Submitted:
19 October 2024
Posted:
21 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Questions
- How is customer satisfaction measured and monitored in SMEs using the BSC framework?
- Which role does technology play in implementing an effective BSC in SMEs?
- What is the impact of the BSC on the performance and motivation of employees in SMEs?
- What challenges do SMEs face when integrating the BSC methodology into their existing management practices?
- How do SMEs customize the BSC framework to align with their specific strategic goals as well as operational contexts?
1.2. Research Motivation
1.3. Research Contribution
1.4. Research Novelty
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
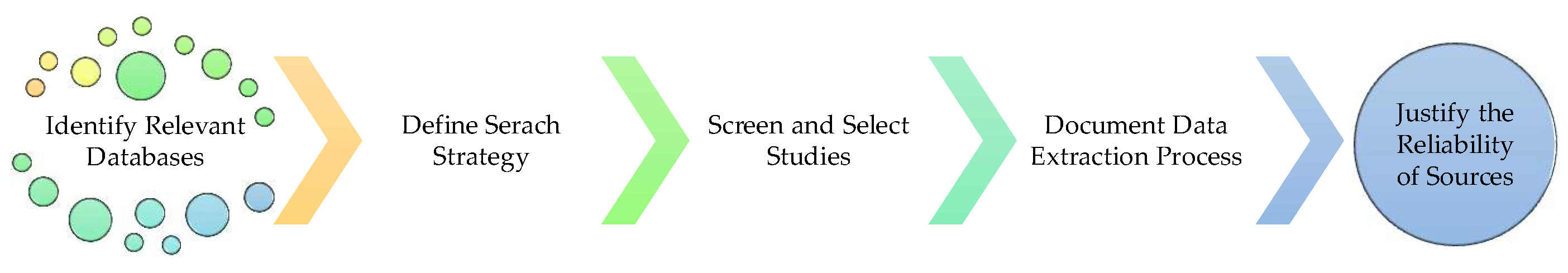
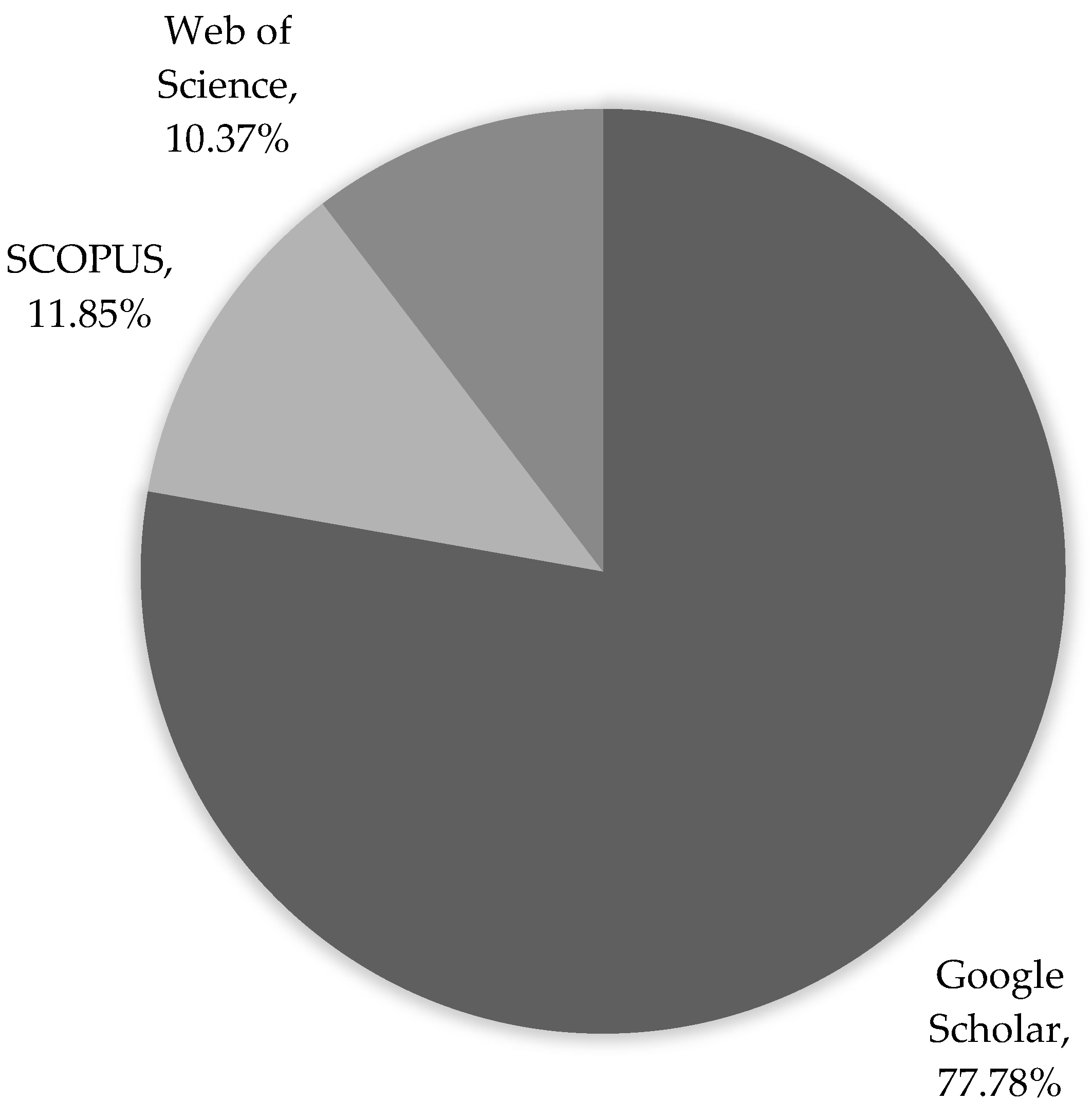
2.1. Information Sources
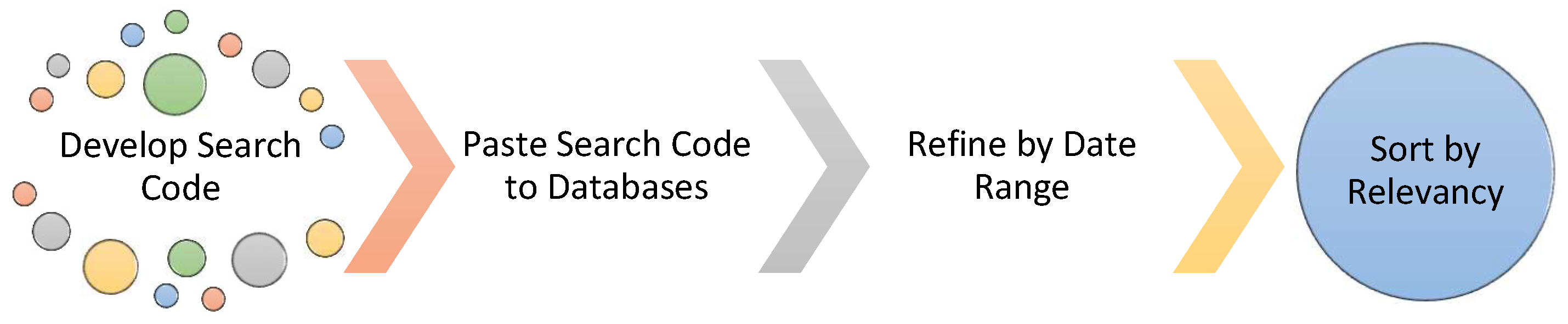
2.1. Search Strategy
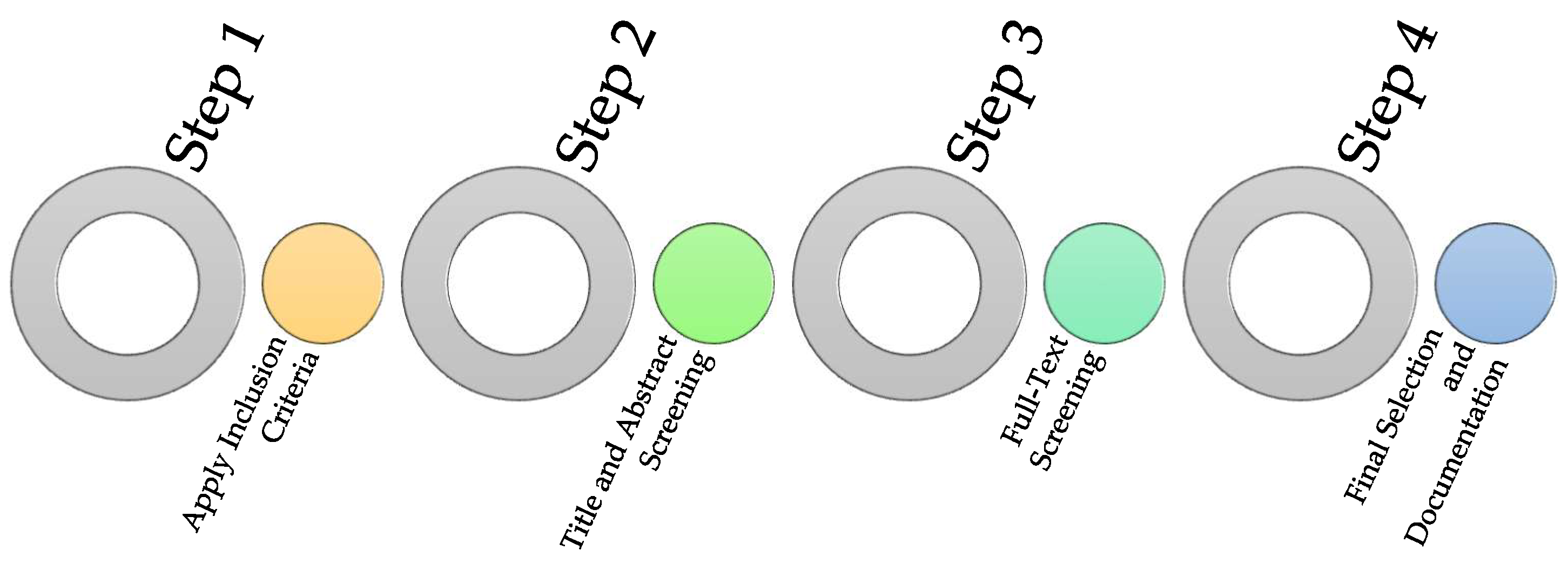
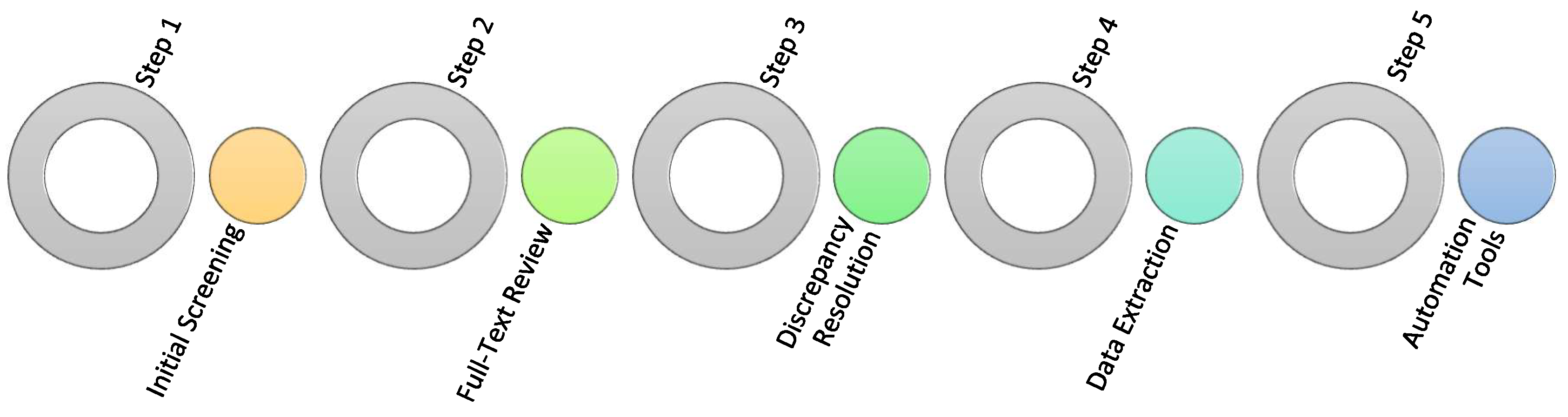
2.1. Selection Process
2.1. Data Collection Process
2.1. Data Items
2.1. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.1. Effect Measures
2.1. Synthesis Methods
2.2. Reporting Bias
2.2. Certainty Assessment
3. Results
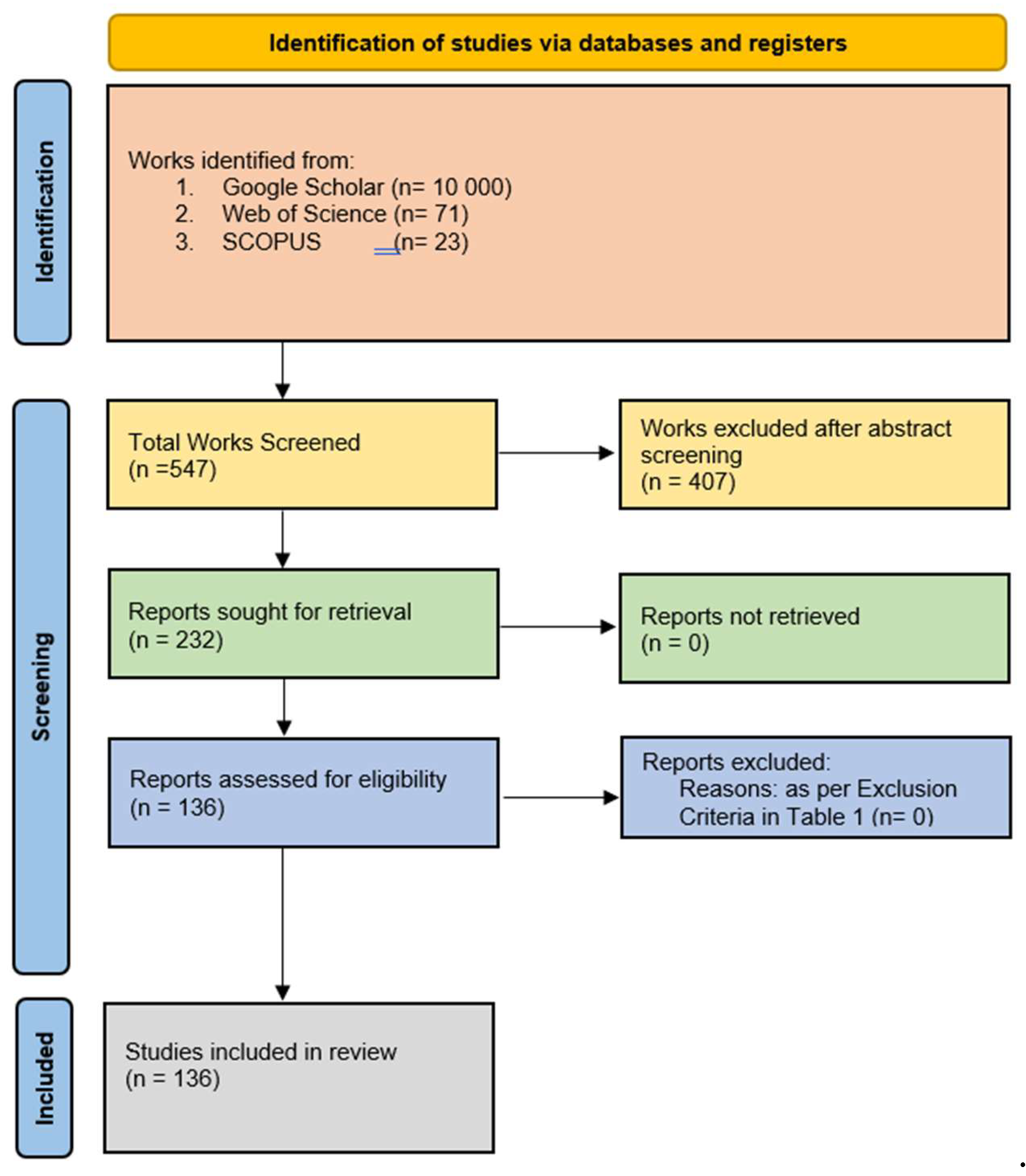
3.1. Study Selection
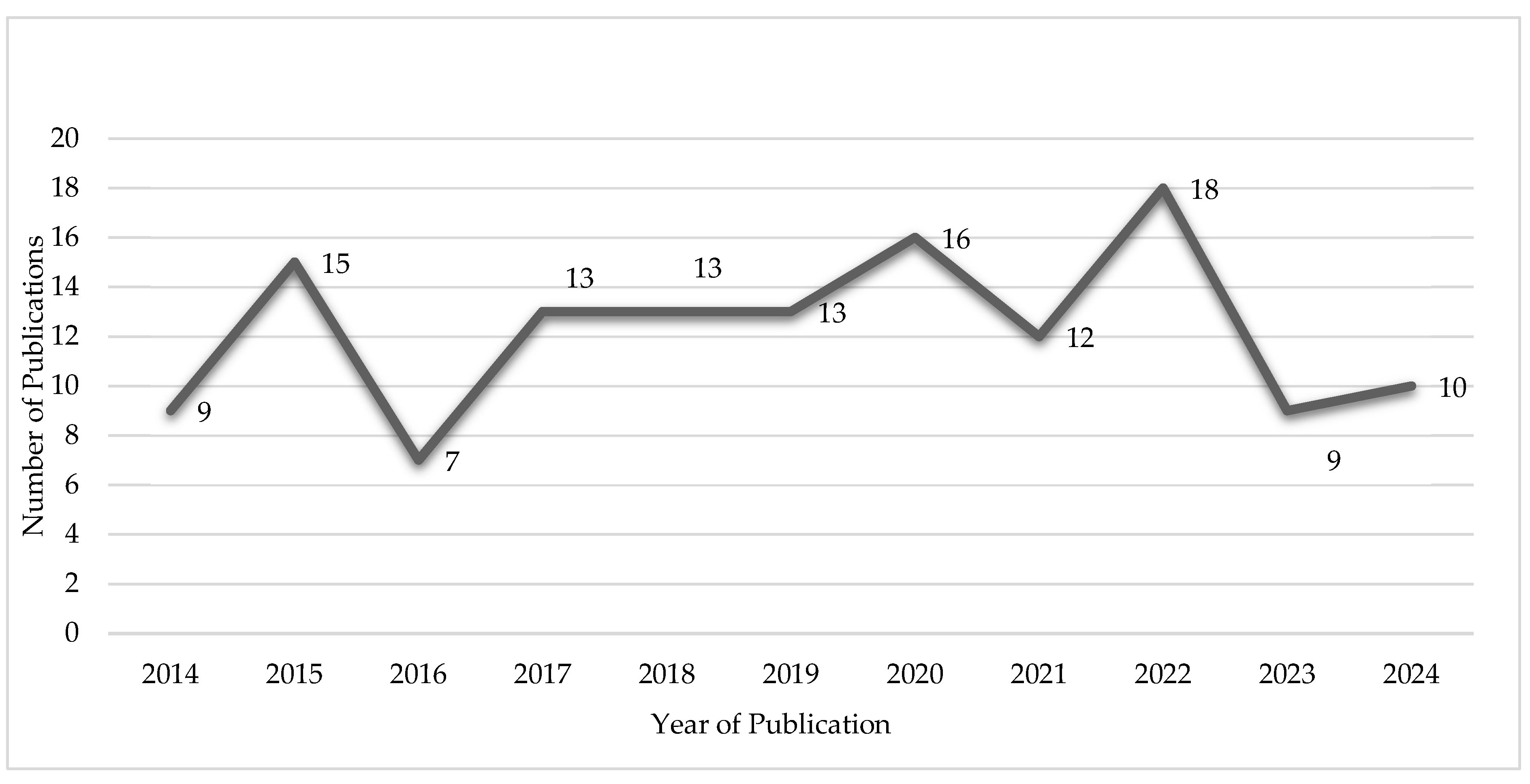
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
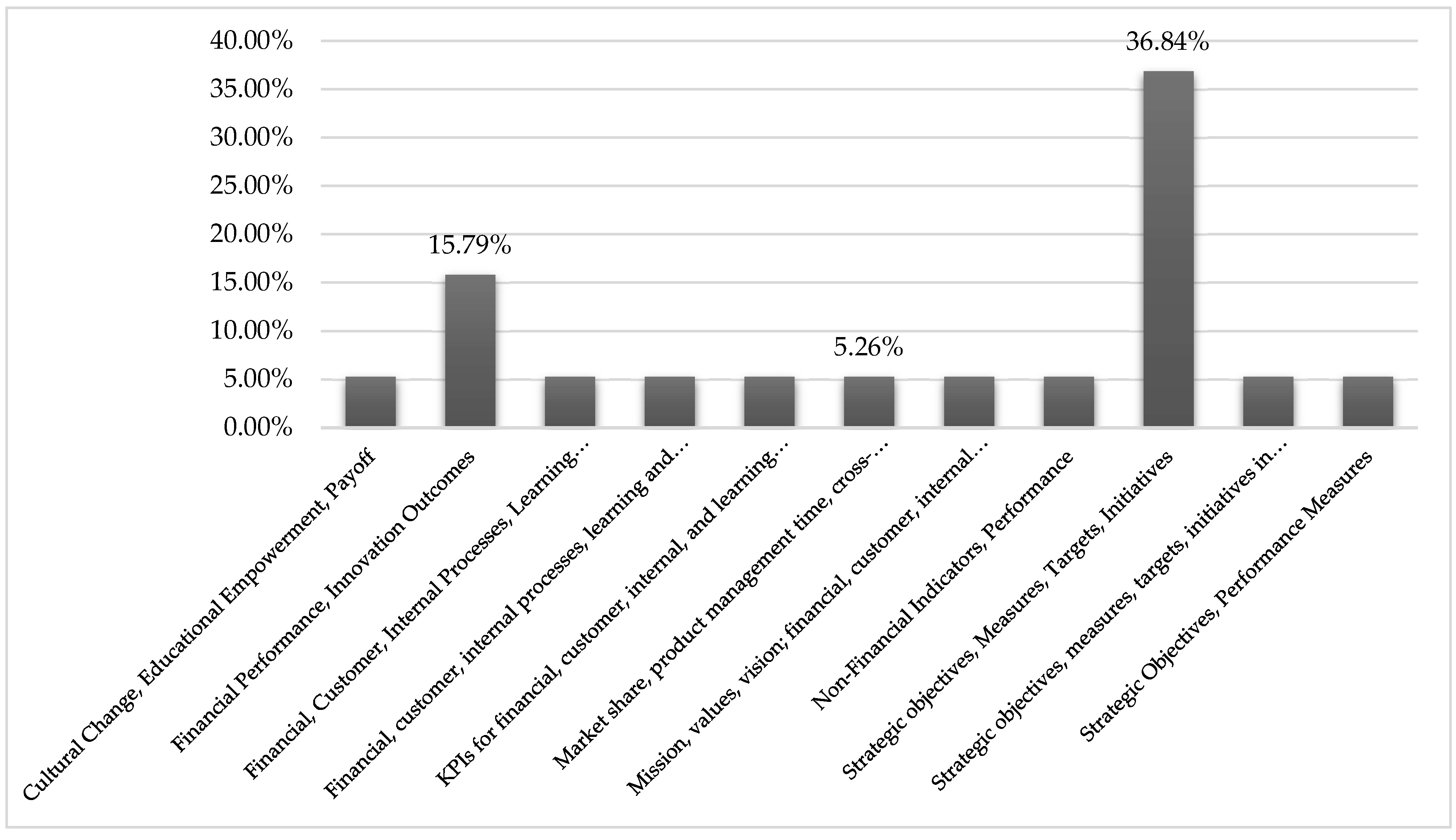
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.5. Results of Syntheses
3.6. Reporting Biases
3.6.1. Assessment of Risk Bias
3.6.2. Tools Utilized
3.6.3. Sensitivity Analysis
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
3.7.1. The Summary of Evidence
4. Practical Recommendations
4.1. Key Findings and Strategic Implications for Business Leaders
4.2. Decision-Making Framework for Implementation
4.3. Proposed Best Practices for Successful Implementation
4.4. Metrics and KPIs for Measuring Performance
4.5. Real Case Studies from Various Industries
4.5 Proposed Roadmap for SMEs Businesses and Policy Recommendations
| Industry | Roadmap Focus | Policy Framework | Strategic Link | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | Ties to Proposed Study | Timeline | Duration | Champion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Implement digital transformation initiatives | Industry 4.0 Roadmap | Enhances automation and operational efficiency | Technological advancement, quality improvement | Increased productivity, reduced downtime | Linked to improving manufacturing KPIs in SMEs | Start in Q1 2025 | 18 months | Chief Technology Officer (CTO) |
| Healthcare | Integrate BSC with patient management systems | National Health Policy | Improves patient outcomes through systematic monitoring | Patient safety, healthcare quality | Enhanced patient care, better resource allocation | Relevant to improving healthcare service delivery KPIs | Start in Q2 2025 | 12 months | Chief Medical Officer (CMO) |
| Retail | Align supply chain management with sustainability goals | Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 12) | Encourages sustainable consumption and production | Environmental compliance, supply chain resilience | Reduced environmental footprint, increased customer satisfaction | Ties with optimizing supply chain management and customer satisfaction | Start in Q3 2025 | 24 months | Supply Chain Manager |
| Telecommunications | Enhance network infrastructure through BSC frameworks | National ICT Policy | Boosts connectivity and customer service | Innovation, service quality | Improved network reliability, increased market share | Supports tracking performance improvements in telecom services | Start in Q1 2026 | 15 months | Chief Operating Officer (COO) |
| Manufacturing | Adopt lean practices for quality improvement | Lean Manufacturing Policy | Aligns production processes with quality standards | Operational efficiency, cost reduction | Reduced production waste, enhanced product quality | Pertains to integrating lean principles within BSC for manufacturing | Start in Q4 2025 | 20 months | Production Manager |
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
References
- R. Malagueño, E. Lopez-Valeiras, and J. Gomez-Conde, Balanced scorecard in SMEs: effects on innovation and financial performance. Small Bus. Econ. 2018, 51, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SSRN. (n.d.). Balanced Scorecard in SMEs. Available at: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3154266. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- H. Afonso and M. do R. Cabrita, Developing a lean supply chain performance framework in a SME: A perspective based on the balanced scorecard. Procedia Eng. 2015, 131, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCDC. (n.d.). Knowledge Horizons - Economics. Available at: http://www.orizonturi.ucdc.ro/arhiva/KHE%20nr.%204%20-%202018/10.%20CASE%20STUDY%20-%20KPIS.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- H. Zaheer, A. Ramzan, K. Mahmood, and M. N. Nagra, Implementation of balanced scorecard and financial performance of SMEs. JAMEB 2023, 8, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Balanced Scorecard Usage for Hotel and Tourism Small and Medium Enterprises Growth in Eswatini: A Proposed Conceptual Framework. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341131461_Balanced_scorecard_usage_for_hotel_and_tourism_small_and_medium_enterprises_growth_in_ESwatini_Former_Swaziland_A_Proposed_conceptual_framework. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- IPB. (n.d.). Biblioteca Digital. Available at: https://bibliotecadigital.ipb.pt/handle/10198/21522. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Reynolds, H. Fourie, and L. Erasmus, A generic balanced scorecard for small and medium manufacturing enterprises in South Africa, South. Afr. J. Entrep. Small Bus. Manag. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar]
- S. Falle, R. Rauter, S. Engert, and R. Baumgartner, Sustainability management with the Sustainability Balanced Scorecard in SMEs: Findings from an Austrian case study. Sustainability 2016, 8, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Oliveira, C. Leal, and A. Pinho, Existing differences between SMEs that apply BSC and those that do not. J. Inf. Organ. Sci. 2021, 45, 375–397. [Google Scholar]
- Social Space Journal. (n.d.). The Impacts of Management Competence on Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Performance: From the Balanced Scorecard Perspective. Available at: https://socialspacejournal.eu/menu-script/index.php/ssj/article/view/166/73. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Dergipark. (n.d.). Tekderg. Available at: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/tekderg/issue/60700/977849. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Cloudfront. (n.d.). Non-Financial Indicators and Their Importance. Available at: https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/78270105/284-libre.pdf?1641534648=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DNon_Financial_Indicators_and_Their_Impor.pdf&Expires=1724019074&Signature=SjnPpWgOVf4vWTGzTvw5YA0LZuMvl-3xMFJSeaCzzkp9rmoZQDyE~vTtCOvZgViA2m5RRx7QopJFjRb6IhL9pPXN3E5cR5G4Ex2ZVRGWiD6bxR4rmjunTYn7uHPjbpvj~iEwJ6DqtVcisxEmRkICw76udGVKlmP1RcbYNNYgYnem4ntyWT4zgsUmZpaQdXNItjW1Ya~gUiRkgicsDEEbHlUnCrlslMz5jBwyRdX8TIKIPaeSHFRIOdZgG3dy-BVR9Bzu0WcTrVxdG5gKeDyixn98~YhmswLpMI~DsO1SL988pwlvxqDTlN1mnYjNP1PuujO8l4yLXoNfH~M-d8~-EA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- E. Benková, P. Gallo, B. Balogová, and J. Nemec, Factors affecting the use of Balanced Scorecard in measuring company performance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Supporting Open Innovation with the Use of a Balanced Scorecard Approach: A Study on Deep Smarts and Effective Knowledge Transfer to SMEs. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323150172_Supporting_Open_Innovation_with_the_use_of_a_Balanced_Scorecard_Approach_A_Study_on_Deep_Smarts_and_Effective_Knowledge_Transfer_to_SMEs_Supporting_Open_Innovation_with_the_use_of_a_Balanced_Scorecard. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- B. W. Permadi, A. Y. Ridwan, and W. Juliani, SCOR-BSC integrated model for a small-medium enterprise clothing industry using MTS-based production strategy in Indonesia, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 598, 012079. [Google Scholar]
- P. Quesado, S. Marques, R. Silva, and A. Ribeiro, The Balanced Scorecard as a strategic management tool in the textile sector. Adm. Sci. 2022, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PublishPK. (n.d.). Article. Available at: https://www.publishpk.net/art/2015%202.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- S. Singh, E. U. Olugu, S. N. Musa, and A. B. Mahat, Fuzzy-based sustainability evaluation method for manufacturing SMEs using balanced scorecard framework. J. Intell. Manuf. 2018, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). SMEs' Perspective on Venture Capital Investment Criteria: A Study of Croatian SMEs. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324902645_SMEs_perspective_on_venture_capital_investment_criteria_-_A_study_of_Croatian_SMEs. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Dergipark. (n.d.). IRM. Available at: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/irmm/issue/32094/355444. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- P. Achenbach, Sustainability Balanced Scorecard as a cost accounting instrument for small and medium sized companies. SHS Web Conf. 2021, 115, 03002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . ResearchGate. (n.d.). Assessing the Impact of Electronic Supply Chain Management on the Performance of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises using the Sustainable Balanced Scorecard Approach: Case Study of Online Stores and In. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Arshia-Taimouri/publication/333419475_Assessing_the_Impact_of_Electronic_Supply_Chain_Management_on_the_Performance_of_Small_and_Medium_sized_Enterprises_using_the_Sustainable_Balanced_Scorecard_Approach_Case_Study_of_Online_Stores_and_In/links/5ceccc96458515026a613c18/Assessing-the-Impact-of-Electronic-Supply-Chain-Management-on-the-Performance-of-Small-and-Medium-sized-Enterprises-using-the-Sustainable-Balanced-Scorecard-Approach-Case-Study-of-Online-Stores-and-In.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). The Influence of Enterprise Risk Management on Firm Performance Measured by the Balanced Scorecard: Evidence from SMEs in Southern Thailand. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Muttanachai-Suttipun/publication/335899816_The_Influence_of_Enterprise_Risk_Management_on_Firm_Performance_Measured_by_the_Balanced_Scorecard_Evidence_from_SMEs_in_Southern_Thailand/links/62e0f78f7782323cf17ec8c6/The-Influence-of-Enterprise-Risk-Management-on-Firm-Performance-Measured-by-the-Balanced-Scorecard-Evidence-from-SMEs-in-Southern-Thailand.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). The Influence of Sufficiency Economy Philosophy Practice on SMEs' Performance in Thailand. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343284749_The_Influence_of_Sufficiency_Economy_Philosophy_Practice_on_SMEs%27_Performance_in_Thailand. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- IEMSJL. (n.d.). Article. Available at: http://www.iemsjl.org/j. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). The Application of a Balanced Scorecard in SME: A Case Study of Milanzo Kids. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358593020_THE_APPLICATION_OF_A_BALANCED_SCORECARD_IN_SME_A_CASE_STUDY_OF_MILANZO_KIDS. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Cruscottodicontrollo.it. (n.d.). The Balanced Scorecard in Large Firms. Available at: https://www.cruscottodicontrollo.it/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/The_Balanced_Scorecard_in_Large_Firms_an.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- F. Owolabi, Balanced score card and performance evaluation in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Nigeria, Core.ac.uk. Available at: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/95550704.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- G. K. Muli, Extent of Balanced Scorecard Implementation and its Effect on the Financial Performance of Small and Medium Enterprises in Nairobi County, 2016.
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Leveraging the Balanced Scorecard - A Tool for SME Advancement. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351639712_Leveraging_the_balanced_scorecard_-_a_tool_for_SME_advancement. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Internationalization and Innovation on Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Among Malaysian Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333509677_Internationalisation_and_innovation_on_balanced_scorecard_BSC_among_Malaysian_small_and_medium_enterprises_SMEs. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Z. Dudic, B. Dudic, M. Gregus, D. Novackova, and I. Djakovic, The Innovativeness and Usage of the Balanced Scorecard Model in SMEs. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S. Sulaiman, N. Md Zin, and N. Abdul Rahman, Exploring the Agile-Adaptive Balanced Scorecard Benefits Towards Improving the Management Accounting System: A Case Study of Iraqi SMEs. Social & Management Research Journal 2022, 19, 139–168. [Google Scholar]
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Effect of Innovation, Knowledge Sharing, and Trust Culture on Hotels' SMEs Growth in Eswatini. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354186670_Effect_of_Innovation_Knowledge_Sharing_and_Trust_Culture_on_Hotels%27_SMEs_Growth_in_Eswatini. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Assumptionjournal.au.edu. (n.d.). The Balanced Scorecard as a Performance Management Tool for Small and Medium Scale Enterprises in Nigeria. Available at: http://www.assumptionjournal.au.edu/index.php/eJIR/article/view/4074/2400. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- C. Suárez-Gargallo and P. Zaragoza-Sáez, How the Balanced Scorecard is Implemented in the Spanish Footwear Industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarras, T. Anagnostopoulos, N. Tsotsolas, I. Salmon, and L. Vryzidis, Applying the Balanced Scorecard and Predictive Analytics in the Administration of a European Funding Program. Adm. Sci. 2020, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Ahmad, N. Abdul Hamid, A. Nur Aizat Ahmad, M. N. Mohd Nawi, N. A. Abdul Rahman, and N. A. Abdul Hamid, The Impact of TQM on Business Performances Based on Balanced Scorecard Approach in Malaysia SMEs. Int. J. Qual. Res. 2022, 16, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Malesios, P. K. Dey, and F. B. Abdelaziz, Supply Chain Sustainability Performance Measurement of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises Using Structural Equation Modeling. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 294, 623–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Balanced Scorecard Practices of Medium and Large Enterprises in the Province of Pampanga. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ma-Cristina-Naguit/publication/321081765_Balanced_Scorecard_practices_of_medium_and_large_enterprises_in_the_Province_of_Pampanga/links/5a0c58be4585153829b1441b/Balanced-Scorecard-practices-of-medium-and-large-enterprises-in-the-Province-of-Pampanga.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Explaining the Impact of a Customer-Oriented Strategy on SMEs' Global Performance: Lessons from the Balanced Scorecard and the CUSTOR Scale Model. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322466991_Explaining_the_impact_of_a_customer-oriented_strategy_on_the_small_and_medium-sized_enterprises%27_SMEs_global_performance_Lessons_from_the_Balanced_Scorecard_and_the_CUSTOR_scale_model. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Advantages and Contributions in the Balanced Scorecard Implementation. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323323907_Advantages_and_contributions_in_the_balanced_scorecard_implementation. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- W. Sewell, R. B. Mason, and P. Venter, Socio-Economic Developmental Strategies as Retail Performance Indicators: A Balanced Scorecard Approach. Dev. South. Afr. 2017, 34, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing. (n.d.). Effect of Entrepreneurial Orientation on Performance of SMEs in Ethiopia: The Mediation Role of Innovation. Available at: https://www.bing.com/search?pglt=41&q=Effect+of+Entrepreneurial+Orientation+on+Performance+of+SMEs+in+Ethiopia%3A+The+Mediation+role+of+Innovation+Gada+Gizachew+Wakjira1+%2C+Kenenisa+Lemi+Debela2*%2C+Shashi+Kant3&cvid=ba3bc35b92514fcab34ef02a89103fc1&gs_lcrp=EgZjaHJvbWUyBggAEEUYOdIBBzg0OWowajGoAgCwAgA&FORM=ANNTA1&PC=U531. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Effect of Innovation, Knowledge Sharing, and Trust Culture on Hotels' SMEs Growth in Eswatini. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354186670_Effect_of_Innovation_Knowledge_Sharing_and_Trust_Culture_on_Hotels'_SMEs_Growth_in_Eswatini. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Eamr-accid.eu. (n.d.). Volume 5, Issue 2. Available at: https://eamr-accid.eu/wp-content/uploads/Volume-5-Issue-2.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Identification of Performance Measures for Textile Supply Chain: Case of Small Medium Size Enterprise. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pranav-Charkha/publication/288841428_Identification_of_performance_measures_for_textile_supply_chain_Case_of_small_medium_size_enterprise/links/5a34b842aca27247eddce429/Identification-of-performance-measures-for-textile-supply-chain-Case-of-small-medium-size-enterprise.pdf. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Employee Retention Practices and the Performance of Small and Medium Enterprises in Nigeria. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363317689_Employee_Retention_Practices_and_the_Performance_of_Small_and_Medium_Enterprises_in_Nigeria. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Applicability of Performance Prism in SMEs: A Multiple Case Study. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338773870_Applicability_of_Performance_Prism_in_SMEs_a_multiple_case_study. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). The Effect of Cloud Accounting Adoption on Organizational Performance in SMEs. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/364111154_The_effect_cloud_accounting_adoption_on_organizational_performance_in_SMEs. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Edu.pe. (n.d.). Inicio. Available at: https://ilagop.edu.pe/. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). A Taxonomy of Knowledge Management Outcomes for SMEs. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286597565_A_taxonomy_of_knowledge_management_outcomes_for_SMEs. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- L. Zhang, A Comparative Study of Modern Management Accounting Practices and SMEs Performance in Malaysia and China: The Moderating Role of Power Distance.
- M. Hidayat, C. I. Musa, S. Haerani, and I. Sudirman, The Design of Curriculum Development Based on Entrepreneurship Through Balanced Scorecard Approach. Int. Educ. Study. 2015, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Identification and Determination of the Priority of Key Performance Indicators: Perspective of Customers on Cocoa Processing Industry of SMEs Scale in South Sulawesi. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326300619_IDENTIFICATION_AND_DETERMINATION_OF_THE_PRIORITY_OF_KEY_PERFORMANCE_INDICATORS_PERSPECTIVE_OF_CUSTOMERS_ON_COCOA_PROCESSING_INDUSTRY_OF_SMEs_SCALE_IN_SOUTH_SULAWESI. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Academia.edu. (n.d.). Ranking of Performance Measurement Systems for Smaller Businesses. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/80974837/Ranking_of_Performance_Measurement_Systems_for_Smaller_Businesses. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Revitalizing Small Business Growth Strategies: Exploring the Risk-Benefit of Strategic Management Approaches. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281234873_Revitalising_Small_Business_Growth_Strategies_Exploring_the_Risk-Benefit_of_Strategic_Management_Approaches. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- European Accounting and Management Review.
- Giannoukou and C., C. Beneki, Towards Sustainability Performance Management System of Tourism Enterprises: A Tourism Sustainable Balanced Scorecard Framework. Int. J. Glob. Environ. Issu. 2018, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Academia.edu. (n.d.). A Green Corridor Balanced Scorecard. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/55344725/A_Green_Corridor_Balanced_Scorecard. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Emerald.com. (n.d.). International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management. Available at: https://www.emerald.com/insight/publication/issn/1741-0401. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- ResearchGate. (n.d.). Effect of Opportunity Recognition and Organization Capability on SME Performance in Indonesia: Moderated by Business Model Innovation. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365743414_Effect_of_Opportunity_Recognition_and_Organisation_Capability_on_SME_Performance_in_Indonesia_Moderated_by_Business_Model_Innovation. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Bing. (n.d.). Implementation of the Balanced Scorecard in Large Firms: A Systematic Review by Zhijun Liu. Available at: https://www.bing.com/search?pglt=41&q=Implementation+of+the+Balanced+Scorecard+in+Large+Firms%3A+A+Systematic+Review+Zhijun+Liu1*&cvid=a797a40e10ce4a90a04bca21a02028bb&gs_lcrp=EgZjaHJvbWUyBggAEEUYOdIBBzc4OGowajGoAgCwAgA&FORM=ANNTA1&PC=U531. (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- N. Sahraen, Risk Mitigation Using Integration of Enterprise Risk Management and Balanced Scorecard Model: A Case Study in a Consulting Services Company in Indonesia. SPEKTRUM IND. 2021, 19, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor & Francis. Performance management of supply chain sustainability in small and medium-sized enterprises using a combined structural equation modelling and data envelopment analysis. [Online]. Available: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781003018551-6/performance-management-supply-chain-sustainability-small-medium-sized-enterprises-using-combined-structural-equation-modelling-data-envelopment-analysis-prasanta-kumar-dey-guo-liang-yang-chrisovaladis-malesios-debashree-de-konstantinos-evangelinos. (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- P. K. Dey, G.-L. Yang, C. Malesios, D. De, and K. Evangelinos, Performance management of supply chain sustainability in small and medium-sized enterprises using a combined structural equation modelling and data envelopment analysis. Computational Economics 2021, 58, 573–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ResearchGate. Supply Chain Sustainability Performance Measurement of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises using Structural Equation Modeling. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328253969_Supply_Chain_Sustainability_Performance_Measurement_of_Small_and_Medium_Sized_Enterprises_using_Structural_Equation_Modeling. (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- C. Malesios, P. K. Dey, and F. B. Abdelaziz, Supply chain sustainability performance measurement of small and medium-sized enterprises using structural equation modeling. Annals of Operations Research 2020, 294, 623–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanced Scorecard, The Strategy Story - Simplifying Business Strategies, Feb. 6, 2024. [Online]. Available: (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- S. Bakhtiari, R. Breunig, L. Magnani, and J. Zhang, Financial constraints and small and medium enterprises: A review. Econ. Rec. 2020, 96, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cput.ac.za. [Online]. Available: https://etd.cput.ac.za/bitstream/20.500.11838/3230/1/Masixole_Solani_205047297.pdf. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331548047_IMPACT_OF_INNOVATION_PRACTICES_ON_SUSTAINABLE_PERFORMANCE_SMEs. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Z. Zhang, H. Zhu, Z. Zhou, and K. Zou, How does innovation matter for sustainable performance? Evidence from small and medium-sized enterprises. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 153, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Academia.edu. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/39198226/IMPACT_OF_INNOVATION_PRACTICES_ON_SUSTAINABLE_PERFORMANCE_SMEs. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Tawse and, P. Tabesh, Thirty years with the balanced scorecard: What we have learned. Bus. Horiz. 2023, 66, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorach and, E. Ottosson, The Balanced Scorecard during the early stages of a tech firm: A multiple case study regarding performance management in Swedish tech startups, 2016.
- Diva-portal.org. [Online]. Available: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:953509/FULLTEXT02.pdf. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Dameshifa, A. Azazi, E. Listiana, H. Malini, and H. Heriyadi, The influence of entrepreneurial and Market Orientation on Business Performance through mediation of innovation capability: Implementation of SMEs in Indonesia. East Afr Sch J Econ Bus Manag.
- Abacademies.org. [Online]. Available: https://www.abacademies.org/articles/The-effect-of-entrepreneurial-orientation-on-1528-2651-22-5-461.pdf. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- V. Oyaneder and S. M. Valderrama, A new balanced scorecard approximation to enhance performance management systems of Chilean wineries. J. Wine Res. 2016, 27, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295396300_A_new_balanced_scorecard_approximation_to_enhance_performance_management_systems_of_Chilean_wineries. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318928910_Business_intelligence_systems_and_bank_performance_in_Ghana_The_balanced_scorecard_approach. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Owusu, Business intelligence systems and bank performance in Ghana: The balanced scorecard approach. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2017, 4, 1364056. [CrossRef]
- Edu.gh. [Online]. Available: https://pure.ug.edu.gh/en/publications/business-intelligence-systems-and-bank-performance-in-ghana-the-b. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Ssrn.com. [Online]. Available: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3481364. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Gov.my. [Online]. Available: https://smecorp.gov.my/images/Publication/MSME_Insights/2022_23/3Chapter%202_Performance%20of%20MSMEs%20in%20Malaysia.pdf. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/375544721_Determining_key_factors_influencing_SMEs'_performance_A_systematic_literature_review_and_experts'_verification. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- N. M. Mustapha and S. Sorooshian, SME performance measurement: A technical review of Malaysia, Edu.my. [Online]. Available: http://umpir.ump.edu.my/id/eprint/25913/1/SME%20performance%20measurement%20a%20technical%20review%20of%20Malaysia.pdf. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Unl.pt. [Online]. Available: https://run.unl.pt/handle/10362/107266?locale=en. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Hegazy, K. Hegazy, and M. Eldeeb, The balanced scorecard: Measures that drive performance evaluation in auditing firms. J. Account. Audit. Finance 2022, 37, 902–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/359479328_Performance_of_Food_and_NonFood_SMIS_Based_on_Marketing_Entrepreneurs_Entrepreneurship_Marketing_Food_and_Non-Food_SMIs_Performance_Balanced_Scorecard. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Neliti.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.neliti.com/publications/410597/marketing-entrepreneurs-performance-of-food-and-non-food-smis-based-on-marketing. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336136888_ASSESSMENT_OF_ENTREPRENEURIAL_MARKETING_PERFORMANCE_IN_SMALL_AND_MEDIUM_FOOD_AND_NON-FOOD_INDUSTRY_IN_INDONESIA_USING_IPA_ANALYSIS. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- D. Gemina, Performance of food and non-food SMIS based on marketing entrepreneurs: Entrepreneurship marketing, food, and non-food SMIs performance, balanced scorecard. International Journal of Economics Development Research (IJEDR) 2020, 1, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Baldo, The implementation of integrating reporting in SMEs: Insights from a pioneering experience in Italy. Meditari Account. Res. 2017, 25, 505–532. [CrossRef]
- Jami Pour and, M. Asarian, Strategic orientations, knowledge management (KM) and business performance: An exploratory study in SMEs using clustering analysis. Kybernetes 2019, 48, 1942–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329819484_Strategic_orientations_knowledge_management_KM_and_business_performance_An_exploratory_study_in_SMEs_using_clustering_analysis. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- B. Song, Y. Li, and L. Zhao, Complementary effect of knowledge management strategy on firm performance: Evidence from Chinese firms. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. S. Lee and K. Y. Wong, Development and validation of knowledge management performance measurement constructs for small and medium enterprises. J. Knowl. Manag. 2015, 19, 711–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306010707_The_Balanced_Scorecard_vs_Total_Quality_Management#:~:text=Empirical%20investigation%20suggests%20that%20numerous%20organizations%20have%20adopted,customer%2C%20internal%20business%20processes%2C%20and%20learning%20and%20growth. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- G. Mehralian, J. A. Nazari, G. Nooriparto, and H. R. Rasekh, TQM and organizational performance using the balanced scorecard approach. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2017, 66, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z. Hoque, Total quality management and the balanced scorecard approach: A critical analysis of their potential relationships and directions for research. Crit. Perspect. Account. 2003, 14, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274573303_Critical_success_factors_for_implementation_of_supply_chain_management_in_Indian_small_and_medium_enterprises_and_their_impact_on_performance#:~:text=this%20paper%20identi%EF%AC%81ed%2013%20critical%20success%20factors%20%28CSFs%29,emerge%20d%20as%20the%20most%20perti%20nent%20CSFs. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- R. Kumar, R. K. Singh, and R. Shankar, Critical success factors for implementation of supply chain management in Indian small and medium enterprises and their impact on performance. IIMB Manag. Rev. 2015, 27, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274573303_Critical_success_factors_for_implementation_of_supply_chain_management_in_Indian_small_and_medium_enterprises_and_their_impact_on_performance. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Taschner, Improving SME logistics performance through benchmarking, Benchmarking 2016, 23, 1780–1797.
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309103764_Improving_SME_logistics_performance_through_benchmarking. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Sciencedirect.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214785321041511#:~:text=For%20deducing%20supply%20chain%20performance%2C%20the%20Balanced%20Scorecard,Envelopment%20Analysis%20%28DEA%29%20and%20Heuristic%20techniques%20based%20models. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- M. Balaji, S. N. Dinesh, P. Manoj Kumar, and K. Hari Ram, Balanced Scorecard approach in deducing supply chain performance. Mater. Today 2021, 47, 5217–5222. [Google Scholar]
- Dau.edu. [Online]. Available: https://www.dau.edu/library/damag/july-august2017/balanced-scorecards-supply-chain-management. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Kosa, I. Mohammad, and D. Ajibie, Entrepreneurial orientation and venture performance in Ethiopia: the moderating role of business sector and enterprise location. J. Glob. Entrep. Res. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. U. Khan, Y. Salamzadeh, H. Kawamorita, and G. Rethi, Entrepreneurial orientation and small and medium-sized enterprises’ performance; Does ‘access to finance’ moderate the relation in emerging economies? Vis. J. Bus. Perspect. 2021, 25, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. Sahraen, Risk mitigation using integration enterprise risk management and balanced scorecard model: A case study in a consulting services company in Indonesia. SPEKTRUM IND. 2021, 19, 73. [CrossRef]
- Z. Liu, Implementation of the balanced scorecard in large firms: A systematic review. Asian Journal of Accounting and Finance 2024, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365743414_Effect_of_Opportunity_Recognition_and_Organisation_Capability_on_SME_Performance_in_Indonesia_Moderated_by_Business_Model_Innovation. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Academia.edu. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/93437960/The_Effect_of_Opportunity_Recognition_and_Organization_Capability_on_SME_Performance_in_Indonesia_Moderated_by_Business_Model_Innovation. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Consensus.app. [Online]. Available: https://consensus.app/papers/opportunity-recognition-organisation-capability-hartono/5834fcd02f535c889d83e40fc527da90/. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- S. Pekkola, M. Saunila, and H. Rantanen, Performance measurement system implementation in a turbulent operating environment, Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2016, 65, 947–958. [Google Scholar]
- Eifert and, C. Julmi, Challenges and how to overcome them in the formulation and implementation process of a Sustainability Balanced Scorecard (SBSC). Sustainability 2022, 14, 14816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. Sewell, R. B. Mason, and P. Venter, Socio-economic developmental strategies as retail performance indicators: A balanced scorecard approach, Dev. South. Afr. 2017, 34, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Gothenburg, S. Sorooshian, N. Aziz, U. M. Pahang, N. Azizan, and Prince Sultan University, Ranking of performance measurement systems for smaller businesses. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2020, 13, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326300619_IDENTIFICATION_AND_DETERMINATION_OF_THE_PRIORITY_OF_KEY_PERFORMANCE_INDICATORS_PERSPECTIVE_OF_CUSTOMERS_ON_COCOA_PROCESSING_INDUSTRY_OF_SMEs_SCALE_IN_SOUTH_SULAWESI. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- M. Dahlan, Ramlawati, and Lamatinulu, Identification and determination of priority of key performance indicator of financial perspectives on industry cocoa SMEs in south Sulawesi. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 175, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Hidayat, C. I. Musa, S. Haerani, and I. Sudirman, The design of curriculum development based on entrepreneurship through balanced scorecard approach. Int. Educ. Stud. 2015, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Lamatinulu, Identification and determination of the priority of key performance indicators perspective of customers on cocoa processing industry of SMEs scale in south Sulawesi. International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology.
- L. Zhang, A comparative study of modern management accounting practices and SMEs performance in Malaysia and China: The moderating role of power distance.
- B. D. Dağıdır and B. Özkan, A comprehensive evaluation of a company performance using sustainability balanced scorecard based on picture fuzzy AHP. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E. Neder, The new relationship among state, market, and political actors in public policies. Mei Zhong Gong Gong Guan Li 2015, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Ssrn.com. [Online]. Available: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4307192. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338773870_Applicability_of_Performance_Prism_in_SMEs_a_multiple_case_study. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363317689_Employee_Retention_Practices_and_the_Performance_of_Small_and_Medium_Enterprises_in_Nigeria. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Innovation-effect-on-SMEs-hotels-growth_tbl1_354186670. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- V. Tuan, Analysis of managerial factors on the performance of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in manufacturing sector in Ho Chi Minh City- Vietnam, 2018.
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286597565_A_taxonomy_of_knowledge_management_outcomes_for_SMEs. (accessed on 28 September 2024).
- Building and Deploying a Balanced Scorecard within SMEs, ICAEW. [Online]. Available: https://www.icaew.com/technical/business/business-performance-management/bpm-tools-templates-and-case-studies/building-and-deploying-a-balanced-scorecard-within-small-and-medium-sized-organisations. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- E. Kirsten, F. Vermaak, and H. Wolmarans, Performance Measurement in Small and Medium Enterprises: South African Accountants’ Perspective. Journal of Economic and Financial Sciences 2015, 8, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Lonbani, S. Sofian, and M. B. Baroto, Balanced Scorecard Implementation in SMEs: Addressing the Moderating Role of Environmental Uncertainty. Global Business and Organizational Excellence 2016, 35, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. J. van Zyl, A Practical Performance Measurement Framework for SMEs in a South African Context, *Stellenbosch University*, [Online]. Available: https://scholar.sun.ac.za/server/api/core/bitstreams/16fc52ae-9ed9-4db8-a610-03602cc6fc0c/content. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- R. Malagueño, E. Lopez-Valeiras, and J. Gomez-Conde, The Balanced Scorecard in SMEs: Effects on Innovation and Financial Performance. Small Business Economics 2018, 51, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Malagueño, E. Lopez-Valeiras, and J. Gomez-Conde, The Balanced Scorecard in SMEs: Effects on Innovation and Financial Performance. Small Business Economics 2017, 51, 221–244. [Google Scholar]
- Balanced Scorecard, Intrafocus, 17 Jun. 2014. [Online]. Available: https://www.intrafocus.com/balanced-scorecard/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- D. M. A. Mba et al., Balanced Scorecard. Der Anaesthesist 2003, 52, 947–956. [Google Scholar]
- Balanced Scorecard Course, Udemy, [Online]. Available: https://www.udemy.com/course/building-balanced-scorecard/?utm_source=bing&utm_medium=udemyads&utm_campaign=BG-Search_DSA_Beta_Prof_la.EN_cc.ROW-English&campaigntype=Search&portfolio=Bing&language=EN&product=Course&test=&audience=DSA&topic=&priority=Beta&utm_content=deal4584&utm_term=_._ag_1329311946398319_._ad__._kw_Finance+en_._de_c_._dm__._pl__._ti_dat-2334881661677439%3Aloc-168_._li_137821_._pd__._&matchtype=b&msclkid=14c20d8ce7e9125baf6f6b671a4d2566&couponCode=2021PM20. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Balanced Scorecard, The Strategy Story, 06 Feb. 2024.
- Balanced Scorecard Institute, BSC Basics, 23 Nov. 2017. [Online]. Available: https://balancedscorecard.org/bsc-basics/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Jurevicius, Balanced Scorecard, Strategic Management Insight, 22 Jan. 2024. [Online]. Available: https://strategicmanagementinsight.com/tools/balanced-scorecard/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- D. Croft, The Four Perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard: Explained and Analyzed, Learn Lean Sigma, 23 Jul. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.learnleansigma.com/improvement-methodology/balanced-scorecard-explained/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- J. Weller, Everything You Need to Know About the Balanced Scorecard, Smartsheet, 27 Jul. 2017.
- Balanced Scorecard Institute, Nine Steps to Success, 09 Apr. 2018. [Online]. Available: https://balancedscorecard.org/about/nine-steps/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- What is a Balanced Scorecard?, Business Insights Blog, 26 Oct. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/balanced-scorecard. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Balanced Scorecard Institute, Balanced Scorecard Basics, 30 Jun. 2018. [Online]. Available: https://balancedscorecard.org/bsc-basics-overview/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- L. Tucci and K. T. Hanna, Balanced Scorecard, CIO, 28 Jul. 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/balanced-scorecard-methodology. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- E. Tarver, What is a Balanced Scorecard (BSC), and How is it Used in Business?, *Investopedia*, 18 Nov. 2003. [Online]. Available: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/balancedscorecard.asp. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Z. Dudić et al., Innovativeness and Usage of the Balanced Scorecard Model in SMEs, *Sustainability* 2020, 12, 3221.
- SMEs and BSC, Bing. [Online]. Available: https://www.bing.com/search?q=SMEs%20and%20BSC&qs=n&form=QBRE&=Search%20%7B0%7D%20for%20%7B1%7D&=Search%20work%20for%20%7B0%7D&=%25eManage%20Your%20Search%20History%25E&sp=-1&ghc=1&lq=0&pq=smes%20and%20bsc&sc=10-12&sk=&cvid=96684DEE8D304762B69E6BC6786AD873&ghsh=0&ghacc=0&ghpl=. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330563573_A_generic_balanced_scorecard_for_small_and_medium_manufacturing_enterprises_in_South_Africa. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Academia.edu. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/24487910/THE_BALANCED_SCORECARD_IN_THE_CONTEXT_OF_SMES_A_LITERATURE_REVIEW. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358161111_Existing_Differences_Between_SMEs_That_Apply_BSC_and_Those_That_Do_Not. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Malagueño, E. Lopez-Valeiras, and J. Gomez-Conde, Balanced scorecard in SMEs: effects on innovation and financial performance. Small Bus. Econ. 2018, 51, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Researchgate.net. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337192218_Balanced_Scorecard_Learning_and_Growth_Perspective. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- How to implement the balanced scorecard framework (with examples), Cascade.app. [Online]. Available: https://www.cascade.app/blog/how-to-implement-the-balanced-scorecard. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- MindTools, Mindtools.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.mindtools.com/arlnxwf/the-balanced-scorecard. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- E. Tarver, What is a balanced scorecard (BSC), how is it used in business?, Investopedia, 18-Nov-2003. [Online]. Available: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/balancedscorecard.asp. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- What is a balanced scorecard?, Business Insights Blog, 26-Oct-2023. [Online]. Available: https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/balanced-scorecard. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Balanced scorecard, Corporate Finance Institute. [Online]. Available: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/management/balanced-scorecard/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Balanced Scorecard, The Strategy Story - Simplifying Business Strategies, 06-Feb-2024.
- D. Croft, The four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard: Explained and analyzed, Learn Lean Sigma, 23-Jul-2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.learnleansigma.com/improvement-methodology/balanced-scorecard-explained/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Lean Transition Solutions LTS, What is Balanced Scorecard (BSC)? Four Perspectives, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://balancedscorecard.ltslean.com/fcil-balanced-scorecard. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Savkín, What is a K&N Balanced Scorecard and the role of its perspectives, Bscdesigner.com, 22-Feb-2019. [Online]. Available: https://bscdesigner.com/four-perspectives.htm. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Marr, The four perspectives in a Balanced Scorecard, Bernard Marr, 02-Jul-2021. [Online]. Available: https://bernardmarr.com/the-four-perspectives-in-a-balanced-scorecard/. (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Tsiu, S.; Ngobeni, M.; Mathabela, L.; Thango, B. Applications and Competitive Advantages of Data Mining and Business Intelligence in SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhize, A.; Mokhothu, K.; Tshikhotho, M.; Thango, B. Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kgakatsi, M.; Galeboe, O.; Molelekwa, K.; Thango, B. The Impact of Big Data on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024090985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molete, O. B.; Mokhele, S. E.; Ntombela, S. D.; Thango, B. A. The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SME Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothapo, M.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Tracking and Measuring Social Media Activity: Key Metrics for SME Strategic Success – A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngcobo, K.; Bhengu, S.; Mudau, A.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Enterprise Data Management: Types, Sources, and Real-Time Applications to Enhance Business Performance - A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohlala, T. T.; Mehlwana, L. L.; Nekhavhambe, U. P.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Strategic Innovation in HRIS and AI for Enhancing Workforce Productivity in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024091996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabalala, K.; Boyana, S.; Kolisi, L.; Thango, B. A.; Matshaka, L. Digital Technologies and Channels for Competitive Advantage in SMEs: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndzabukelwako, Z.; Mereko, O.; Sambo, T. V.; Thango, B. The Impact of Porter’s Five Forces Model on SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswanganyi, N. G.; Fumani, N. M.; Khoza, J. K.; Thango, B. A.; Matshaka, L. Evaluating the Impact of Database and Data Warehouse Technologies on Organizational Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumede, T. T.; Chiworeka, J. M.; Magoda, A. S.; Thango, B. Building Effective Social Media Strategies for Business: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myataza, A.; Mafunga, M.; Mkhulisi, N. S.; Thango, B. A. A Systematic Review of ERP, CRM, and HRM Systems for SMEs: Managerial and Employee Support. Preprints 2024, 2024100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudau, M. C.; Moshapo, L. W.; Monyela, T. M.; Thango, B. A. A The Role of Manufacturing Operations in SMEs Performance: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanyi, M.; Xaba, S.; Mlotshwa, N.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. The Role of Data Networks and APIs in Enhancing Operational Efficiency in SME: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skosana, S.; Mlambo, S.; Madiope, T.; Thango, B. Evaluating Wireless Network Technologies (3G, 4G, 5G) and Their Infrastructure: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtjilibe, T.; Rameetse, E.; Mgwenya, N.; Thango, B. Exploring the Challenges and Opportunities of Social Media for Organizational Engagement in SMEs: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


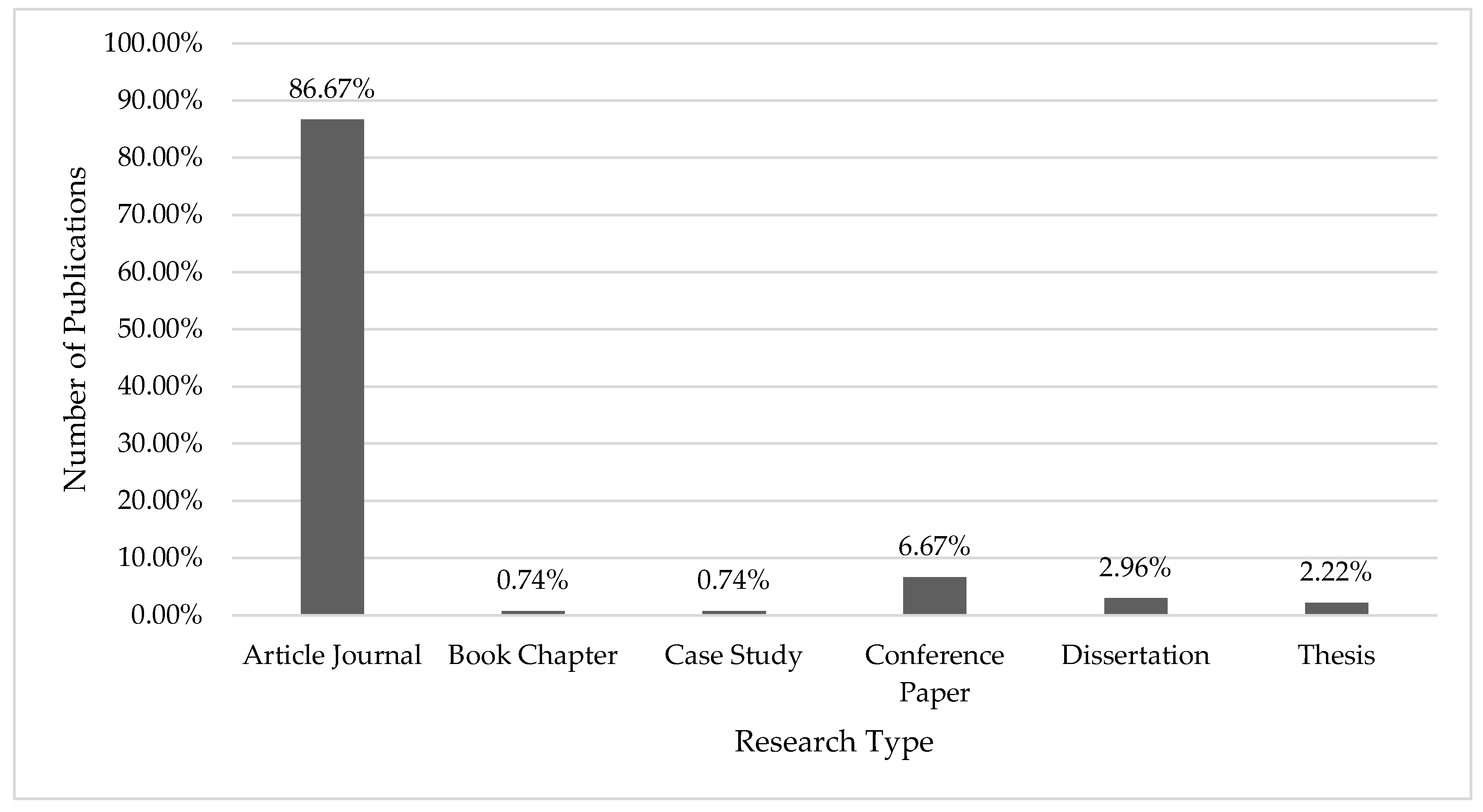
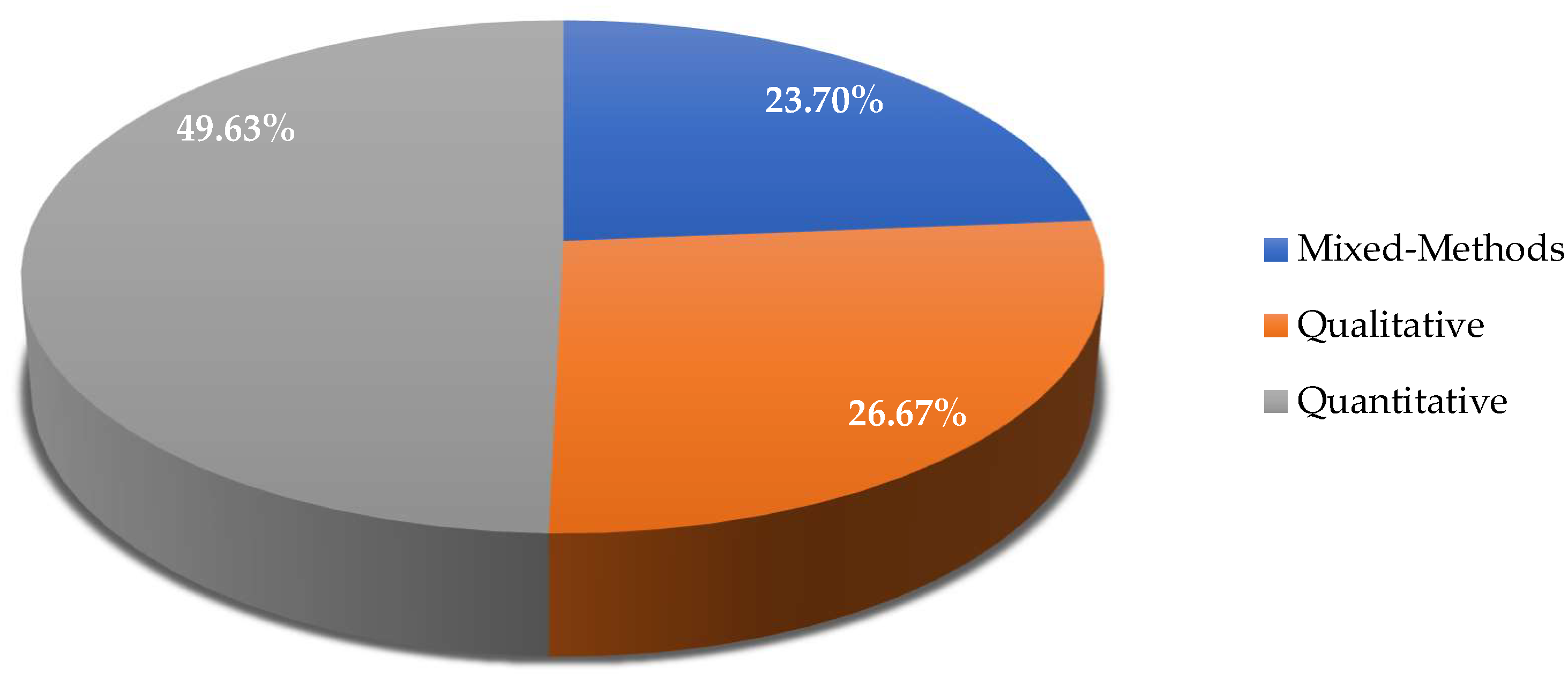

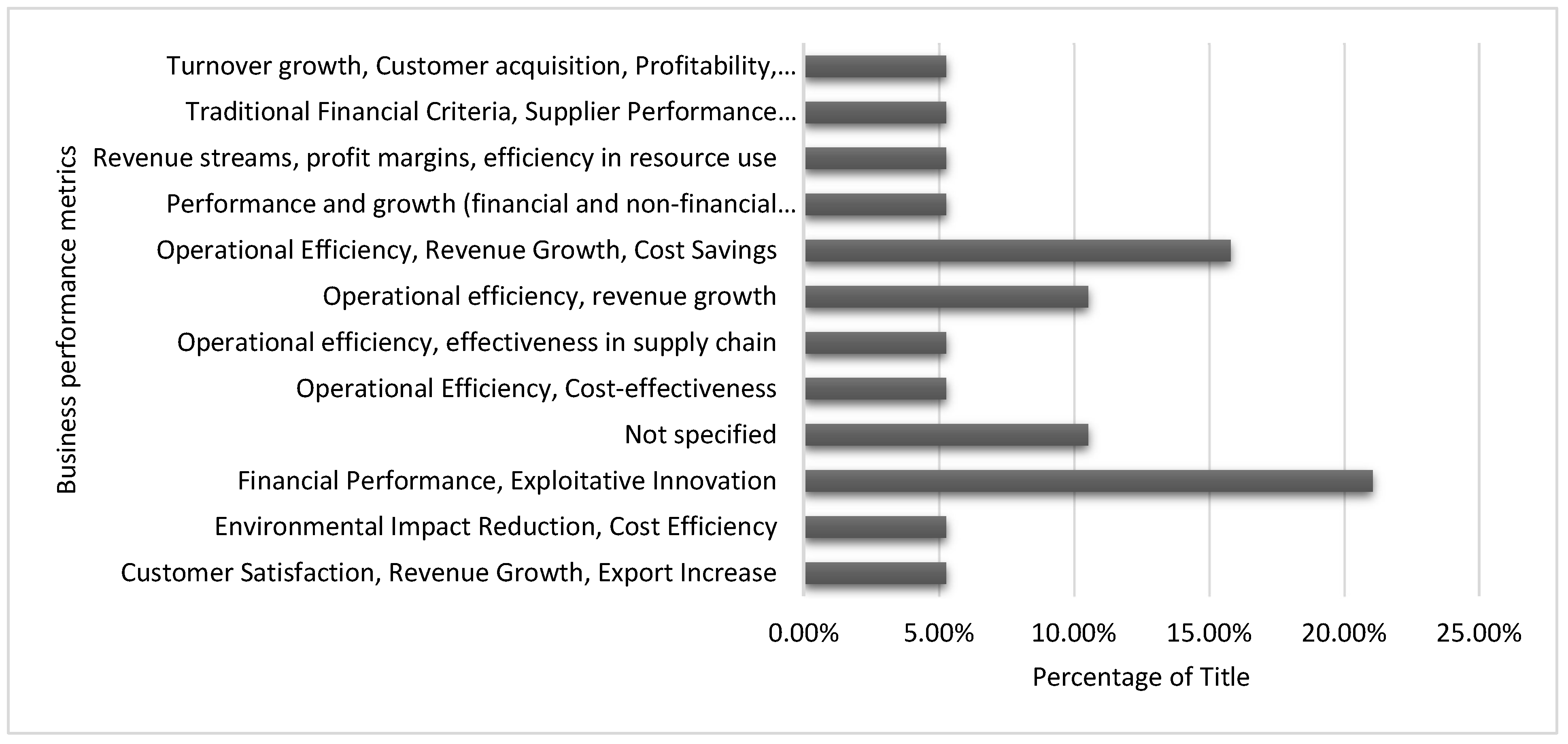




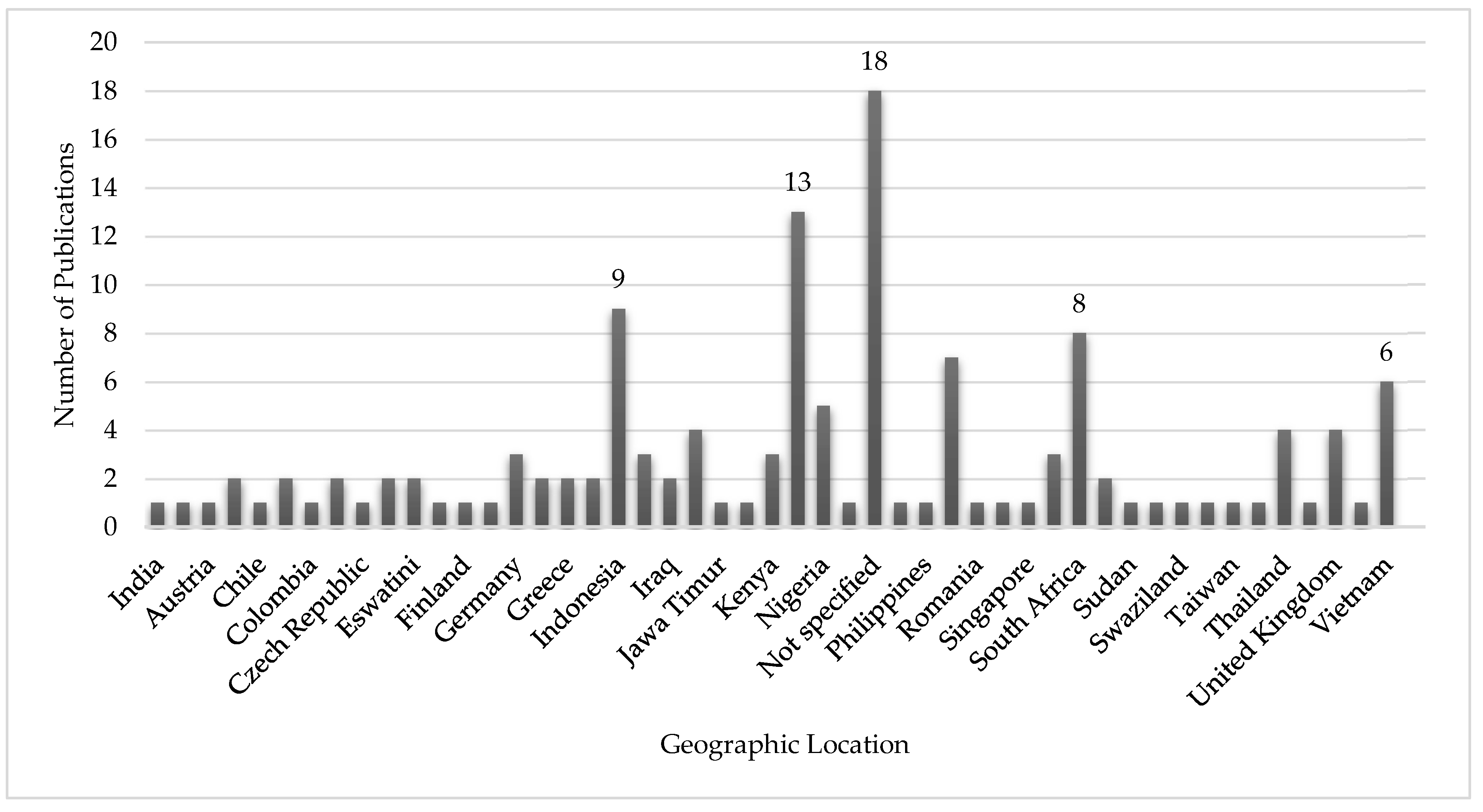

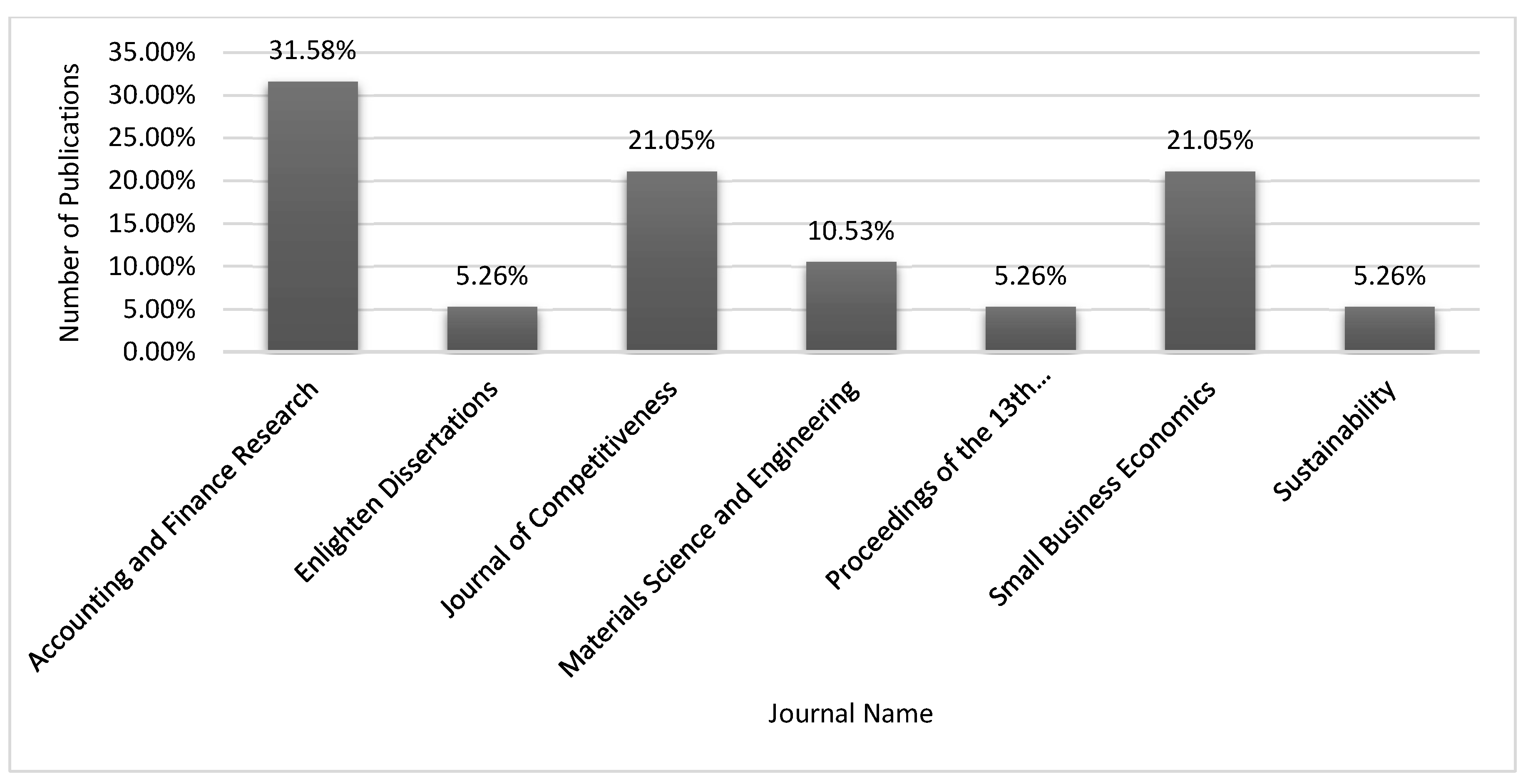
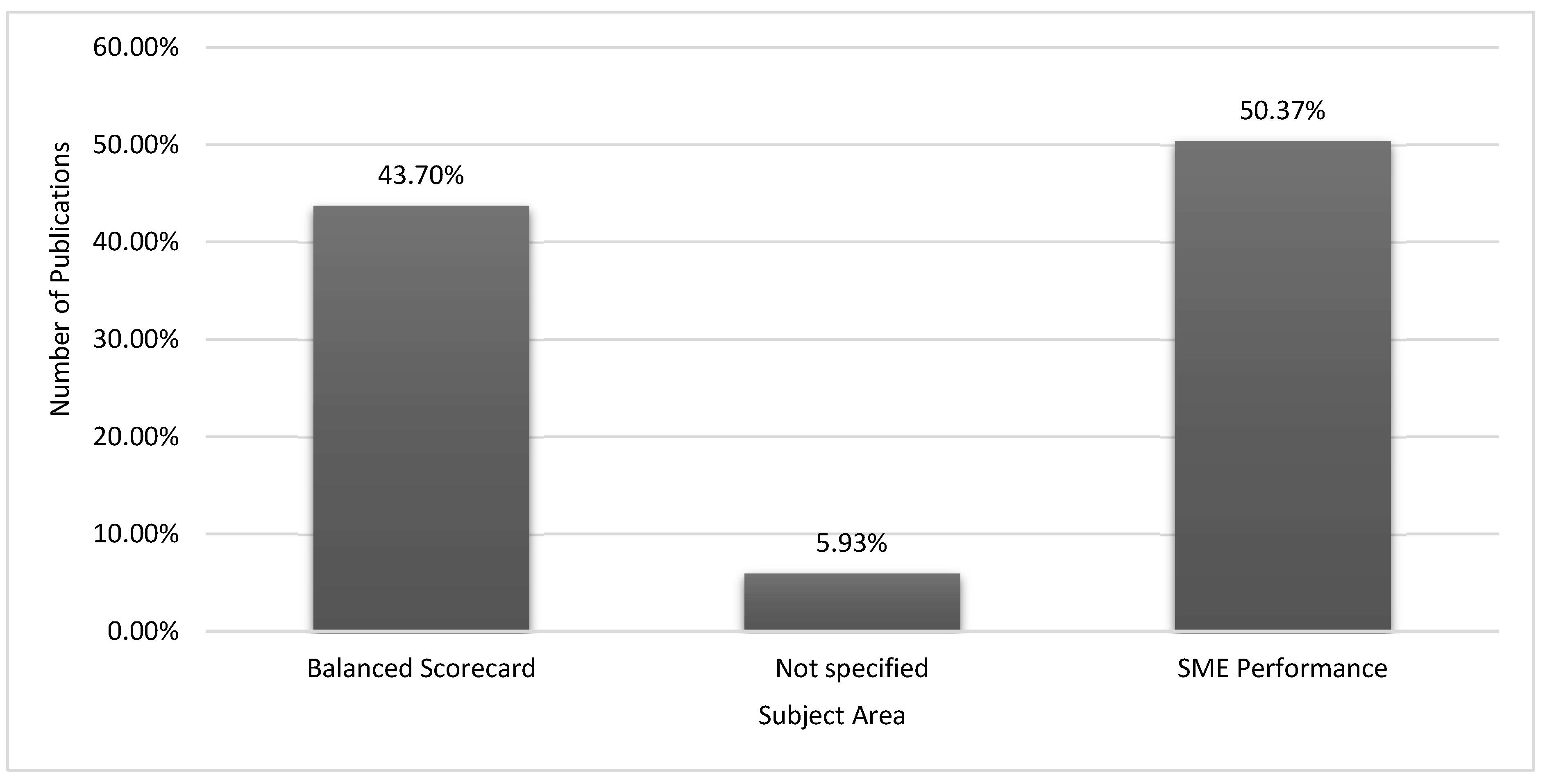
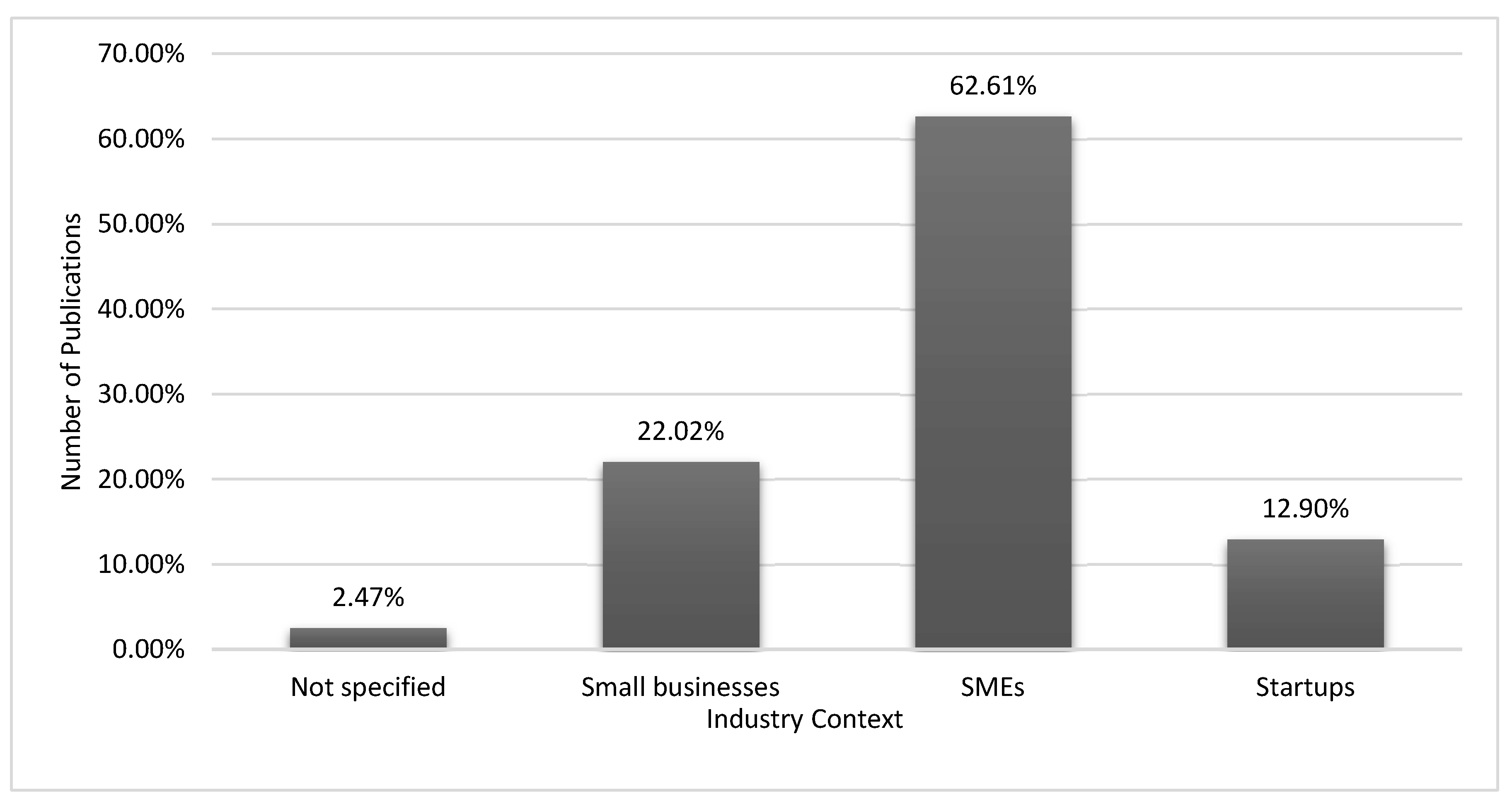
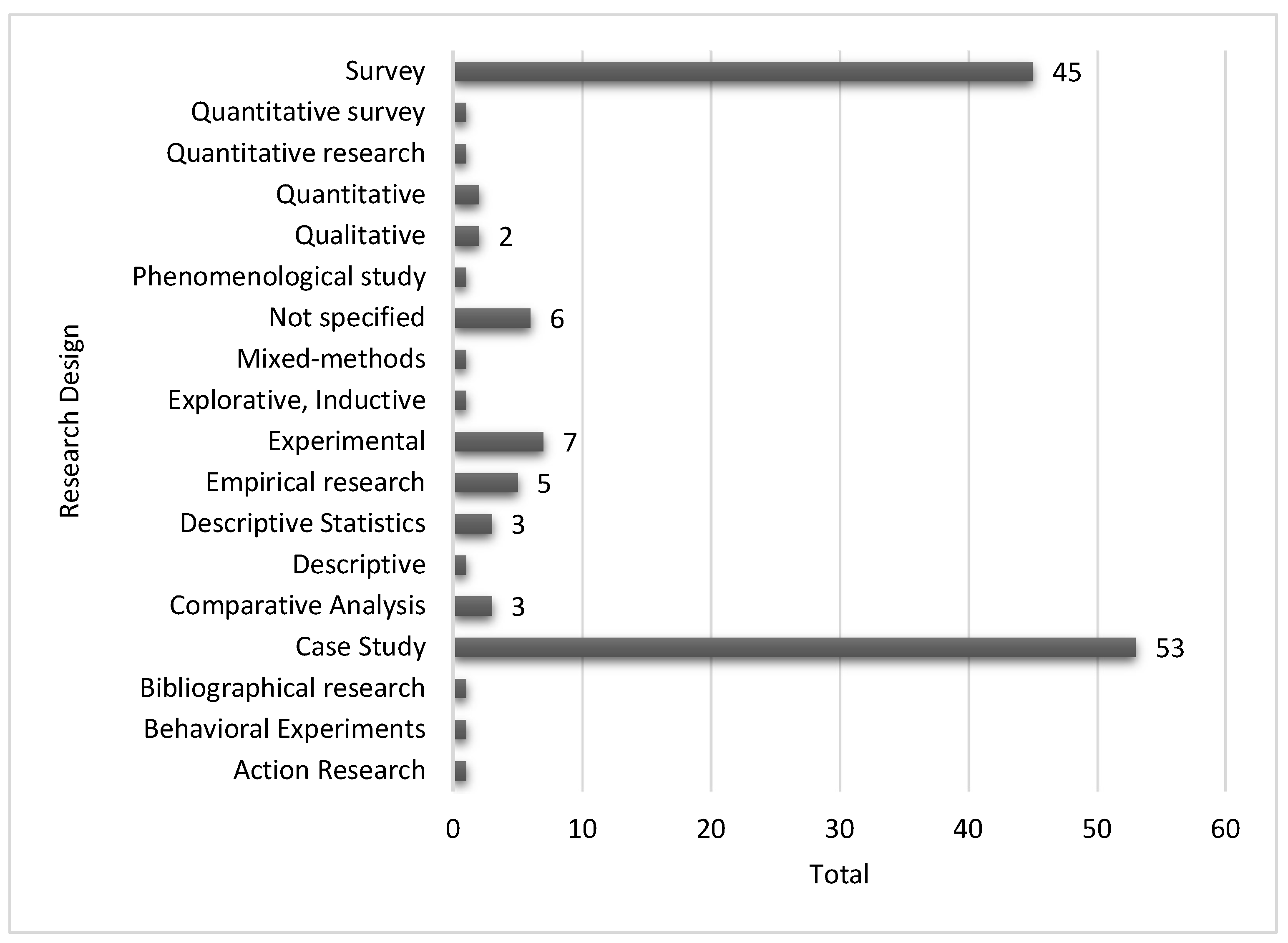
| Ref | Cites | Year | Contribution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | 21 | 2014 | Address the gap in the literature regarding the use of the Balanced Scorecard in SMEs, and it reviews existing research and suggests an agenda for future studies specific to SMEs. | Emphasizes the lack of SME-focused BSC research. | The paper may not include specific quantitative data from SMEs. |
| [22] | 50 | 2015 | Pinpoints the current state of research and highlights the barriers and limitations faced by small businesses in implementing these concepts. | Offers a comprehensive review of how the BSC can integrate sustainability into small business management. | The research paper may not provide new empirical data or case studies. |
| [23] | 13 | 2016 | It assesses the benefits, implementation, as well as limitations of the BSC, particularly in SMEs. | Provides a comprehensive review of BSC across different sectors. | It is limited to research papers from specific quality ratings (Scopus), missing relevant research from other sources. |
| [24] | 44 | 2016 | Details the use, development, design, as well as consequences of BSC in SMEs, with particular attention to family firms. | Highlights research gaps and it provides guidance for studies in the future. | The review is limited to European, Australian, and North American contexts, and it overlooks other regions. |
| [25] | 10 | 2017 | Examines the BSC's efficacy, attributes, merits, and demerits, which provides a comprehensive evaluation of its application and implementation. | Identifies the potential benefits as well as characteristics of BSCs in large firms. | Only focuses on large organizations, potentially missing insights relevant to smaller organizations. |
| [26] | 5 | 2018 | Explores the constraints of the BSC model, its practice, its execution, and it assesses whether the BSC is a definitive solution for corporate performance measurement. | Contributes to the development of the model for performance measurement research. | Overshadows the benefits of BSCs because it only focuses on the constraints and limitations of BSCs. |
| [27] | 55 | 2020 | Organizes knowledge on the use stage of the Sustainability Balanced Scorecard (SBSC) and provides an overview of recent research. | Provides a comprehensive and literature review, maps research streams, and presents potential future research avenues in SBSC. | Limited to peer-reviewed articles in English from 2000–2020, which might exclude appropriate studies outside this scope. Focuses on ABS-ranked journals, resulting in missing other insights. |
| [28] | 201 | 2021 | Determines the current state of research on SBSCs related to environmental performance outcomes and proposes a conceptual framework. | Systematic literature review with a main focus on environmental performance outcomes; proposes a novel model linking SBSC, environmental performance, and expert managers. | Lacks consensus on the relationship between BSC architecture and environmental performance; constrained to articles published in double-blind peer-reviewed journals from 2001-2020. |
| [29] | 83 | 2021 | Reviews literature on the BSC system, focusing on the BSC-compensation link and its impact on company performance. | Comprehensive analysis of 117 empirical studies; identifies gaps in research, particularly in the BSC-compensation link. | 30 studies adequately capture the BSC as suggested by Kaplan and Norton; BSC's relevance in improving performance stays unproven. |
| [30] | 80 | 2022 | Reviews and evaluates the development of research on the balanced scorecard, exploring in detail its applications and criticisms. | Reviews and evaluates the development of research on the balanced scorecard, exploring in detail its applications and criticisms. | Restricted to studies from Q1 journals, which may exclude accurate research from lower-ranked sources; some skepticism exists regarding BSC's effectiveness. |
| [31] | 1 | 2022 | Reviews the relationship between strategic management and the development of Small and Medium Enterprises, focusing on the variation between ad hoc planning and structured strategic planning. It presents the lack of studies in developing economies. | Addresses a gap in literature regarding strategic management in SMEs, particularly in developing economies. | Limited empirical evidence on the direct relationship between strategic management and SMEs' performance; mainly focuses on theoretical frameworks. |
| [32] | 201 | 2023 | Reviews the application of the Balanced Scorecard across various fields and identifies the perspectives used in measuring organizational performance. | Provides a comprehensive overview of the Balanced Scorecard's implementation in different sectors. | Restricted to 30 articles and focuses solely on Indonesian authors, which may limit generalizability. |
| Summary | The reviewed literature underscore various aspects of Balanced Scorecard implementation in SMEs, including benefits, limitations, as well as regional applications. It identifies gaps in regional focus, empirical data, and scope of research, suggesting areas for further investigation such as integrating sustainability as well as expanding geographical coverage. | Provides a very comprehensive analysis of BSC implementation, underscores barriers, and suggests future research agendas. Covers many sectors and applications, contributing valuable insights to the field. | Limited by sectoral and regional focus, lack of new empirical data, as well as reliance on specific types of publications. Overemphasis on theoretical aspects, and restricted generalizability due to narrow research scopes. | ||
| Proposed Literature | Identifies new trends in the measurement of business performances, and it offers an important evaluation of how the implementation of BSC in SMEs evolved over time. | Provides comprehensive insights of the implementation of BSC in SMEs and helps uncover trends and findings that are new in performance measurement. | Limited by available data. Analysis is complex and time consuming. | ||
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
| Topic | Research papers focusing on Balanced Scorecard Methodology: Performance metrics and strategy execution | Research papers not focusing on Balanced Scorecard Methodology |
| Research Framework | The article must include a methodology for the implementation of BSC in SMEs | Articles that lack a clear methodology for BSC implementation |
| Language | Articles must be written in English | Articles written in other languages |
| Period | Publications between 2014 and 2024 | Publications outside the period 2014 and 2024 |
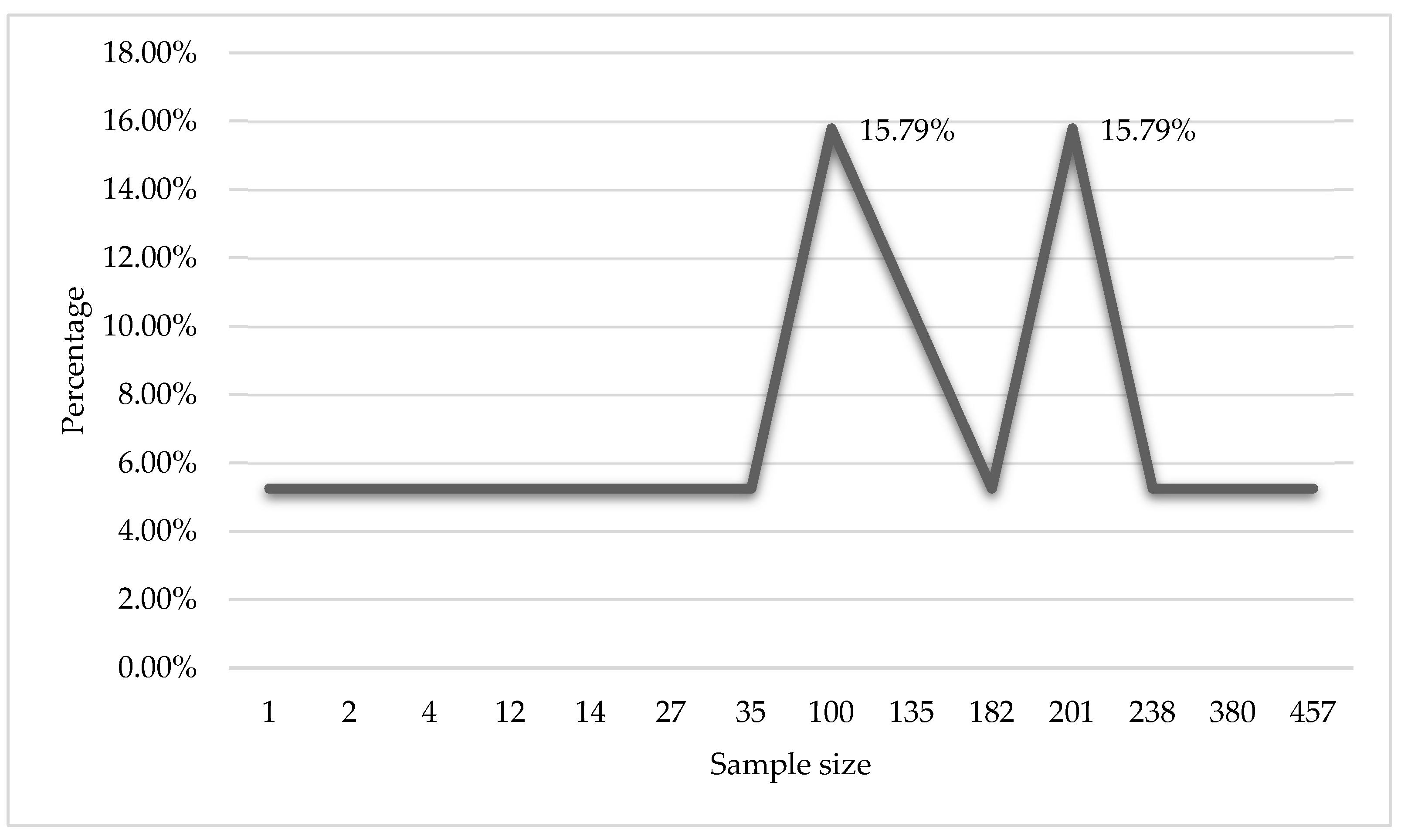
| Ref | Sample size | Subject Area | Perspectives of BSC | KPIs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
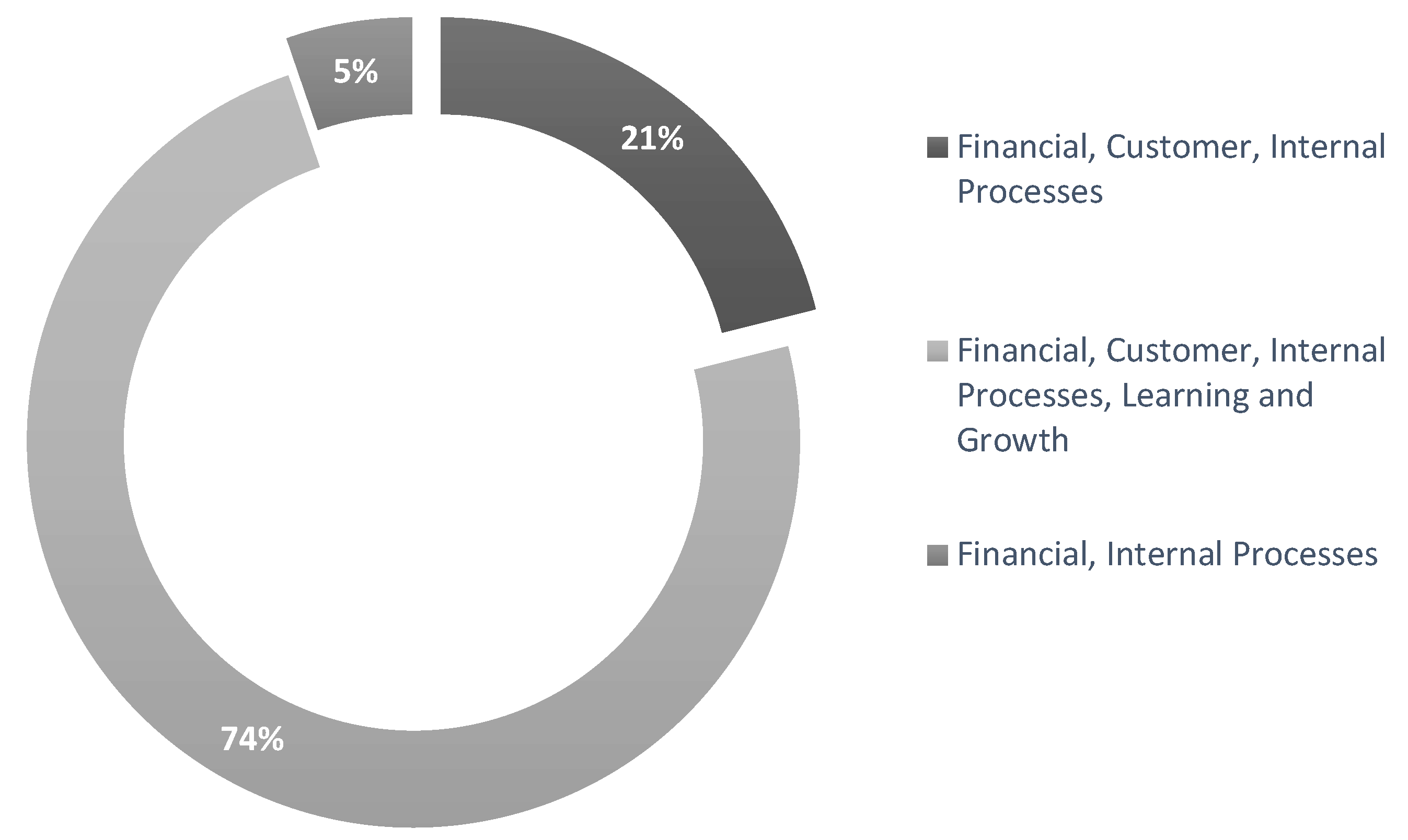
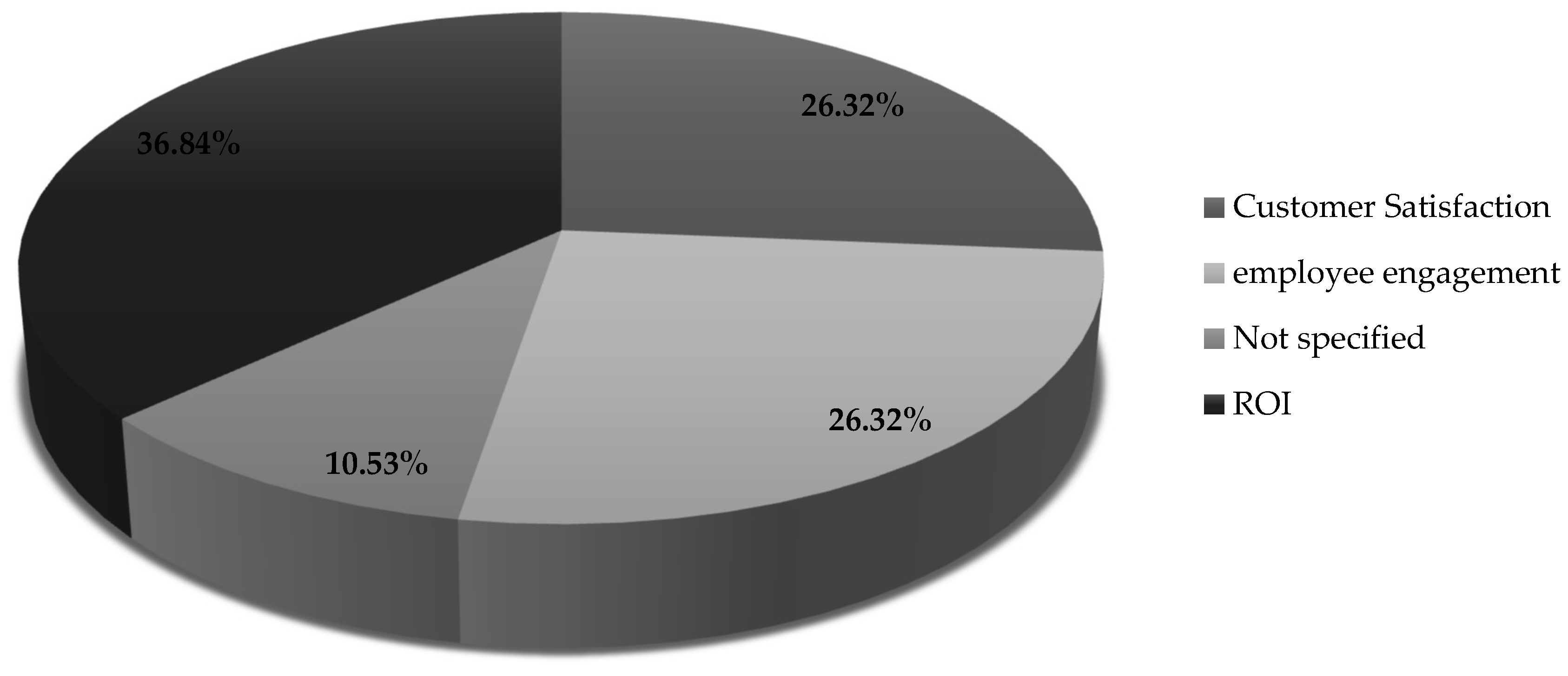
| [36] | 201 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [37] | 238 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Internal Processes | Customer satisfaction |
| [38] | 100 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [39] | 1 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes | ROI |
| [40] | 380 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [41] | 135 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [42] | 35 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [43] | 4 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [44] | 27 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [45] | 14 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [46] | 2 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [47] | 457 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [48] | 12 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [49] | 135 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [50] | 182 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Internal Processes | Not specified |
| [51] | 100 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [52] | 100 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [53] | 201 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | Customer satisfaction |
| [54] | 201 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [55] | 549 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Internal Processes | ROI |
| [56] | 14 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Not specified |
| [57] | 12 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [58] | 160 | SME performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [59] | 549 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [60] | 14 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [61] | Not specified |
SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [62] | 111 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [63] | 29 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Internal Processes | Not specified |
| [64] | 385 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [65] | 600 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [66] | 12 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal processes, Learning and growth | Employee engagement |
| [67] | Not specified |
SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Not specified |
| [68] | Not specified |
Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal processes, Learning and growth | Employee engagement |
| [69] | 1 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [70] | 50 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [71] | 67 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [72] | 5 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Not specified |
| [73] | Not specified |
Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [74] | 202 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [75] | 4 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Internal Processes | Customer satisfaction |
| [76] | 225 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [77] | 5 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | Customer satisfaction |
| [78] | 200 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [79] | 7 | Not specified | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [80] | 4071 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [81] | 130 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [82] | 120 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [83] | 529 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [84] | 100 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [85] | 5 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Not specified |
| [86] | 31 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | Customer satisfaction |
| [87] | 5 | Balanced Scorecard | customer, Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [88] | 111 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [89] | 386 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [90] | 40 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [91] | 150 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal processes, Learning and growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [92] | 100 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [93] | 2 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [94] | 154 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [95] | 10 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [96] | 15 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [97] | 8 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [98] | 20 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [99] | 30 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [100] | 12 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [101] | 10 | Not specified | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [102] | 4739 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [103] | 4739 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [104] | 8 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [105] | 274 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [106] | 160 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Internal Processes | Not specified |
| [107] | 384 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [108] | 135 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal processes, Learning and growth | Employee engagement |
| [109] | 156 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [110] | 12 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Not specified |
| [111] | 309 | SME Performance | Financial, Internal Processes | Employee engagement |
| [112] | 219 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [113] | 135 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [114] | 1 000 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Customer satisfaction |
| [115] | 120 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [116] | 400 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [117] | 156 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [118] | 40 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [119] | 107 | SME Performance | Customer, Internal Processes | Employee engagement |
| [120] | 15 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [121] | 100 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [122] | 16 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes | Employee engagement |
| [123] | 750 | Not specified | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [124] | 88 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [125] | 15 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [126] | 4071 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer Satisfaction | Customer satisfaction |
| [127] | 225 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [128] | 5 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [129] | 30 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [130] | 200 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [131] | 350 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | Customer satisfaction |
| [132] | 404 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [133] | 5 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [134] | 277 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal processes, Learning and growth | Employee engagement |
| [135] | Not specified |
SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [136] | 1 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [137] | 6 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [138] | 79 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [139] | Not specified |
SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [140] | 15 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Not specified |
| [141] | 223 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [142] | 60 | Not specified | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [143] | 10 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [144] | 20 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [145] | 15 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal processes | ROI |
| [146] | Not specified |
Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Customer satisfaction |
| [147] | Not specified |
SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [148] | Not specified |
Not specified | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [149] | 1 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [150] | 100 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes | ROI |
| [151] | Not specified |
Balanced Scorecard | Financial, customer, internal processes, learning and growth | Employee engagement |
| [152] | Not specified |
Not specified | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [153] | 451 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Not specified |
| [154] | 399 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [155] | Not specified |
Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [156] | 3 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [157] | 251 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [158] | 933 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [159] | 101 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [160] | 227 | Not specified | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [161] | 10 | SME Performance | Finance, customer, internal processes | Not specified |
| [162] | 200 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Employee engagement |
| [163] | 10 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [164] | Not specified |
Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Not specified |
| [165] | 130 | Not specified | Finance, customer, internal processes | Employee engagement |
| [166] | 813 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| [167] | 130 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal processes, Learning and growth | Not specified |
| [168] | 143 | Balanced Scorecard | Finance, customer, internal processes | ROI |
| [169] | 346 | SME Performance | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | Not specified |
| [170] | 56 | Balanced Scorecard | Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth | ROI |
| Ref | Random sequence Generation | Allocation Concealment | Blinding of Participants & Personnel | Blinding of Outcome Assessment | Incomplete Outcome Data | Selective Reporting | Other Bias | Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [36] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [37] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| [38] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR |
| [39] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR |
| [40] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [41] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | HIGH | HIGH |
| [42] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [43] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [44] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [45] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| [46] | UNCLEAR | HIGH | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | HIGH |
| [47] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [48] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW |
| [49] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | HIGH | HIGH |
| [50] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [51] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| [52] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | HIGH | HIGH |
| [53] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [54] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [55] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| [160] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [161] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| [162] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| [163] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | HIGH | HIGH |
| [164] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| [165] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [166] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| [167] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [168] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | UNCLEAR | HIGH | HIGH |
| [169] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | UNCLEAR |
| [170] | UNCLEAR | UNCLEAR | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
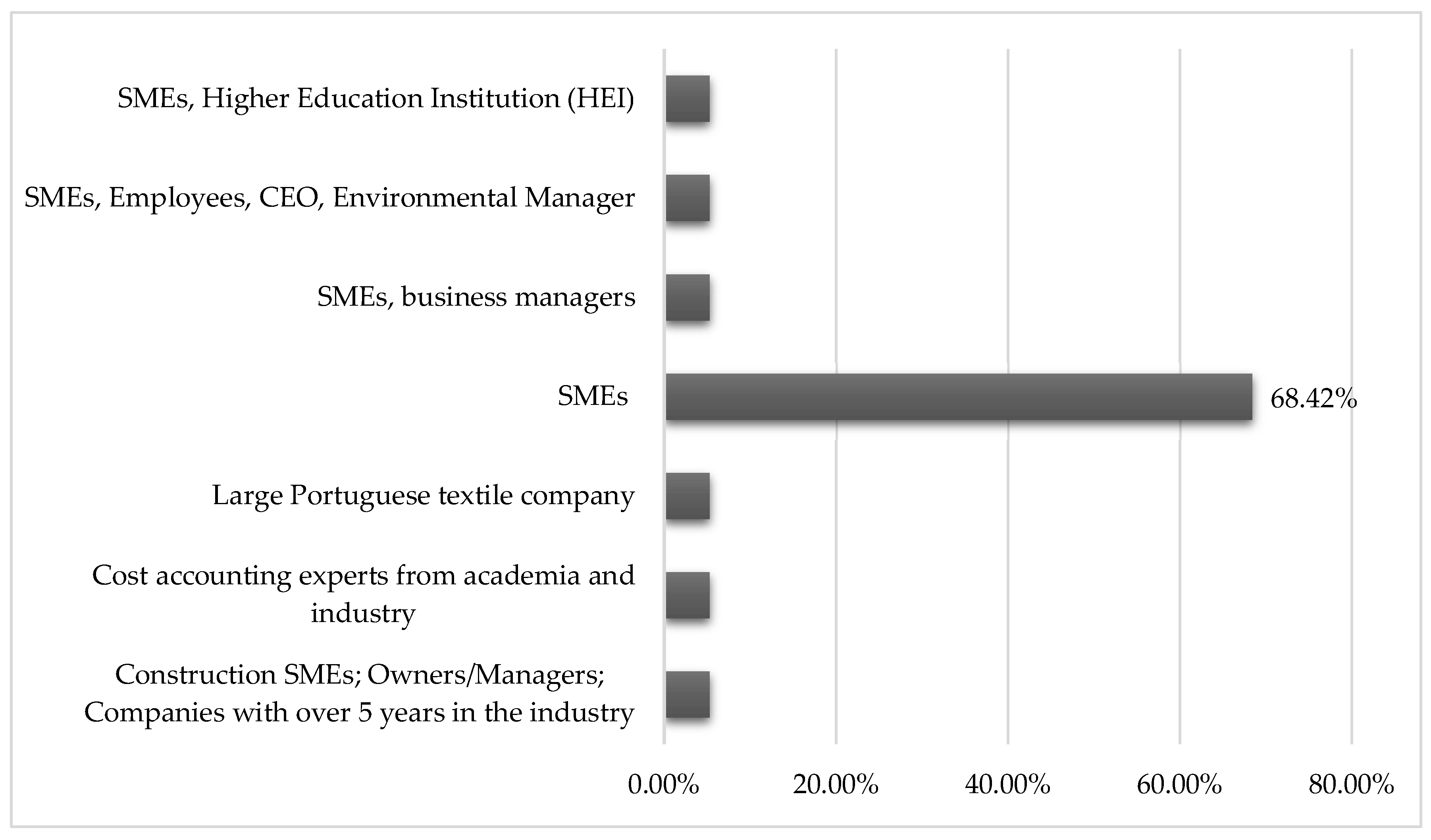
| Ref | Year | Country | Financial | Customer | Internal process | Learning and growth | Organizational outcomes | Long-term impacts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [36] | 2017 | Spain | yes | Yes | yes | no | Not specified | Enhanced organizational efficiencies |
| [37] | 2018 | Vietnam | yes | Yes | no | no | Not specified | Improved Performance, Strategic Alignment |
| [38] | 2015 | Portugal | yes | Yes | yes | no | Awareness of lean practices, improved performance | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [39] | 2018 | Romania | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Improved strategic management, high efficiency in resource use | Enhanced strategic management, potential for increased market share |
| [40] | 2023 | Pakistan | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Improved communication, better understanding of goals | Enhanced performance, potential competitive advantage |
| [41] | 2018 | United Kingdom | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Top-management commitment, employee education, organizational buy-in | Positive return on investment, enhanced implementation of BSC in SMEs |
| [42] | 2020 | Eswatini | yes | No | yes | no | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction, innovation | Business sustainability, growth, competitive advantage |
| [43] | 2018 | Portugal | yes | No | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, Customer loyalty, Increased training hours | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage, Market consolidation |
| [44] | 2019 | South Africa | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Improved decision-making, process optimization | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [45] | 2016 | Austria | no | No | no | no | Employee Motivation, Customer Service | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [46] | 2021 | Portugal | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Improved Communication, Organizational Performance | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [47] | 2023 | Vietnam | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [48] | 2022 | United Kingdom | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [49] | 2018 | Slovakia | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [50] | 2020 | Slovakia | yes | no | yes | no | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [51] | 2024 | United Kingdom | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Knowledge Transfer Effectiveness, Improved Performance | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [52] | 2019 | Indonesia | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Employee Training Participation, Customer Retention | Business Growth, Improved Performance Monitoring |
| [53] | 2015 | Egypt | yes | Yes | yes | no | Employee satisfaction, Customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [54] | 2022 | Portugal | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Employee and organizational alignment, communication of strategic objectives | Potential improvement in organizational performance, strategic alignment, sustainability |
| [55] | 2015 | Portugal | yes | no | yes | no | Not specified | Not specified |
| [56] | 2015 | Malaysia | no | no | no | no | Not specified | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [57] | 2015 | Norway | yes | yes | yes | yes | Not specified | Not specified |
| [58] | 2017 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Not specified | Not specified |
| [59] | 2016 | Portugal | yes | yes | yes | no | Use of BSC | Enhanced Organizational Performance |
| [60] | 2020 | Eswatini | yes | yes | yes | yes | High repeat and new customer visits, Need for continuous improvement and innovations | Business sustainability, Enhanced performance and growth, Competitive advantage |
| [61] | 2016 | Not specified | yes | yes | yes | yes | Improved competitive advantage, Employee focus | Enhanced long-term performance, Better alignment with organizational goals |
| [62] | 2015 | Iran | yes | yes | yes | no | Positive impact on economic and learning and growth performances; limited impact on social and environmental outcomes | Expected increase in use and integration in manufacturing and service sectors |
| [63] | 2017 | Croatia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Not specified | Not specified |
| [64] | 2018 | Thailand | yes | no | yes | no | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [65] | 2020 | Thailand | yes | yes | yes | no | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [66] | 2022 | Indonesia | yes | yes | yes | no | Increased productivity, Improved performance | Business excellence, Competitive advantage |
| [67] | 2022 | Indonesia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage, improvement in performance metrics |
| [68] | 2014 | Egypt | yes | yes | yes | yes | Benefits of BSC (communication, coordination, strategic vision description) | Addressing internal and external factors affecting SME performance, improving strategic planning |
| [69] | 2018 | Italy | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, partner commitment | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [70] | 2020 | Nigeria | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Potential for improved performance, competitive advantage |
| [71] | 2016 | Kenya | yes | yes | yes | yes | Increased Profitability, Improved Financial Performance | Increased Profitability, Improved Financial Performance |
| [72] | 2024 | Brazil | yes | yes | yes | yes | Improved decision-making, Strategic alignment | Enhanced competitiveness, Better strategic planning |
| [73] | 2022 | Europe | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, customer feedback | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [74] | 2019 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [75] | 2022 | Iraq | yes | no | yes | No | Improved decision-making, customer and stakeholder relationships | Enhanced business environment, response to economic fluctuations |
| [76] | 2020 | Slovakia | yes | yes | yes | no | Business Improvement, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [77] | 2023 | South Africa | yes | yes | yes | No | Not specified | Sustainable growth, competitive advantage |
| [78] | 2019 | Nigeria | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [79] | 2021 | Spain | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee and Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability |
| [80] | 2020 | Greece | yes | yes | yes | no | Financial performance improvements | Competitive advantage, business sustainability |
| [81] | 2021 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Low level of quality certification (35.9% MS ISO 9001) | Need for improvement in quality and environmental management systems |
| [82] | 2018 | Not specified | yes | yes | yes | no | Regional sustainability scores, Benchmarking of SMEs | Business sustainability, Feedback to policymakers |
| [83] | 2023 | Philippines | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [84] | 2021 | Indonesia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, Customer loyalty, Improved services | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage, Market differentiation |
| [85] | 2023 | South Africa | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [86] | 2015 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | no | Increased customer satisfaction | Improved business performance, Enhanced SME productivity |
| [87] | 2017 | Not specified | yes | yes | yes | yes | Customer satisfaction, global performance | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [88] | 2015 | Tehran | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee satisfaction, Customer service improvement | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [89] | 2022 | Kenya | no | no | no | no | Improved growth and performance of SMEs | Enhanced strategic implementation and growth |
| [90] | 2019 | Jordan | yes | yes | yes | yes | Customer Satisfaction, Employee Satisfaction | Competitive Advantage, Business Sustainability |
| [91] | 2015 | South Africa | yes | yes | yes | yes | Managerial Decision Support, Performance Improvement | Business Survival, Economic Growth |
| [92] | 2018 | Portugal | yes | yes | yes | yes | Improvement in strategy communication, organizational learning | Enhanced strategic alignment, business sustainability |
| [93] | 2023 | United Kingdom | yes | yes | yes | yes | Business Performance Improvement | Competitive Advantage, Enhanced Adoption of Technology |
| [94] | 2014 | Taiwan | yes | yes | yes | yes | Interaction between leadership styles and BSC implementations | Synergy of leadership styles and BSC, improved organizational performance |
| [95] | 2020 | Europe | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee Engagement, Customer Satisfaction | Competitive Advantage, Business Sustainability |
| [96] | 2022 | North America | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Growth | Long-term Growth, Market Positioning |
| [97] | 2019 | Asia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Customer Satisfaction, Employee Engagement | Business Adaptability, Competitive Position |
| [98] | 2021 | Latin America | yes | yes | yes | yes | Customer Satisfaction, Employee Performance | Market Penetration, Sustainable Development |
| [99] | 2018 | Africa | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Long-term Strategic Growth, Business Resilience |
| [100] | 2023 | North America | no | no | no | no | Customer Satisfaction, Employee Engagement | Technology Adoption, Competitive Advantage |
| [101] | 2024 | Africa | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee Engagement, Customer Satisfaction | Market Expansion, Sustainable Practices |
| [102] | 2021 | Germany | yes | yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Increased Welfare, Long-term Business Sustainability |
| [103] | 2022 | South Africa | yes | yes | yes | yes | Performance improvement of the grant-funded programme | Enhanced programme effectiveness, improved grant application success, development impact in SMEs |
| [104] | 2021 | South Africa | yes | yes | yes | yes | Improved data collection and management, increased interaction and measurement capabilities | Increased economic development, enhanced incubator performance, improved entrepreneurial activity |
| [105] | 2022 | Vietnam | yes | yes | yes | yes | Enhanced Operational Efficiency | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [106] | 2014 | Malaysia | yes | no | yes | No | Employee satisfaction, Customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [107] | 2022 | Thailand | yes | yes | yes | No | Employee performance, Organizational assessment | Risk mitigation, Enhanced organizational control |
| [108] | 2020 | Singapore | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, Manager satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [109] | 2021 | France | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Not specified | Not specified |
| [110] | 2022 | Sudan | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Not specified | Enhancing understanding of BSC in emerging economies |
| [111] | 2017 | Italy | yes | No | yes | no | Improved firm management | Business growth |
| [112] | 2020 | Italy | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Financial performance | Economic Sustainability |
| [113] | 2020 | Vietnam | yes | yes | yes | No | Improving Business and Development Efficiency | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [114] | 2014 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | No | Customer Satisfaction, Process Efficiency | Business Sustainability |
| [115] | 2020 | Vietnam | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Not specified | Sustainability |
| [116] | 2019 | Thailand | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [117] | 2023 | Europe | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Flexibility, competitiveness | Long-term prosperity, better customer value, adaptability to changes |
| [118] | 2020 | Nigeria | yes | yes | yes | No | Customer Satisfaction, Employee Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [119] | 2024 | Jawa Timur | yes | No | yes | no | Improved Performance in Customer & Internal Processes | Enhanced Business Models, Competitive Advantage |
| [120] | 2017 | Czech Republic | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Company’s attitude to risk | Business competitiveness, Company performance |
| [121] | 2019 | South Africa | yes | Yes | yes | yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [122] | 2015 | India | yes | Yes | yes | No | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [123] | 2014 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, Customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [124] | 2017 | Indonesia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Customer Satisfaction, Employee Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [125] | 2017 | Colombia | yes | yes | yes | yes | Strengths and weaknesses identification, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, improved decision-making |
| [126] | 2022 | Greece | yes | yes | no | No | Customer satisfaction, proposal submission, e-shop | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [127] | 2024 | Ghana | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, Customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [128] | 2019 | Iraq | yes | yes | yes | No | Improved strategic performance, cost reduction | Enhanced competitiveness, sustainable strategic performance |
| [129] | 2014 | Australia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee development, Customer satisfaction | Sustainable competitive advantage, Business performance |
| [130] | 2018 | Vietnam | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, Customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [131] | 2021 | Swaziland | yes | yes | yes | No | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [132] | 2022 | Nigeria | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, retention rates | Business sustainability, improved performance |
| [133] | 2019 | Brazil | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [134] | 2023 | Saudi Arabia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [135] | 2015 | United States | yes | yes | yes | No | Social stability, policy effectiveness | Enhanced state-civil society relationship, improved policy implementation |
| [136] | 2024 | Turkey | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Adherence to traditional framework | Improved performance measurement, potential for enhanced sustainability |
| [137] | 2022 | China | yes | yes | yes | No | Not specified | Insights on MMAPs adoption and performance |
| [138] | 2015 | Indonesia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Curriculum development, teaching strategy | Enhanced entrepreneurship education, integrated curriculum |
| [139] | 2018 | Sulawesi | yes | yes | yes | No | Improved performance, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [140] | 2020 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Enhanced strategic focus, improved financial performance | Increased business success, enhanced strategic management |
| [141] | 2015 | Nigeria | yes | yes | yes | No | Strategy implementation effectiveness | Business sustainability, Economic development |
| [142] | 2017 | South Africa | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee and community engagement, reputation | Socio-economic development, knowledge-sharing, sustainability |
| [143] | 2022 | Germany | yes | yes | yes | No | Employee engagement, Stakeholder communication | Improved sustainability practices, Competitive advantage |
| [144] | 2022 | North America | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Customer satisfaction, Employee satisfaction | Enhanced corporate sustainability, Strategic alignment |
| [145] | 2021 | Europe | yes | yes | yes | No | Increased employee morale, Better customer relations | Long-term operational excellence, Improved market position |
| [146] | 2017 | Not specified | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Not specified | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [147] | 2018 | Not specified | yes | yes | yes | No | Not specified | Business sustainability, rational decision-making process |
| [148] | 2014 | Europe | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Network-oriented controlling, Strategic management | Efficient, innovative, safe, and environmentally friendly corridor development |
| [149] | 2014 | Finland | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Adaptability of PMS, challenges in implementation | Business sustainability, adaptability to market changes |
| [150] | 2022 | Indonesia | yes | yes | yes | no | Performance metrics include customer satisfaction, financial performance | Enhanced SME performance, improved capability, moderated by innovation |
| [151] | 2024 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [152] | 2021 | Indonesia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Risk Reduction, Stakeholder Decision Making | Business Performance Improvement, Risk Management Enhancement |
| [153] | 2024 | Ethiopia | yes | yes | yes | No | Impact of innovation on organizational performance | Improvement of organizational performance through innovation; insights for future research |
| [154] | 2024 | Kenya | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Superior operational performance, Quality product | Competitive edge, Improved enterprise performance |
| [155] | 2021 | India | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, Customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [156] | 2016 | Germany | yes | yes | yes | No | Employee Satisfaction, Internal Discussions on Logistics Contribution | Improved Competitiveness, Process and Organizational Enhancements |
| [157] | 2015 | India | yes | yes | yes | No | Customer satisfaction, employee satisfaction | Competitive advantage, business sustainability |
| [158] | 2017 | Iran | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [159] | 2015 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | No | Employee satisfaction, Customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [160] | 2019 | Iran | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Improved Strategic Resource Allocation |
| [161] | 2017 | Italy | yes | yes | yes | No | Employee satisfaction, stakeholder engagement | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [162] | 2020 | Not specified | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [163] | 2014 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Customer satisfaction, employee satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [164] | 2020 | China | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [165] | 2024 | Malaysia | yes | yes | yes | No | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| [166] | 2019 | Republic of Croatia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee Satisfaction, Customer Satisfaction | Business Sustainability, Competitive Advantage |
| [167] | 2017 | Ghana | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Not specified | Not specified |
| [168] | 2016 | Chile | yes | yes | yes | No | Employee satisfaction, Customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage |
| [169] | 2019 | Indonesia | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Not specified | Not specified |
| [170] | 2016 | Sweden | yes | yes | yes | Yes | Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction | Business sustainability, competitive advantage |
| Ref | Study | Title |
|---|---|---|
| [36] | A | Balanced scorecard in SMEs: effects on innovation and financial performance |
| [37] | B | An Investigation of the Effects of Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Implementation on Small and Medium Sized Enterprises (SMEs) Performance: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches (A Case of Egypt) |
| [38] | C | Developing a lean supply chain performance framework in a SME: a perspective based on the balanced scorecard |
| [39] | D | Implementation of Balanced Scorecard and Financial Performance of SMEs |
| [40] | E | How does the Balanced Scorecard work for SMEs? An explorative study |
| [41] | F | Sustainability Management with the Sustainability Balanced Scorecard in SMEs: Findings from an Austrian Case Study |
| [42] | G | Existing Differences Between SMEs That Apply BSC and Those That Do Not |
| [43] | H | Architecture of Balanced Scorecard for SMEs |
| Study | Missing data | Selective reporting | Protocol inconsistencies |
Outcome reporting | Overall risk of bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | No | No | No | Yes | Low |
| B | Yes | No | No | Yes | Moderate |
| C | No | Yes | No | Yes | High |
| D | No | No | No | Yes | Low |
| E | No | No | Yes | No | Moderate |
| F | No | No | No | Yes | Low |
| G | No | No | Yes | Yes | High |
| H | No | No | No | Yes | Low |
| Industry | Key Finding | Strategic Implications for Business Leaders | Opportunities | Challenges | Relevance to Proposed Systematic Review | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Integration of BSC with operational frameworks like Lean or Six Sigma improves process efficiency. | Adopt BSC alongside Lean or Six Sigma to optimize operational efficiency. | Streamlined processes and waste reduction. | High initial investment in training and resources. | 36.84% of studies focused on operational performance and process alignment, reflecting the review’s emphasis on aligning strategic objectives with practical improvements in SMEs. | Operational efficiency; strategic alignment. | Enhanced productivity and competitive advantage. |
| Healthcare | BSC aligns clinical outcomes with organizational objectives, improving patient care. | Use BSC to connect clinical outcomes with strategic goals for better decision-making. | Potential to improve patient care quality and service delivery. | Balancing clinical priorities with financial targets. | 26.32% of studies focused on non-financial metrics like customer satisfaction and employee engagement, relevant to improving patient care and aligning with strategic outcomes in the review. | Employee engagement; customer satisfaction (patient outcomes). | Improved quality of care and organizational performance. |
| Information Technology | BSC encourages continuous innovation by linking learning metrics to tech initiatives. | Utilize BSC to track technological advancements and link them to skill development. | Promotes new technology adoption and skill development. | Rapid technological changes can outpace metric updates. | 31.58% of studies applied thematic analysis to assess qualitative dimensions like innovation, relevant for IT's dynamic and evolving nature as discussed in the review. | Learning and growth; technological innovation. | Increased innovation capability and market competitiveness. |
| Retail | BSC aligns financial objectives with customer satisfaction, boosting sales outcomes. | Integrate customer feedback and financial metrics to guide strategic decisions. | Opportunity to enhance customer loyalty and revenue growth. | Balancing cost reduction with improving customer experience. | 26.32% of studies emphasized customer satisfaction as a critical KPI, aligning with the systematic review's findings on the importance of customer-focused performance metrics. | Customer satisfaction; financial performance. | Strengthened customer loyalty and increased sales. |
| Energy | BSC aids in tracking sustainability alongside financial metrics, promoting eco-friendly practices. | Link sustainability initiatives with financial goals using the BSC for holistic performance. | Enhances brand reputation and regulatory compliance. | High costs and complexity in sustainability metric implementation. | 5.26% of studies integrated sustainability perspectives, highlighting the review's attention to including environmental considerations in performance management. | Sustainability; financial alignment. | Improved sustainability reporting and long-term business viability. |
| Education | BSC aligns educational goals with performance metrics, enhancing student outcomes. | Use BSC to set clear learning objectives and track educational progress. | Opportunity to improve educational quality and institutional reputation. | Standardizing educational KPIs across diverse environments can be challenging. | 43.70% of literature focused on the BSC methodology itself, aligning with educational applications and non-financial performance indicators reviewed. | Learning and growth; stakeholder satisfaction (student success). | Enhanced educational quality and institutional performance. |
| Financial Services | BSC integrates risk management into strategic planning, improving compliance outcomes. | Use BSC to monitor regulatory compliance and financial targets concurrently. | Opportunity to reduce regulatory risks and increase transparency. | Complexity in adapting BSC to include compliance metrics. | 38.52% of studies emphasized long-term impacts like business sustainability and competitive advantage, which relate to compliance and risk management in the financial sector. | Risk management; compliance. | Improved compliance and risk mitigation strategies. |
| Agriculture | BSC links productivity with sustainability, optimizing resource use and market access. | Adopt BSC to track productivity and sustainability efforts for better resource management. | Opportunity to implement sustainable practices and improve market reach. | Customizing BSC metrics for agriculture-specific performance can be difficult. | 5.26% of studies discussed sector-specific metrics, suggesting the need for customized BSC frameworks relevant to agricultural sustainability highlighted in the review. | Productivity; sustainability; market alignment. | Increased productivity, market reach, and sustainable practices. |
| Automotive | BSC aligns production goals with quality standards for better operational control. | Integrate quality control metrics with production objectives using the BSC. | Potential to improve manufacturing efficiency and product quality. | High costs for integrated quality management systems. | 49.63% of studies utilized quantitative approaches focusing on measurable metrics like production quality, which aligns with the systematic review's emphasis on operational performance. | Quality management; operational efficiency. | Enhanced product quality and manufacturing efficiency. |
| Industry | Step | Framework Focus | Key Features | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | Ties to Proposed Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Compliance and Risk Management | Identify regulatory requirements and risk factors | Compliance, risk mitigation | Improved compliance, reduced risk exposure | Addresses compliance focus in 38.52% of studies |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Security and Data Management | Choose platforms with robust security features | Data protection, regulatory compliance | Secure communication and data handling | Reflects findings on security requirements | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Regulatory Integration | Test platform's integration with regulatory frameworks | Seamless integration with existing processes | Reduced disruptions during implementation | Mirrors the emphasis on integration in BSC studies | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Standardization | Implement platform across all departments | Consistency in regulatory practices | Unified compliance management | Supports holistic BSC approach across departments | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuous Risk Monitoring | Ongoing assessment of risk management processes | Dynamic adaptation to regulatory changes | Enhanced risk management strategies | Correlates with the review's focus on dynamic adaptation | |
| Technology | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Customer-Centric Approach | Assess customer needs and user feedback | Customer satisfaction, user engagement | Improved user experience, higher customer retention | Aligns with 26.32% of studies on customer satisfaction |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Innovation Focus | Choose platforms with advanced collaboration features | Innovation, technology adoption | Enhanced collaboration, faster decision-making | Related to findings on innovation in 21.05% of studies | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | User Experience | Test user-friendliness and integration capabilities | User acceptance, ease of use | High user adoption rates, seamless integration | Reflects studies emphasizing pilot testing | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Cross-Functional Integration | Implement across multiple teams and departments | Cross-functional collaboration, agile processes | Improved agility, streamlined operations | Tied to BSC focus on internal processes and efficiency | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuous Feedback and Updates | Regular updates based on user feedback | Adaptation to changing user needs | High user satisfaction, continuous improvement | Supports findings on the importance of continuous optimization | |
| Manufacturing | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Supply Chain Optimization | Identify bottlenecks and efficiency opportunities | Cost reduction, efficiency improvement | Lower production costs, streamlined processes | Relates to BSC focus on internal processes (43.70%) |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Production Monitoring | Choose platforms with real-time monitoring features | Operational efficiency, productivity | Real-time data visibility, reduced downtime | Supports findings on monitoring and KPI tracking | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Process Alignment | Test platform with small-scale production | Process optimization, employee training | Improved workflow efficiency, reduced errors | Reflects importance of pilot testing in 53 studies | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Automation | Implement automated systems across production lines | Automation, process standardization | Higher productivity, consistent quality | Aligned with BSC metrics focusing on internal processes | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuous Improvement | Regular upgrades based on production feedback | Lean practices, Six Sigma implementation | Enhanced quality control, continuous efficiency gains | Mirrors findings on process optimization | |
| Retail | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Customer Engagement | Evaluate customer preferences and market trends | Customer retention, sales growth | Improved sales performance, enhanced customer loyalty | Linked to 26.32% studies on customer satisfaction |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Omni-Channel Integration | Choose platforms supporting seamless multi-channel | Digital transformation, e-commerce growth | Consistent customer experience across channels | Supports studies focusing on digital transformation | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Promotion and Feedback Loop | Test platform with selected promotional campaigns | Campaign effectiveness, customer insights | Optimized marketing strategies, increased sales | Correlates with emphasis on feedback loops | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Loyalty Program Integration | Expand to include loyalty programs across platforms | Customer loyalty, repeat sales | Higher customer retention, long-term revenue growth | Mirrors findings on loyalty programs and sales impact | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Dynamic Pricing and Inventory Management | Update based on customer behavior and market data | Competitive pricing, stock management | Improved margins, optimized inventory turnover | Reflects the importance of optimization for agility | |
| Healthcare | Step 1: Needs Analysis | Patient-Centric Services | Evaluate patient needs and data management practices | Patient satisfaction, data privacy | Enhanced patient care, better data management | Related to studies on patient satisfaction and data handling |
| Step 2: Select Platform | Data Security and Privacy | Select platforms with robust data protection features | Compliance with health regulations, data integrity | Secure patient data handling, regulatory compliance | Correlates with findings on healthcare data challenges | |
| Step 3: Pilot Testing | Data Handling Procedures | Test integration with electronic health records (EHR) | Seamless data transfer, system compatibility | Reduced data entry errors, enhanced patient care | Mirrors emphasis on system integration in healthcare | |
| Step 4: Full Integration | Interoperability | Full-scale integration with healthcare systems | System interoperability, efficient patient care | Improved workflow, better coordination among departments | Reflects findings on integrated healthcare systems | |
| Step 5: Optimization | Continuous Quality Improvement | Regular updates based on patient feedback and data analysis | Quality of care, patient safety | Higher patient satisfaction, continuous quality enhancements | Related to continuous improvement focus in BSC |
| Industry | Best Practice | SME Type | Operational Challenge | Strategic Drivers | Expected Impact | Ties to Systematic Review Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | 1. Align Compliance Requirements | Regulated SMEs | Adhering to complex financial regulations | Compliance, risk management | Improved compliance, reduced penalties | Correlates with studies highlighting regulatory focus |
| 2. Implement Data-Driven Decision Making | Tech-Enabled Financial SMEs | Integrating data analytics for strategic decisions | Data accuracy, customer insight | Better decision-making, strategic agility | Reflects 31.58% thematic analysis emphasis | |
| 3. Foster a Culture of Continuous Learning | Small Brokerage Firms | Keeping up with financial market changes | Learning and growth, employee engagement | Increased adaptability, enhanced employee skills | Aligns with BSC's learning and growth dimension | |
| Technology | 1. Prioritize User Experience | High-Growth Tech Startups | Enhancing platform usability and adoption | Customer satisfaction, innovation | Higher user retention, improved product features | Linked to 26.32% studies focusing on customer satisfaction |
| 2. Drive Innovation Through Cross-Functional Teams | Mid-Sized IT Consulting Firms | Bridging communication gaps across departments | Collaboration, agile development | Faster time-to-market, cohesive team environment | Mirrors emphasis on cross-functional integration | |
| 3. Leverage AI for Predictive Analytics | Emerging Tech SMEs | Adopting advanced technologies for market trends | Predictive capabilities, data-driven decisions | Improved forecasting, strategic planning capabilities | Tied to findings on the strategic use of technology | |
| Manufacturing | 1. Integrate Lean Principles with BSC | Lean-Adopting Manufacturing SMEs | Reducing waste and improving process efficiency | Cost reduction, process standardization | Lower production costs, streamlined workflows | Relates to 43.70% studies emphasizing internal processes |
| 2. Use Real-Time Monitoring Systems | High-Volume Production SMEs | Enhancing operational visibility | Operational efficiency, productivity | Reduced downtime, increased production capacity | Supports findings on monitoring and automation | |
| 3. Train Employees on Process Optimization | Small Family-Owned Manufacturers | Minimizing human errors, improving quality | Employee skills development, continuous improvement | Enhanced product quality, higher employee productivity | Reflects process optimization focus in BSC literature | |
| Retail | 1. Implement Omnichannel Strategies | Digital-Transforming Retail SMEs | Maintaining consistent customer experiences | Customer engagement, digital transformation | Improved sales performance, higher customer satisfaction | Aligns with 26.32% focus on customer experience |
| 2. Develop Data-Driven Pricing Strategies | Growing E-Commerce Platforms | Adjusting prices dynamically based on market data | Competitive pricing, revenue maximization | Optimized pricing models, increased revenue | Correlates with findings on pricing optimization | |
| 3. Foster Customer Loyalty Programs | Small Brick-and-Mortar Stores | Retaining customers amidst competition | Customer loyalty, repeat sales | Higher retention rates, long-term revenue growth | Mirrors studies linking loyalty programs to sales impact | |
| Healthcare | 1. Ensure Data Privacy and Security | Health-Tech Startups | Meeting regulatory requirements on patient data | Compliance, patient data protection | Reduced data breaches, higher trust levels | Reflects findings on data security challenges |
| 2. Optimize Patient Care Workflows | Small Clinics | Reducing administrative inefficiencies | Workflow efficiency, patient satisfaction | Faster service delivery, enhanced patient care | Supports findings on the importance of operational workflows | |
| 3. Promote Continuous Quality Improvement | Mid-Sized Healthcare Providers | Meeting evolving healthcare standards | Quality of care, patient safety | Improved compliance, ongoing service quality enhancement | Related to 5.26% of studies on continuous quality improvements |
| Industry | Key Metrics/KPIs | Measurement Focus | Strategic Drivers | Expected Outcome | Ties to Systematic Review Findings | Priority (1 = Highest, 2 = Medium, 3 = Low) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | 1. Return on Investment (ROI) | Financial performance measurement | Profitability, risk management | Improved financial stability | Tied to 36.84% studies focusing on financial metrics | 1 |
| 2. Customer Retention Rate | Customer satisfaction and loyalty | Customer engagement, service quality | Higher customer retention, increased lifetime value | Reflects emphasis on customer satisfaction in 26.32% | 2 | |
| 3. Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to legal and industry standards | Compliance, data protection | Reduced legal risks, enhanced reputation | Supports findings related to compliance requirements | 1 | |
| Technology | 1. Time to Market | Innovation and product development speed | Agile development, rapid iteration | Faster delivery cycles, increased competitiveness | Linked to findings on strategic agility | 1 |
| 2. System Uptime | Operational efficiency and system reliability | Service availability, customer satisfaction | Enhanced user experience, fewer service disruptions | Correlates with 43.70% studies on internal processes | 2 | |
| 3. Employee Productivity | Workforce efficiency and task completion | Skills development, resource utilization | Higher output, optimized resource allocation | Aligns with the learning and growth dimension in BSC | 2 | |
| Manufacturing | 1. Production Lead Time | Efficiency of production processes | Process optimization, cost reduction | Reduced production costs, faster order fulfillment | Related to findings on manufacturing efficiency | 1 |
| 2. Defect Rate | Quality control and product standardization | Quality assurance, continuous improvement | Fewer returns, higher customer satisfaction | Reflects the focus on process quality in 43.70% studies | 1 | |
| 3. Inventory Turnover | Inventory management and cash flow | Operational efficiency, demand forecasting | Lower inventory holding costs, improved cash flow | Supports insights on lean principles | 2 | |
| Retail | 1. Average Transaction Value | Sales performance and revenue generation | Revenue growth, competitive pricing | Increased sales, higher profit margins | Mirrors 26.32% studies focusing on financial and customer metrics | 1 |
| 2. Conversion Rate | Effectiveness of sales strategies | Customer engagement, digital transformation | More sales conversions, improved marketing ROI | Correlates with findings on customer-focused strategies | 1 | |
| 3. Customer Feedback Score | Quality of customer service and product offering | Customer satisfaction, service improvement | Better customer experiences, increased loyalty | Linked to the importance of customer feedback in BSC | 2 | |
| Healthcare | 1. Patient Wait Time | Efficiency of patient care and service delivery | Workflow efficiency, patient satisfaction | Shorter wait times, higher patient satisfaction | Supports findings on optimizing patient care workflows | 1 |
| 2. Readmission Rate | Quality of care and treatment effectiveness | Patient safety, quality of care | Fewer readmissions, improved health outcomes | Tied to 5.26% studies on continuous quality improvement | 1 | |
| 3. Employee Training Hours | Workforce development and skills enhancement | Learning and growth, compliance | Higher staff competency, compliance with standards | Reflects findings on learning and growth in BSC | 2 |
| Industry | Case Study | Implementation | Outcome | Reference |
| Automotive | Volkswagen do Brasil: Driving Strategy with the Balanced Scorecard | Utilized BSC to align strategic objectives across finance, customer, internal processes, and growth, introducing a strategy map to drive cultural change. | Improved employee engagement, increased quality, and operational performance, and helped restore market share. |
[LINK] |
| Healthcare | Boston Children's Hospital | Applied BSC to integrate hospital-wide objectives, focusing on patient and employee development. | Enhanced patient outcomes, staff training efficiency, and financial stability, leading to improved service quality. | [LINK] |
| Retail | Tesco | Deployed BSC t XLRI Academic Information Systemement, emphasizing customer satisfaction, financial growth, internal efficiency, and employee training. |
Achieved significant growth in customer loyalty, boosted revenue from increased sales, and improved operational efficiency, especially in supply chain management. | [LINK] |
| Manufacturing | Siemens | BSC used to drive strategy execution across multiple divisions, focusing on innovation, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. | Resulted in improved R&D outcomes, higher quality standards, and better alignment of divisional goals with corporate strategy. | [LINK] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





