1. Introduction
Ionizing radiation (IR) produces through direct and indirect action many types of DNA lesions, such as single strand breaks (SSBs), double-strand breaks (DSBs), and a variety of base modifications (base damage (BD)). Clustered DNA damage sites are defined as two or more elemental lesions that are formed within one or two helical turns of DNA (~base-pairs) by a single radiation track [
1,
2,
3]. Complex clustered damage is defined by the occurrence of three or more SSB or BD within 10 bp. IR is an efficient inducer of both complex DSB and non-DSB end structures, including the presence of BD or SSB near DSB and complex SSB. The co-location of BD near DSB or SSB may interfere with repair pathway choice and efficient repair [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Therefore, complex clustered lesions are expected to play a major role in determining the repairability of DNA lesions [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8], with a wide range of implications for describing radiation induced cell death, mutation including chromosomal aberrations, genomic instability, and aberrant signaling pathways. The understanding of complex clustered DNA damage thus plays an important role for mechanistic models of low dose risk assessments and in radiation oncology.
Monte-Carlo (MC) track structure simulations of DNA damage including simple and complex breaks have been developed using detailed volume or atomistic models of DNA and the hydration shell surrounding DNA, including models of the early chemistry leading to indirect DNA damage [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. MC based simulations have made comparisons of total yields of SSB and DSB to experimental data for a variety of particle types as a function of linear energy transfer (LET), while providing predictions of complex clustered damage of a variety of SSB and DSB types with or without additional base damage. Predictions of the role of BD, such as abasic sites, has been more limited in MC simulations.
Experimental approaches to describe DNA damage include pulsed-field electrophoresis (PFGE) on DSB’s yields, including studies with restriction enzymes [
5,
6,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20] to study the role of damaged bases and abasic sites near SSB or DSB and their possible role in inhibiting repair. The use of atomic force microscopy has recently provided data on a wider variety of clustered damage types [
21]. Immunohistochemistry is used to observe DNA repair foci for proteins specific to non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), homologous recombination (HR), and other signaling pathways [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. The kinetics of the loss of foci with time after exposure, studied with different doses, radiation qualities, and time after irradiation, has been used as an indicator of complex damage. However, experimental methods to measure the wide spectrum of damage types predicted by computational models have not been developed.
In Charlton et al. [
9], MC track structure simulations using a cylindrical volume representing a segment of DNA with 54 base pairs was used to consider the types of complex breaks induced by electrons, and high LET α-particles. Results suggested a model where the spectrum of energy imparted in the volume containing DNA folded with the probability of producing a DNA damage was predictive of yields for a variety of combinations of simple and complex SSB and DSB. In this approach the yield of a specific damage type
, j, per Gy is evaluated as:
where c is conversion constant for
evaluating yields as per Gy per bp (or similarly for per Gy per Dalton or per
Gy per cell), and dF/dε is the differential distribution of energy imparted, ε
per Gy. The function
is the probability of producing a specific damage type,
j for energy imparted, ε. Based on track-structure MC simulations Charlton et al. [
9] found these probabilities to be largely independent of radiation quality, and a strong correlation occurs between energy imparted to a volume model of DNA containing 54 bp and the probability of simple and complex break types. Charlton et al. [
9] considered only direct effects for SSB and DSB formation for a 54 bp segment, while ignoring BD and indirect effects, and found a neglible probability of no damage above ~100 eV.
In this paper I develop a multinomial probability model that predicts the spectrum of DNA damage types, including yield of simple and complex DNA breaks and BD that can be applied to all types of radiation; photons, electrons, protons, helium ions and heavy ions. The model is based on probabilities for SSB, DSB, BD and their combinations using a multinomial probability formalism. Charlton et al. [
9] found a 54 bp segment was sufficient to describe DNA damage for high LET alpha particles. However, to describe
12C and other heavy ions I use a larger segment. For comparisons to experiment, I apply the frequency distribution of energy imparted for a 5x5 nm cylindrical volume representing a significant fraction of a nucleosome containing ~73 bp. The model provides predictions of SSB and DSB of increasing complexity along with the frequency of breaks with or without BD.
2. Multinomial Probability Model
A multinomial distribution is a generalization of a binomial distribution extended to the case of multiple event outcomes. In applying this model to predict clustered DNA lesions, I consider four types of events resulting from energy imparted to the volume: A) direct ionization of sugar-phosphate moieties with probability PA leading to a SSB, B) ionization of water leading to OH- radicals with probability, PB, C) direct damage to DNA bases with probability PC, and D) energy imparted to histone proteins and other co-located molecules in the volume not leading to SSB or BD, PD. DNA-protein crosslinks are not considered. Evaluating the distributions in number of the A, B, C, and D probabilities to high-order allows for predictions of clustered damages of increasing complexity.
The threshold energy imparted for each type of damage (A, B, C, and D) vary to some extent with the threshold energy for OH- production of 13 eV, and several MC based simulation results use 17.5 eV for SSB [
10,
11,
12]. Threshold energies for BD ionization are reported in a similar range [
27]. In order to simplify the formalism, I assume the threshold is approximately the same for each type and use a normal distribution with a central estimate of
th=17.5 eV and standard deviation
of 5 eV in calculations. The assumption of a single threshold for each type of
event can be removed as discussed below.
Above the energy threshold for a single event (denoted as 1
st order) the following condition occurs for the summed probability of each outcome,
Because the energy thresholds for ionization across the molecules considered have similar values, the probabilities in Eq. (2) are estimated simply by the fraction of the volume taken up by each component. As the energy imparted, ε, increases the number of possible events increases. I introduce an index
JTOT(ε) to evaluate the total number of events for a given energy imparted,
, which is found as,
The number of each type of event that occurs is constrained by,
The multinomial probability for various combinations of events is,
The probabilities of Eq. (5) are enumerated and marginal distributions formed to evaluate various types and combinations of DNA damage. Note that based on calculations of frequency distributions for a 5x5 nm cylindrical volume considered [
28,
29,
30] and an order of importance of up to
JTOT~6 for low LET radiation, and much higher values (
JTOT >10) of importance for high LET radiation.
As JTOT increases complex clustered damages occur, including multiple SSB, DSB, and BD within 10 bp. Application of the model will show that a large fraction of SSB and DSB are formed in combination with BD for JTOT>2 The frequency of simple SSB are denoted as nSSB(S), and complex SSB defined as the occurrence of two SSB on the same strand within 10 bp, denoted as nSSB(+). If the two SSB are on opposite strands within 10 bp a simple DSB occurs, denoted as nDSB(S). If more than one isolated SSB occurs, its frequency is denoted nSSB(Sm) where m is the number of ‘isolated’ simple SSB. Similarly, complex DSB, with frequency denoted as nDSB(+), is the occurrence of a DSB with an additional SSB within 10 bp. More complex SSBs and DSBs containing >3 SSB or >2 DSB are grouped together and denoted nDSB(++) and nSSB(++), respectively. In this report BD are considered using the notation nBD(m). Analysis of probabilities for SSB and DSB frequencies that consider the spatial distance to BD with higher resolution than within the 73 bp segment will be considered in a future report.
Additional probabilities are needed to evaluate SSB, DSB, and BD and their combination probabilities. The first is to account for the spatial location of multiple SSB in accordance of the two or more within the bp
<10 criteria for a DSB or a complex SSB. I assume this possibility is equally probable with an operation that adds SSB on opposite and identical strands with mathematical operators
and
with magnitude
This leads to the following condition, with
the mathematical operator for the introduction of
an additional SSB that is farther than 10 bp apart from a previous one. The
overall magnitude of these operations obeys unit probability,
The values in Eq. (6) are dependent on the number of SSB induced because as the number increases they are more likely to fall within 10 bp separation. Estimates of the probability not to produce a cluster for the addition on each additional SSB are added, q0 were made for 73 bp segments using Monte-Carlo sampling for J=2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 and found to be 0.87, 0.74, 0.6, 0.475 and 0.35, and 0.12, respectively. A similar consideration holds as JB is increased allowing for increased radical production such that additional SSBs are added into a lesion.
A second probability is needed to estimate if an SSB or a BD is formed by OH
- radical attack, with probabilities denoted as
r1 and
r2, respectively. Schoel et al. [
31] made an estimate of interactions by OH- radicals of 80% with bases and 20% with sugar-phosphate moieties. This estimate is combined with an estimated 65% probability of conversion to SSB in MC codes [
10,
11,
12] after fitting experimental data, which leads to an overall 13% probability for SSB from OH
- radicals. The same criteria is used here to estimate a probability for BD, which is 0.8x65%=52% This leads to the parameter estimate of
r1~0.13 for conversion to SSB and
r2~0.52 for conversion to BD, while
r3=1-r1-r2 represents the probability that no SSB or BD were formed after OH
- induction.
To evaluate terms with multiplicative probabilities
such as
PAPA, I treat the probabilities using a
mathematical operator,
with a numerical value, denoted by lower-case,
pj, times the operator that combines multiple damages in the volume considering the
<10 bp criteria to determine which type of damage occurs. The operator describes the lesion location and their possible complexity as SSB’s are added into a volume representing a small DNA segment. The operator
is defined,
where the operand appears in square brackets. In addition, to simplify notation the magnitude of product terms to order JA is written,.
In the following, the
pj constant factors are not shown to simplify the formula, while their values for various permutations in Eq. (5) are easily identified. The 2
nd-order term
PAPA is found to contain 3 branching probabilities that are weighted with the identical multinomial probabilities defined in Eq. (5):
The 3
rd-order term leads to 5 branches,
In Equation (9),
nSSB(++) denotes the occurrence of three SSB’s within 10 bp located on a single strand. Equation (9) shows that the probability of the lesion DSB+ exceeds that of the SSB++ probability by 3-fold in their first occurrence of the 3
rd order term, while DSB and SSB+ have equivalent weighing at both 2
nd and 3
rd order.
Table 1 illustrates the action of the
operator on various operands (several SSB and DSB
types). A factor of 2 occurs in Eq. (9) when the
operator acts on prior lesions with 2 SSBs since
the operator acts on both SSBs, and note that the factor of 2 is also needed to
obey the conservation rule of Eq. (6).
The operator for formation of SSB and BD by OH
- radical attack is defined,
At first order the r3 probability does not produce any effect, however in general, the r3 component of the B1 operator on any operand, [O] is simply r3O.
At 2
nd order, the first-term in Eq. (10) introduces clustered SSBs, and 6 branching probabilities occur,
In Equation (12) the last branch involving B1 is applied with the multinomial coefficient of Equation (5) for the B2 probability.
2.1. Higher-Order Terms
The higher-order terms in
AJ and
BJ or their products will have many components. For higher order terms in
Bj an accurate approximation is to keep only terms up to
r12, since for higher powers,
p>2,
r1p <<1. For the case of a mixture of three and higher order terms with involvement of OH
- radicals this leads to the approximation,
Useful recursion relations for the
operator acting on products of A-terms are found as,
and for
B2,
In Equations (14) and (15) and several equations below, for compactness of notation, terms are written with additions, however each term in these equations represents a probability of a specific damage cluster event.
Higher order terms in the
C,
D or mixtures of
C and
D probabilities are evaluated as simple products. The terms with
B or
A probabilities with
C and
D to any order are evaluated as simple products, however with the
A and
B terms more complex to evaluate. Mixtures with
B probabilities then involve use of the approximation of Eq. (13) and recursion relations of Eq.’s (14) and (15). For mixtures of heterogeneous terms, the order of the probabilities is invariant. Results for 1
st and 2
nd order terms
JTOT-
JD=4 are shown in
Table 2 and in
Table 3 for
3rd order in
JTOT-
JD. For
JTOT-
JD=4, there are 15 terms amongst
A,
B and
C with several of the 4
th order terms cumbersome to evaluate because of the many components (
Table 3).
The terms of 5
th and higher order in the
A probability become increasingly difficult to evaluate. However, at large values of energy imparted the dominance of complex clustered DNA damage is expected. This observation leads to an approximation method to evaluate these probabilities. First, I note that terms to order
JA must follow an inherent binomial probability rule for the factor
. Therefore, the expansion in terms of increasing
powers of
q0(2q1) should be the basis for
evaluating higher terms. This expansion is described using binomial
coefficients:
This form occurs in Eq. (9) for
A3, and the 4
th order term in the
A-probability which is found as,
with
As noted above the value of
q0 decreases as
JA increases. Therefore, the 5
th and higher-order terms are dominated by SSB and DSB of increasing complexity, and limit to complex DSB++ or larger lesions for
JA>>1. It follows that for
JA>4 an accurate approximation is to evaluate contributions in powers up to 3
rd order in
q1 (i.e., up to
q13), and tally all the higher order terms in the binomial expansion into the
nDSB(++) and
nSSB(++) category using the binomial expansion coefficients (Eq. (16)) with terms similar to equation (17). This summation is quite transparent when one notes that the summation of the binomial coefficients is given by 2
J, while
q1 limits to ½ at large
JA. Therefore, for
JA>>1 where
q0~0, the summation of the series limits to an effective population of highly complex DSB or SSB. To facilitate the calculation of higher order terms in
JA the following is useful,
With the approximation that cubic terms in q1 (q13 ) and higher powers are counted in the nDSB(++) population.
2.2. Summations of Probabilities for Simple and Complex Damage Probabilities
Total yields for SSB, DSB, and BD or mixtures are found using marginal distributions formed by summing various probabilities where at least a lesion type of interest occurs or other criteria. For example, the probability for one or more DSB is,
where
indicates to only include combinations of A and B probabilities where a DSB occurs.
3. Results
To estimate the
pj probabilities the molecular weight of each component is considered. The average molecular weight of each of the 8 histone proteins is 14 kDa, and of DNA 0.65 kDa pe bp. The number of water molecules varies under specific conditions with estimates of ~3000 per nucleosome [
32]. Bases on these estimates, calculations were made with approximate values of
pA=0.2,
pB=0.2,
pC=0.2, and
pD=0.4 representing estimates of the fraction of energy imparted to the 5x5 nm target volume by each component.
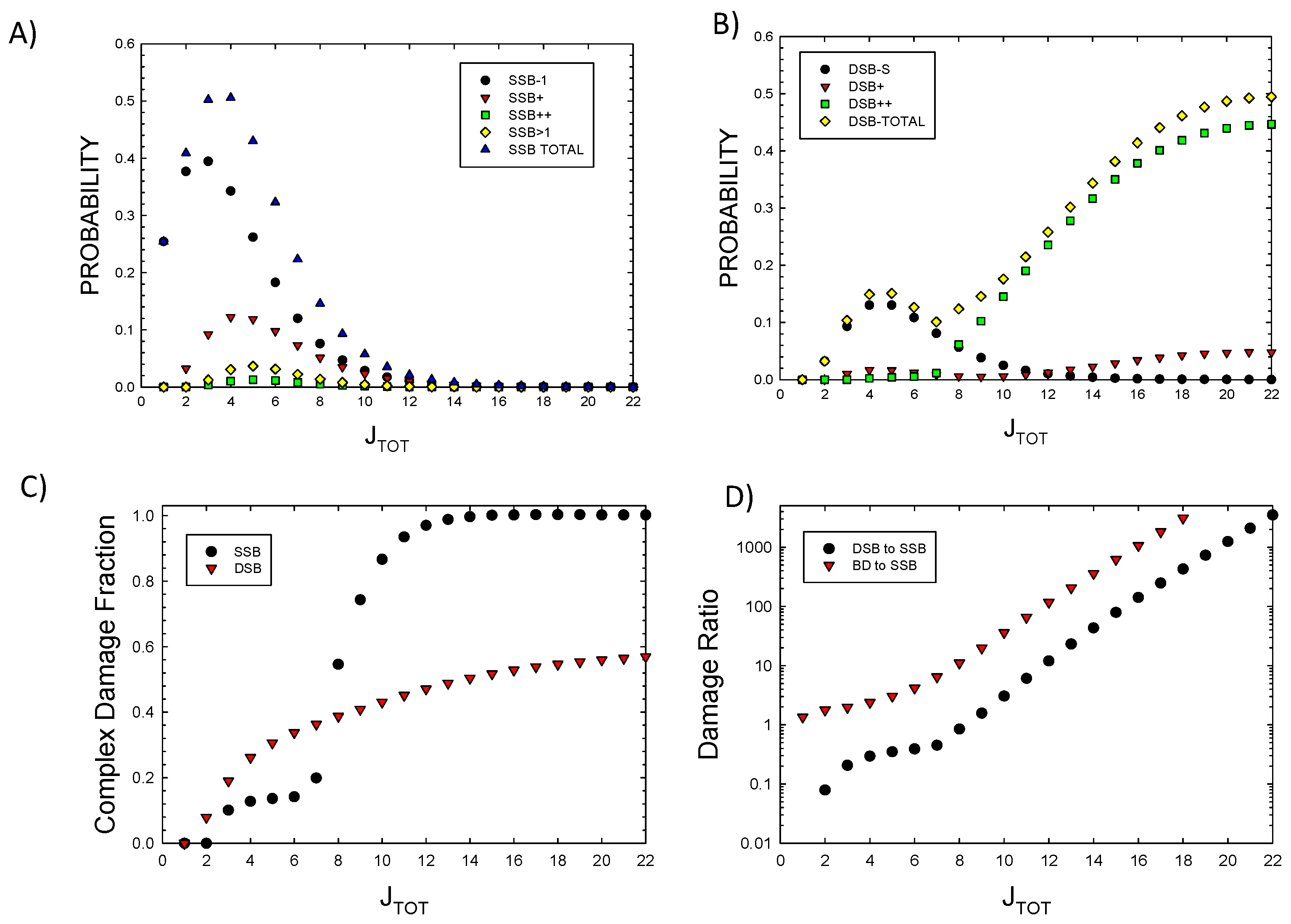
Figure 1A and 1B show probabilities for SSB and DSB of various complexity as a function of
JTOT. Results show the dominance of DSB++ for
JTOT>~6. In
Figure 1C result for the fraction of complex SSB and DSB versus
JTOT are shown. Complex DSB dominate with increasing
JTOT due to the impacts of clustering, which reduces the probability of complex SSB at large
JTOT. Large damage clusters are more likely to form complex DSB as predicted by higher-order terms described above. Isolated SSB are found with some frequency for
JTOT up to ~10 as they can occur in the 73 bp segment at some distance from a main cluster.
In
Figure 1D prediction of the ratio of DSB to SSB and BD to SSB are shown. SSB and BD occur with similar probability at low
JTOT (<5), while BD and DSB probabilities greatly exceed SSBs at large
JTOT. DSBs exceed SSBs due to increased clustering leading to the dominance of a complex DSB relative to SSB at large
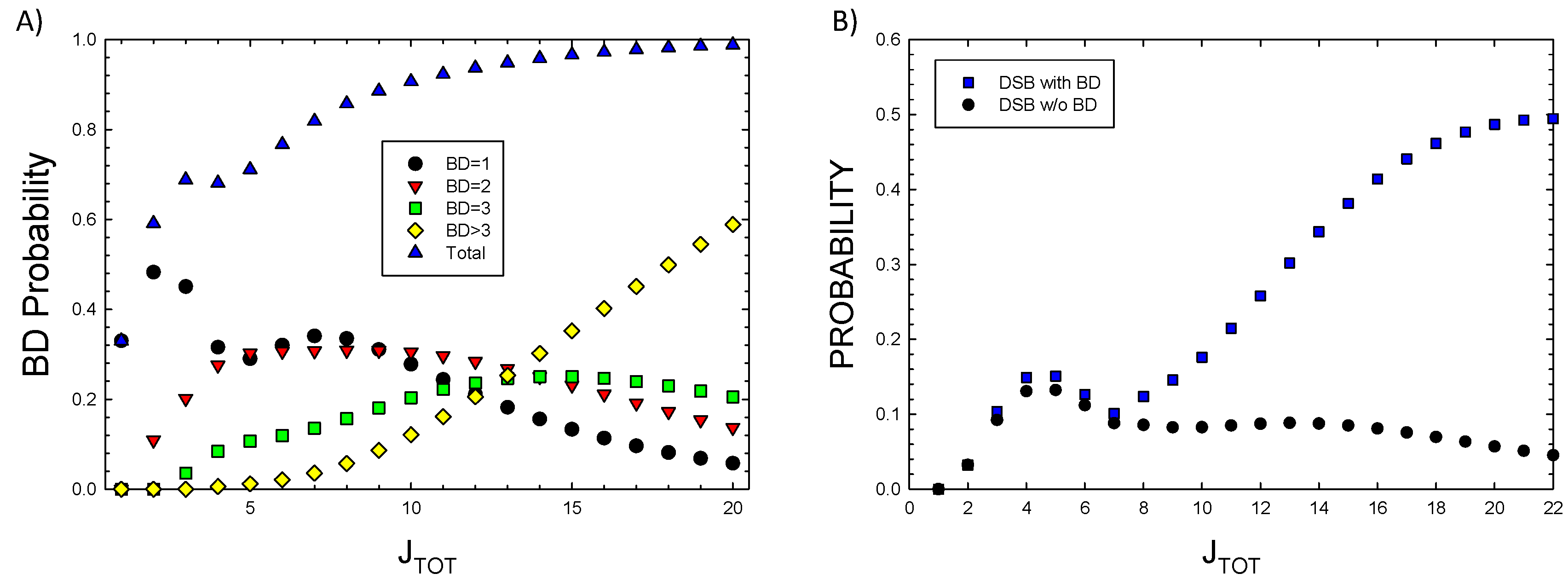
JTOT. Detailed considerations of BD clustering will be described in a future report. Here preliminary observations can be made based on the results of
Figure 2A where probabilities for 1, 2, 3, or >3 BD’s are plotted versus
JTOT. A more detailed analysis of BD clustering and their occurrence nearby SSB or DSB is not possible at small values of
JTOT, however for
JTOT >10, important for high LET radiation, these results suggest BD will be co-located within 10 bp to SSB or DSB in almost all events. In
Figure 2B the probability of DSB occurrence with and without BD formation is estimated by setting
r2 = 0 in applying the multinomial probabilities for cluster formalism. As expected very few DSB’s are predicted to be formed at large
JTOT with BD not co-located.
3.1. Predictions for Radiation Induced DSBs
Predictions for 100 keV electrons representative of X-rays and
4He and
12C ions with energies from 0.1 to 10,000 MeV/u were made and compared to experimental data. For the electrons results for frequency distributions from the Monte-Carlo results of Nikjoo et al. [
29] were fitted assuming the integral spectrum is an exponential function. For ions we use the formalism developed by Cucinotta
et al. [
30], which combines direct effects where the ion passes through the target volume, and δ-ray effects where the ion passes outside of the target volume. For these δ-ray events electron spectra as a function of radial distance from the ions path are folded with Monte-Carlo results for electron energy imparted spectra from [
29]. In
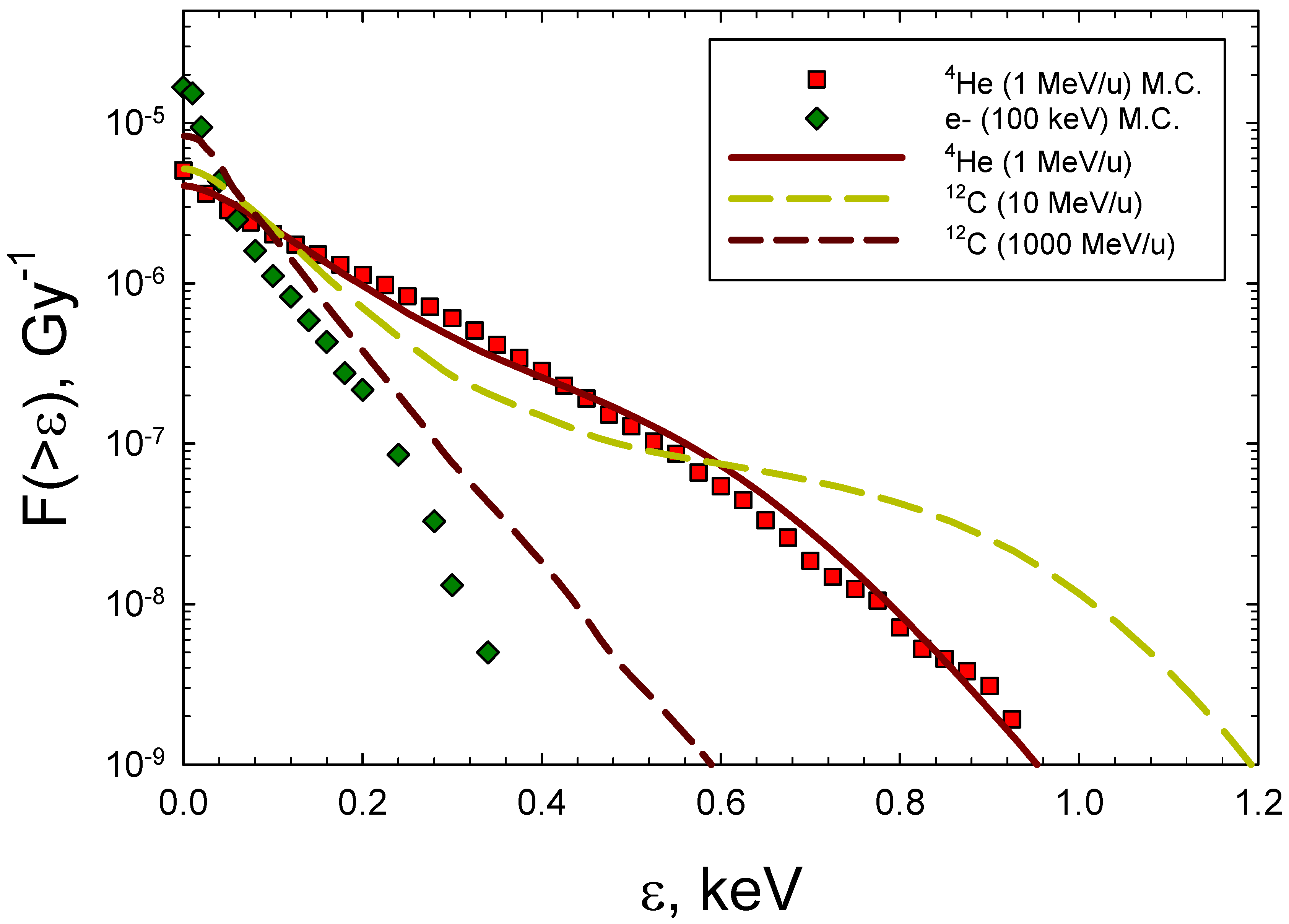
Figure 3 representative frequency distributions are shown for 100 keV electrons, 1 MeV/u
4He of energy 1 MeV/ (LET=104 keV/μm) and
12C ions of 10 MeV/u (LET=166 keV/μm) and 1000 MeV/u (8 keV/μm). The results of
Figure 3 show that the analytic formalism is in good agreement the MC simulations for low energy
4He ions [
28].
Table 5 shows the spectra of DNA yields for the radiation types considered in
Figure 3. The integral DSB yield for 100 keV electrons of 9.9 DSB per Gy per Gbp can be compared to values from experiments in human skin fibroblasts or V79 cells of 6.0 for 250 kVp X-rays, 7.6 for
60Co gamma-rays, and 11.9 for
137Cs gamma-rays, and for 15 MeV electrons 6.01 [
33,
34,
35,
36], which were reported using several experimental methods. Optimization of the values of
pi by fits to experimental data was not made, however we note that introducing relative variations of +/- 20% leads to similar relative changes in the predicted break yields. Yields of BD compared to DSBs are about 10-fold higher dependent on radiation quality. If complex BD are considered as 2 or more BD in a small DNA segment, a much higher probability of complex BD compared to complex DSB are suggested, however a large fraction of both these types will occur in the same lesion.
For ions we considered the damage frequencies expressed as an action cross section in units of number of breaks per Gbp per particle, which is found as,
where dF/dε is normalized to unity,
nBP=73, and
is the frequency mean specific energy to the volume.
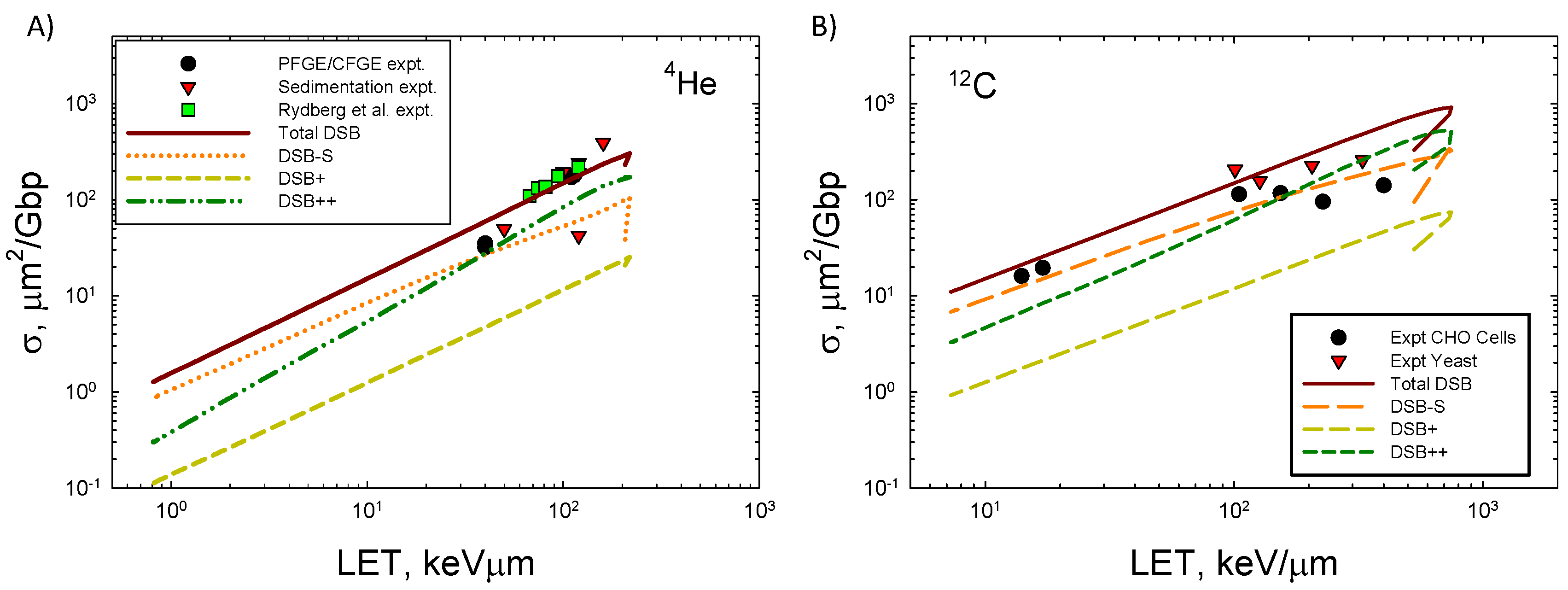
Figure 4 shows the LET dependence of DSB formation for
4He and
12C ions compared to experimental data [
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. Agreement of the model to the measurements is good especially when the variation in data reported from different labs employing PFGE or sedimentation is considered [
33]. At the highest LET values for both ions experimental methods are expected to under-count the number of DSBs that occur. Here experimental methods such as PFGE and sedimentation are expected to under-estimate DSB counts because more than one DSB in an extended region of DNA will be identified as a single DSB. A preliminary estimate correction for multiple DSB’s within the 73 bp segment suggests a correction of ~50% at high LET if DSB++ is counted as single DSB. Future studies with the present model will estimate the correction considering larger regions of DNA, which will be especially important for high energy and charge (HZE) ions. Action cross sections, σ, decrease at high LET as the ion’s velocity decreases and indicate an overkill effect, which leads to a decrease in relative biological effectiveness (RBE) ~σ/LET.
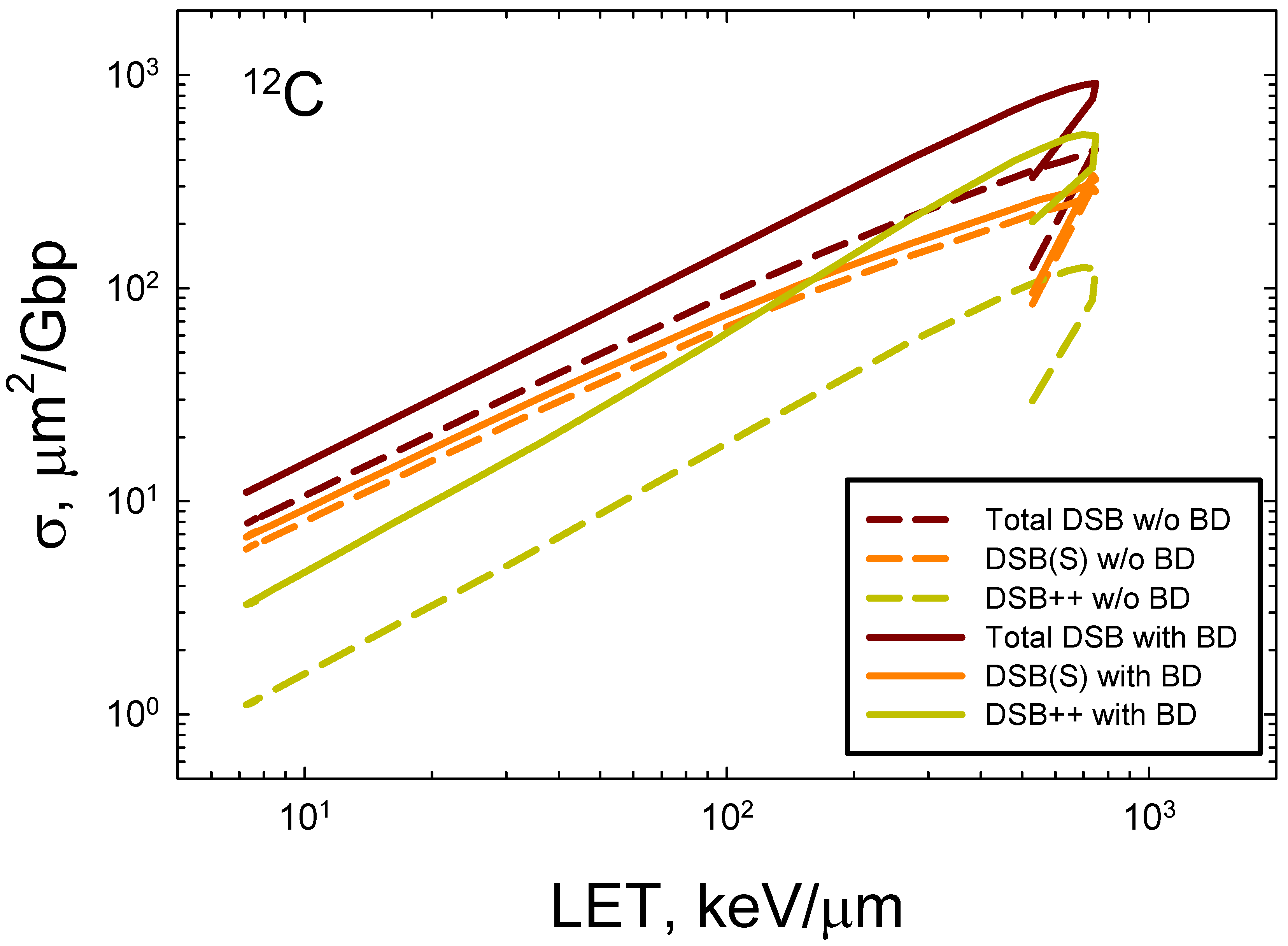
In Figure 5 we consider prediction of action cross sections for DSBs induce by
12C with and without the occurrence of base-damage in the same 73 bp DNA structure using the approach described for
Figure 2B. Reductions of about 2-fold occur at high LET and reducing to ~30% for relativistic
12C ions. The largest reduction is for DSB++ lesions, which is more than 4-fold at LET>100 keV/μm. These results reveal the expected severe clustering that occurs for high LET ions that go beyond the contributions of clustered breaks alone.
4. Discussion
In this paper a novel approach to describing clustered DNA damage using multinomial probabilities was developed. The use of energy imparted spectra for a 5x5 nm cylindrical volume offers a fast-computational approach for any radiation type in comparison to the more computational expensive application of stochastic MC-based radiation tracks to model DNA damage [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. The order of averaging made using frequency distributions is a basic difference compared to full MC track structure simulations which average results over many MC histories using either volume models of DNA or scoring ionizations in atomistic DNA model structures. These descriptions are often combined with kinetics models of early chemical reactions leading to indirect effects. The MC approach averages over the orientation of the track relative to the DNA structures, while simulations take many hours of cpu time on typical computer work stations and often ignore the role of BD.
The approach herein uses frequency spectra that average energy imparted over a similar volume used in MC track structure simulations, which are then combined with the multinomial probability functions to predict DNA lesions. This results in predictions of the full DNA damage spectra obtained in a computationally efficient manner (cpu time ~1 second) for any radiation type. This aspect is highly favorable for space radiation studies where 28 elemental groups over a wide energy ranges (<0.1 MeV/u to ~50 GeV/u) are typically considered [
40]. Also, in hadron therapy with
12C or other ions [
41] where the wide distribution of secondary particles and energies due to Coulomb slowing down and nuclear fragmentation and spallation calls for computational efficient models.
Measurements with the PFGE are the main source of experimental data for DSB yields, however are expected to under-estimate yields when multiple DSB are produced within several 10’s of kbp’s [
33,
42,
43]. Therefore, comparison to heavy ions such as
56Fe are not included in the present work. In future work radial distributions of energy imparted for high-charge and energy (HZE) ions [
30], and models of higher-order DNA structures will be used to make comparisons to heavy ion DNA damage experiments [
38,
39,
44].
The present approach is similar to full MC track structure simulations in the use of a simple energy threshold for SSB, BD and radical formation. However, in the present calculations a normal distribution of energy thresholds is used because it is unlikely that a single energy threshold occurs in ionizations leading to SSB or BD formation when one considers the complexity of the molecules involved. The use of an identical threshold in equations (4) and (5) could be relaxed by allowing the Ji indexes to increase with a more complex dependency on energy imparted, however is unlikely to lead to important changes at higher values of energy imparted where many terms contribute to damage production.
The use of cluster probabilities (
q0 or
q1) based on simple random probability criteria ignores possible details of radiation tracks, such as low energy electrons and their distinct angular trajectories versus straight-line trajectories of higher energy electrons produced by ions. It is likely that estimates of
q0 for increasing
JA/JB based on a random distribution over-estimates clustering that occurs, which is suggested by the predictions of higher probability of DSB++ compared to MC track structure simulations predictions [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. An alternative can be considered using a weighted combination of random distribution and a probability of straight-line motion of radiation tracks. We used values of
r1 and
r2 related to indirect effects from radical production on water molecules based on MC estimates [
10,
11] and the estimate from Scholes et al. [
31]. In future work the values of various parameters as fitted to experimental data can be considered to investigate if deviation from a random pattern or MC model estimates are suggested.
The use of enzymatic probes, such as endonuclease III (Nth) to detect oxidized pyrimidines, formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase (Fpg) to detect oxidized purines, and Nfo protein (endonuclease IV) to detect abasic sites, have revealed higher frequencies of clustered BD compared to DSBs [
5,
6,
8,
17,
18,
35,
45]. The present model only predicts a generic category of BD. For
137Cs gamma-rays, Tsao et al. [
35] report 9.5, 11.87, and 10.68 per Gbp per Gy for endo IV, Fpg, and endo III clusters respectively.
Table 5 for 100 keV electrons shows yields of 17.2, 8.7, and 4.4 per Gbp per Gy for BD clusters of 2, 3, and >3, respectively. These values would be increased in approximately linear fashion with increases in the value of the
r2 parameter. Radiation yields for all possible base modifications have not been reported and additional BD lesions are likely [
46,
47]. It would be interesting to introduce an empirical approach to model specific base lesions for X-rays or gamma-rays to explore their ability to predict equivalent lesions for high LET radiation using the present approach. In addition, additional damages are produced in the processing of SSB or BD in base excision repair (BER) or other pathways [
5,
46] and it useful to predict the initial rates of production for comparison purposes.
A main focus of the current approach is to develop a model that can be compared to experimental data while considering the distribution of DNA end-structures that are substrates for various repair pathways for use in mathematical models of DNA repair [
48,
49,
50]. The presence of BD nearby SSB [
8,
51] or BD and SSB near DSB are possible impairments to faithful repair [
4,
7,
8,
19,
51,
52]. The high frequency of complex DSB’s leading to small DNA fragments is shown to reduce the efficiency of Ku70/80 from binding to DNA [
53,
54]. Differences in clustered DSB such as DSB++, between 100 keV electrons and high LET alpha particles and
12C ions are only about 2-fold in the present results, however larger differences will occur when larger DNA structures are considered or for lesions such as DSB+++. These aspects will be considered in future work using the present approach.
The wide range of distinct DNA lesions that will occur across a cell points to differences between low and high dose and low and high LET radiation. The higher frequency of BD or SSB are likely dominant at low doses of low LET irradiation were few DSB per cell are formed, while as dose is increased the number of clustered DSB’s increases, such that DSB repair likely becomes more dominant in cellular responses. For high LET radiation clustered DSB’s will occur at all doses and the importance of the additional BD and clustered SSB is suggested to play a smaller role. However, an exception is the large transverse distribution of delta-rays (high energy electrons) produced about the path of HZE ions leading to frequent low dose cellular energy deposition in many cells not traversed by the ion [
55]. This aspect should play an important role for risk assessments for the low dose and dos-rate space radiation exposures.
The range of complexity shown here that increases with ionization density (or LET) is consistent with the so-called “overkill effect” used to describe the high LET dependence of radiation effects. The increase in ionization density (or LET) presents a transition from the dominance of simple DNA damage to highly complex DSB as shown by the developed formalism. Saturation due to highly complex DSBs is predicted as the energy imparted increases to high levels (>~200 eV) and highly complex DSBs are predicted to dominate initial damage [
1,
56]. The more complex damage likely favors cell death while intermediate damage levels favor mis-repair and mutation in the repair of complex SSB and BD, and single DSB’s with additional BD.
Figure 1.
Probabilities of various type of DNA lesions versus JTOT. A) single strand breaks, B) double strand breaks, C) the fraction of complex SSB and DSB. D) Ratio of DSB to SSB and BD to SSB.
Figure 1.
Probabilities of various type of DNA lesions versus JTOT. A) single strand breaks, B) double strand breaks, C) the fraction of complex SSB and DSB. D) Ratio of DSB to SSB and BD to SSB.
Figure 2.
Model results for A) Probability of single or multiple base-damage (BD) showing contributions from the number clustered BD frequencies for increasing damage numbers, JTOT, and B) DSB probability with or without BD. Calculations assume a 73 bp segment.
Figure 2.
Model results for A) Probability of single or multiple base-damage (BD) showing contributions from the number clustered BD frequencies for increasing damage numbers, JTOT, and B) DSB probability with or without BD. Calculations assume a 73 bp segment.
Figure 3.
Frequency distributions of energy imparted to a 5x5 nm cylindrical volume for 100 keV electrons,
4He and
12C ions. Symbols are Monte-Carlo results from Charlton et al. [
28] for
4He, and Nikjoo et al. [
29] for electrons. Lines show results from calculations of the model of Cucinotta et al. [
30].
Figure 3.
Frequency distributions of energy imparted to a 5x5 nm cylindrical volume for 100 keV electrons,
4He and
12C ions. Symbols are Monte-Carlo results from Charlton et al. [
28] for
4He, and Nikjoo et al. [
29] for electrons. Lines show results from calculations of the model of Cucinotta et al. [
30].
Figure 4.
Comparison of model to experimental data [
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37] for A)
4He ions and B)
12C ions of action cross section versus LET for DSBs. Calculations correspond to 40 ion energies from 0.1 MeV/u to 10,000 MeV/u.
Figure 4.
Comparison of model to experimental data [
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37] for A)
4He ions and B)
12C ions of action cross section versus LET for DSBs. Calculations correspond to 40 ion energies from 0.1 MeV/u to 10,000 MeV/u.
Figure 6.
Prediction of action cross sections for DSB with and without (w/o) the occurrence of base-damage in the a 73 bp DNA structure for 12C ions.
Figure 6.
Prediction of action cross sections for DSB with and without (w/o) the occurrence of base-damage in the a 73 bp DNA structure for 12C ions.
Table 1.
Action of the operator on several SSB and DSB operands of increasing complexity.
Table 1.
Action of the operator on several SSB and DSB operands of increasing complexity.
| Operand |
Branching Probabilities |
| SSB(S) |
q0 nSSB(S2)+q1[nSSB(+)+nDSB(S)] |
| SSB(+) |
q0 nSSB(+)nSSB(S)+q1[nSSB(++)+nDSB(+)] |
| DSB(S) |
q0 nDSB(S)nSSB(S)+2q1nDSB(+) |
| DSB(+) |
q0 nDSB(+)nSSB(S)+ 2q1nDSB(++) |
| DSB(S) x SSB(S) |
q0 nDSB(S)nSSB(S2)+q1[nDSB(+)nSSB(S)+ nDSB(S)nDSB(S)] |
| SSB(+) x SSB(S) |
q0 nSSB(+)nSSB(S2)+q1/2 [nDSB(+)nSSB(S)+ nSSB(++)nSSB(S)+nSSB(+)nDSB(S)+nSSB(+)nSSB(+)] |
Table 2.
Evaluation of JTOT(ε)-JD=1 and 2 terms in multinomial DNA damage model for SSB, DSB, and BD. The constant factors, pA, pB, and pC are suppressed in the formulas, and are found easily by considering the definition of the term defined in the 2nd column. Addition of probabilities are shown, while marginal distributions select for lesions of specific type.
Table 2.
Evaluation of JTOT(ε)-JD=1 and 2 terms in multinomial DNA damage model for SSB, DSB, and BD. The constant factors, pA, pB, and pC are suppressed in the formulas, and are found easily by considering the definition of the term defined in the 2nd column. Addition of probabilities are shown, while marginal distributions select for lesions of specific type.
| Order |
Term |
Components |
| 1 |
PA
|
nSSB(S) |
| 1 |
PB
|
r1nSSB(S)+ r2nBD(1) |
| 1 |
PC
|
nBD(1) |
| 2 |
PAPA
|
q0nSSB(S2)+ q1nDSB(S)+ q1nSSB(+) |
| 2 |
PAPB
|
r1q0nSSB(S2)+ r1q1nDSB(S)+ r1q1nSSB(+)+ r2nSSB(S)nBD(1)+r3nSSB(S) |
| 2 |
PAPC
|
nSSB(S)nBD(1) |
| 2 |
PBPB
|
r12 [q0nSSB(S2)+ q1nDSB(S)+ q1nSSB(+)]+ 2r1r2nSSB(S)nBD(1)+ r22nBD(2) +r3[r1nSSB(S)+r2nBD(1)] |
| 2 |
PBPC
|
[r1nSSB(S)+r3]nBD(1)+ r2nBD(2) |
| 2 |
PCPC
|
nBD(2) |
Table 3.
Evaluation of JTOT(ε)-JD=3 terms in multinomial DNA damage model for SSB, DSB, and BD. The constant factors, pA, pB, and pC are suppressed in the formulas, and are found easily by considering the definition of the term defined in the left-hand column. Addition of probabilities are shown, while marginal distributions select for lesions of specific type.
Table 3.
Evaluation of JTOT(ε)-JD=3 terms in multinomial DNA damage model for SSB, DSB, and BD. The constant factors, pA, pB, and pC are suppressed in the formulas, and are found easily by considering the definition of the term defined in the left-hand column. Addition of probabilities are shown, while marginal distributions select for lesions of specific type.
| Term |
Components |
| PAPAPA
|
q02nSSB(S3)+2q0q1[nDSB(S)nSSB(S)+nSSB(+)nSSB(S)]+q12[3nDSB(+)+nSSB(++)] |
| PAPAPB
|
r1{q02 nSSB(S3)+q0q1[nDSB(S)nSSB(S)+nSSB(+)nSSB(S)]+
q12/2[3nDSB(+)+nSSB(++)]}+
r2{q0nSSB(S2)+q1[nDSB(S)+nSSB(+)]}nBD(1)+
r3{q0nSSB(S2)+q1[nDSB(S)+nSSB(+)]} |
| PAPAPC
|
A2 nBD(1) |
| PAPBPB
|
r12{q02nSSB(S3)+3q0q1[nSSB(S)nSSB(S)+nSSB(+)nSSB(S)]+q12/2[3nDSB(+)+nSSB(++)]}+
2r1r2{q0nSSB(2)+q1nDSB(S)+q1nSSB(+)]nBD(1)+r2r3nSSB(2)nBD(1)}+
r1r3{q0nSSB(S3)+q1nDSB(S)nSSB(S)+q1nSSB(+)nSSB(S)+
q0nSSB(S2)+q1nDSB(S)+q1nSSB(+)}+
r22nSSB(S)nBD(1)+r32nSSB(2) |
| PAPCPC
|
nSSB(S) nBD(2) |
| PAPBPC
|
r1[q0nSSB(S2)+q1nDSB(S)+ q1nSSB(+)]nBD(1)+r2nSSB(S)nBD(3)+r3nSSB(S)nBD(1) |
| PBPBPB
|
~Β2 r2nBD(1)+r3B1
|
| PBPBPC
|
B2 r2nBD (1) +r3B1 |
| PBPCPC
|
[r1nSSB(S)+r3]nBD(2)+ r2nBD(3) |
| PCPCPC
|
nBD(3) |
Table 4.
Evaluation of JTOT-JD=4 terms in multinomial DNA damage model for SSB and DSB. The constant factors, pA, pB, and pC are suppressed in the formulas, and are found easily by considering the definition of the term defined in the left-hand column. Addition of probabilities are shown, while marginal distributions select for lesions of specific type.
Table 4.
Evaluation of JTOT-JD=4 terms in multinomial DNA damage model for SSB and DSB. The constant factors, pA, pB, and pC are suppressed in the formulas, and are found easily by considering the definition of the term defined in the left-hand column. Addition of probabilities are shown, while marginal distributions select for lesions of specific type.
| Term |
Components |
| PAPAPAPA
|
See Equation (17)
|
| PAPAPAPB
|
r1A4+[r2nBD(1)+r3]A3
|
| PAPAPAPC
|
A3 nBD(1) |
| PAPAPBPB
|
See Equation (15) |
| PAPAPCPC
|
A2nBD(2) |
| PAPAPBPC
|
r1A3nBD(1)+[r2nBD(2)+r3nBD(1)]A2
|
| PAPBPBPC
|
A1B2 nBD(1) |
| PAPBPBPB
|
~A1B2 r2nBD(1) |
| PAPCPCPC
|
nSSB(S)nBD(3) |
| PAPBPCPC
|
A1B1nBD(2) |
| PBPBPBPB
|
~B2 [r22nBD(2)+r32+2r2r3nBD(1)] |
| PBPBPBPC
|
r12 [q0nSSB(S2)+q1nDSB(S)+q1nSSB(C)]nBD(2)+2r1r2nSSB(S)nBD(3)+r22nBD(4) |
| PBPBPCPC
|
B2nBD(2) |
| PCPCPCPA
|
nBD(3)nSSB(S) |
| PCPCPCPB
|
[r1nSSB(S)+r3]nBD(3)+r2nBD(4) |
| PCPCPCPC
|
nBD(4) |
Table 5.
Predictions of yields of several types of DNA lesions per Gbp per Gy for several types of ionizing radiation.
Table 5.
Predictions of yields of several types of DNA lesions per Gbp per Gy for several types of ionizing radiation.
Radiation Type /
Lesion |
Electrons
(100 keV) |
4He
(1 MeV/u,
LET=104 keV/μm) |
12C
(10 MeV/u,
LET=163 keV/μm) |
12C
(1000 MeV/u,
LET=8 keV/μm) |
| SSB-S |
26.5 |
10.1 |
14.8 |
20.7 |
| SSBS2 |
6.1 |
0.7 |
0.9 |
1.3 |
| SSB+ |
6.1 |
3.1 |
4.0 |
5.4 |
| SSB++ |
0.5 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.4 |
| Total SSB* |
63.4 |
18.5 |
25.7 |
35.4 |
| DSB-S |
6.5 |
3.3 |
4.3 |
5.8 |
| DSB+ |
0.8 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
0.8 |
| DSB++ |
2.7 |
5.3 |
4.3 |
2.8 |
| Total DSB |
9.9 |
9.3 |
9.3 |
9.4 |
| BD-1 |
36.7 |
15.0 |
20.5 |
27.0 |
| BD-2 |
17.2 |
10.9 |
12.7 |
15.4 |
| BD-3 |
8.7 |
8.0 |
8.1 |
8.4 |
| BD>3 |
4.4 |
7.5 |
6.2 |
4.4 |
| Total BD* |
112.9 |
90.7 |
95.3 |
100.6 |