1. Introduction
In the field of aerospace, more and more applications require powerful computing power, such as deep learning, image processing, data analysis, etc. Traditional single satellite chassis typically offer computing power not exceeding 10Tops with a weight of 10kg and large volume, making it challenging to meet the demands of current space missions' rapid development [
1]. As a crucial component of satellite systems, on-orbit computing capacity for individual satellites is often constrained by factors such as volume, weight, and energy efficiency ratio [
2]. Therefore, it is imperative to minimize size and weight while meeting performance requirements. Various approaches are commonly employed to enhance on-orbit computing power for individual satellites through hardware upgrades, software optimization, task allocation adjustments among others. With advancements in emerging technologies like 6G communication networks, laser communication systems artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms and chips, the development of low-Earth orbit (LEO) constellations has become a focal point of competition globally, with the global remote sensing satellite observation progressively transitioning into the satellite internet era. Due to the limited transmission capability of space information such as remote sensing and navigation, insufficient on-orbit computing capacity and low real-time service efficiency, it is difficult to promote space information from professional applications to military and civilian applications and services to the public [
3]. Nevertheless, with the growing number of satellites in orbit, large-scale deployment of on-board computing power is achievable through intelligent reconfiguration and distributed design. We need to focus on the following aspects. The first is to study multi-satellite networking, one-satellite multi-purpose, space and Earth interconnection and satellite network integration, and form a satellite network that integrates satellite clusters and Earth. The second is to study space-ground collaboration, inter-satellite communication, networking communication and on-demand services to achieve smooth service. The third is to study space anti-irradiation, edge computing, ultra-lightweight deployment, software-defined satellites, etc., and achieve mission-driven and event-aware real-time remote sensing application models for Earth observation [
4,
5].
With the continuous expansion of Earth observation and deep space exploration, as well as the increasing demand for real-time space information services in ocean navigation and space exploration domains, countries worldwide are strategically implementing the development of medium-Earth orbit (MEO) or LEO constellations or ultra-low Earth orbit constellations to establish seamless global coverage and ubiquitous services for building space-based situational awareness network capabilities. The rapid expansion of the commercial aerospace and aerospace electronic components industries has facilitated the utilization of certain commercial high-performance and cost-effective components in space environments through simple anti-irradiation reinforcement, thereby expediting the iterative update of spaceborne computing products. Central Processing Units (CPUs), Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), and Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) effectively harness the computational advantages of these devices to develop compact and lightweight space-grade computing and storage devices, which can be swiftly deployed in orbit to establish extensive space computing power. This enables on-orbit execution of computing, storage, communication, scheduling, and sensing tasks at satellite edges, reducing service response time while alleviating data return communication pressure. According to publicly available information, SpaceX's Starlink project has launched over 6,600 satellites equipped with more than 440,000 computers as of June 2024. With a multitude of space computers forming vast computational resources after deploying a series of Starlink satellites, real-time on-orbit computing tasks that pose challenges for individual satellites can be accomplished without transmitting massive amounts of data back to Earth for processing. Moreover, the optimal approach entails mitigating the burden of transmitting voluminous computer-generated data from space to Earth by conducting real-time computation entirely in orbit and subsequently transmitting the results directly.
As the expansion of space-based computing power continues, enhancing the service capabilities of space-based edge computing networks primarily involves considerations in two areas: individual satellite computational capacity and the utilization of satellite network computational resources. Regarding single satellite computing power, based on the space environment radiation resistance and protection of space-based edge computing chips and other components, a lightweight, low-cost, energy-efficient co-satellite processing platform for hardware and software is developed. This platform should be capable of processing unstructured data and executing efficient parallel computing tasks, while also addressing aspects such as reliability, data flow control, and energy management. In terms of the utilization of satellite network computing resources, under the restrictive conditions of high dynamics, narrow bandwidth and long delay of space-based satellite networks, a distributed and collaborative cloud computing and satellite edge computing framework is built for the large-scale space-based computing resources dispersed in space, so as to achieve resource sharing and task coordination, so as to obtain a multiplier effect. Drawing on the development trend of space-based large-scale computing resources, as well as the current construction of ultra-low orbit constellations and the status quo of commercial space-based computing chips, this paper presents a sub-level analysis and summary to design a distributed collaborative processing framework utilizing large-scale dispersed space-based computing resources. This framework can provide effective theoretical support and serve as a reference for subsequent service scenario designs for ultra-low orbit satellite constellations.
2. Research Progress on Aerospace Intelligent Remote Sensing Satellites
2.1. Research Status of On-Orbit Processing of Space Remote Sensing
Since the 1990s, researchers have progressively conducted investigations on the pivotal technologies of space-based intelligent remote sensing satellites. In recent years, global space powers have placed significant emphasis on the real-time onboard data processing capability in orbit and its application in national defense infrastructure and space security. Due to the vast amount of remote sensing satellite image data, the scarcity of domestic satellite ground receiving stations, and the limitations in satellite-ground data communication bandwidth, there are practical application demands for efficient down transmission, rapid information extraction, and emergency support concerning massive remote sensing data. Therefore, the intelligence of space-based remote sensing satellites constitutes the mainstream in the development of advanced remote sensing satellite systems. The concept of space-based intelligent remote sensing satellites emerged from on-orbit real-time processing technology. With advancements in intelligent chip and artificial intelligence, the research and application of intelligent remote sensing satellites are encountering novel challenges and opportunities [
6].
The United States has been developing satellite real-time processing technology in orbit according to the established plan. As early as around 2000, they initiated the development of intelligent remote sensing satellites. In terms of hyperspectral remote sensing data, the US Air Force has equipped the onboard autonomous processor on TacSat-3 tactical satellite, enabling independent planning of acquisition mode for the onboard hyperspectral imager as well as real-time processing and storage of image data [
7]. The United States Naval Research Institute has deployed an image parallel processing array on the Naval EarthMap Observer (NEMO) satellite, which is based on multiple digital signal processing units [
8]. This advanced system enables real-time feature extraction and data compression of hyperspectral data onboard, with the processed results directly transmitted to the ground for immediate application. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched the EO-1 hyperspectral satellite with the objective of enabling applications such as extraction of hyperspectral image information and detection of changes in orbit, thereby optimizing data acquisition time for downstream transmission to various applications [
9]. In terms of infrared remote sensing images, the space-based early warning satellites in the US National Defense Support Program achieve image redundancy background data removal, target detection and tracking, and fast data down transmission through on-orbit processing. The extended Space Based Infrared System (SBIRS) is employed for direct recognition and extraction of multiple targets at the missile terminal [
1]. In terms of video data, the United States Skybox company has applied H.264 and other general video coding technologies to satellite video compression, enabling direct application of video data for target recognition and tracking [
8]. The US Department of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency and SpaceX have launched the "Black Jack" low-orbit satellite constellation project, leveraging the cost-effective benefits of commercial satellite platforms and payloads, integrating cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and on-orbit large-scale distributed computing to achieve autonomous real-time processing of satellite data in orbit [
9]. This initiative caters to global military intelligence reconnaissance, combat command and control, and other application scenarios.
European space agencies have also made significant advancements in the development of intelligent remote sensing satellites, as well as conducted extensive research on on-orbit processing technology for various types of remote sensing image data, resulting in notable achievements [
1,
3]. Around 2000, the European Space Agency initiated the PROBA project to conduct research on on-orbit processing of remote sensing data. Subsequently, in 2009, they launched the PROBA-2 satellite with enhanced capabilities for on-board spectral channel programming, merging, and on-orbit data processing of imaging spectral data. Since 2017, research on space-based image processing in orbit has been conducted using the Hyperscout-2 satellite-borne imager. The Phisat-1 satellite is equipped with an embedded intelligent processing unit within a neural network, exhibiting fundamental characteristics of an intelligent remote sensing satellite [
10]. In October 2001, the German Space Center developed the BIRD small satellite, which was equipped with on-board processing capabilities to accomplish tasks such as preprocessing visible light and infrared data and conducting on-orbit application analysis [
11]. Since 2011, the French Space Center has successfully launched the Pleiades series of high-resolution optical satellites, namely Pleiades-1A and Pleiades-1B satellites, to accomplish on-orbit real-time acquisition, correction, compression, and other onboard preprocessing tasks for optical remote sensing image data [
12].
Numerous research institutes in China have conducted extensive investigations on space-based intelligent remote sensing satellite technologies at various levels. The "Tianzhi-1" intelligent optical remote sensing satellite, launched by Institute of Software Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISCAS) in 2018, represents China's pioneering software-defined satellite operating in orbit [
13]. It encompasses intelligent deployment tasks, advanced measurement and operation control capabilities, as well as sophisticated information processing functionalities. Leveraging cloud computing platforms, it intelligently deploys on-orbit data processing tasks and achieves rapid pre-processing for ground-based analysis. The first intelligent remote sensing scientific test satellite, Luojia3 was jointly developed by Wuhan University and Aerospace Dongfang Hong Satellite Co., Ltd. It is equipped with a software-defined multi-mode optical imaging payload. Additionally, an intelligent on-orbit real-time processing technology system of "mission planning → sensor calibration → target detection → intelligent compression" has been proposed [
1]. The Wuhan University and Yantai Municipal Government of Shandong Province have jointly proposed the establishment of the Oriental Smart Eye (OSE) intelligent remote sensing satellite constellation program. This program incorporates an autonomous on-orbit intelligent processing terminal, integrates Beidou short message and inter-satellite real-time transmission terminals, and employs cooperative networking, intelligent scheduling, joint observation, and interconnection of intelligent terminals within the satellite constellation to achieve real-time intelligent service for satellite remote sensing information. The ultra-low orbit satellite Integrated constellation developed by China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation (CASIC) establishes a real-time remote sensing service application demonstration system through on-board intelligent processing, end-to-end satellite connectivity, and inter-satellite communication. This enables intelligent computation of on-orbit remote sensing satellites, precise "sensing" capabilities at the nanometer scale, and real-time "transmission" at the minute level [
14].
With the advancement of commercial space development, the "Jilin-1" satellite series developed by Changguang Satellite Technology Co., Ltd. incorporates on-orbit real-time intelligent processing systems into its spectral 01 and 02 magnitude platforms, facilitating on-orbit image compression, algorithm injection deployment, and on-orbit update functionalities. Notably, the Jilin-1 platform's satellites 02A01 and 02A02 have achieved a groundbreaking milestone in China by enabling ultra-high-speed high-resolution remote sensing image transmission through inter-satellite laser technology at a rate of 100Gbps, successfully transmitting inter-satellite data to ground stations [
15]. The "Chaohu-1" series synthetic aperture radar (SAR) remote sensing satellite, developed by Changsha Tianyi Space Science and Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd., is equipped with a high-performance on-board processing platform to achieve real-time target identification and segmentation of SAR images in orbit, enabling transmission of the report through the Beidou System. The "Taijing III-02 satellite developed by Beijing Minospace Technology Co., Ltd. is equipped with a high-performance intelligent computing platform, enabling efficient optical image compression, target recognition, and positioning services for users [
16]. In the realm of commercial space remote sensing satellite constellations, such as the "PIESAT constellation," "Tianfu constellation," and "Zhuhai-1," various levels of experiments on space-based on-orbit data processing have been conducted. Targeting the research, production, and service mode of domestic civilian and commercial remote sensing satellite systems, this study aims to overcome key technologies such as space-based high-performance computing architecture, intelligent mission scheduling and planning, and on-orbit real-time intelligent service. It strives to establish a space-based information real-time intelligent service system with a space-based cloud brain system, seamless integration of space-time data, and intelligent decision-making capabilities. The objective is to provide users with real-time access to space-based remote sensing observations in order to enhance the efficiency, timeliness, and accuracy of remote sensing satellite applications [
17].
2.2. Development Status of Space On-Orbit Processing Platform
The application mode of space remote sensing satellites involves the collection of image data in orbit, transmission of data to the location processing center through satellite-ground communication links, and realization of various data processing, sharing, and distribution for different professional fields or application departments at all levels on the ground. However, there are increasing challenges related to contradictions between satellite remote sensing data and satellite-ground data transmission links as well as a shortage of domestic ground receiving stations. The traditional application mode "space-sensing ground-computing" was unable to meet the demands for high time-sensitive and emergency tasks. On-orbit real-time calculation of satellite remote sensing images presents an effective solution; however, insufficient space-based on-orbit computing power remains a major obstacle. Typically, the computing power of traditional remote sensing satellite chassis is less than 10Tops with a weight around 10kg primarily consisting of CPUs which fails to meet current rapid development requirements for space missions. Considering that 1kg weight corresponds to a launch cost of approximately 150,000 yuan (CNY), it becomes crucial for onboard processing machines as part of the satellite in orbit system to fulfill performance requirements while minimizing volume and weight [
18].
The processors of space-based on-orbit intelligent processing platform primarily consist of CPU, GPU, FPGA, neural processing unit (NPU), digital signal processing (DSP), and other types [
19]. Considering the characteristics of on-board computing tasks, the CPU serves as the computing and control core of a computer and is mainly utilized for instruction scheduling and control. It is suitable for scalar computation but not for accelerated computation of deep learning models. The GPU exhibits high parallelism, high memory bandwidth, and fast execution speed. By employing CPU control calls, the computational performance of the GPU can be significantly enhanced. The multi-core clustering mode satisfies the requirements for highly parallel computing in large-scale data processing and complex computational tasks. The NPU emulates biological neural network systems by simulating biological neurons and synapses at the circuit level while customizing designs to accommodate deep learning networks' characteristics thereby achieving processor storage integration with computation capabilities. The FPGA operates closer to underlying IOs with abundant logic units enabling efficient parallel acceleration of deep learning processing models; however, it faces challenges in implementing complex algorithms due to its high-cost implications. As a specialized microprocessor, the DSP is predominantly employed for matrix multiplication and addition operations necessitating combinations with multiple DSPs alongside other processors [
20].
The United States Space Development Agency (SDA) has proposed the National Defense Space Architecture (NDSA) for strategic space development deployment, based on military operational requirements such as space-based high-performance computing [
22]. This architecture is structured into seven layers: transmission, combat management, tracking, supervision, emerging capability (deterrence), navigation, and support. Each NDSA satellite in the combat management layer is equipped with edge computing payload primarily responsible for on-orbit data processing. It possesses intelligent distributed management capabilities along with space-based task processing and communication transmission abilities. Amazon Web Services leverages onboard computing to eliminate data transmission delays and bandwidth limitations by deploying a suite of edge computing products on low-orbit satellites. By utilizing cloud technology directly on the satellite, it enables automatic collection and analysis of vast amounts of raw satellite data while transmitting valuable results through satellite-based communications for storage or further analysis.
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center has pioneered a novel hybrid space-based on-orbit data processing scheme that integrates commercial devices with radiation hardening methods, proposing an advanced space-based computing architecture capable of optimizing the performance of CPUs, DSPs, and FPGAs [
20]. Microchip has collaborated with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory to design and manufacture high-performance space computing (HPSC) processors, aiming to develop a space-resistant system on chip (SoC) that can replace the existing spacecraft's space-grade chips while maintaining identical power consumption, size, and weight. Consequently, the computational capabilities in space have been enhanced by over 100 times [
23]. In August 2023, Sidus Space, a US-based satellite manufacturing company, acquired Exo-Space, a leading company specializing in space edge computing. This acquisition aims to integrate advanced artificial intelligence software technology into Earth observation satellites. Exo-Space combines anti-radiation hardening hardware with flexible and customizable elastic software. By leveraging the software platform, it enables on-board transmission optimization, updates and modifications of payloads. Furthermore, this integration facilitates collaboration among satellite constellations, computing chips, and software platforms to enhance the comprehensive utilization value of satellite hardware while unlocking their application potential across diverse fields [
24]. The on-board processing load of the BIRD satellite consists of FPGA, DSP, and other processors. The on-board high-resolution imaging spectrum processing system of the PROBA-2 satellite is a dedicated DSP system. Additionally, the on-board processor of the Pleiades series satellites utilizes FPGA technology to accomplish image processing tasks in orbit [
21].
The domestic space-based on-orbit computing capacity has reached parity with that of the United States, and it possesses a robust domestic independent and controllable research and development capability, which has been validated through the successful operation of numerous civil and commercial satellites or constellations. Zhuhai Hangyu Micro Technology Co., Ltd. is engaged in developing a new generation of aerospace SOC series chips as well as various space-based computers for satellite, spacecraft, aircraft, and other applications. These advancements encompass mainstream architecture systems such as scalable processor architecture (SPARC) and reduced instruction set computer (RISC), including navigation and communication chips, master control chips, artificial intelligence chips, and general computing chips [
24]. Notably among these developments is the independently developed Yulong 810A chip featuring a primary processor utilizing a 4-core advanced RISC machines (ARM) A9 along with a coprocessor comprising GPU and the neural network accelerator (NNA) units; this chip boasts an impressive floating point computing capacity of 64GFlops alongside a fixed-point computing capacity of 12Tops. The BM3883MARH, a third-generation domestic 8-core processor developed by the Beijing Institute of Microelectronics Technology, adopts the anti-radiation SPARC architecture and achieves a floating-point operation performance of 32GFlops and a fixed-point operation performance of 16GOPS [
25]. For space-based on-orbit processing, Xi'an Jiaotong University has designed a heterogeneous computing unit consisting of class 4 FPGA and class 6 DSP reconfigurable components. Additionally, Xi'an Institute of Space Radio Technology has developed an on-board processing platform utilizing large-scale FPGA and multi-core DSP to support intelligent processing and analysis of remote sensing images in orbit. Shandong Aerospace Electronics Technology Institute has also developed an on-board image real-time processor with a hybrid architecture combining FPGA+CPU+NPU+DSP/GPU based on the domestic commercial Cambrian Chuangzhi-2. Customized anti-irradiation reinforcement and system heat dissipation design have been implemented according to the requirements for space radiation environment applications [
20]. StarDetect Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd., for the first time, has adopted a super-heterogeneous computing system comprising intelligent reconfigurable CPU+FPGA+GPU+AI, along with conducting multi-dimensional system-level COST chip anti-irradiation reinforcement design to achieve high computing power up to 275Tops per kilogram intelligent load and high energy efficiency ratio of 4Tops/Watt. This technology leads two generations ahead compared to foreign FPGA+GPU architectures with an on-orbit time exceeding international peers by more than one year.
In the field of artificial intelligence chips, CPUs or ARM cores are initially employed for scheduling processing tasks, followed by achieving large-scale parallel computing through GPUs, FPGAs, or ASICs with diverse architectures such as Google's TPU, Horizon's BPU, Cambrian and Huawei's NPU. On-board intelligent computers face a dilemma in meeting the increasingly high-performance requirements for space-based cloud computing and massive remote sensing image processing tasks due to the inability to use traditional anti-irradiation chips while being hesitant to adopt high-performance commercial devices [
26]. The on-board intelligent processing platform is capable of effectively meeting the requirements for intelligent processing of remote sensing images, with special reinforcement processing necessary for satellite-borne environments. Depending on the specific demands of space applications such as computing power and localization, different architectures are typically adopted. For high-orbit applications, FPGA+DSP architecture is commonly employed to ensure reliability; whereas low-orbit satellite constellations tend to favor CPU+GPU/NPU architecture in order to meet the demand for extensive computing power. In terms of device selection, notable domestic high-performance processors include Feiteng CPU, Fudan University Microelectronics 7 series FPGA, National University of Defense Technology FT-M6678 DSP, Huawei Atlas 200 intelligent processing module etc., while foreign NVIDIA companies offer high-performance GPUs such as TX2, AGX and Orin [
27].
2.3. Research Status of Intelligent Processing Algorithms on Satellites
In the interpretation and analysis of remote sensing images, a wide range of neural network models have been utilized, encompassing shallow architectures such as early back propagation (BP) neural networks and support vector machines (SVM), as well as deep learning frameworks like convolutional neural networks (CNN) and the you only look once (YOLO) series, these techniques have found extensive applications in remote sensing domains including target detection and recognition, semantic segmentation and classification, as well as change monitoring. Moreover, it has expanded into research areas such as multi-modal fusion of remote sensing data, image description, and knowledge deduction based on artificial intelligence [
28]. In addition to academic research efforts, commercial companies have also conducted investigations into large models for remote sensing applications. The intelligent processing and analysis of remote sensing image based on deep learning realizes end-to-end detection through sample set construction, model training and prediction. However, compared with natural scenes, remote sensing image samples are relatively insufficient, models are fragmented, data sources are diversified, etc. Therefore, it is imperative to explore intelligent processing methods for remote sensing images such as small sample learning, incremental learning and transfer learning [
29]. Additionally, considering the limited computing resources of satellites, the effectiveness and efficiency of applying model algorithms on the ground may not meet the application requirements of the actual scene. In addition, when deploying the algorithm model on the satellite, it is also necessary to perform model lightweighting and algorithm acceleration processes such as pruning, quantization, and weight sharing.
The research on intelligent real-time processing algorithm of space-based remote sensing data primarily focuses on mission planning, data acquisition, processing and analysis, storage and distribution, as well as transmission of the acquired data [
30]. Due to the vast amount of remote sensing image data, the conventional process-oriented model for producing remote sensing products is no longer suitable for on-board processing, necessitating a shift towards task-driven or event-based sensing. In terms of on-orbit processing algorithms for remote sensing images, extensive research and verification work has been conducted by both domestic and international research institutes as well as commercial companies, such as on-orbit real-time task planning, image analysis, calibration and correction, intelligent interpretation and data compression [
31]. As an illustrative example, the United States Space Development Administration and commercial space enterprise SpaceX have integrated artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other advanced technologies to automate the processing, in-depth analysis, and practical utilization of space remote sensing images. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the German Space Center, and other institutions employ on-board mission scheduling planning and data analysis to facilitate real-time utilization of on-orbit data in military target identification and fire detection scenarios. This serves to support time-critical task requirements such as military target reconnaissance, combat command and dispatch, as well as geospatial intelligence acquisition. Chinese scientific research institutions such as Wuhan University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences have conducted extensive research on on-orbit processing algorithms for satellites. They possess the capability to effectively utilize high-resolution optical, infrared, and SAR remote sensing images for a range of on-orbit processing tasks, encompassing image compression, aircraft and ship target detection, cloud and fog identification, as well as supporting algorithm model updates during satellite operation [
32].
2.3.1. On-Orbit Satellites Task Scheduling
With the improvement of satellite payload capacity, space business has gradually transformed into non-single exploration missions. China has developed a real-time space information service system that integrates satellite positioning, navigation, timing, remote sensing, and communication (PNTRC) to achieve the goal of providing intelligent space information services in real-time through single-satellite multi-purpose functionality, multi-satellite collaboration, and satellite-ground inter-connection [
33]. The common technical key point of different mission satellites is to give satellites the ability of autonomous decision-making, communication coordination, scheduling and other on-board mission planning according to dynamic observation requirements, operation status and mission content [
34].
The satellites task scheduling planning can be categorized into two levels: single-satellite autonomous task scheduling planning and multi-satellite cooperative task scheduling planning. The evolution of single-satellite autonomous task scheduling has progressed from ground-based off-line scheduling to on-board scheduling and integrated satellite-ground scheduling. However, multi-satellite cooperative mission scheduling has developed from multi-satellite ground scheduling to multi-satellite on-board scheduling to multi-satellite cooperative scheduling. The primary methods of single-satellite scheduling strategy encompass the Autonomy Generic Architecture - Test and Application (AGATA) utilized by the Pleiades series satellites of the French Space Agency, NASA's Remote agent (RA), and the Continuous Activity Scheduling Planning Execution and Replanning System (CASPER) [
35]. The small-scale multi-satellite mission scheduling in terms of multi-satellite cooperative scheduling typically employs traditional algorithms such as greedy and backtracking [
36]. On the other hand, the more complex multi-satellite online system mission scheduling adopts a centralized architecture where one spacecraft serves as the primary satellite within the satellite formation [
37]. This approach enables mission planning and scheduling based on resource balancing among the primary satellite of the satellite cluster. Subsequently, in order to avoid the disadvantages caused by the failure of the central satellite, scholars proposed that the decentralized distributed task scheduling method has better environmental adaptability [
38].
2.3.2. On-Orbit Data Compression
As one of the key technologies in on-orbit information processing, on-orbit data compression plays a crucial role in alleviating storage constraints for remote sensing satellites. Employing high compression ratio algorithms enables the transmission of more valuable information within limited communication bandwidth [
39]. The differential pulse code modulation (DPCM) compression algorithm was initially implemented in optical satellites such as SPOT, QuickBird, WorldView, and GeoEye series [
40]. These satellites utilize two primary algorithms for data compression on radar imaging satellites: block adaptive quantization (BAQ) and block floating point quantization (BFPQ) [
41]. The "Ziyuan" series satellites have achieved on-board data compression using pulse code modulation (PCM) and DPCM encoders for the first time in China. The discrete wavelet transform (DWT) method is widely used in on-orbit satellite image data compression, such as Pleiades-1, ICESat-2, Gaojing-1, Taijing-3, etc. However, the on-orbit compression ratio achieved by the DWT method is typically less than 10 times [
22]. In recent years, the advancement of artificial intelligence technology has led to the emergence of more sophisticated on-board data compression methods. Among these methods, task-oriented intelligent compression techniques have demonstrated superior capabilities in achieving higher rates of data compression for on-board remote sensing images. The information extraction methods such as target detection, change monitoring and image segmentation are used to extract the region of interest (ROI) for Luojia-3, and then selects a compression model suitable for ROI, the bit rate is allocated adaptively to improve the compression ratio and data transmission efficiency of on-orbit images [
1].
2.3.3. On-Orbit Data Intelligent Interpretation
The primary objective of intelligent interpretation of satellite remote sensing im-ages is to accurately locate, classify, and identify changes in the target of interest. In military intelligence reconnaissance, target monitoring, and disaster emergency rescue operations, computational efficiency plays a crucial role in ensuring effective implementation. The algorithms for object detection in remote sensing images based on deep learning can be categorized into two groups: region-based methods using candidate regions and regression analysis. The target detection method based on the candidate region is divided into two steps. Firstly, a series of candidate regions that potentially contain targets are generated. Secondly, the target and background boundary box of each candidate region are classified through regression. Representative algorithms for this approach include region convolutional neural network (R-CNN) and a series of enhanced algorithms based on Faster R-CNN, which aim to improve the representation of target features, optimize the generation and processing of regions of interest, and enhance the accuracy of target positioning [
42]. The remote sensing target detection based on regression analysis has two types of algorithms based on YOLO and single shot multi-box detector (SSD) frameworks [
43]. The main difference is that there is no need to generate a separate candidate region. Instead, the bounding boxes and categories of the target are directly regression analyzed from multiple positions of the input image. The YOLO series algorithm has the advantage of easy lightweight deployment, and the on-orbit verification is the most in real time processing on board. The difficulty of on-orbit target detection lies in balancing the contradiction between detection accuracy and on-orbit computing resources. The YOLO and other algorithms using downsampling will lead to information loss, while using sliding window detection will affect the detection efficiency, and will face the existence of multi-target, small target and multi-scale target detection problems. However, the introduction of attention mechanism based on Transformer model or combined with improved algorithms such as YOLO can achieve effective detection of multi-scale targets [
42]. In view of the characteristics of high resolution and high real-time remote sensing on board, it is necessary to study and design a lightweight and efficient network model suitable for remote sensing data processing on board [
44].
In view of the application requirements of on-orbit processing in remote sensing images, it has important research significance in the algorithms of small unsupervised learning target detection based on depth science, dynamic target detection of satellite video data, multi-source data fusion target detection and so on [
45]. In addition to the application of object detection, there are also application directions such as image scene classification, semantic segmentation and change detection. When the above algorithms are implemented in on-orbit real-time processing on board, scene segmentation classification is a data processing based on a single data source, which has something in common with the object detection algorithm in terms of algorithms [
46]. The main difference between them lies in the difference of network model construction, sample set production and output results [
47]. However, the remote sensing image change monitoring algorithm is the comparative analysis of multi-period data [
48]. Usually, based on the change monitoring of multi-period remote sensing images, the image is classified first, and then the difference of the classification is compared, so as to realize the change detection and monitoring of remote sensing images, which puts forward higher requirements for the change detection of remote sensing images on board [
49].
With the development of natural language processing (NLP) technology, the application of large models in all walks of life has gradually emerged, as shown in
Table 1. Remote sensing large model is also called remote sensing pre-training basic model. A large number of unlabeled remote sensing images are used to train large model to extract general feature representation, so as to improve performance, efficiency and versatility. Three key factors are involved: the pre-training dataset, the number of model parameters and the pre-training technique. However, the drawbacks of large model training cost and large number of parameters are not conducive to practical application, such as generative pre-trained transformer 4 (GPT 4) training on 25,000 A100 Gpus, with 1.8 trillion parameters, inference cost of 525 billion Davinchi, its cost is about
$60 million. To develop large-scale visual language models for multi-modal data analysis in the field of Remote Sensing, such as the remote sensing foundation model (RingMo) first proposed by the Institute of Aerospace Information Innovation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences for generative pre-training of cross-modal remote sensing data [
50]. The model can automatically extract common features of remote sensing ground objects, and has strong generalization ability for new tasks, and supports multi-modal multitasking. Subsequently, the SenseEarth large model of SenseTime Technology and the AI Earth segmentation foundation model (AIE-SEG) of Alidama Institute appeared successively. The contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP), remote sensing GPT (RSGPT) and other multi-modal remote sensing intelligent interpretation models built on video, image and text data have been successfully applied to remote sensing image target recognition, object classification, image description and other aspects, gradually deepening the intelligent application of remote sensing data.
In summary, when various large remote sensing models are deployed and applied on the ground, many problems such as the simplification, fragmentation and cross-modal application of deep learning models can be solved. However, the deployment and use of large models requires sufficient computing power resources and sample resources to ensure the training application of large models. If the large model of remote sensing is deployed to the satellite for on-orbit application, it needs the support of large-scale computing power and the lightweight of the algorithm model. Therefore, building a space computing network with large-scale computing power is the primary prerequisite for realizing intelligent computing on large model satellites.
3. Distributed Processing Framework Based on Large-Scale On-Board Computing Power
3.1. Overall Framework Design
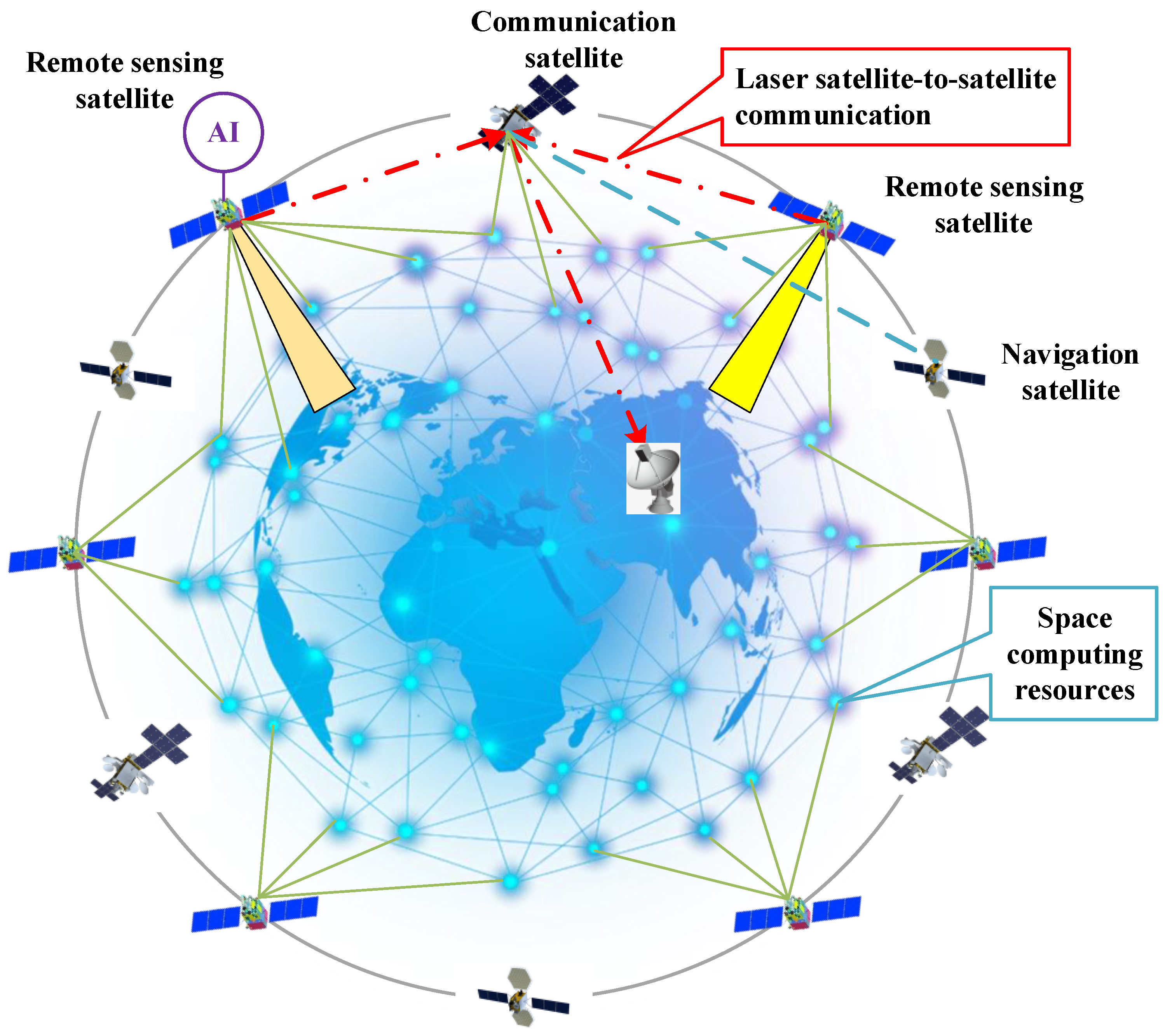
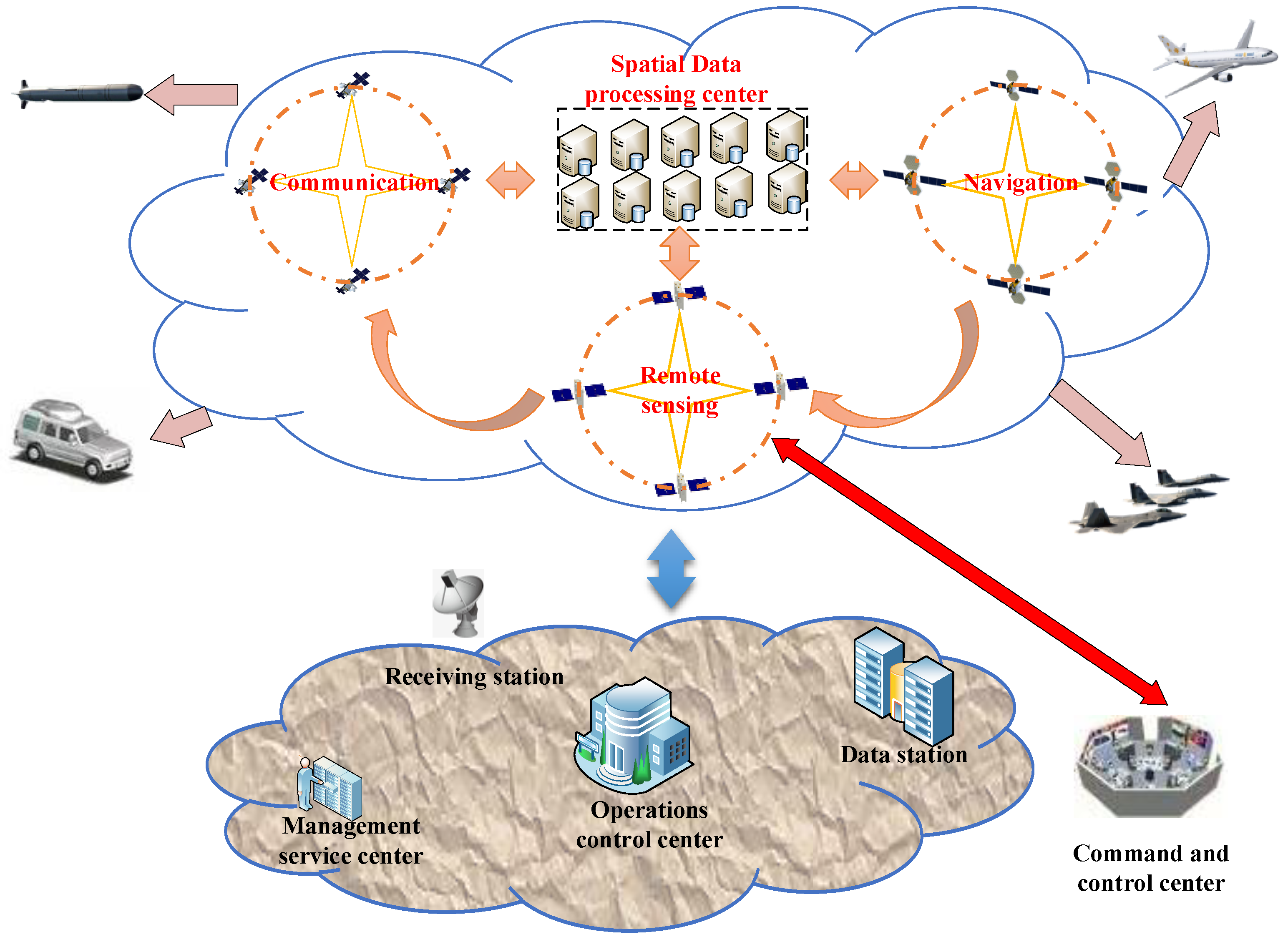
The construction of space intelligent satellite constellation will promote the explosion of single-satellite computing power and the number of computing power on the satellite. The distributed on-orbit processing framework is designed based on large-scale computing power, taking into account the characteristics of the space environment such as ultra-low temperature, thermal vacuum, and strong radiation. This framework aims to address challenges including limited space satellite storage resources, restricted bandwidth of satellite-earth communication, and delayed service response. Its ultimate goal is to achieve high-precision on-orbit real-time service for space remote sensing satellite data. As shown in
Figure 1, the overall design idea of the distributed on-orbit real-time processing framework based on large-scale spatial computing power is shown in the figure below. The design principle of distributed processing framework based on space large-scale computing resources is the effective utilization of space discrete large-scale computing resources. It consists of six parts: a space-based intelligent service system integrating communication, navigation and remote sensing, a large-scale space computing resource, a high-performance on-orbit processing platform, a space security communication and data transmission system, an on-board intelligent mission scheduling and planning system, and an on-orbit real-time imaging intelligent processing and analysis algorithm.
3.2. High Performance On-Orbit Real-Time Processing Architecture
The particle radiation emitted by the complex space radiation environment not only possesses high energy, but also exhibits a diverse range of types. This radiation is capable of penetrating the shielding layer of space probes and causing damage to onboard electronic components, thereby impacting the normal operation of satellites. In consideration of the highly challenging electromagnetic conditions prevailing in space, it becomes imperative to employ specialized materials and structures across hardware, system, and application layers for reinforcing aerospace-grade computing chips against irradiation. This will significantly enhance the satellite edge computing equipment's resistance to radiation interference and its ability to operate reliably within the harsh space environment. The single-satellite high-performance on-board ultra-heterogeneous edge computing platform is an integrated on-board computing system that combines various computational resources. As shown in
Figure 2, it utilizes the ultra-heterogeneous CPU+FPGA+GPU+AI computing architecture, achieving an exceptional performance ratio of over 1 Tops/W and providing a carrying efficiency of 275 Tops per kg for on-orbit computations. The ultra-heterogeneous edge computing platform is based on a full-stack Linux system, essential software library, and development toolchain, offering an open ecosystem for APP deployment that enables updates and redefines on-orbit computing functions through over-the-air (OTA) technology. The system level reinforcement design based on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) devices can realize the high efficiency, high reliability and stable operation of traditional algorithm and AI algorithm on-orbit. Combined with multi-soc ultra-heterogeneous computing system and software-defined architecture, it can simultaneously meet the requirements of high performance, low power consumption, miniaturization, versatility and high reliability of satellite on-orbit computing tasks. According to the on-orbit operation situation, after retraining the model on the ground, the weight of the on-orbit calculation model can be updated at any time according to needs, and the on-orbit AI calculation capability of space remote sensing satellites can be continuously improved.
3.3. On-Orbit Intelligent Task Scheduling and Planning
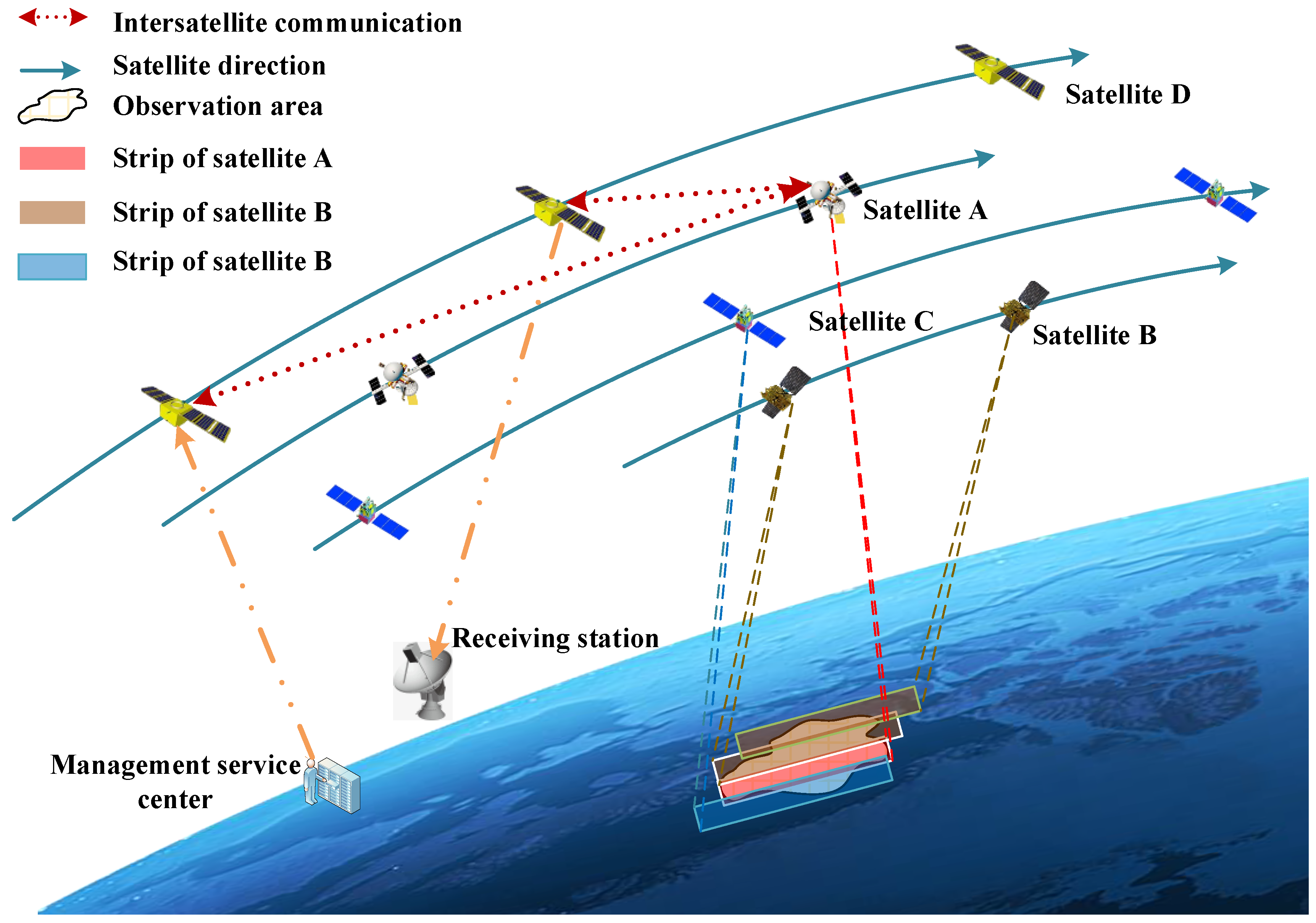
The on-orbit task scheduling and planning of intelligent remote sensing satellite are mainly aimed at the application scenarios of real-time remote sensing. The observation task requirements are submitted to the client, and the satellite is inputted through a satellite-Earth communication link. The on-orbit intelligent task scheduling and planning system calculates the mission planning scheme with optimal observation timeliness and maximum benefit by considering constraints such as the observation window, transit time, and location of the target area. It intelligently schedules satellites from the constellation that are most suitable for observing the target area, while also planning satellite observation missions. Furthermore, the on-board intelligent task planning integrates the intelligent processing results of on-board images to autonomously assess whether the observed target data satisfies user requirements and dynamically adjusts observation tasks based on changes in ground application tasks and event perception. The implementation of intelligent task planning and scheduling reduces the volume of information in task instructions and minimizes the response time from demand to execution. Consequently, the Earth remote sensing observation application model shifts from being product-driven to becoming task-driven with event sensing capabilities.
With the increase in the number of Earth observation satellites, and the different orbital satellites have different advantages in observation band, resolution and imaging observation mode, the cooperative observation scheme of satellite-based, inter-satellite and cluster remote sensing satellite constellations such as high orbit, medium orbit and low orbit is constructed. This approach makes full use of the observation advantages of different satellites in the cluster, and achieves the effect of multi-satellite cooperative observation, such as discovery of medium-high orbit satellites, identification and confirmation of low-orbit satellites, and tracking of ultra-low orbit satellites. When the on-orbit single satellite computing power increases and the on-orbit computing power accumulates to a certain scale, sufficient on-orbit computing resources will be formed. A space cloud computing architecture is established on board the satellite, enabling cooperative scheduling and planning of observation missions for high and low orbit satellite constellations through intersatellite laser communication and resource sharing. By leveraging the strengths of diverse remote sensing satellite resources, as shown in
Figure 3, this approach enables consideration of task-specific observation time windows, spectral characteristics, and resolution requirements, thereby enhancing the observation efficiency and comprehensive utilization rate of remote sensing satellites. The multi-satellite in-orbit intelligent mission scheduling planning based on large-scale on-board computing power is shown in the above figure.
3.4. On-Orbit Real-Time Imaging Processing and Analysis
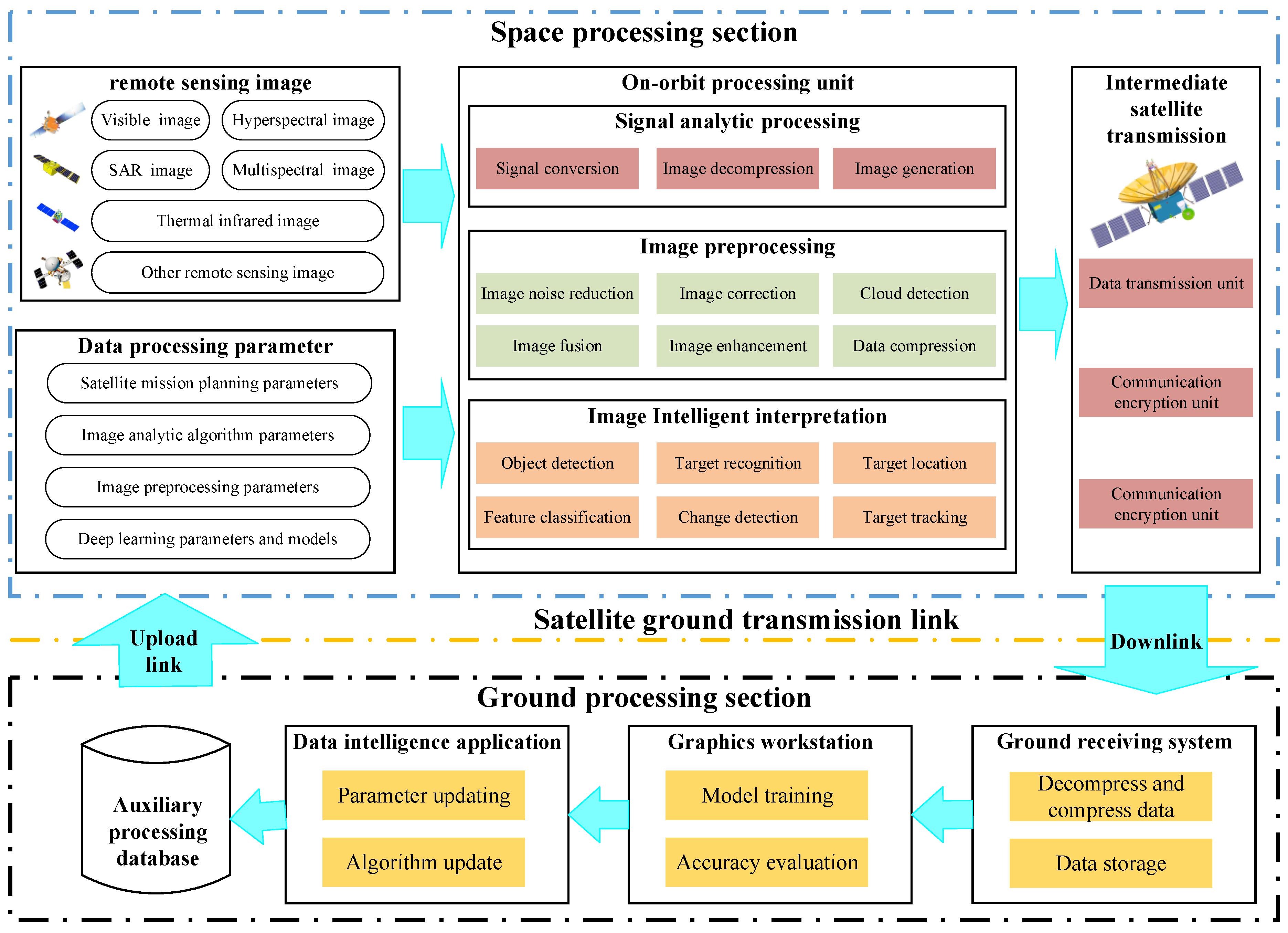
As shown in
Figure 4, the remote sensing satellite mission scheduling and planning implementation of Earth observation acquisition of different remote sensing image data, from digital signal acquisition to imaging processing needs to go through a series of steps, it is necessary to fully consider the processing algorithm's requirements for on-orbit computing power, so as to realize the real-time processing from data acquisition to results display. The on-orbit processing integrates a variety of sensor analysis and data processing technologies, involving data acquisition, data processing, image generation and other links. The digital signal acquired by the sensor is converted into the image by the steps of eliminating interference, enhancing signal and correcting deviation. The key to real-time imaging lies in the computing power and data transmission rate of the on-board processing unit. In order to achieve real-time performance for on-orbit imaging processing and analysis, the data processing unit employs a high-performance ultra-heterogeneous hardware system comprising multi-core CPU, GPU, and FPGA. Additionally, it leverages a large-scale on-board computing power cluster calculation to effectively allocate hardware and software characteristics. This optimization enhances algorithm operation efficiency and streamlines the data processing flow, resulting in reduced imaging processing time. In addition, when the storage capacity of the on-board system is insufficient, the on-board data processing is not stored on disk to reduce the storage consumption of intermediate processing data.
During the on-orbit processing and analysis of remote sensing images, the data processing algorithms involved in digital signal analytic imaging and basic image processing follow a standardized procedure. However, due to variations in sensors, different processing steps may be required, and the above process processing algorithms are mainly based on traditional methods. In view of the general processing steps of radiation and geometry, considering the key hardware conditions such as on-board computer performance and storage supported by the algorithm, the on-board real-time processing algorithm only needs to be professionally modified and optimized. The target recognition and classification algorithms applied to intelligent interpretation based on standard products are mainly artificial intelligence algorithms, which need to be deployed in the on-board processing computer after model training of samples from different data sources and lightweight processing such as pruning. Based on large-scale on-board computing power, the sharing of algorithms, computing power and storage resources in space can be realized, which can effectively use space computing resources. In this paper, the architecture design of on-orbit real-time imaging processing and analysis based on large-scale on-board computing power is shown in the above figure.
3.5. Space Security Communication and Data Transmission
The communication in space comprises of two components: the inter-satellite communication link and the satellite-Earth communication link, thereby establishing two distinct application modes: satellite-Earth-Earth-satellite and satellite-satellite-Earth. The inter-satellite communication exhibits minimal space clutter, unaffected by atmospheric conditions or obstacles, thereby enabling high direct transmission rates. The inter-constellation communication can be autonomously networked, reducing the reliance on ground stations and expanding satellite communication coverage to facilitate cross-regional and transnational connectivity. It is difficult to achieve large-capacity and stable communication transmission in satellite-ground communication, and the ground receiving network belongs to regional coverage, which is difficult to support fast global satellite communication. In the case of large-scale on-board computing power deployment, after the satellite completes the calculation in orbit, it can directly obtain the result information required by users, and even transmit the result by short means such as short messages. Therefore, the drawback of untimely transmission caused by massive original remote sensing image data is solved.
With the advancement of information technology, a multitude of high, medium, and low orbit remote sensing satellite constellations have been deployed in the public space environment, leading to an increasingly prominent issue of satellite network security communication. In satellite communication, ground-station uplink, satellite-ground station downlink and inter-satellite link mainly face interference attacks, interception attacks and tampering attacks. The security of communication link can be strengthened by anti-interference, anti-interception, regular monitoring of communication link, data encryption and integrity check. The communication encryption technology based on security protocol and cryptographic algorithm is an important means to ensure the communication security of inter-satellite communication and satellite-Earth communication. Based on the encryption technology, the information in the communication transmission process can be encrypted, and the information receiver and sender can directly obtain and analyze the information content through the key, so as to realize the identity authentication, key negotiation secret protection and anti-attack capabilities in the satellite communication process. Because the existing satellite communication mechanisms are different, the unified space communication protocol system and the algorithm encryption to realize the secure communication of constellation is one of the effective solutions.
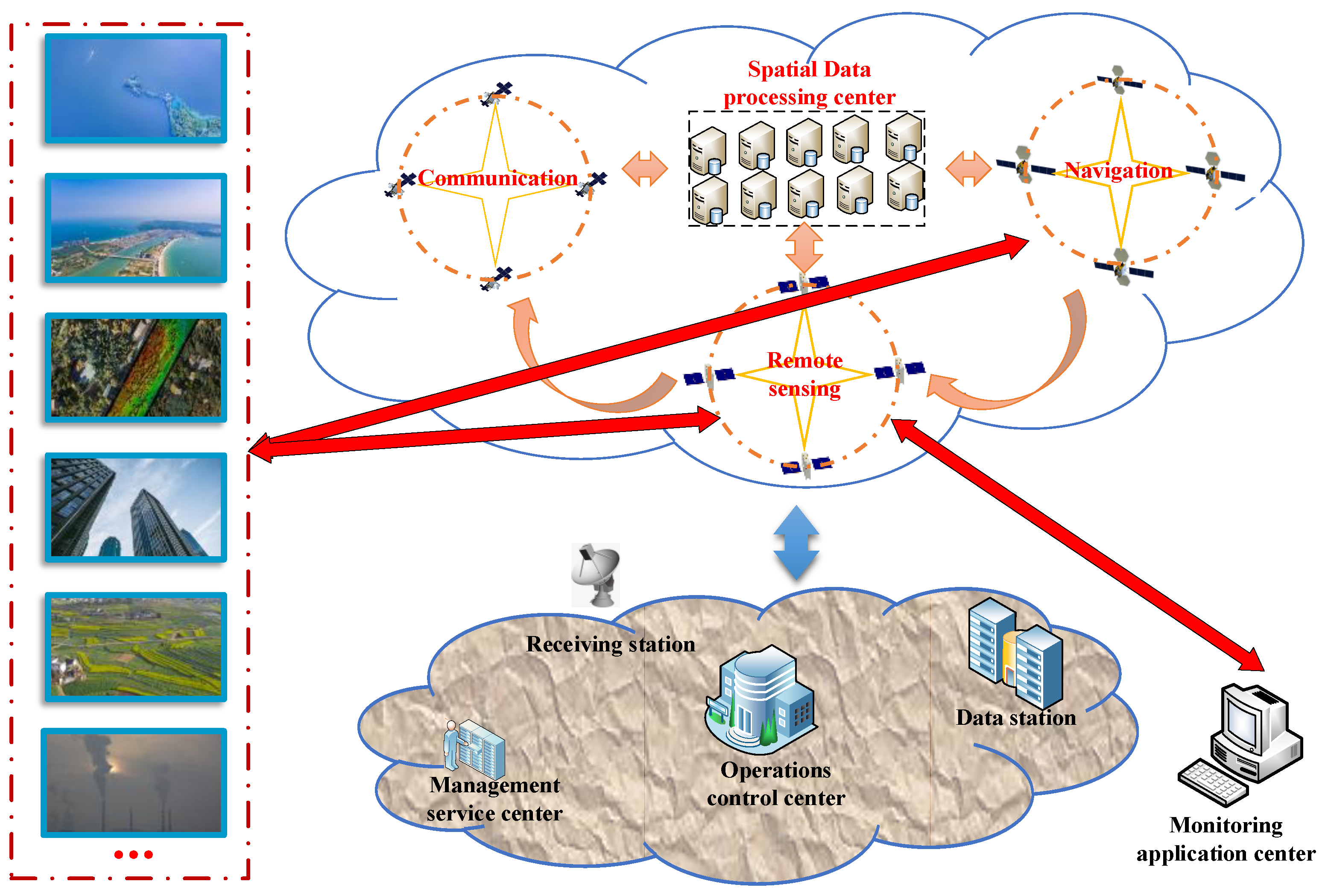
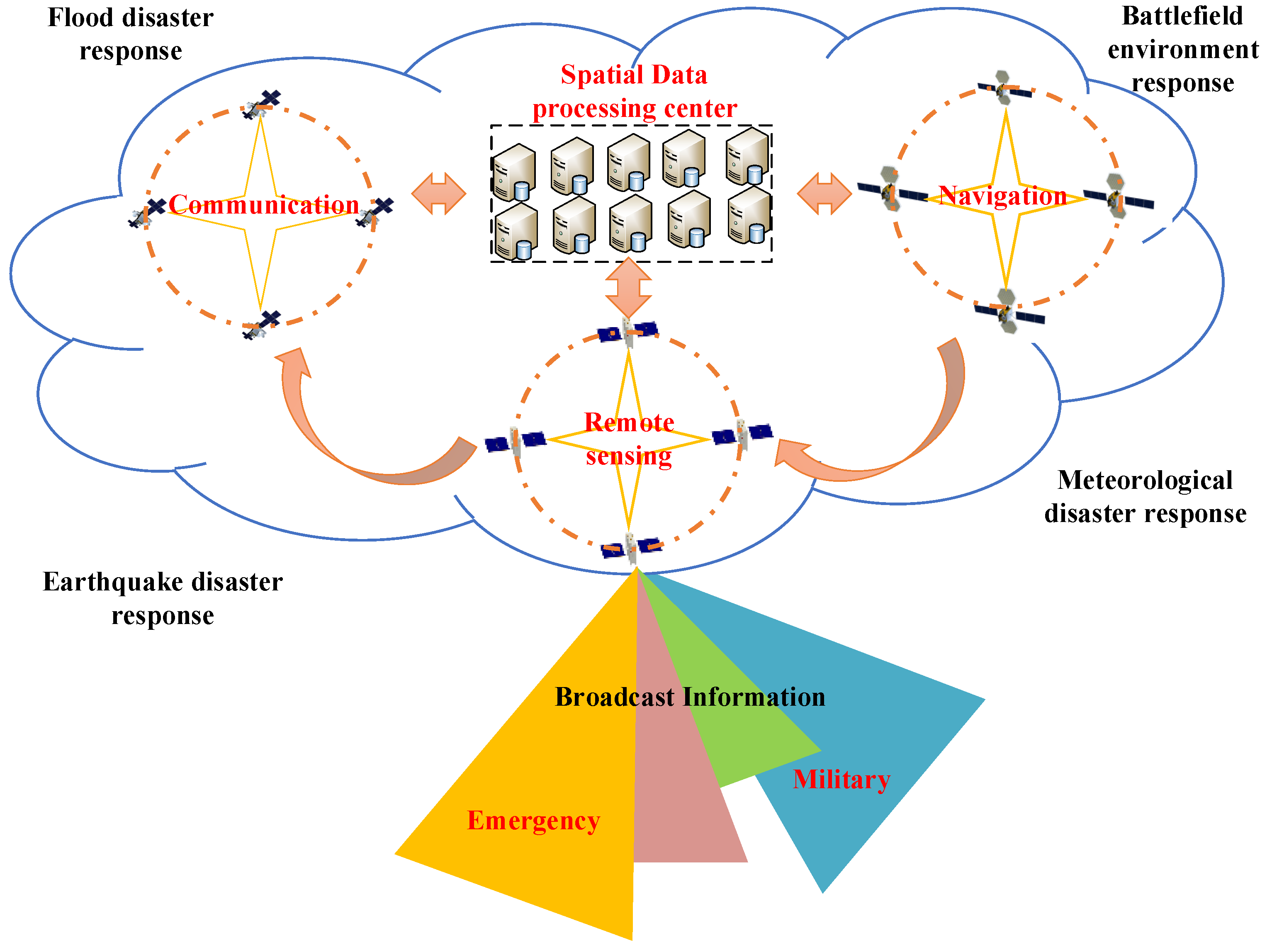
4. Real-Time Service Scenario Design for Ultra-Low Orbit Satellites
The real-time service mode of intelligent remote sensing satellite is mainly used in typical scenarios such as natural resources, agriculture and forestry, ecological environmental protection, military combat command, emergency and rapid response, etc. However, most industries have low requirements on the timeliness of data collection. In the application of traditional remote sensing satellites, the user segment transmits monitoring demand information to the satellite constellation. Subsequently, during normal on-orbit operation, the satellite constellation acquires remote sensing image data for Earth observation. The obtained remote sensing data is then transmitted to the ground gateway station and forwarded to the ground data processing center for analysis and processing of the original observational data. Finally, the processed primary data product is delivered to the user's monitoring application center through a terrestrial transmission network. In the case of ground network failure or special needs such as emergency and military operations, the data can be analyzed and processed directly in the space data processing center for limited needs, and then the data can be sent directly to the user's monitoring application center through the satellite-ground communication network.
Based on 6G+ ultra-low orbit constellation, a fully connected world with the integration of ground network and satellite communication can be built, which can realize the three-way fusion and coordination mode of remote sensing observation, satellite communication and ground network reception. It will help realize high-resolution real-time remote sensing services, and Earth observation can be extended to more scenarios, such as real-time traffic scheduling, real-time remote sensing maps for civil use, high-precision navigation combined with remote sensing positioning technology, and rapid emergency response to disasters. The real-time remote sensing service for 6G+ ultra-low orbit constellation mainly includes three typical real-time service scenarios: information collection, command and control, and broadcast and distribution.
4.1. Real-Time Information Collection Service - Fast Surveying and Mapping Support Service
As shown in
Figure 5, according to the on-board computing capability and characteristics of ultra-low orbit satellite, a real-time information acquisition service scenario is designed. First of all, the intelligent processing unit on the ultra-low orbit constellation carries out real-time imaging acquisition and processing analysis of the data, and then transmits it back to the ground user segment receiving center through the satellite-ground transmission link. Finally, real-time distribution and sharing are carried out through the ground network, so as to realize the real-time remote sensing intelligent information collection service of the remote sensing satellite at the minute level. The ultra-low orbit satellite constellation is equipped with a 0.5m optical camera. For example, in the rapid mapping scene, the information collection service of the target area is realized through the intelligent scheduling of nearby satellites in the constellation, and the pre-processing steps such as image analysis, radiation correction, geometric correction and image fusion of high-resolution optical remote sensing images are realized on-orbit, so as to realize the rapid on-orbit production of surveying and mapping products such as orthophoto of the target area.
4.2. Real-Time Command and Control Service - Weapon Precision Guided Combat
As shown in
Figure 6, the command and control of real-time service applications are primarily utilized in military operations, specifically for the establishment of combat missions. In this context, the ground command and control center can establish connectivity with an ultra-low orbit satellite constellation through both the ground network and space communication network. Through the ground management service platform, space network, computing power and other resources are allocated, and real-time monitoring and control of aircraft, vehicles and other mobile terminals are realized based on the space computing support of large-scale satellite on-orbit computing power. For command and control scenarios with high real-time requirements and weapons precision guidance for military operations, a direct control link between ultra-low orbit satellites and the operational end is generally established to achieve the end-to-end weapon strike combat mode, so as to reduce the strike error caused by the change of moving targets caused by network delay.
4.3. Real-Time Broadcasting Distribution Service - Emergency Monitoring Information Extraction
As shown in
Figure 7, the broadcast distribution real-time service application scenarios are mainly for emergency response requirements of natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and typhoons. It is necessary to distribute the natural disaster information in the affected area in a wide area, or to issue the whole-area combat instructions in the remote theater. In the natural disaster monitoring mode, based on the large-scale on-board computing power, the data collected by the satellite sensor is calculated in real time in orbit, and the monitoring information of the disaster area is distributed in a fixed time every day. When the satellite sensor monitoring information exceeds the warning threshold, the space computing center opens the emergency response mode, and immediately sends disaster information (such as earthquake, flood, fire, etc.) or battlefield situation directly to the ground user through the space network. In the emergency rescue scenario, the "three interruption" problem of communication interruption, power interruption and traffic interruption will occur in the general disaster-stricken area. On-orbit calculation and real-time distribution of disaster information based on large-scale spatial computing power can effectively solve the dilemma caused by "three interruption".
5. Application Prospects
Relying on large-scale space computing resources in orbit, along with advanced technologies such as inter-satellite laser communication and integration of transmission and computation, the computational speed for load data processing and storage of constellations can be significantly enhanced. The explosion of large-scale computing resources in space will promote the application of remote sensing large models on satellite, make space situational awareness systems more flexible in strain and adaptation, and optimize space equipment deployment and production research, thus breaking through the application model innovation of space-based sensing.
(1) Satellite-Earth collaborative computing to strengthen real-time support capabilities for space information.
Based on satellite computing resources with different functions, the "space distributed computing network" aims to build a fully connected world with the integration of ground network, communication, navigation, and remote sensing, and will achieve "high-speed ubiquitous, space-Earth integration, and computing network fusion." Thus, Earth observation can be extended to more business scenarios, such as real-time traffic scheduling, civilian real-time remote sensing maps, high-precision navigation combined with remote sensing positioning technology, and rapid emergency response to disasters.
(2) Large-scale on-orbit computing to create new space infrastructure.
With the goal of forming large-scale space computing power through the high-frequency launch networking deployment of satellite constellations, relying on the construction of satellite space infrastructure to pull the development of the satellite industry, and promoting the aggregation and landing of supporting industrial chains such as payloads, satellite components, chips and software. Large-scale space computing resources support the needs of space digital governance, promote the industrialization and marketization of remote sensing data space cloud computing technology, and provide a hardware support environment for the ultra-lightweight on-orbit deployment of remote sensing large models. At the same time, high-frequency satellite launches will greatly improve the rapid development of space information industries such as commercial satellites and launch manufacturing. Drive the digital transformation of rocket launch, satellite manufacturing, data application and other industries, and empower the digital economy.
(3) Promote innovation in the application model of satellite data for consumers.
When the space on-orbit computing power has accumulated to a certain scale, an on-orbit real-time intelligent interpretation service system for consumer terminals will be established, a data-connected satellite data community will be created, a new satellite application industry ecology will be incubated, and the innovation of the application model of satellite data for consumers will be promoted. Based on the edge of space computing, it can overcome the obstacles such as the direct connection between satellite and Earth and the lack of on-orbit computing power, so that the satellite data can be calculated in real time in orbit and reach the user through the terminal. Whether it is enterprise users or consumer users, it is necessary to build a new type of satellite data cloud ecology by real-time demand, define the form and model of satellite data according to the demand, and truly realize the application of remote sensing satellites into thousands of households.
6. Conclusions
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current development status of space-based intelligent remote sensing satellites, and evaluates the level of engineering advancement based on the research progress in satellite remote sensing on-orbit processing. The analysis indicates that the present stage of on-orbit processing for remote sensing satellites is still at an early developmental phase, lacking systematic engineering applications as typical examples. The study examines the hardware and software architecture employed by the on-orbit mission computer, analyzing it within the context of a space-based on-orbit processing platform. Additionally, an overview is provided on current research advancements in satellite intelligent remote sensing processing algorithms, encompassing areas such as on-orbit mission scheduling, data compression, and intelligent interpretation. The findings indicate that despite significant progress, on-orbit processing continues to face several critical technical challenges that have garnered considerable attention from scholars worldwide. Based on the explosion of large-scale computing resources in space and the integration of emerging technologies such as 6G, cloud computing, artificial intelligence and edge computing, this paper constructs the real-time remote sensing on-orbit intelligent processing architecture for Earth observation mission coordination of satellite network. The large-scale computing resources scattered in the space physical environment are used to realize on-orbit processing of intelligent remote sensing satellites and real-time transmission back to Earth, supporting the rapid response of remote sensing satellites from observation to decision making, and intelligent application services. Aiming at the characteristics of ultra-low orbit constellation and space large-scale computing resources, three typical applications of rapid mapping support service, weapon precision guidance operation, emergency monitoring information extraction are designed, covering the application scenarios of three real-time services: information collection, command and control, and broadcast and distribution.
References
- Zhang, Z.; Qu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Cao, J.; Xie, G. Expandable On-Board Real-Time Edge Computing Architecture for Luojia3 Intelligent Remote Sensing Satellite. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, H.; Massawe, J. Semantic Representation of Space Device and Material for Remote Sensing Satellite. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 644, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roithmayr, C.M.; Lukashin, C.; Speth, P.W.; Kopp, G.; Thome, K.; Wielicki, B.A.; Young, D.F. CLARREO Approach for Reference Intercalibration of Reflected Solar Sensors: On-Orbit Data Matching and Sampling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6762–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Ruf, C.; Keihm, S.; Kitiyakara, A. Jason Microwave Radiometer Performance and On-Orbit Calibration. Mar. Geod. 2004, 27, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lin, M.; Zhao, J.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, C. On-Orbit Calibration Method for Correction Microwave Radiometer of the HY-2 Satellite Constellation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, B.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Nie, C. On-Orbit Calibration Approach Based on Partial Calibration-Field Coverage for the GF-1/WFV Camera. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2019, 85, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, F. Intelligent remote sensing satellite and remote sensing image realtime intelligent service. Acta Geod. Cart. Sin. 2019, 48, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, C.O.; Horan, D.M.; Corson, M.R. On-orbit calibration of the Naval Earth Map Observer (NEMO) coastal ocean imaging spectrometer (COIS). Imaging Spectrom. VI 2000, 4132, 250–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Liu, S.Y.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Q.B. Technology Prospective of Intelligent Remote Sensing Satellite. Spacecr. Eng. 2017, 26, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y. On-Orbit Calibration of Installation Parameter of Multiple Star Sensors System for Optical Remote Sensing Satellite with Ground Control Points. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Ruf, C.; Keihm, S.; Kitiyakara, A. Jason Microwave Radiometer Performance and On-Orbit Calibration. Mar. Geod. 2004, 27, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, X.; Wang, M. Study of full-link on-orbit geometric calibration using multi-attitude imaging with linear agile optical satellite. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 980–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Chang, X.; Jin, S.; Zhu, Y. On-orbit geometric calibration and geometric quality assessment for the high-resolution geostationary optical satellite GaoFen4. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Pan, J.; Wang, M. Dynamic Task Planning Method for Multi-Source Remote Sensing Satellite Cooperative Observation in Complex Scenarios. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Yang H; Yang, M.; Yang, R.; Leng, S. Automatic Task Planning and Its On-Orbit Verification of Agile Remote Sensing Satellite. Int. J. Aerospace Eng. 2023, 2023, 8923088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, R.; Liu, N.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X. On-Board Ortho-Rectification for Images Based on an FPGA. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Meng, D.; Zong, Y.; Wang, F.; Xin, T. A Modeling and Analysis Strategy of Constellation Availability Using On-Orbit and Ground Added Launch Backup and Its Application in The Reliability Design for a Remote Sensing Satellite. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 168781401876978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, S.; Dmytro, F.; Yohei, K.; Masahiko, U; Shunsuke, O. In-Orbit FPGA Reprogramming Device for Small Satellites. Adv Space Res. 2023, 71, 4549–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Efficient Object Detection Framework and Hardware Architecture for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, G.S.; Gabriel, W.; French, M.; Flatley, T.; Villalpando, C.Y. SpaceCubeX: A Framework for Evaluating Hybrid Multi-core CPU/FPGA/DSP Architectures. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4-11 March 2017; Volume 1-10. [Google Scholar]
- Glein, R.; Rittner, F.; Heuberger, A. Adaptive single-event effect mitigation for dependable processing systems based on FPGAs. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2018, 59, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, G.; Yu, L.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, H. Self-Organizing Method on Mission-Level Task Allocation of Large-Scale Remote Sensing Satellite Swarm. Int. J. Aerospace Eng. 2022, 2022, 9307837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R. Solar particle events from a risk management perspective. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2000, 28, 2103–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Gong, W. An On-Orbit Task-Offloading Strategy Based on Satellite Edge Computing. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabogal, S.; George, A.; Wilson, C. Reconfigurable Framework for Environmentally Adaptive Resilience in Hybrid Space Systems. ACM Trans. Reconfigurable Technol. Syst. (TRETS) 2020, 13, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.D.; Wilson, C.M. Onboard Processing with Hybrid and Reconfigurable Computing on Small Satellites. Proc. IEEE. 2018, 106, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wei, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, W. FPGA Implementation for CNN-Based Optical Remote Sensing Object Detection. Electronics. 2021, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Margaret, K.; Mateo, G.; Yao, J.; Nasser, N. Advances in Geocomputation and Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI) for Mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformat. 2023, 120, 103300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jiang, S.; He, G.; Zhang, B.; Yu, Hao. TEANS: A Target Enhancement and Attenuated Nonmaximum Suppression Object Detector for Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, PP, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Shen, X.; Li, D.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J.; Yao, Wei. Super-agile satellites imaging mission planning method considering degradation of image MTF in dynamic imaging. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformat. 2024, 131, 103968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; R, Pan. Mission planning for distributed multiple agile Earth observing satellites by attention-based deep reinforcement learning method. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 2388–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P. , Shangguan, B., Hu, L., Jiang, L., Zhang, C., Cao, Z., Pan, Y. Towards a Training Data Model for Artificial Intelligence in Earth Observation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2022, 36, 2113–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Z. Large-Scale Multi-Objective Imaging Satellite Task Planning Algorithm for Vast Area Mapping. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Z. Multi-Objective Multi-Satellite Imaging Mission Planning Algorithm for Regional Mapping Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Shen, X.; Li, D.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang Di; Shen, S. Multiple super-agile satellite collaborative mission planning for area target imaging. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformat. 2023, 117, 103211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, F.; Jin, Z. Deep reinforcement learning-based autonomous mission planning method for high and low orbit multiple agile Earth observing satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 3478–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Zheng, H. Autonomous Phase Control Combining EKF and Adaptive Neural Network for Remote Sensing Satellites. Int. J. Aerospace Eng. 2022, 2022, 7153667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, M.; Dai, G.; Chen, X. A Novel Technique to Compute the Revisit Time of Satellites and Its Application in Remote Sensing Satellite Optimization Design. Int. J. Aerospace Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, S.; Ko, K. On-Board Orbit Propagator and Orbit Data Compression for Lunar Explorer using B-spline. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space. 2016, 17, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashnikov M., V.; Glumov N., I. Onboard processing of hyperspectral data in remote sensing systems based on hierarchical compression. Comput. Opt. 2016, 40, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joan, R.; Ian, B.; Francesc, L.; Joan, S.; Victor, S.; Michael W, M. A Lightweight Contextual Arithmetic Coder for On-Board Remote Sensing Data Compression. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4825–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, W.; Deng, D. Improved YOLOv3 Based on Attention Mechanism for Fast and Accurate Ship Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 660–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin-nosuke, I.; Masato, T.; Masato, T.; Yasunobu, U.; Kazunari, M.; Peihsuan, L.; Taiki, O.; Masao, Y. Example-based Explainable AI and its Application for Remote Sensing Image Classification. INT J Int. J. Appl. Obs. 2023, 118, 103215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Sang, Q.; Chen, H.; Xie, Y. An Efficient FPGA-Based Implementation for Quantized Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification Network. Electronics 2020, 9, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Shi, H.; Chen, L.; Lin, T.; Shao, X. A Novel CNN Architecture on FPGA-based SoC for Remote Sensing Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 11-13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, N.; Jing, M.; Ji, C.; Cheng, L. Evaluation of Ten Deep-Learning-Based Out-of-Distribution Detection Methods for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P. , Shangguan, B., Hu, L., Jiang, L., Zhang, C., Cao, Z., Pan, Y. Towards a training data model for artificial intelligence in earth observation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2022, 36, 2113–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrun, S.; Prashanth, V.; Sowmya, V.; Vinayakumar, R. Transformer based ensemble deep learning approach for remote sensing natural scene classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 3289–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhang, L. Scale-aware deep reinforcement learning for high resolution remote sensing imagery classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 209, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazi, Y.; Bashmal, L.; Rahhal, A.M.M.; Ricci, R.; Melgani, F. RS-LLaVA: A Large Vision-Language Model for Joint Captioning and Question Answering in Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).