Submitted:
21 October 2024
Posted:
22 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Subject Inclusion
2.2. Sedation and Anesthesia Protocols and Computed Tomography Image Acquisition
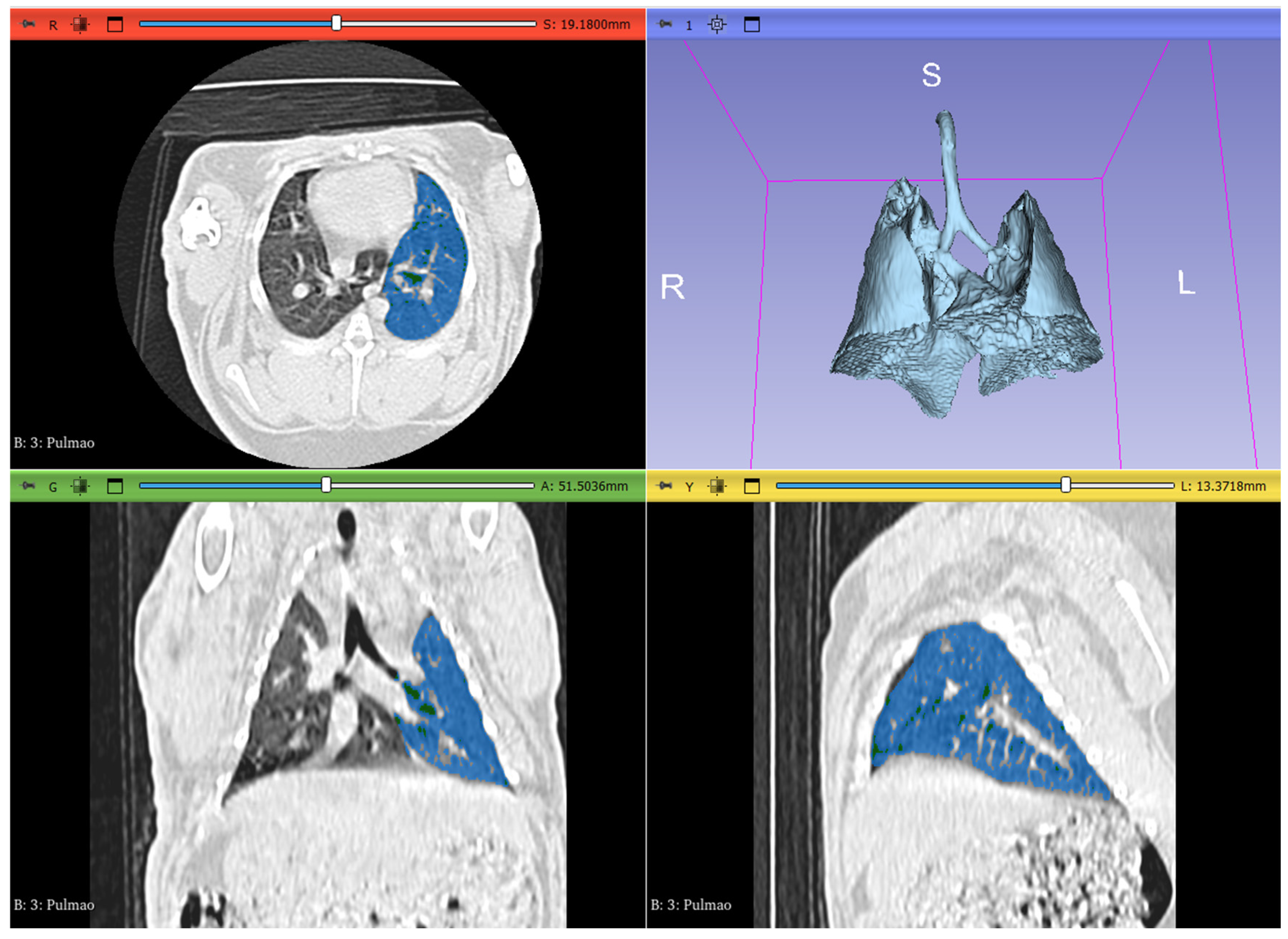
2.3. Image Analysis and Segmentation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Lung Volume and Attenuation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson-Delaney, C.A.; Orosz, S.E. Rabbit Respiratory System: Clinical Anatomy, Physiology and Disease. Veterinary Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2011, 14, 257–266. [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J. Respiratory Disease. In BSAVA Manual of Rabbit Medicine; Meredith, Lord, Eds.; British Small Animal Veterinary Association, 2014; pp. 160–167 ISBN 978-1-905319-49-7.
- Lennox, A.M.; Mancinelli, E. Respiratory Disease. In Ferrets, Rabbits, and Rodents; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 188–200 ISBN 978-0-323-48435-0.
- Jekl, V. Respiratory Disorders in Rabbits. Veterinary Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2021, 24, 459–482. [CrossRef]
- Veraa, S.; Schoemaker, N. CT and MRI Scanning and Interpretation. In BSAVA Manual of Rabbit Surgery, Dentistry and Imaging; Harcourt-Brown, Chitty, Eds.; British Small Animal Veterinary Association, 2013; pp. 107–114 ISBN 978-1-905319-41-1.
- Capello, V.; Lennox, A.M. Diagnostic Imaging of the Respiratory System in Exotic Companion Mammals. Veterinary Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2011, 14, 369–389. [CrossRef]
- Müllhaupt, D.; Wenger, S.; Kircher, P.; Pfammatter, N.; Hatt, J.-M.; Ohlerth, S. Computed Tomography of the Thorax in Rabbits: A Prospective Study in Ten Clinically Healthy New Zealand White Rabbits. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 72. [CrossRef]
- Jekl, V. Respiratory Disorders in Rabbits. Veterinary Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2021, 24, 459–482. [CrossRef]
- Grint, N. Anaesthesia. In BSAVA Manual of Rabbit Surgery, Dentistry and Imaging; Harcourt-Brown, Chitty, Eds.; British Small Animal Veterinary Association, 2013; pp. 1–25 ISBN 978-1-905319-41-1.
- Thrall, D.E. Principles of Radiographic Interpretation of the Thorax. In Textbook of Veterinary Diagnostic Radiology; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 568–582 ISBN 978-0-323-48247-9.
- Monte, V.D.; Grasso, S.; Marzo, C.D.; Crovace, A.; Staffieri, F. Effects of Reduction of Inspired Oxygen Fraction or Application of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure after an Alveolar Recruitment Maneuver on Respiratory Mechanics, Gas Exchange, and Lung Aeration in Dogs during Anesthesia and Neuromuscular Blockade. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Hunt, T.D.; Wallack, S.T. Minimal Atelectasis and Poorly Aerated Lung on Thoracic CT Images of Normal Dogs Acquired under Sedation. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2021, 62, 647–656. [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, L.; Spahn, D.R. New Concepts of Atelectasis during General Anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2003, 91, 61–72. [CrossRef]
- Reimegård, E.; Lee, H.T.N.; Westgren, F. Prevalence of Lung Atelectasis in Sedated Dogs Examined with Computed Tomography. Acta Vet. Scand. 2022, 64, 25. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis: Hoboken, 2013; ISBN 978-0-8058-0283-2.
- Slicer/SlicerLungCTAnalyzer 2024.
- Bumm, R.; Zaffino, P.; Lasso, A.; Estépar, R.S.J.; Pieper, S.; Wasserthal, J.; Spadea, M.F.; Latshang, T.; Kawel-Böhm, N.; Wäckerlin, A.; et al. From Voxels to Prognosis: AI-Driven Quantitative Chest CT Analysis Forecasts ICU Requirements in 78 COVID-19 Cases. Res. Sq. 2023, rs.3.rs-3027617. [CrossRef]
- Reimegård, E.; Lee, H.T.N.; Westgren, F. Prevalence of Lung Atelectasis in Sedated Dogs Examined with Computed Tomography. Acta Vet. Scand. 2022, 64, 25. [CrossRef]
- Roels, E.; Couvreur, T.; Farnir, F.; Clercx, C.; Verschakelen, J.; Bolen, G. Comparison between sedation and general anesthesia for high resolution computed tomographic characterization of canine idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in west highland white terriers. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound Off. J. Am. Coll. Vet. Radiol. Int. Vet. Radiol. Assoc. 2017, 58, 284–294. [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.W.M.; Chen, P.P.; So, N.M.C.; Metreweli, C. Sedation versus General Anaesthesia in Paediatric Patients Undergoing Chest Ct. Acta Radiol. 1998, 39, 298–300. [CrossRef]
- Negroni, D.; Zagaria, D.; Paladini, A.; Falaschi, Z.; Arcoraci, A.; Barini, M.; Carriero, A. COVID-19 CT Scan Lung Segmentation: How We Do It. J. Digit. Imaging 2022, 35, 424–431. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Koh, D.; Ong, C.N. Statistical Evaluation of Agreement between Two Methods for Measuring a Quantitative Variable. Comput. Biol. Med. 1989, 19, 61–70. [CrossRef]
- Boatman - 1977 - A Morphometric and Morphological Study of the Lung.Pdf.
- Veraa, S.; Schoemaker, N. CT and MRI Scanning and Interpretation; BSAVA Library, 2013; pp. 107–114; ISBN 978-1-910443-16-3.
- Duggan, M.; Kavanagh, B.P.; Warltier, D.C. Pulmonary Atelectasis: A Pathogenic Perioperative Entity. Anesthesiology 2005, 102, 838–854. [CrossRef]
- Hedenstierna, G. 1 Effects of Anaesthesia on Respiratory Function. Baillières Clin. Anaesthesiol. 1996, 10, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Sacks, M.; Raidal, S.; Catanchin, C.S.M.; Hosgood, G.; Mosing, M. Impact of Sedation, Body Position Change and Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Distribution of Ventilation in Healthy Foals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9. [CrossRef]
- Brismar, B.; Hedenstierna, G.; Lundquist, H.; Strandberg, Å.; Svensson, L.; Tokics, L. Pulmonary Densities during Anesthesia with Muscular Relaxation—A Proposal of Atelectasis. Anesthesiology 1985, 62, 422–428. [CrossRef]
- Foo, T.S.; Pilton, J.L.; Hall, E.J.; Martinez-Taboada, F.; Makara, M. Effect of Body Position and Time on Quantitative Computed Tomographic Measurements of Lung Volume and Attenuation in Healthy Anesthetized Cats. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Guarracino, A.; Lacitignola, L.; Auriemma, E.; De Monte, V.; Grasso, S.; Crovace, A.; Staffieri, F. Which Airway Pressure Should Be Applied During Breath-Hold in Dogs Undergoing Thoracic Computed Tomography? Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2016, 57, 475–481. [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.R.C.; Ambrósio, A.M.; Fantoni, D.T.; Pinto, A.C.B.C.F.; Villamizar-Martinez, L.A.; Soares, J.H.N.; Otsuki, D.A.; Malbouisson, L.M.S. Computed Tomography Assessment of Tidal Lung Overinflation in Domestic Cats Undergoing Pressure-Controlled Mechanical Ventilation During General Anesthesia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.F.; Ambrósio, A.M.; Pinto, A.C.B.C.F.; Pereira, M.A.A.; Andrade, F.S.R.M.; Rodrigues, R.R.; de Carvalho Martins, A.R.; Baroni, C.O.; Ferrante, B.; Fantoni, D.T. Effects of a Stepwise Alveolar Recruitment Maneuver on Lung Volume Distribution in Dogs Assessed by Computed Tomography. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 10. [CrossRef]
- Henao-Guerrero, N.; Ricco, C.; Jones, J.C.; Buechner-Maxwell, V.; Daniel, G.B. Comparison of Four Ventilatory Protocols for Computed Tomography of the Thorax in Healthy Cats. 2012. [CrossRef]
| Variable | Session | Minimum | Maximum | Mean±SD | Paired t-test | ICC (95%CI) |
| Right lung volume | I | 28.739 | 46.423 | 38.82±5.11 | 0.994 | 0.96 (0.905-0.987) |
| II | 28.450 | 46.973 | 38.82±4.95 | |||
| Left lung volume | I | 22.456 | 39.974 | 30.57±5.54 | 0.208 | 0.976 (0.936-0.991) |
| II | 21.289 | 40.085 | 30.97±5.82 | |||
| Total lung volume | I | 52.513 | 85.769 | 69.39±10.04 | 0.060 | 0.998 (0.995-0.998) |
| II | 53.016 | 86.05 | 69.68±9.89 | |||
| Aerated right lung attenuation | I | -698.944 | -634.225 | -675.08±18.23 | 0.747 | 0.996 (0.99-0.999) |
| II | -699.133 | -636.572 | -675.21±18.37 | |||
| Aerated left lung attenuation | I | -708.961 | -666.244 | -690.03±14.19 | 0.862 | 0.992 (0.978-0.997) |
| II | -708.822 | -664.883 | -689.96±13.96 |
| Variable | Session | Minimum | Maximum | Mean±SD | Paired t-test | ICC (95%CI) |
| Total lung volume | I | 18.952 | 35.261 | 27.82±5.40 | 0.707 | 0.976 (0.934-0.991) |
| II | 19.164 | 35.276 | 27.70±5.62 | |||
| Left lung volume | I | 12.632 | 29.688 | 19.28±4.41 | 0.200 | 0.979 (0.943-0.992) |
| II | 12.970 | 30.215 | 19.58±4.56 | |||
| Total lung volume | I | 32.861 | 64.832 | 47.10±9.28 | 0.470 | 0.994 (0.983-0.998) |
| II | 33.441 | 65.491 | 47.29±9.60 | |||
| Aerated right lung attenuation | I | -685.725 | -578.192 | -633.48±36.15 | 0.069 | 0.999 (0.997-1.000) |
| II | -685.825 | -579.140 | -632.73±35.61 | |||
| Aerated left lung attenuation | I | -692.192 | -574.591 | -632.24±38.75 | 0.124 | 0.998 (0.994-0.999) |
| II | -691.120 | -574.792 | -631.20±39.63 |
| Variable | Session | Minimum | Maximum | Mean±SD | Paired t-test | ICC (95%CI) |
| Total lung volume | I | 19.678 | 35.231 | 28.26±3.88 | 0.916 | 0.923 (0.801-0.971) |
| II | 18.982 | 35.619 | 28.22±4.56 | |||
| Left lung volume | I | 13.258 | 30.957 | 20.34±4.36 | 0.618 | 0.917 (0.787-0.969) |
| II | 14.754 | 31.021 | 20.13±4.11 | |||
| Total lung volume | I | 36.141 | 66.188 | 48.60±7.40 | 0.614 | 0.964 (0.903-0.987) |
| II | 35.057 | 66.640 | 48.35±7.81 | |||
| Aerated right lung attenuation | I | -676.742 | -544.738 | -627.23±35.02 | 0.349 | 1.000 (0.999-1.000) |
| II | -675.811 | -544.447 | -627.05±35.02 | |||
| Aerated left lung attenuation | I | -696.140 | -555.915 | -632.77±38.28 | 0.092 | 0.999 (0.999-1.000) |
| II | -695.299 | -552.714 | -632.27±38.59 |
| Lung region | Sedated | Anesthesia | Apnea | ||||
| Volume | Attenuation | Volume | Attenuation | Volume | Attenuation | ||
| Dorsal | Right Lung | 16.10±2.53 | -684.16±19.62 | 10.37±3.54 | -644.60±36.64 | 13.09±3.14 | -648.95±34.56 |
| Left Lung | 12,46±2.38 | -692.65±16.67 | 7,41±2.93 | -657.67±36 | 9,50±2.66 | -659.53±34.86 | |
| Ventral | Right Lung | 11.52±2.57 | -667.33±18.35 | 5.50±2.89 | -624.74±32.94 | 6.73±2.54 | -621.54±34.56 |
| Left Lung | 10,30±2.26 | -686.80±18.39 | 4,80±3.07 | -632.61±33.31 | 5,96±2.50 | -624.52±28.93 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





