Submitted:
25 October 2024
Posted:
28 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solvents and Materials
- -
- The Lewis’s acid solvents such as chloroform (DN=0, AN=22.54) and dichloromethane (DN=5.02, AN=16.27)
- -
- The amphoteric solvents such as: benzene (DN=0.42, AN=0.72), ethanol (DN=80.35, AN=43.27), acetonitrile (DN=59.01, AN=19.65), and toluene (DN=16.32, AN=3.98)
- -
- The Lewis’s base solvents such as: acetone (DN=71.15, AN=10.49), ethyl acetate (DN=71.56, AN=6.39), diethyl ether (DN=80.35, AN=5.91), cyclohexane (DN=5.89, AN=0.17), and tetrahydrofuran (THF) (DN=83.70, AN=2.29)
2.2. Inverse Gas Chromatography
2.3. Thermodynamic Methods
3. Experimental Results
3.1. London Dispersive Surface Energy of the SBR Copolymer
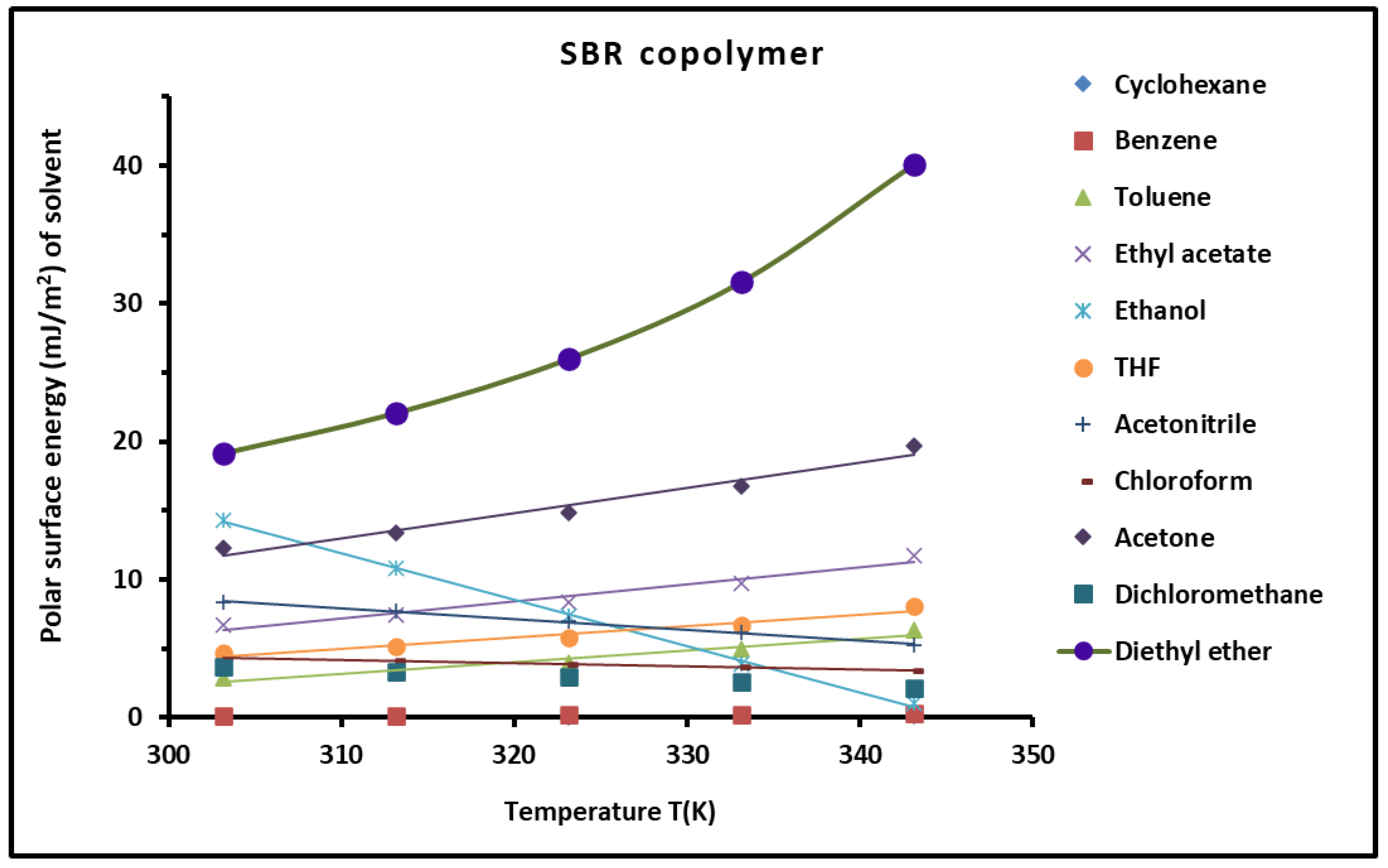
3.3. Variations of Polar Free Surface Energy () of SBR Copolymer
3.4. Lewis Acid-Base Constants of Poly(styrene-co-butadiene)
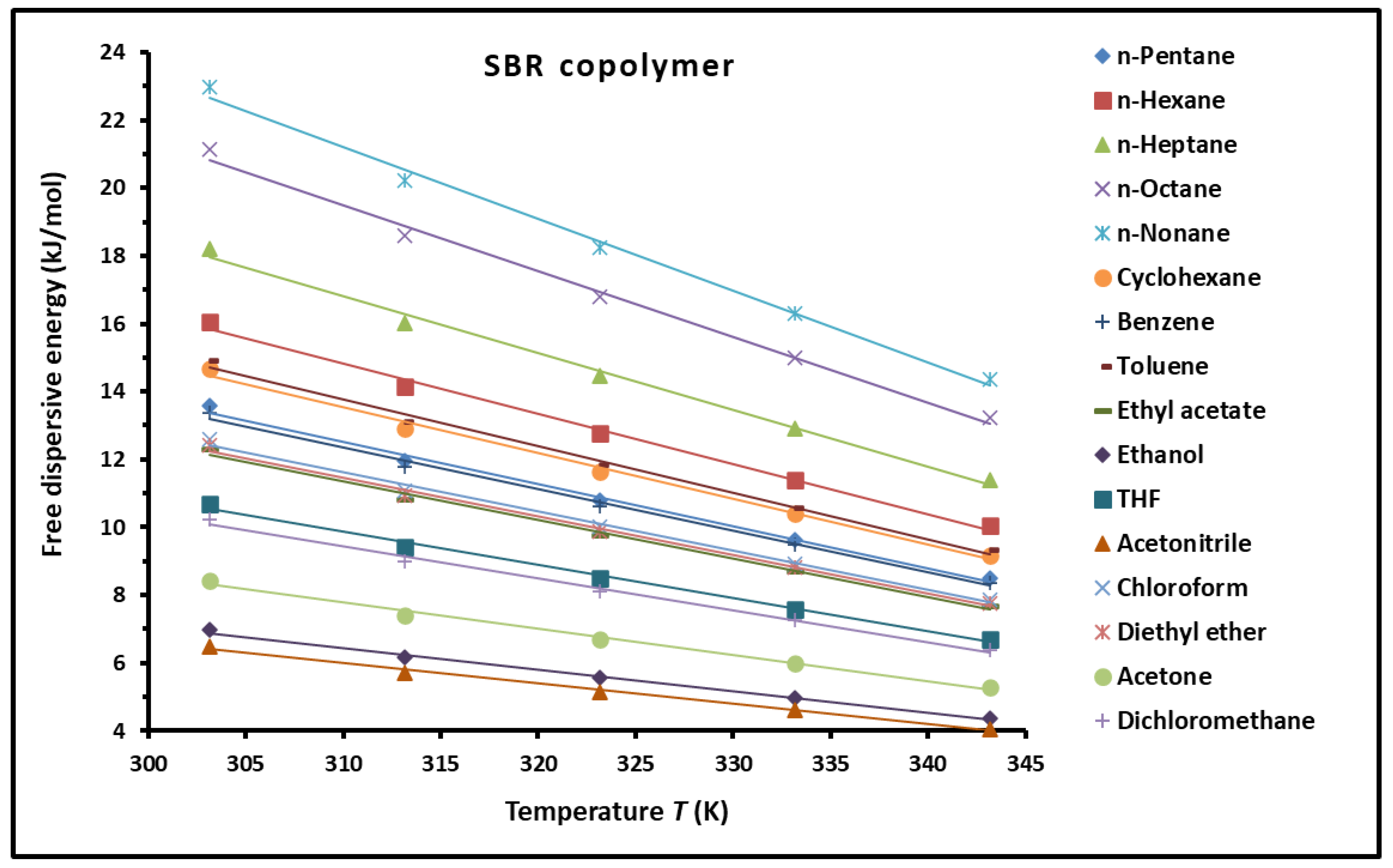
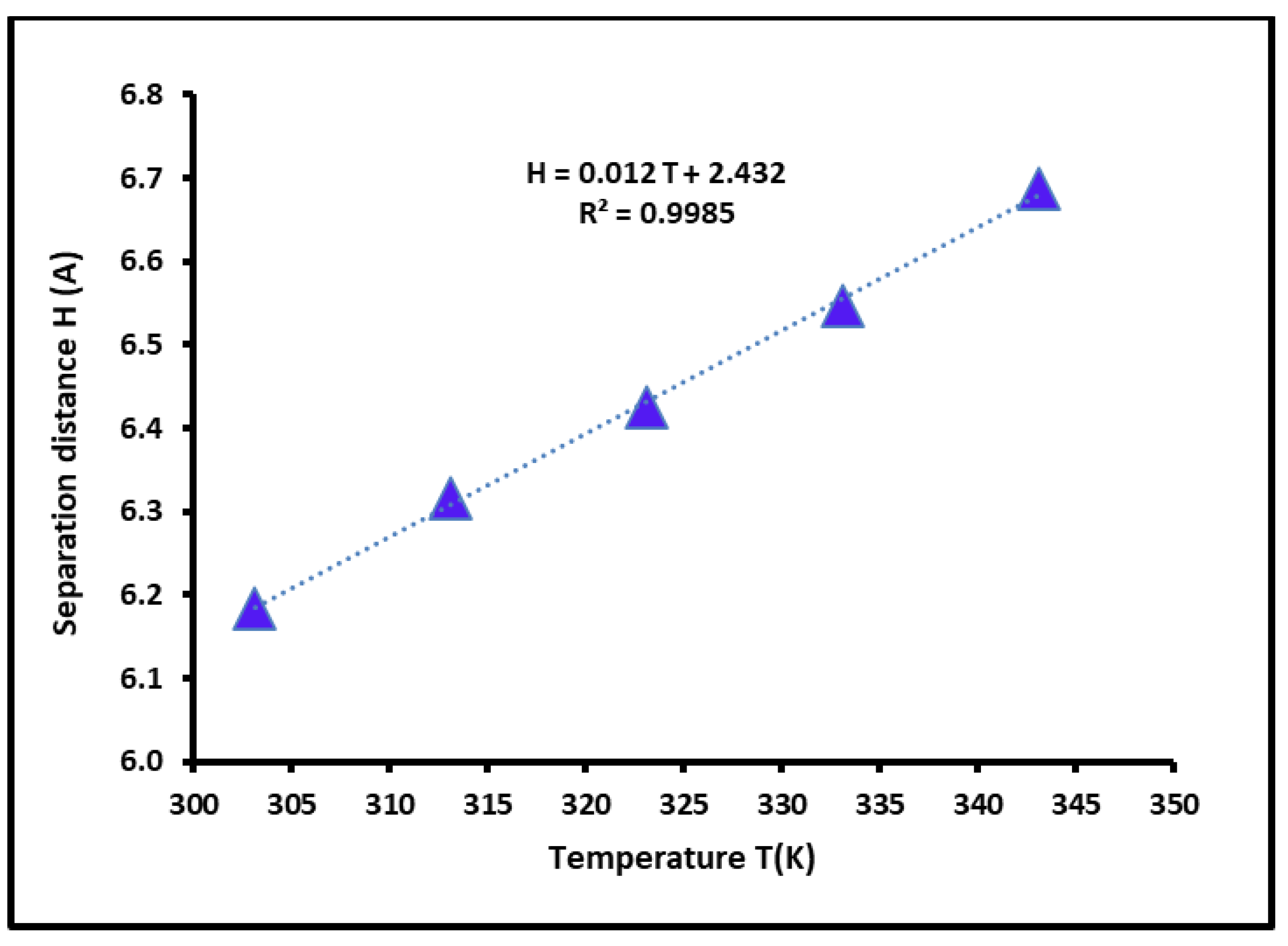
3.5. Dispersive Free Energy and Interaction Distance Between the Solvents and SBR Copolymer
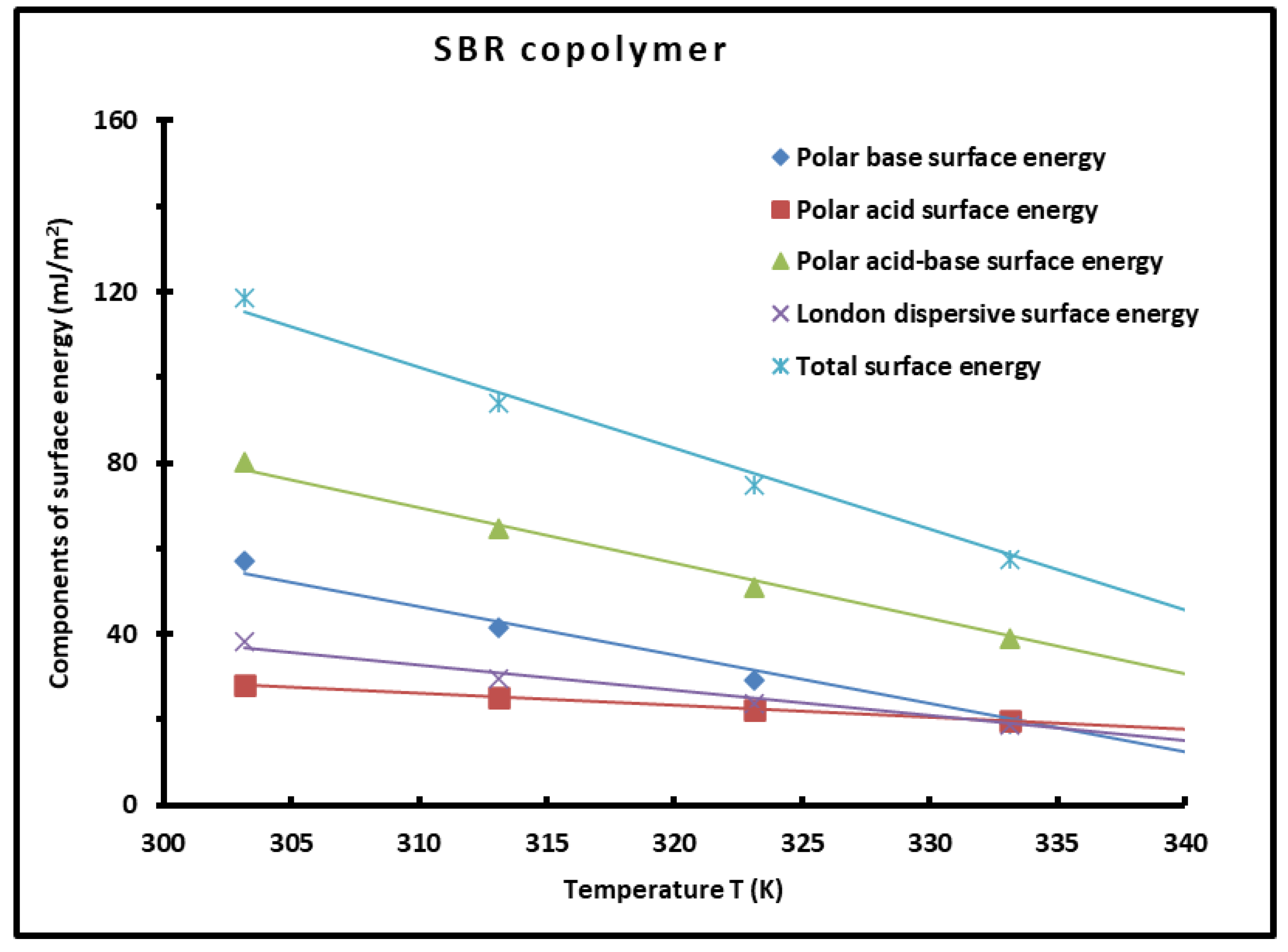
3.6. Determination of Polar Acid-Base Surface Energies and Total Surface Energy of the Copolymer
4. Conclusions
| Surface energy component | Equation |
| Polar base surface energy | = -1.132T + 397.42 |
| Polar acid surface energy | = -0.273T + 110.70 |
| Polar acid-base surface energy | = -1.295T + 471.08 |
| London dispersive surface energy | = -0.590T + 215.36 |
| Total surface energy | = -1.885T + 686.43 |
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- G. Ovejero, M.D. Romero, E. Díez, I. Díaz, Thermodynamic interactions of three SBS (styrene–butadiene–styrene) triblock copolymers with different solvents, by means of intrinsic viscosity measurements, European Polymer Journal 46 (2010) 2261–2268.
- Smith WF, Hashemi J. Foundations of materials science and technology. Mexico DF: McGraw-Hill; 2006.
- Biao Zuo, Manabu Inutsuka, Daisuke Kawaguchi, Xinping Wang et Keiji Tanaka, Conformational Relaxation of Poly(styrene-co-butadiene) Chains at Substrate Interface in Spin-Coated and Solvent-Cast Films, Macromolecules 2018 51 (6), 2180-2186, . [CrossRef]
- Jancar, J.; Douglas, J. F.; Starr, F. W.; Kumar, S. K.; Cassagnau, P.; Lesser, A. J.; Sternstein, S. S.; Buehler, M. J. Current Issues in Research on Structure-Property Relationships in Polymer Nanocomposites. Polymer 2010, 51, 3321−3343.
- Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Concepts and Conflicts in Nanoparticles Reinforcement to Polymers beyond Hydrodynamics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 84, 1−58.
- Boonstra, B. B. Role of Particulate Fillers in Elastomer Reinforcement: a Review. Polymer 1979, 20, 691−704.
- Edwards, D. C. Polymer-Filler Interactions in Rubber Reinforcement. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 4175−4185.
- Balazs, A. C.; Emrick, T.; Russell, T. P. Nanoparticle Polymer, Composites: Where Two Small Worlds Meet. Science 2006, 314, 1107−1110.
- Kumar, S. K.; Benicewicz, B. C.; Vaia, R. A.; Winey, K. I. Are Polymer Nanocomposites Practical for Applications? Macromolecules, 2017, 50, 714−731.
- Radhakrishnan, C.K., Sujith, A. & Unnikrishnan, G. Thermal behaviour of styrene butadiene rubber/poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) blends. J Therm Anal Calorim 90, 191–199 (2007). [CrossRef]
- I. C. McNeill, Thermal Degradation, in Comprehensive Polymer Science, Vol. 6, G. Allen, Ed., Pergamon Press, New York 1989, Ch. 15.
- Rybiński, P., Janowska, G., Antkowicz, W. et al. Thermal stability and flammability of butadiene- acrylonitrile rubber cross-linked with iodoform. J Therm Anal Calorim 81, 9–13 (2005). [CrossRef]
- Vo, L. T.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Giannelis, E.P., Dielectric study of Poly(styrene-co-butadiene) Composites with Carbon Black, Silica, and Nanoclay, Macromolecules 2011, 44, 15, 6162–6171.
- Pilar Posadas, Pilar Bernal-Ortega, M. Mar Bernal, Aurora Nogales, Rodrigo Navarro, Juan L. Valentín. From Nanoscale to Macroscale Characterization of Sulfur-Modified Oxidized Carbon Nanotubes in Styrene Butadiene Rubber Compounds. ACS Omega 2024, 9 (29) , 31669-31683. [CrossRef]
- Clément, F.; Lapra, A.; Bokobza, L.; Monnerie, L.; Ménez, P. Atomic Force Microscopy Investigation of Filled Elastomers and Comparison with Transmission Electron Microscopy - Application to Silica-Filled Silicone Elastomers. Polymer 2001, 42 (14), 6259– 6270, . [CrossRef]
- Špírková, M.; Pavličević, J.; Strachota, A.; Poreba, R.; Bera, O.; Kaprálková, L.; Baldrian, J.; Šlouf, M.; Lazić, N.; Budinski-Simendić, J. Novel Polycarbonate-Based Polyurethane Elastomers: Composition-Property Relationship. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 959– 972, . [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, J.; Yu, S. New Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber/Carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposite. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1127– 1132, . [CrossRef]
- Bertora, A.; Castellano, M.; Marsano, E.; Alessi, M.; Conzatti, L.; Stagnaro, P.; Colucci, G.; Priola, A.; Turturro, A. A New Modifier for Silica in Reinforcing SBR Elastomers for the Tyre Industry. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296 (5), 455– 464, . [CrossRef]
- Ward, A. A.; Khalf, A. I. Electrical and Mechanical Properties of SBR Filled with Carbon Black-Silica Blends. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2007, 60 (11), 623– 630.
- Sae-Oui, P.; Suchiva, K.; Sirisinha, C.; Intiya, W.; Yodjun, P.; Thepsuwan, U. Effects of Blend Ratio and SBR Type on Properties of Carbon Black-Filled and Silica-Filled SBR/BR Tire Tread Compounds. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 2476101, . [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Biswas, S.; Bhowmick, A. K. Permeation Characteristics and Modeling of Barrier Properties of Multifunctional Rubber Nanocomposites. Polymer 2011, 52, 1562– 1576, . [CrossRef]
- Stephen, R.; Ranganathaiah, C.; Varghese, S.; Joseph, K.; Thomas, S. Gas Transport through Nano and Micro Composites of Natural Rubber (NR) and Their Blends with Carboxylated Styrene Butadiene Rubber (XSBR) Latex Membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 858– 870, . [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. L.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z. Z.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L. Q.; Mai, Y. W. Microstructure and Properties of Highly Filled Rubber/Clay Nanocomposites Prepared by Melt Blending. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2903– 2913, . [CrossRef]
- Peddini, S. K.; Bosnyak, C. P.; Henderson, N. M.; Ellison, C. J.; Paul, D. R. Nanocomposites from Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNT) Part 2: Mechanical Properties. Polymer 2015, 56, 443– 451, . [CrossRef]
- Bokobza, L.; Bresson, B.; Garnaud, G.; Zhang, J. Mechanical and AFM Investigations of Elastomers Filled with Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes. Compos. Interfaces 2012, 19 (5), 285– 295, . [CrossRef]
- E. Díez, G. Ovejero, M.D. Romero, I. Díaz, Polymer–solvent interaction parameters of SBS rubbers by inverse gas chromatography measurements, Fluid Phase Equilibria 308 (2011) 107– 113, . [CrossRef]
- 2021; 27. Hassiba Benguergoura, Amina Allel, Waseem Sharaf Saeed, Taïeb Aouak, Capillary column inverse gas chromatography to determine the thermodynamic parameters of binary solvent poly (styrene-block-butadiene) rubber systems, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 14 (4), 2021, 103040, . [CrossRef]
- Farshchi, N., Abbasian, A. & Larijani, K. Is Inverse Gas Chromatography (IGC) a Convenient Method to Determine Compatibility of Rubber Materials?. Chromatographia 82, 1709–1719 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, D.T.; Brookman, D.J. Thermodynamically based gas chromatographic retention index for organic molecules using salt-modified aluminas and porous silica beads, Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 1847-1850. [CrossRef]
- Conder, J. R.; Young, C. L. Physical measurements by gas chromatography. Eds: John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, New York, 1979, 632 pages.
- Schultz, J.; Lavielle, L.; Martin, C. The role of the interface in carbon fibre-epoxy composites. J. Adhes. 1987, 23, 45-60.
- Saint-Flour, C.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography. A method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short glass fibers. 1. Through adsorption isotherms, Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 337-341, . [CrossRef]
- Saint-Flour, C.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography: method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short fibers. 2. Through retention volumes measured near zero surface coverage, Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 666-669, . [CrossRef]
- Donnet, J.-B.; Park, S.; Balard, H. Evaluation of specific interactions of solid surfaces by inverse gas chromatography, Chromatographia. 1991, 31, 434–440.
- Brendlé, E.; Papirer, E. A new topological index for molecular probes used in inverse gas chromatography for the surface nanorugosity evaluation, 1. Method of Evaluation, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 194, 207–216.
- Brendlé, E.; Papirer, E. A new topological index for molecular probes used in inverse gas chromatography for the surface nanorugosity evaluation, 2. Application for the Evaluation of the Solid Surface Specific Interaction Potential, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 194, 217–2224.
- Hamieh, T.; Schultz, J. New approach to characterize physicochemical properties of solid substrates by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. Some new methods to determine the surface areas of some molecules adsorbed on solid surfaces. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 969, 17–47. [CrossRef]
- Voelkel, A. Inverse gas chromatography: Characterization of polymers, fibers, modified silicas, and surfactants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1991, 22, 411–439. [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, S.K.; Panayiotou, C. Assessment of the thermodynamic properties of poly(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl methacrylate) by inverse gas chromatography, J. Chromatogr. A, 2014, 1324, 207– 214. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Study of the temperature effect on the surface area of model organic molecules, the dispersive surface energy and the surface properties of solids by inverse gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1627, 461372.
- Hamieh, T. New methodology to study the dispersive component of the surface energy and acid–base properties of silica particles by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2022, 60, 126–142. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T.; Ahmad, A.A.; Roques-Carmes, T.; Toufaily, J. New approach to determine the surface and interface thermodynamic properties of H-β-zeolite/rhodium catalysts by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20894. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Some Irregularities in the Evaluation of Surface Parameters of Solid Materials by Inverse Gas Chromatography, Langmuir 2023 39, 17059-17070, . [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.M. in: Surface and interfacial aspects of biomedical polymers, Vol. I, pp. 337-372, Ed: J. D. Andrade, Plenum Press, New York, 1985.
- Hamieh, T. New physicochemical methodology for the determination of the surface thermodynamic properties of solid particles. Appl. Chem. 2023, 3, 229–255. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. New Progress on London Dispersive Energy, Polar Surface Interactions, and Lewis’s Acid–Base Properties of Solid Surfaces. Molecules 2024, 29, 949. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. London Dispersive and Lewis Acid-Base Surface Energy of 2D Single-Crystalline and Polycrystalline Covalent Organic Frameworks. Crystals 2024, 14, 148. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Inverse Gas Chromatography to Characterize the Surface Properties of Solid Materials. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 2231–2244. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Effect of Tacticity on London Dispersive Surface Energy, Polar Free Energy and Lewis Acid-Base Surface Energies of Poly Methyl Methacrylate by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Macromol 2024, 4, 356-375. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. The Effect of Temperature on the London Dispersive and Lewis Acid-Base Surface Energies of Polymethyl Methacrylate Adsorbed on Silica by Inverse Gas Chromatography. Thermo 2024, 4, 202-221. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Temperature Dependence of the Polar and Lewis Acid–Base Properties of Poly Methyl Methacrylate Adsorbed on Silica via Inverse Gas Chromatography. Molecules 2024, 29, 1688. [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, V. The Donor-Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1978.
- Riddle, F.L.; Fowkes, F.M. Spectral shifts in acid-base chemistry. Van der Waals contributions to acceptor numbers, Spectral shifts in acid-base chemistry. 1. van der Waals contributions to acceptor numbers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 3259–3264. [CrossRef]
- G.M. Dorris, D.G. Gray, Adsorption of n-alkanes at zero surface coverage on cellulose paper and wood fibers, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 77 (1980) 353–362.
- F.M. Fowkes, in: Surface and interfacial aspects of biomedical polymers, Vol. I, pp. 337-372, Ed: J. D. Andrade, Plenum Press, New York (1985).
- C.J. Van Oss, R.J. Good, M.K. Chaudhury, Additive and nonadditive surface tension components and the interpretation of contact angles, Langmuir, 1988, 4 (4) 884. [CrossRef]
- Hamieh, T. Exploring the Application of Advanced Chromatographic Methods to Characterize the Surface Physicochemical Properties and Transition Phenomena of Polystyrene-b-poly(4-vinylpyridine). Molecules 2024, 29, 4812. [CrossRef]
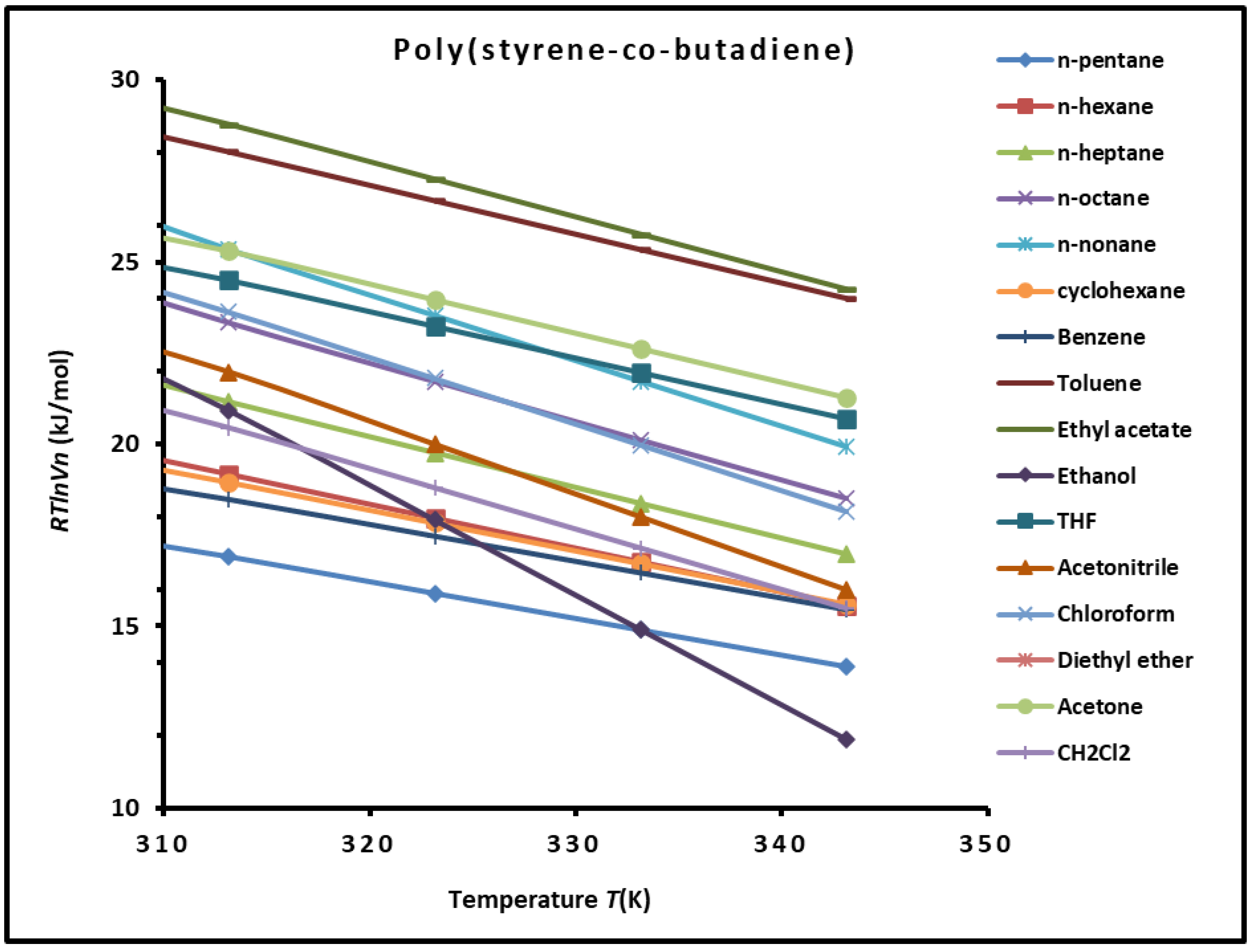
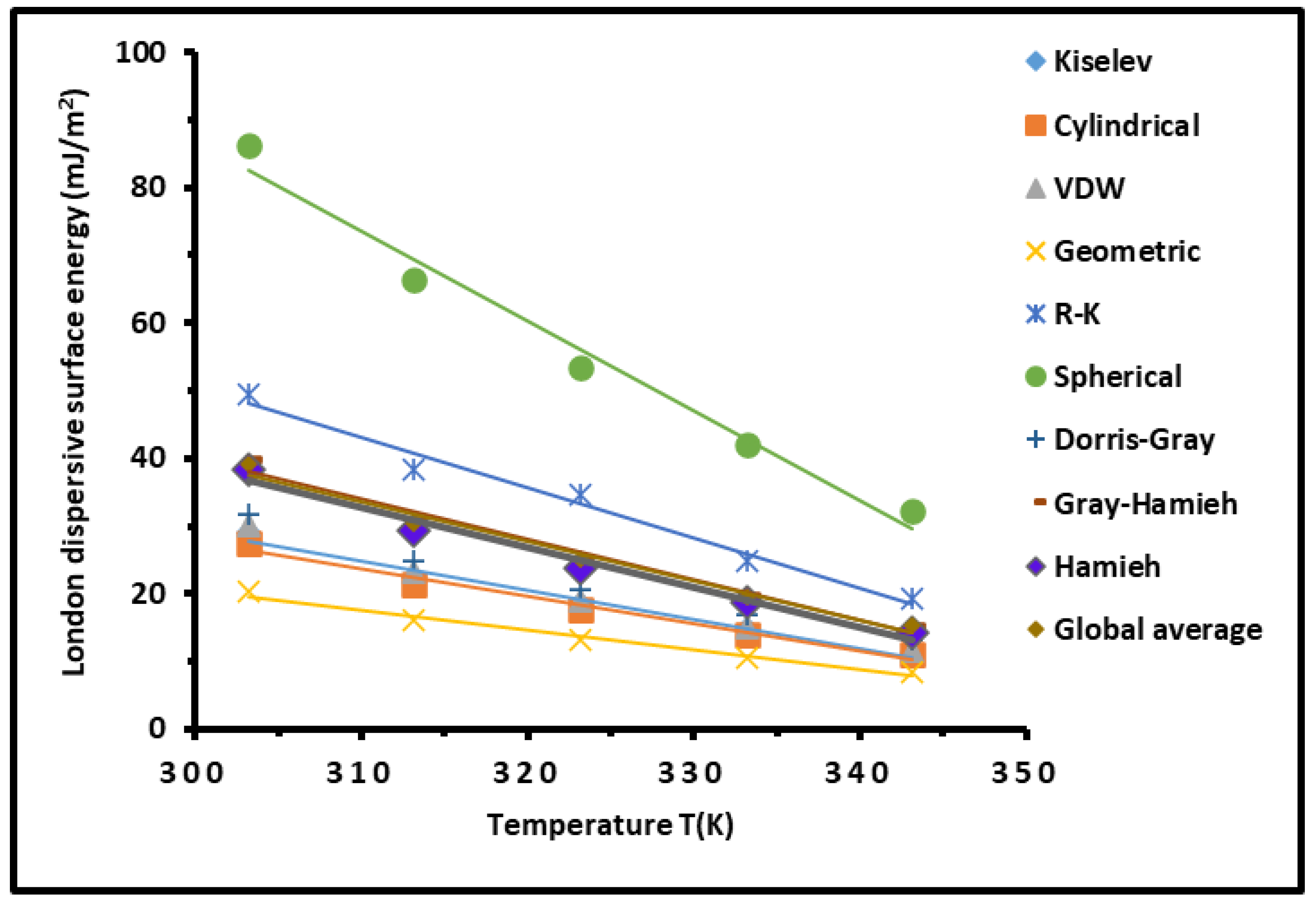
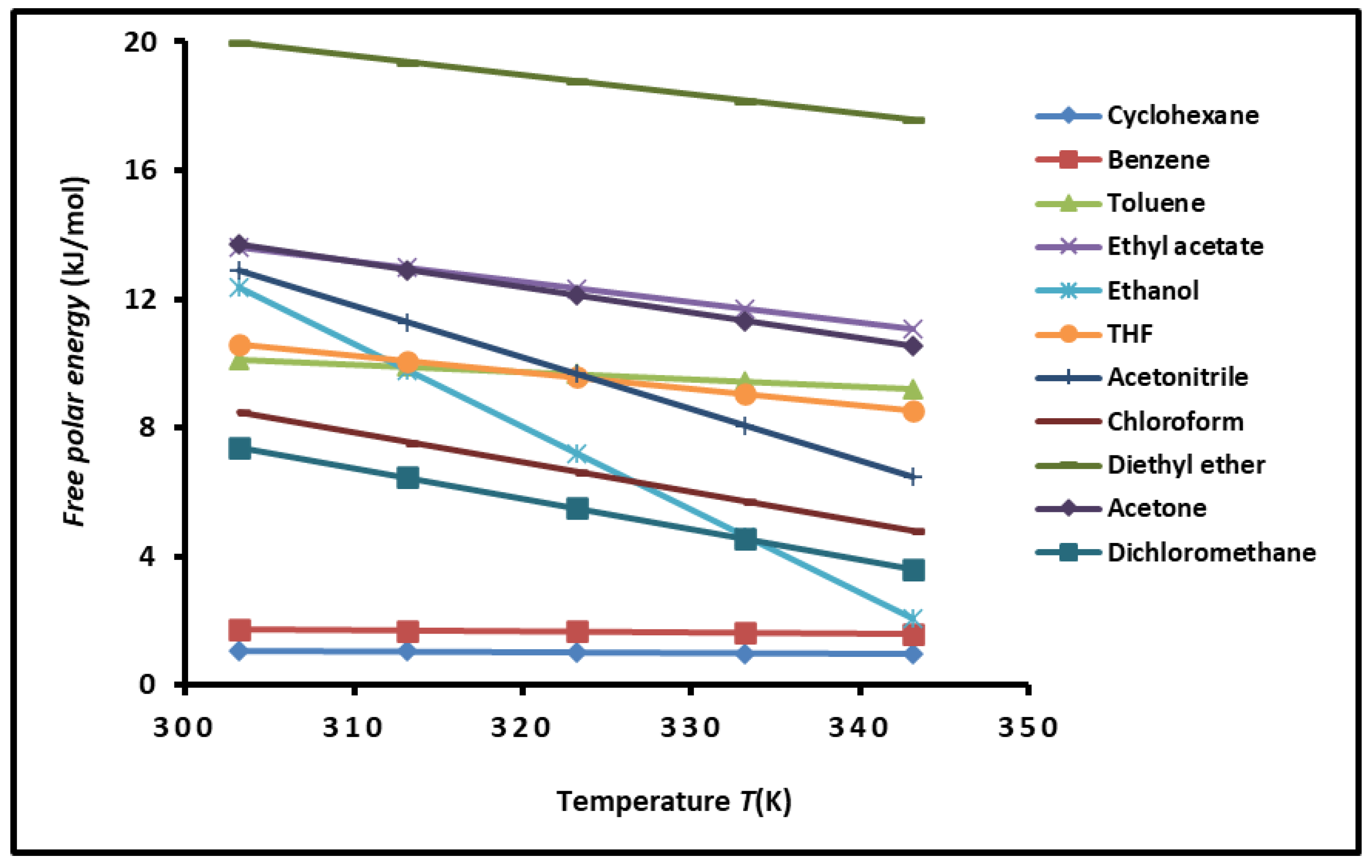
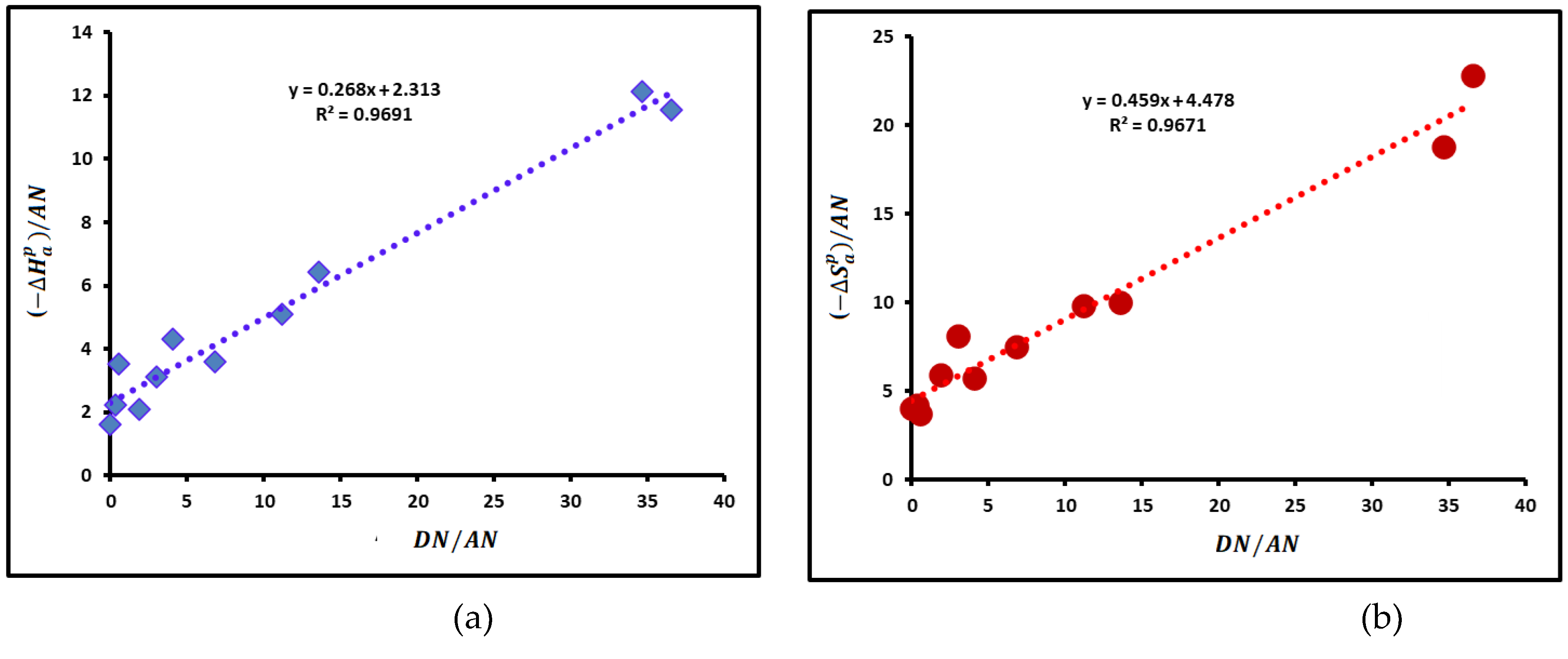
| Molecular model | (mJ/m2) | (mJ m-2 K-1) | (mJ/m2) | (K) | R2 |
| Kiselev | = -0.43 T + 158.83 | -0.43 | 158.83 | 367.66 | 0.9809 |
| Cylindrical | = -0.40 T + 148.22 | -0.40 | 148.22 | 368.61 | 0.9815 |
| VDW | = -0.45 T + 165.22 | -0.45 | 165.22 | 367.40 | 0.9808 |
| Geometric | = -0.29 T + 108.25 | -0.29 | 108.25 | 370.09 | 0.9821 |
| Redlich-Kwong | = -0.74 T + 271.53 | -0.74 | 271.53 | 368.28 | 0.9811 |
| Spherical | = -1.32 T + 483.45 | -1.32 | 483.45 | 365.59 | 0.9795 |
| Dorris-Gray | = -0.45 T + 165.93 | -0.45 | 165.93 | 371.13 | 0.9817 |
| Gray-Hamieh | = -0.60 T + 219.89 | -0.60 | 219.89 | 366.91 | 0.9799 |
| Hamieh | = -0.59 T + 215.36 | -0.59 | 215.36 | 365.45 | 0.9793 |
| Global average | = -0.59 T + 215.19 | -0.59 | 215.19 | 367.5 | 0.9824 |
| Probes | Equation of ( (kJ/mol)) |
| Cyclohexane | ( = -0.0032T + 2.060 |
| Benzene | ( = -0.0027T + 2.542 |
| Toluene | ( = -0.023T + 17.108 |
| Ethyl acetate | ( = -0.0627T + 37.598 |
| Ethanol | ( = 0.2574T +90.377 |
| THF | ( = -0.0522T + 26.434 |
| Acetonitrile | ( = -0.1103T + 91.466 |
| Chloroform | ( = 0.0918T +76.300 |
| Diethyl ether | ( = -0.0593T +37.928 |
| Acetone | ( = -0.0791T + 57.669 |
| Dichloromethane | ( = -0.0689T + 36.204 |
| Probes | ( (J/k.mol) | ( (kJ/mol)) |
| Cyclohexane | 3.2 | 2.060 |
| Benzene | 2.7 | 2.542 |
| Toluene | 23.0 | 17.108 |
| Ethyl acetate | 62.7 | 32.598 |
| Ethanol | 257.4 | 90.377 |
| THF | 52.2 | 26.434 |
| Acetonitrile | 160.3 | 61.466 |
| Chloroform | 91.8 | 36.300 |
| Diethyl ether | 59.3 | 37.928 |
| Acetone | 79.1 | 37.669 |
| Dichloromethane | 68.9 | 36.204 |
| Lewis’s acid-base parameter | Values | R2 |
| 0.268 | 0.9691 | |
| 2.313 | 0.9691 | |
| / | 8.631 | 0.9691 |
| 2.581 | 0.9691 | |
| 0.459 | 0.9671 | |
| 4.478 | 0.9671 | |
| 9.756 | 0.9671 | |
| 4.937 | 0.9671 |
| T(K) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303.15 | 56.95 | 28.17 | 80.11 | 38.36 | 118.47 |
| 313.15 | 41.59 | 25.10 | 64.62 | 29.47 | 94.08 |
| 323.15 | 29.09 | 22.26 | 50.90 | 23.75 | 74.65 |
| 333.15 | 19.17 | 19.65 | 38.82 | 18.69 | 57.50 |
| 343.15 | 11.57 | 17.25 | 28.25 | 14.28 | 42.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





