Submitted:
25 October 2024
Posted:
28 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Conventional Modes of Drug Delivery
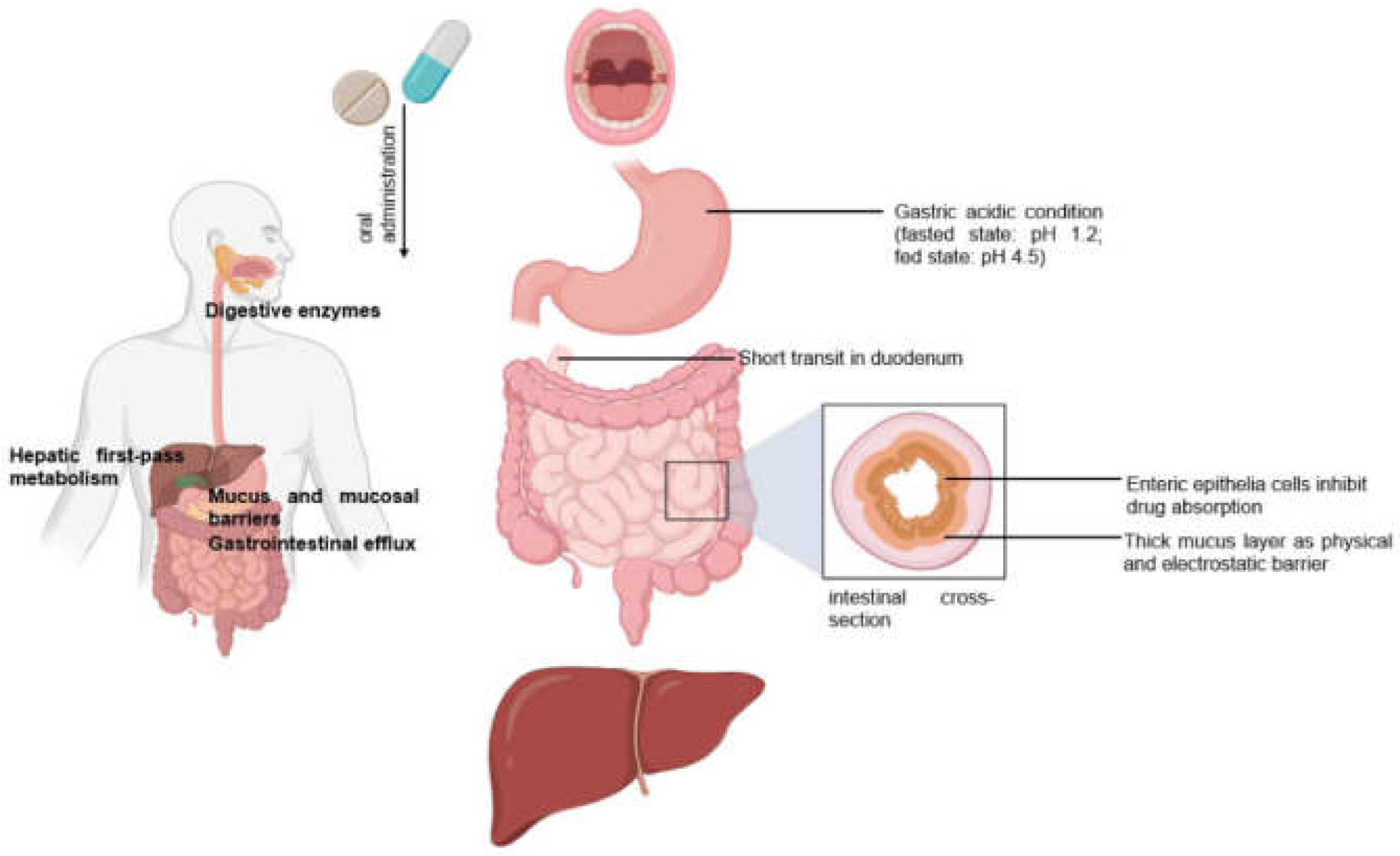
2.1. Oral drug Delivery
2.2. Sublingual and Buccal Drug Delivery
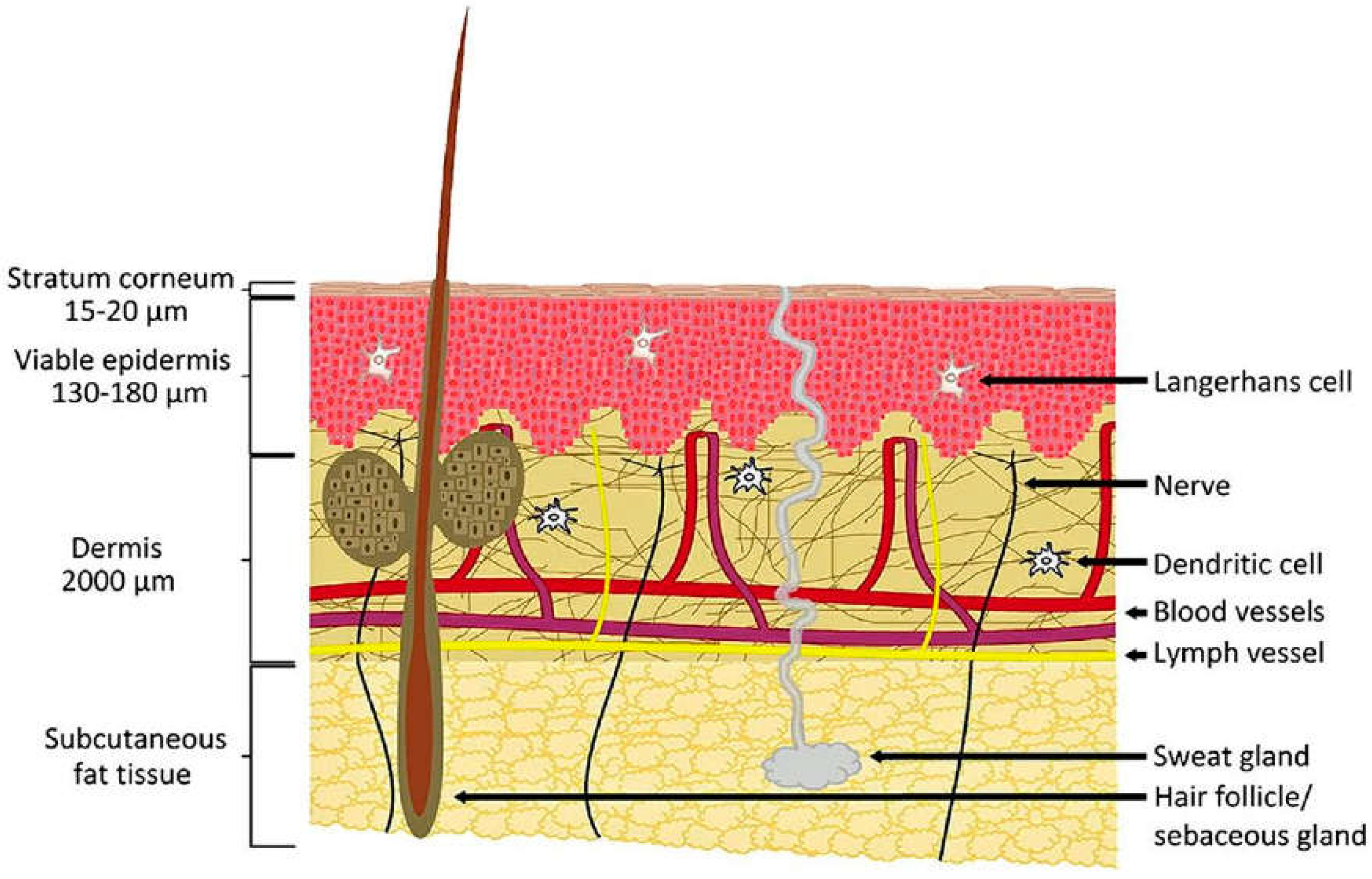
2.3. Transdermal Drug Delivery
2.4. Intramuscular, Intravenous and Subcutaneous Drug Delivery
2.5. Limitations of Conventional Modes of Drug Delivery
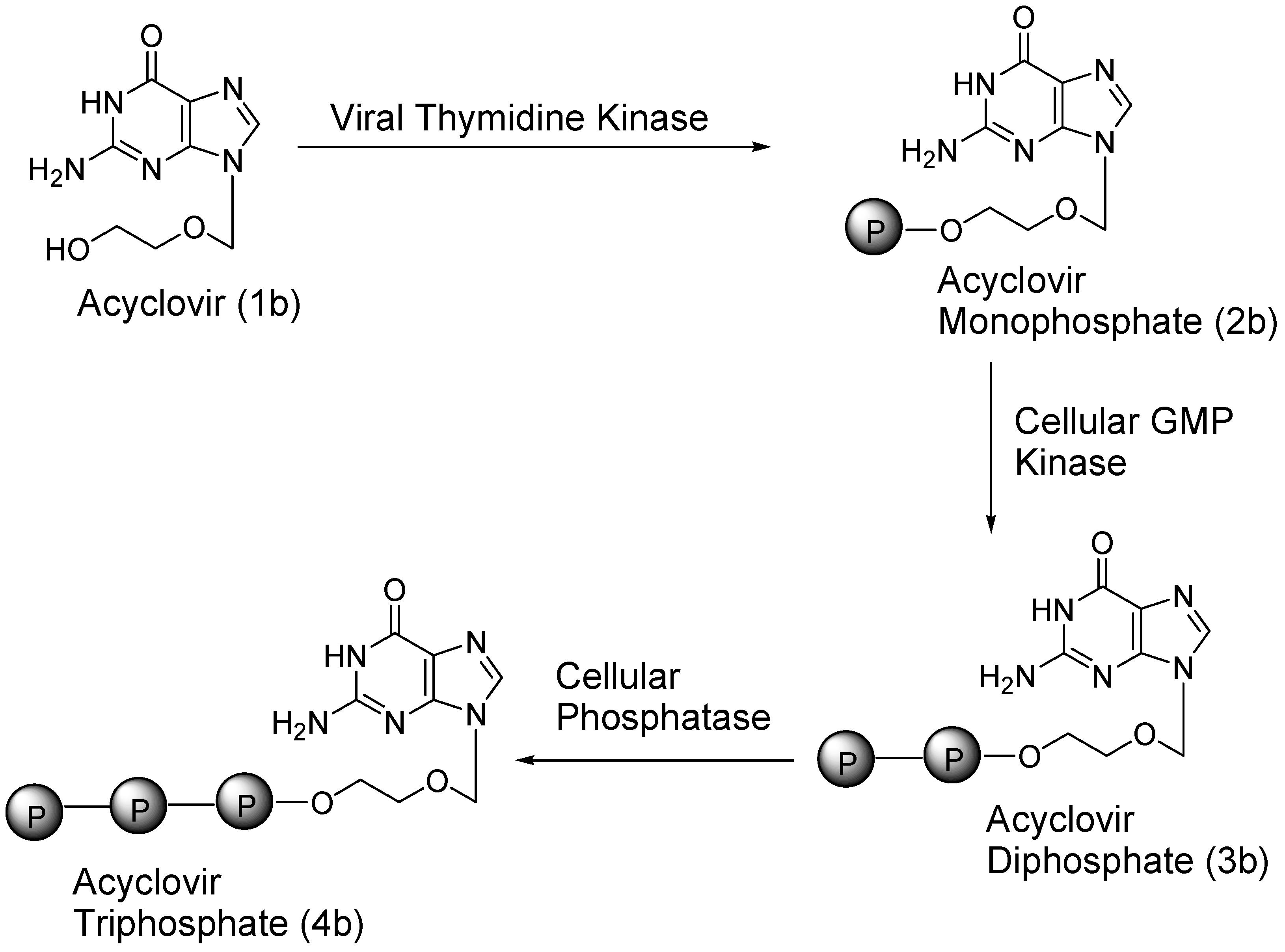
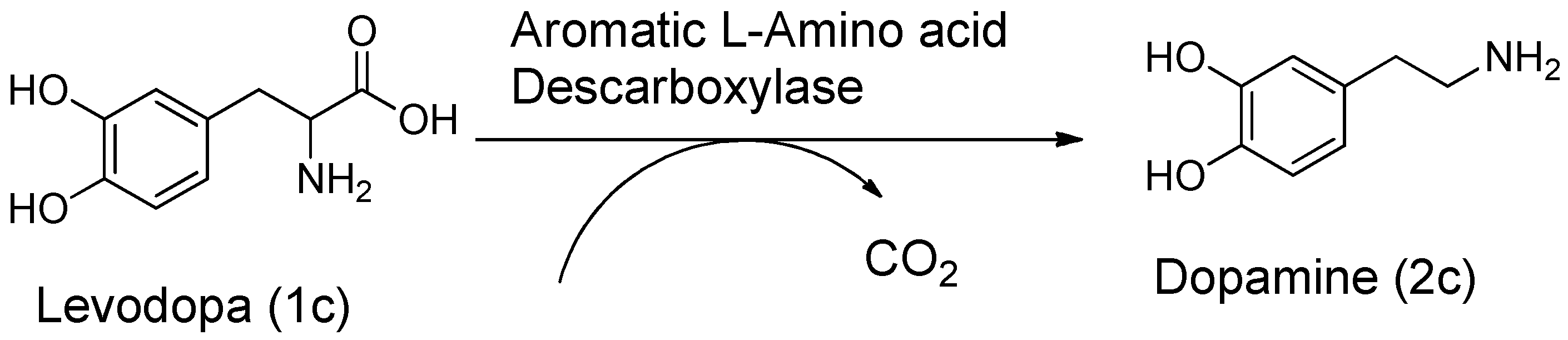
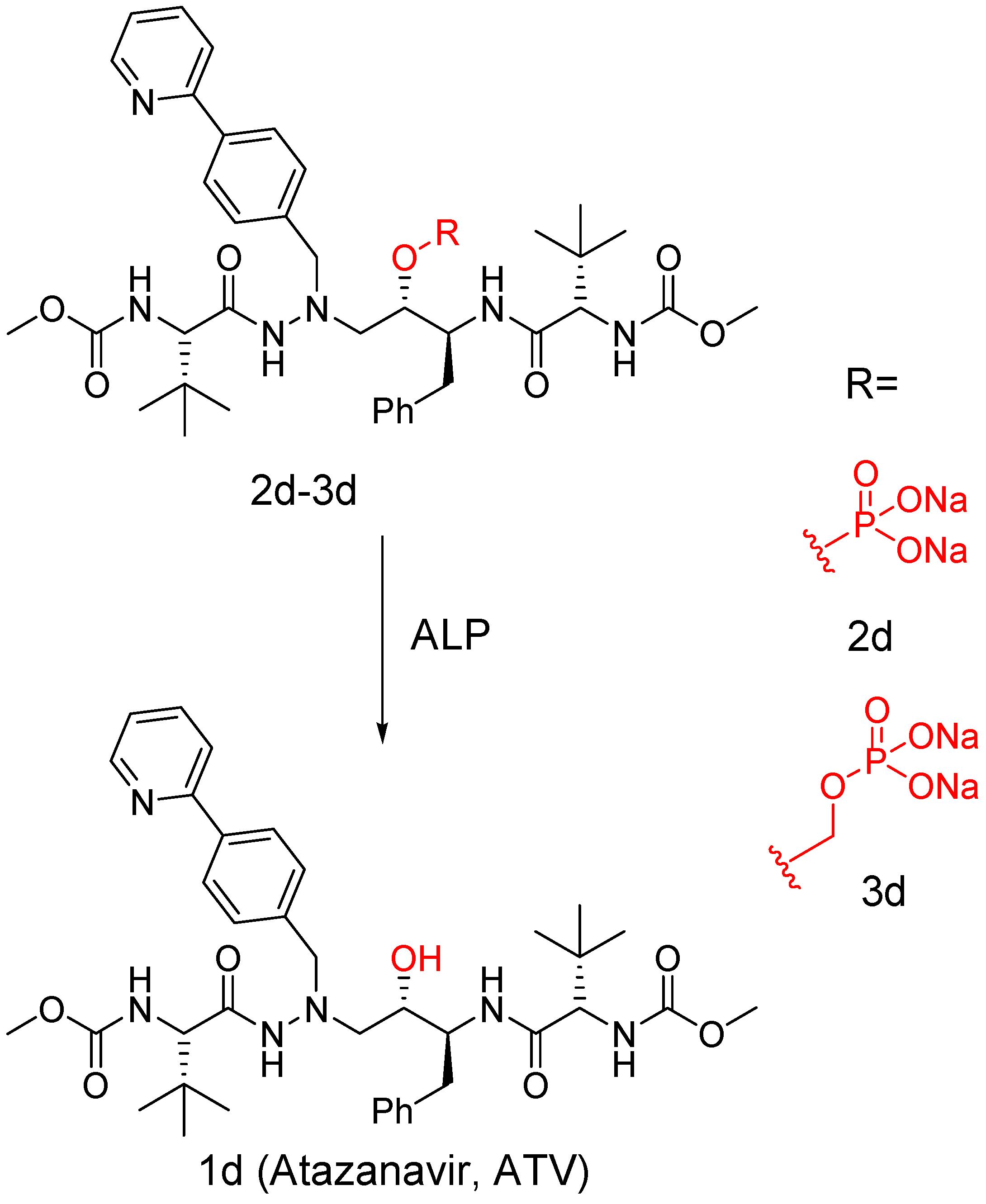
3. Carrier and Bioprecursor Prodrugs as an Alternative to Overcome Limitations of Drug Delivery
4. Nanotechnology in Smart Drug Delivery
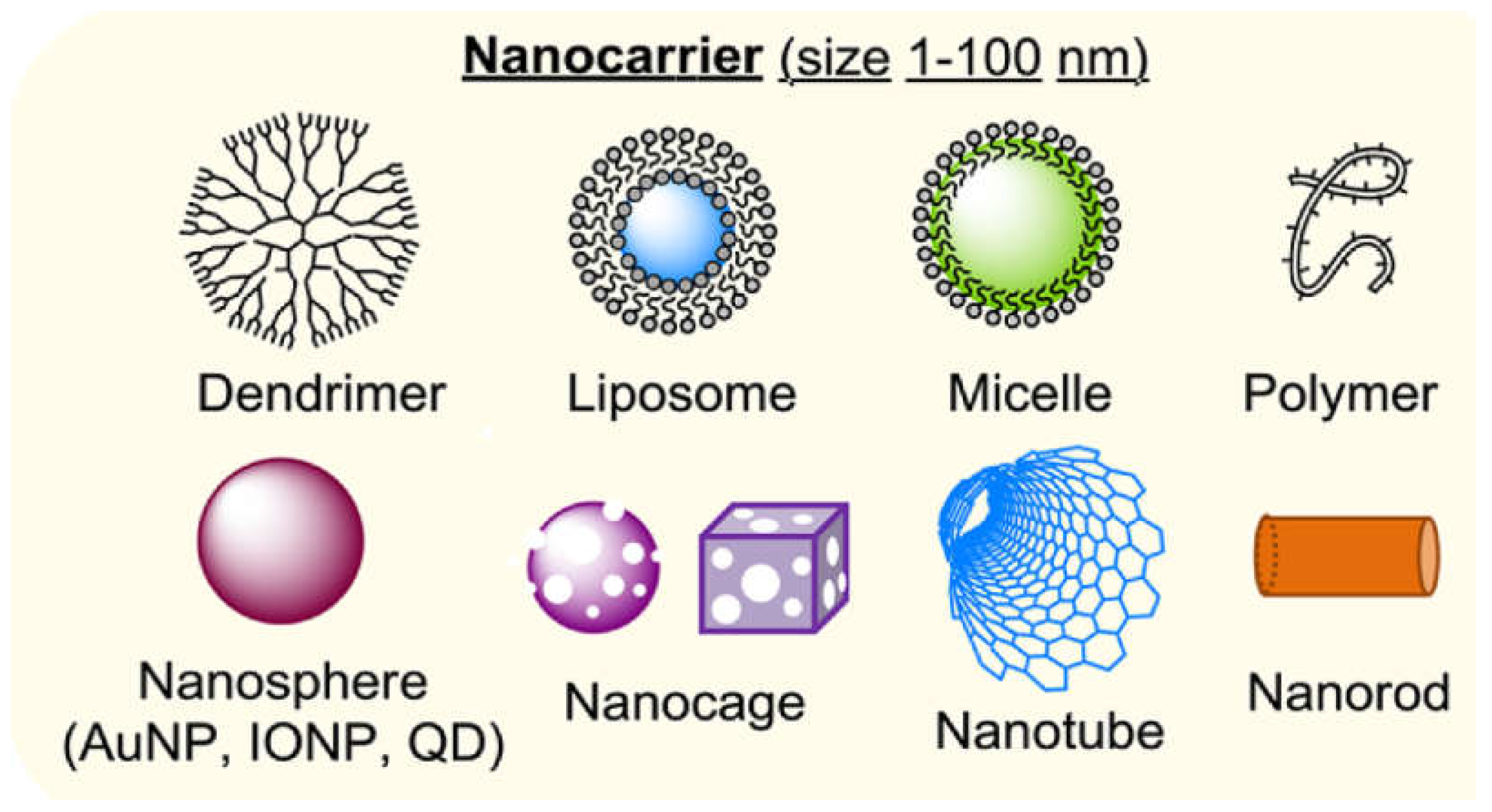
5. Colloidal Nanocarriers in Drug Delivery
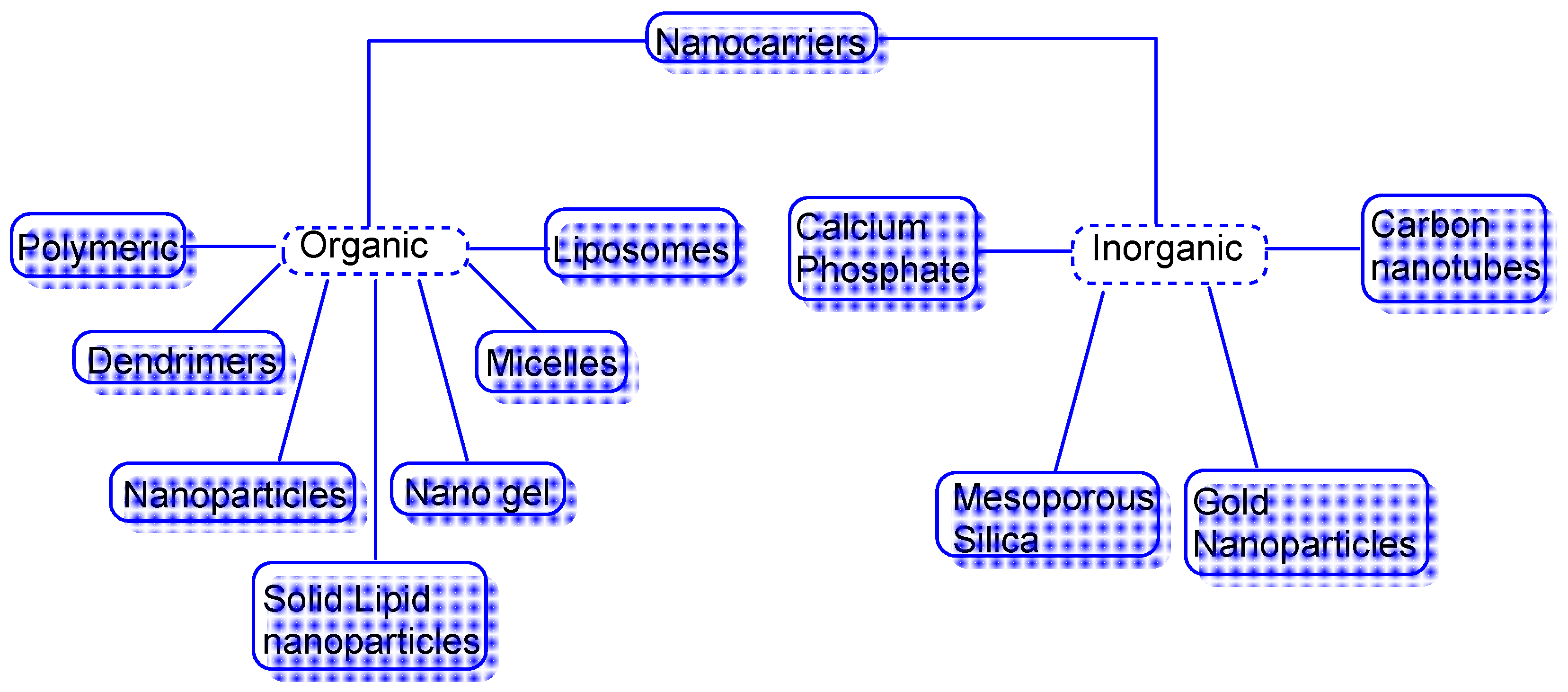
5.1. Nanocarriers as Organic, Inorganic or Hybrid
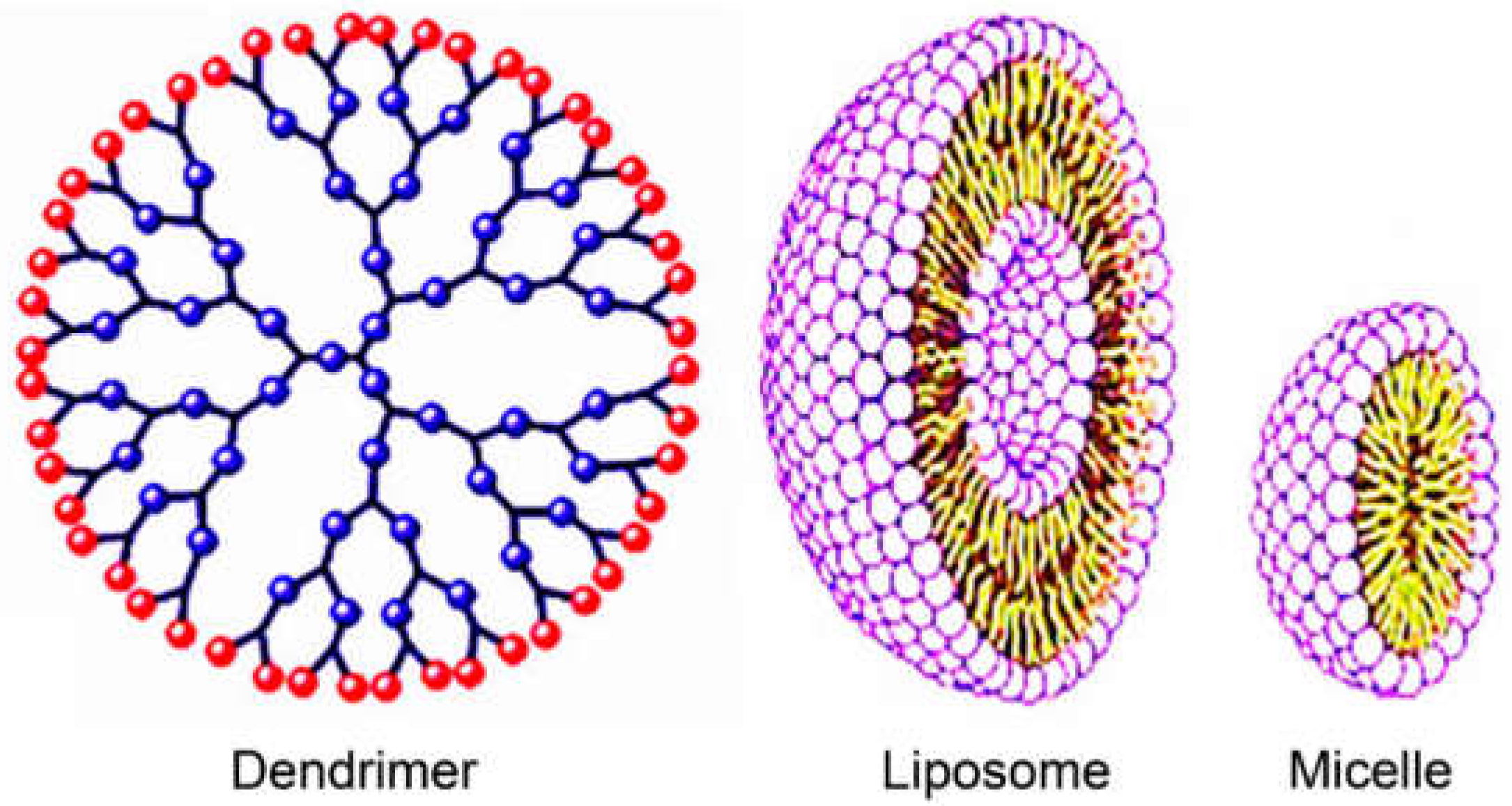
5.2. Organic Nanocarriers
5.3. Inorganic Nanocarriers
5.4. Application of Nanocarriers
5.5. Delivery of Drugs Through Nanocarriers
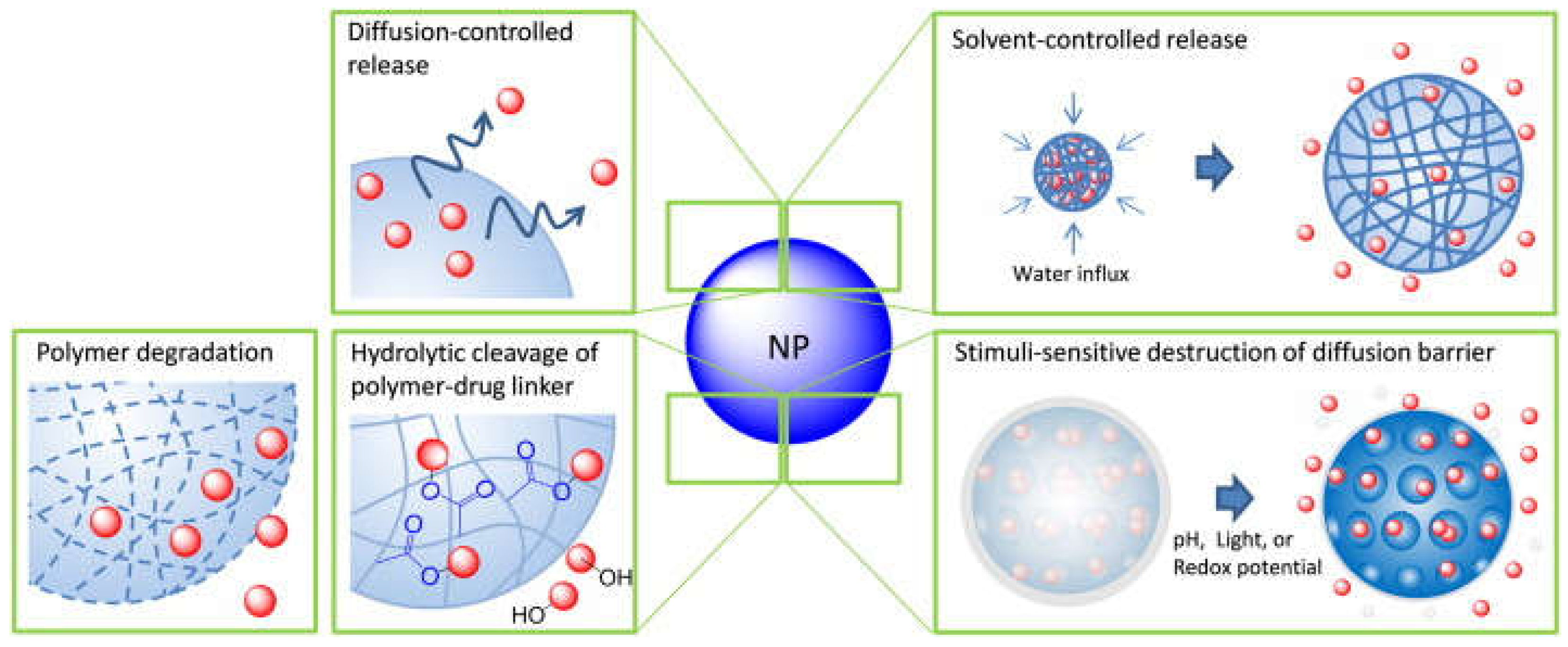
5.6. Release of Conjugated Drugs from Nanocarriers
5.7. The Effectiveness of Nanocarriers
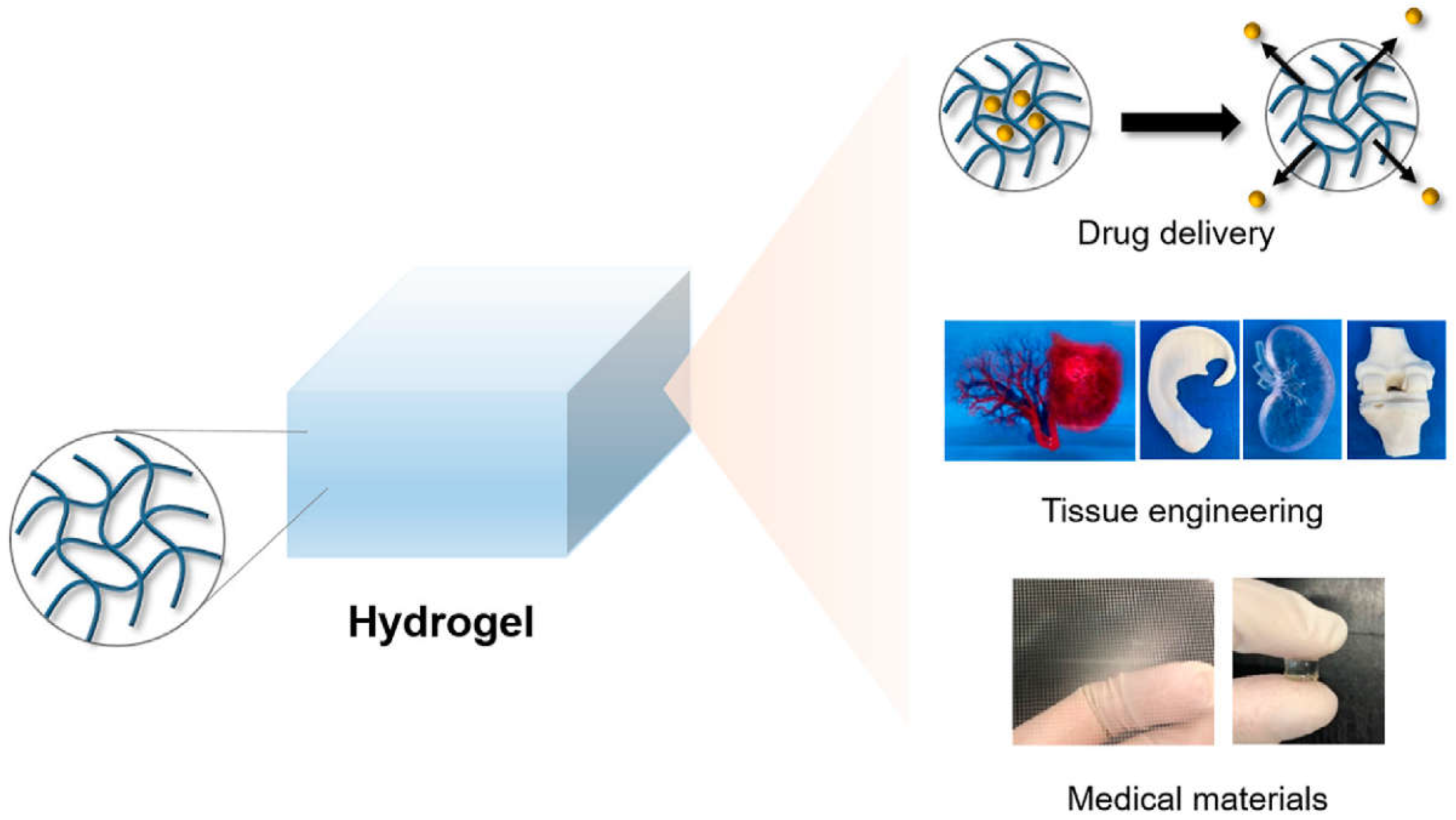
6. Hydrogel-Based Nanocarriers
6.1. Composition of Hydrogels
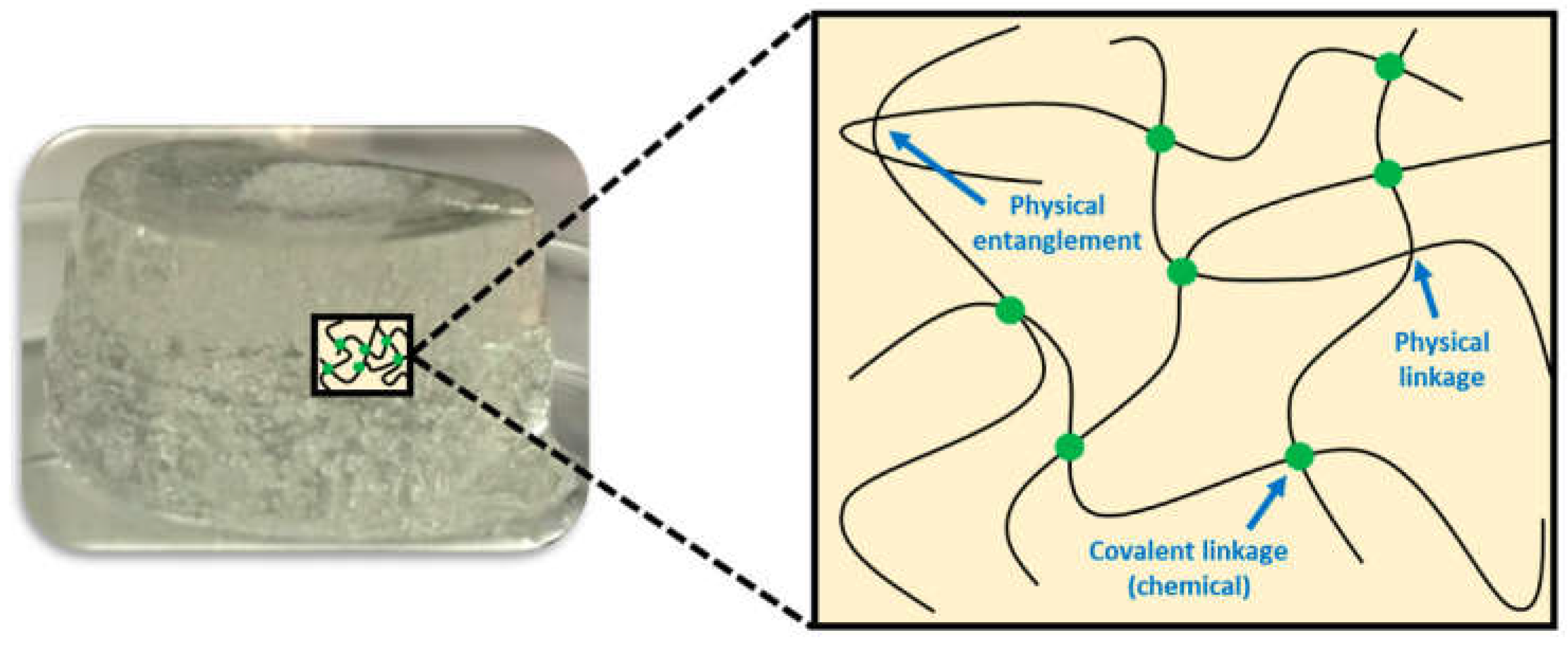
6.2. Chemical and Physical Hydrogels
6.3. High and Low Molecular Weight Hydrogels
6.4. Low Molecular Weight Hydrogels
6.5. Polymer-Based Hydrogels
6.6. Loading of Drugs into a Hydrogel
6.7. Interaction Between Loaded Drug and Polymer Chain
6.8. Delivery of Drug-Loaded Hydrogels
6.9. Release of Loaded Drugs Through Surface or Bulk Erosion of Hydrogels
7. Peptide-Based Hydrogels
7.1. Natural Amino Acids
7.2. Peptide Synthesis
7.3. Folding of Peptides
7.4. Self-Assembly of Peptides
7.5. Hydrogelation of Peptides
7.6. Lego Game: Understanding the Influence of Functional Groups on the Gelation of Hydrogels
7.7. Self-Assembly of Peptide Hydrogels at the Molecular Level
8. Non-Canonical Amino Acids and Their Applications in Peptide Hydrogels Results
8.1. Natural and Synthetic Non-Canonical Amino Acids
8.2. Synthesis of Non-Canonical Amino Acids
8.3. Application of Non-Canonical Amino Acids in Hydrogelators
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of Clinical Drug Development Fails and How to Improve It? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murteira, S.; Ghezaiel, Z.; Karray, S.; Lamure, M. Drug Reformulations and Repositioning in Pharmaceutical Industry and Its Impact on Market Access: Reassessment of Nomenclature. J. Mark. Access Heal. Policy 2013, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, A.; Zare, M.; Thomas, V.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Conventional Drug Delivery Routes, Recent Developments and Future Prospects. Med. Drug Discov. 2022, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakalyani Adepu, S.R. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems : Current Status and Future Directions. Molecules 2021, 26, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Bannerjee, S.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Sriwastawa, B. Drug Delivery Systems: An Updated Review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamundeeswari, M.; Jeslin, J.; Verma, M.L. Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 849–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezike, T.C.; Okpala, U.S.; Onoja, U.L.; Nwike, C.P.; Ezeako, E.C.; Okpara, O.J.; Okoroafor, C.C.; Eze, S.C.; Kalu, O.L.; Odoh, E.C.; et al. Advances in Drug Delivery Systems, Challenges and Future Directions. Heliyon 2023, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.Y.; Kwon, M.; Choi, H.E.; Kim, K.S. Recent Advances in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernstmeyer, K. Chapter 1 Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK595006/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Dinh, L.; Yan, B. Oral Drug Delivery via Intestinal Lymphatic Transport Utilizing Lipid-Based Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Liquids 2023, 3, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, U.; Basu, T.; Majumdar, S. Oral Drug Delivery: Conventional to Long Acting New-Age Designs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 162, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.B.P.; Gomes, V.; Ferreira, P.M.T.; Martins, J.A.; Jervis, P.J. Peptide-Based Supramolecular Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Agents: Recent Advances. Gels 2022, 8, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenthamara, D.; Subramaniam, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.G.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Essa, M.M.; Lin, F.H.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Therapeutic Efficacy of Nanoparticles and Routes of Administration. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S. Physiological and Pharmaceutical Considerations for Rectal Drug Formulations. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S. Advances in Oral Drug Delivery for Regional Targeting in the Gastrointestinal Tract - Influence of Physiological, Pathophysiological and Pharmaceutical Factors. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S. Advances in Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Approaches for Sublingual and Buccal Administration. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinna Reddy, P.; Chaitanya, K.S.C.; Madhusudan Rao, Y. A Review on Bioadhesive Buccal Drug Delivery Systems: Current Status of Formulation and Evaluation Methods. DARU, J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 19, 385–403. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid M. El-Say, T.A.A. Buccal Route of Drug Delivery. In The ADME Encyclopedia. Springer, Cham; 2022; pp. 222–231 ISBN 978-3-030-84859-0.
- Javier, J. Polania Gutierrez; Sunil Munakomi. Intramuscular Injection. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556121 (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Medication Administration: Intramuscular Injection - CE/NCPD. Available online: https://elsevier.health/en-US/preview/intramuscular-injections-acute-care (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Heremans, J.; Chevillard, L.; Mannes, M.; Mangialetto, J.; Leroy, K.; White, J.F.; Lamouroux, A.; Vinken, M.; Gardiner, J.; Van Mele, B.; et al. Impact of Doubling Peptide Length on in Vivo Hydrogel Stability and Sustained Drug Release. J. Control. Release 2022, 350, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, D.N.; Porter, C.J.H.; Charman, S.A. Subcutaneous Drug Delivery and the Role of the Lymphatics. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2005, 2, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christine Case-Lo What Is a Subcutaneous Injection? Available online: https://www.healthline.com/health/subcutaneous-injection (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Labiris, N.R.; Dolovich, M.B. Pulmonary Drug Delivery. Part I: Physiological Factors Affecting Therapeutic Effectiveness of Aerosolized Medications. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 56, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drugs That Are Administered Transdermally. Available online: https://deserthopetreatment.com/addiction-guide/administration-methods/transdermal/ (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Lončar, M.; Jakovljević, M.; Šubarić, D.; Pavlić, M.; Služek, V.B.; Cindrić, I.; Molnar, M. Coumarins in Food and Methods of Their Determination. Foods 2020, 9, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritschel, W.A.; Brady, M.E.; Tan, H.S.I.; Hoffmann, K.A.; Yiu, I.M.; Grummich, K.W. Pharmacokinetics of Coumarin and Its 7-Hydroxy-Metabolites upon Intravenous and Peroral Administration of Coumarin in Man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1977, 12, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonart, L.P.; Gasparetto, J.C.; Pontes, F.L.D.; Cerqueira, L.B.; De Francisco, T.M.G.; Pontarolo, R. New Metabolites of Coumarin Detected in Human Urine Using Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2017, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramelet, A.-A. Venoactive Drugs. In Sclerotherapy; Elsevier, 2011; pp. 369–377.
- Hawthorne, D.; Pannala, A.; Sandeman, S.; Lloyd, A. Sustained and Targeted Delivery of Hydrophilic Drug Compounds: A Review of Existing and Novel Technologies from Bench to Bedside. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 78, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Mehta, D.; Dasgupta, U.; Bajaj, A. Advances in Engineering of Low Molecular Weight Hydrogels for Chemotherapeutic Applications. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaiah, M.A.M.; Rautio, J.; Meanwell, N.A. Prodrugs as Empowering Tools in Drug Discovery and Development: Recent Strategic Applications of Drug Delivery Solutions to Mitigate Challenges Associated with Lead Compounds and Drug Candidates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 2099–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, M.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Dahan, A. Prodrugs for Improved Drug Delivery: Lessons Learned from Recently Developed and Marketed Products. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarkko Rautio, Hanna Kumpulainen, Tycho Heimbach, Reza Oliyai, Dooman Oh, T.J.& J.S. Prodrugs: Design and Clinical Applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 255–270. [CrossRef]
- Zawilska, J.B.; Wojcieszak, J.; Olejniczak, A.B. Prodrugs: A Challenge for the Drug Development. Pharmacol. Reports 2013, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, Z.; Miao, Y.; Xia, J.; Wu, M. Editorial: Prodrug Design and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerd Mikus and Johanna Weiss Influence of CYP2D6 Genetics on Opioid Kinetics, Metabolism and Response. Curr. Pharmacogenomics 2005, 3, 43–52. [CrossRef]
- Brian J. Anderson, C.J.C. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Children. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/nursing-and-health-professions/codeine (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Pharmacological Profiles and Opioid Conversion Tables. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537482/ (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Basil V. Peechakara; Jack G. Tharp; Ike I. Eriator; Mohit Gupta Codeine. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526029/ (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Pratiwi, R.; Noviana, E.; Fauziati, R.; Carrão, D.B.; Gandhi, F.A.; Majid, M.A.; Saputri, F.A. A Review of Analytical Methods for Codeine Determination. Molecules 2021, 26, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thang, N.H.; Chien, T.B.; Cuong, D.X. Polymer-Based Hydrogels Applied in Drug Delivery: An Overview. Gels 2023, 9, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano Based Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S. Smart Drug Delivery Systems : Concepts and Clinical Applications. In Proceedings of the The Second International Conference on Applications of Advanced Technologies (ICAAT); 2021; Vol. 29, pp. 1–26.
- Singh, A.P.; Biswas, A.; Shukla, A.; Maiti, P. Targeted Therapy in Chronic Diseases Using Nanomaterial-Based Drug Delivery Vehicles. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debjit Bhowmik, Harish Gopinath, B. Pragati Kumar, S. Duraivel, K.P.S.K. Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems. Pharma Innov. J. 2012, 1, 24–32.
- Shweta Gupta, Rajesh Kesarla, and A.O. Formulation Strategies to Improve the Bioavailability of Poorly Absorbed Drugs with Special Emphasis on Self-Emulsifying Systems. ISRN Pharm. 2013, 4, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Darvin, P.; Chandrasekharan, A.; Kumar, T.R.S. Introduction to Smart Drug Delivery Systems. In Biomimetic Nanoengineered Materials for Advanced Drug Delivery; 2019; pp. 1–9 ISBN 978-0-12-814944-7. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, F.; Xiong, F.; Gu, N. The Smart Drug Delivery System and Its Clinical Potential. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1306–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, J. V.; Darwitan, A.; Barathi, V.A.; Ang, M.; Htoon, H.M.; Boey, F.; Tam, K.C.; Wong, T.T.; Venkatraman, S.S. Sustained Drug Release in Nanomedicine: A Long-Acting Nanocarrier-Based Formulation for Glaucoma. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvirdipour, S.; Huang, X.; Mihali, V.; Schoenenberger, C.A.; Palivan, C.G. Peptide-Based Nanoassemblies in Gene Therapy and Diagnosis: Paving the Way for Clinical Application. Molecules 2020, 25, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, M.F.; Anton, N.; Wallyn, J.; Omran, Z.; Vandamme, T.F. An Overview of Active and Passive Targeting Strategies to Improve the Nanocarriers Efficiency to Tumour Sites. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Nasrolahi Shirazi, A.; Parang, K. Self-Assembly of Peptides to Nanostructures. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 3544–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.T.; Choi, S.K. Mechanisms of Drug Release in Nanotherapeutic Delivery Systems. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3388–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. The Nanomedicine Revolution Part 1 : Emerging Concepts. A Peer-Reviewed J. Formul. Manag. 2012, 37, 512–518. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, N.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Kamaly, N.; Farokhzad, O.C. The Impact of Passive and Active Targeting in the Era of Modern Cancer Biology. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2014, 66, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.K.; Kim, J.O. Nanomedicine-Based Commercial Formulations: Current Developments and Future Prospects. J. Pharm. Investig. 2023, 53, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Varalakshmi, T. Karpagam, A.V.A.& B.B. Nanoscale Smart Drug Delivery Systems and Techniques of Drug Loading to Nanoarchitectures. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-80371-1_2.
- Milewska, S.; Niemirowicz-Laskowska, K.; Siemiaszko, G.; Nowicki, P.; Wilczewska, A.Z.; Car, H. Current Trends and Challenges in Pharmacoeconomic Aspects of Nanocarriers as Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 6593–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Velikov, K.P. Colloidal Delivery Systems in Foods: A General Comparison with Oral Drug Delivery. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1958–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Patel, B.B.; Tiwari, S. Colloidal Nanocarriers: A Review on Formulation Technology, Types and Applications toward Targeted Drug Delivery. Nanomedicine Nanotechnology, Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, I.; Gilani, E.; Nazir, A.; Bukhari, A. Detail Review on Chemical, Physical and Green Synthesis, Classification, Characterizations and Applications of Nanoparticles. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2020, 13, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, N.A.N.; El-Kemary, M.; Leporatti, S. Micelles Structure Development as a Strategy to Improve Smart Cancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2018, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Yamada, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Kubo, G.; Yoshida, K.; Tabata, E.; Miyake, R.; Sanada, Y.; Akiba, I.; Okobira, T.; et al. Platonic Micelles: Monodisperse Micelles with Discrete Aggregation Numbers Corresponding to Regular Polyhedra. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Atchudan, R.; Lee, W. A Review of Polymeric Micelles and Their Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, G.W.; Henise, J.; Reid, R.; Santi, D. V. Hydrogel Drug Delivery System with Predictable and Tunable Drug Release and Degradation Rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovone, G.; Steiner, F.; Guzzi, E.A.; Tibbitt, M.W. Automated and Continuous Production of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, T.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mei, L. Inorganic Nano-Carriers Based Smart Drug Delivery Systems for Tumor Therapy. Smart Mater. Med. 2020, 1, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, Y.; Kamareddine, M.H.; Tawk, A.; Elia, C.; El Mahmoud, A.; Terro, K.; El Harake, N.; El-Baba, B.; Makdessi, J.; Farhat, S. Inorganic Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems and Their Potential Role in the Treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crintea, A.; Dutu, A.G.; Sovrea, A.; Constantin, A.M.; Samasca, G.; Masalar, A.L.; Ifju, B.; Linga, E.; Neamti, L.; Tranca, R.A.; et al. Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery: An Overview with Emphasis on Vitamin D and K Transportation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyen, E.; Martin, C.; Caveliers, V.; Madder, A.; Van Mele, B.; Hoogenboom, R.; Hernot, S.; Ballet, S. In Vivo Imaging of the Stability and Sustained Cargo Release of an Injectable Amphipathic Peptide-Based Hydrogel. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, M.H.; Foudah, A.I.; Alam, A.; Salkini, M.A.; Muharram, M.M.; Labrou, N.E.; Rawat, P. Coumarin-Encapsulated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as an Effective Therapy against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivki, M.; Bachtiar, A.M.; Informatika, T.; Teknik, F.; Indonesia, U.K. Colloids in Drug Delivery; Monzer Fanun, Ed.; CRC Press, 2016; ISBN 9781138199156.
- Chen, K.; Cai, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Gu, Z.; Gong, Q.; Luo, K. Stimuli-Responsive Polymer-Doxorubicin Conjugate: Antitumor Mechanism and Potential as Nano-Prodrug. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Xu, B.; Yao, H.; Lu, X.; Tan, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. Schiff-Linked PEGylated Doxorubicin Prodrug Forming PH-Responsive Nanoparticles With High Drug Loading and Effective Anticancer Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.A.; Waterhouse, D.N.; Mayer, L.D.; Cullis, P.R.; Madden, T.D.; Bally, M.B. The Liposomal Formulation of Doxorubicin. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 391, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Taslakjian, B.; Kim, S.; Tirrell, M. V.; Guler, M.O. Therapeutic Peptides, Proteins and Their Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Precision Medicine. ChemBioChem 2024, 25, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
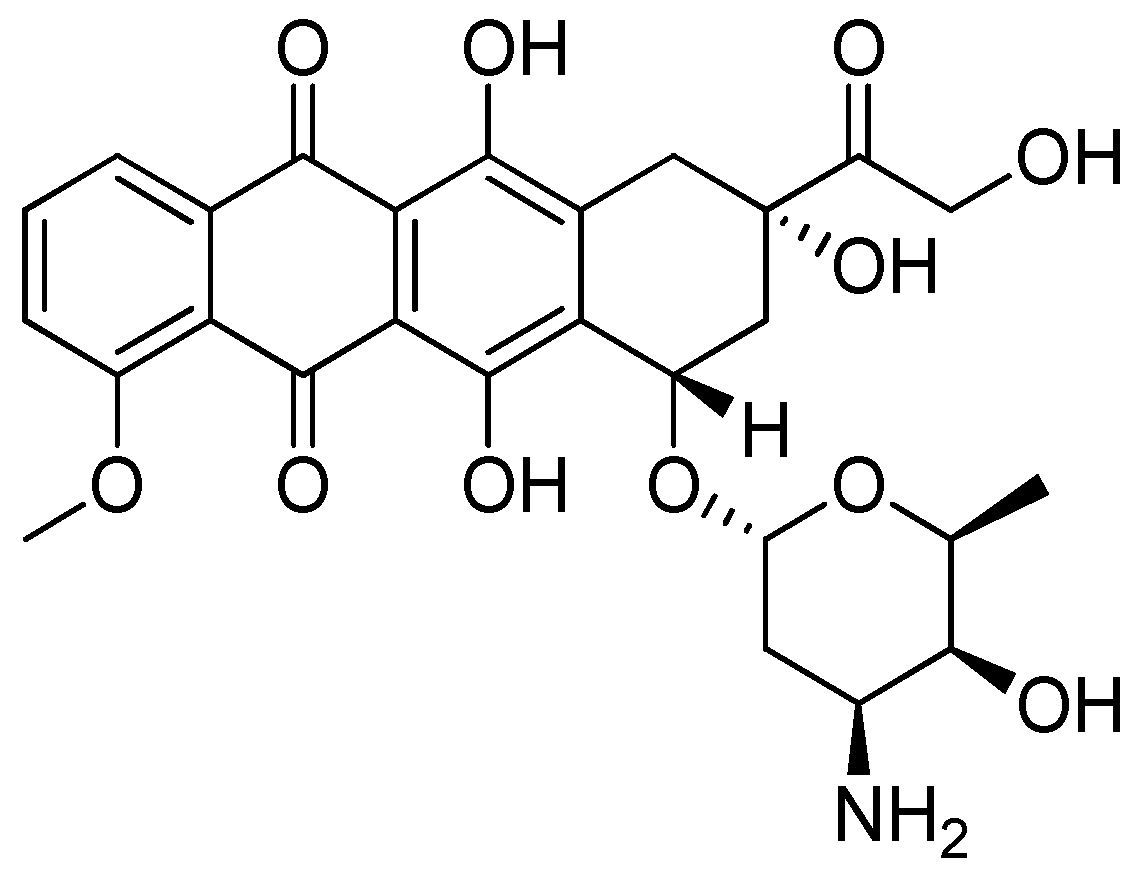
- Nebigil, C.G.; Désaubry, L. Updates in Anthracycline-Mediated Cardiotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloss, K.; Hamar, P. Recent Preclinical and Clinical Progress in Liposomal Doxorubicin. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, D.N.; Tardi, P.G.; Mayer, L.D.; Bally, M.B. A Comparison of Liposomal Formulations of Doxorubicin with Drug Administered in Free Form. Drug-Safety 2001, 24, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankhar, R.; Vyas, S.P.; Jain, A.K.; Arora, S.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Advances in Novel Drug Delivery Strategies for Breast Cancer Therapy. Artif. Cells, Blood Substitutes, Biotechnol. 2010, 38, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelepukin, I. V.; Griaznova, O.Y.; Shevchenko, K.G.; Ivanov, A. V.; Baidyuk, E. V.; Serejnikova, N.B.; Volovetskiy, A.B.; Deyev, S.M.; Zvyagin, A. V. Flash Drug Release from Nanoparticles Accumulated in the Targeted Blood Vessels Facilitates the Tumour Treatment. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yeo, Y. Controlled Drug Release from Pharmaceutical Nanocarriers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 125, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzina, M.A.; Kartsev, D.D.; Stratonovich, A. V.; Levkin, P.A. Organogels versus Hydrogels: Advantages, Challenges, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinç-Özakar, R.; Seyret, E.; Özakar, E.; Adıgüzel, M.C. Nanoemulsion-Based Hydrogels and Organogels Containing Propolis and Dexpanthenol: Preparation, Characterization, and Comparative Evaluation of Stability, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Properties. Gels 2022, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minehan, R.L.; Del Borgo, M.P. Controlled Release of Therapeutics From Enzyme-Responsive Biomaterials. Front. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. Injectable Hydrogels Delivering Therapeutic Agents for Disease Treatment and Tissue Engineering. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jianyu Li and David J. Mooney Designing Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. Nat Rev Mater 2016, 1. [CrossRef]
- Madduma-Bandarage, U.S.K.; Madihally, S. V. Synthetic Hydrogels: Synthesis, Novel Trends, and Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Jeong, J.O.; Park, S.H. State-of-the-Art Irradiation Technology for Polymeric Hydrogel Fabrication and Application in Drug Release System. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, G.A.; Ary, B.E.; Dear, A.J.; Rohn, M.C.H.; Payson, A.M.; Lee, D.S.M.; Parry, R.C.; Friedman, C.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Linse, S.; et al. On the Mechanism of Self-Assembly by a Hydrogel-Forming Peptide. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4781–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.D.; Thordarson, P. Beyond Fmoc: A Review of Aromatic Peptide Capping Groups. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, T.R.; Kohane, D.S. Hydrogels in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Polymer (Guildf). 2008, 49, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Holmes, T.C.; DiPersio, C.M.; Hynes, R.O.; Su, X.; Rich, A. Self-Complementary Oligopeptide Matrices Support Mammalian Cell Attachment. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almawash, S.; Osman, S.K.; Mustafa, G.; El Hamd, M.A. Current and Future Prospective of Injectable Hydrogels—Design Challenges and Limitations. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Liu, H.; Chen, J. Preparation and Applications of Peptide-Based Injectable Hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 28299–28311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Penn, M.; Hennessy, M.G. Optimal Loading of Hydrogel-Based Drug-Delivery Systems. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 112, 649–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Oyen, E.; Van Wanseele, Y.; Haddou, T. Ben; Schmidhammer, H.; Andrade, J.; Waddington, L.; Van Eeckhaut, A.; Van Mele, B.; Gardiner, J.; et al. Injectable Peptide-Based Hydrogel Formulations for the Extended in Vivo Release of Opioids. Mater. Today Chem. 2017, 3, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Hina, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rajpar, A.H.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Alghamdi, N.A.; Wageh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Fundamental Concepts of Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Their Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2020, 12, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante-Torres, M.; Romero-Fierro, D.; Arcentales-Vera, B.; Palomino, K.; Magaña, H.; Bucio, E. Hydrogels Classification According to the Physical or Chemical Interactions and as Stimuli-Sensitive Materials. Gels 2021, 7, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Mondal, J.H.; Das, D. Peptide Hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9117–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binaymotlagh, R.; Chronopoulou, L.; Haghighi, F.H.; Fratoddi, I.; Palocci, C. Peptide-Based Hydrogels: New Materials for Biosensing and Biomedical Applications. Materials (Basel). 2022, 15, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, T.; Ogura, Y.; Sakurai, E.; Tabata, Y.; Kimura, H. Intraocular Sustained Drug Delivery Using Implantable Polymeric Devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chan, H.P.; Chung, T.W.; Shu, C.W.; Chuang, K.P.; Duh, T.H.; Yang, M.H.; Tyan, Y.C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buwalda, S.J.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels for Therapeutic Delivery: Current Developments and Future Directions. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, Z.; Salman, S.; Khan, S.A.; Amin, A.; Rahman, Z.U.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; Akhtar, K.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Versatility of Hydrogels: From Synthetic Strategies, Classification, and Properties to Biomedical Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O. Wichterle & D. Lim Hydrophilic Gels for Biological Use. Nature 1960, 185, 117–118. [CrossRef]
- Morteza Bahram, N.M. and; Moghtader, M. An Introduction to Hydrogels and Some Recent Applications. In Emerging Concepts in Analysis and Applications of Hydrogels; 2016; pp. 1–266 ISBN 978-953-51-2510-5.
- Alonso, J.M.; Del Olmo, J.A.; Gonzalez, R.P.; Saez-martinez, V. Injectable Hydrogels: From Laboratory to Industrialization. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Oyen, E.; Mangelschots, J.; Bibian, M.; Ben Haddou, T.; Andrade, J.; Gardiner, J.; Van Mele, B.; Madder, A.; Hoogenboom, R.; et al. Injectable Peptide Hydrogels for Controlled-Release of Opioids. Medchemcomm 2016, 7, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuri, D.; Zanna, N.; Tomasini, C. Low Molecular Weight Gelators Based on Functionalized L-Dopa Promote Organogels Formation. Gels 2019, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toews, P.; Bates, J. Influence of Drug and Polymer Molecular Weight on Release Kinetics from HEMA and HPMA Hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanabusa, K.; Suzuki, M. Development of Low-Molecular-Weight Gelators and Polymer-Based Gelators. Polym. J. 2014, 46, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Mooney, D.J. Chemical Strategies to Engineer Hydrogels for Cell Culture. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 726–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, J.N.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Li, Z.; MacLachlan, M.J. Mouldable Multicomponent Low Molecular Weight Supergelators. Supramol. Chem. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Das, S.; Nandi, A.K. A Review on Recent Advances in Polymer and Peptide Hydrogels. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 1404–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, D.M.; Abraham, B.L.; Fujita, T.; Watrous, M.J.; Toriki, E.S.; Takano, T.; Nilsson, B.L. Low-Molecular-Weight Supramolecular Hydrogels for Sustained and Localized in Vivo Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2116–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hany F. Nour, Ahmed M. Salama, B.H.A.A.-D. and A.F.S. Low-Molecular-Weight Hydrogels: Synthetic Methodologies, Gelation Mechanisms, and Biomedical Applications. In Hydrogels and Nanogels - Applications in Medicine; 2023; pp. 1–25 ISBN 9788578110796. [CrossRef]
- Draper, E.R.; Adams, D.J. Low-Molecular-Weight Gels: The State of the Art. Chem 2017, 3, 390–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, V.; Veloso, S.R.S.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Ferreira, P.M.T.; Castanheira, E.M.S. Tuning Peptide-Based Hydrogels: Co-Assembly with Composites Driving the Highway to Technological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, L.; Zheng, R.; Sun, R. Self-Assembly Dipeptide Hydrogel: The Structures and Properties. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, E.R.; Adams, D.J. Probing the Self-Assembled Structures and p K a of Hydrogels Using Electrochemical Methods. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiew, S.H.; Wang, J.K.; Koh, K.; Yang, H.; Bacha, A.; Lin, J.; Yip, Y.S.; Vos, M.I.G.; Chen, L.; Sobota, R.M.; et al. Bioinspired Short Peptide Hydrogel for Versatile Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Growth Factor Therapeutics. Acta Biomater. 2021, 136, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D. Recent Advances in Hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 1987–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Tan, H. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels: From Polymer to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, J.; Pan, B.; Yang, H.Y.; Liu, G. Bin; Lu, K. Fabrication of the Low Molecular Weight Peptide-Based Hydrogels and Analysis of Gelation Behaviors. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H., Ansari, M., Darvishi, A. et al. Polyacrylic Acid: A Biocompatible and Biodegradable Polymer for Controlled Drug Delivery. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2023, 65, 702–713. [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Jr., J.W.L. Nanoparticle-Based Targeted Drug Delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [CrossRef]
- Liechty, W.B.; Kryscio, D.R.; Slaughter, B. V.; Peppas, N.A. Polymers for Drug Delivery Systems. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2010, 1, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marga C Lensen, Vera Schulte, M.D. Cell Adhesion and Spreading on an Intrinsically Anti-Adhesive PEG Biomaterial. In Biomaterials - Physics and Chemistry; 2011; pp. 1–504 ISBN 978-953-307-418-4.
- Simões, S. Modular Hydrogels for Drug Delivery. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 3, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiary, N.; Ghalandari, B.; Ghorbani, F.; Varma, S.N.; Liu, C. Advances in Peptide-Based Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2023, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D.; Martins, M.; Freitas, F. Exploring the Drug-Loading and Release Ability of FucoPol Hydrogel Membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim SW, Bae YH, O.T. Hydrogels: Swelling, Drug Loading, and Release. Pharm Res 1992, 9, 283–290. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Das, D. Rational Design of Peptide-Based Smart Hydrogels for Therapeutic Applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.T.; Irwan, R.M.; Li, Z.; Goh, K.B. Quantifying How Drug-Polymer Interaction and Volume Phase Transition Modulate the Drug Release Kinetics from Core-Shell Microgels. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 622, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibian, M.; Mangelschots, J.; Gardiner, J.; Waddington, L.; Diaz Acevedo, M.M.; De Geest, B.G.; Van Mele, B.; Madder, A.; Hoogenboom, R.; Ballet, S. Rational Design of a Hexapeptide Hydrogelator for Controlled-Release Drug Delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, A.M.; Lo, D.W.P.M.; Hest, J.C.M. Van Peptide- and Protein-Based Hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.C.; Smith, A.A.A.; Appel, E.A. Structural Considerations for Physical Hydrogels Based on Polymer-Nanoparticle Interactions. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2020, 5, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, N.; Rao, P.; Jadhav, G.S.; Kulkarni, B.; Kanakavalli, N.; Kirad, S.; Salunke, S.; Tanpure, V.; Sahu, B. Emerging Role of Injectable Dipeptide Hydrogels in Biomedical Applications. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 3551–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Torres García, D.; Salehi, M.; Webber, M.J.; van Kasteren, S.I.; Eelkema, R. Dynamic Covalent Dextran Hydrogels as Injectable, Self-Adjuvating Peptide Vaccine Depots. ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, 18, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, M.M.; Ayres, N. Dynamic Covalent Bonds in Self-Healing, Shape Memory, and Controllable Stiffness Hydrogels. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtering, W.; Saunders, B.R. Gel Architectures and Their Complexity. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3695–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Tang, L.; Shi, D.; Lam, E.; Bae, J. 3D Shape Morphing of Stimuli-Responsive Composite Hydrogels. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 5989–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Maktedar, S.S. Structural, Functional and Mechanical Performance of Advanced Graphene-Based Composite Hydrogels. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, F.; Zafar, H.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Ullah, A.; Khan, A.U.; He, X.; Han, H.; Aquib, M.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.O.; et al. A Review on Recent Advances in Stabilizing Peptides/Proteins upon Fabrication in Hydrogels from Biodegradable Polymers. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.E.; Hindley, J.W.; Baxani, D.K.; Ces, O.; Elani, Y. Hydrogels as Functional Components in Artificial Cell Systems. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkouri, H.; Chamkouri, M. A Review of Hydrogels, Their Properties and Applications in Medicine. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res. 2021, 11, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boimvaser, S.; Mariano, R.N.; Turino, L.N.; Vega, J.R. In Vitro Bulk/Surface Erosion Pattern of PLGA Implant in Physiological Conditions: A Study Based on Auxiliary Microsphere Systems. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, L.N.; Grunlan, M.A. Hydrolytic Degradation and Erosion of Polyester Biomaterials. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friederike, von B.; Luise, S.; Achim, G. Why Degradable Polymers Undergo Surface Erosion or Bulk Erosion. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4221–4231. [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.C.; Guedes, R.M.; Tita, V. Considerations for the Design of Polymeric Biodegradable Products. J. Polym. Eng. 2013, 33, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, S.; Barnard, E.; Hyatt, B.; Rathinam, M.; Zustiak, S.P. Predicting Drug Release From Degradable Hydrogels Using Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy and Mathematical Modeling. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y. Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Hydrogels for Wound Tissue Repair. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Workman, V.L.; O’Brien, M.; McLaren, J.; White, L.; Ragunath, K.; Rose, F.; Saiani, A.; Gough, J.E. Peptide Hydrogels—A Tissue Engineering Strategy for the Prevention of Oesophageal Strictures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Soto-Gutierrez, A.; Chen, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Rivas-Carrillo, J.D.; Navarro-Alvarez, N.; Tanaka, K.; Miki, A.; Takei, J.; et al. PuraMatrixTM Facilitates Bone Regeneration in Bone Defects of Calvaria in Mice. Cell Transplant. 2006, 15, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, J.; Richey, G.; Kim, S.; Guler, M.O. Peptide Hydrogels and Nanostructures Controlling Biological Machinery. Langmuir 2023, 39, 11935–11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Holmes, T.C.; DiPersio, C.M.; Hynes, R.O.; Su, X.; Rich, A.; J. Penn, M.; Hennessy, M.G.; Lee, J.H.H.; Yeo, Y.; et al. Beyond 20 in the 21st Century: Prospects and Challenges of Non-Canonical Amino Acids in Peptide Drug Discovery. Molecules 2023, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschning, A. On the Evolutionary History of the Twenty Encoded Amino Acids. Chemistry 2022, 28, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Mohammad, A.R.; Karodia, N.; Rahman, A. Multimodal Role of Amino Acids in Microbial Control and Drug Development. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibba, M.; Stathopoulos, C.; Söll, D. Protein Synthesis: Twenty Three Amino Acids and Counting. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, T.G.; Melle-Franco, M.; Sousa, C.E.A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Marcos, J.C. Non-Canonical Amino Acids as Building Blocks for Peptidomimetics: Structure, Function, and Applications. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J. Ayon, N. Features, Roles and Chiral Analyses of Proteinogenic Amino Acids. AIMS Mol. Sci. 2020, 7, 229–268. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, F.; Nouranian, S.; Mahdavi, M.; Al-Ostaz, A. Molecular Simulation Insights on the in Vacuo Adsorption of Amino Acids on Graphene Oxide Surfaces with Varying Surface Oxygen Densities. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulbagi, M.; Wang, L.; Siddig, O.; Di, B.; Li, B. D-Amino Acids and D-Amino Acid-Containing Peptides: Potential Disease Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, G.L.; Rosini, E.; Crespi, E.; Pollegioni, L. D-Amino Acids in Foods. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, D. V.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Pokrovskaya, M. V.; Sokolov, N.N. D-Amino Acids in Nature, Agriculture and Biomedicine. All Life 2020, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.-X.; Wang, H.-F.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Chen, F.-E. Natural Occurrence, Biological Functions, and Analysis of D-Amino Acids. Pharm. Front. 2020, 02, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, A.D.; Chalmers, J.H.; Bada, J.L.; Grunthaner, F.J.; Amashukeli, X.; Willis, P.; Skelley, A.M.; Mathies, R.A.; Quinn, R.C.; Zent, A.P.; et al. The Urey Instrument: An Advanced in Situ Organic and Oxidant Detector for Mars Exploration. Astrobiology 2008, 8, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, P.; Piekarski, D.G.; Capron, M.; Domaracka, A.; Adoui, L.; Martín, F.; Alcamí, M.; Díaz-Tendero, S.; Huber, B.A. Polypeptide Formation in Clusters of β-Alanine Amino Acids by Single Ion Impact. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Gong, J.; Qiu, Z.; Li, Y.; Qiao, J.; Huo, Y.-X. Incorporation of Non-Canonical Amino Acids into Antimicrobial Peptides: Advances, Challenges, and Perspectives. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrudu, S.; Simerska, P.; Toth, I. Chemical Methods for Peptide and Protein Production. Molecules 2013, 18, 4373–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffler, F.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Fortsch, T.; Dorsam, E.; Bischoff, R.; Breitling, F.; Nesterov-Muller, A. Biofunctional Xerography. In Biotechnology of Biopolymers; InTech, 2011; pp. 275–298.
- Bertouille, J.; Kasas, S.; Martin, C.; Hennecke, U.; Ballet, S.; Willaert, R.G. Fast Self-Assembly Dynamics of a β-Sheet Peptide Soft Material. Small 2023, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBenedictis, E.P.; Keten, S. Mechanical Unfolding of Alpha- and Beta-Helical Protein Motifs. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orders of Protein Structure. Available online: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/macromolecules/proteins-and-amino-acids/a/orders-of-protein-structure.
- Haimov, B.; Srebnik, S. A Closer Look into the α-Helix Basin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.; Del Valle, L.J.; Alemán, C.; Puiggalí, J. Peptide Self-Assembly into Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications Related to Hydroxyapatite. Gels 2019, 5, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D. The Discovery of the α-Helix and β-Sheet, the Principal Structural Features of Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 11207–11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Xing, R.; Yan, X. Peptide Self-Assembly: Thermodynamics and Kinetics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5589–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Trinh, T.H.T.; Yoo, M.; Shin, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Hwang, E.; Lim, Y.B.; Ryou, C. Self-Assembling Peptides and Their Application in the Treatment of Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Noonan, B.J.; Kamboukos, A.; Todorova, N.; Yarovsky, I. Self-Assembling Peptide Biomaterials: Insights from Spontaneous and Enhanced Sampling Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Chem. Phys. Rev. 2023, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.J.; Langenstein, M.G.; Pochan, D.J.; Kloxin, C.J.; Saven, J.G. Peptide Design and Self-Assembly into Targeted Nanostructure and Functional Materials. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13915–13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Marie Lehn Supramolecular Chemistry—Scope and Perspectives Molecules, Supermolecules, and Molecular Devices (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 1988, 27, 89–112. [CrossRef]
- Stefan Loic Amino Acids Modification to Improve and Fine-Tune Peptide-Based Hydrogels. In Amino Acid - New Insights and Roles in Plant and Animal; 2017; pp. 1–294 ISBN 978-953-51-3242-4.
- Nagai, Y.; Yokoi, H.; Kaihara, K.; Naruse, K. The Mechanical Stimulation of Cells in 3D Culture within a Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogel. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, D.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Nagaraj, R.; Chaudhary, N. Hydrogel Formation by an Aromatic Analogue of a β-Amyloid Fragment, Aβ16-22: A Scaffold for 3D Cell Culture. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawy, M.A.; Smith, A.M.; Hodson, N.; Squires, A.; Miller, A.F.; Saiani, A. Modification of β-Sheet Forming Peptide Hydrophobic Face: Effect on Self-Assembly and Gelation. Langmuir 2016, 32, 4917–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggeli, A. Engineering of Peptide β-Sheet Nanotapes. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wychowaniec, J.K.; Smith, A.M.; Ligorio, C.; Mykhaylyk, O.O.; Miller, A.F.; Saiani, A. Role of Sheet-Edge Interactions in β-Sheet Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2285–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.P.; Pochan, D.J.; Ozbas, B.; Rajagopal, K.; Pakstis, L.; Kretsinger, J. Responsive Hydrogels from the Intramolecular Folding and Self-Assembly of a Designed Peptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 15030–15037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Xu, B. Supramolecular Hydrogelators and Hydrogels: From Soft Matter to Molecular Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13165–13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokuma, T. Synthesis of Non-Canonical Amino Acids and Peptide Containing Them for Establishment of the Template for Drug Discovery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheology Testing. Available online: https://www.instron.com/en/resources/test-types/rheology-testing (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Menger, F.M.; Caran, K.L. Anatomy of a Gel. Amino Acid Derivatives That Rigidify Water at Submillimolar Concentrations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11679–11691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsheed, A.C.; Zevallos-Delgado, C.; Yu, L.T.; Saeidifard, S.; Swain, J.W.R.; Makhoul, J.T.; Thomas, A.J.; Cole, C.C.; Garcia Huitron, E.; Grande-Allen, K.J.; et al. Tunable Macroscopic Alignment of Self-Assembling Peptide Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 12477–12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Miller, A.F.; Saiani, A. Peptide Hydrogels as Mucoadhesives for Local Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hantash, B.M. Support of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Multipotency by a Poloxamer-Octapeptide Hybrid Hydrogel. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5122–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Weng, S.; Jiang, X. Super Strong and Tough Anisotropic Hydrogels through Synergy of Directional Freeze-Casting, Metal Complexation and Salting Out. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Hou, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y. Biostable Hydrogels Consisting of Hybrid β-Sheet Fibrils Assembled by a Pair of Enantiomeric Peptides. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettens, T.; Lacanau, V.; Van Lommel, R.; De Maeseneer, T.; Vandeplassche, W.; Bertouille, J.; Brancart, J.; Barlow, T.M.A.; Woller, T.; Van Den Brande, N.; et al. Towards the Understanding of Halogenation in Peptide Hydrogels: A Quantum Chemical Approach. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4792–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue Fenga, Marc Tarabanb, and Y.B.Y. The Effect of Ionic Strength on the Mechanical, Structural and Transport Properties of Peptide Hydrogels. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 11723–11731. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Maris, T.; Zhu, X.X.; Wuest, J.D. Probing the Relationship between Gelation and Crystallization by Using Salts of Lithocholic Acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, K. Smith Supramolecular Gels – a Panorama of Low-Molecular-Weight Gelators from Ancient Origins to next-Generation Technologies. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 10–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yuan, C.; Yan, X. Computational Approaches for Understanding and Predicting the Self-Assembled Peptide Hydrogels. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Levin, A.; Chen, W.; Xing, R.; Zou, Q.; Herling, T.W.; Challa, P.K.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Yan, X. Nucleation and Growth of Amino Acid and Peptide Supramolecular Polymers through Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18116–18123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnquist, M.; Michaels, T.C.T.; Sanagavarapu, K.; Yang, X.; Meisl, G.; Cohen, S.I.A.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Linse, S. Secondary Nucleation in Amyloid Formation. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8667–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunce, S.J.; Wang, Y.; Stewart, K.L.; Ashcroft, A.E.; Radford, S.E.; Hall, C.K.; Wilson, A.J. Molecular Insights into the Surface-Catalyzed Secondary Nucleation of Amyloid-40 (A40) by the Peptide Fragment A16–22. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, T.; Rampioni, A.; Poger, D.; Mark, A.E. Molecular Insights into the Dynamics of Amyloid Fibril Growth: Elongation and Lateral Assembly of GNNQQNY Protofibrils. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 15, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Su, Z.; Reynolds, N.P.; Arosio, P.; Hamley, I.W.; Gazit, E.; Mezzenga, R. Self-Assembling Peptide and Protein Amyloids: From Structure to Tailored Function in Nanotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4661–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinauro, D.J.; Chiti, F.; Vendruscolo, M.; Limbocker, R. Misfolded Protein Oligomers: Mechanisms of Formation, Cytotoxic Effects, and Pharmacological Approaches against Protein Misfolding Diseases. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanspal, M.A.; Dobson, C.M.; Yerbury, J.J.; Kumita, J.R. The Relevance of Contact-Independent Cell-to-Cell Transfer of TDP-43 and SOD1 in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linse, S. Mechanism of Amyloid Protein Aggregation and the Role of Inhibitors. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Hall, C.K. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Spontaneous Fibril Formation by Random-Coil Peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004, 101, 16180–16185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, D.; Barghouth, M.; Bless, M.; Zhang, E.; Linse, S. Direct Observation of Secondary Nucleation along the Fibril Surface of the Amyloid β 42 Peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2023, 120, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.I.A.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M.; Knowles, T.P.J. From Macroscopic Measurements to Microscopic Mechanisms of Protein Aggregation. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 421, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linse, S. Monomer-Dependent Secondary Nucleation in Amyloid Formation. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillam, J.E.; Macphee, C.E. Modelling Amyloid Fibril Formation Kinetics: Mechanisms of Nucleation and Growth. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelletto, V.; Hamley, I.W. Amyloid and Hydrogel Formation of a Peptide Sequence from a Coronavirus Spike Protein. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Jingyao, and F.Z. Amyloids as Building Blocks for Macroscopic Functional Materials: Designs, Applications and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Mathes, T.G.; Monirizad, M.; Ermis, M.; de Barros, N.R.; Rodriguez, M.; Kraatz, H.B.; Jucaud, V.; Khademhosseini, A.; Falcone, N. Effects of Amyloid-β-Mimicking Peptide Hydrogel Matrix on Neuronal Progenitor Cell Phenotype. Acta Biomater. 2024, 183, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.M.; Anderson, S.B.; Nilsson, B.L. The Influence of Side-Chain Halogenation on the Self-Assembly and Hydrogelation of Fmoc-Phenylalanine Derivatives. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3220–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettig, P.; Koch, N.G.; Budisa, N. Non-Canonical Amino Acids in Analyses of Protease Structure and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnatural Amino Acids / Non Canonical Amino Acids. Available online: https://www.tocris.com/product-type/unnatural-amino-acids (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Chen, L.; Xin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Xu, Z. Advances in Biosynthesis of Non-Canonical Amino Acids (NcAAs) and the Methods of NcAAs Incorporation into Proteins. Molecules 2023, 28, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almhjell, P.J.; Boville, C.E.; Arnold, F.H. Engineering Enzymes for Noncanonical Amino Acid Synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8980–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning Vogt, S.B. Recent Approaches towards the Asymmetric Synthesis of Alpha,Alpha-Disubstituted Alpha-Amino Acids. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 406–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, E.; Zhou, H.; Krasinska, K.M.; Chien, A.; Becker, C.H. Azetidine-2-Carboxylic Acid in Garden Beets (Beta Vulgaris). Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennig, A.; Blaschke, F.; Gandomkar, S.; Tassano, E.; Nidetzky, B. Preparative Asymmetric Synthesis of Canonical and Non-Canonical a-Amino Acids through Formal Enantioselective Biocatalytic Amination of Carboxylic Acids. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, W.D.G.; Lloyd, C.M.; Cobb, S.L. Synthesis of Complex Unnatural Fluorine-Containing Amino Acids. J. Fluor. Chem. 2020, 239, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugtenburg, T.; Gran-Scheuch, A.; Drienovská, I. Non-Canonical Amino Acids as a Tool for the Thermal Stabilization of Enzymes. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2023, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









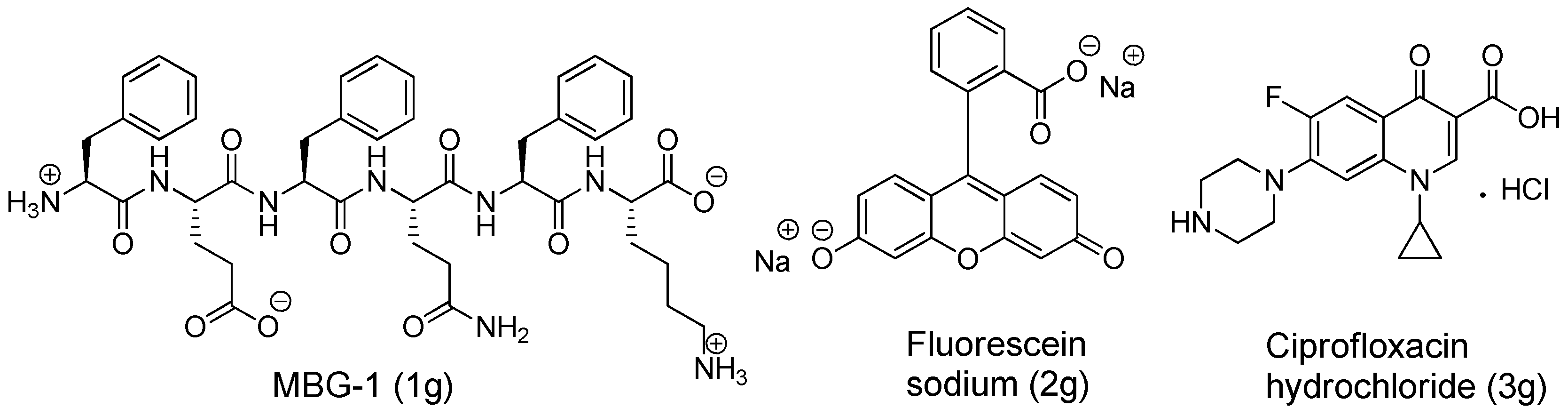
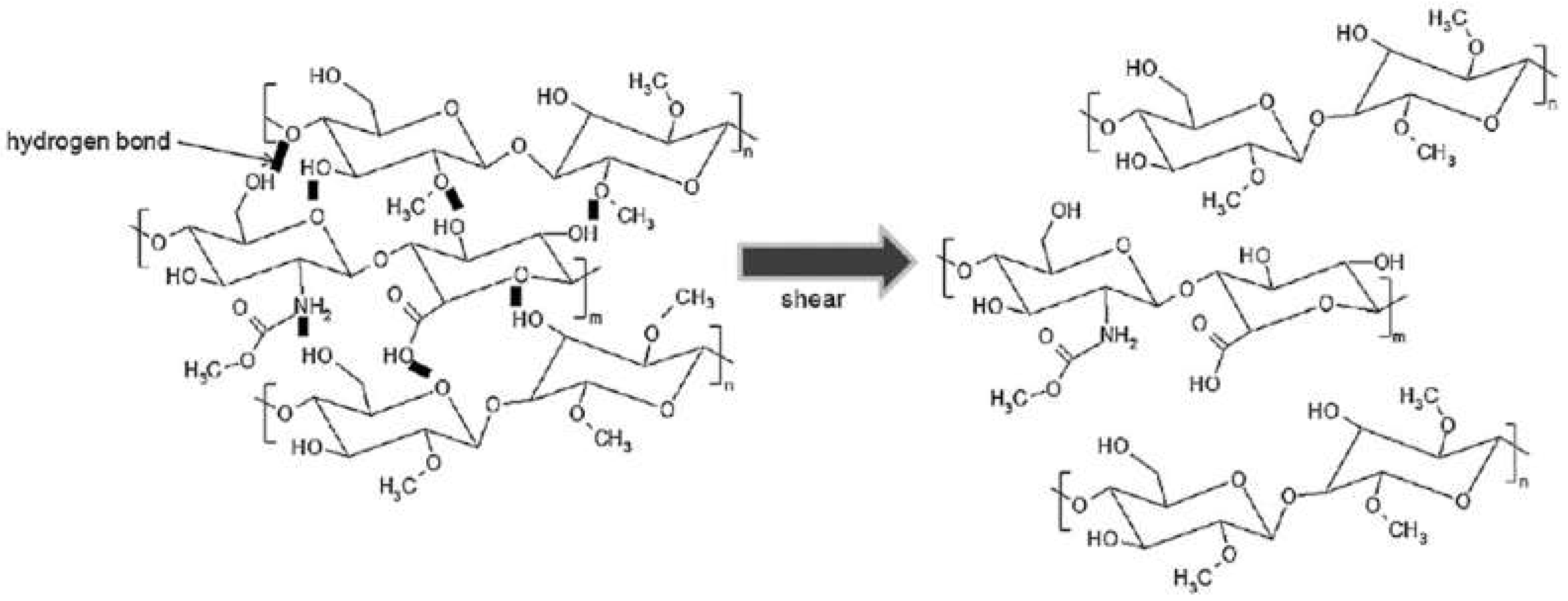




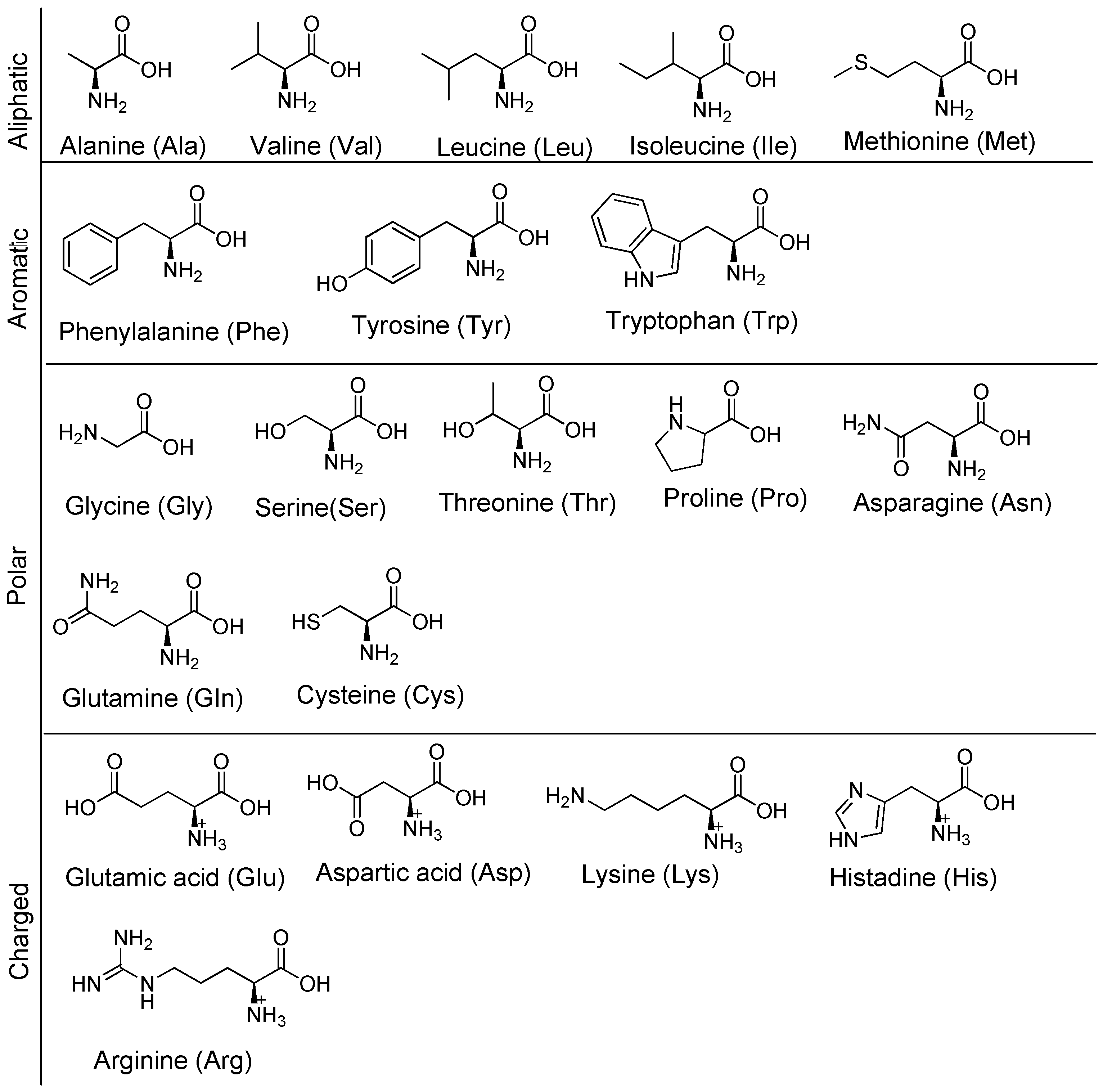





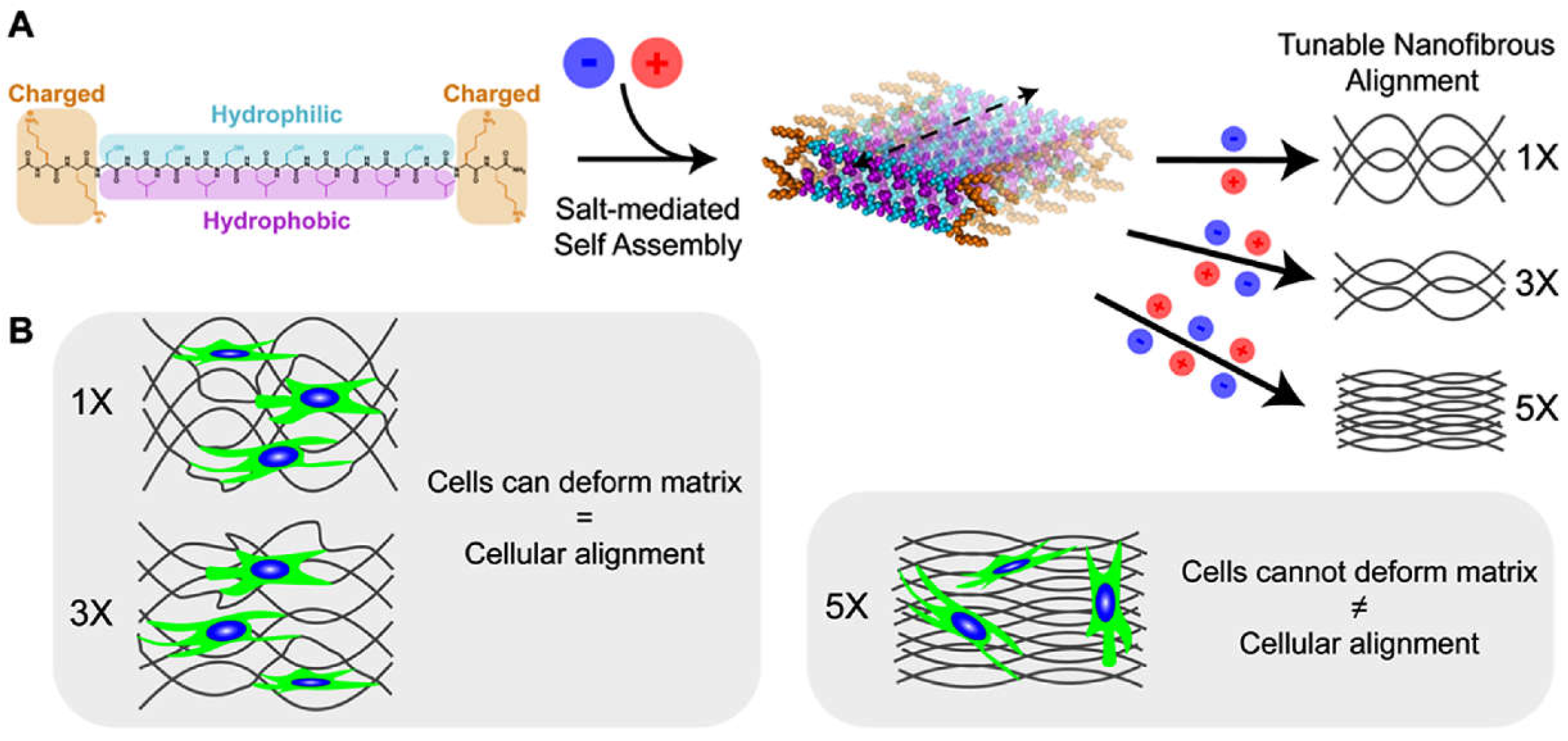









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).








