Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has expanded at a fast rate, transforming whole sectors by more easily connecting people, systems, and objects than ever before. In addition, the number of IOT devices has increased rapidly, with predictions indicating that it will jump from 9.7 billion in 2020 to 29 billion by 2030, indicating a growth in IoT usage (Statista, 2023). Also, the growing adoption of IoT can be attributed to developments in big data analytics, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, which have all improved real-time data collection, analysis, and action (Tippannavar et al., 2023). Moreover, the rapid growth of the IoT industry is demonstrated by its critical role in transforming industries including manufacturing, healthcare, energy, transportation, food and agriculture (Omotayo et al., 2023).
With a growth rate of 21.5%, the global IoT market reached $201 billion in 2022, demonstrating the crucial impact that IoT continues to have across a wide range of industries (Statista, 2023). IoT has become a crucial tool for supply chain management improving transparency, efficiency, and decision-making. IoT lowers operating costs and increases customer satisfaction by allowing real-time tracking of items, inventory control, and equipment predictive maintenance (Gubbi et al., 2013). IoT's potential in streamlining supply chains is much enhanced by its capacity to interact with other technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence (Omotayo et al., 2023). IoT sensors, for example, can track the state of commodities in transit, thereby ensuring that perishable items are kept at the right temperature and so minimising waste and damage (Chukwudebe et al., 2021). IoT-driven data analytics also lets businesses proactively manage supply chain interruptions and precisely estimate demand (Sundmaeker et al., 2010, De Vass et al., 2020). IoT has strategic relevance in supply chain management since businesses are spending more and more on IoT solutions to acquire a competitive edge on the worldwide market (Aljabhan, 2022).
Although IoT technologies are still in their early years in Nigeria, their adoption has great potential especially in sectors such as manufacturing, online retail market, food, transportation and agriculture (Oluwi et al., 2021). Despite challenges including poor infrastructure, high implementation costs, and low technological knowledge, Nigerian companies are beginning to see the transforming possibilities of IoT. IoT is being used, for example, in agriculture to monitor soil moisture levels, optimise irrigation systems, and raise agricultural output boosting food security (Iorliam et al., 2021). IoT is helping the energy sector to minimise energy losses and boost the efficiency of power distribution networks (Shah et al., 2020; Oluwi et al., 2021). The industrial sector is also looking to IoT to help streamline manufacturing processes and increase product quality (Otitoju et al., 2023). However given the above-mentioned challenges, Nigeria's IoT adoption rate is slower than that of developed countries. However, when given constant investments in digital infrastructure and growing awareness of its benefits, IoT seems to have a bright future in Nigerian companies.
Despite the growing global popularity and clear benefits of IoT technologies across various fields, their application in Nigerian supply chains remains underexplored in the literature. Most existing studies focus on IoT applications in developed countries, leaving a gap in understanding the unique challenges and opportunities within the Nigerian supply chain context (Omotayo et al., 2023). While some research highlights IoT's potential in sectors like energy and agriculture in Nigeria, there is limited empirical evidence on its effective integration into supply chain management to address specific logistical challenges faced by Nigerian companies (Oke et al., 2020). This lack of research has hindered the development of strategies tailored to the Nigerian market, which faces issues such as inadequate infrastructure, varying levels of technological awareness, and regulatory challenges (Terab et al., 2023). Although IoT is known to enhance transparency, decision-making, and efficiency in supply chains (de Vass et al., 2021), there is a significant shortage of empirical data on its impact onNigerian businesses. The available studies are mostly conceptual or based on case studies from other countries, which may not accurately reflect the realities of Nigerian supply chains (Omotayo et al., 2023). Without empirical research, it is challenging to assess IoT's potential to address inefficiencies such as delays, losses, and high operational costs in Nigeria (Oke et al., 2020). Understanding how IoT can be adapted to meet the specific needs of Nigerian supply chains requires empirical studies that measure performance before and after IoT implementation (Aamer et al., 2021). Such data would not only validate the theoretical benefits of IoT but also identify the conditions under which these technologies are most effective in the Nigerian context (Omotayo et al., 2023). Moreover, empirical findings could guide industry stakeholders and policymakers in making informed decisions about investing in IoT infrastructure and developing regulations that encourage IoT adoption in Nigerian supply chains (Chukwudebe et al., 2021).
The primary aim of this research is to evaluate the impact of IoT adoption on supply chain efficiency within five Nigerian companies. To achieve this, the study will focus on assessing the level of IoT adoption in these companies and examining its effect on key supply chain efficiency metrics, including lead time, inventory turnover, and order accuracy. The research seeks to answer two main questions: the extent of IoT adoption in the selected companies and how this adoption influences supply chain efficiency. The study posits two hypotheses;
H1: Companies with higher levels of IoT integration exhibit a reduction in lead time for order delivery compared to companies with lower levels of IoT integration.
H1 (Null Hypothesis): There is no significant difference in lead time for order delivery between companies with higher levels of IoT integration and those with lower levels of IoT integration.
H2: Companies that have adopted IoT technologies in their supply chain operations are more likely to cite cost reduction as their primary motivation for adoption compared to companies that have not adopted IoT technologies.
H2 (Null Hypothesis): Companies that have adopted IoT technologies in their supply chain operations are not more likely to cite cost reduction as their primary motivation for adoption compared to companies that have not adopted IoT technologies.
Literature Review
Overview of IoT Technologies
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of networked devices that exchange and collect data. These devices, which are equipped with sensors and actuators, interact with their surroundings and communicate data with other connected devices and systems via the internet, enabling a wide range of automated procedures (Khan et al., 2022). Again, the key components of IoT include hardware (sensors and devices), software (middleware, data management, and analytics), and communication technologies (network protocols, cloud computing) (Saleh et al., 2023). Hence, the Internet of Things (IoT) is a major technology in Industry 4.0, allowing the physical and digital worlds to be integrated through smart devices that gather and process massive volumes of data in order to optimise operations and drive innovation.
The Role of IoT in Supply Chain Management
IoT improves visibility, efficiency, and operational flexibility thereby transforming supply chain management (SCM). Real-time item tracking made possible by it is absolutely vital for effective inventory control and logistics (Behl & Dhir, 2022). By tracking the whereabouts and condition of goods across the supply chain, RFID and GPS technology help companies to guarantee timely delivery and quality control (Akyuz & Bicer, 2022).
Moreover, IoT is crucial for predictive maintenance which uses data from linked devices to identify and prevent equipment problems, hence reducing downtime and maintenance costs (Cui et al. 2020). This raises general effectiveness in operations inside supply chains. IoT combined with other new technologies like blockchain increases supply chain traceability and openness. Particularly crucial in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, this mix guarantees that goods are obtained and provided in conformity with specified criteria (Pal & Yasar, 2021). While enabling new degrees of openness and innovation using interaction with other digital technologies, IoT considerably boosts tracking, maintenance, and operating efficiency in supply chain management (Saleh et al., 2023).
Impact of IoT on Supply Chain Metrics
Empirical studies have shown that IoT has a considerable impact on many supply chain variables, such as lead time, inventory turnover, and order correctness. For example, de Vass et al. (2021) discovered that IoT adoption in supply chains resulted in a significant reduction in lead times by improving real-time visibility and communication throughout the supply chain network. Also, the capacity to monitor and track commodities in real time enables faster decision-making and modifications, minimising delays and increasing overall efficiency (de Vass et al., 2021). Similarly, IoT has been demonstrated to increase inventory turnover rates by allowing for more precise demand forecasts and inventory management. IoT and predictive analytics solutions help companies to maximise inventory levels, therefore reducing the chance of overstocking or stockouts. Monsreal and Benitez (2022) study found that companies using IoT-based inventory management systems experienced a significant increase in inventory turnover since they helped to better match inventory levels with actual demand.
Furthermore, IoT use has been linked to increases in order accuracy. More importantly, the usage of IoT-enabled tracking and verification technologies ensures that orders are processed correctly and on schedule. For example, Aljabhan (2022) claimed that enterprises implementing IoT technologies in their logistics and supply chain operations saw a considerable improvement in order accuracy, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and lower return rates.
IoT Adoption in Developing Countries
Since IoT technologies can solve a range of socioeconomic issues, their acceptance in developing countries has drawn more attention. IoT deployment in undeveloped countries usually requires an analysis of its application in some sectors, such agriculture, healthcare, and smart cities. These studies revealed that although IoT has the ability to increase productivity and efficiency, its adoption faces significant barrier including lack of infrastructure, high pricing, and regulatory issues even if it may improve these areas. In a study on IoT adoption in Malawi, Twabi and Mikeka (2021) for instance find that the main obstacles to IoT implementation for waste management systems are inadequate infrastructure, high implementation costs, and security issues. Also, in undeveloped nations, López-Vargas et al. (2020) also observe that effective adoption depends on low-cost IoT solutions and technological limitations. However, despite these difficulties, IoT has great opportunities in developing countries. By enhancing access to important services, raising productivity, and hence fostering economic growth, technology can help to meet the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). López-Vargas et al. (2020) underline that IoT, when combined with low-cost, pay-as-go strategies, can encourage general adoption in low-income areas, therefore supporting sustainable development.
Challenges and Opportunities for IoT Adoption in Nigeria
IoT has potential as well as challenges in Nigeria. Lack of appropriate infrastructure is one of the most important problems since it prevents IoT technology development in several fields. Chukwudebe et al. (2021) claim that two main obstacles to IoT deployment in Nigeria are the lack of robust legal frameworks and the great expense of equipment. Their study claims that governments have to help IoT thrive by allocating sufficient spectrum, enhancing connectivity, and so supporting each other (Chukwudebe et al., 2021). Also, the advantages of IoT acceptance in Nigeria cannot be emphasised for instance, by enabling real-time monitoring and control of devices, thereby improving power grid management a vital need in a nation prone to power outages in the energy sector. Olufemi and Akinwole (2023) claim that Nigerian power plants have already used IoT technologies, therefore increasing visibility and stability in the network of power grid. Moreover, combining IoT with other developing technologies like blockchain opens fresh opportunities for raising efficiency and transparency in Nigerian businesses. In sectors like healthcare and agriculture where IoT helps maximise resource management and enhance service delivery, this connectivity can especially be beneficial. Otitoju et al. (2023), for instance, show how IoT-driven Climate-Smart Agriculture Technologies (CSATs) could change Nigerian agriculture by improving yields while reducing environmental effects.
Theoretical Frameworks Linking IoT Adoption to Supply Chain Efficiency
Many theoretical frameworks has highlighted the integration of technology to increase supply chain efficiency; these provide the basis for the application of the Internet of Things (IoT) in supply chain management. The Resource-Based View (RBV) is one such concept that asserts that IoT technology may be used to generate highly valuable, uncommon, and unique resources hence improving supply chain performance. IoT's real-time data collecting and analysis helps to optimise inventory management, reduce lead times, and increase order accuracy by means of which lead times could be improved. Moreover, using IoT, organisations can enhance supply chain responsiveness and flexibility through internal and external competency integration, reconfiguration, and adaptation to rapidly changing environments (Pimsakul et al., 2021). The Dynamic Capability View (DCV) architecture helps companies to increase these aspects.
Results
43 responses were received as against 50 respondents targeted. The findings in
Table 1 indicate a diverse representation across various supply chain sectors, with the Transportation sector being the most prominent at 23.3%, followed by the Pharmaceutical/Healthcare Supply Chain at 20.9%. Companies such as DHL and Emzor are notably prominent within their respective sectors, each accounting for 23.3% and 20.9% of the total sample, respectively. Positions within the companies are skewed towards Operations Managers, who constitute 41.9% of the respondents, highlighting their critical role in supply chain management. Additionally, the majority of respondents have between 5 to 10 years of experience (51.2%), suggesting a relatively experienced workforce. Notably, company size appears to be concentrated in the medium-sized category, with 41.9% of companies employing between 50 to 200 and 201 to 500 employees, indicating that mid-sized companies are predominant in this study. The findings suggested that mid-sized companies, particularly in the Transportation and Pharmaceutical sectors, with experienced Operations Managers, play a significant role in the supply chain landscape. This diversity in sectors and company sizes offers a comprehensive view of the supply chain dynamics, reflecting the importance of experience and operational management in these industries.
Table 2 reveals significant adoption of IoT technologies within various sectors, with 74.4% of companies implementing IoT in their supply chain operations. The primary motivation is improving operational efficiency, cited by 57.1% of respondents. However, full integration of IoT across all supply chain processes remains limited (8.6%), with most companies (65.7%) only partially integrated. The transportation sector leads in IoT adoption, reflecting its critical role in logistics. Additionally, a strong belief exists that government policy and infrastructure development can enhance IoT adoption, with 72.1% of respondents affirming this perspective. These findings underscore the need for further IoT integration and supportive policies.
Table 3 highlights the significant positive impact of IoT adoption on various supply chain metrics. The highest improvements are observed in customer satisfaction and order accuracy, with 18 and 17 respondents, respectively, rating these metrics as significantly improved (Rating 5). Operational cost efficiency also shows strong improvement, with 16 respondents indicating significant gains. Lead time and inventory turnover have more moderate improvements, with the majority of responses clustered around Ratings 3 and 4. Notably, no respondents indicated a lack of improvement (Rating 1) in lead time or inventory turnover, suggesting overall positive effects of IoT integration.
Rating Scale: Rating 1: No Improvement, Rating 2: Slight Improvement, Rating 3: Moderate Improvement, Rating 4: Good Improvement and Rating 5: Significant Improvement
Table 4 illustrates the widespread adoption of various IoT applications within supply chains. Automated warehouse management and smart sensors for equipment maintenance are the most implemented, with 60% of respondents indicating their use. Real-time tracking of inventory is also prevalent, with 54.3% of companies adopting this technology. Real-time monitoring of goods in transit and IoT-enabled supply chain analytics follow, with 45.7% and 42.9% adoption, respectively. IoT-based demand forecasting, while less common, is still utilised by 31.4% of respondents. These findings suggest a strong emphasis on automation, real-time data, and analytics in improving supply chain operations through IoT.
The
Table 5 showcases the key benefits observed from IoT adoption in supply chains. Enhanced operational efficiency stands out as the most significant benefit, reported by 96.9% of respondents. Improved order accuracy, better decision-making capabilities, and increased customer satisfaction each garnered 50% of responses, highlighting their importance in IoT implementation. Reduced lead times (37.5%) and increased inventory turnover (31.3%) are also notable, though less prevalent. These findings indicate that while operational efficiency is the most widely recognised benefit, other advantages like accuracy, decision-making, and customer satisfaction are also critical outcomes of IoT integration in supply chains.
Table 6 outlines the primary challenges encountered in the adoption of IoT within supply chains. Inadequate technological infrastructure is the most significant barrier, with 90.6% of respondents highlighting it as a challenge. A substantial 84.4% of respondents also report a lack of skilled personnel, indicating a critical need for specialised training. High implementation costs, cited by 81.3%, further emphasise the financial hurdles companies face. Security and privacy concerns affect 28.1% of respondents, while resistance to change within the organisation (12.5%) and regulatory issues (9.4%) are less common but still notable challenges. These challenges underscore the complexity of IoT adoption.
Table 7 highlights the future IoT applications that companies plan to implement. The most anticipated application is IoT-enabled customer engagement tools, with 72.1% of respondents expressing interest, indicating a focus on enhancing customer interaction and experience. Advanced predictive analytics follows closely, with 69.8% of respondents recognising its potential to improve decision-making and forecasting. Blockchain for supply chain transparency is also a significant interest area, noted by 53.5% of respondents, reflecting the growing emphasis on accountability and traceability. Additionally, 48.8% of respondents plan to explore autonomous vehicles and drones, while 44.2% are interested in AI-driven automation, underscoring the drive towards increased automation and efficiency.
Hypothesis Testing
H1: Companies with higher levels of IoT integration exhibit a reduction in lead time for order delivery compared to companies with lower levels of IoT integration.
H1 (Null Hypothesis): There is no significant difference in lead time for order delivery between companies with higher levels of IoT integration and those with lower levels of IoT integration.
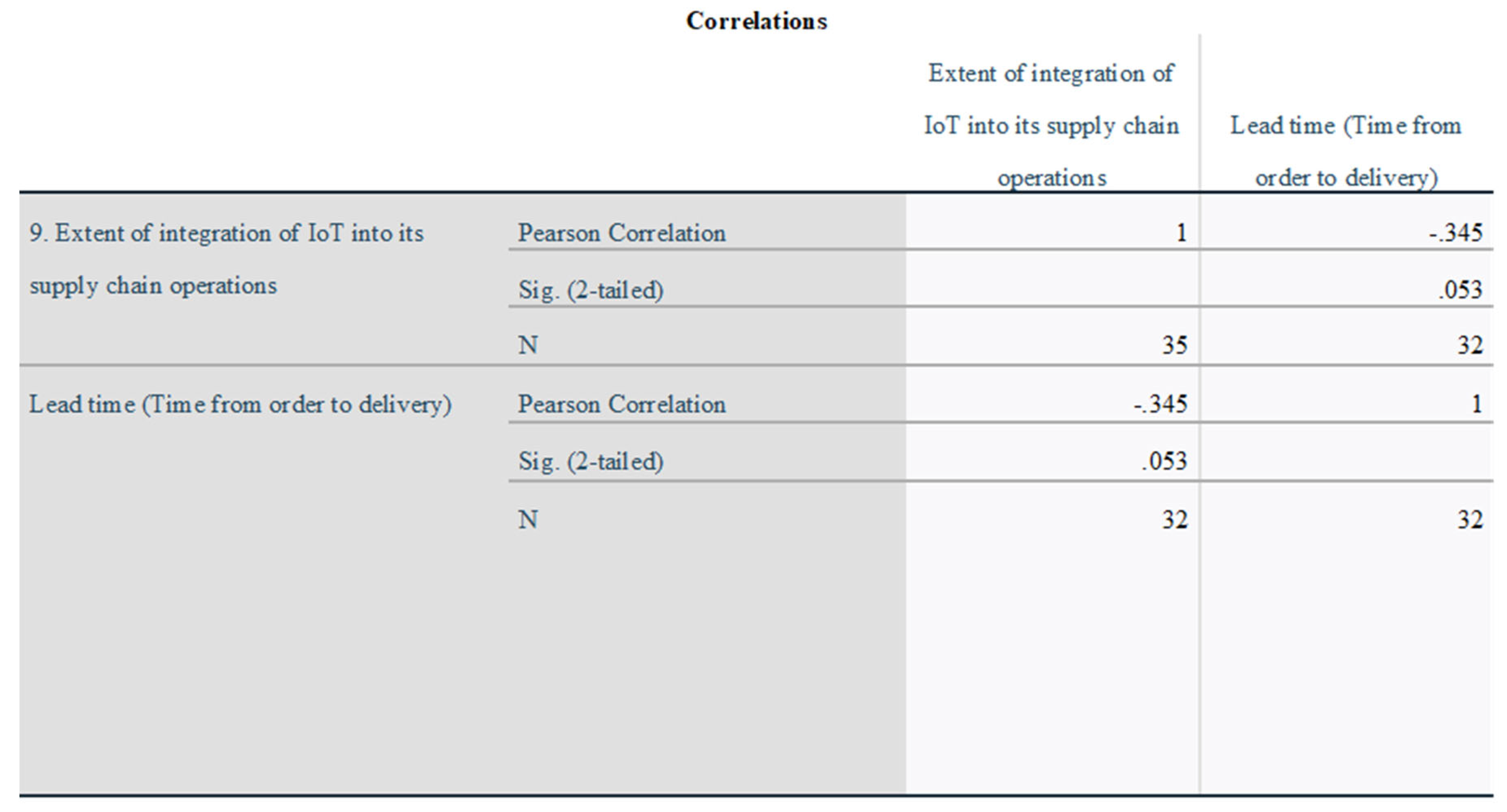
The Pearson correlation analysis shows a negative correlation (-0.345) between the extent of IoT integration and lead time, suggesting that increased IoT integration is associated with shorter lead times. However, the p-value of 0.053 is slightly above the conventional significance threshold of 0.05. This indicates that while the data suggests a moderate relationship, the evidence is not statistically significant. As a result, the null hypothesis cannot be rejected at this time, and further investigation with a larger sample size is warranted to confirm these findings.
H2: Companies that have adopted IoT technologies in their supply chain operations are more likely to cite cost reduction as their primary motivation for adoption compared to companies that have not adopted IoT technologies.
H2 (Null Hypothesis): Companies that have adopted IoT technologies in their supply chain operations are not more likely to cite cost reduction as their primary motivation for adoption compared to companies that have not adopted IoT technologies.
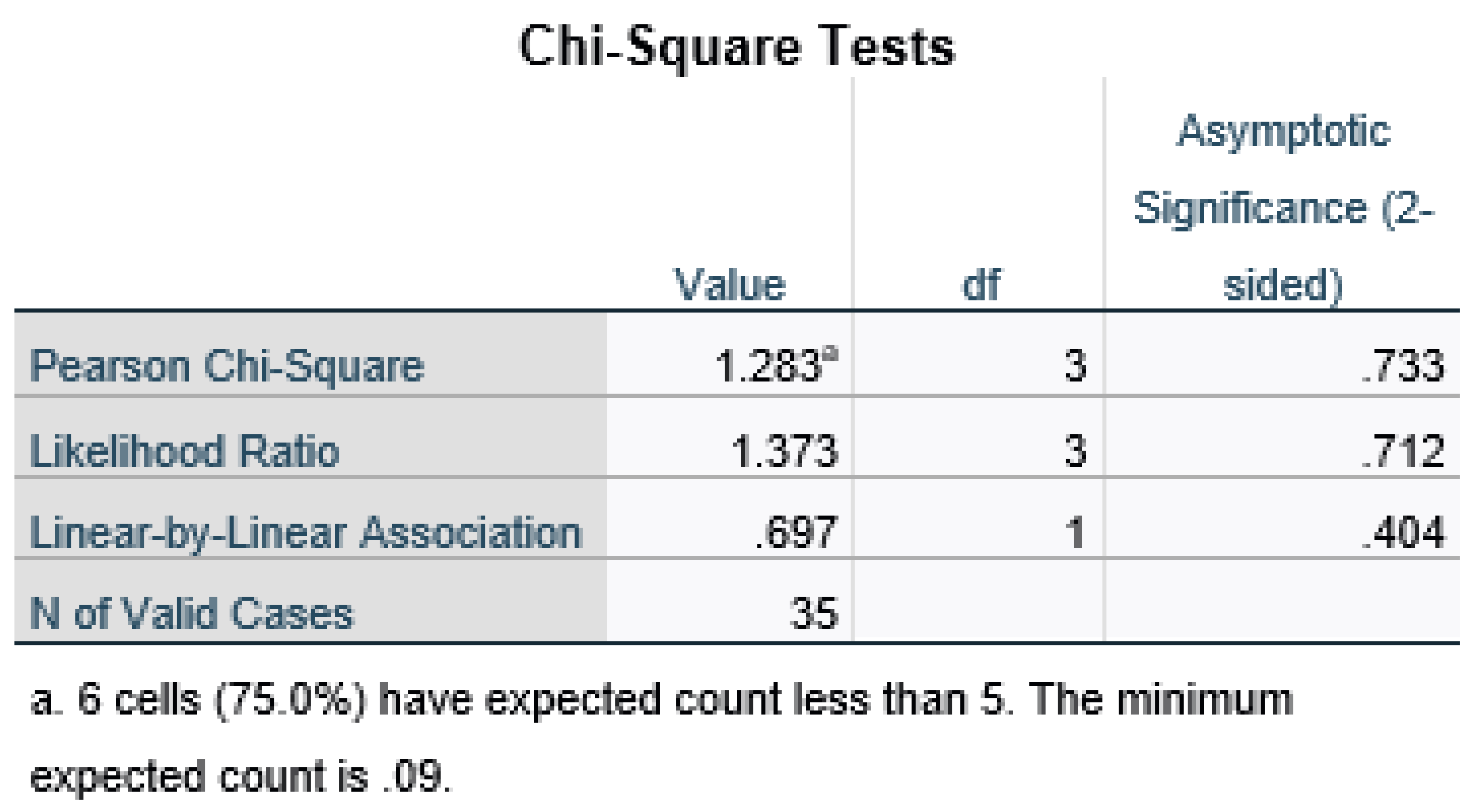
The Chi-square test results indicate a Pearson Chi-square value of 1.283 with a p-value of 0.733. Given that the p-value is much higher than the standard significance threshold of 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. This result suggests that there is no statistically significant association between IoT adoption in supply chain operations and citing cost reduction as the primary motivation for adoption. Consequently, the hypothesis (H2) that companies adopting IoT are more likely to cite cost reduction as their primary motivation is not supported by the data.
Discussion of Findings
The mixed results of this study reflect broader trends and nuances in the literature on IoT adoption and supply chain management. While the potential for IoT to enhance supply chain efficiency is well-supported in the literature, the realisation of these benefits is often contingent on a variety of contextual factors. The finding that IoT integration is associated with reduced lead times, although not statistically significant, aligns with studies that emphasise the efficiency gains from real-time data and improved supply chain visibility (de Vass et al., 2021; Monsreal & Benitez, 2022). However, the lack of significant evidence supporting cost reduction as a primary motivation contrasts with the literature that frequently highlights this as a major driver for IoT adoption (Akyuz & Bicer, 2022). This contrast suggests that while IoT can theoretically lead to cost savings, in practice, particularly within the Nigerian context, companies may face substantial upfront costs and infrastructural challenges that overshadow these potential savings. This is consistent with findings from other developing countries, where the high costs of IoT implementation and the lack of supporting infrastructure often pose significant barriers to adoption (Twabi & Mikeka, 2021). Additionally, the study’s emphasis on the importance of government policy and infrastructure development in enhancing IoT adoption aligns with the broader literature, which highlights the critical role of supportive regulatory frameworks and investments in digital infrastructure to facilitate the effective deployment of IoT technologies (Omotayo et al., 2023).
Moreover, the study's findings regarding the primary motivations for IoT adoption, such as improving operational efficiency and enhancing customer service, reflect a more nuanced understanding of how companies in developing economies approach IoT. This aligns with studies by López-Vargas et al. (2020), who argue that in contexts with significant infrastructural challenges, companies may prioritise immediate operational improvements over cost savings. The findings of this study, therefore, contribute to the growing body of research that underscores the importance of contextual factors in shaping the outcomes of IoT adoption and provide valuable insights for policymakers and industry stakeholders in Nigeria.
The first hypothesis (H1) suggested that higher IoT integration would reduce lead times. The study found a negative correlation between IoT adoption and lead time, indicating shorter lead times with increased IoT use. However, the result was not statistically significant (p = 0.053), which partially aligns with existing literature, such as de Vass et al. (2021), which confirms that IoT enhances real-time visibility and reduces delays. The marginal significance of this study contrasts with more definitive findings in developed countries, likely due to Nigeria's infrastructural limitations and technological gaps (Oluwi et al., 2021). The second hypothesis (H2) proposed that companies adopting IoT would prioritise cost reduction. Contrary to this, the study found no significant association between IoT adoption and cost reduction, with a high p-value from the Chi-square test. This finding contrasts with much of the literature, where cost reduction is often cited as a key driver for IoT adoption (Aljabhan, 2022). For instance, Cui et al. (2020) highlighted that IoT reduces operational costs through predictive maintenance and optimised inventory management. The divergence in this study may reflect Nigeria's unique challenges, where companies may focus more on improving operational efficiency and customer service than on immediate cost savings, possibly due to high implementation costs and infrastructural hurdles (Chukwudebe et al., 2021).