1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a major global health challenge due to its high morbidity and mortality rates. As of 2020, HCC accounted for approximately 830,180 deaths worldwide, making it the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death. The five-year survival rate for advanced HCC is around 18%, highlighting the aggressive nature of this malignancy [
1]. Due to the significant resistance to chemotherapy, patients with advanced HCC have traditionally been treated with systemic therapy. The tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib has been the sole treatment option for advanced HCC since 2008 [
2]. Therefore, the development of new drugs with specific cytotoxicity against HCC cells is clinically significant for HCC treatment.
Anticancer peptides (ACPs) are a class of naturally occurring peptides with anticancer activity [
3]. Compared to traditional chemotherapy drugs, ACPs have the advantages such as biocompatibility, efficient therapeutic efficacy, low risk of drug resistance appearing in tumor cells, and limited or no toxicity against mammalian cells [
4,
5]. Additionally, ACPs have immunogenicity and low difficulty in synthesis and modification, with a short half-life
in vivo, making them promising candidates for clinical anticancer drug development [
4]. ACPs exert anticancer activity through membrane disruptive and non-membrane disruptive mechanisms including mediation of the necrosis or apoptosis of cancer cells, inhibition of angiogenesis, recruitment of immune cells and activation of certain regulatory functional proteins [
6]. In the Drug Bank Database, there are nearly 460 compounds targeting cancer, including 29 peptide or polypeptide-based anti-cancer drugs. Most of 29 peptides are still in the phases of preclinicals or clinical trials. Currently, there are only five approved peptides for therapeutic purposes by regulatory agencies like Food and Drug Administration (FDA), USA and European Medicines Agencies (EMA) [
7]. Therefore, there is an urgent need for the research and development of novel anticancer peptide.
NK-lysin is a type of granulysin originally isolated from swine intestinal tissues and identified as an effector peptide secreted by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and natural killer (NK) cells [
8]. NK-lysin and its derivatives were demonstrated to have antimicrobial activity, anticancer activity and immunomodulatory functions [
9,
10]. In our previous studies, the porcine recombinant NK-lysin (prNK-lysin) was expressed using Pichia pastoris expression system [
11], and demonstrated to significantly inhibit the proliferation, migration, adhesion, and invasion of HCC cells
in vitro [
12]. However, it is unclear whether the prNK-lysin can inhibit the growth and metastasis of HCC
in vivo. The present study was to evaluate the prNK-lysin in animal models as peptide candidate with potential therapy for HCC and its mechanism of anti-HCC activity.
2. Result
2.1. prNK-Lysin Inhibits the Proliferation of Hepa 1-6 Cells In Vitro
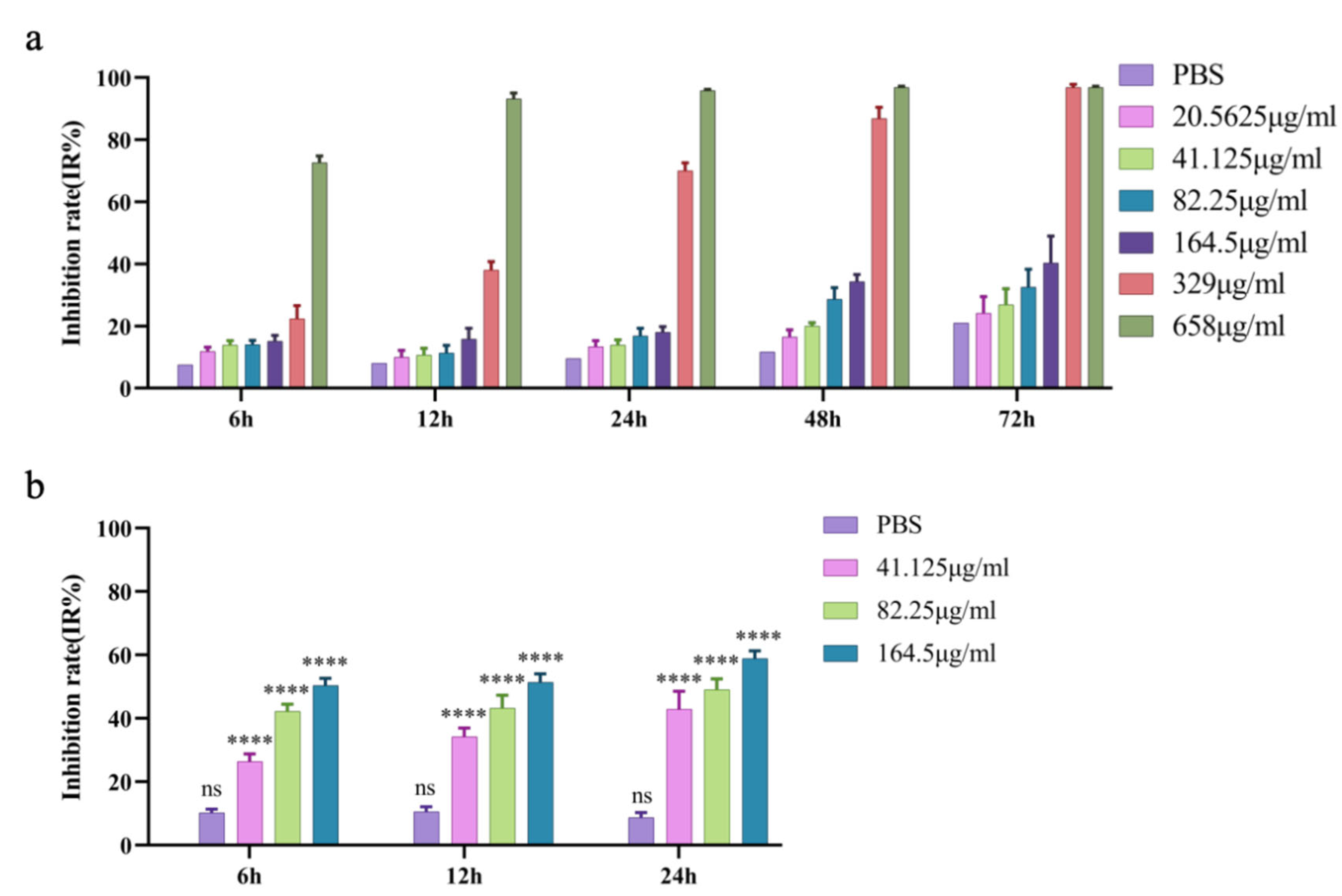
The MTT assay results showed that the inhibitory rate of prNK-lysin at 164.5 μg/mL on AML-12 hepatocytes proliferation did not exceed 20% within 24 h (
Figure 1a), so 164.5 μg/mL was used as the maximum safe concentration (MNTC) for prNK-lysin to AML-12 hepatocyte within 24 h. Subsequently, 41.125, 82.25 and 164.5 μg/mL of prNK-lysin were used to treat Hepa 1-6 cells within 24 h. The results demonstrate that compared to the control group, prNK-lysin significantly inhibited the proliferation of Hepa 1-6 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner (
Figure 1b).
2.2. prNK-Lysin Induces Oncosis in Hepa 1-6 Cells
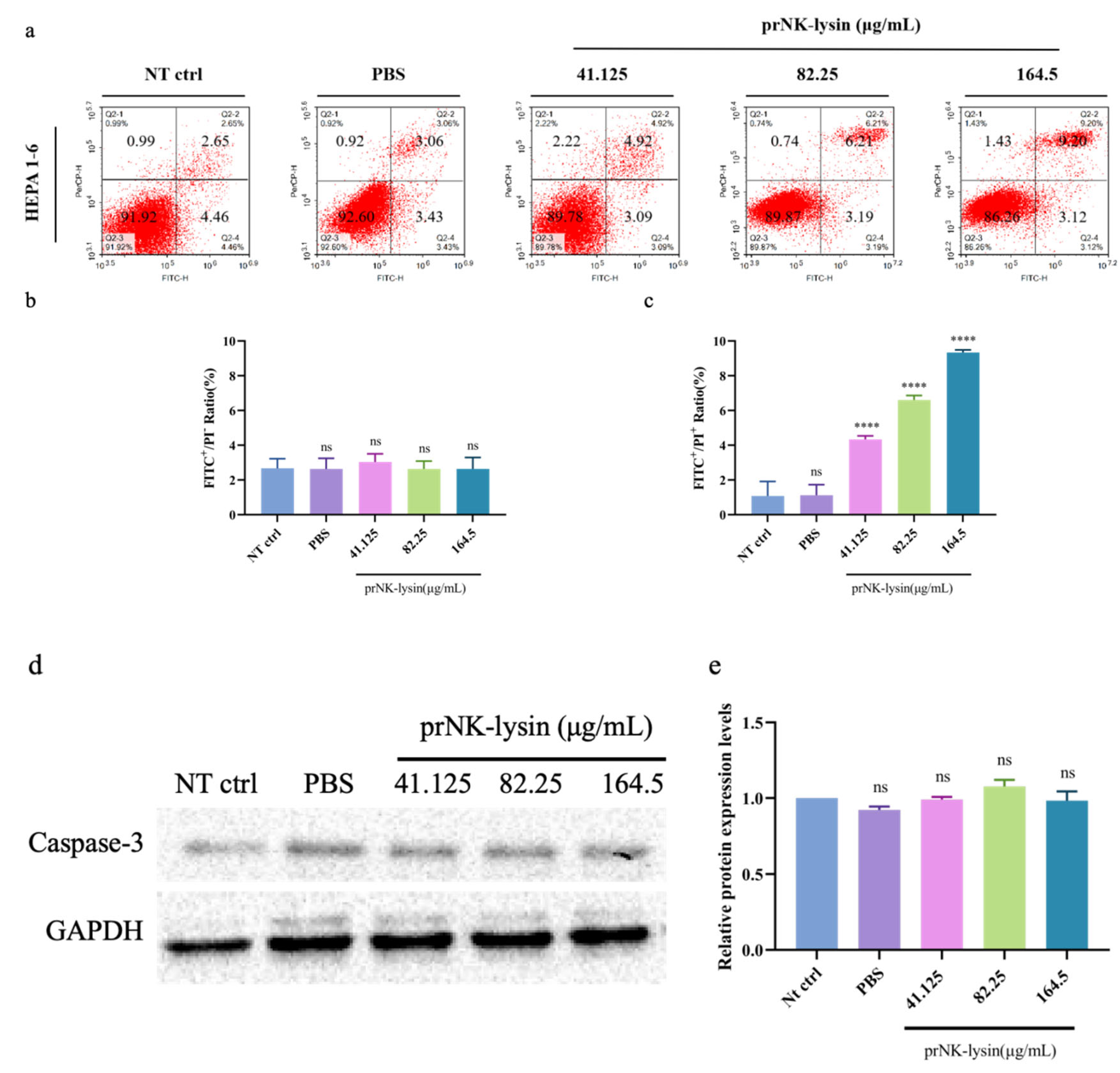
Double staining with Annexin V-FITC/PI was used to evaluate the cell apoptosis induced by prNK-lysin in Hepa 1-6 cells. The results showed that prNK-lysin significantly increased the number of FITC
+/PI
+ cells , but not FITC
+/PI
- cells (
Figure 2a, 2b and 2c). Additionally, there was no significant changes for the number of caspase-3 positive cells in the prNK-lysin treatment groups (
Figure 2d and 2e). These results indicated that prNK-lysin induced non-apoptotic cell death.
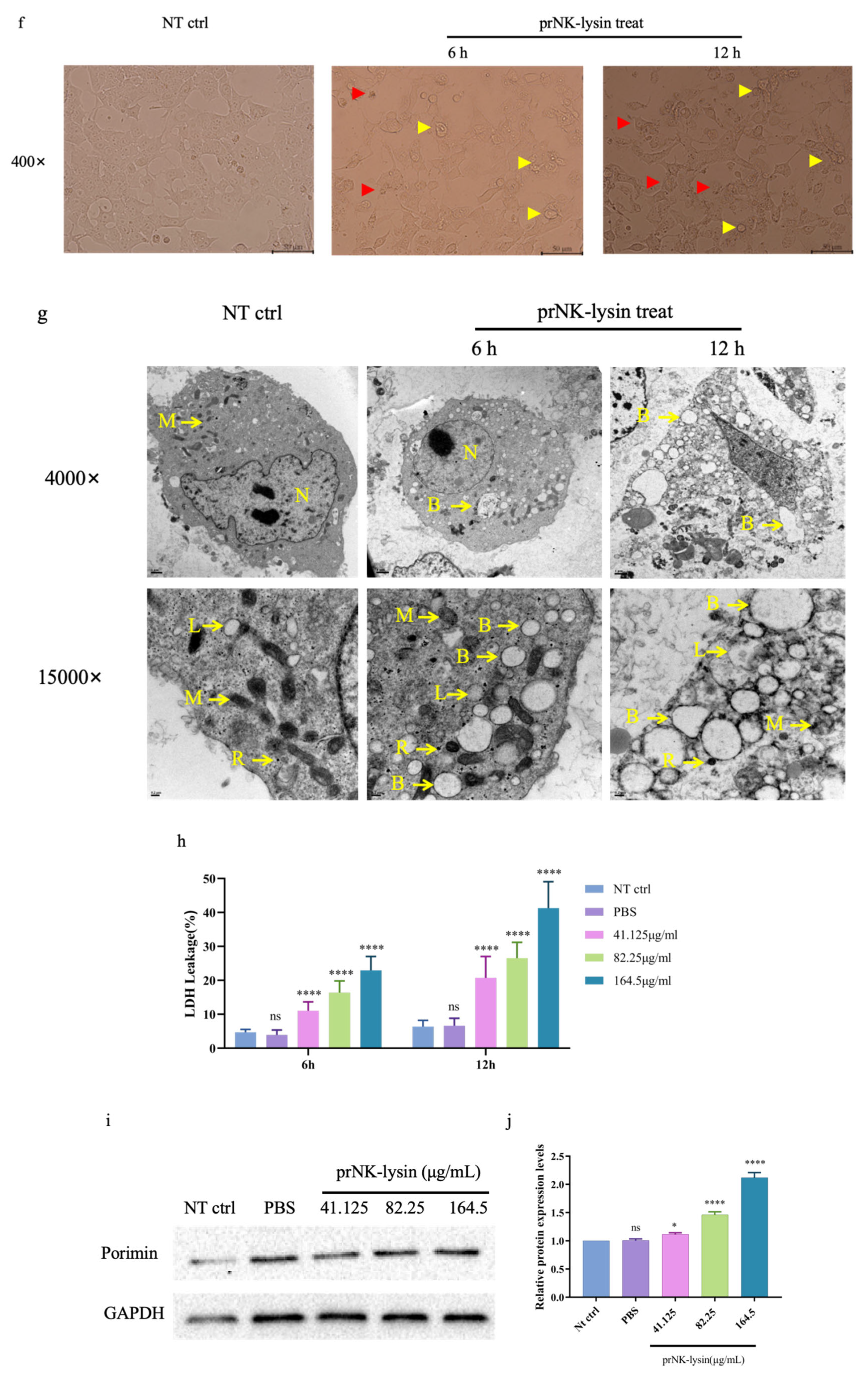
We also investigated the changes of cell morphology, the levels of extracellular lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and porimin expression. Compared to the control group, cellular swelling and membrane surface blebs were observed in the prNK-lysin treatment groups (
Figure 2f). Numerous vacuoles, mitochondrial swelling and karyolysis were detected inside the cell (
Figure 2g). Compared to the control group, prNK-lysin treatment significantly increased the level of LDH released by Hepa 1-6 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner (
Figure 2h). Compared with the control group, prNK-lysin treatment also significantly increased the level of porimin expression in Hepa 1-6 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner (
Figure 2i and 2j).
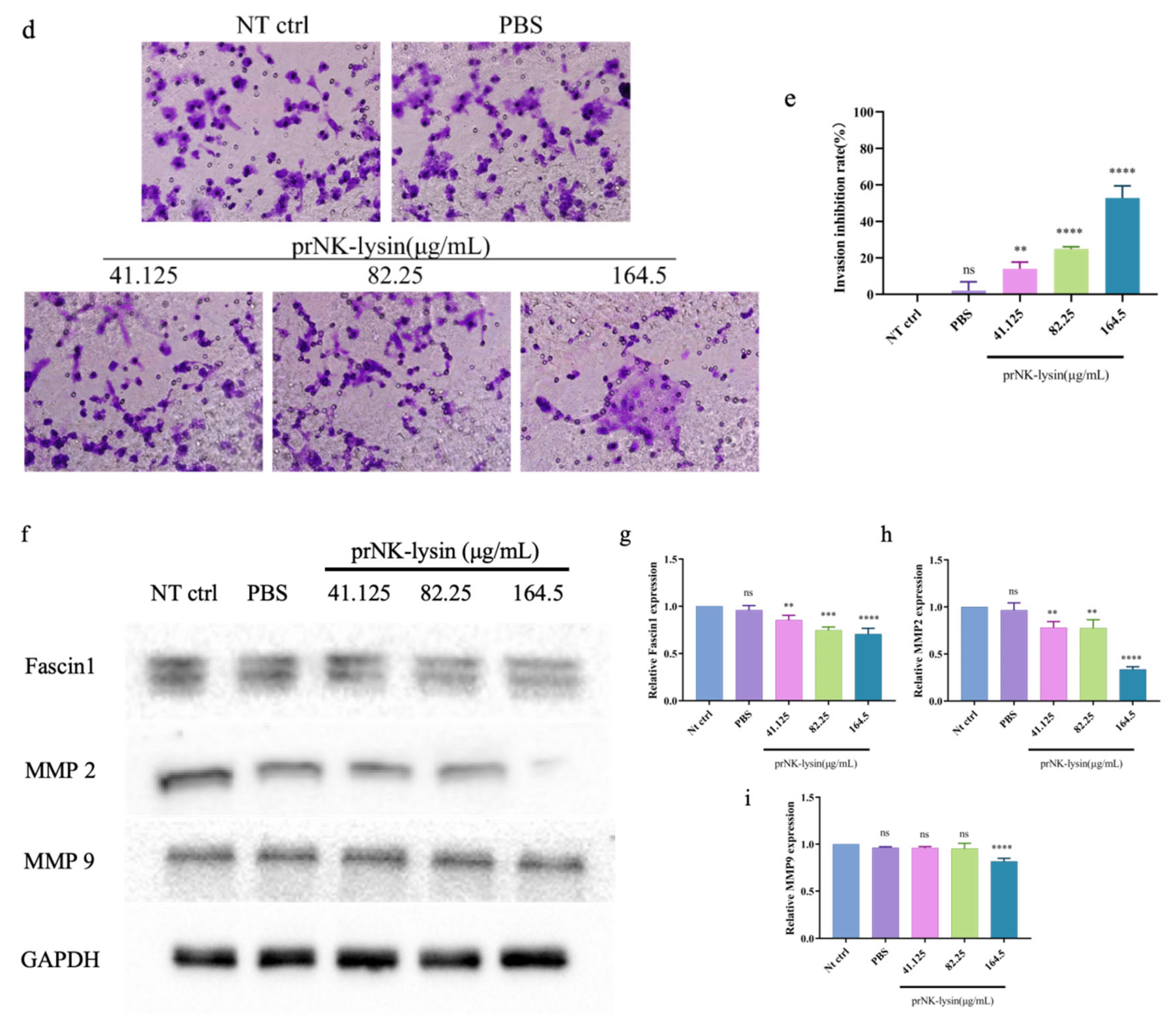
2.3. prNK-Lysin Inhibits Metastasis of Hepa 1-6 Cells In Vitro
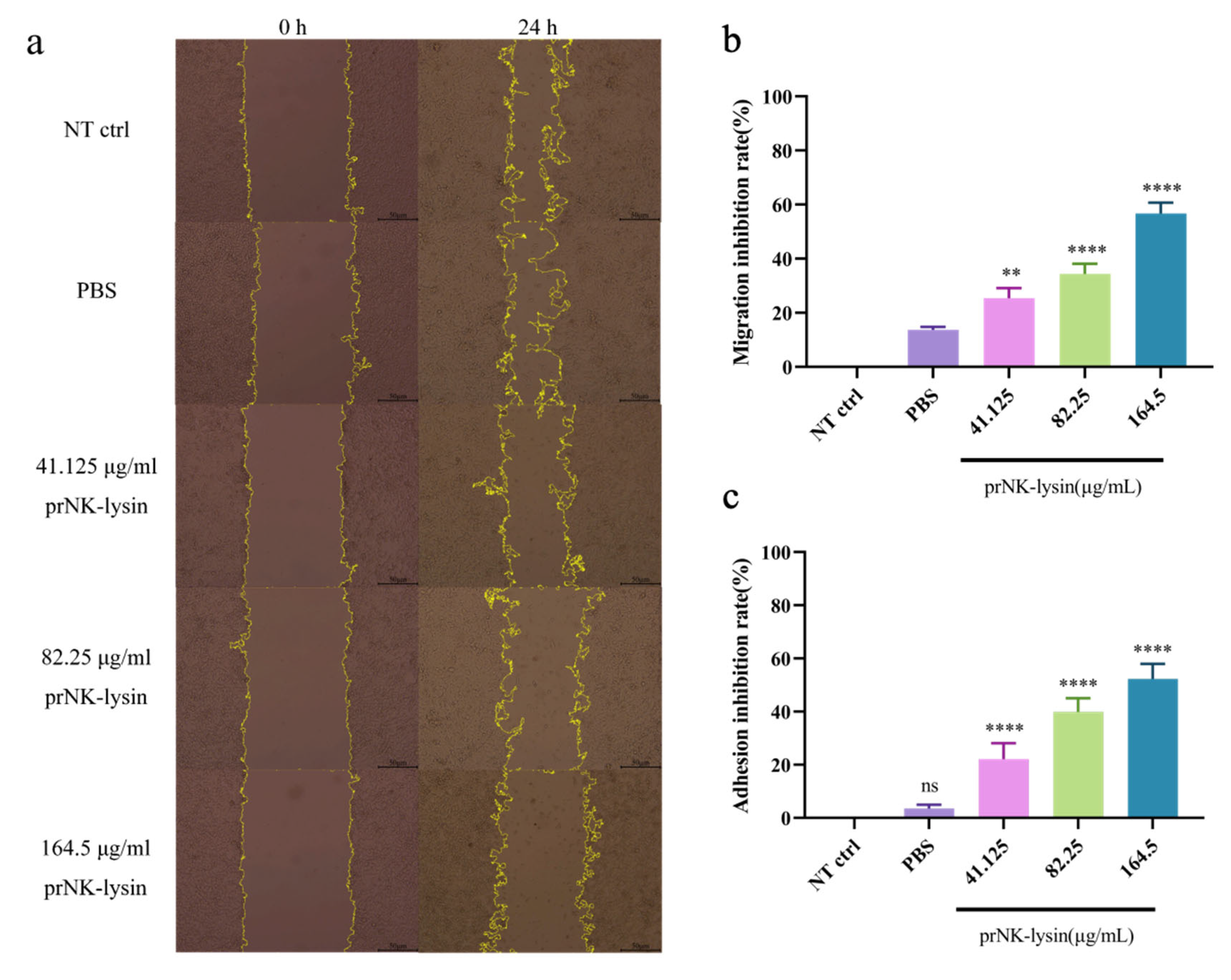
The results showed that prNK-lysin 24 h treatment significantly decreased the migration, adhesion, and invasion ability of Hepa 1-6 cells. The scratch assay revealed that the inhibition rate of the 41.125 µg/mL, 82.25 µg/mL and 164.5 µg/mL prNK-lysin treatments were 28%, 37%, and 59% , respectively (
Figure 3a). The results of adhesion assay showed that the inhibition rate of 41.125 µg/mL, 82.25 µg/mL and 164.5 µg/mL prNK-lysin treatments were 31%, 50%, and 67%, respectively (
Figure 3b). The results of migration and invasion assay showed that the inhibition rate of 41.125 µg/mL, 82.25 µg/mL and 164.5 µg/mL prNK-lysin treatments were 17%, 26%, and 61%, respectively (
Figure 3c). These results demonstrated that prNK-lysin treatment significantly inhibits metastasis of Hepa 1-6 cells
in vitro in a dose-dependent manner.
Elevated levels of Fascin-1 are linked to increased tumor invasiveness, affecting metastasis severity and leading to poor prognosis and shorter overall survival times. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs, such as MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-9) facilitate the breakdown of proteins in the extracellular matrix, enabling cell migration [
13]. The level of Fascin-1, MMP-2 and MMP-3 in Hepa 1-6 cells were detected using Western Blot. The results showed that the expression of Fascin-1, MMP-2 and MMP-3 were down-regulated in Hepa 1-6 cells treated with prNK-lysin (
Figure 3f, 3g, 3h and 3i). This indicated that prNK-lysin inhibits of metastasis Hepa 1-6 cells by inhibiting Fascin-1, MMP-2 and MMP-3 expression.
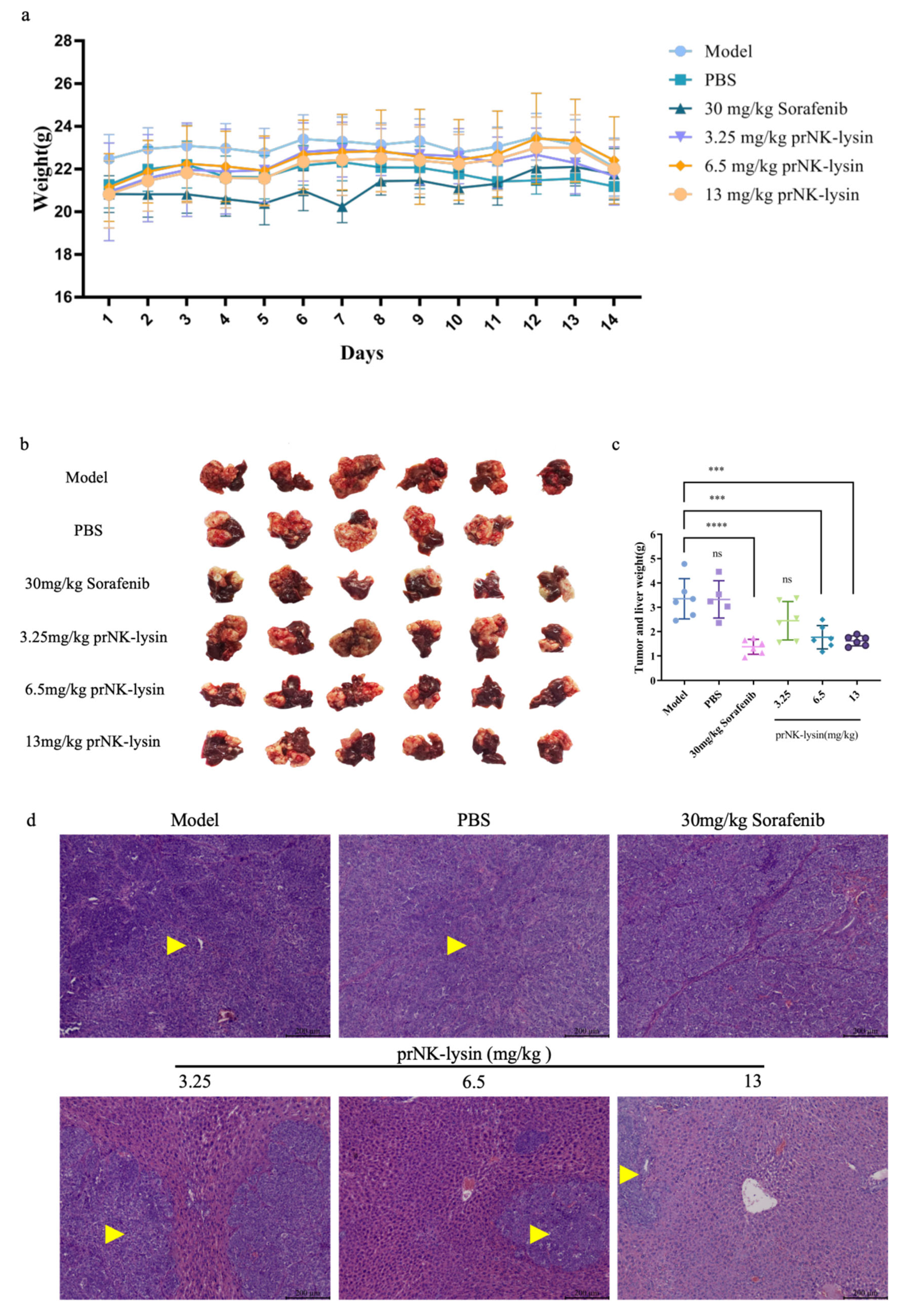
2.4. prNK-Lysin Inhibits the Growth of Hepa 1-6 Cells in Mouse Liver Orthotopic Implantation Model
The prNK-lysin effect on HCC growth
in vivo was evaluated in mouse seeded with Hepa 1-6 cells into liver for. As shown in
Figure 4a, there was no significant difference in the body weight among all of groups showed. The liver tissues of mice were taken and the weight of tumors isolated from liver were measured. The tumor weight in Sorafenib group, groups treated prNK-lysin at 6.5mg/kg and 13mg/kg significantly less than other group (
Figure 4b and 4c). The liver tissues in HE staining showed that in the the model group and the PBS group, the liver lobule structure was unclear, the hepatic cords were disorganized, the hepatic sinusoids were reduced or even disappeared, some hepatocytes were necrotic, the sizes of hepatocyte nuclei varied, and the liver cancer cells were distributed in diffuse form, most of them appearing as immature cells. In the 3.25mg/kg prNK-lysin group, the hepatic sinusoids disappeared, and liver cancer cells were diffusely distributed. In the 6.5mg/kg prNK-lysin group, the hepatic sinusoids were smaller, with a clear boundary between normal hepatocytes and liver cancer cells. In the 13mg/kg prNK-lysin group and the Sorafenib group, the liver lobule structure was clear, the hepatic cords were orderly arranged, the hepatic sinusoids were normal, the sizes of hepatocyte nuclei were uniform, and the distribution of liver cancer cells was reduced (
Figure 4d). The results above indicated prNK-lysin inhibited growth of Hepa 1-6 cells
in vivo.
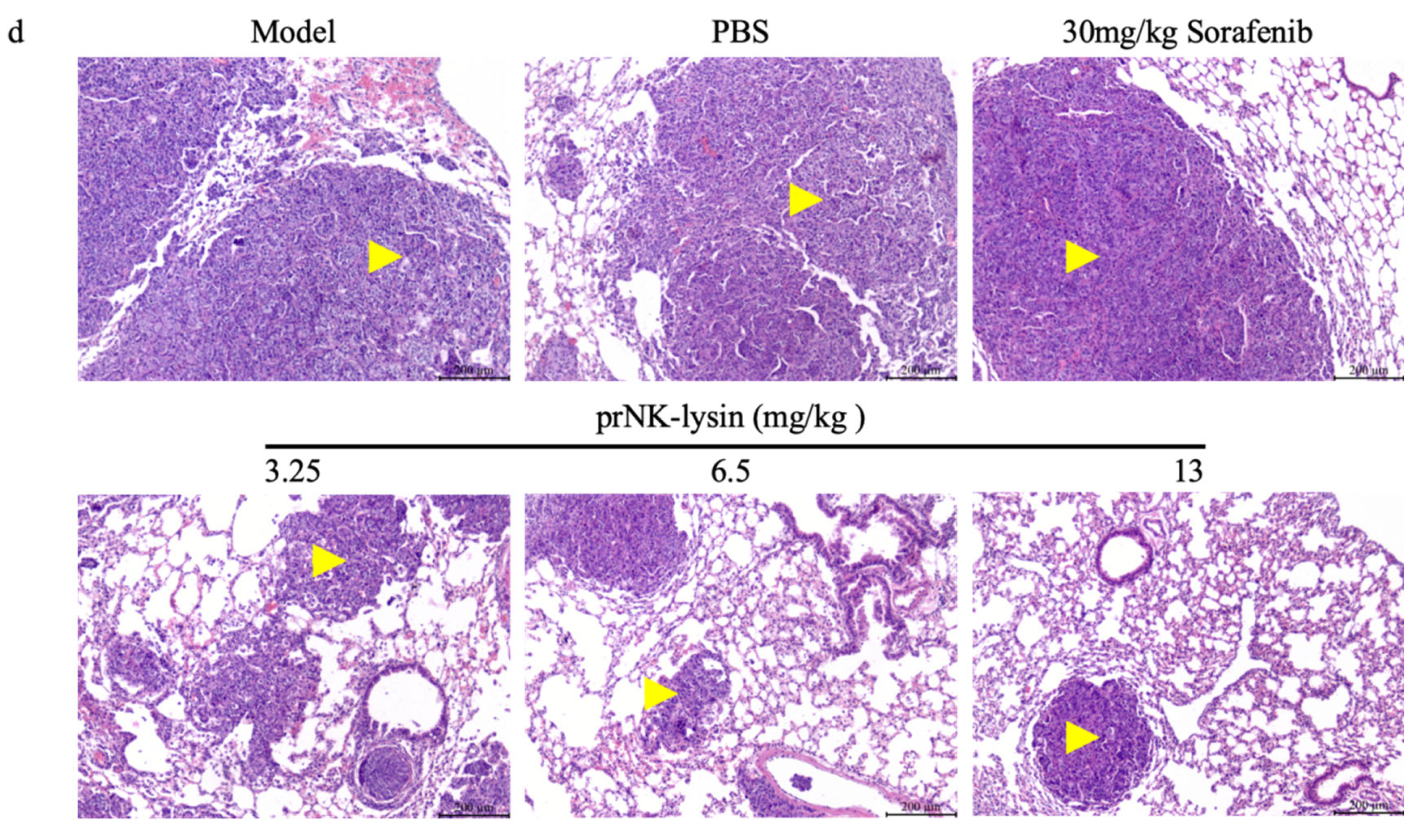
2.5. prNK-Lysin Inhibits the Metastasis of Hepa 1-6 Cells in Mouse Lung Metastasis Model
The prNK-lysin effect on HCC metastasis
in vivo, was studied in lung metastasis model of mouse injected with Hepa 1-6 cells. As shown in
Figure 5a, the body weight showed no significant difference between all of groups. The lung tissues of mice were taken and the number of tumor nodules were counted. The number of tumor nodules in the PBS group, the Sorafenib group, the 3.25mg/kg, 6.5mg/kg and 13mg/kg prNK-lysin group were less than the model group, but there were no statistically significant differences between the groups except 13mg/kg prNK-lysin group (
Figure 5b and 5c). The HE staining of liver tissues showed that the cancer nests in the model group, PBS group and Sorafenib group occupied almost the whole lung tissue and the boundary between the tumor and normal lung tissue is blurry. In the 3.25mg/kg and 6.5mg/kg prNK-lysin group, the cancer nest area was smaller than the model group, but had blurred boundary with normal lung tissue. The cancer nest area of 13mg/kg prNK-lysin was obviously smaller than other group and had clear boundary with normal lung tissue (
Figure 5d). This indicated that prNK-lysin inhibited metastasis of Hepa 1-6 cells
in vivo.
3. Discussion
In the previous studies, we found that prNK-lysin could inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of human HCC cells when non-toxic concentration of prNK-lysin to normal hepatocytes L-02
in vitro was applied [
12]. In this study, we demonstrated the inhibitory effect of the prNK-lysin on murine HCC cells Hepa 1-6 with the non-toxic concentration to AML-12 hepatocyte
in vitro and
in vivo.
The apoptosis has traditionally been a key target for anticancer therapy. The recombinant NK-lysin could induce apoptosis of Jurkat cells [
14]. However, our results indicated that the cell death of Hepa 1-6 cells induced by the prNK-lysin was non-apoptotic cell death. Hepa 1-6 cells treated with prNK-lysin exhibited distinctive features, including cellular swelling, membrane surface blebs with vacuoles, mitochondrial swelling and karyolysis inside cells. The morphological manifestations of Hepa 1-6 cells were not typical of apoptosis. Oncosis is a form of death characterized by cell swelling and karyolysis [
15]. The morphological characteristics include cell enlargement, swelling, cell vesicles, a lack of organelles in the vesicles, the destruction of cell membrane integrity, the swelling of the endoplasmic reticulum, the swelling of mitochondria, a swollen nuclear membrane, dispersion, and the agglutination of chromatin [
16,
17,
18]. Additionally, LDH leakage, an indicator of the integrity of the cell membrane is associated with oncosis [
19], and the porimin is specifically expressed on the surface of oncotic cells [
20]. Furthermore, prNK-lysin was found to induce LDH leakage and elevate porimin levels in Hepa 1-6 cells, indicating that prNK-lysin-induced cell death is oncosis.
Metastasis involves the spread of cancer cells from the primary tumor to the surrounding tissues and other distant organs and is the primary cause of cancer morbidity and mortality. Inhibiting cancer metastasis plays a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of cancer treatment, improving patient outcomes, and maintaining a better quality of life. Fascin-1 is a protein closely related to the cross-linking of filaments in actin-rich protrusions [
21]. Its overexpression is observed in metastatic cancer. Hence, fascin-1 is believed to promote migration and invasion of cancer cells [
22,
23], and has been considered as a clinical prognostic marker of metastatic tumors [
24]. Gelatin is one of the major component of extracellular matrix (ECM) around the cancer cell. Since ECM acts as a biochemical and biophysical barrier for cancer cells migration and invasion into the blood/lymphatic vessels, ECM degradation must be preceded for cancer metastasis. There are more than 20 matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) which are major enzymes that degrade components of ECM. Among of them, MMP-2 and MMP-9 are two major gelatin-degrading enzymes, gelatinases [
25]. In the present study, we performed selective assays which were related with cancer cell migration and invasion in murine HCC cells to clarify the anti-metastatic effects of prNK-lysin. The prNK-lysin significantly inhibited migration, Migration, adhesion, and invasion of Hepa 1-6 cells. The expression of Fascin-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 were also suppressed by the treatment of prNK-lysin. Subsequent animal experiments provided further validation of prNK-lysin’s inhibitory effect on murine HCC growth and metastasis. The anti-cancer effect of prNK-lysin was better than that of the Sorafenib group.
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cells and Cell Culture
Alpha mouse liver 12 (AML-12) hepatocyte was purchased from Servicebio Technology (Wuhan, China). Murine hepatocellular carcinoma cell Hepa 1-6 was purchased from Institute of Basic Medical Sciences for Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. These cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s Minimum Essential Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS), 100U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin, at 37 ℃ in a 5% CO2 incubator.
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
AML-12 hepatocytes and Hepa 1-6 cells were seeded into a 96-well cell culture plate with 5×103 cells/well for overnight growth and then treated with prNK-lysin at different concentrations at different time periods. Then, the culture supernatant was discarded and the cells were incubated with 30 μL MTT reagent for 4 h, and further incubated for 30min by adding 100 μL DMSO reagent. Subsequently, the absorbance value was measured at 490 nm using SpectraMax i3x Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (Molecular Devices, USA).
4.3. Cell Death Detection
Hepa 1-6 cells were seeded into a 6-well cell culture plate with 5×104 cells/well for overnight growth, and then treated with prNK-lysin at different concentrations for 24 h. The cells were collected using trypsin digestion without EDTA, washed with cold PBS, and stained in the dark according to the instructions of Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Detection Kit. Cell death was detected using FACScan Flow Cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Germany).
4.4. Light Microscope
Hepa 1-6 cells were seeded into a 96-well cell culture plate with 5×103 cells/well for overnight growth and then treated with 164.5 μg/mL prNK-lysin for 6 and 12 h. The cells were monitored and images were taken using an inverted Microscope (Olympus, Japan).
4.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
Hepa 1-6 cells were seeded into a 100mm cell culture plate with 6×105 cells/well for overnight growth and then treated with 164.5 μg/mL prNK-lysin for 6 and 12 h. The cells were washed with PBS and fixed with an electron microscope fixative. The cell samples were placed on the copper mesh for staining, observeing using H-7650 Transmission Electron Microscopy (Hitachi, Japan).
4.6. LDH Detection
Hepa 1-6 cells were seeded into a 96-well cell culture plate with 5×103 cells/well for overnight growth and then treated with prNK-lysin at different concentrations for 6 and 12 h. The supernatant was collected according to the instructions of the Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay Kit, and the LDH level was evaluated by measuring the absorbance at 490 nm using SpectraMax i3x Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (Molecular Devices, USA).
4.7. Scratch Assay
Hepa 1-6 cells were seeded into a 6-well cell culture plate with 5×104 cells/well and incubated until they reach 100% confluence. A scratch was created through the cell monolayer using a 100 μL pipette tip manually. Cells and debris were rinsed with PBS . Then the cells were treated with prNK-lysin at different concentrations. Images of the scratch area were taken immediately after making the scratch (0 h) and at 24 h for further incubation. The width of the scratch was determined based on the images taken and the rate of cell migration was calculated using Image J (NIH Image, USA).
4.8. Adhesion Assay
Hepa 1-6 cells were seeded into a 6-well cell culture plate with 5×104 cells/well overnight and then treated with prNK-lysin at different concentrations for 24 h. 100 µL cell suspension treated with prNK-lysin was added into the 96-well cell culture plate coated with Matrigel and incubated for 1 h. The wells were washed with PBS to remove non-adherent cells. The adherent cells were incubated with 30 μL MTT reagent for 4 h, and further incubated for 30 min by adding 100 μL DMSO reagent. Subsequently, the absorbance value was measured at 490 nm using SpectraMax i3x Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (Molecular Devices, USA).
4.9. Migration and Invasion Assay
The upper chamber of the Transwell inserts was coated with a thin layer of Matrigel and incubated at 37°C for 2 h to allow the Matrigel to solidify. 200 μL FBS-free DMEM medium containing 4×104 cells and prNK-lysin at different concentrations were added into the the upper chamber of the Matrigel-coated Transwell insert. 500 µl of DMEM medium containing 20% FBS was added to the lower chamber. The Transwell inserts were in the lower chamber and incubated for 24 h. Removed non-invaded cells from the upper surface of the insert using a cotton swab. Fixed the cells that have invaded through the Matrigel to the lower surface of the insert with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes. Stained the cells with crystal violet for 30 minutes, then rinsed with PBS. Counted the stained cells under inverted microscope (Olympus, Japan).
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
Hepa 1-6 cells were seeded into a 100mm cell culture plate with 6×105 cells/well for overnight growth and then treated with prNK-lysin of different concentrations for 24 h. The cells were lysed using RIPA lysis buffer containing 1% cocktail and 1% PMSF. The protein concentration determined by BCA Protein Kit. The protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to the 0.45 μm PVDF membrane. Then, the membrane was blocked with 10% skimmed milk for 2 h. The membranes were incubated with primary antibody inculding Caspase3 Antibody (1:1000; CST, USA), Porimin Antibody (1:500; NOVUS, USA), Fascin-1 Antibody (1:25000; ABCAM, USA), MMP-2 Antibody (1:2500; ABCAM, USA), MMP-9 Antibody (1:5000; ABCAM, USA), and GAPDH Antibody (1:30000; Proteintech, China) overnight at 4 ℃. and then the membranes were incubated with secondary antibodys inculding Goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (1:20000, Cwbio, China) and Goat anti-mouse IgG-HRP (1:20000, Absin, China) at room temperature by shaking for 1 h. Subsequently, the target protein was visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (MeilunBio, China), and the membrane was imaged using the Chemi Doc XRS+ imaging system (BioRad, USA).
4.11. Animals
Animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanxi Agricultural University (approval document No. 2022NM.ZA-005010001 for mouse liver orthotopic implantation model and SXAU-EAW-2022M.FC.008011002 for mouse lung metastasis model). All animals received care according to the standards outlined in the National Standard Animal Experiment Endpoint Evaluation Guidelines of the People's Republic of China. Male BALB/cA-nu mice were purchased from Beijing HFK Bioscience Co., Ltd. (animal license #: SCXK Beijing 2024-0003, China). All animals were fed under standard SPF-grade conditions at 25 ℃ with 50% relative humidity, with free access of drinking water.
4.12. Establishment of Mouse Orthotopic Model by Seeding Hepa 1-6 Cells Into Mouse Liver
The 7 weeks old male mouse was anesthetized using isoflurane. The mouse was placed in a supine position with the abdominal area sterilized, then a subcostal incision was made to expose the liver. Hepa 1-6 cells (5×105 cells/mouse) were injected into the left lobe of the liver using a fine-gauge needle. The abdominal muscle layer was closed with absorbable sutures and the skin closed with non-absorbable sutures. The mouse was closely monitored until it was fully recovered from anesthesia. 24 h after surgery, mice were randomly divided into model group, PBS group, 30mg/kg Sorafenib group, 3.25mg/kg prNK-lysin group, 6.5mg/kg prNK-lysin group and 13mg/kg prNK-lysin group (n=6). The sorafenib was dissolved in 5% DMSO and 95% PBS, and the prNK-lysin was dissolved in PBS. Except the model group, PBS or drugs were administered into the mice of other groups by intraperitoneal injection once a day for 14 consecutive days. The mice were monitored daily for weight loss, health and welfare.
4.13. Establishment of Mouse Lung Metastasis Model
The 5 weeks old male mouse was anesthetizede using isoflurane for cell injection. Hepa 1-6 cells (2×105 cells/mouse) were injected into the tail vein using a fine-gauge needle for 5 consecutive days. From 6th day, mice were randomly divided into model group, PBS group, 30mg/kg Sorafenib group, 3.25mg/kg prNK-lysin group, 6.5mg/kg prNK-lysin group and 13mg/kg prNK-lysin group (n=6). Except the model group, PBS or drugs were administered into the mice of other groups by intraperitoneal injection once a day for 14 consecutive days. The mice were monitored daily for weight loss, health and welfare..
4.14. Histopathology Analysis
The liver and lung of the mouse were collected, fixed and and processed to paraffin-embedded (FFPE) blocks. The hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining on mouse liver and lung was performed. The stained slides were photographed and analysed using an upright microscope (Leica, Germany).
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis were performed with one-way ANOVA comparing the samples with their respective control using GraphPad Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Software Inc., USA). A significant difference was considered when P<0.05.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Kuohai Fan and Hongquan Li; Data curation, Kuohai Fan, Zhiwei Feng and Dahai Zhao; Formal analysis, Kuohai Fan, Zhiwei Feng and Dahai Zhao; Funding acquisition, Hongquan Li; Investigation, Kuohai Fan, Zhiwei Feng and Dahai Zhao; Methodology, Kuohai Fan; Project administration, Hongquan Li; Resources, Wei Yin, Na Sun and Panpan Sun; Supervision, Wei Yin, Na Sun, Panpan Sun and Hongquan Li; Validation, Wei Yin, Na Sun and Panpan Sun; Visualization, Zhiwei Feng, Jianhua Guo and Xiaozhong Zheng; Writing – original draft, Kuohai Fan and Zhiwei Feng; Writing – review & editing, Jianhua Guo and Xiaozhong Zheng. All authors will be informed about each step of manuscript processing including submission, revision, revision reminder, etc. via emails from our system or assigned Assistant Editor.