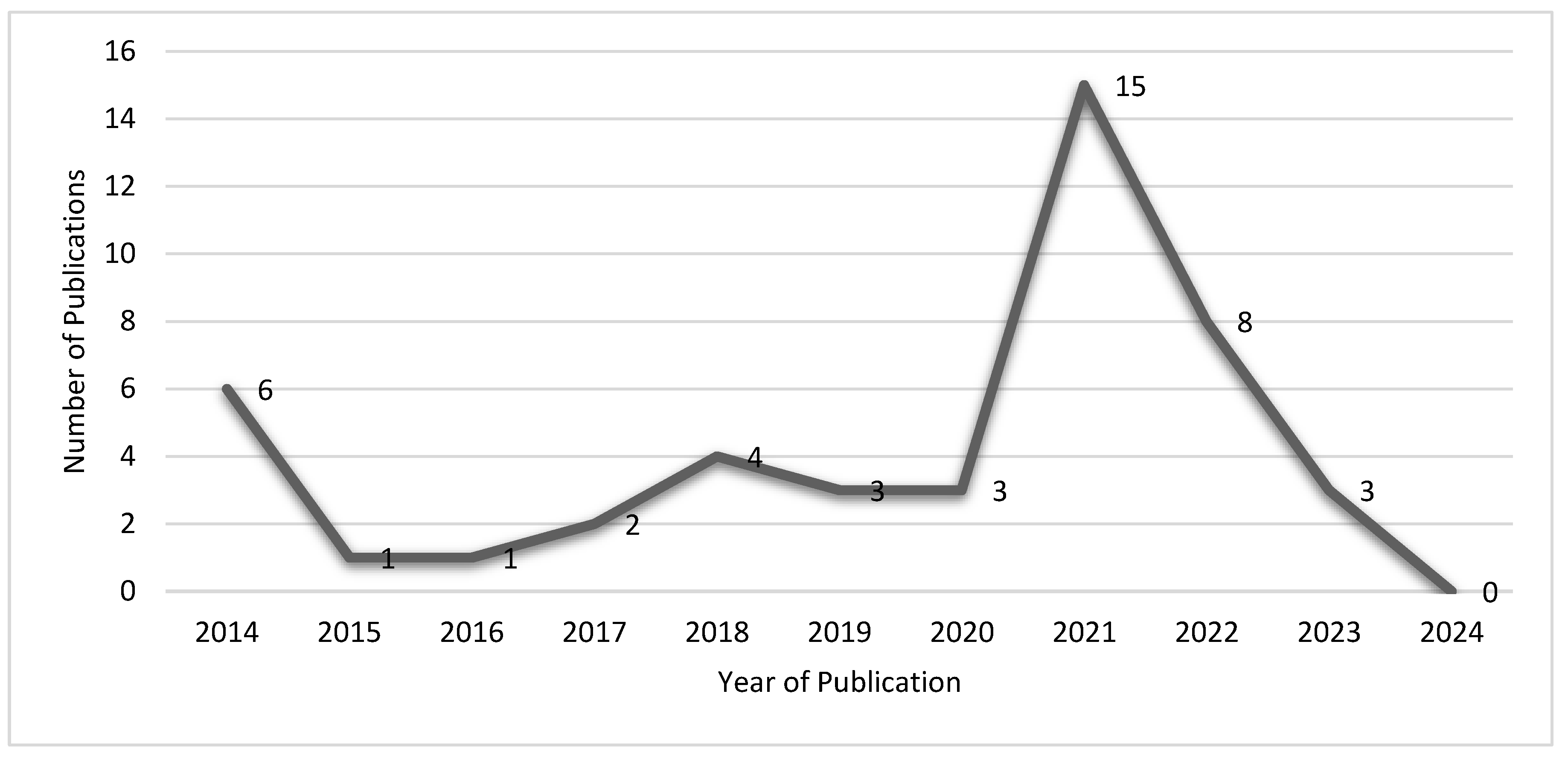
| Published Year | Book Chapter | Conference Paper | Dissertation | Journal Article |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 2015 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 1 |
| 2016 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2017 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2018 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 2019 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 2020 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 2021 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 14 |
| 2022 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 2023 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
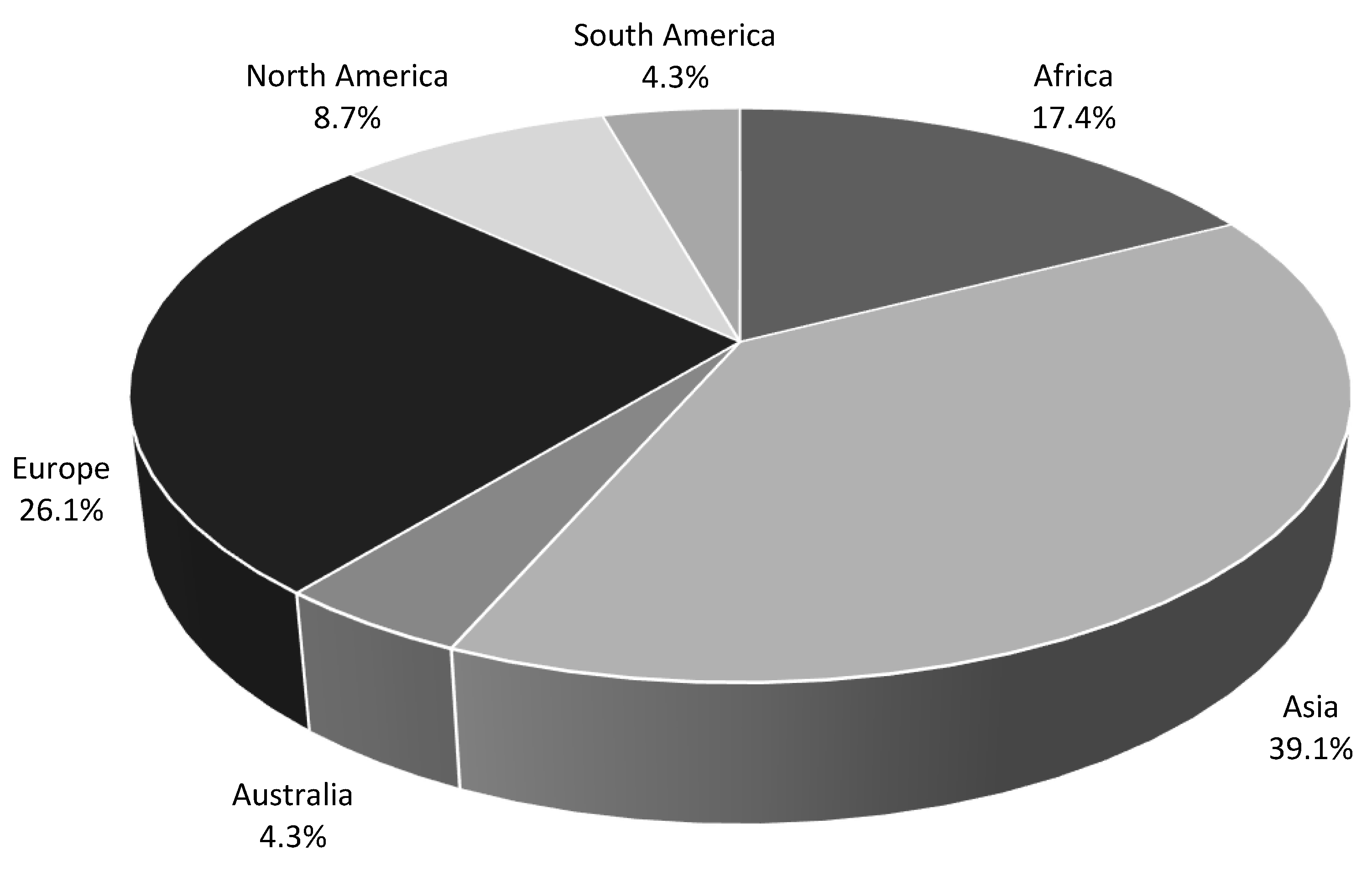
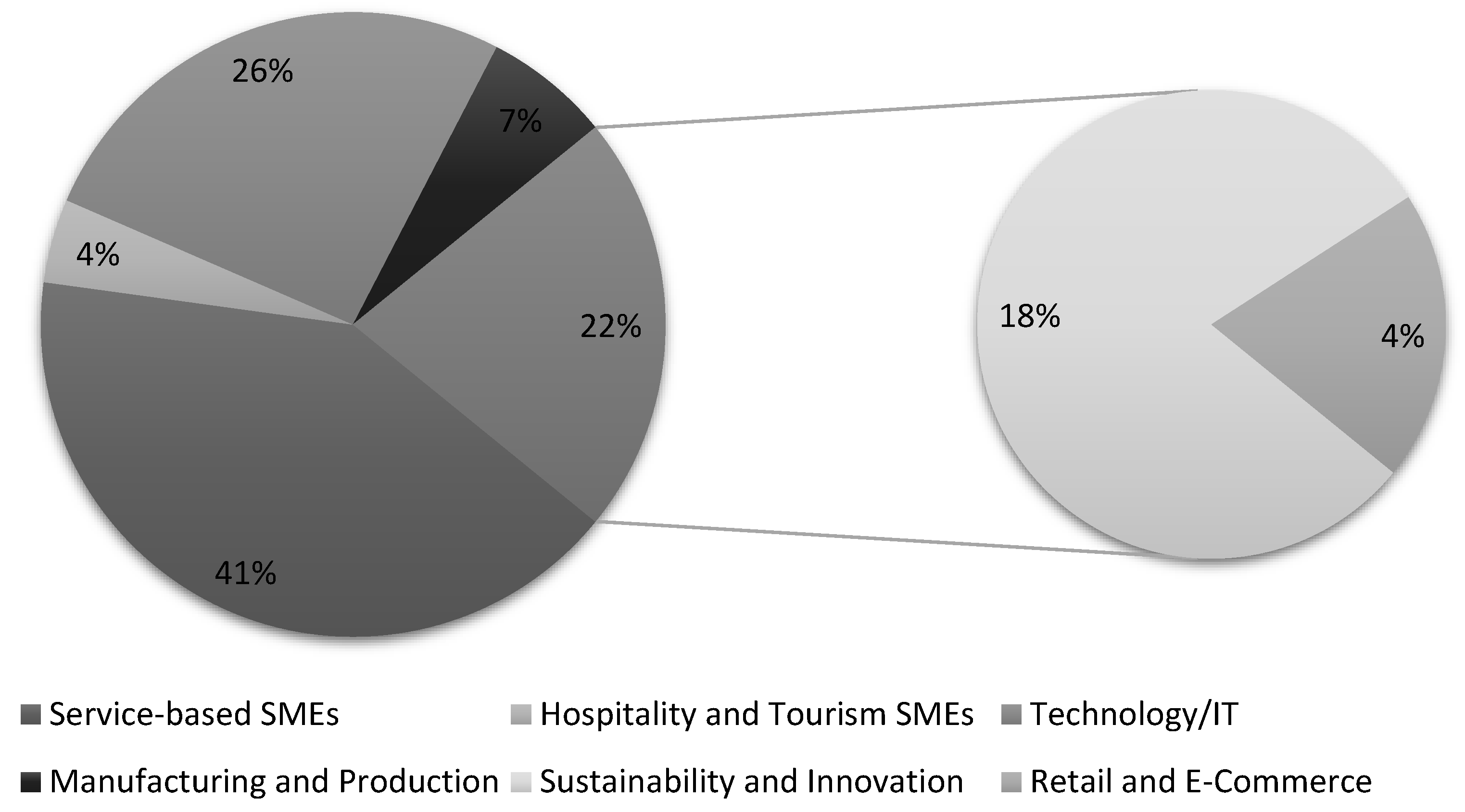
| Industry | Count | % |
|---|---|---|
| Service Industries | 20 | 44 |
| Technology and Innovation | 21 | 45 |
| Manufacturing and Retail | 5 | 11 |
| Study | Sample Size | CRM Type | CRM Performance Metrics | Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [41] | 21 | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Key Customer Focus | Provides valuable insights for industry planning, and technology providers to enhance CRM practices and competitiveness |
| [42] | 59 | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Key Customer Focus | Re-conceptualizes key customer focus, knowledge management and relationship marketing |
| [43] | 44 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Engagement, Satisfaction | Improve customer satisfaction and market share. |
| [44] | 143 | Not Specified | Customer Satisfaction, Knowledge Retention | Determining the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) for long-term competitive advantage. |
| [45] | 100 | Analytical CRM | Perception Of CRM, Employee Involvement | Understand impact on customer retention mediated by customer satisfaction. |
| [46] | 51 | Operational CRM | Customer Engagement, Satisfaction | Influence of customer orientation on SMEs performance. |
| [47] | 13 | Operational CRM | Customer Loyalty, Retention Rate | Improved customer relationships, Business sustainability, and brand reinforcement. |
| [48] | 112 | Operational CRM | Customer Acquisition | CRM dimensions are viewed as tools to improve performance among establishments worldwide. |
| [49] | 25 | Operational CRM | - | Relation of retention to CRM strategy and customer loyalty |
| [50] | 130 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Engagement, Satisfaction | CRM Influence on company performance |
| [51] | 46 | Operational CRM | - | Effect of CRM practices on cost associated with customer acquisition. |
| [52] | 19 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Engagement, Satisfaction | Focuses on operational efficiency and organizational performance |
| [53] | 63 | Operational CRM | Improved Customer Relationships | Develops analytical frameworks and integrates data into their CRM systems. |
| [54] | Operational CRM | Integrated Customer Database | The influence of CRM with the dimensions of customer initiation, customer maintenance and customer termination. | |
| [55] | 23 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Engagement, Satisfaction | effect of CRM on the SMEs that improves the performance of industries and companies. |
| [56] | 8 | Operational CRM | Customer Orientation, Service Quality | Implementing CRM results in market performance of sales and the profitability of the entire organization. |
| [57] | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Efficiency | Improved customer relationships and enhanced business survival | |
| [58] | Analytical CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty | CRM systems help organizations acquire and continuously generate customer knowledge. | |
| [59] | Analytical CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Retention | Drawing on the Resource-Advantage theory of sustainable competitive advantages | |
| [60] | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Performance Metrics | Improved customer loyalty and performance improvement | |
| [61] | 46 | Analytical CRM | - | Organizations seek to improve customer service through CRM systems. |
| [62] | 47 | Operational CRM | ||
| [63] | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Retention | ||
| [64] | 48 | Operational CRM | Customer Acquisition, Retention Rate | |
| [65] | 44 | Operational CRM | ||
| [66] | 23 | Operational CRM | Firm Performance, Customer Loyalty | Building general research model through CRM practices, innovation capability, and firm performance. |
| [67] | 6 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Engagement, Satisfaction | Relative advantages, compatibility, top management support, organizational culture, and technology readiness. |
| [68] | 1 | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty | Communication-distribution infrastructure, business dynamics, customer relations and innovation-quality factors affect CRM. |
| [69] | 0 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Engagement | Social CRM acceptance in improving the performance of companies and their services delivery. |
| [70] | 0 | Operational CRM | Customer Retention, Acquisition | The resilience of MSMEs as a function of firm size and customer management. |
| [71] | 0 | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction | Maintaining information security in the era of digitalization. |
| [72] | 7 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Brand Loyalty | customer orientation has a positive impact on business sustainability. |
| [73] | 0 | Analytical CRM | Customer Acquisition | Positive and significant correlation between marketing communication effectiveness, customer value creation, product innovation, and financial performance. |
| [74] | 0 | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction | Impact of Social Customer Relationship Management (SCRM) on competitive advantage, innovation capability, and SME performance |
| [75] | 4 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Engagement, Satisfaction | Building and enhancing relationships to increase long term profitability of the company. |
| [76] | 71 | Operational CRM | Customer Acquisition, Retention Rate, Customer Satisfaction | |
| [37] | Operational CRM | |||
| [78] | 8 | Analytical CRM | Performance Indicators, Customer Satisfaction | Utilizing subjective measures; future studies could utilize objective performance measures in order to relate CRM and SC with performance. |
| [79] | 118 | Operational CRM | Customer Retention, Satisfaction | |
| [80] | 0 | Analytical CRM | Customer Engagement | Helps improve customer engagement and innovation performance. |
| [81] | 0 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Loyalty | SCRM has a positive impact on CL formation in the MSME sector. |
| [82] | 0 | Analytical CRM | Customer Satisfaction | There is a significant mediation role of SCR between CRM practices and customer satisfaction |
| [83] | 2 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Engagement, Satisfaction | Incorporating social media into CRM strategies and implementations on SMEs performance. |
| [84] | Operational CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty | ||
| [85] | Operational CRM | |||
| [86] | 3 | Collaborative/Social CRM | Customer Satisfaction, Engagement | The mediating role of sustainable dynamic capabilities in the effect of s-CRM on sustainable competitive advantage. |
| Ref | Random Sequence Generation (Selection Bias) | Allocation Concealment (Selection Bias) | Binding of Participants and Personnel (Performance Bias) | Binding of Outcome Assessment (Detection Bias) | Incomplete Outcome Data (Attrition Bias) | Selective Reporting (Reporting Bias) | Other Sources of Bias | Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [41] | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Moderate |
| [42] | Unclear | Unclear | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| [43] | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear |
| [44] | Unclear | High | High | High | High | Unclear | High | High |
| [45] | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [46] | Unclear | Unclear | Moderate | High | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| [47] | Unclear | Unclear | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low | Unclear | Unclear |
| [48] | Low | Low | Unclear | Hight | Low | Unclear | High | Moderate |
| [49] | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High | Low |
| [50] | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Unclear | Unclear |
| [51] | Unclear | Unclear | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate | High | Unclear |
| [52] | Low | Unclear | High | High | Moderate | Low | High | Low |
| [53] | Low | Low | Moderate | Unclear | Low | Moderate | Unclear | Low |
| [54] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Low | Low | Unclear | Unclear |
| [55] | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low |
| [56] | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Unclear |
| [57] | Low | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low |
| [58] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Moderate | Low | Low |
| [59] | Low | Low | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Unclear |
| [60] | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Unclear |
| [61] | Low | Low | Unclear | Hight | Low | Unclear | High | Moderate |
| [62] | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High | Low |
| [63] | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Unclear | Unclear |
| [64] | Unclear | Unclear | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate | High | Unclear |
| [65] | Low | Unclear | High | High | Moderate | Low | High | Low |
| [66] | Low | Low | Moderate | Unclear | Low | Moderate | Unclear | Low |
| [67] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Low | Low | Unclear | Unclear |
| [68] | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low |
| [69] | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Unclear |
| [70] | Low | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low |
| [71] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Moderate | Low | Low |
| [72] | Low | Low | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Unclear |
| [73] | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Unclear |
| [74] | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low |
| [75] | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Unclear |
| [76] | Low | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low |
| [77] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Moderate | Low | Low |
| [78] | Low | Low | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Unclear |
| [79] | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Unclear |
| [80] | Low | Low | Unclear | Hight | Low | Unclear | High | Moderate |
| [81] | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High | Low |
| [82] | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low |
| [83] | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Low | Low | Unclear | Unclear |
| [84] | Low | Unclear | Moderate | Unclear | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Low |
| [85] | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Unclear |
| [86] | Low | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Study | Reporting Bias | Impact on Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| [1-10], [12-15], [17-20], [22-23] | Reported significant improvements in customer satisfaction and retention metrics, suggesting a positive effect of CRM on SMEs. | Reliable, but long-term impact unclear. |
| [11, 13, 16], [18, 21, 24-30], [32-35] | Did not provide comprehensive data on financial performance and growth due to CRM implementation. | Less reliable due to missing information. |
| [31, 36-40], [42-45], [47] | Reported mixed results regarding the impact of CRM on operational efficiency and employee engagement in SMEs. | Moderately reliable, requires more comprehensive data. |
| Industry | Key Finding | Strategic Implications for Business Leaders | Opportunities | Challenges | Relevance to Proposed Systematic Review | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | CRM improves operational efficiency by 30% through process automation and better data management. | Invest in CRM tools to streamline operations and reduce manual workflows, thus boosting productivity. | Opportunity to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. | Initial high investment in CRM software and integration. | Reinforces CRM’s impact on operational efficiency. | Process automation, data management | Increased production efficiency and cost savings. |
| Retail & E-Commerce | CRM adoption leads to a 25-40% increase in customer retention rates. | Focus on customer engagement strategies to boost retention and lifetime value using personalized communication. | Leverage data-driven insights for targeted marketing and personalized offers. | Difficulty in integrating CRM with existing e-commerce platforms. | Aligns with the review's focus on CRM's impact on customer retention. | Personalized customer engagement, targeted marketing | Higher customer retention and increased sales. |
| Hospitality | CRM enhances customer satisfaction by up to 35% through improved service delivery and guest experience. | Utilize CRM to optimize guest feedback management and tailor services to meet customer expectations. | Opportunity to improve service quality and customer satisfaction. | Staff training and resistance to adopting new CRM processes. | Connects to review’s findings on CRM's role in customer satisfaction. | Service quality improvement, customer feedback integration | Enhanced guest satisfaction and repeat business. |
| Technology & IT | CRM implementation supports a 20-30% increase in sales by enabling data-driven decision-making. | Utilize CRM analytics to inform sales strategies and improve the efficiency of sales teams. | Unlock new revenue streams through data-driven sales strategies. | Challenges in ensuring data privacy and regulatory compliance. | Provides evidence for CRM’s impact on data-driven decision-making. | Data analytics, sales strategy optimization | Growth in sales revenue and market share. |
| Automotive | CRM helps improve customer acquisition rates by 20-25% through better customer profiling and follow-ups. | Implement CRM-based lead management to boost sales conversion rates. | Streamline the sales funnel to reduce time to convert leads. | Managing the complexity of customer data integration. | Demonstrates CRM's influence on customer acquisition. | Lead management, sales funnel optimization | Higher customer acquisition rates and conversion efficiency. |
| Pharmaceuticals | CRM adoption facilitates compliance tracking and enhances customer relationships by 15-25%. | Leverage CRM tools for compliance management and improving communication with healthcare providers. | Strengthen regulatory adherence and relationship management. | Complexity in managing sensitive patient data. | Highlights CRM's role in compliance and relationship management. | Compliance management, relationship enhancement | Better regulatory compliance and stronger client relationships. |
| Industry | Step | Framework Focus | Key Features | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | Ties to Proposed Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Assess current operational challenges and CRM readiness. | Identify process inefficiencies and data management gaps. | Operational efficiency, process improvement | Clear understanding of areas where CRM can enhance productivity. | Links to CRM's role in improving operational efficiency. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose a CRM platform that integrates well with existing systems. | Prioritize platforms with manufacturing-specific features. | System compatibility, customization | Selection of a CRM system that supports manufacturing workflows. | Supports findings on customization's role in CRM success. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Implement a pilot phase with selected teams or departments. | Monitor CRM's impact on production processes and data accuracy. | Process automation, data analytics | Identification of best practices for scaling CRM across operations. | Connects to case studies demonstrating phased CRM adoption. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Expand CRM deployment to cover all production areas. | Integrate with supply chain and quality management systems. | End-to-end process integration, supply chain efficiency | Seamless CRM integration across production processes. | Validates CRM's contribution to operational optimization. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuously monitor and adjust CRM usage for process improvements. | Utilize CRM data to optimize production schedules and workflows. | Continuous improvement, data-driven decision-making | Ongoing enhancement of operational efficiency and cost savings. | Reinforces CRM's long-term impact on manufacturing performance. | |
| Retail & E-Commerce | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Evaluate customer engagement gaps and sales process inefficiencies. | Identify key areas for improving customer experience. | Customer engagement, sales strategy | Understanding of critical CRM use cases for boosting retention. | Links to findings on CRM's role in enhancing customer retention. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose a CRM platform with strong e-commerce capabilities. | Look for features such as automated marketing and analytics. | Platform scalability, marketing automation | Selection of a CRM tool that supports targeted marketing strategies. | Supports the review's focus on personalized customer engagement. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Test CRM features like personalized promotions with a customer subset. | Track improvements in customer engagement and sales. | Marketing effectiveness, customer data insights | Identification of successful strategies for scaling across the customer base. | Aligns with case studies on targeted CRM implementations. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Roll out CRM to all customer touchpoints and sales channels. | Integrate CRM with e-commerce platforms and customer service. | Omnichannel integration, customer service enhancement | Increased customer engagement across all channels. | Highlights CRM's role in boosting customer lifetime value. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Use CRM analytics to refine marketing campaigns and sales tactics. | Optimize promotional strategies based on customer behavior data. | Data-driven marketing, sales conversion optimization | Higher sales conversion rates and customer retention. | Validates the review’s findings on data-driven CRM strategies. | |
| Hospitality | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Identify service delivery gaps and customer satisfaction issues. | Assess the quality of guest experience and feedback mechanisms. | Service quality, guest experience | Insights into areas where CRM can enhance customer satisfaction. | Ties to CRM's impact on service delivery in the hospitality sector. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose a CRM platform that supports guest feedback and reservations. | Look for features enabling real-time service updates. | Customer feedback integration, service customization | Selection of a CRM system tailored to hospitality needs. | Supports findings on CRM's role in enhancing service quality. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Implement CRM in specific departments (e.g., front desk, concierge). | Measure improvements in guest satisfaction scores. | Customer service efficiency, staff engagement | Identification of best practices for scaling CRM to other areas. | Aligns with phased approaches in CRM adoption for hospitality. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Extend CRM use to all guest-facing services and back-end operations. | Integrate CRM with property management and guest service systems. | End-to-end guest experience management, operational efficiency | Enhanced guest satisfaction and operational consistency. | Reinforces the review's findings on CRM’s long-term benefits. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuously refine guest services based on CRM insights. | Use data to adjust service standards and anticipate guest needs. | Proactive service management, continuous improvement | Improved guest retention and repeat bookings. | Ties to the role of CRM in driving guest loyalty. | |
| Technology & IT | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Analyze current sales processes and data management systems. | Identify bottlenecks in sales cycles and information flow. | Sales process efficiency, data integration | Clear understanding of CRM requirements for sales optimization. | Links to findings on CRM's impact on data-driven decision-making. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose a CRM solution that supports complex sales cycles and analytics. | Prioritize platforms with robust data analytics capabilities. | Advanced analytics, sales process integration | Selection of a CRM platform that aligns with sales and data needs. | Supports findings on the importance of analytics in CRM success. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Implement CRM with select sales teams for data analysis and reporting. | Monitor changes in sales performance and data accuracy. | Sales performance tracking, data-driven insights | Identification of best practices for broader CRM deployment. | Connects with evidence on phased CRM adoption strategies. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Scale CRM across all sales teams and integrate with existing IT systems. | Ensure CRM is used for all customer interactions and data tracking. | Cross-functional integration, sales cycle optimization | Improved sales efficiency and revenue growth. | Validates the review’s conclusions on CRM’s role in sales growth. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuously refine sales strategies using CRM analytics. | Adjust sales targets and tactics based on CRM insights. | Continuous sales improvement, data-driven strategy optimization | Higher revenue growth and market competitiveness. | Reinforces CRM's impact on long-term sales performance. | |
| Automotive | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Evaluate current lead management processes and customer follow-up practices. | Identify gaps in customer acquisition and sales conversion. | Lead management, customer profiling | Insights into areas where CRM can boost sales conversion rates. | Ties to findings on CRM’s role in customer acquisition. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose a CRM system that supports customer profiling and follow-up automation. | Focus on features like lead scoring and automated reminders. | Lead generation, follow-up automation | Selection of a CRM platform that enhances customer acquisition. | Supports findings on the need for CRM customization in automotive. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Implement CRM with a specific sales region or dealership. | Monitor improvements in sales conversion rates and lead tracking. | Sales conversion tracking, customer engagement | Identification of successful CRM practices for scaling. | Aligns with phased approaches to CRM implementation. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Roll out CRM across all sales locations and integrate with service departments. | Ensure seamless data flow between sales and service functions. | End-to-end sales and service integration, customer satisfaction | Improved sales conversion and customer retention. | Validates the review’s conclusions on end-to-end CRM integration. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Refine sales tactics and customer engagement strategies using CRM insights. | Use data-driven strategies to optimize customer follow-up. | Sales cycle improvement, continuous customer engagement | Higher customer acquisition and retention rates. | Ties to long-term impacts of CRM on sales performance. | |
| Pharmaceuticals | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Assess compliance management and customer relationship challenges. | Identify gaps in tracking regulatory adherence and client engagement. | Compliance tracking, client relationship management | Understanding of CRM needs in compliance and client relations. | Links to findings on CRM’s role in compliance management. |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Choose a CRM system that supports compliance tracking and secure data management. | Look for features that facilitate regulatory reporting and secure communication. | Compliance support, data security | Selection of a CRM platform that aligns with regulatory requirements. | Supports findings on the importance of compliance in CRM success. | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Test CRM features related to compliance and customer interactions. | Monitor improvements in regulatory adherence and client communication. | Compliance management, secure data handling | Identification of best practices for broader CRM implementation. | Connects to phased adoption approaches for sensitive industries. | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Expand CRM deployment to all departments handling compliance and client relations. | Ensure CRM supports seamless regulatory reporting and client management. | Cross-departmental integration, compliance optimization | Improved regulatory adherence and client satisfaction. | Validates the review’s conclusions on CRM’s impact on compliance. | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuously refine compliance processes and client interactions using CRM data. | Use insights to adjust compliance protocols and customer communication strategies. | Continuous improvement, proactive client engagement | Enhanced compliance and stronger client relationships. | Reinforces the review’s findings on long-term CRM benefits. |
| Industry | Best Practice | SME Type | Operational Challenge | Strategic Drivers | Expected Impact | Ties to Systematic Review Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 1. Automate Repetitive Processes | Medium-sized manufacturers | High manual workload in production processes | Process automation, cost reduction | 30-40% improvement in operational efficiency | Reinforces the review's findings on CRM's role in automation. |
| 2. Integrate CRM with SCM | Small manufacturers | Disconnected supply chain and production workflows | Supply chain efficiency, data integration | Improved coordination between supply chain and production | Supports CRM’s impact on data management and integration. | |
| 3. Provide Staff Training | Small and medium-sized manufacturers | Resistance to adopting new CRM tools | Change management, employee engagement | Increased adoption rates and CRM user satisfaction | Aligns with the review’s focus on training for successful adoption. | |
| Retail & E-Commerce | 1. Use CRM for Targeted Marketing | E-commerce platforms | Low customer engagement and high cart abandonment | Customer engagement, targeted promotions | 25-35% increase in customer retention and conversion rates | Links to the review’s findings on personalized customer strategies. |
| 2. Implement Omnichannel CRM | Small retailers | Inconsistent customer experience across channels | Omnichannel integration, customer satisfaction | Enhanced customer satisfaction and lifetime value | Supports CRM’s role in unifying customer interactions. | |
| 3. Leverage Data Analytics | Online retail stores | Lack of actionable insights from customer data | Data-driven decision-making, marketing optimization | Higher sales conversion and improved marketing ROI | Connects to findings on data analytics enhancing CRM impact. | |
| Hospitality | 1. Personalize Guest Experiences | Small hotels | Inability to cater to individual guest preferences | Service quality, customer satisfaction | 30-50% improvement in guest satisfaction scores | Ties to findings on CRM’s role in improving service delivery. |
| 2. Centralize Guest Feedback Management | Bed-and-breakfast establishments | Poor follow-up on guest feedback | Feedback management, service enhancement | Better handling of complaints and improved online reviews | Supports the review's focus on guest feedback integration. | |
| 3. Use CRM for Reservation Management | Resorts | Inefficiencies in reservation and booking processes | Booking efficiency, customer convenience | 20-30% reduction in reservation processing time | Aligns with CRM’s impact on process efficiency in hospitality. | |
| Technology & IT | 1. Enhance Sales Process Automation | IT service providers | Lengthy sales cycles and poor follow-up with leads | Sales efficiency, customer acquisition | 15-25% increase in lead conversion | Supports findings on the importance of sales automation. |
| 2. Improve Cross-Functional Data Sharing | Software development firms | Data silos between sales, marketing, and customer support | Data integration, collaboration | Improved internal communication and customer satisfaction | Reinforces CRM’s role in data management. | |
| 3. Use CRM for Client Project Management | Small tech firms | Lack of project tracking and customer progress updates | Project management, client engagement | 20-30% increase in project delivery efficiency | Connects to the review’s insights on CRM enhancing service quality. | |
| Automotive | 1. Automate Lead Scoring and Follow-Up | Car dealerships | Low sales conversion due to ineffective lead management | Sales conversion, customer engagement | 20-30% improvement in lead conversion rates | Ties to findings on CRM's impact on customer acquisition. |
| 2. Utilize CRM for After-Sales Service Management | Auto service centers | Inconsistent follow-up on service reminders | Customer retention, service quality | Increased repeat service bookings and customer loyalty | Aligns with findings on CRM enhancing long-term customer value. | |
| 3. Integrate CRM with Inventory Systems | Parts distributors | Inefficiencies in managing inventory and order fulfillment | Inventory management, operational efficiency | Better stock management and reduced order processing times | Supports the review’s focus on CRM’s impact on inventory control. | |
| Pharmaceuticals | 1. Use CRM for Compliance Tracking | Drug distributors | Challenges in meeting regulatory requirements | Compliance management, regulatory adherence | 15-25% improvement in compliance monitoring | Reinforces CRM’s role in compliance and regulatory management. |
| 2. Streamline CRM with Sales and Marketing | Small pharmaceutical companies | Disconnected sales and marketing strategies | Sales optimization, marketing alignment | Better coordination and higher sales performance | Supports findings on CRM improving sales and marketing synergy. | |
| 3. Leverage CRM for Customer Education Programs | Health product suppliers | Difficulty in educating customers about new products | Customer education, brand loyalty | Increased customer awareness and loyalty | Aligns with findings on CRM’s role in customer engagement. |
| Industry | Key Metrics/KPIs | Measurement Focus | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | Ties to Systematic Review Findings | Priority (1 = Highest, 2 = Medium, 3 = Low) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 1. Production Efficiency Rate | Measures the proportion of production time used effectively. | Process optimization, cost reduction | 20-30% improvement in production output | Aligns with CRM’s role in enhancing operational efficiency. | 1 |
| 2. Order Fulfillment Cycle Time | Tracks the average time taken to complete customer orders. | Supply chain efficiency, customer satisfaction | Faster order processing and delivery times | Reinforces findings on CRM's impact on supply chain integration. | 2 | |
| 3. Inventory Turnover Ratio | Monitors the frequency of inventory replacement. | Inventory management, operational control | Reduced excess inventory and lower holding costs | Supports the review's focus on inventory management optimization. | 2 | |
| Retail & E-Commerce | 1. Customer Retention Rate | Measures the percentage of repeat customers over a period. | Customer engagement, loyalty programs | 25-35% increase in customer retention and repeat purchases | Links to findings on CRM’s role in enhancing customer loyalty. | 1 |
| 2. Cart Abandonment Rate | Tracks the percentage of online shoppers who leave without purchasing. | Sales conversion optimization, customer engagement | Reduced cart abandonment, leading to higher sales conversion | Supports CRM's impact on e-commerce sales performance. | 1 | |
| 3. Average Order Value (AOV) | Measures the average revenue generated per transaction. | Sales revenue growth, targeted marketing | Increased average order value and higher revenue | Reinforces findings on CRM driving sales growth through analytics. | 2 | |
| Hospitality | 1. Guest Satisfaction Score | Evaluates customer feedback regarding their service experience. | Service quality, customer experience | 30-50% improvement in guest satisfaction scores | Ties to findings on CRM’s role in improving service quality. | 1 |
| 2. Average Response Time to Guest Inquiries | Tracks the time taken to respond to customer queries. | Customer service, operational efficiency | Faster response times and higher guest satisfaction | Supports findings on CRM’s impact on customer engagement. | 2 | |
| 3. Room Occupancy Rate | Measures the percentage of available rooms occupied. | Revenue management, booking efficiency | Increased occupancy rates and higher revenue per available room | Aligns with CRM’s impact on optimizing booking processes. | 3 | |
| Technology & IT | 1. Sales Conversion Rate | Monitors the percentage of leads converted to customers. | Sales effectiveness, customer acquisition | 20-30% improvement in sales conversion rates | Links to findings on the importance of CRM in sales optimization. | 1 |
| 2. Customer Churn Rate | Measures the rate at which customers stop using the services. | Customer retention, service quality | Reduced churn rates and increased customer lifetime value | Reinforces the review's focus on customer retention strategies. | 2 | |
| 3. Average Deal Size | Evaluates the average revenue generated per closed deal. | Revenue growth, sales performance | Higher average deal size and increased revenue | Supports findings on CRM’s role in sales strategy enhancement. | 2 | |
| Automotive | 1. Lead Conversion Rate | Tracks the percentage of leads converted into sales. | Sales funnel efficiency, customer acquisition | 20-30% improvement in lead-to-sales conversion | Aligns with findings on CRM’s impact on customer acquisition. | 1 |
| 2. Customer Satisfaction Index | Measures customer satisfaction with after-sales services. | Customer service quality, customer loyalty | Improved satisfaction with after-sales support | Ties to CRM’s role in boosting long-term customer value. | 2 | |
| 3. Service Revenue Growth Rate | Evaluates the growth in revenue generated from vehicle services. | Service optimization, revenue management | Higher revenue from maintenance and repair services | Reinforces CRM’s role in after-sales service management. | 2 | |
| Pharmaceuticals | 1. Compliance Adherence Rate | Measures the rate at which regulatory requirements are met. | Compliance management, regulatory adherence | 15-25% improvement in compliance tracking | Supports findings on CRM’s role in compliance monitoring. | 1 |
| 2. Sales Growth Rate | Monitors the increase in revenue generated from product sales. | Sales performance, market expansion | Higher sales growth through targeted customer engagement | Links to CRM's role in enhancing sales performance. | 1 | |
| 3. Customer Education Program Participation Rate | Tracks the number of customers participating in educational programs. | Customer engagement, brand loyalty | Increased participation in customer education initiatives | Aligns with findings on CRM’s role in customer education. | 3 |
| Industry | Roadmap Focus | Policy Framework | Strategic Link | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | When to Undertake | Estimated Duration | Champion | Ties to Proposed Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 1. Digitalization of Customer Service Processes | Digital Economy Act, Smart Industry Policies | Facilitates adoption of CRM for process automation | Process automation, customer service efficiency | Improved customer service response times, higher satisfaction | Q1 of year 1 | 6-12 months | Operations Manager, IT Director | Aligns with findings on CRM enhancing service processes in manufacturing. |
| 2. Integration with Supply Chain Systems | Industry 4.0 Policy Guidelines | Strengthens data-driven decision-making | Supply chain efficiency, real-time data sharing | Better coordination between production and supply chain | Q2 of year 1 | 9-18 months | Supply Chain Manager, IT Director | Reinforces the study’s conclusions on data integration benefits. | |
| 3. Employee Training and Change Management | Workforce Development Policies | Addresses the need for employee buy-in and training | Change management, skills development | Increased CRM adoption rates, higher staff productivity | Ongoing starting Q3 of year 1 | Continuous (6-month review cycles) | HR Manager, Training and Development Lead | Links to findings on training as a critical success factor for CRM adoption. | |
| Retail & E-Commerce | 1. Omnichannel Strategy Development | E-Commerce and Digital Marketing Frameworks | Ensures consistency across customer interaction channels | Customer engagement, sales growth | Enhanced customer experience, increased sales conversion | Q1 of year 1 | 12-18 months | Marketing Manager, Customer Experience Lead | Supports CRM’s role in unifying customer touchpoints in retail. |
| 2. Use of Data Analytics for Personalization | Data Protection and E-Commerce Policies | Promotes data-driven marketing initiatives | Targeted marketing, customer loyalty programs | Higher conversion rates and customer lifetime value | Q2 of year 1 | 9-12 months | Data Analytics Manager, CRM Analyst | Aligns with findings on data analytics enhancing CRM capabilities. | |
| 3. Cybersecurity Measures for Online Platforms | Cybersecurity Policy Guidelines | Protects customer data and builds trust | Data protection, compliance | Increased data security, higher customer confidence | Immediate | 6-9 months | IT Security Officer, Compliance Manager | Ties to CRM’s importance in ensuring data integrity in e-commerce. | |
| Hospitality | 1. Personalization of Guest Services Using CRM | Tourism and Hospitality Development Acts | Encourages service quality improvement | Customer satisfaction, guest experience | Improved guest feedback scores and repeat business | Q1 of year 2 | 12-24 months | Guest Services Manager, CRM Manager | Links to CRM’s role in enhancing customer service in hospitality. |
| 2. Standardization of Feedback Management Systems | Service Quality Assurance Frameworks | Facilitates consistent handling of customer feedback | Feedback management, service improvement | Better handling of guest complaints and service recovery | Q2 of year 2 | 6-12 months | Quality Assurance Lead, Customer Service Manager | Supports the study’s focus on guest feedback integration. | |
| 3. Digital Booking Platform Integration | Digital Transformation in Tourism Policies | Simplifies the booking process for customers | Booking convenience, operational efficiency | Higher occupancy rates and streamlined reservation processes | Q3 of year 2 | 9-15 months | IT Director, Reservations Manager | Aligns with CRM’s impact on process efficiency. | |
| Technology & IT | 1. Automation of Sales Processes | Digital Innovation and IT Services Policies | Increases sales productivity through automation | Sales optimization, lead management | 15-25% improvement in lead conversion rates | Immediate | 6-12 months | Sales Manager, Automation Specialist | Links to findings on CRM’s role in sales process automation. |
| 2. Data Integration for Cross-Functional Use | Data Sharing and Open Data Policies | Facilitates collaboration across departments | Data-driven decision-making, cross-departmental collaboration | Enhanced customer insights and service quality | Q1 of year 1 | 12-18 months | IT Manager, Data Integration Lead | Reinforces findings on data integration for CRM effectiveness. | |
| 3. Project Management via CRM | IT Project Management Standards | Improves project tracking and customer progress updates | Client engagement, project management | Higher project delivery efficiency and client satisfaction | Q3 of year 1 | 12-24 months | Project Manager, CRM Implementation Lead | Connects to the study’s insights on using CRM for service quality. | |
| Automotive | 1. Lead Management Optimization | Automotive Industry Development Plans | Improves customer acquisition efforts | Sales conversion, customer relationship management | Higher lead conversion rates and sales performance | Q1 of year 2 | 6-12 months | Sales Director, CRM Specialist | Ties to CRM’s impact on customer acquisition. |
| 2. Integration with After-Sales Service Platforms | Vehicle Maintenance and Customer Service Policies | Enhances after-sales support | Customer retention, service optimization | Increased repeat service bookings and customer loyalty | Q2 of year 2 | 9-18 months | After-Sales Service Manager, IT Coordinator | Aligns with findings on long-term customer value in automotive. | |
| 3. Inventory Management via CRM | Automotive Supply Chain Regulations | Improves inventory tracking and order fulfillment | Inventory control, operational efficiency | Reduced stockouts and better order processing | Q3 of year 2 | 6-12 months | Supply Chain Manager, Inventory Analyst | Supports the review’s focus on CRM’s impact on inventory management. | |
| Pharmaceuticals | 1. Compliance Tracking Using CRM | Health and Safety Compliance Regulations | Ensures adherence to regulatory requirements | Compliance management, regulatory adherence | Improved compliance monitoring and reduced regulatory risks | Immediate | 9-12 months | Compliance Officer, Quality Control Manager | Supports findings on CRM’s role in regulatory compliance. |
| 2. Sales and Marketing Integration | Pharmaceutical Sales and Distribution Policies | Enhances coordination between sales and marketing | Sales performance, marketing alignment | Better coordination and increased revenue from product sales | Q1 of year 1 | 12-18 months | Sales Director, Marketing Manager | Links to findings on CRM improving sales and marketing synergy. | |
| 3. Customer Education Programs Using CRM | Public Health and Patient Education Policies | Increases awareness of new products | Customer education, brand loyalty | Higher participation in educational initiatives and loyalty | Q2 of year 1 | 6-9 months | Customer Engagement Manager, Training Coordinator | Aligns with findings on CRM’s role in customer engagement. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





