Submitted:
25 October 2024
Posted:
29 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
1.Redundant Manipulator Kinematics and Control
1.The Traditional Task Space Formulation
1.Organization of the Paper and its Contributions
- An explicit set-valued inverse kinematic mapping is derived for input coordinates as functions of task and self -motion coordinates.
- Extended operational coordinates are shown to be equivalent to input coordinates in parameterizing robot configuration space.
- ODE of robot dynamics are derived with extended operational coordinates as state variables.
- Robot control laws are defined and implemented using extended operational coordinates and operational space ODE.
- Four control examples are treated using a redundant planar robot with one degree of redundancy, demonstrating superior performance of the extended operational space formulation relative to the traditional task space approach.
- A control example is treated for a robot with eight degrees of redundancy, further demonstrating superiority of the extended operational space appproach.
Redundant Serial Robot Kinematics
2.Velocity Space Kinematics
2.Deficiencies in Redundant Robot Velocity Space Kinematics
2.Traditional Task Space Dynamics of Redundant Serial Robots
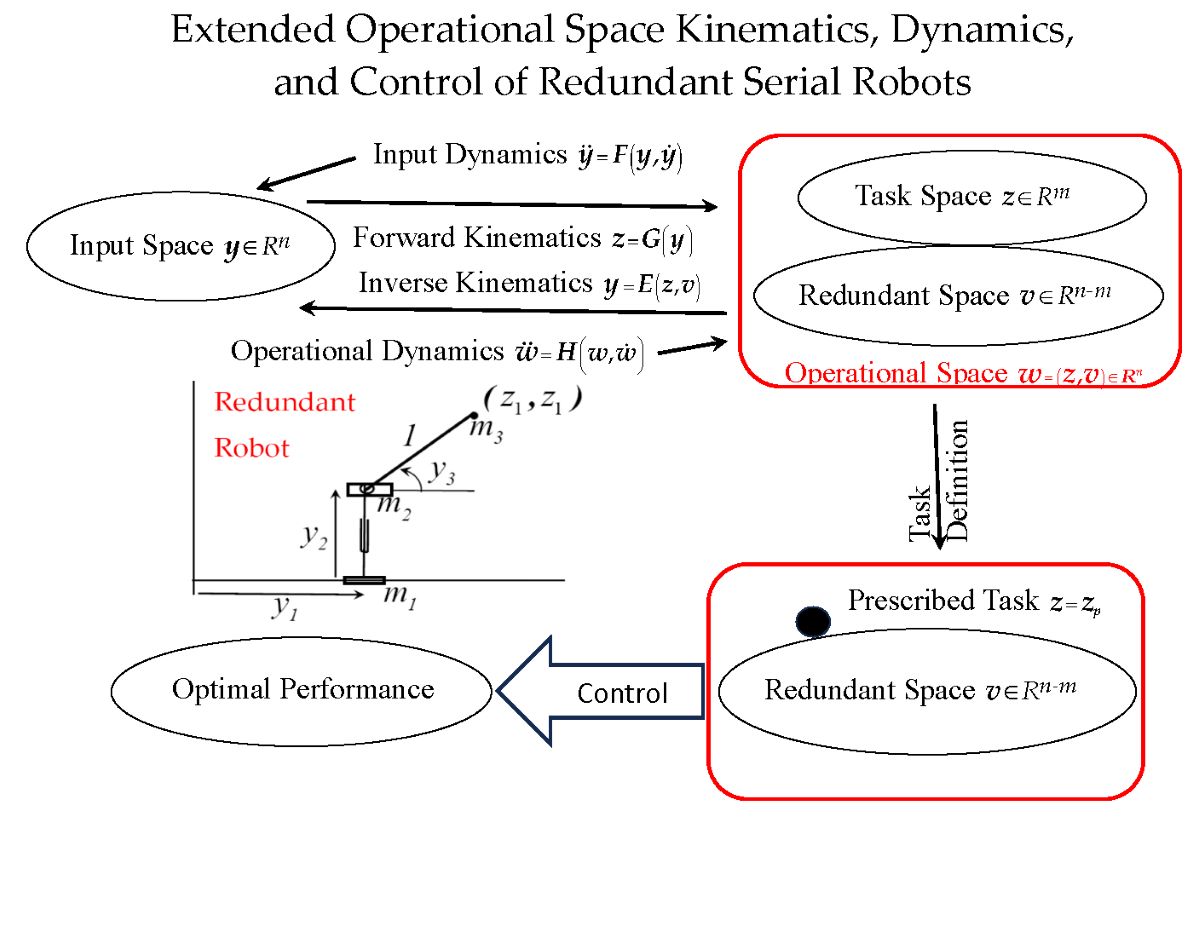
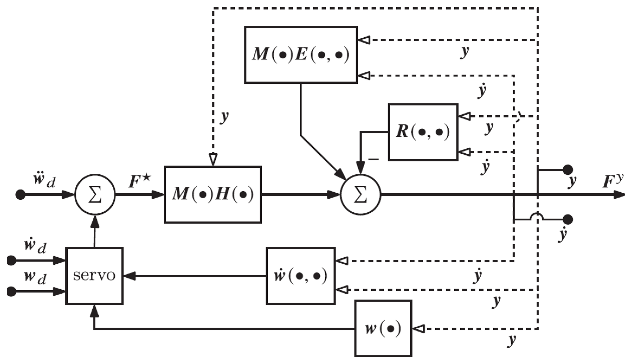
The Extended Operational Space
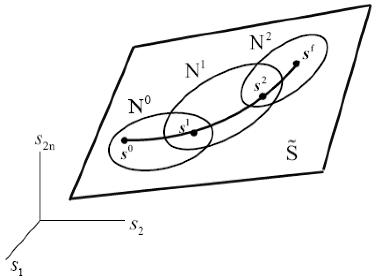
3.Inverse Configuration Kinematics
3.The Robot Extended Operational Space
3.The Robot Functional Configuration Space
3.Velocity Kinematics on the Extended Operational Space
3.Acceleration Kinematics on the Extended Operational Space
3.6 Computation of
ODE of Input and Extended Operational Space Dynamics
4.Input Space ODE of Dynamics
4.Extended Operational Space ODE of Dynamics
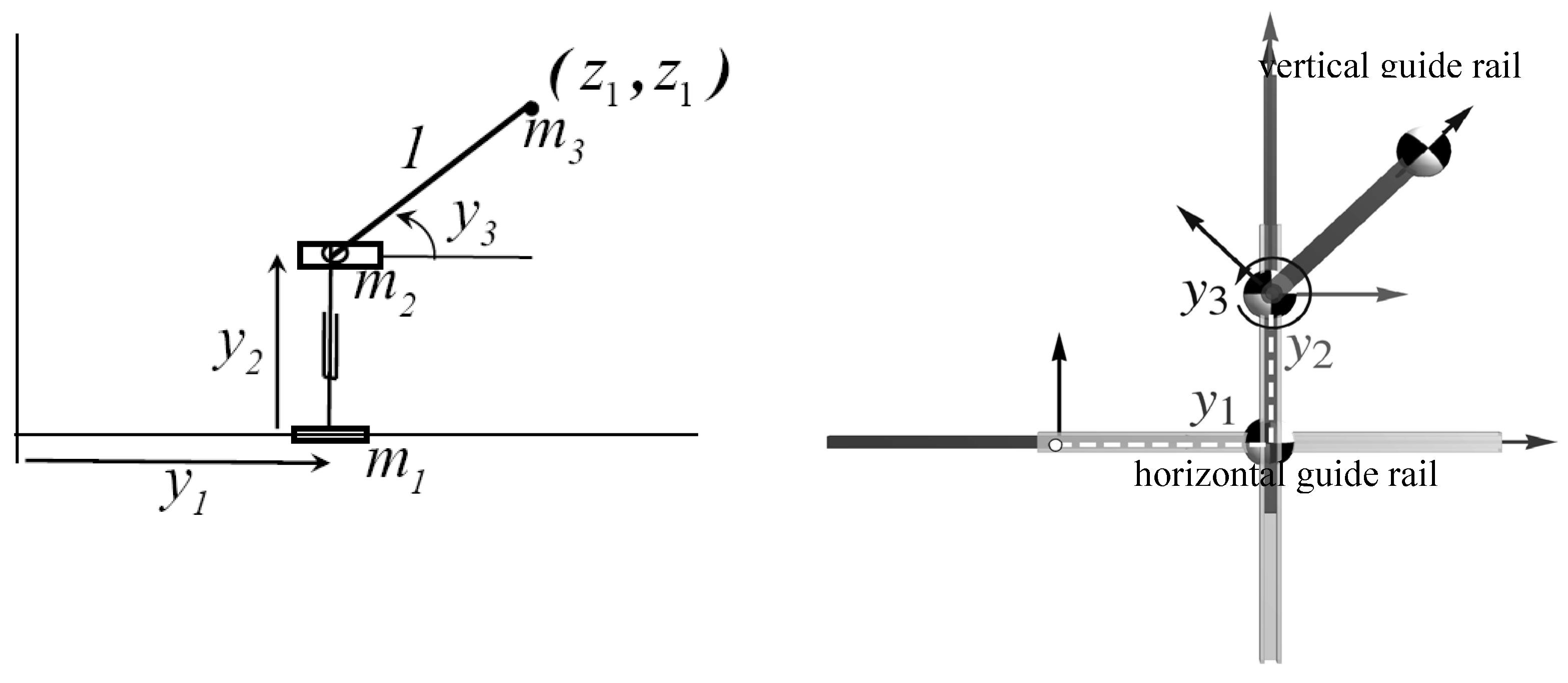
4.A Single Degree of Redundancy Serial Robot Example
Extended Operational Space Control
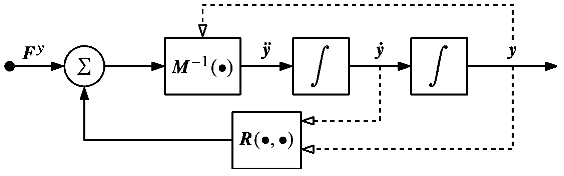
5.A Traditional Task Space Example
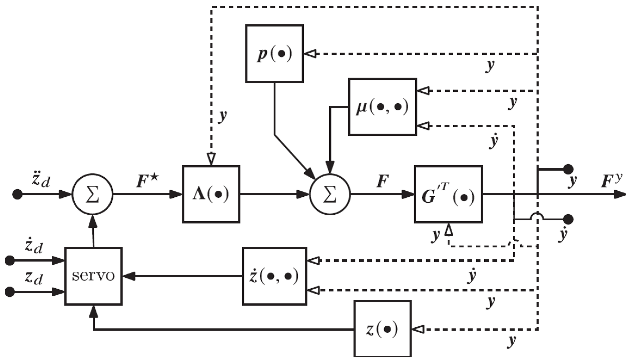
5.An Extended Operational Space Example with Objective
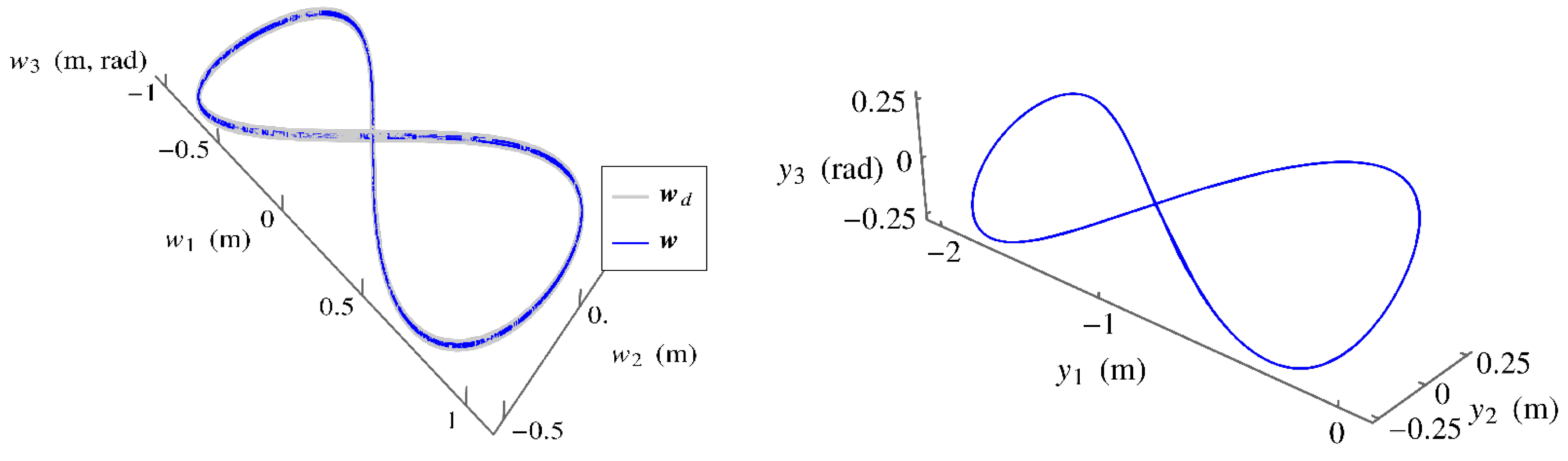
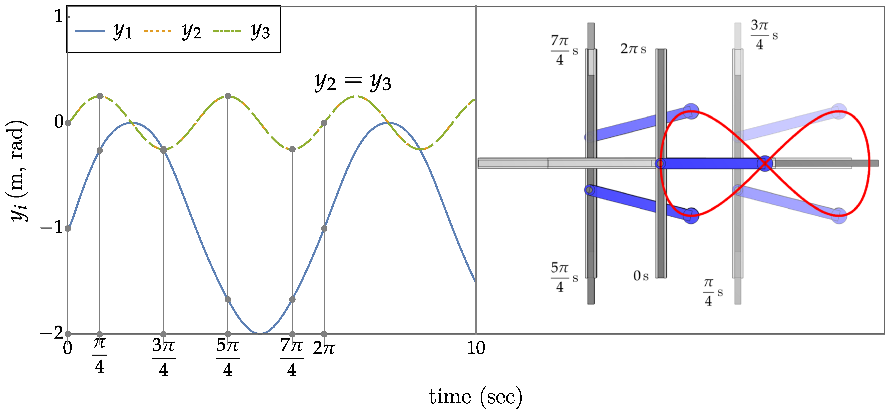
5.An Example with Minimum Kinetic Energy Objective
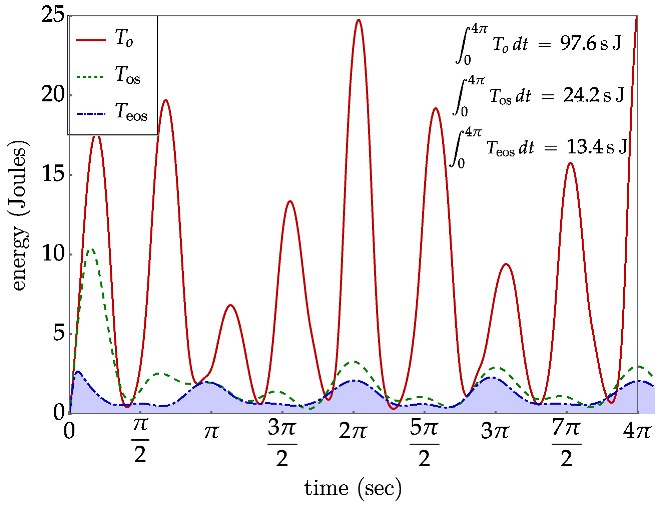
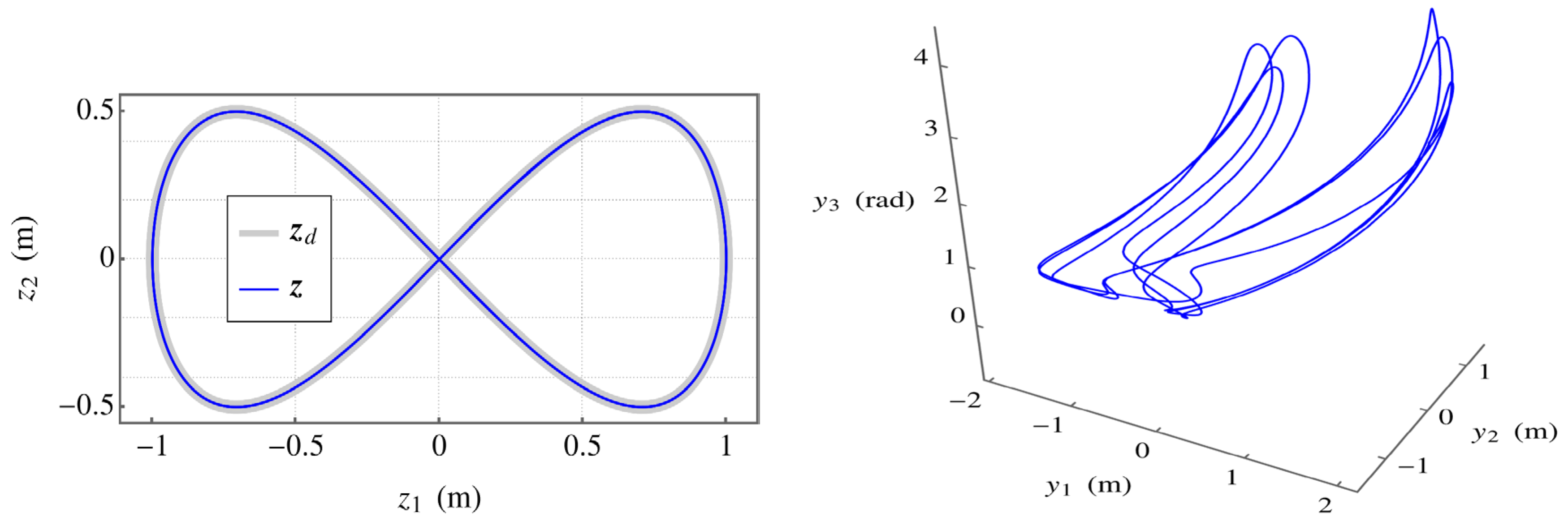
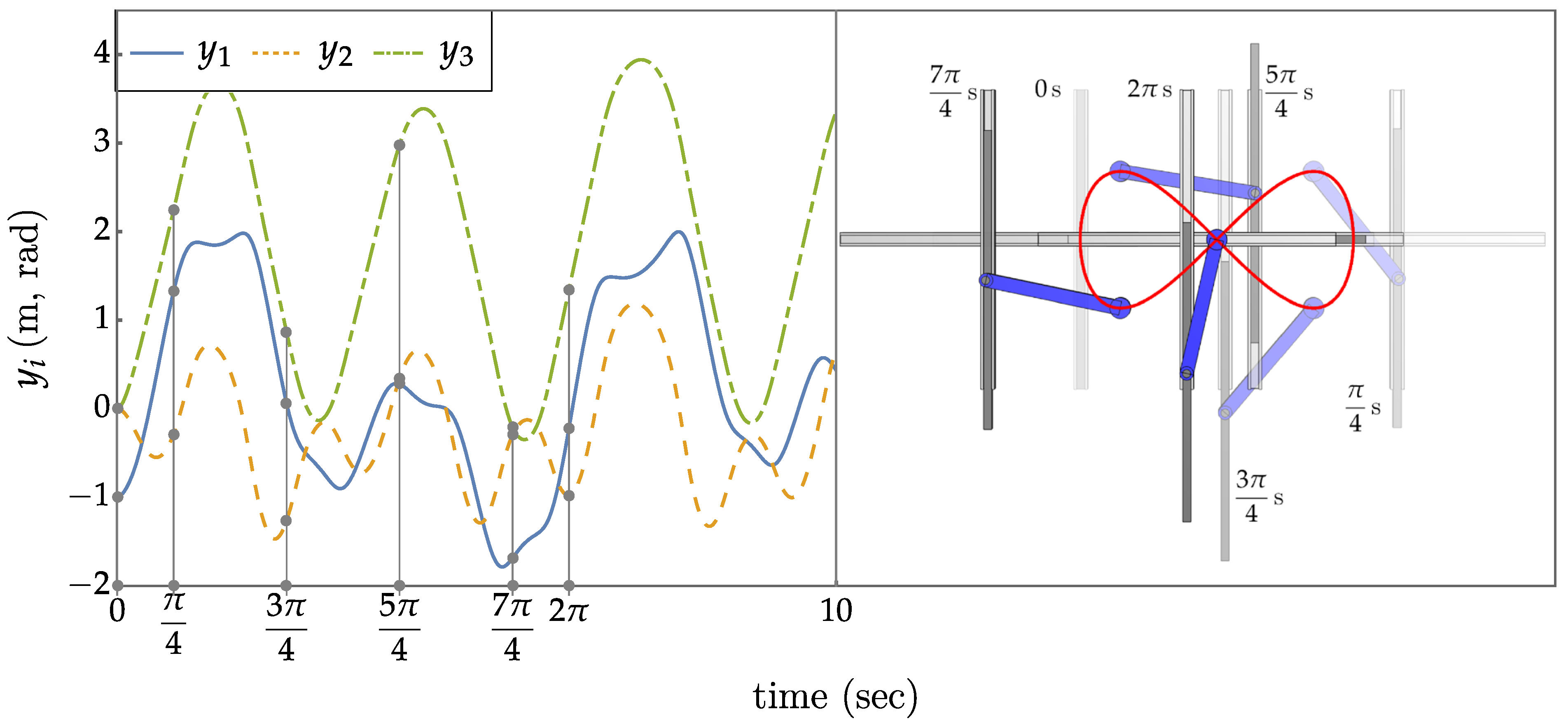
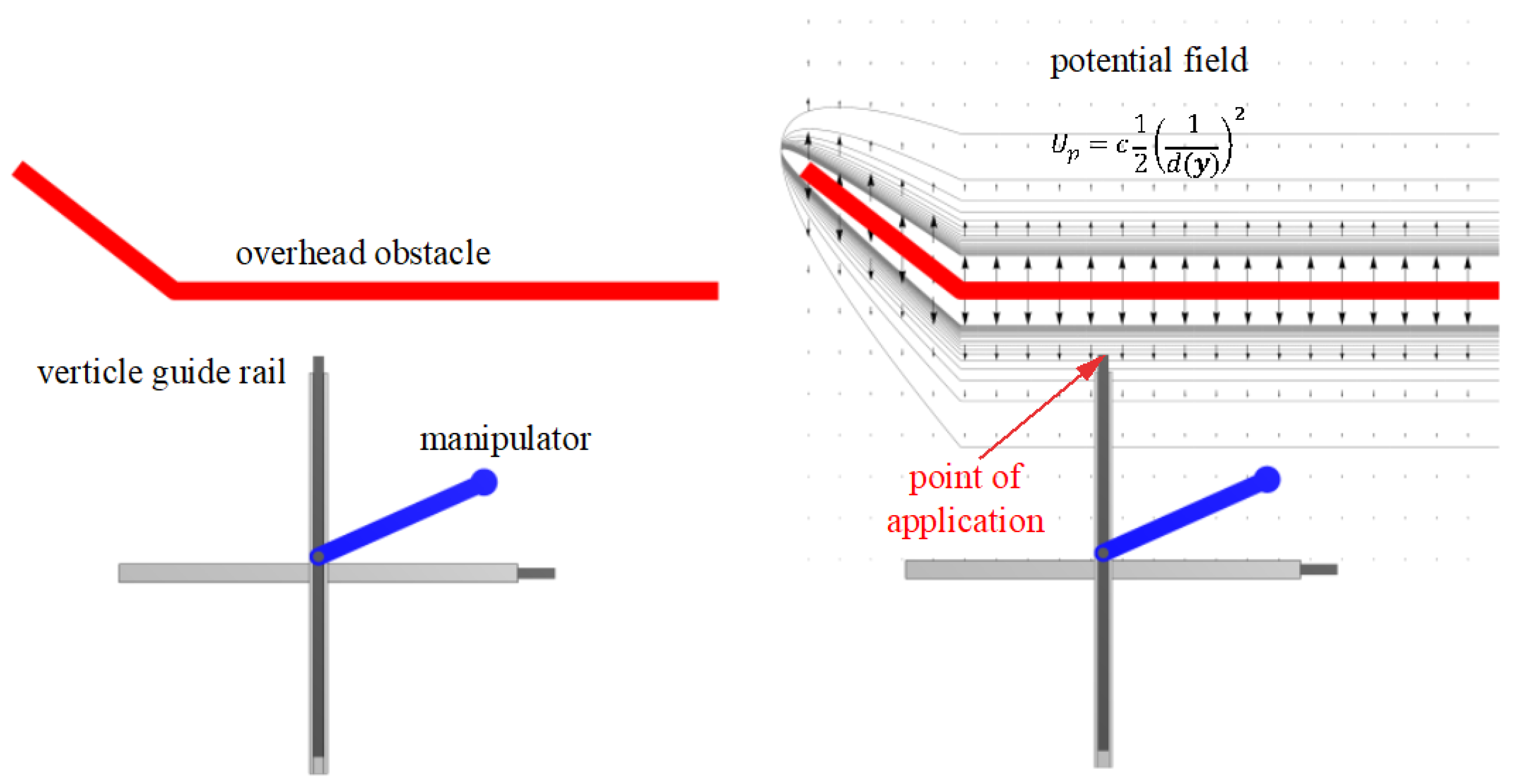
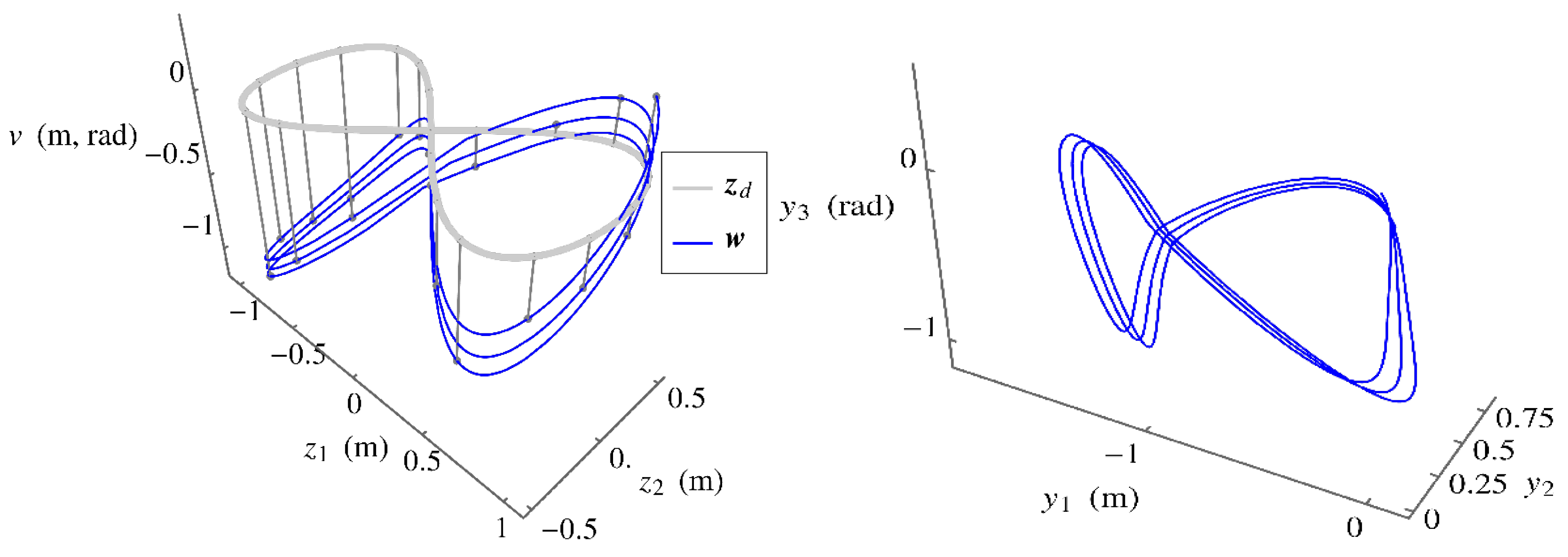
5.An Extended Operational Space Example with Obstacle Avoidance
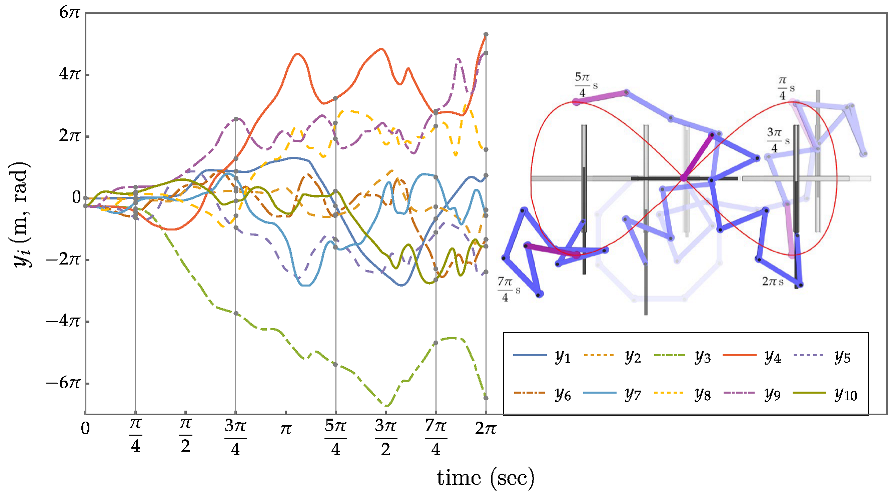
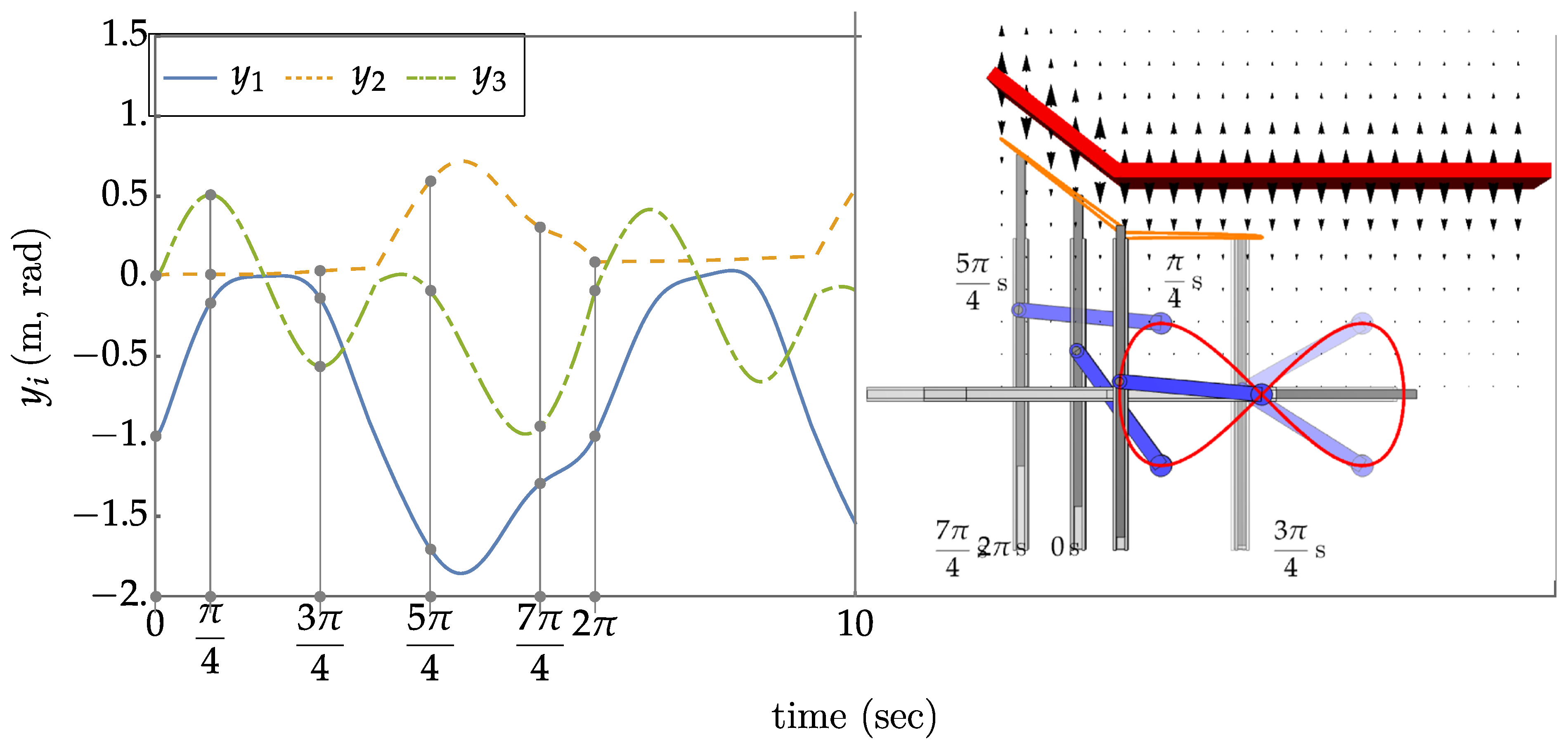
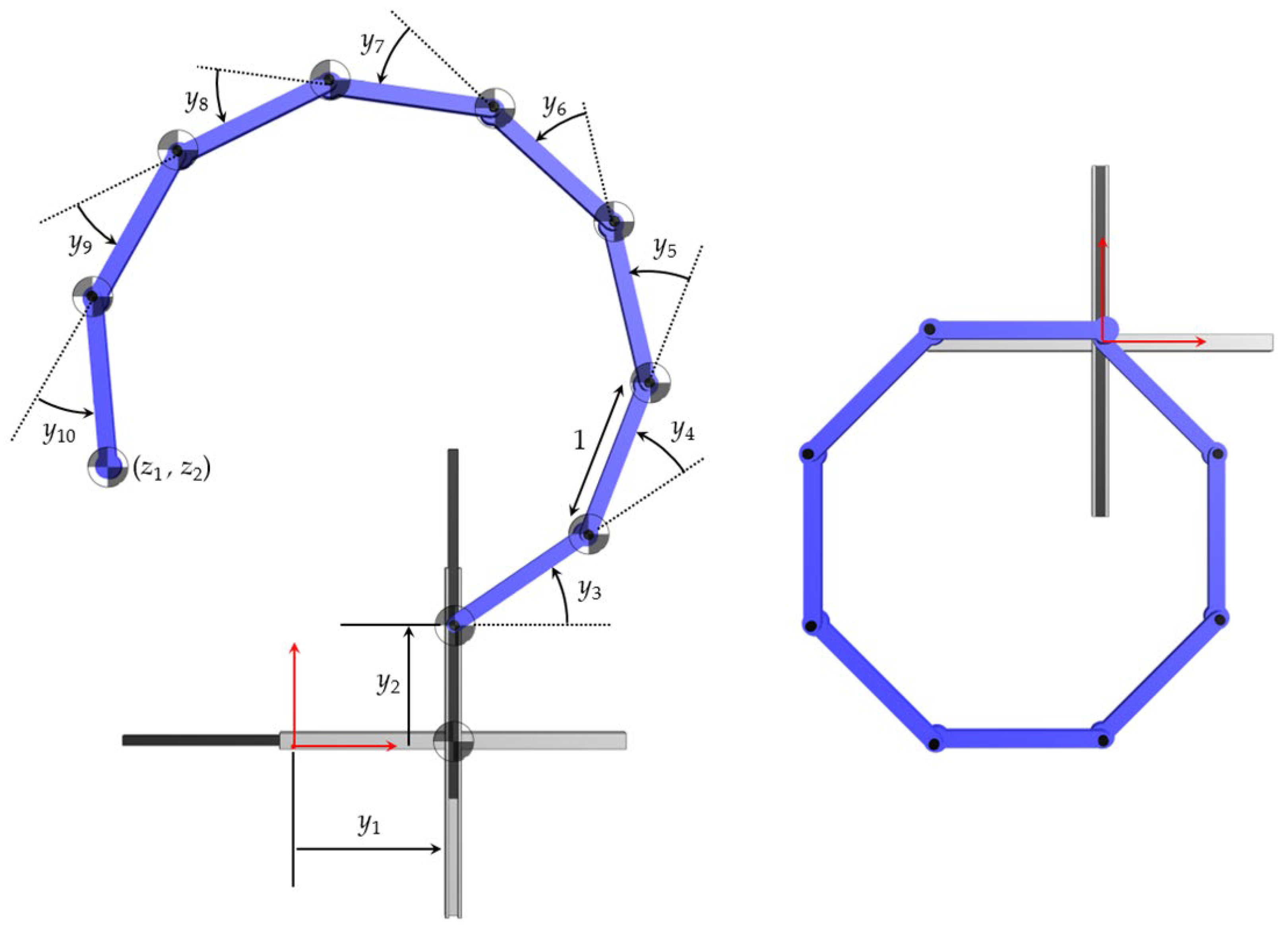
An Eight Degree of Redundancy Test Problem
6.Traditional Operational Space Control
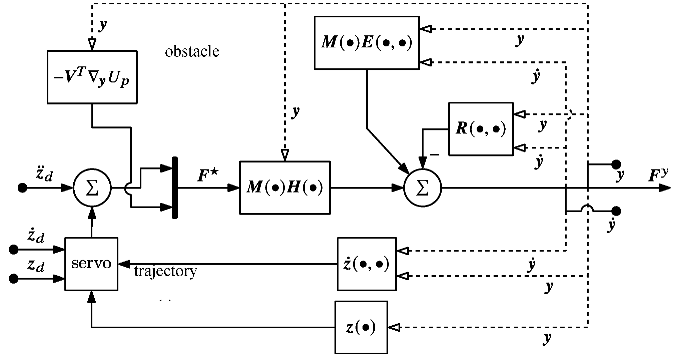
6.Extended Operational Space Control
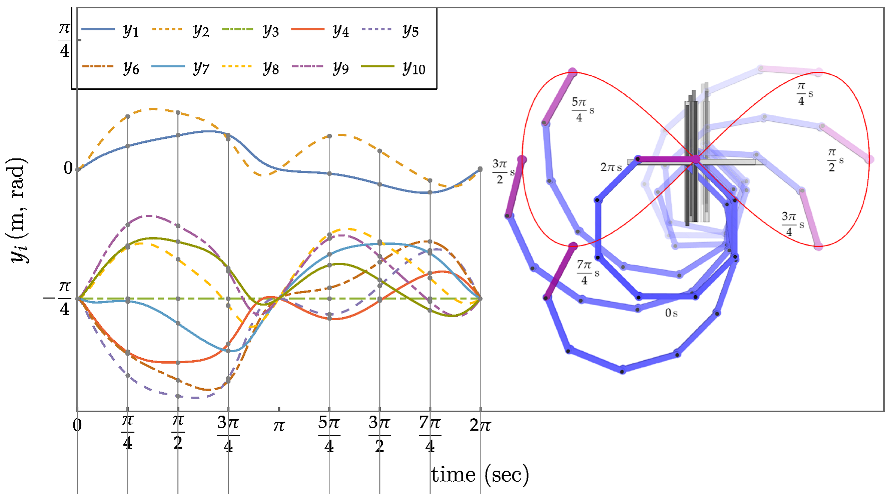
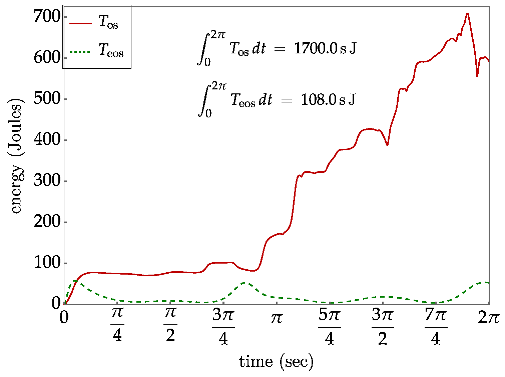
Conclusions and Recommendations for Future Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Financial Support
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiaverini, S., Oriolo, G., and Maciejewski, A. A., Redundant Robots, Siciliano and Khatib eds, Springer Handbook of Robotics, 2nd ed, Springer-Verlag Berlin, 2016.
- Whitney, D. E., Resolved Motion Rate Control of Manipulators and Human Prostheses, IEEE Transactions on Man-Machine Systems, 1969, Vol.10, No. 2, pp. 47-53. [CrossRef]
- Haug, E. J., Redundant Serial Manipulator Inverse Position Kinematics and Dynamics, Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2024, Vol. 16, p. 081008. [CrossRef]
- Khatib, O., A Unified Approach for Motion and Force Control of Robot Manipulators: The Operational Space Formulation”, IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, 1987, Vol. RA-3, No. 1, pp. 43-53. [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, J., Cory, R., Mistry, M., Peters, J., and Schaal, S., Operational Space Control: A Theoretical and Empirical Comparison, The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2008, Vol. 27, No. 6, pp. 737-757. [CrossRef]
- Park, K. C., Chang, P.-H., and Lee, S., Analysis and control of redundant manipulator dynamics based on an extended operational space, Robotica, 2001, Vol. 19, pp. 649-662. [CrossRef]
- De Sapio, V., Advanced Analytical Dynamics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2017.
- Haack, W., and Wendland, W., Lectures on Partial and Pfaffian Differential Equations, Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1972.
- De Luca, A., and Oriolo, G., Nonholonomic Behavior in Redundant Robots Under Kinematic Control, IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1997, Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 776-782. [CrossRef]
- Shamir, T., and Yomdin, Y., Repeatability of Redundant Manipulators: Mathematical Solution of the Problem, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1988, Vol. 33, No. 11, pp. 1004-1009. [CrossRef]
- Haug, E. J., A Cyclic Differentiable Manifold Representation of Redundant Manipulator Kinematics, Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2024, Vol. 16, p. 061005. [CrossRef]
- Klein, C. A., and Huang, C.-H., Review of Pseudoinverse Control for Use with Kinematically Redundant Manipulators, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1983, Vol. SMC-13, No. 3, pp. 245-250. [CrossRef]
- Khatib, O., Inertial Properties in Robotic Manipulation: An Object-Level Framework, The International Journal of Robotics Research, 1995, Vol. 13, No. 1, pp. 19-36. [CrossRef]
- Deo, A., and Walker, I., Overview of Damped Least- Squares Methods for Inverse Kinematics of Robot Manipulators, Journal of Intelligent Robotic Systems, 1995, Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 43-68. [CrossRef]
- Hogan, N., Impedance Control: An Approach to Manipulation: Part I - Theory, Part II - Implementation, Part III – Applications, Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1985, Vol. 107, No. 1, pp. 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Hollerbach, J., and Suh, K. C., Redundancy Resolution of Manipulators Through Torque Optimization, IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, 1987, Vol. RA-3, No. 4, pp. 308–316. [CrossRef]
- Simas, H., and Di Gregorio, R., A Technique Based on Adaptive Extended Jacobians for Improving the Robustness of the Inverse Numerical Kinematics of Redundant Robots, Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2010, Vol. 11, p. 020913.
- Dietrich, A., Ott, C., and Albu-Schäeffer, A., An Overview of Null Space Projections for Redundant, Torque-Controlled Robots, The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2015, Vol. 34, No. 11, pp. 1385-1400. [CrossRef]
- Haug, E. J., Computer-Aided Kinematics and Dynamics of Mechanical Systems, Volume II: Modern Methods, Fourth Ed., Amazon.com, 2024.
- Lee, J. M., Introduction to Smooth Manifolds, Second Ed., Springer, New York, 2013.
- Robbin, J. W., and Salamon, D. A., Introduction to Differential Geometry, Springer, Berlin, 2022.
- Atkinson, K. E., An Introduction to Numerical Analysis, Second Ed., Wiley, New York, 1989. [CrossRef]
- Corwin, L. J., and Szczarba, R. H., Multivariable Calculus, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1982.
- Haug, E. J., and Peidro, A., Redundant Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics on Differentiable Manifolds, Journal of Computational and Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022, Vol. 17, p. 111008. [CrossRef]
- Peidro, A., and Haug, E. J., Obstacle Avoidance in Operational Configuration Space of Kinematically Redundant Serial Manipulators, Machines, 2024, Vol. 12, No. 10. [CrossRef]
- Chung, W. K., Fu, L. C., and Kröger, T., Motion control, In Siciliano, B, and Khatib, O, (eds), Springer Handbook of Robotics, 2016, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 174-177.
- Haug, E. J., Redundant Non-Serial Implicit Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics, Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2024, Vol. 16, p. 061017. [CrossRef]
- Haug, E. J., Redundant Non-Serial Compound Manipulator Kinematics and Dynamics, Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2024, Vol. 200, p. 105717. [CrossRef]
- Nicolis, D., Allevi, F., and Rocco, P., Operational space model predictive sliding mode control for redundant manipulators, IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2020, Vol. 36, No. 4, pp. 1348-1355. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




