Submitted:
23 October 2024
Posted:
24 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
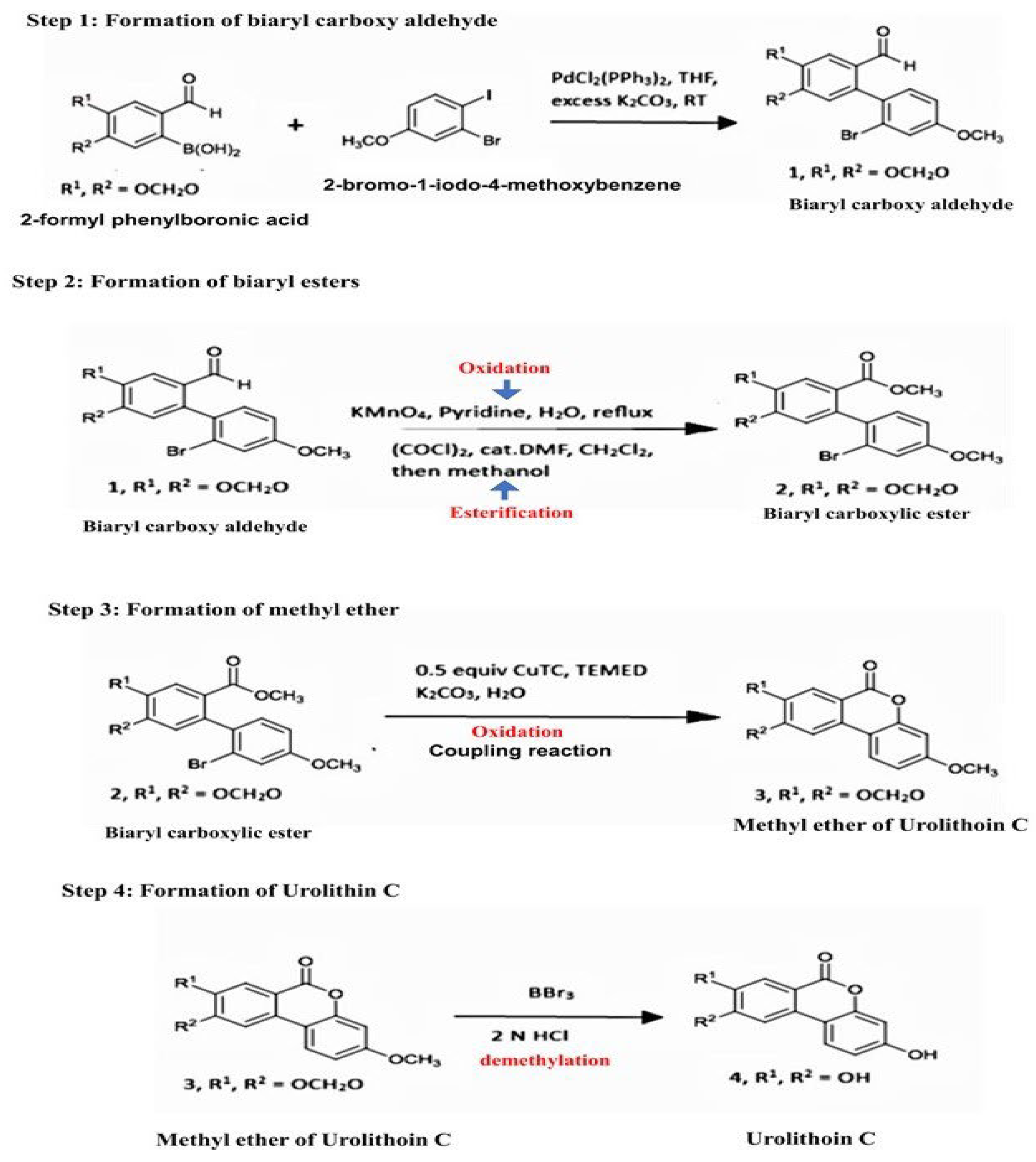
2.1. Synthesis of Urolithin-C:
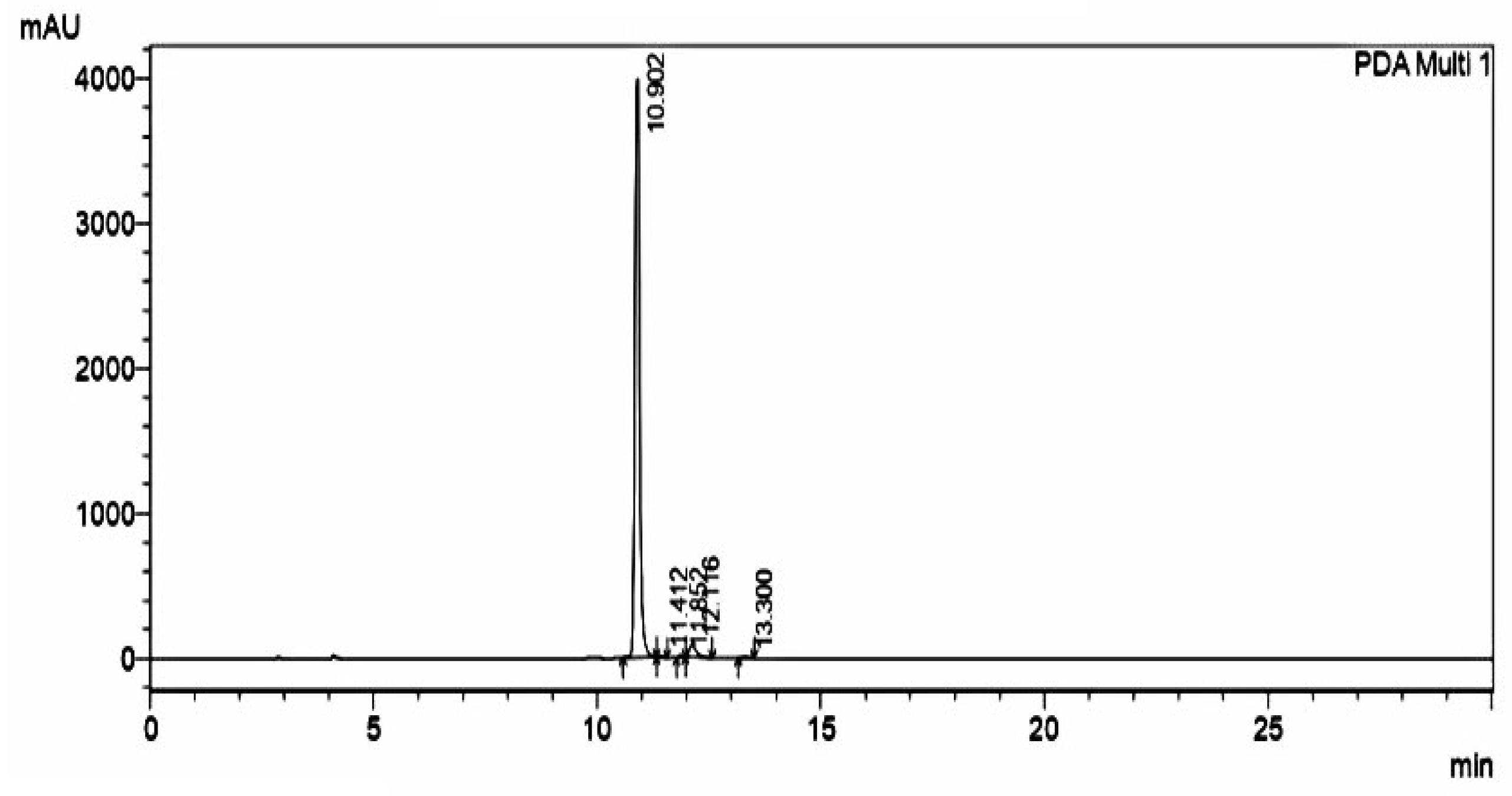
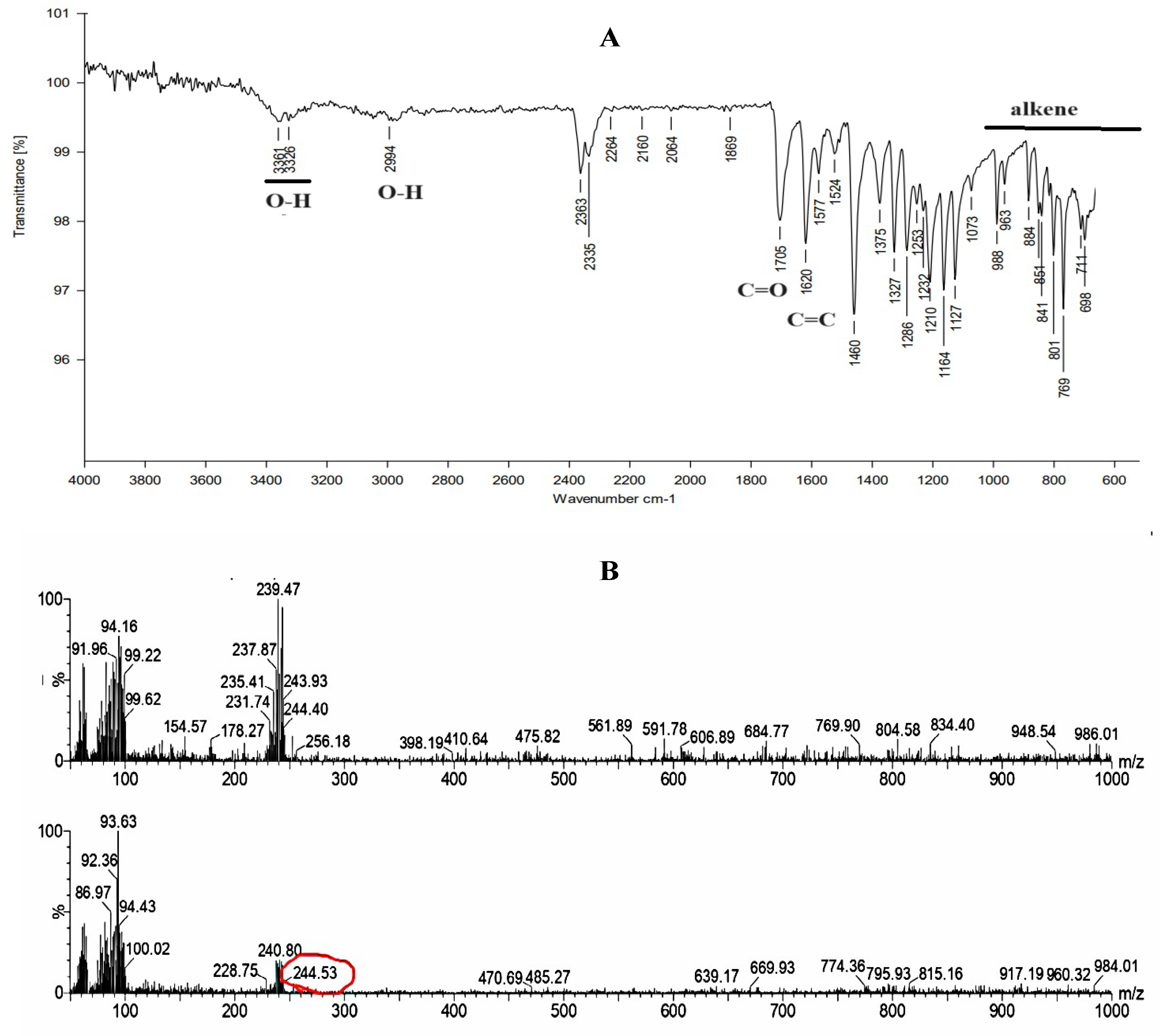
2.2. Purification and Characterization of Synthesized Urolithin-C:
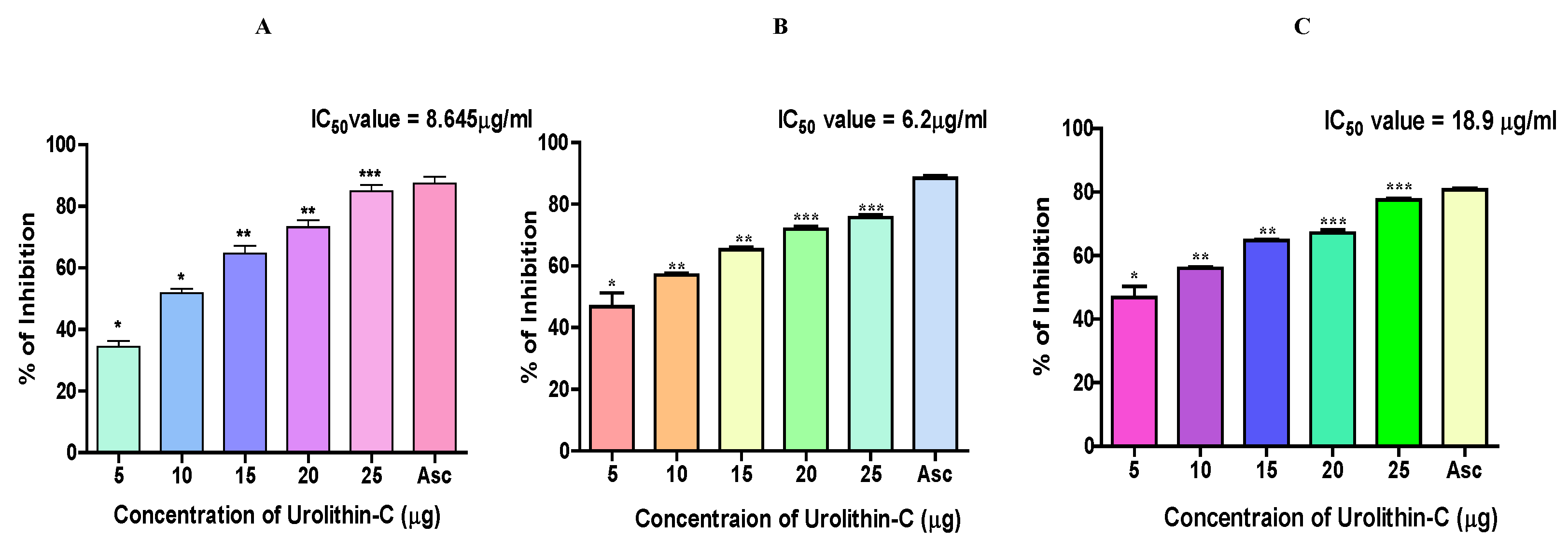
2.3. Urolithin-C Exhibits Antioxidant Property by Scavenging DPPH, H2O2 and FRAP Radicals:
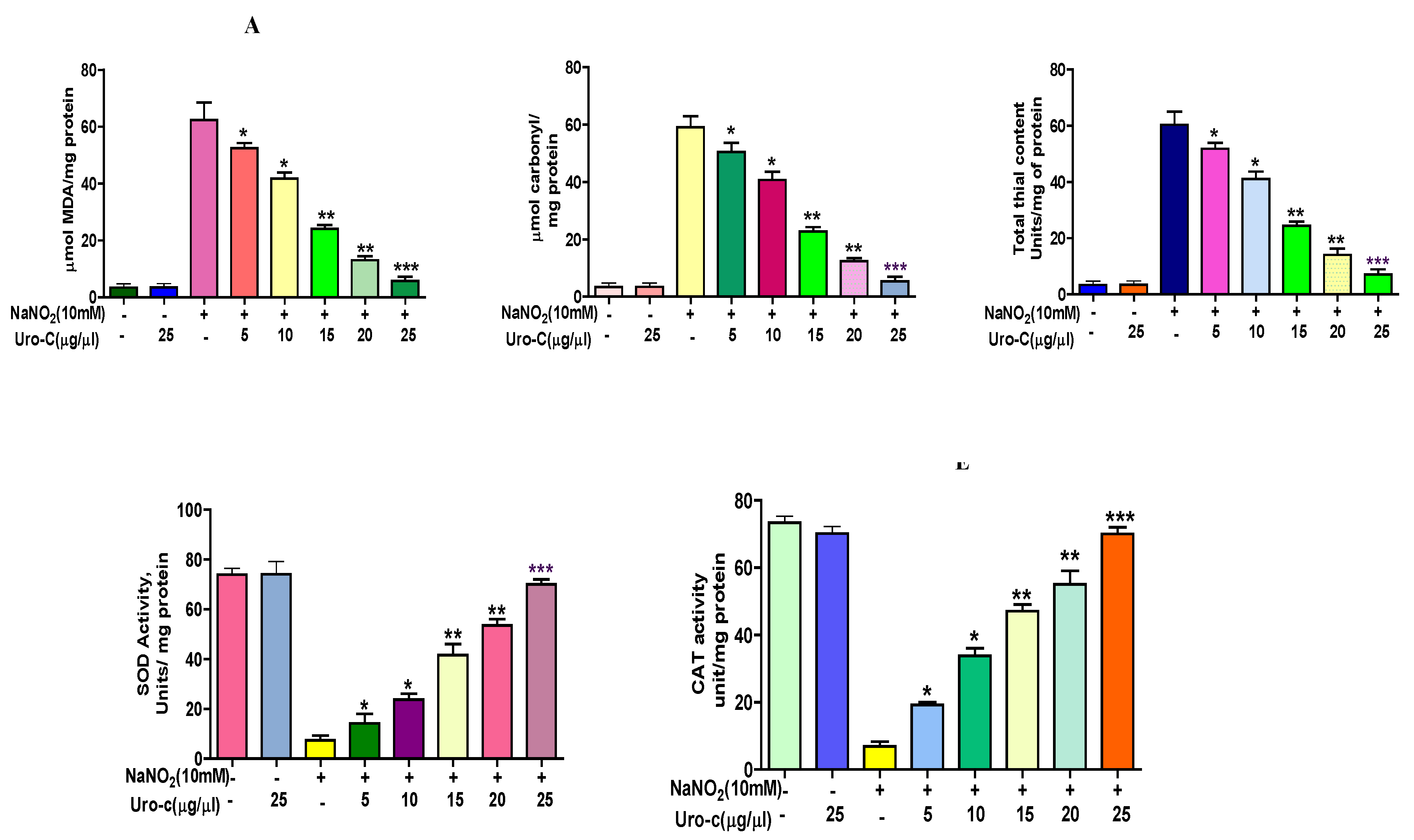
2.4. Urolithin-C Ameliorates the Oxidative Stress Parameters in the Sodium Nitrite (NaNO2) Induced Oxidative Stress in RBCs (In-Vitro):
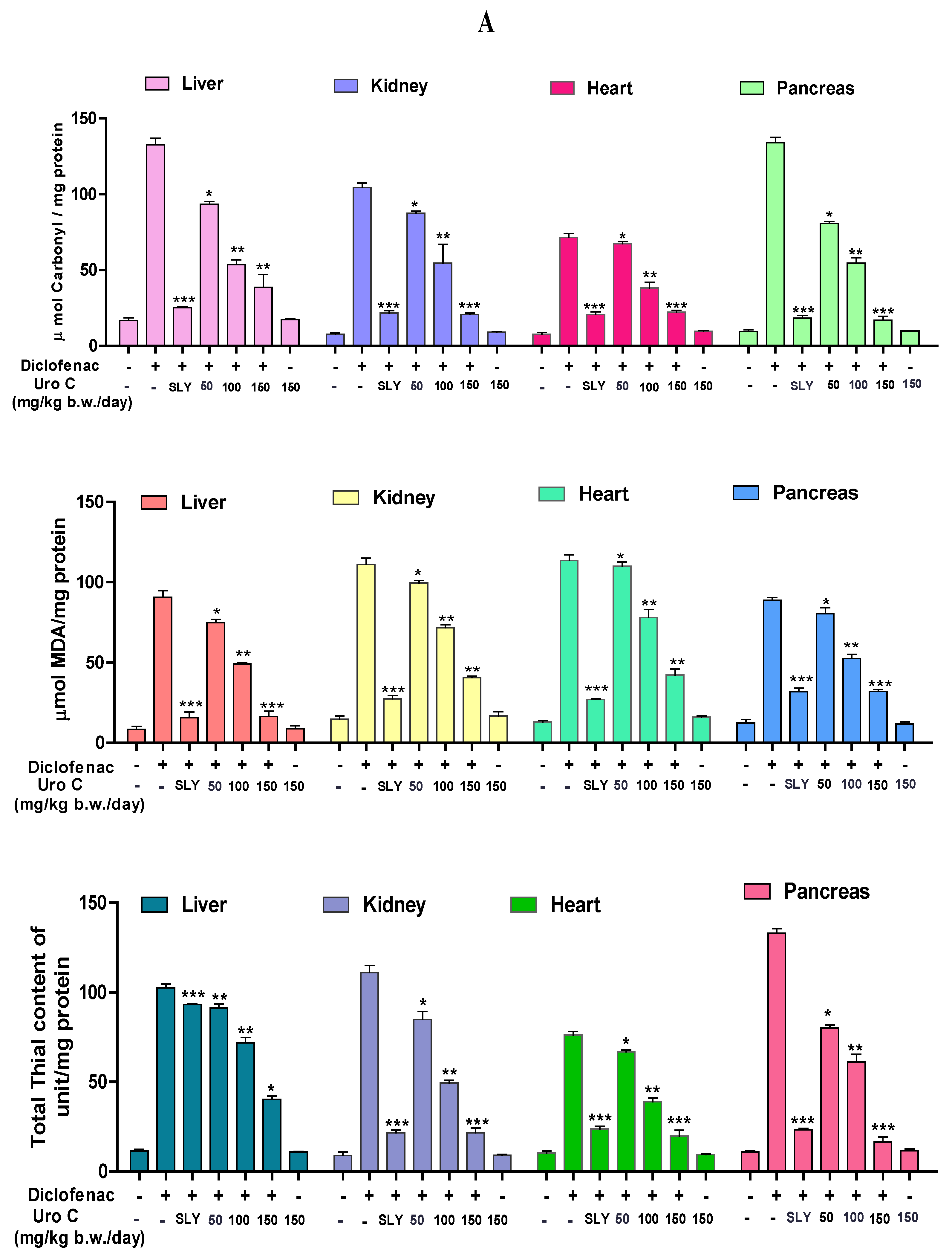
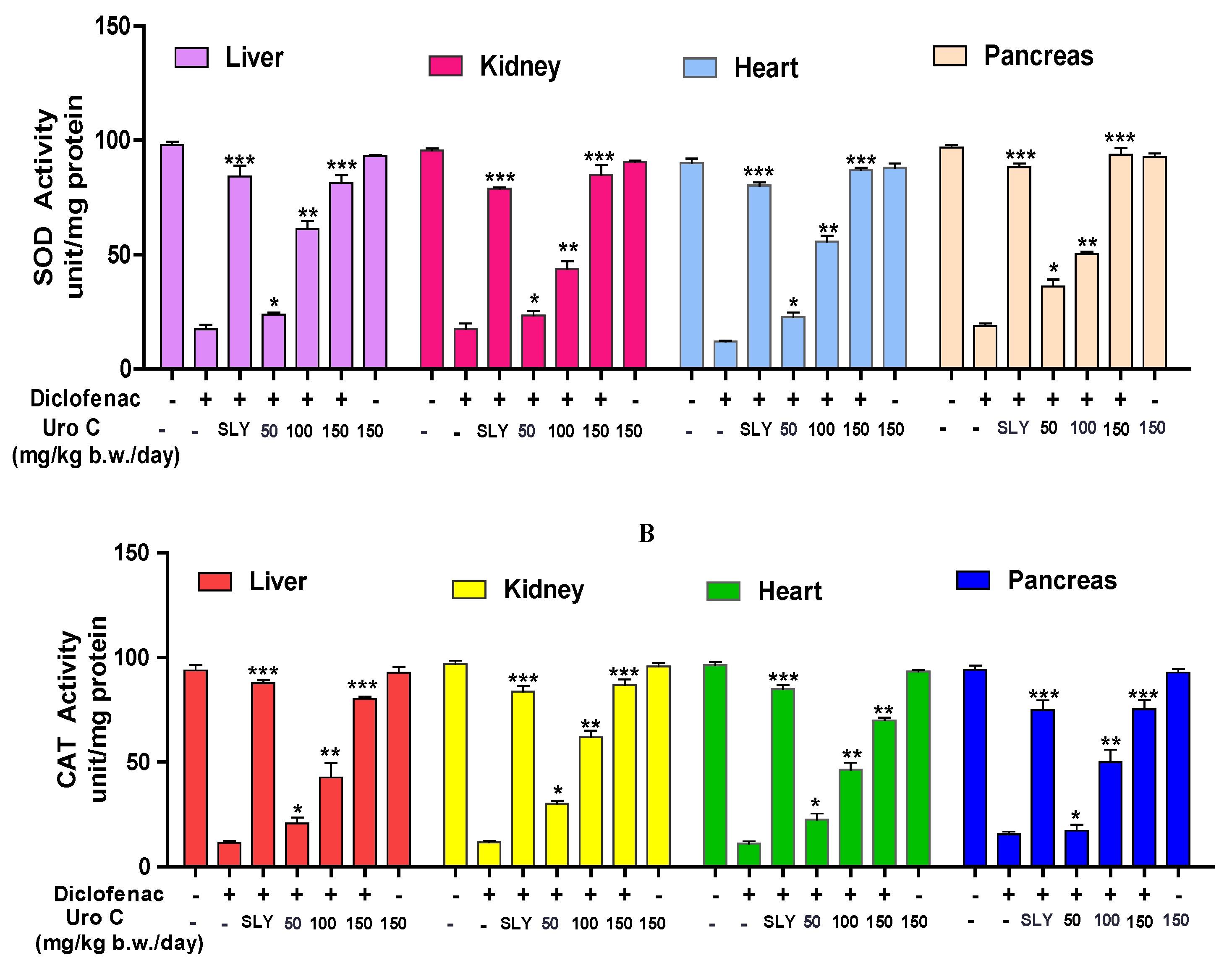
2.5. Urolithin-C Regulates the Diclofenac Induced Oxidative Stress Parameter in Animal Model (In-Vivo):
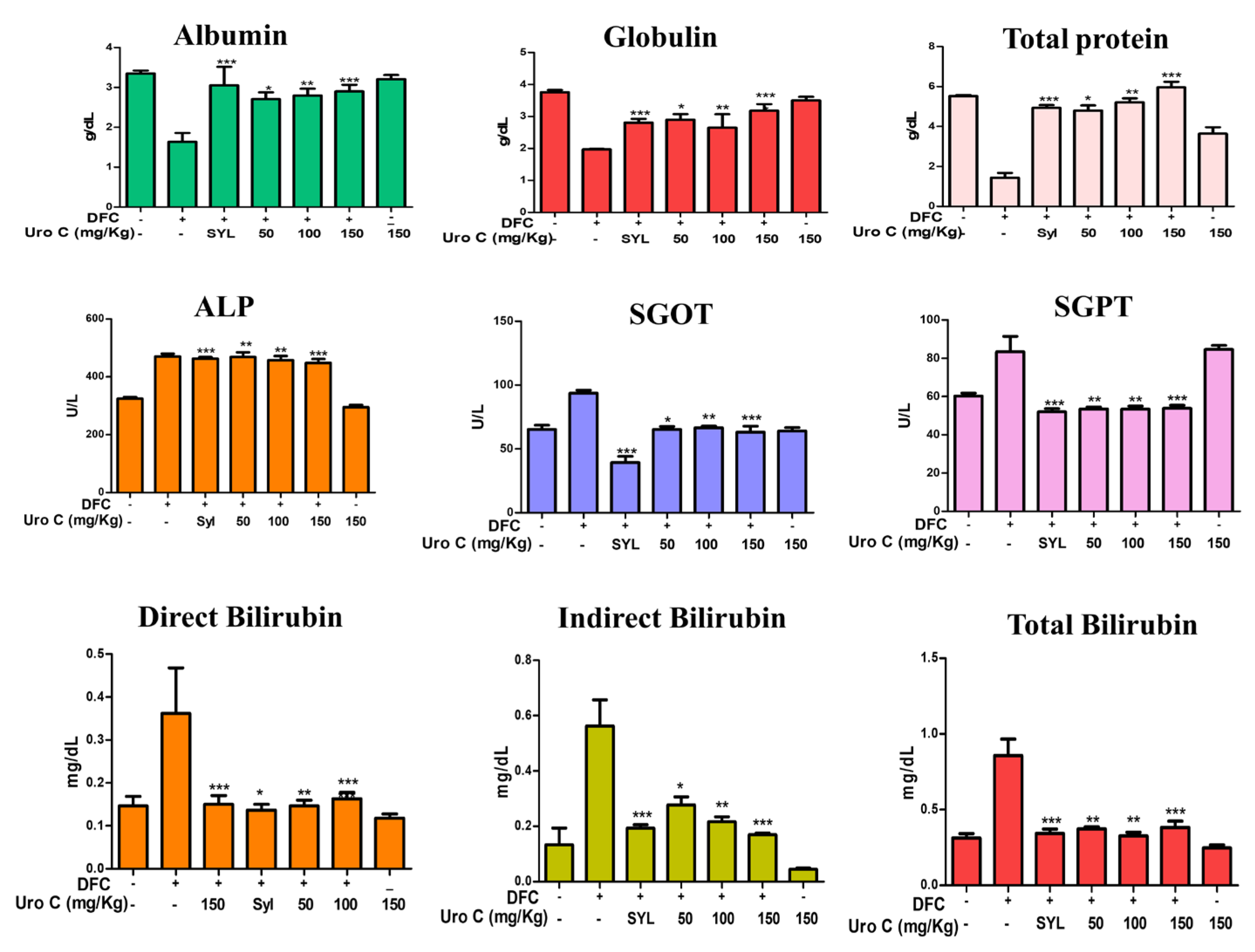
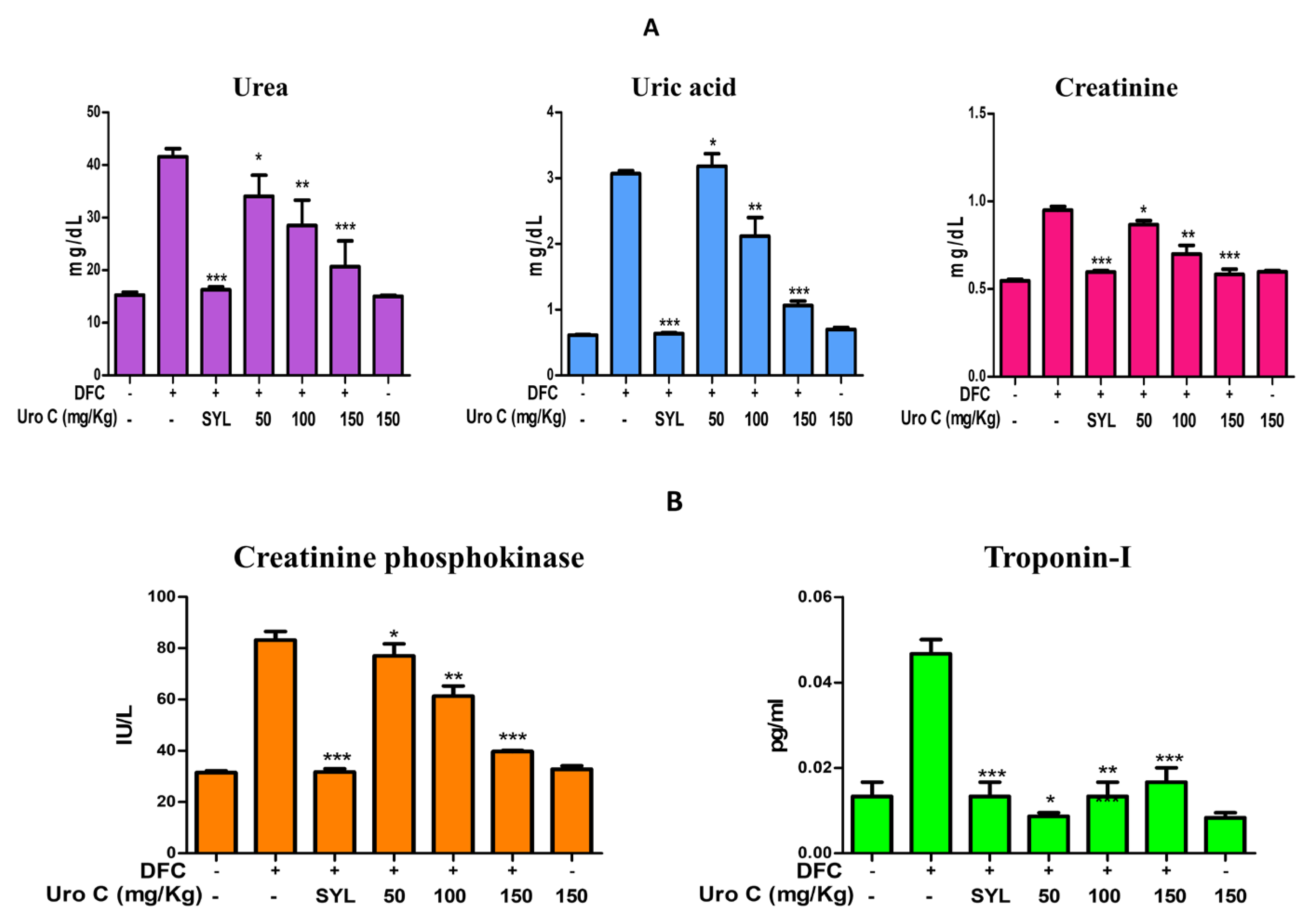
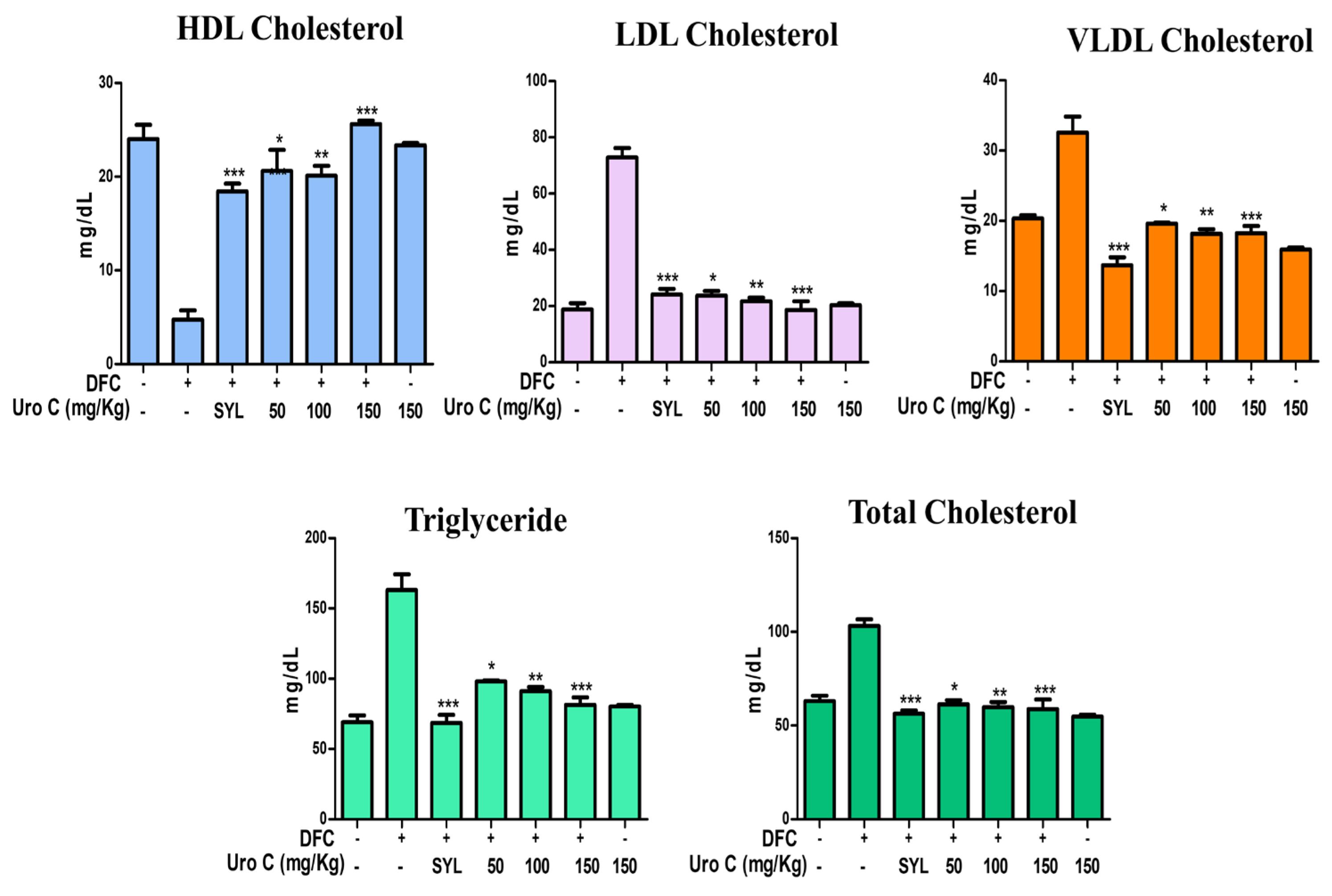
2.6. Urolithin-C Restores the Biochemical Parameters in Diclofenac Injected Rat’s Serum:
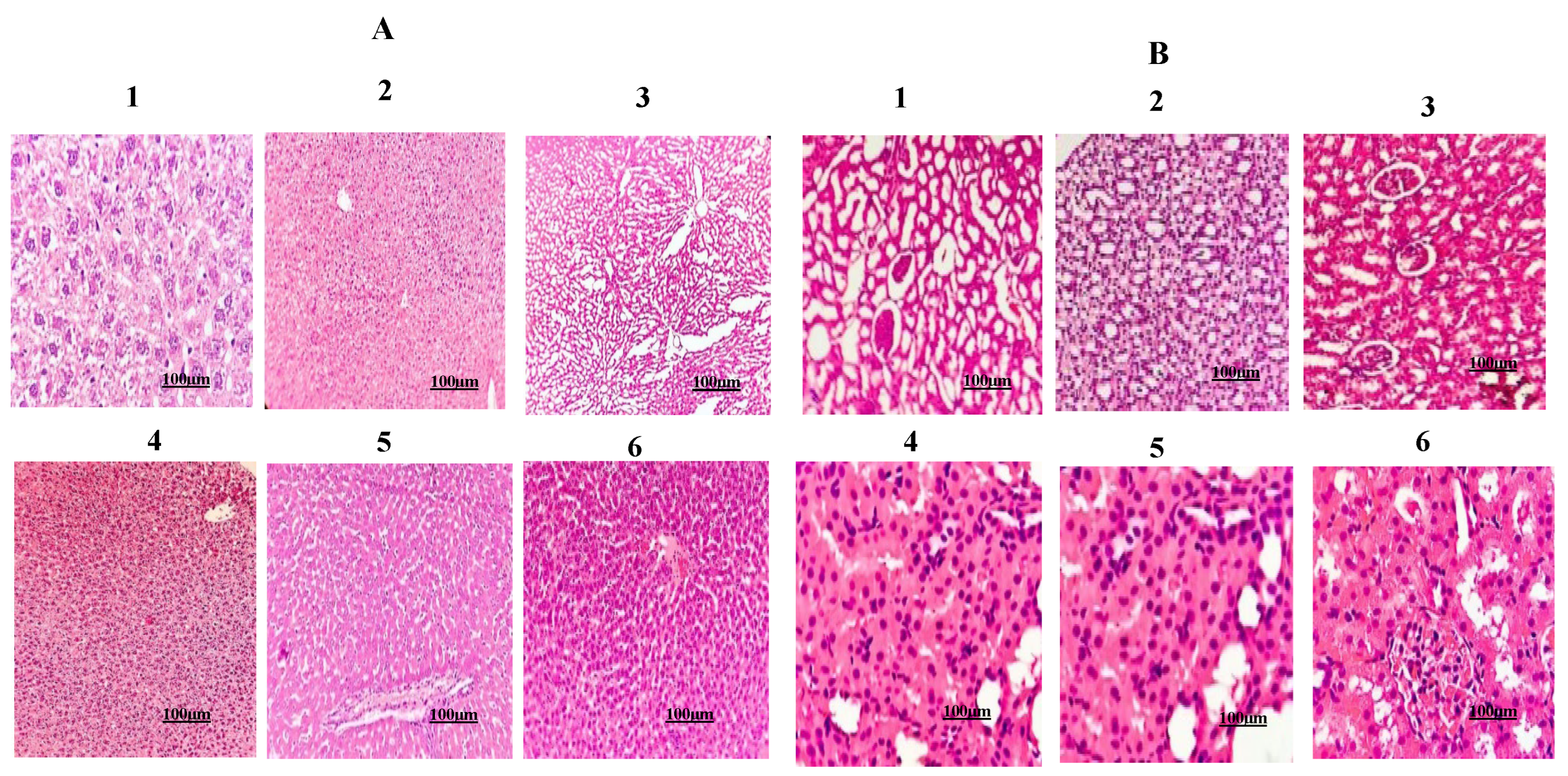
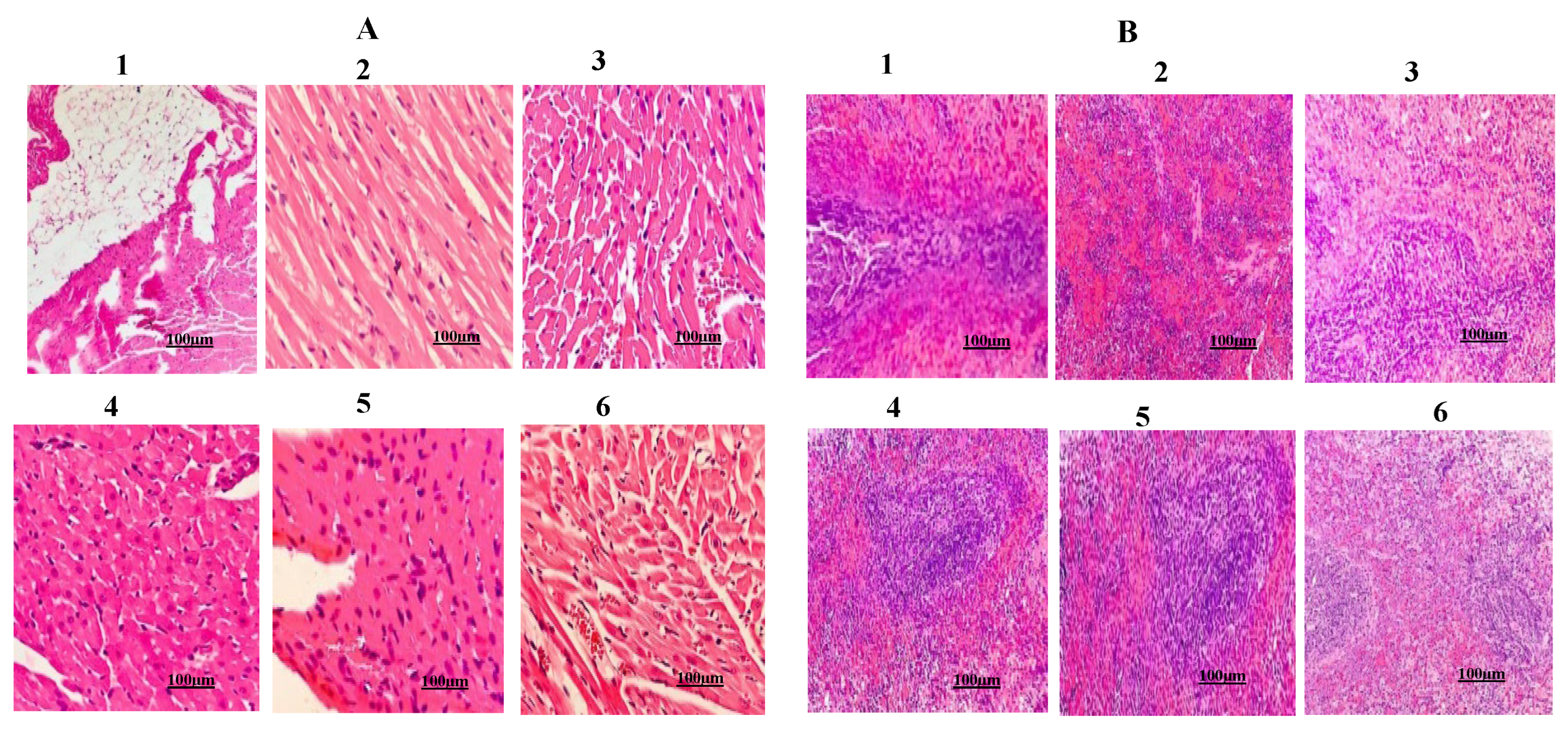
2.7. Urolithin-C Normalizes the Liver, Kidney, Heart and Pancreas Morphology:
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents:
4.2. Synthesis of Urolithin-C:
4.2.1. Synthesis of Urolthin C Was Carried Out by Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling Method [38,39]
4.2.2. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC):
4.2.3. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC):
4.2.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR):
4.2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR):
4.2.6. Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LCMS):
4.3. Antioxidant Activity:
4.3.1. DPPH Method:
4.3.2. Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Scavenging Assay:
4.3.3. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP):
4.4. Preparation of (2 %) Hematocrit:
4.4.1. Oxidative Stress Induced by NaNO2:
4.4.2. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation (LPO):
4.4.3. Determination of Protein Carbonyl Content (PCC):
4.4.4. Estimation of Total Thiol Content:
4.4.5. Determination of Activities of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Catalase (CAT):
4.5. Animal Grouping:
4.5.1. Histopathological Examination:
4.6. Statistical Analysis:
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, C.H.; Leitch, H.A. Iron Overload-Induced Oxidative Stress in Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Its Cellular Sequelae. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 2021, 163, 103367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonocore, G.; Perrone, S.; Tataranno, M.L. Oxygen Toxicity: Chemistry and Biology of Reactive Oxygen Species. Seminars in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine 2010, 15, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacic, P.; Pozos, R.S.; Somanathan, R.; Shangari, N.; O’Brien, P.J. Mechanism of Mitochondrial Uncouplers, Inhibitors, and Toxins: Focus on Electron Transfer, Free Radicals, and Structure -Activity Relationships. CMC 2005, 12, 2601–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boni, R.; Cecchini Gualandi, S. Relationship between Oxidative Stress and Endometritis: Exploiting Knowledge Gained in Mares and Cows. Animals 2022, 12, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ďuračková, Z. Some Current Insights into Oxidative Stress. Physiol Res 2010, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-C.; Sheen, J.-M.; Hu, W.L.; Hung, Y.-C. Polyphenols and Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis-Related Ischemic Heart Disease and Stroke. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2017, 2017, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlanetto, V.; Zagotto, G.; Pasquale, R.; Moro, S.; Gatto, B. Ellagic Acid and Polyhydroxylated Urolithins Are Potent Cata-lytic Inhibitors of Human Topoisomerase II: An in Vitro Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9162–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passi, S.J. Prevention of Non-Communicable Diseases by Balanced Nutrition: Population- Specific Effective Public Health Approaches in Developing Countries. CDR 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarshan, K.; Yarlagadda, S.; Sengupta, S. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Diarylheptanoids. Chemistry An Asian Journal 2024, 19, e202400380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, M.; Sinha, S.; Sudarshan, K.; Aidhen, I.S.; Doble, M. Inhibition of the Enzymes in the Leukotriene and Prostaglandin Pathways in Inflammation by 3-Aryl Isocoumarins. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2016, 124, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.-J.; Zhou, N.; Wang, X.; Li, J.-J.; Ma, H.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, J.-H.; Lin, P.-C.; Shang, X.-Y. Three New Ursane-Type Triterpenoids from Rosmarinus Officinalis and Their Biological Activities. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines 2022, 20, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kurokawa, M.; Miura, M.; Kakegawa, T.; Motohashi, S.; Yasukawa, K. Bioactivity and Synthesis of Diarylheptanoids From Alpinia Officinarum. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier, 2016; Vol. 49, pp. 157–187. ISBN 9780444636010. [Google Scholar]
- Aloia, A.; Casiello, M.; D’Accolti, L.; Fusco, C.; Nacci, A.; Monopoli, A. Direct Synthesis of 3-Aryl Substituted Isocoumarins and Phthalides through Palladium Acetate Catalyzed C( Sp 2 )−H Activation in Ionic Liquids. Chemistry A European J 2022, 28, e202202350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thbayh, D.K.; Fiser, B. Computational Study of Synthetic and Natural Polymer Additives — Antioxidant Potential of BHA, TBHQ, BHT, and Curcumin. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2022, 201, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandylis, P.; Kokkinomagoulos, E. Food Applications and Potential Health Benefits of Pomegranate and Its Deriva-tives. Foods 2020, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemistry and Biology of Ellagitannins: An Underestimated Class of Bioactive Plant Polyphenol; Quideau, S., Ed.; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 9789812797407. [Google Scholar]
- Montes-Ávila, J.; López-Angulo, G.; Delgado-Vargas, F. Tannins in Fruits and Vegetables: Chemistry and Biological Func-tions. In Fruit and Vegetable Phytochemicals; Yahia, E.M., Ed.; Wiley, 2017; pp. 221–268. ISBN 9781119157946. [Google Scholar]
- Gulcan, H.O.; Unlu, S.; Esiringu, İ.; Ercetin, T.; Sahin, Y.; Oz, D.; Sahin, M.F. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 6H-Benzo[c]Chromen-6-One, and 7,8,9,10-Tetrahydro-Benzo[c]Chromen-6-One Derivatives as Potential Cholinesterase Inhibitors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2014, 22, 5141–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Barrio, R.; Truchado, P.; Ito, H.; Espín, J.C.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. UV and MS Identification of Urolithins and Nasutins, the Bioavailable Metabolites of Ellagitannins and Ellagic Acid in Different Mammals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vini, R.; Azeez, J.M.; Remadevi, V.; Susmi, T.R.; Ayswarya, R.S.; Sujatha, A.S.; Muraleedharan, P.; Lathika, L.M.; Sreeharshan, S. Urolithins: The Colon Microbiota Metabolites as Endocrine Modulators: Prospects and Perspectives. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 800990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espín, J.C.; Larrosa, M.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Tomás-Barberán, F. Biological Significance of Urolithins, the Gut Microbial Ellagic Acid-Derived Metabolites: The Evidence So Far. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013, 2013, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Zhang, J.; Yan, L.; Yang, L.; Sun, L.; Shi, L.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y. Urolithin-C, a Gut Metabolite of Ellagic Acid, Induces Apoptosis in PC12 Cells through a Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17254–17263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; González-Sarrías, A.; García-Villalba, R.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.A.; Selma, M.V.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Espín, J.C. Urolithins, the Rescue of “Old” Metabolites to Understand a “New” Concept: Metabotypes as a Nexus among Phenolic Metabolism, Microbiota Dysbiosis, and Host Health Status. Molecular Nutrition Food Res 2017, 61, 1500901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Jiang, J.; Song, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Huang, X.; Feng, X. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel 6H-Benzo[c]Chromen-6-One Derivatives as Potential Phosphodiesterase II Inhibitors. IJMS 2021, 22, 5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moco, S.; Barron, D. Bioactive Interactions in Food and Natural Extracts. In Nutrigenomics and Proteomics in Health and Disease; Kussmann, M., Stover, P.J., Eds.; Wiley, 2017; pp. 65–91. ISBN 9781119098836. [Google Scholar]
- Betteridge, D.J. What Is Oxidative Stress? Metabolism 2000, 49, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirdeeva, Y.; Fedorova, O.; Daks, A.; Barlev, N.; Shuvalov, O. How Should the Worldwide Knowledge of Traditional Cancer Healing Be Integrated with Herbs and Mushrooms into Modern Molecular Pharmacology? Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, R. Synthetic Antioxidants: Biochemical Actions and Interference with Radiation, Toxic Compounds, Chemical Muta-gens and Chemical Carcinogens. Toxicology 1984, 33, 185–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free Radicals, Antioxidants and Functional Foods: Impact on Human Health. Phcog Rev 2010, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouayed, J.; Bohn, T. Exogenous Antioxidants—Double-Edged Swords in Cellular Redox State: Health Beneficial Effects at Physiologic Doses versus Deleterious Effects at High Doses. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2010, 3, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Pharmacy, Bundelkhand University, Jhansi-284128, Uttar Pradesh, India; Prajapati, R.N.; Kumar, S.; Institute of Pharmacy, Bundelkhand University, Jhansi-284128, Uttar Pradesh, India THE ROLE, SCOPE, HEALTH BENEFITS AND MARKET GROWTH OF NUTRACEUTICALS: AN OVERVIEW. Curr. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 30–42. [CrossRef]
- Kengaiah, J.; Nandish, S.K.M.; Ramachandraiah, C.; Chandramma; Shivaiah, A.; Vishalakshi, G.J.; Paul, M.; Santhosh, M.S.; Shankar, R.L.; Sannaningaiah, D. Protective Effect of Tamarind Seed Coat Ethanol Extract on Eryptosis Induced by Oxidative Stress. Biochemistry Moscow 2020, 85, 119–129. [CrossRef]
- Dreischer, P.; Duszenko, M.; Stein, J.; Wieder, T. Eryptosis: Programmed Death of Nucleus-Free, Iron-Filled Blood Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwozdzinski, K.; Pieniazek, A.; Gwozdzinski, L. Reactive Oxygen Species and Their Involvement in Red Blood Cell Damage in Chronic Kidney Disease. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2021, 2021, 6639199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, U.M.; Monjas, L.; Akladios, F.; Matic, J.; Andresen, E.; Nagel, C.H.; Hagkvist, M.; Håversen, L.; Kim, W.; Uhlen, M.; et al. Exploration of Novel Urolithin-C Derivatives as Non-Competitive Inhibitors of Liver Pyruvate Ki-nase. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatappa, M.M.; Udagani, C.; Hanume Gowda, S.M.; Venkataramaiah, S.; Casini, R.; Moussa, I.M.; Achur, R.; San-naningaiah, D.; Elansary, H.O. Green Synthesised TiO2 Nanoparticles-Mediated Terenna Asiatica: Evaluation of Their Role in Reducing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Human Breast Cancer Proliferation. Molecules 2023, 28, 5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, T.; Hosen, I.; Islam, M.M.T.; Shekhar, H.U. Oxidative Stress and Human Health. Advances in Bioscience and Bio-technology 2012, 3, 997–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nealmongkol, P.; Tangdenpaisal, K.; Sitthimonchai, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Thasana, N. Cu(I)-Mediated Lactone Formation in Subcritical Water: A Benign Synthesis of Benzopyranones and Urolithins A–C. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 9277–9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.-C.; Wu, J.-Y.; Fang, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-C.; Liu, Y.-W.; Ho, S.-T. Absorption and Metabolism of Urolithin A and Ellagic Acid in Mice and Their Cytotoxicity in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2023, 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battisti, U.M.; Monjas, L.; Akladios, F.; Matic, J.; Andresen, E.; Nagel, C.H.; Hagkvist, M.; Håversen, L.; Kim, W.; Uhlen, M.; et al. Exploration of Novel Urolithin-C Derivatives as Non-Competitive Inhibitors of Liver Pyruvate Kinase. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Zhang, J.; Yan, L.; Yang, L.; Sun, L.; Shi, L.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y. Urolithin-C, a Gut Metabolite of Ellagic Acid, Induces Apoptosis in PC12 Cells through a Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17254–17263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa, P.; Phatikulrungsun, P.; Prathumthong, S. FT-IR Characteristics, Phenolic Profiles and Inhibitory Potential against Digestive Enzymes of 25 Herbal Infusions. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Jiang, J.; Song, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Huang, X.; Feng, X. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Urolithins Derivatives as Potential Phosphodiesterase II Inhibitors. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 23792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoh, S.; Asekun, O.; Familoni, O.; Afolayan, A. Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging Capacity of Seed and Shell Es-sential Oils Extracted from Abrus Precatorius (L). Antioxidants 2014, 3, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Ghosh, G.; Das, D.; Nayak, S. Phytochemical Investigation and In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of an Indigenous Medicinal Plant Alpinia Nigra B.L. Burtt. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine 2013, 3, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-S.; Liou, S.-Y.; Wu, H.-C.; Tsai, F.-J.; Tsai, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-L. New Analytical Method for Investigating the Antioxidant Power of Food Extracts on the Basis of Their Electron-Donating Ability: Comparison to the Ferric Reduc-ing/Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8477–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatappa, M.M.; Udagani, C.; Hanumegowda, S.M.; Pramod, S.N.; Venkataramaiah, S.; Rangappa, R.; Achur, R.; Alataway, A.; Dewidar, A.Z.; Al-Yafrsi, M.; et al. Effect of Biofunctional Green Synthesized MgO-Nanoparticles on Oxida-tive-Stress-Induced Tissue Damage and Thrombosis. Molecules 2022, 27, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for Lipid Peroxides in Animal Tissues by Thiobarbituric Acid Reaction. Analytical Biochemistry 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, A.-G.; Costabel, U.; Shaltiel, S.; Levine, R.L. Determination of Carbonyl Groups in Oxidatively Modified Proteins by Reduction with Tritiated Sodium Borohydride. Analytical Biochemistry 1989, 177, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Usai, M.F.; Chessa, R.; Deiana, L.; Carru, C. Thiol Redox Status Evaluation in Red Blood Cells by Ca-pillary Electrophoresis-Laser Induced Fluorescence Detection. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, M.S.; Hemshekhar, M.; Santhosh, M.S.; Paul, M.; Sunitha, K.; Thushara, R.M.; NaveenKumar, S.K.; Naveen, S.; Devaraja, S.; Rangappa, K.S.; et al. Tamarind Seed (Tamarindus Indica) Extract Ameliorates Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis via Regulating the Mediators of Cartilage/Bone Degeneration, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangari, N.; O’Brien, P.J. Catalase Activity Assays. CP Toxicology 2006, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




