1. Introduction
Bone fractures are a significant worldwide public health issue that imposes serious economic and social burdens [
1]. Fractures can lead to absence from work, decreased productivity, disability, poor quality of life, loss of health, and high healthcare costs, imposing a substantial burden on individuals, their family members, and healthcare systems [
2]. According to Ai-Min Wu et al., in 2019, there were 178 million new fractures, 455 million prevalent cases of acute or long-term fracture symptoms, and 25.8 million YLDs (years lived with disability) worldwide [
3]. From a meta-analysis of 113 studies, the collective spending for hip fracture management in hospitals is estimated to be US
$10,075, and total health and social care costs per hip fracture averaged US
$43,669.7 at 12 months [
4]. Given the global trend of increasing aging and obesity in the population and the associated increased risk of fractures, the search for new effective treatments for fractures is of great importance [
5,
6]. Particular attention should be paid to complex clinical conditions that require enhanced bone tissue regeneration, such as the reconstruction of large bone defects resulting from trauma, infection, tumor resection, and skeletal abnormalities, as they often cannot heal on their own [
7].
Currently, there are many different approaches to restoring the impaired or “insufficient” process of bone tissue regeneration, among which the most frequently used is bone grafting - a surgical method in which the missing bone is replaced with a bone graft [
8]. In bone grafting, implantation of bone autografts, allografts, metal devices, porous glasses, and ceramics is used [
9]. Each year, several million bone-grafting operations are performed worldwide, where the main bone grafts are natural bone autografts and allografts [
10]. However, natural bone grafts have their own disadvantages and limitations, the main ones being their high cost, limited availability, and possible risks of infection of the recipient [
11]. Therefore, an alternative approach is the use of synthetic bone grafts, which have no risk of disease transmission and good reproducibility of the chemical composition and porous structure [
9]. In particular, biodegradable synthetic transplants are of considerable interest since they are capable of being absorbed into the human body and, over time, replaced by natural bone tissue, which makes it possible to avoid repeated surgical interventions.
Among the biodegradable synthetic bone grafts available, the most commonly used are calcium phosphate ceramic implants: synthetic hydroxyapatite (Ca
10 (PO
4)
6(OH)
2, HA) and tricalcium phosphate (Ca
3(PO
4)
2, β-TCP) and their mixtures called biphasic calcium phosphates (BCP) [
12]. β-TCP is highly biocompatible and bioresorbable and enhances bone regeneration [
13,
14,
15,
16] due to the similarity in crystal structure and chemical composition with the inorganic phase of natural bone [
17,
18]. β-TCP is capable of filling critical-sized bone defects and possesses osteoinductive and osteoconductive properties, as well as the ability to promote biomineralization [
18]. In addition, β-TCP is a more rapidly absorbable ceramic compared to HA, which makes β-TCP more convenient for clinical use [
19]. It was shown that β -TCP grafts are completely replaced by natural bone within 3 years after transplantation [
20].
Currently, β-TCP is commercially available and is used as a bone graft by brands such as ChronOS
®, GUIDOR
® easy-graft, Poresorbs-TCP
®, etc. Its efficacy and safety were proven in many clinical studies [
17,
21]. However, despite the faster bone regeneration compared to HA, the osteoinductive potential of β - TCP is still not enough to achieve parameters identical to natural bone or bone grafts, and its resorption rate is still lower than the rate of new bone formation [
18,
22]. The introduction of transition metal ions, also present in the human body, can circumvent these problems by offering characteristics that are suited for specific applications. These ions can impart additional properties, such as enhanced mechanical strength and antimicrobial activity, to the ceramic material [
23,
24]. Moreover, the controlled release of these ions can stimulate cellular responses and promote tissue regeneration in biological environments [
18,
25,
26].
Among the known trace elements, special attention is given to strontium, which is often used to improve the physicochemical properties of biomaterials [
27]. It was shown that the replacement of calcium (Ca
2+) by strontium (Sr
2+) in the crystal structures of β-TCP increased its solubility and improved the mechanical properties of β-TCP, enhancing compressive strength and density [
28]. It also enhanced its biocompatibility, promoting cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation [
29,
30,
31,
32]. Sr-doped β-TCP exhibited better osteogenesis and slower degradation in vivo compared to pure β-TCP [
29]. Recently, other studies have shown that β-TCP Si/Zn-substituted with Sr-apatite coating improved the osteoinductive properties of the graft [
33]. The addition of Sr to collagen/β-TCP scaffolds increased alkaline phosphatase activity in mesenchymal stem cells [
34]. Overall, Sr doping of β-TCP showed potential for enhancing bone regeneration and creating controlled-release bone graft materials [
35].
Another important challenge in bone grafting with β-TCP implants is the lack of inherent antibacterial activity, which increases the risks of bacterial colonization and bone infection, potentially leading to serious complications in patients [
36,
37,
38]. One promising approach to enhance the antibacterial properties of the implant is though chemical doping of bioceramics with ions that possess antibacterial action [
37,
38]. Recently, elements such as silver (Ag), zinc (Zn), cerium (Ce), samarium (Sm), and copper (Cu) have been incorporated into implant coatings, effectively suppressing microbial growth at the implantation site [
37,
38]. In 2016, it was demonstrated that the antimicrobial activity of β-TCP-substituted compounds increased in the order of Ag <Fe <Cu <Zn [
39]. Notably, there has been renewed interest in copper as an essential trace mineral with numerous biological functions, including antibacterial properties, angiogenesis, and osteogenesis stimulation [
9]. In the works of Fadeeva et al., the addition of Cu ions to β-TCP improved its antibacterial properties without compromising the biocompatibility, making it a more attractive option than pure β-TCP for clinical applications [
40].
However, given the fact that a higher copper content in biomaterials provides a better antibacterial effect, but increases cytotoxicity, a number of studies have utilized joint substitution or so-called binary doping of copper with various ions to reduce side effects [
41,
42,
43], and it is reasonable to assume that strontium might be a good candidate for binary doping with Cu. As an example, Huang et al. showed that binary doping with strontium and copper hydroxyapatite (SrCuHA) on commercially pure titanium (CP-Ti) effectively compensated the cytotoxicity of Cu and stimulated osteogenic differentiation [
43]. In a similar study, a bioimplant composed of bioactive glass doped with strontium and copper had osteoinductive and antibacterial effects and also stimulated angiogenesis in vitro and promoted wound healing in rats [
42]. Lebedev et al. showed that Sr, Cu-co-doped solid solutions of the composition Ca
9.5–xSr
xCu(PO
4)
7 possessed significant inhibitory activity against pathogenic strains
Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus [
24]. Recent studies have demonstrated that Sr ions alone also possess antimicrobial effect. Sr-TCP coatings, produced using Ionized Jet Deposition technique, have significantly inhibited
Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus growth by reducing bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation [
44]. Additionally, the study by Rau et al. demonstrated that coating a zinc-lithium (Zn-Li) biodegradable alloy with double-doped strontium and copper resorbable tricalcium phosphate (SrCu-TCP) using the Pulsed Laser Deposition method inhibited the growth of four bacterial strains by 24–35% [
45]. Given the information provided, in this study, we synthesized tricalcium phosphate co-doped with copper and strontium and evaluated its cytotoxicity, hemolytic properties, osteogenic, and angiogenic potential in vitro, with the goal of advancing to in vivo studies.
Based on the information provided above, this study focused on evaluating cytotoxicity, hemolytic properties, osteogenic, and angiogenic potential in vitro of synthesized granules of tricalcium phosphate co-doped with strontium and copper, with the aim of progressing towards in vivo studies.
2. Materials and Methods
TCP granules synthesis and doping with Sr and Cu
Double-substituted tricalcium phosphate powder with copper and strontium was synthesized using the solid-phase method, as previously described [
24,
46]. Briefly, the initial reagents were combined in a planetary mill in quantities determined by reaction (1):
The mixture of 2.42 g of copper nitrate tetrahydrate, 2.12 g of strontium nitrate, 13.6 g of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate, and 5 g of calcium carbonate was placed in a corundum crucible and heated at 1150°C in a chamber furnace with silicon carbide heaters for 4 hours. The resulting ceramic was milled with corundum balls in a planetary mill for 30 min, after which the mixture was again placed in a corundum crucible and heated for 4 hours. The described operations were repeated 5 times. The phase composition of the obtained powder was determined by X-ray diffraction analysis using a Rigaku diffractometer (Tokyo, Japan) with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 0.154 nm) in the angular range of 10-60 degrees 2θ scale. The ceramic targets were obtained from synthesized powder of double-substituted tricalcium phosphate with copper and strontium by double-sided uniaxial pressing in steel molds at a specific pressing pressure of 200 kgf/cm2. The targets were sintered in a chamber furnace with silicon carbide heaters at a temperature of 1200°C for 2 hours. The solubility and ion release from the prepared ceramics were studied at 37°C and pH 7.4 in a model solution of 0.9% sodium chloride solution with TRIS buffer by measuring the concentration of calcium, copper, and strontium ions. The ratio of ceramics to saline solution was 5 mg/ml. The ion concentrations were determined at specific time intervals in the model solution using an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer Ultima II.
Ceramic CuSr TCP granules were prepared as described in [
47]. Briefly, a suspension of CuSr TCP powder with a 5% aqueous solution of polyacrylamide (PAA) was prepared in a powder: PAA solution ratio of 1:5 by weight. The resulting suspension was impregnated into a polyurethane sponge, dried in room temperature, and then fired at a temperature of 1200°C for 2 hours. The phase composition of the obtained granules was determined as described above.
CCK-8 viability assay
CCK-8 (96992, Sigma Aldrich) was used to evaluate the proliferation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and human osteoblast cell line hFOB1.19 (CRL-3602, ATCC) in vitro. In brief, 5 x 103 cells were seeded into each well of a 96-well plate and incubated for 1, 2, 3, 7 and 14 days with CuSr TCP granules-enriched media in different concentrations – 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/ml (3-day extract). Once incubated, 10µl of CCK-8 solution was added to each well and incubated for 4 hours. A control group was incubated in the plain DMEM media with no implant extracts. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (Bio Tek Synergy H1, USA).
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay for Cytotoxicity
5 x 10
3 cells were seeded into each well and incubated for 24 hours with granules enriched (3-day extract). The next day, lysis buffer was added to the maximum LDH release wells, and sterile water to others. After 45 min of incubation at 37°C, 50µl media from each well was transferred to another plate. A 50µl reaction mixture was added to each well and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. After incubation, 50 µl of stop solution was added to each well, and absorbance was read at 490 nm and 580 nm. No treatment wells were referred to as a spontaneous LDH activity group. The maximum LDH activity group served as a 100% cytotoxicity level. The cytotoxicity was calculated using the following equation:
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
CuSr TCP discs were seeded with 1 x 10
4 BM-MSCs cells and cultured in complete DMEM/F-12 (DMEM/F-12 + 10% FBS (F2442, Sigma Aldrich + 1% Penicillin-streptomycin) for 48 hours. The protocol for staining was adopted and modified by Geekiyanage et al. [
45]. Then, cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes and stained with 1M Osmium Tetroxide for 1 hour, rinsed twice with Milli-Q water for 10 minutes, dehydrated with Ethanol (from 70% to 100%), and incubated with HDMS (hexamethyldisilazane for 30 minutes. Following 30 minutes of drying, samples were covered with a 20 nm layer of gold. An assessment of the sample’s topography was performed by Zeiss Crossbeam 540 (Zeiss, Germany).
Transwell Migration Assay
BM-MSCs were seeded in the upper membrane of transwell plates with a concentration of 6×10
4 cells each in 100 μL serum-free DMEM (D6046, Sigma Aldrich) +1% Penicillin-streptomycin (15140122, Gibco) medium per well and the lower wells were poured with 1mL complete DMEM (DMEM + 10% FBS (F2442, Sigma Aldrich) + 1% Penicillin-streptomycin). Then, the plate was incubated at 37°C, 5% CO
2, with a humidifier for 8 hours. After incubation, the cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde for 30 min and washed. Finally, 0.2% Crystal Violet (V5265, Sigma Aldrich) was used to fix and stain migrated cells on the lower compartment of the upper chamber. Ultra-pure water was used to wash the stain, and then 5 pictures of each compartment were randomly photographed in a 200× microscope field. The total number of migrating BM MSCs was calculated and compared for each group using Image J software. The methodology was modified from the protocol by Justus et al. [
49].
Alkaline Phosphatase Assay
Human premature osteoblast cells (hFOB1.19, ATCC, CRL-3602) were seeded at 8x104 cells per well density to the 48-well plate and cultured until 90% confluency was reached. Then, cells were transferred to 39°C for osteogenic differentiation induction. Further, cells were treated with CuSr TCP granules-enriched media (3-day extract) for 2 weeks. Then, cell medium supernatants were collected, and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) levels were measured using an ALP Assay Kit (ab83369, Abcam). ALP enzyme of known concentration was plated in a serial dilution to create a standard curve. pNPP substrates were added to each standard and sample well and incubated for 60 min at room temperature. ALP enzyme converts pNPP substrates to a colored p-nitrophenol (pNP). After incubation, a stop solution was added, and absorbance was recorded at OD405nm with a microplate reader (Bio Tek Synergy H1, USA). Groups with plain DMEM media served as a negative control for differentiation. No treatment group served as a control.
Alizarin Red S
BM-MSCs were seeded at 8 x 104 cells per well density into the 48well plate and cultured until 90% confluency. Then, the cells were cultured in osteogenic media (Osteogenesis Assay Kit, ECM815, Merck) and incubated with granules for 3 days. At week 5th of differentiation, cells were washed, fixed with 500µl 4% formaldehyde for 30min and stained with 500µL 2% Alizarin Red S (A5533, Sigma Aldrich) for 1 hour, then washed 5 times with MulliQ water for 30 min each time. After the washing, the stain was extracted from the differentiated monolayer with 400ul 10% acetic acid, heated at 85°C for 10 min, and centrifuged to 20000 rcf for 15min. The supernatant was collected, and the pH was adjusted to 4.1-4.5. Then, the supernatant was transferred to a microplate reader OD 405 nm, and the concentration of Alizarin Red S was calculated from the standard curve obtained from the standards.
Angiogenesis assay
An angiogenesis starter kit (A14-609-0, Gibco) was used to assess the angiogenesis. Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC, C-003-5C, Gibco) were pre-treated in media with different TCP granule concentrations (1mg/ml, 0.5mg/ml, 0.1mg/ml) for 72 hours. HUVEC in the concentration of 4.2 x 103 per well were seeded in a GelTrex matrix-coated 24-well plate for 16h. After 16 hours, the plate was stained with 2 µg/ml of Calcein AM, incubated for 30 min, and imaged at 4X magnification with Cytation 5 (BioTek, USA). Images were assessed with the Image J Angiogenesis Analyzer Plugin.
Blood hemolysis test
The in vitro hemolysis assay was performed on human erythrocytes. All procedures related to the blood collection were performed according to the protocols approved by the Local Ethics Committee of National Laboratory Astana (Registration number IORG 0006963, N02-2022, 01.04.2022). Briefly, blood samples were collected from healthy volunteers in K2-EDTA vacutainers and centrifuged at 500 × g for 10 min. After several PBS washes, the plasma from the fresh blood sample was removed, and red blood cells (RBC) were diluted to prepare a 4% (v/v) RBC solution in PBS. Subsequently, 800 μL of RBC solution in separate Eppendorf microtubes were mixed with either 200 μL of PBS (used as a negative control), Triton-X solution (positive control), or TCP granules diluted in 0.2 mL of PBS in concentrations of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/mL. The mixture was then incubated for 2 hours at 37 °C with mild stirring breaks every half-hour. Following the incubation period, the mixture was centrifuged for 10 min at 2,000 × g. Then, 100 μL of the supernatant was taken into the 96-well plates. The absorbance (OD) at 570 nm was determined using a Synergy Hybrid H1 Microplate Reader (Biotek, USA). The percentage of hemolysis was calculated using the following equation:
2.1. Characterization of CuSr TCP
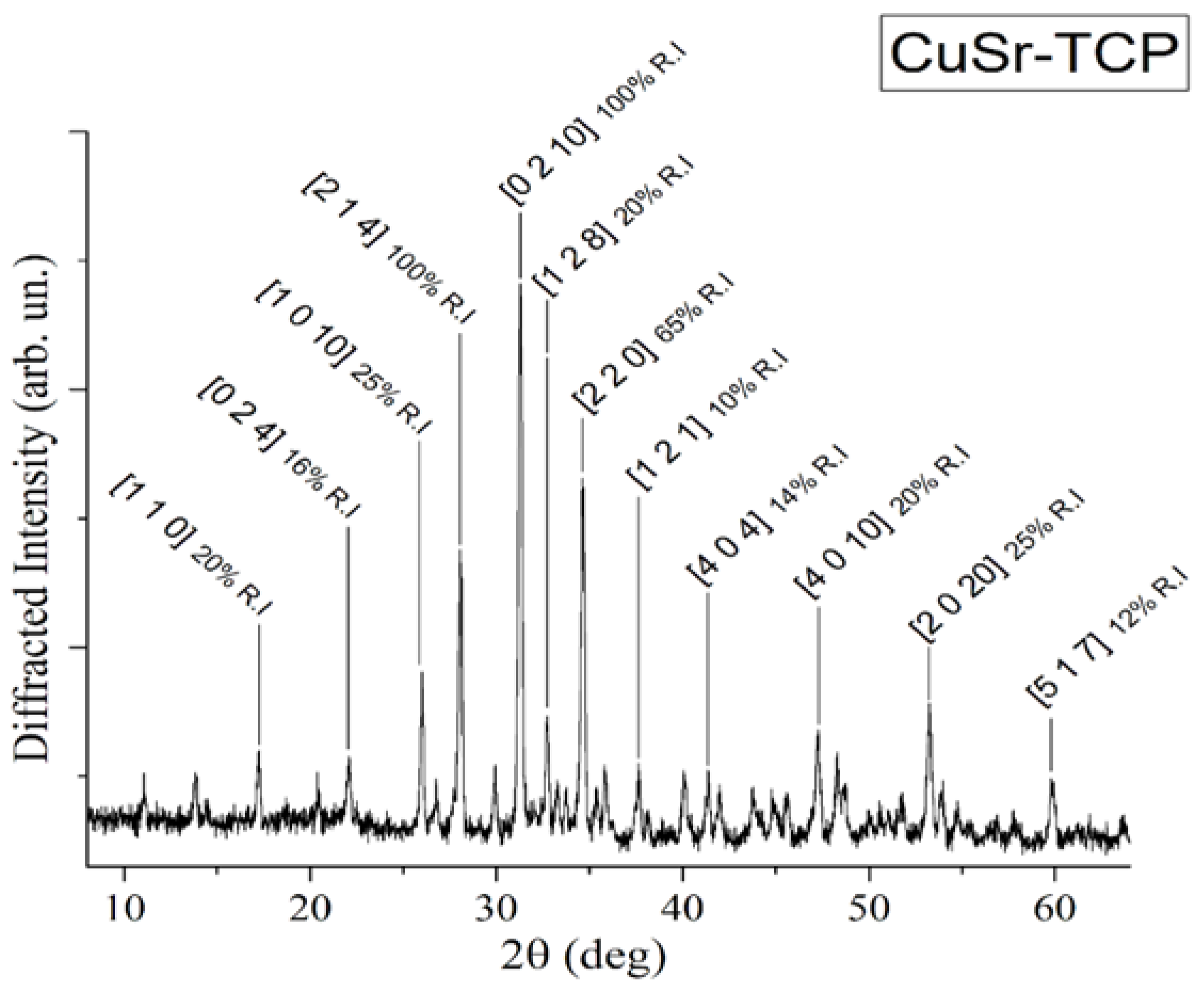
XRD pattern of CuSr substituted TCP ceramic is shown in
Figure 1.
The analysis of the diffraction pattern indicated that the sample is of the β-TCP structural type, in agreement with the work of Deyneko et al. [
46]. No diffraction peaks of impurities from apatite or pyrophosphate phases were detected, thereby verifying the completeness of the synthesis process.
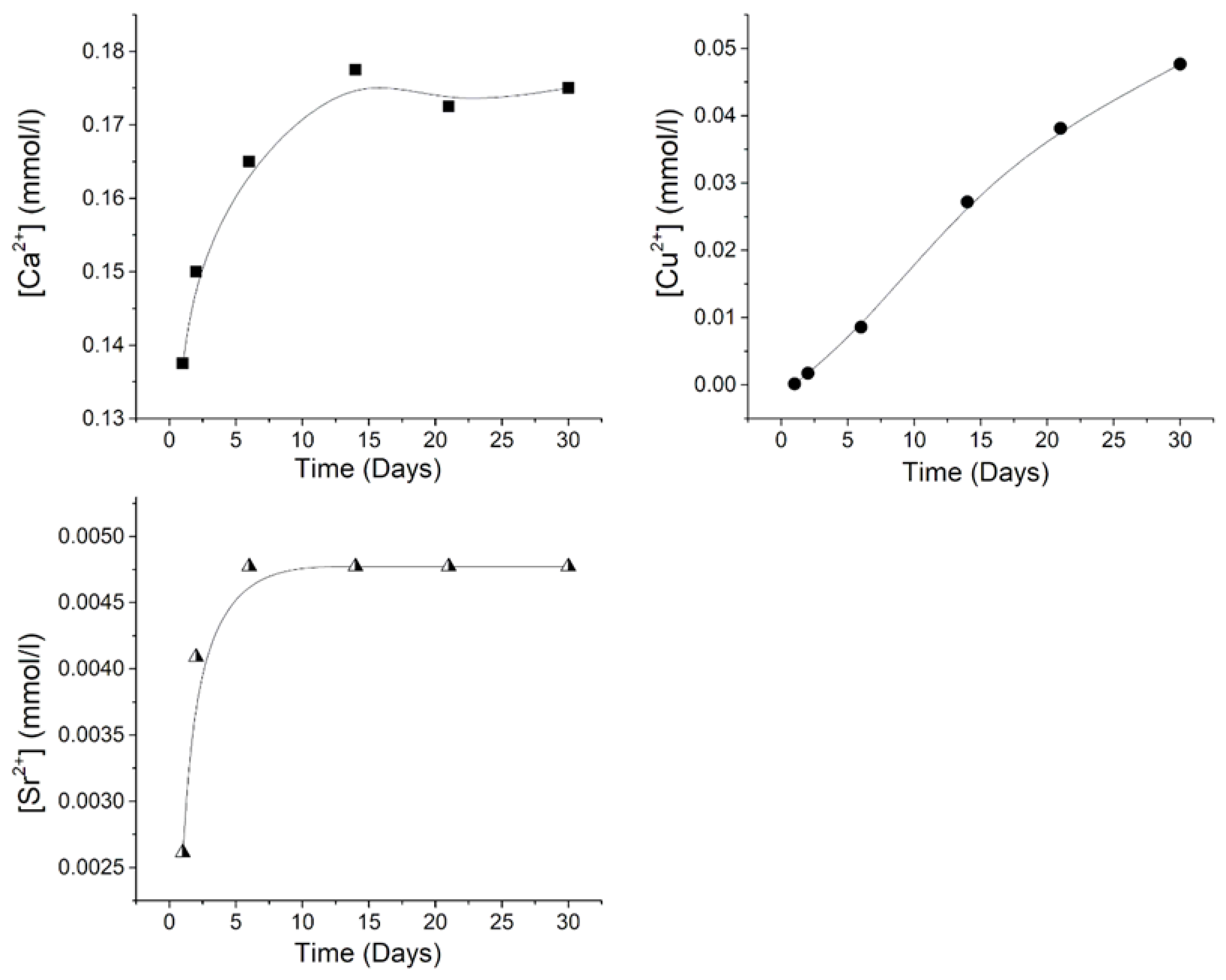
The cumulative release of Ca
2+, Cu
2+, and Sr
2+ ions from CuSr TCP ceramics after soaking for 30 days in a 0.9% sodium chloride solution with TRIS buffer is illustrated in
Figure 2. As can be seen from the obtained results, distinct release behaviors are observed for all detected ions. The concentration of Ca
2+ reaches a plateau of approximately 0.175 mmol/L after 15 days of soaking. Conversely, the Cu
2+ concentration exhibits an almost linear trend throughout the entire 30-day period, with the highest value of 0.048 mmol/L, while the Sr
2+ concentration plateaus after 7 days, reaching a value of 0.00475 mm/L.
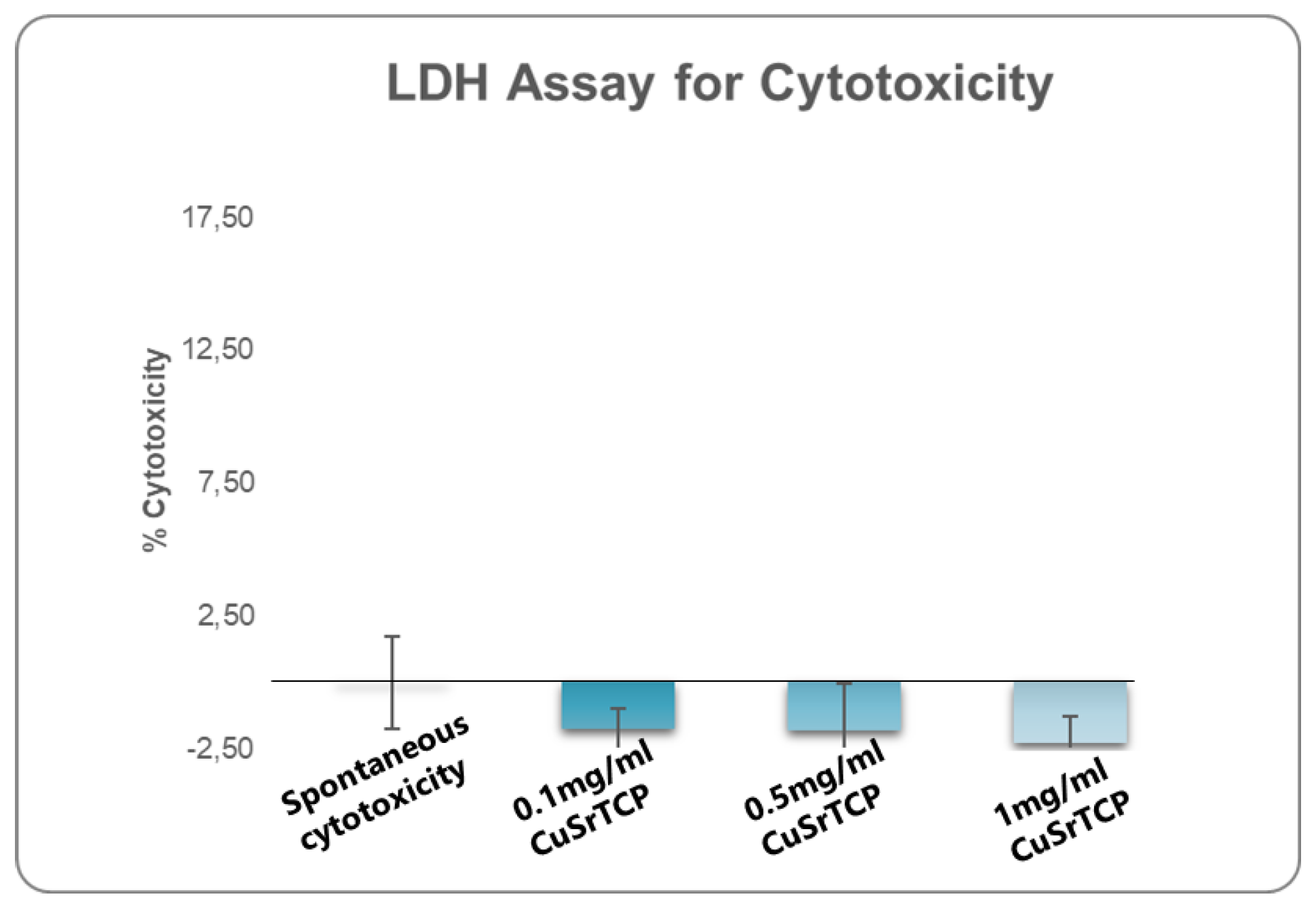
2.2. Cytotoxicity and Hemocompatibility of CuSr TCP
One of the fundamental assays commonly employed in standard cytotoxicity testing is the assessment of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. LDH is a stable cytoplasmic enzyme present in all cells, and its release into the extracellular environment serves as a marker of cell membrane integrity [
50]. When cells undergo damage or death, primarily through necrosis or late apoptosis, the compromised cell membrane allows LDH to leak into the surrounding culture medium. Quantification of the amount of LDH provides a reliable measure of cell death and membrane damage. In our study, a media enriched with Sr, Cu-TCP in concentrations ranging from 0.1 mg/ml to 1 mg/ml did not show significant cell damage that would exceed 2% (
Figure 3).
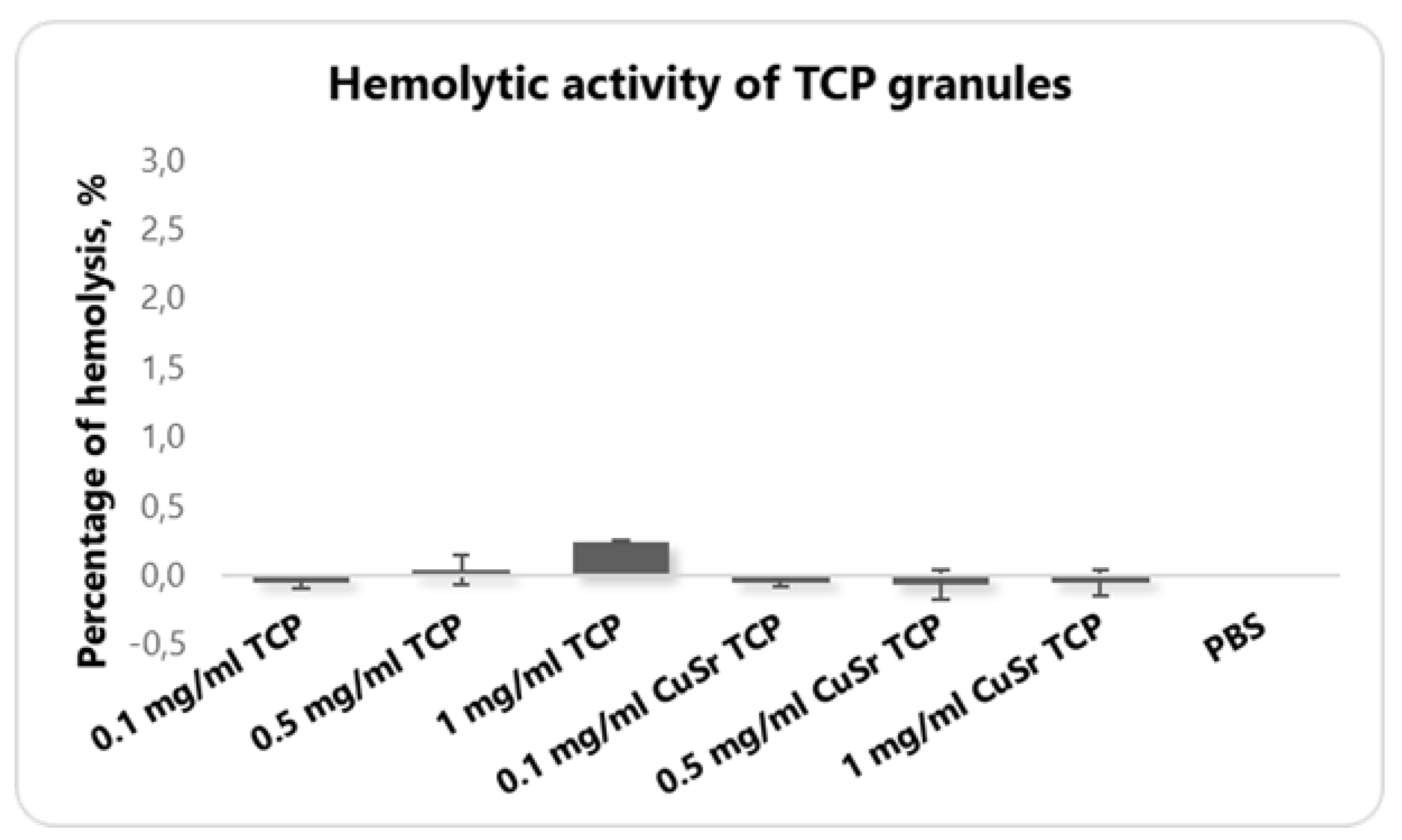
The hemolytic activity assay is an essential part of preclinical safety testing, ensuring that the material is biocompatible and reducing the risk of systemic toxicity during in vivo experimentation. Hemolysis refers to the destruction of red blood cells (RBCs), leading to the release of hemoglobin into the surrounding plasma. An in vitro hemolytic assay evaluates the potential for a material to cause RBC membrane damage, which is important for determining its biocompatibility and safety before proceeding with in vivo studies. A hemolysis rate of less than 5% is generally considered acceptable for materials intended for in vivo applications, as this indicates minimal disruption of RBC integrity. None of the groups demonstrated the hemolysis that exceeds even 1% (
Figure 4).
2.3. Effects of CuSr TCP on Cell Proliferation and Motility
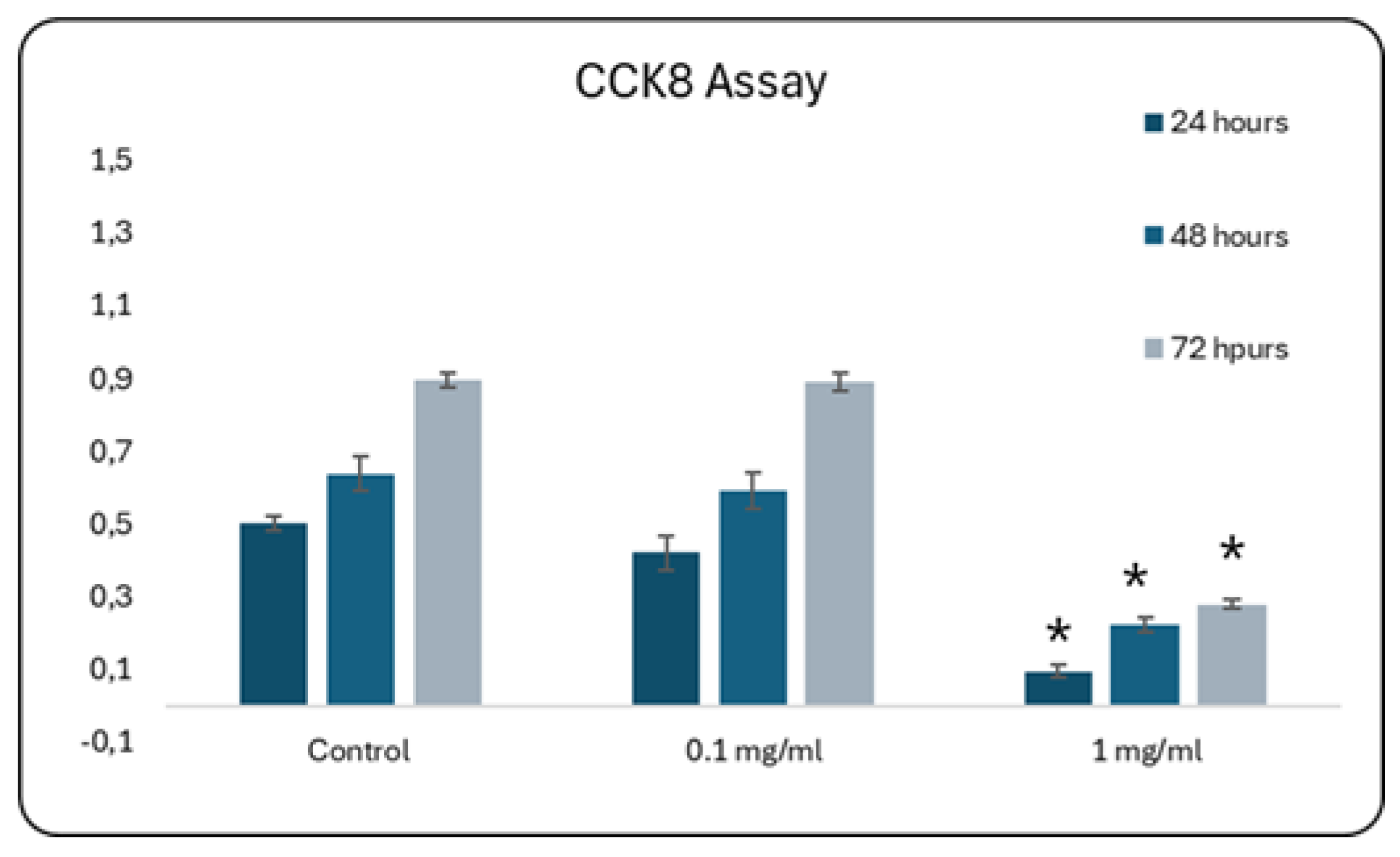
The next step in accessing the in vitro biocompatibility of double-ion-doped CuSr-TCP was aimed at elaborating the concentration of ceramic granules that would not affect cell growth. We assessed the proliferation of primary rat MSCs as a model of the bone progenitor cells during 72 hours using CCK8 (Sigma-Aldrich) assay. CCK8 is based on producing a water-soluble formazan dye when the tetrazolium salt, WST-8, is reduced by dehydrogenases in live cells. In our study, a media enriched with 0.1 mg/ml of CuSr TCP did not significantly affect cell growth and was comparable to no treatment control (
Figure 5).
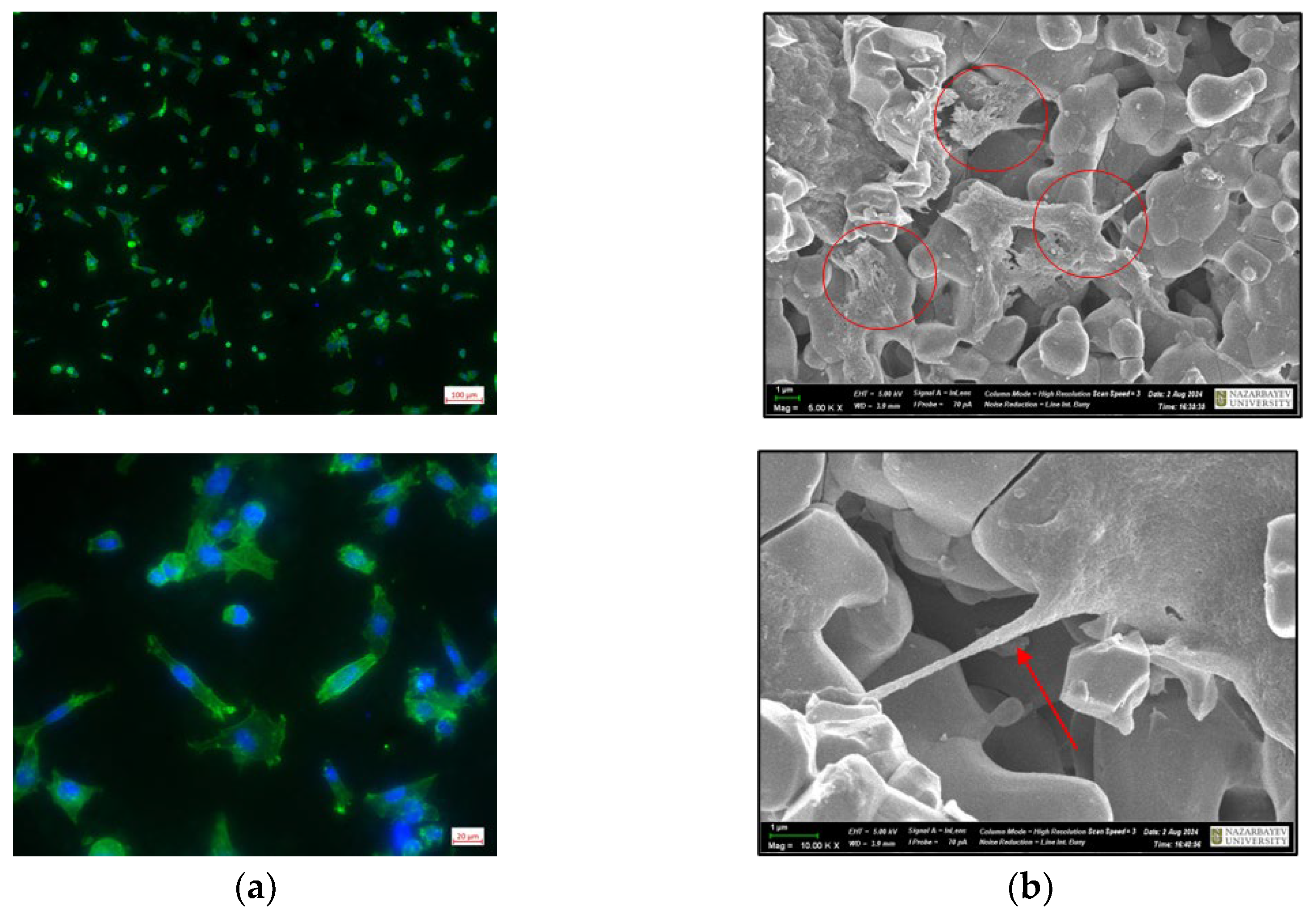
Cells can sense the three-dimensional structure of the substrate on which they grow, and, in turn, substrate topography can significantly affect cellular morphology and functions. In our study, we applied inverted fluorescent and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to assess the interaction of BM-MSCs with the CuSr TCP surface. Immunofluorescent images of the BM-MSCs attached to the CuSr TCP discs after 2 days of culture are presented in
Figure 6A. Visualized through phalloidin staining, the actin filaments exhibited a well-defined structure with prominent stress fibers and cortical actin, indicating proper cytoskeletal organization. SEM images of the BM-MSCs attached to the CuSr TCP discs after 2 days of culture are presented in
Figure 6B. We have found that BM-MSCs are capable of adhering inside the pores (shown with arrows) while maintaining spindle fibroblast-like morphology typical for MSCs.
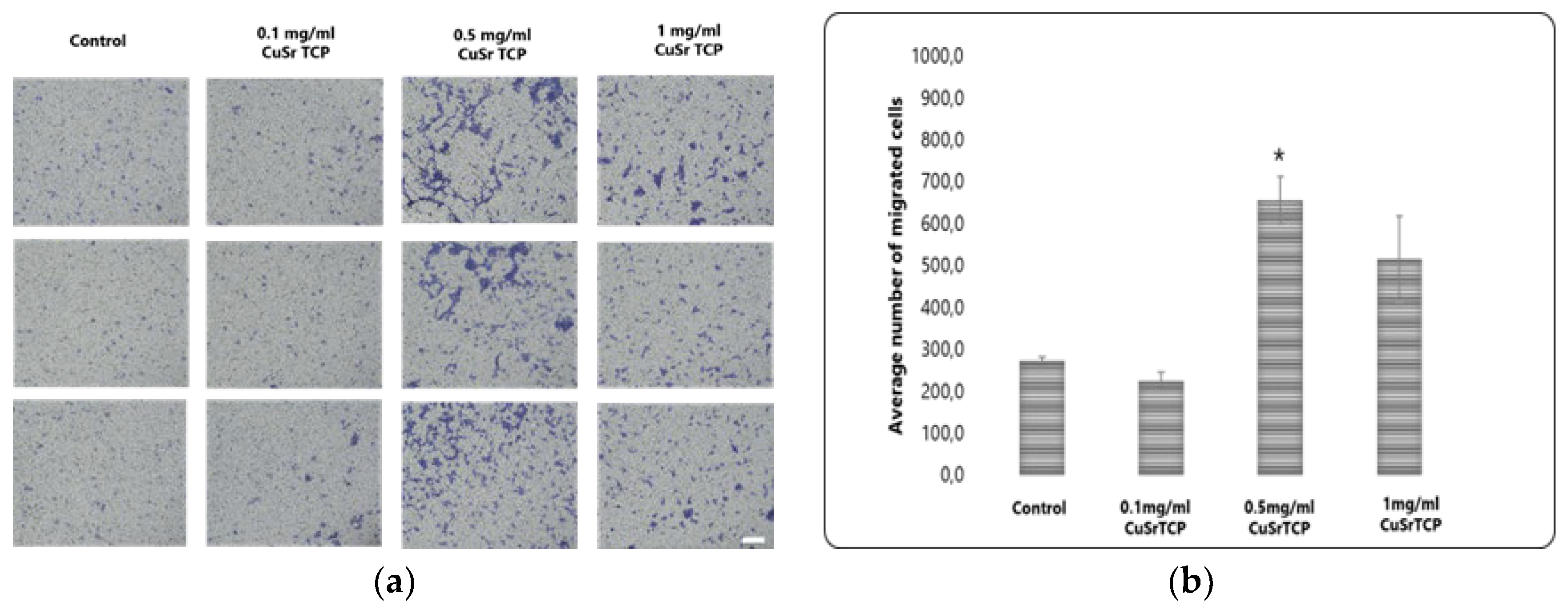
Transwell migration assay provides valuable insights into how cells respond to environmental cues. BM-MSCs were cultured in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 72 hours, then were seeded in a density of 6 x104 cells per well in 12-well plate inserts and allowed to migrate for 8 hours, then fixed, stained with Crystal Violet, and imaged under the microscope Axio Observer (Zeiss, Germany) (
Figure 7A). According to our data, media enriched with 0.1 mg/ml of granules did not significantly affect the migration ability of MSCs, while the cells in a group of 0.5 mg/ml CuSr TCP migrated more efficiently (2.5 times) than the control (
Figure 7B). The excess ions released from the CuSr TCP granules could modify the biology of a cell, resulting in increased cell motility. Overall, it is a valuable tool in developing therapeutic strategies targeting cell migration and invasion.
2.4. Effects of CuSr TCP on the Osteogenic Potential of BM-MSCs
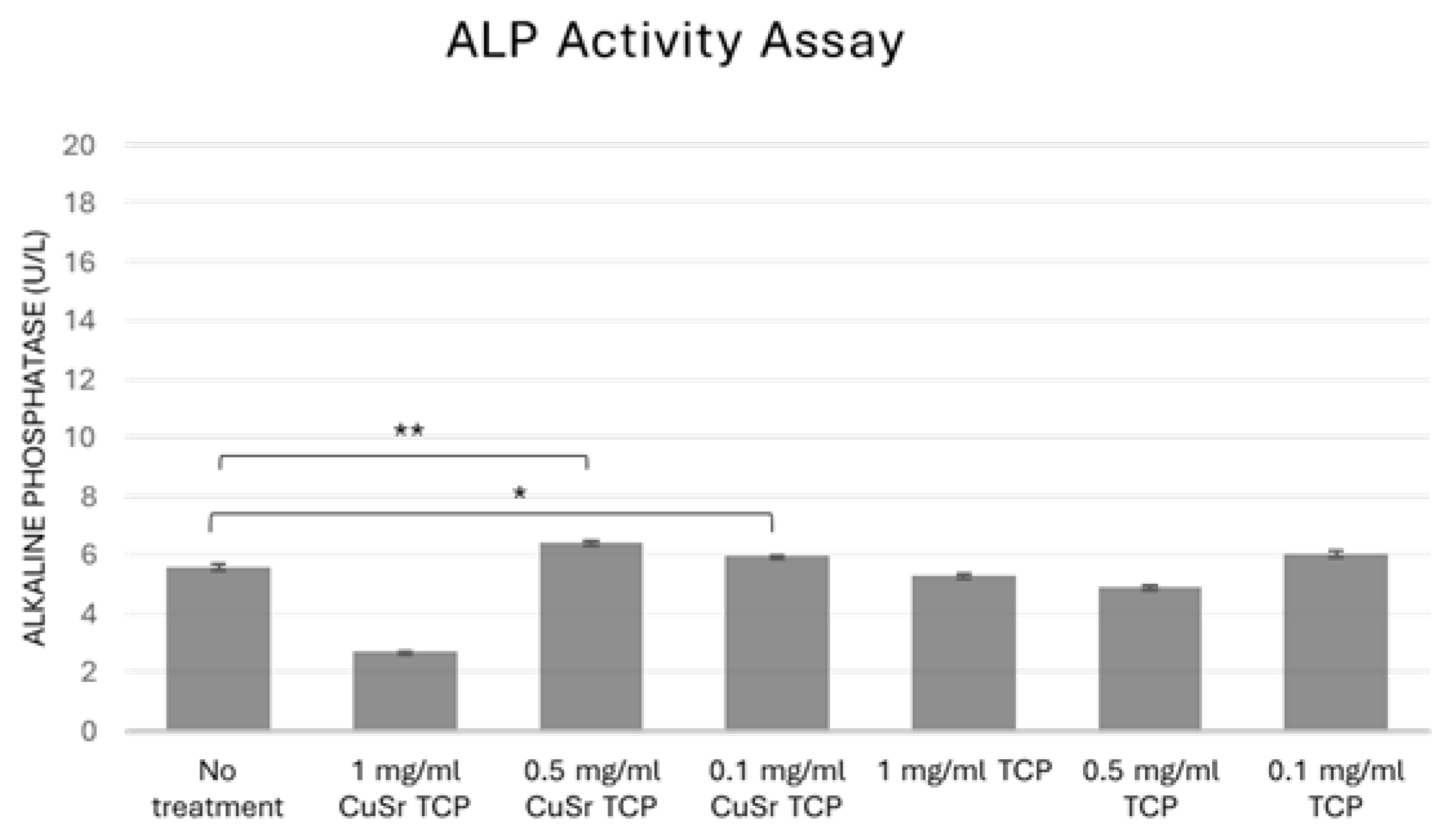
In bone biology, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is produced by osteoblasts. It is considered a key marker of bone formation, as it facilitates the deposition of calcium and phosphate in the bone matrix. Measuring ALP activity can, therefore, provide insights into bone metabolism, regeneration, and disorders like osteoporosis. In tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, assessing ALP activity is essential when developing biomaterials or therapies to promote bone growth or healing, as it is an early indicator of osteogenic differentiation. In our study, human osteoblast progenitor cells (hFOB1.19) were cultured in CuSr-TCP or TCP-enriched osteogenic media for 14 days. According to the results shown in
Figure 8, TCP-enriched media did not significantly affect osteogenic differentiation of the human preosteoblasts. At the same time, a group treated with media enriched with 0.1 mg/ml and 0.5 mg/ml of CuSr TCP showed a 5-7% increase in early osteogenesis compared to the control, suggesting that Sr, Cu-TCP may stimulate osteogenic properties of bone progenitor cells.
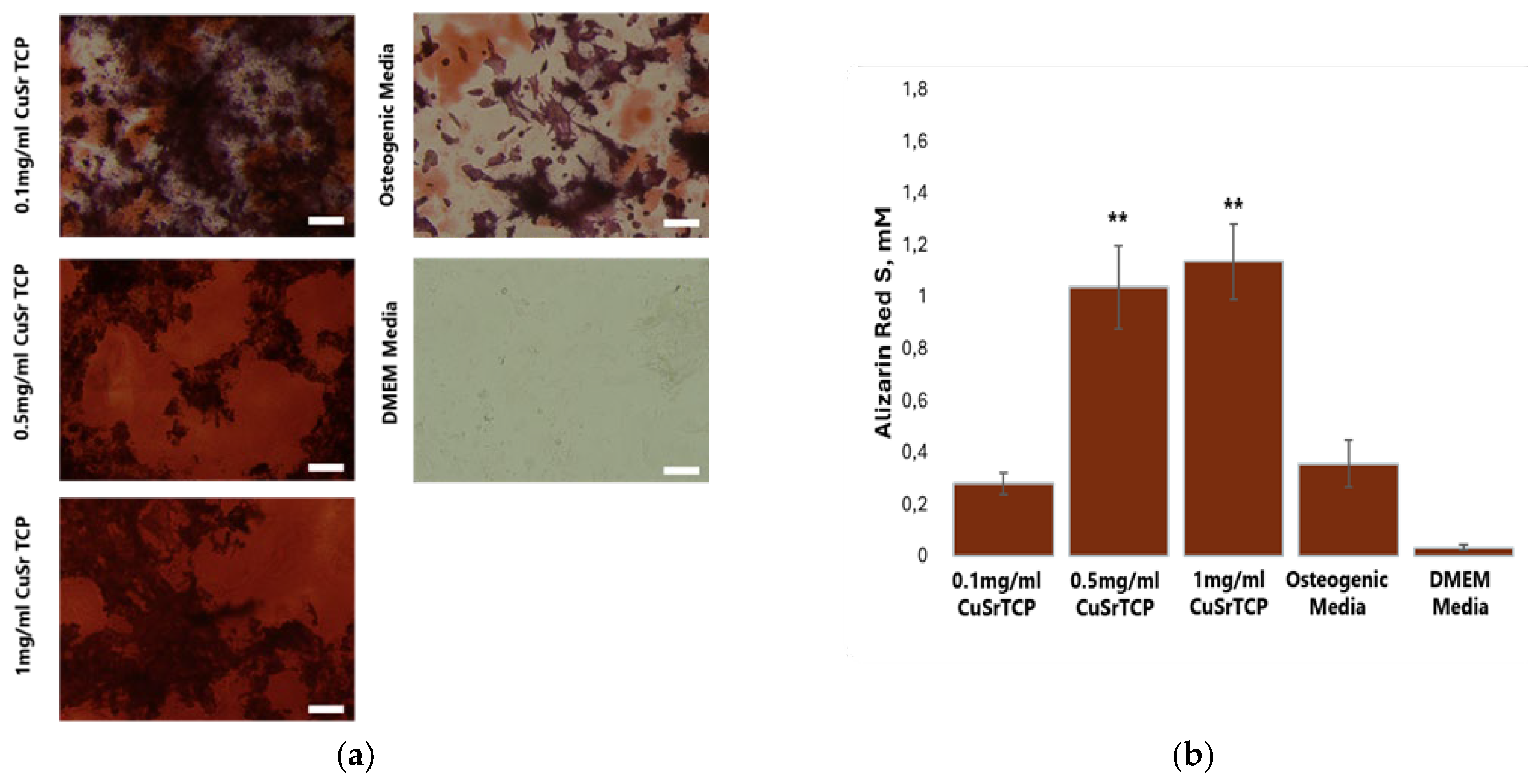
To further confirm the osteogenic potential of Sr, Cu-TCP, Alizarin Red S staining was performed on BM-MSCs on their 5th week of osteogenesis (
Figure 9A), with the concentration of the dye in stained cell extracts being calculated according to the standard curve (
Figure 9B). As Alizarin Red S dye stains calcium deposits in the osteoblasts, this method is considered the main approach to quantify osteoblast mineralization and it is a marker of osteogenesis. To perform osteogenesis, osteoblast differentiation media was enriched with TCP ceramic porous granules modified with Sr and Cu at 0.1 mg/ml, 0.5 mg/ml, and 1 mg/ml. The results confirmed that CuSr TCP increased osteogenic activity and osteoblast mineralization in BM-MSCs in a concentration-dependent manner, with granules concentration of 1 and 0.5 mg/ml inducing the highest osteogenic activity as compared to undifferentiated cells and cells that have undergone standard differentiation with no CuSr TCP enrichment.
2.5. Angiogenic Potential of CuSr TCP
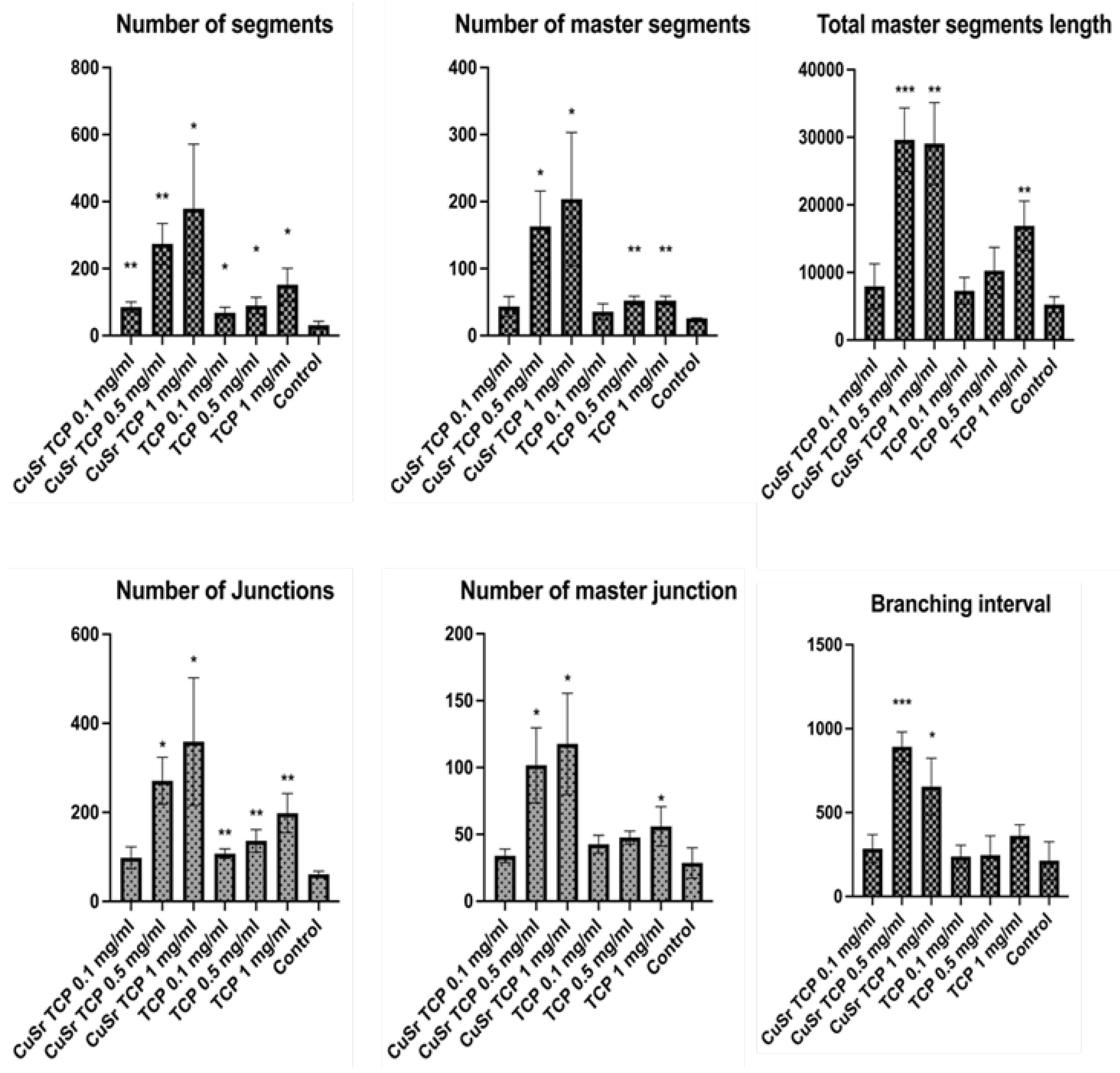
The influence of Sr and Cu-substituted TCP on angiogenesis was investigated in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Key parameters examined included the number of junctions, branches, master junctions, segments, master segments, total branching length, total branch length, branching interval, and total master segment length (
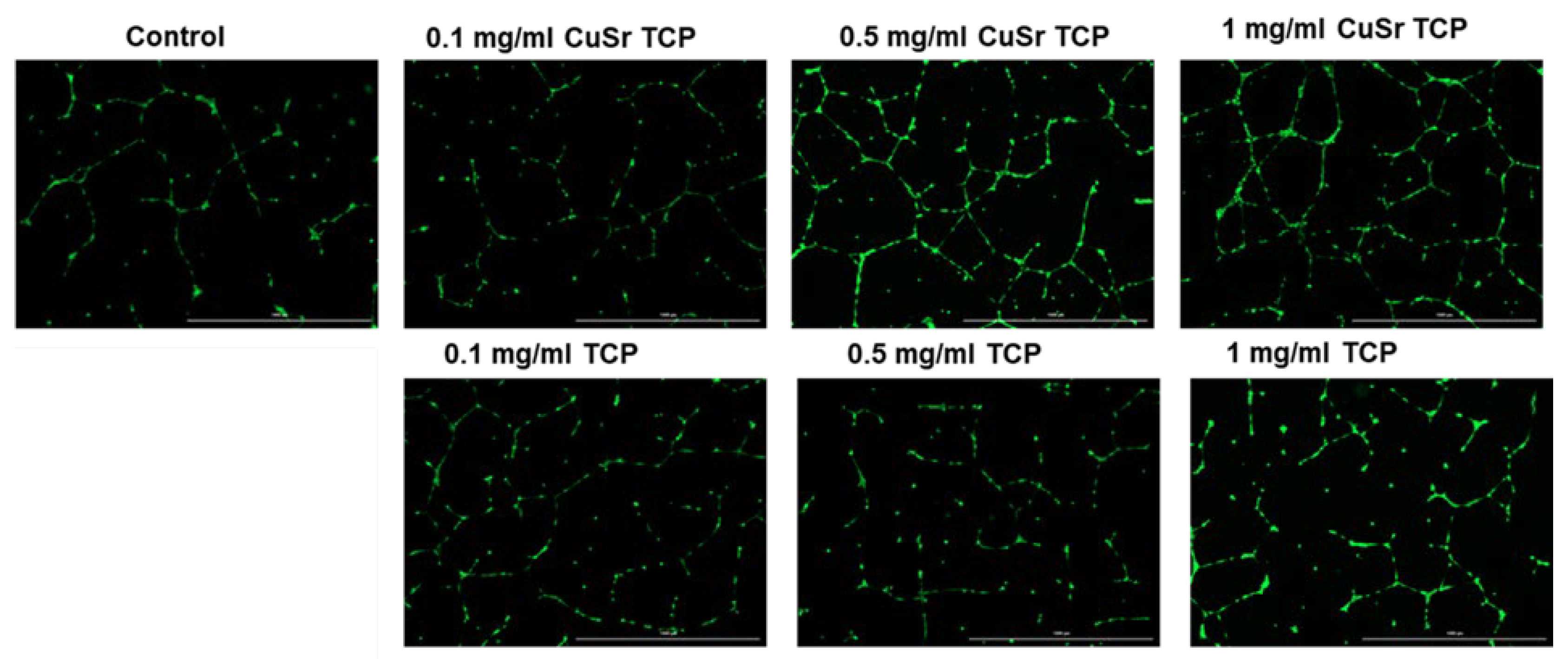
Figure 10). Media enriched with CuSr TCP in concentrations of 0.5 mg/ml and 1 mg/ml showed the most prominent angiogenic effect. The number of segments in those groups was 8 and 12 times higher, respectively. The number of master segments and following segments length were subsequently increased. During the vessel development cells form tubular structures and begin sprouting. The number of junctions are considered to be a measure of the sprouting. Both groups (0.5 and 1 mg/ml) showed a 4.5 and 6-fold increase in junctions, master junctions, and branching interval compared to the control. The TCP-treated groups, while effective to some extent, do not reach the same level of effect as CuSr-treated groups. The results demonstrated that Sr and Cu substitutions in TCP particles significantly enhanced the measured angiogenic parameters compared to control and unsubstituted TCP granules. Furthermore, the angiogenic effects were concentration-dependent, with 0.5 mg/ml Cu-Sr-TCP showing better results than 0.1 mg/ml, and 1 mg/ml showing the most substantial improvements. Representative images were taken for each group to demonstrate the tube-like formations and sprouting (
Figure 11).
3. Discussion
Tricalcium phosphate ceramics offer significant advantages in bone engineering due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and osteoconductivity. Unlike hydroxyapatite, TCP is resorbable and can be completely replaced by new bone tissue [
52]. TCP ceramics promote rapid bone infiltration and ingrowth when implanted in cancellous or cortical bone. They can be fabricated into porous scaffolds with suitable mechanical properties and porosity for bone tissue engineering [
53]. TCP ceramics have shown superior tissue compatibility compared to other synthetic materials and have been successfully used in various clinical applications, including periodontal defect repair.
In our study, CuSr TCP granules were synthesized, characterized, and subjected to cytotoxic analysis with the LDH assay. During the studies, none of the concentrations revealed an adverse effect on cell viability that would exceed spontaneous cell death events. Another essential preliminary step in evaluating the biocompatibility of materials is an analysis of the hemolytic activity of TCP granules. This assay assesses the potential of the material to cause the destruction of red blood cells, which can lead to adverse biological responses if the material is incorporated into the body. The results from the hemolytic activity were promising, showing the hemolytic activity in a range of less than 2%, indicating that CuSr TCP granules exhibit low hemolytic potential.
The optimal concentration for cell growth in CuSr TCP-enriched media was also established during the proliferation studies, with the highest dose of 1 mg/ml reducing the cells’ ability to proliferate. BM-MSCs were also seeded directly on the surface of CuSr TCP granules. Immunofluorescent images have demonstrated that the cells maintained a healthy morphology, as evidenced by the organized and intact arrangement of F-actin filaments within the cytoskeleton. This arrangement is crucial for cell integrity, shape maintenance, and overall cellular health, suggesting that the cells were not only alive but also functionally active and structurally intact. SEM images confirmed the spindle-shaped fibroblast-like morphology typical for MSCs, along with their migratory behavior, as we observed the cells adhering within the pores.
Further, the motility potential of BM-MSCs cultured in CuSr TCP-enriched media was assessed with a Transwell migration assay. According to our data, media enriched with 0.1 mg/ml of granules did not significantly affect the migration ability of MSCs, while the cells in a group of 0.5 mg/ml CuSr TCP migrated more efficiently than the control. The findings of He et al. indicated that the improved migration potential of MSCs promoted osteogenic differentiation by activating the canonical Wnt-β-catenin pathway [
54]. In this context, the positive effect of CuSr TCP on the migration of cells would favor the process of osteogenesis.
Further confirming the osteogenic potential of new Sr and Cu-TCP, early and late osteogenesis analyses demonstrated a significant positive effect in the group treated with TCP doped with Sr and Cu. In this regard, Sr
2+ ions have been shown to stimulate osteogenic differentiation [
55] and suppress osteoclast activity [
56,
57]. One of the mechanisms by which Sr
2+ can influence cellular functions is through its involvement in calcium homeostasis [
58], specifically by binding to the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) homolog [
59]. This receptor normally senses the levels of extracellular Ca
2+ ions but also can be activated by divalent Sr ion and, therefore, activate downstream signaling pathways [
55], leading to enhanced proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts, stimulating the expression of osteogenic genes such as osteocalcin and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), which are crucial for bone formation, growth and mineralization in the process of osteogenesis [
55]. Further, activation of Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) happens. RUNX2 is a key transcription factor in the matrix mineralization and differentiation of osteoblasts, and its activation induces expression of bone differentiation markers such as Alkaline Phosphatase and Osteocalcin [
56,
60,
61]. In contrast, osteoclastogenesis refers to the process of osteoclast differentiation, the cells primarily responsible for bone resorption. Sr2+ ions have been shown to induce apoptosis of mature osteoclasts and decrease the receptor activator of NFkB ligand (RANKL) mRNA content [
56,
57]. Additionally, β-TCP ceramics themselves can stimulate the expression of bone-related genes and proteins, including BMP-2, TGF-β, and Runx2 [
62].
Angiogenesis plays a vital role in bone regeneration, as the formation of new blood vessels is essential for delivering nutrients and oxygen to the regenerating tissue. It has been shown that β-TCP can promote angiogenesis through increased VEGF secretion [
63,
64]. In our study, in vitro analysis of angiogenesis was performed with human umbilical vessel endothelial cells pre-treated in CuSr TCP-enriched media. These cells were chosen based on their ability to form tubular vessel-like structures. Further, the walls of the newly formed vessels were stained with a fluorescent dye and imaged, and a number of parameters were analyzed. We demonstrated that media enriched with CuSr TCP in concentrations of 0.5 mg/ml and 1 mg/ml significantly increased the number of segments, the number of master segments, the total length of master segments, the number of junctions and master junctions, and the branching interval. The number of segments refers to the individual sections between two junctions. In contrast, master segments are the main or primary vessels in the network from which smaller branches or secondary segments originate [
51]. An increase in the number of master segments indicates a more complex and hierarchical vascular network, which is crucial for the stability and functionality of newly formed vessels. The total length of master segments implies the development of longer, potentially more durable vessel-like structures. Our data suggests that CuSr TCP granules not only enhance the quantity but also improve the quality of the vascular structures, providing a solid foundation for the overall vessel network.
4. Conclusions
Our findings demonstrate that TCP granules double-doped with Cu and Sr ions promote osteodifferentiation and angiogenesis in vitro. The cytotoxicity and hemolytic activity assay results revealed the absence of toxic effects on rat BM-MSCs and human RBC cell correspondingly, showing less than 2% in both scenarios. A concentration of 0.5 mg/ml has shown a 2.5-fold increase in the migration potential of BM-MSCs, providing the ground for improved osteogenic ability. Early and late osteogenesis supported previous findings. A group of 0.5 mg/ml CuSr TCP with 6 U/L of ALP showed a 7% improvement in early osteogenesis of hFOB1.19 compared to the control group, and a more profound positive effect in late osteogenesis revealed a 2.5-fold increase in Alizarin Red S activity (1mM). The angiogenic analysis in HUVECs also showed promising results with a significant increase in group of 0.5mg/ml and 1 mg/ml CuSr TCP in the number of segments (9 and 12-fold, respectively), in number of master segments (6.3 and 8-fold, respectively), in total master segments length (5.6 and 5.5-fold respectively), number of junctions (4.4 and 5.9-fold respectively), number of master junctions (3.5 and 4.1-fold) and branching interval (4.2 and 3- fold respectively).
The absence of cytotoxic effects in these experiments underscores its biocompatibility, a crucial factor for materials used in medical applications. The increased migration potential of BM-MSCs further supports the ability of CuSr-doped TCP to promote bone formation, positioning it as a promising candidate for advanced preclinical studies. However, additional in vivo research is required to validate these in vitro results. Transitioning to animal models will provide greater insights into the material’s long-term safety, efficacy, and clinical relevance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S., S.A. and J.V.R.; methodology, Y.S., I.V.F., J.V.R.; software, A.N., A.S.; validation, A.S., A.N. and A.K.; formal analysis, B.U.; investigation, Y.S., A.N., A.S., F.O., A.K., I.V.F., J.V.R.; resources, Y.S., S.A., J.V.R.; data curation, B.U., S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.S.; writing—review and editing, S.A.; visualization, B.U.; supervision, S.A., J.V.R.; project administration, Y.S.; funding acquisition, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education RK, grant project No AP13068215.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Local Ethics Committee of National Laboratory Astana (Registration number IORG 0006963, N02-2022, 01.04.2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon a reasonable written request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere gratitude to the Nazarbayev University Core Facility, with special thanks to Dr. Alexander Arbuz for his expert assistance with scanning electron microscopy. We also wish to express our deep appreciation to Dr. Dinara Begimbetova and the Laboratory of Molecular Oncology at National Laboratory Astana for their invaluable support and for providing access to the Cytation 5 Multimode Reader (BioTek, USA), which significantly contributed to the success of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Polinder, S.; Haagsma, J.; Panneman, M.; Scholten, A.; Brugmans, M.; Van Beeck, E. The economic burden of injury: Health care and productivity costs of injuries in the Netherlands. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 93, 92–100. [CrossRef]
- Borgström, F.; Karlsson, L.; Ortsäter, G.; Norton, N.; Halbout, P.; Cooper, C.; Lorentzon, M.; McCloskey, E.V.; Harvey, N.C.; Javaid, M.K.; et al. Fragility fractures in Europe: burden, management and opportunities. Arch. Osteoporos. 2020, 15, 59. [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.-M., et al., Global, regional, and national burden of bone fractures in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet Healthy Longevity, 2021. 2(9): p. e580-e592. [CrossRef]
- Williamson, S.; Landeiro, F.; McConnell, T.; Fulford-Smith, L.; Javaid, M.K.; Judge, A.; Leal, J. Costs of fragility hip fractures globally: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 2791–2800. [CrossRef]
- Schlickewei, C.W.; Kleinertz, H.; Thiesen, D.M.; Mader, K.; Priemel, M.; Frosch, K.-H.; Keller, J. Current and Future Concepts for the Treatment of Impaired Fracture Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5805. [CrossRef]
- Hagen, A., V. Gorenoi, and M.P. Schönermark, Bone graft substitutes for the treatment of traumatic fractures of the extremities. GMS Health Technol Assess, 2012. 8: p. Doc04. [CrossRef]
- Roddy, E.; DeBaun, M.R.; Daoud-Gray, A.; Yang, Y.P.; Gardner, M.J. Treatment of critical-sized bone defects: clinical and tissue engineering perspectives. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2017, 28, 351–362. [CrossRef]
- Archunan, M.W.; Petronis, S. Bone Grafts in Trauma and Orthopaedics. Cureus 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yeung, K.W.K. Bone grafts and biomaterials substitutes for bone defect repair: A review. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 224–247. [CrossRef]
- Sallent, I.; Capella-Monsonís, H.; Procter, P.; Bozo, I.Y.; Deev, R.V.; Zubov, D.; Vasyliev, R.; Perale, G.; Pertici, G.; Baker, J.; et al. The Few Who Made It: Commercially and Clinically Successful Innovative Bone Grafts. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8. [CrossRef]
- St John, T.A., et al., Physical and monetary costs associated with autogenous bone graft harvesting. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ), 2003. 32(1): p. 18-23.
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Calcium orthophosphates (CaPO4): occurrence and properties. Prog. Biomater. 2015, 5, 9–70. [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-J.; Makkar, P.; Padalhin, A.R.; Lee, G.-H.; Im, S.-B.; Lee, B.-T. Comparative study on biodegradation and biocompatibility of multichannel calcium phosphate based bone substitutes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110694. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Gorla, L.; Boos, F.; Okamoto, R.; Júnior, I.G.; Hochuli-Vieira, E. Use of autogenous bone and beta-tricalcium phosphate in maxillary sinus lifting: histomorphometric study and immunohistochemical assessment of RUNX2 and VEGF. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 503–510. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E. and K. Park, Recent Advances of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Bioceramics for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, 2020. 1250: p. 177-188.
- Lu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, L.; Ji, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Current Application of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate in Bone Repair and Its Mechanism to Regulate Osteogenesis. Front. Mater. 2021, 8. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, J.H.; Shim, J.H.; Hwang, N.S.; Heo, C.Y. Bioactive calcium phosphate materials and applications in bone regeneration. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 4. [CrossRef]
- Bohner, M.; Santoni, B.L.G.; Döbelin, N. β-tricalcium phosphate for bone substitution: Synthesis and properties. Acta Biomater. 2020, 113, 23–41. [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, T.S.; Jayasekera, N.; Kuiper, J.-H.; Richardson, J.B. Long-term clinical outcomes following the use of synthetic hydroxyapatite and bone graft in impaction in revision hip arthroplasty. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1732–1738. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T., et al., Bone formation and resorption in patients after implantation of beta-tricalcium phosphate blocks with 60% and 75% porosity in opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2008. 86(2): p. 453-9. [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, L., et al., Maxillary sinus grafting with Bio-Oss or Straumann Bone Ceramic: histomorphometric results from a randomized controlled multicenter clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2008. 19(8): p. 796-803. [CrossRef]
- Kira, T.; Akahane, M.; Omokawa, S.; Shimizu, T.; Kawate, K.; Onishi, T.; Tanaka, Y. Bone regeneration with osteogenic matrix cell sheet and tricalcium phosphate: An experimental study in sheep. World J. Orthop. 2017, 8, 754–760. [CrossRef]
- Somers, N., et al., Mg2+, Sr2+, Ag+, and Cu2+ co-doped β-tricalcium phosphate: Improved thermal stability and mechanical and biological properties. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023. 106(7): p. 4061-4075. [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.N.; Kharovskaya, M.I.; Lazoryak, B.I.; Solovieva, A.O.; Fadeeva, I.V.; Amirov, A.A.; Koliushenkov, M.A.; Orudzhev, F.F.; Baryshnikova, O.V.; Yankova, V.G.; et al. Strontium and Copper Co-Doped Multifunctional Calcium Phosphates: Biomimetic and Antibacterial Materials for Bone Implants. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 252. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Roy, A.; Lee, B.; Kumta, P.N. Study of hMSC proliferation and differentiation on Mg and Mg–Sr containing biphasic β-tricalcium phosphate and amorphous calcium phosphate ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 64, 219–228. [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Xu, M.; Chang, J.; Chakravorty, N.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y. Lithium release from β-tricalcium phosphate inducing cementogenic and osteogenic differentiation of both hPDLCs and hBMSCs. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 1230–1243. [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.H.; Shepherd, D.V.; Best, S.M. Substituted hydroxyapatites for bone repair. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 2335–2347. [CrossRef]
- DeVoe, K.; Banerjee, S.; Roy, M.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, S. Resorbable Tricalcium Phosphates for Bone Tissue Engineering: Influence of SrO Doping. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 3095–3102. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.M., et al., Doping β-TCP as a Strategy for Enhancing the Regenerative Potential of Composite β-TCP-Alkali-Free Bioactive Glass Bone Grafts. Experimental Study in Rats. Materials (Basel), 2018. 12(1).
- Caverzasio, J. Strontium ranelate promotes osteoblastic cell replication through at least two different mechanisms. Bone 2008, 42, 1131–1136. [CrossRef]
- Ke, D., et al., Effects of MgO, ZnO, SrO, and SiO(2) in tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on in vitro gene expression and in vivo osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2019. 96: p. 10-19. [CrossRef]
- Bonnelye, E.; Chabadel, A.; Saltel, F.; Jurdic, P. Dual effect of strontium ranelate: Stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of osteoclast formation and resorption in vitro. Bone 2008, 42, 129–138. [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, H.; Inagaki, Y.; Furukawa, A.; Kira, T.; Kawasaki, S.; Uchihara, Y.; Akahane, M.; Tanaka, Y. Silicate/zinc-substituted strontium apatite coating improves the osteoinductive properties of β-tricalcium phosphate bone graft substitute. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, H., et al., Preparation and Characterization of Nanocomposite Scaffolds (Collagen/β-TCP/SrO) for Bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2019. 16(3): p. 237-251. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, L.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, G. Strontium doping stimulates the phase composition and evolution of β-tricalcium phosphate prepared by wet chemical method. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 318. [CrossRef]
- Nisyrios, T.; Karygianni, L.; Fretwurst, T.; Nelson, K.; Hellwig, E.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Al-Ahmad, A. High Potential of Bacterial Adhesion on Block Bone Graft Materials. Materials 2020, 13, 2102. [CrossRef]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8533–8554. [CrossRef]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the clinical implications of anti-infective biomaterials and infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8018–8029. [CrossRef]
- Fadeeva, I.; Gafurov, M.; Kiiaeva, I.; Orlinskii, S.; Kuznetsova, L.; Filippov, Y.; Fomin, A.; Davydova, G.; Selezneva, I.; Barinov, S. Tricalcium Phosphate Ceramics Doped with Silver, Copper, Zinc, and Iron (III) Ions in Concentrations of Less Than 0.5 wt.% for Bone Tissue Regeneration. BioNanoScience 2016, 7, 434–438. [CrossRef]
- Fadeeva, I.V.; Lazoryak, B.I.; Davidova, G.A.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Gabbasov, B.F.; Petrakova, N.V.; Fosca, M.; Barinov, S.M.; Vadalà, G.; Uskoković, V.; et al. Antibacterial and cell-friendly copper-substituted tricalcium phosphate ceramics for biomedical implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 129, 112410. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Mao, H.; Li, T.; Zhao, R.; Yan, Y.; Pang, X. Osteoblastic cell responses and antibacterial efficacy of Cu/Zn co-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings on pure titanium using electrodeposition method. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17076–17086. [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Boda, S.K.; Teusink, M.J.; Shuler, F.D.; Li, X.; Xie, J. Binary Doping of Strontium and Copper Enhancing Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis of Bioactive Glass Nanofibers while Suppressing Osteoclast Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24484–24496. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hao, M.; Nian, X.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, G.; Guo, J.; Pang, X.; Zhang, H. Strontium and copper co-substituted hydroxyapatite-based coatings with improved antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility fabricated by electrodeposition. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 11876–11888. [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, D.; Graziani, G.; Cappelletti, M.; Fadeeva, I.V.; Montesissa, M.; Sassoni, E.; Borciani, G.; Barbaro, K.; Boi, M.; Baldini, N.; et al. New strontium-based coatings show activity against pathogenic bacteria in spine infection. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1347811. [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.V.; De Bonis, A.; Curcio, M.; Barbaro, K.; Fosca, M.; Fadeeva, I.V.; Cardoso, G.C.; Teghil, R.; Slonskaya, T.K.; Zheng, Y. Coated Biodegradable Zinc Lithium Alloys: Development and Characterization of Co-Doped Strontium Copper Tricalcium Phosphate Coating for Antimicrobial Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 1073. [CrossRef]
- Deyneko, D.V., et al., Antimicrobial properties of co-doped tricalcium phosphates Ca3-2x(MˊMˊˊ)x(PO4)2 (M = Zn2+, Cu2+, Mn2+ and Sr2+). Ceramics International, 2022. 48(20): p. 29770-29781. [CrossRef]
- Barinov S.M., F.I.V., Fomin A.S., Petrakova N.V., Method for producing porous ceramics from calcium phosphates for treating bone tissue defects, P.o.t.R.F.N. 2578435, Editor. 2015.
- Geekiyanage, N.M.; Balanant, M.A.; Sauret, E.; Saha, S.; Flower, R.; Lim, C.T.; Gu, Y. A coarse-grained red blood cell membrane model to study stomatocyte-discocyte-echinocyte morphologies. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0215447. [CrossRef]
- Justus, C.R., et al., In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J Vis Exp, 2014(88).
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, G., et al., Angiogenesis Analyzer for ImageJ - A comparative morphometric analysis of "Endothelial Tube Formation Assay" and "Fibrin Bead Assay". Sci Rep, 2020. 10(1): p. 11568.
- Kamitakahara, M.; Ohtsuki, C.; Miyazaki, T. Review Paper: Behavior of Ceramic Biomaterials Derived from Tricalcium Phosphate in Physiological Condition. J. Biomater. Appl. 2008, 23, 197–212. [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, A.; Yang, F.; Sun, K.; Sun, X. β-tricalcium phosphate and octacalcium phosphate composite bioceramic material for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 34, 1294–1299. [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, B.; Wu, F. Migration critically meditates osteoblastic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells through activating canonical Wnt signal pathway. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 205–213. [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Zhou, G.; Luk, K.D.; Cheung, K.M.; Li, Z.; Lam, W.M.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, W.W. Strontium Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through the Ras/MAPK Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 23, 165–174. [CrossRef]
- Brennan, T.; Rybchyn, M.S.; Green, W.; Atwa, S.; Conigrave, A.; Mason, R. Osteoblasts play key roles in the mechanisms of action of strontium ranelate. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 1291–1300. [CrossRef]
- Hurtel-Lemaire, A.S.; Mentaverri, R.; Caudrillier, A.; Cournarie, F.; Wattel, A.; Kamel, S.; Terwilliger, E.F.; Brown, E.M.; Brazier, M. The Calcium-sensing Receptor Is Involved in Strontium Ranelate-induced Osteoclast Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 575–584. [CrossRef]
- Marx, D.; Yazdi, A.R.; Papini, M.; Towler, M. A review of the latest insights into the mechanism of action of strontium in bone. Bone Rep. 2020, 12, 100273. [CrossRef]
- Goltzman, D.; Hendy, G.N. The calcium-sensing receptor in bone—mechanistic and therapeutic insights. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 298–307. [CrossRef]
- Takaoka, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yano, S.; Yamauchi, M.; Sugimoto, T. The Calcium-sensing Receptor (CaR) is Involved in Strontium Ranelate-induced Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 627–631. [CrossRef]
- Saidak, Z.; Haÿ, E.; Marty, C.; Barbara, A.; Marie, P.J. Strontium ranelate rebalances bone marrow adipogenesis and osteoblastogenesis in senescent osteopenic mice through NFATc/Maf and Wnt signaling. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 467–474. [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Wang, C.; Xue, Y.; Lin, K.; Chang, J.; Sun, J. Osteogenic differentiation of osteoblasts induced by calcium silicate and calcium silicate/β-tricalcium phosphate composite bioceramics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100B, 1237–1244. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.C.; Benelli, R.; Canciani, B.; Scaranari, M.; Daculsi, G.; Cancedda, R.; Gentili, C. Beta-tricalcium phosphate ceramic triggers fast and robust bone formation by human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 1007–1018. [CrossRef]
- Barradas, A.M.C.; Monticone, V.; Hulsman, M.; Danoux, C.; Fernandes, H.; Birgani, Z.T.; Groot, F.B.-D.; Yuan, H.; Reinders, M.; Habibovic, P.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of biomaterial-driven osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stromal cells. Integr. Biol. 2013, 5, 920–931. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of CuSr TCP ceramic target.
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of CuSr TCP ceramic target.
Figure 2.
The cumulative release amount of Ca2+(filled squares), Cu2+(filled dots), and Sr2+ (half-filled triangles) ions from CuSr TCP ceramics after soaking in model liquid over 30 days. The release profile of each ion is plotted with a black line.
Figure 2.
The cumulative release amount of Ca2+(filled squares), Cu2+(filled dots), and Sr2+ (half-filled triangles) ions from CuSr TCP ceramics after soaking in model liquid over 30 days. The release profile of each ion is plotted with a black line.
Figure 3.
Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay for Cytotoxicity. BM MSCs were cultured in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 24 hours. CyQUANT™ LDH Cytotoxicity Assay (C20300, Thermo Fisher) was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity.
Figure 3.
Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay for Cytotoxicity. BM MSCs were cultured in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 24 hours. CyQUANT™ LDH Cytotoxicity Assay (C20300, Thermo Fisher) was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity.
Figure 4.
Blood hemolysis test with human RBCs. Blood samples were collected from healthy volunteers in K2-EDTA vacutainers, and plasma and buffy coats were removed. RBC solutions were incubated with various concentrations of CuSr TCP and TCP alone at 37 °C for 2 hours. Absorbance was measured at a specter of wavelengths from 300 to 700 nm on a 96-well plate with Hybrid Reader Synergy H1 (Biotek, USA). The percentage of the hemolysis was calculated.
Figure 4.
Blood hemolysis test with human RBCs. Blood samples were collected from healthy volunteers in K2-EDTA vacutainers, and plasma and buffy coats were removed. RBC solutions were incubated with various concentrations of CuSr TCP and TCP alone at 37 °C for 2 hours. Absorbance was measured at a specter of wavelengths from 300 to 700 nm on a 96-well plate with Hybrid Reader Synergy H1 (Biotek, USA). The percentage of the hemolysis was calculated.
Figure 5.
Proliferation Assay with CCK-8 during 72 hours. Mesenchymal stem cells were cultured in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 24-72 hours. CCK-8 (96992, Sigma Aldrich) was used to assess the number of proliferated cells. * - p value≤ 0.05.
Figure 5.
Proliferation Assay with CCK-8 during 72 hours. Mesenchymal stem cells were cultured in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 24-72 hours. CCK-8 (96992, Sigma Aldrich) was used to assess the number of proliferated cells. * - p value≤ 0.05.
Figure 6.
IFM images of BM-MSCs on the surface of CuSr TCP granules: (a) cells were seeded in concentration 1x104 cells per well, fixed and double stained with DAPI and Phalloidin. SEM images of BM-MSCs on the surface of CuSr TCP granules; (b) cells were seeded in concentration 1x104 cells per well, fixed, stained with 1M Osmium Tetroxide and covered with 20nm gold. Imaged with Zeiss Crossbeam 540 (Zeiss, Germany).
Figure 6.
IFM images of BM-MSCs on the surface of CuSr TCP granules: (a) cells were seeded in concentration 1x104 cells per well, fixed and double stained with DAPI and Phalloidin. SEM images of BM-MSCs on the surface of CuSr TCP granules; (b) cells were seeded in concentration 1x104 cells per well, fixed, stained with 1M Osmium Tetroxide and covered with 20nm gold. Imaged with Zeiss Crossbeam 540 (Zeiss, Germany).
Figure 7.
Transwell migration assay. Images were analyzed with ImageJ and migrated cells were counted (scale 100µm). * - p value≤ 0.05 compared to the control group .
Figure 7.
Transwell migration assay. Images were analyzed with ImageJ and migrated cells were counted (scale 100µm). * - p value≤ 0.05 compared to the control group .
Figure 8.
Alkaline phosphatase activity assay. hFOB1.19 were cultured in CuSr TCP or TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 14 days. Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit (ab83369, Abcam) was used to assess the osteogenic differentiation. * - p value≤ 0.05 compared to the no treatment group, ** - p value≤ 0.005 compared to the no treatment group.
Figure 8.
Alkaline phosphatase activity assay. hFOB1.19 were cultured in CuSr TCP or TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 14 days. Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit (ab83369, Abcam) was used to assess the osteogenic differentiation. * - p value≤ 0.05 compared to the no treatment group, ** - p value≤ 0.005 compared to the no treatment group.
Figure 9.
Alizarin Red S Assay. BM-MSCs were cultured in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 72 hours. Alizarin Red S (A5533, Sigma Aldrich) was used to evaluate the number of proliferated cells. ** - p value≤ 0.005 compared to the osteogenic media group (scale 100µm).
Figure 9.
Alizarin Red S Assay. BM-MSCs were cultured in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 72 hours. Alizarin Red S (A5533, Sigma Aldrich) was used to evaluate the number of proliferated cells. ** - p value≤ 0.005 compared to the osteogenic media group (scale 100µm).
Figure 10.
Angiogenesis assay. HUVEC (C-003-5C, Gibco) were pre-treated in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 72 hours and seeded in the concentration of 4.2 x 10
3 per well in a GelTrex matrix-coated 24-well plate for 16h. Cells were then stained with Calcein AM and imaged at 4X magnification. Images were assessed with the Image J Angiogenesis Analyzer Plugin [
51].
Figure 10.
Angiogenesis assay. HUVEC (C-003-5C, Gibco) were pre-treated in CuSr TCP-enriched media (3-day extract) for 72 hours and seeded in the concentration of 4.2 x 10
3 per well in a GelTrex matrix-coated 24-well plate for 16h. Cells were then stained with Calcein AM and imaged at 4X magnification. Images were assessed with the Image J Angiogenesis Analyzer Plugin [
51].
Figure 11.
Representative images of angiogenesis assay. Images were acquired with Cytation 5 Multimode Reader (Biotek, USA).
Figure 11.
Representative images of angiogenesis assay. Images were acquired with Cytation 5 Multimode Reader (Biotek, USA).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).