Submitted:
29 October 2024
Posted:
29 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
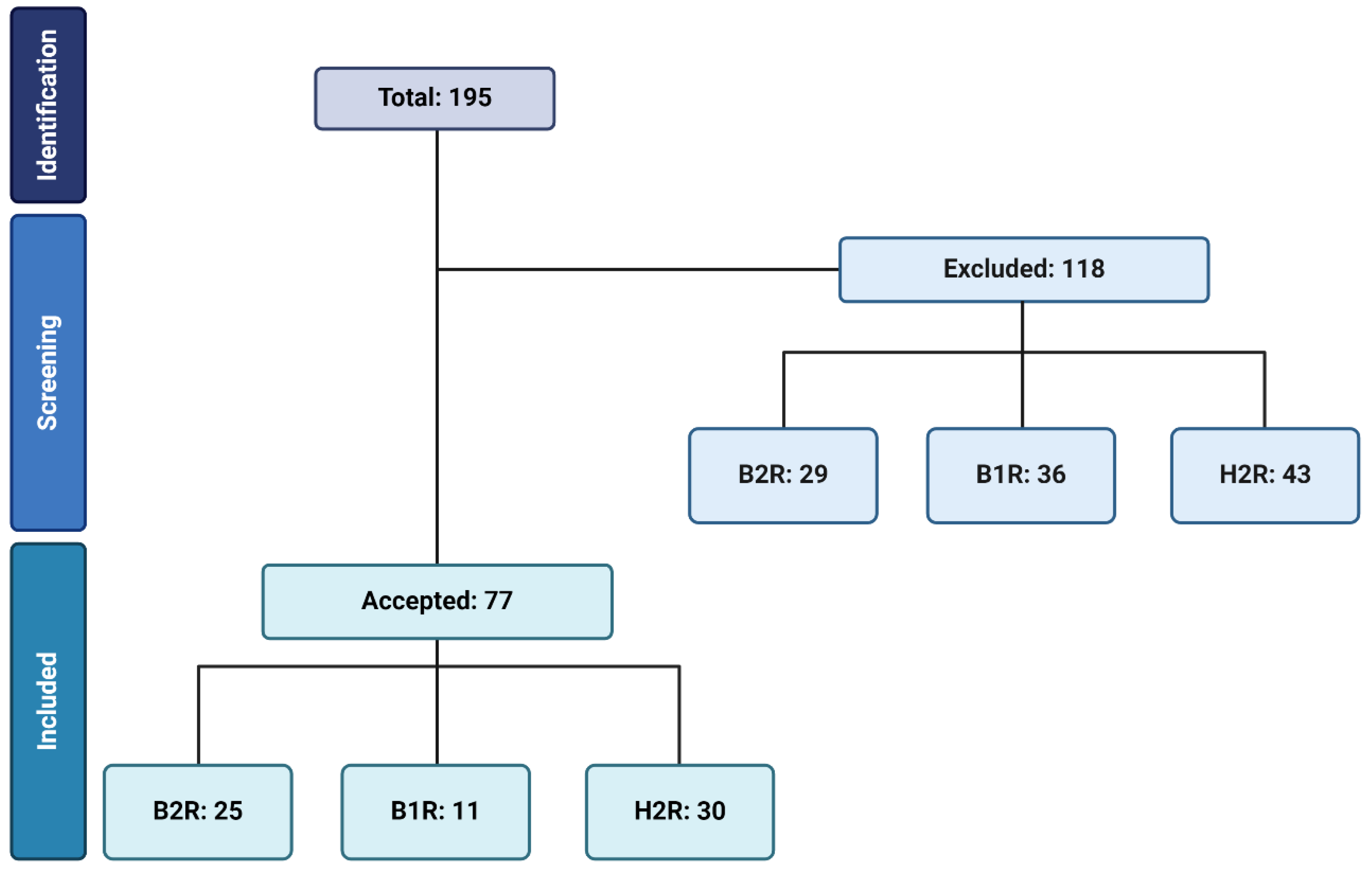
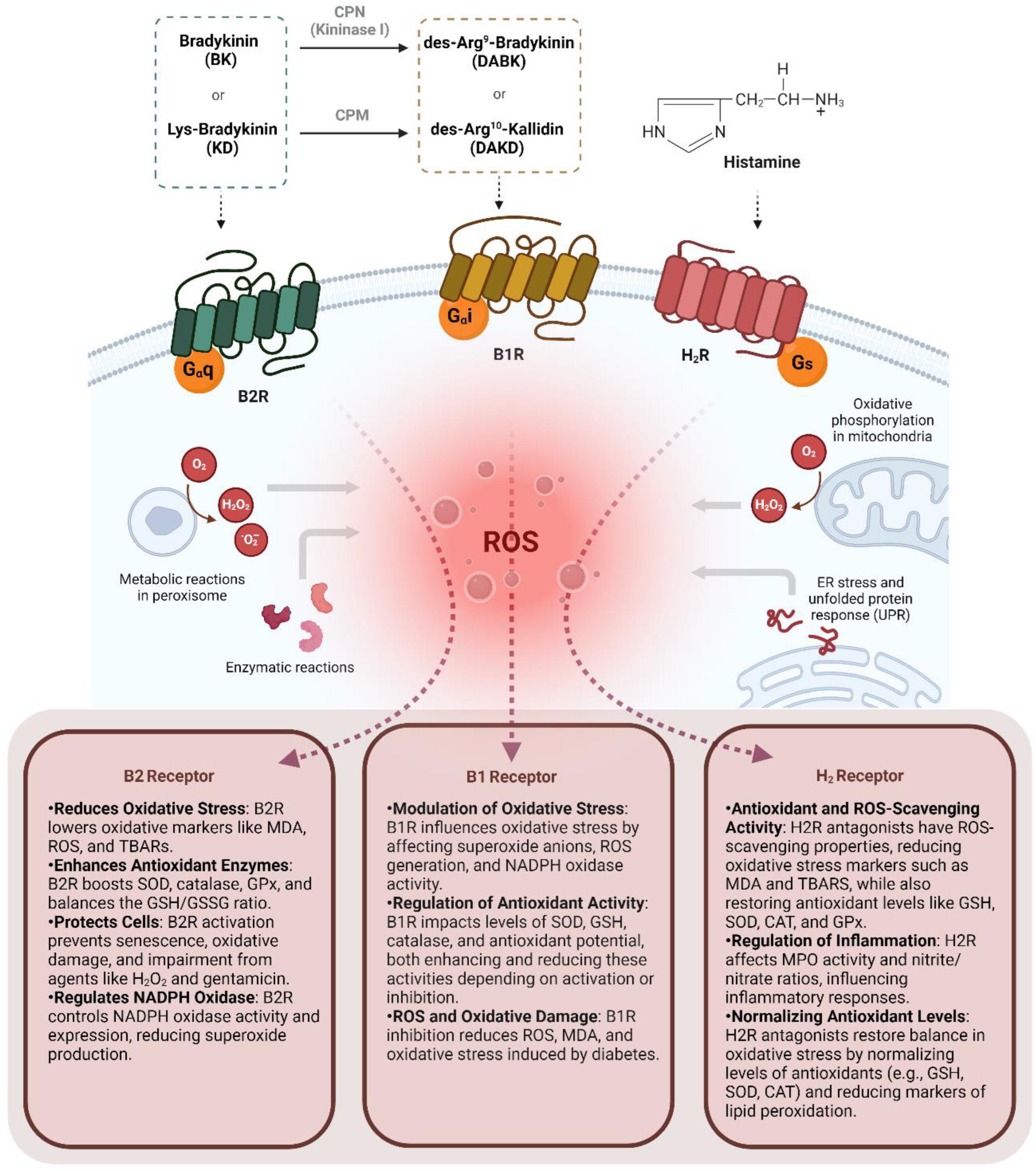
3. Kinin B2 Receptor on Oxidative Stress
4. Kinin B1 Receptor on Oxidative Stress
5. Histamine H2 Receptor on Oxidative Stress
| Target receptor | Sample | Tissue | Main methods | Main outcomes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1R | Male rats | Thoracic aortic rings | High glucose feeding, B1R antagonist (SSR240612) | B1R inibition did not affected superoxide anions (O2•─) production. | Dias et al., 2007 |
| B1R | C57BL/6 and B1KO mice | Heart | Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes, B1R antagonist (R-954) | B1R absence partially reversed increased nitrotyrosine and myeloperoxidase levels induced by diabetes. | Westermann et al., 2009 |
| B1R | Male rats | Thoracic aortic rings | High glucose feeding, B1R antagonist (SSR240612), B1R agonist (Sar[D-Phe8]des-Arg9-BK) | B1R activation increased superoxide anions (O2•─) production, increased NADPH oxidase activity, SOD gene expression, and catalase protein expression. | Dias et al., 2010 |
| B1R | Male rats | Ocular tissue (retina) | Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes, B1R antagonist (LF22-0542) | B1R antagonist normalized the elevated B1R levels and reduced superoxide production. | Pouliot et al., 2012 |
| B1R | Male rats | Sciatic nerve | Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes, B1R antagonist (R-954) | B1R inhibition reversed diabetes-induced increases in MDA levels and restored the reduced GSH activity, antioxidant potential, and SOD content. | Catanzaro et al., 2013 |
| B1R | Male rats | Optic nerve, visual cortex, plasma | Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes,B1R antagonist (R-954) | B1R inhibition reversed diabetes-induced increases in MDA levels across all tissues and restored the reduced GSH content in all tissues. | Catanzaro et al., 2017 |
| B1R | Male rats | Thoracic aortic, renal cortex | High glucose infusion, carboxypeptidase M/carboxypeptidase N inhibitor (Mergetpa), iNOS inhibitor (1,400 W) | COM/CPN inhibitor corrected increased aortic superoxide production and increased nitrotyrosine renal cortex protein expression. | Haddad et al., 2017 |
| B1R | Neonatal mice | Hypothalamic neurons | Angiotensin II, B1R antagonist (R715) | B1R activation induces partially ROS generation and NADPH oxidases (Nox2 and 4) gene expression. | Parekh et al., 2020 |
| B1R | Human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells , C57BL/6, and B1KO mice | Kidney | DOCA-salt hypertension, B1R agonist (des-Arg10-kallidin, DAKD), B1R antagonist (R715), B2R antagonist (HOE 140) | B1R absence decreased kidney ROS generation in vivo, B1R increased ROS generation in vitro. | Basuli et al., 2022 |
| B1R | C57BL/6 male mice | Hypothalamic neurons | DOCA-salt hypertension, Lys-[des-Arg9]-Bradykinin (LDABK), B1R antagonist (R715), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) | B1R activation induces ROS production, with ROS generation partially mediated by TNF, LPS, and H2O2. | Theobald et al., 2023 |
| B1R/ B2R | Human endothelial cells (AECs) | _ | High glucose, ACEi (Temocapril), BK antagonist (Icatibant), B1R antagonist (Lys-(Des-Arg9, Leu8)-Bradykinin) | B2R reversed increased oxidative stress mediated by high glucose treatment. | Yasunari et al., 2003 |
| B1R/ B2R | B1KO and B2KO | Plasma | Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection | The absence of both B2R and B1R led to an increase in plasma oxidative stress. | Delemasure et al., 2013 |
| B1R/ B2R | C57BL/6, B1KO, and B2KO | Heart | Knockout mice adaptations description | The absence of both B2R and B1R resulted in increased NADPH oxidase protein expression, superoxide anion levels, NO, and peroxynitrite production, while simultaneously decreasing the expression and activity of SOD. | Mesquita et al., 2019 |
| B1R/ B2R | C57BL/6 female mice | Ovary | Cisplatin-induced ovarian toxicity | In the cisplatin-treated group, B1R and B2R regulation resulted in increased levels of superoxide, NAG, and MPO, while GSH levels were reduced. | Ayres et al., 2020 |
| B2R | Female and male cats | Hearts | Ischemimia/reperfusion model, B2R antagonist (HOE 140) | B2R activation led to an increase in thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) 60 minutes following reperfusion. | Kumari et al., 2003 |
| B2R | Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive (DS) rats | Heart (LV) | Hypersodica diet, ACEi (Quinapril), and B2R antagonist (FR172357) | B2R activation increased eNOS, while decreased NADPH oxidase. | Kobayashi et al., 2006 |
| B2R | Rats | Kidney | Isquemia/reperfusion model, kallikrein, B2R antagonist (HOE 140), and B1R antagonist (Lys-(Des-Arg9, Leu8)-Bradykinin) | B2R activation increased ROS, MDA, and oxigen peroxide levels, while decreased GSH. | Chiang et al., 2006 |
| B2R | Male rats | Kidney | Adenovirus carrying the human tissue kallikrein gene, BK antagonist (Icatibant) | B2R partially restored nitrite/nitrate levels reduced by gentamicin and decreased gentamicin-induced NADH oxidase activity and superoxide production. | Bledsoe et al., 2006 |
| B2R | Male rats | Kidney | DOCA-salt hypertension, adenovirus carrying the human tissue kallikrein gene, BK antagonist (Icatibant) | B2R partially corrected the increased NADH oxidase activity and superoxide anion formation. | Bledsoe et al., 2006 |
| B2R | Male rats | Heart | Abdominal aorta contriction, cardiac hipertrophy model | B2R reduced NADH/NADPH oxidase activity, superoxide production, as well as the phosphorylation of MAPKs, ERKs, and AKT. | Li et al., 2007 |
| B2R | Rats | Serum | Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes, ACEi (Ramipril), B2R antagonist (HOE 140) | B2R increased GPx activity while decreasing MDA content. | Allard et al., 2007 |
| B2R | Rats | Heart (LV) | Hypersodica diet, angiotensin II receptor blocker (Valsartan), B2R antagonist (FR172,357) | B2R reduced both the activity and expression of NADPH oxidase. | Yoshida et al., 2007 |
| B2R | Male rats | Hearts | Coronary ligation infarction model, tissue kallikrein, BK antagonist (Icatibant) | B2R reduced NADH oxidase activity, p22 gene expression, and MDA content, while partially decreasing superoxide production. | Yao et al., 2007 |
| B2R | Male rats | Kidney | Gentamicin, kallikrein infusion, and BK antagonist (Icatibant) | B2R reduced gentamicin-induced superoxide production in the kidney. | Bledsoe et al., 2008 |
| B2R | Male rats | Hearts | Ischemia/reperfusion model, human tissue kallikrein gene, BK antagonist (Icatibant), NG-Nitro- l-Arginine Methyl Ester (L-NAME) | B2R increased heart NO production and normalized superoxide levels. | Yin et al., 2008 |
| B2R | Bovine Aorta Endothelial Cells (BAECs) | _ | ROS-induced senescence, in vitro scratch model, BK, B2R antagonist (HOE 140), NO inhibitor (Nω-Methyl-L-arginine acetate salt) | B2R protected cells from H2O2-induced senescence, DNA damage, and impaired migration. | Oeseburg et al., 2009 |
| B2R | C57BL/6 and B2KO mice | Kidney | Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes | B2R absence upregulated SOD expression. | Jaffa et al., 2012 |
| B2R | Rat cardiomyocytes cell line (H9C2) | _ | ROS-induced senescence, eNOS inhibitor (Nω-methyl-L-arginine acetate salt), BK, and B2R antagonist (HOE 140) | B2R inhibited H2O2-induced effects: reduced B2R expression, increased ROS, decreased SOD levels and activity, and elevated NADPH oxidase expression and activity. | Dong et al., 2013 |
| B2R | Swiss mice | Ipsilateral cortex | Traumatic brain injury model | B2R partially reduced NADPH oxidase activity and TBARs. | Ferreira et al., 2014 |
| B2R | Humans DM patients mononuclear cells | _ | Plasmatic measurements, BK or B2R antagonist (HOE 140) treatments | B2R increased RB mRNA, AKT phosphorylation, and cyclin D1; decreased ROS and cellular senescence; inversely correlated with plasma MPO levels. | Fu et al., 2015 |
| B2R | Male rats | Hearts | Sinoaortic denervation, ACEi (Ramipril), B2R antagonist (HOE 140), AT1R antagonist (Losartan) | B2R normalized TBARS, GSH/GSSG ratio, and NADPH oxidase activity. | Lu et al., 2015 |
| B2R | C57BL/6 and B2KO mice | Heart, Serum | Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection | B2R absence increased ROS, serum/heart MDA, and NADPH oxidase expression; decreased heart/serum SOD activity, heart SOD protein, and catalase expression. | Feng et al., 2016 |
| B2R | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) | Endothelium | BK and B2R antagonist (HOE 140) treatments | B2R increased ROS, SOD, and catalase. | Niewiarowska-Sendo et al., 2018 |
| B2R | Female rats | Lower extremity veins | Thromboangitis obliterans model, B2R antagonist (HOE 140) treatment | B2R blockade increased reactive species and caspase-3 activity, and decreased Pi3k expression. | Du et al., 2019 |
| H2R | Cardiomyoblasts lineage (H9C2) | _ | Phenylephrine (alfa 1 agonist), H2 antagonist (Famotidine) | Famotidine reduced ROS and lipid peroxidation and restored SOD and PRX levels after phenylephrine treatment. | Potnuri et al., 2020 |
| H2R | Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | BSA glycation, H2R antagonist (Famotidine, Ranitdine, Cimetidine) | Ranitidine showed the strongest anti-glycation and ROS-scavenging effects. | Biedrzycki et al., 2023 |
| H2R | Human blood and rats | Plasma and gastric lumen | H2R antagonist (Famotidine, Ranitdine, Cimetidine) reaction test | H2 antagonists scavenge OH radicals; cimetidine also chelates iron. | Lapenna et al., 1994 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Chronic ethanol-induced mucosal injury, H2R antagonist (Famotidine) | H2 inhibition raised TBARS at 24-48h, lowered it at 72h, reduced SROS at 48h, and increased glutathione at 48-72h. | Hernández-Muñoz et atl., 2000 |
| H2R | Male rats | Esophageal mucosa | Reflux esophagitis model, antioxidant (DA9601), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist have antioxidant properties, scavenging ROS and offering protection against oxidative stress. | Oh et al., 2001 |
| H2R | Male rats | Esophageal mucosa | Reflux esophagitis model, antioxidant (DA9601), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist did not affect MDA, GSH, or MPO levels. | Lee et al., 2001 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Reflux esophagitis model, antioxidant (DA9601), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist had no impact on MDA, GSH, or MPO activity. | Oh et al., 2001 |
| H2R | Male humans | Neutrophils | Opzonized zymosan (OZ), Acetate phorbol (PMA), calcium ionophore, Rebamipide, H2R antagonist (Cimetidine) | H2 antagonist reduced MPO activity but not superoxide generation. | Shimoyama et al., 2003 |
| H2R | Rats, guinea pigs (both genders) | Blood | Ethanol gastric injutry model, piloric ligation gastric model, histamine, H2R antagonist (Ranitidine), plant extract (ocimum sanctum) | H2 antagonist partially reduced histamine-induced MDA increase and SOD decrease. | Kath et al., 2006 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | HCl/ethanol gastric lesion model, indomethacin gastric lesion model, plant extract (kolaviron), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist partially restored GSH, SOD, CAT, and reduced MDA. | Olaleye et al., 2006 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Ethanol gastric injury model, H2R antagonist (Ranitidine, Famotidine) | H2 antagonist corrected MPO activity raised by gastric ulcers. | Singh et al., 2007 |
| H2R | Rats | Gastric mucosa | Ethanol gastric injury model, plant extract (Onosma armeniacum), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist partially restored GSH and NO and reduced MPO and MDA, but not SOD. | Cadirci et al., 2007 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Acetic acid gastric injury model, proton-pump inhibitor (Pantoprazole), H2R antagonist (Famotidine), Indomethacin | H2 antagonist did not affect ulcer-induced MDA increase. | Fornai et al., 2009 |
| H2R | Female rats | Gastric mucosa | Indomethacin gastric ulcer model, H2R antagonist (Famotidine), PDE inhibitor (Vardenafil) | H2 antagonist lowered MDA and restored NO levels. | Karakaya et al., 2009 |
| H2R | Rats | Gastric mucosa | Indomethacin gastric ulcer model, CRS ulcer model, angiotensin II receptor antagonist (Telmisartan, Candesartan), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist normalized MDA and nitrite/nitrate ratio. | Morsy et al., 2009 |
| H2R | Male rats | Hepatic tissue | DDC hepatic toxicity model, ascorbic acid, H2R antagonist (Cimetidine), calcium channel antagonist (Nifedipine) | H2 antagonist partially corrected MDA and GSH; SOD was unaffected. | Gaafa et al., 2011 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Indomethacin gastric ulcer model, plant extract (Ficus asperifolia bark), H2R antagonist (Cimetidine) | H2 antagonist restored SOD and CAT activities; MDA was unaffected. | Raji et al., 2011 |
| H2R | Mouse brain-derived endothelial cells | _ | Rotenone, Carnosine, H2R antagonist (Cimetidine e Zolantidine) | H2 inhibition reversed carnosine's mitochondrial protective effects. | Zhang et al., 2012 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Ethanol gastric injury model, oleuropein (OLE), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist partially corrected GSH, GPx, and TBARS but not SOD and CAT. | Alirezaei et al., 2012 |
| H2R | Male rats | Hepatic tissue | Ischemia/reperfusion model, histamine, H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | Positive histamine effects on MDA and GSH were H2-independent. | El-Mahdy et al., 2013 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Ulceral models, rutin, H2R antagonist (Cimetidine) | H2 antagonist reduced MDA, restored vitamin C, and increased GPx. | Olaleye et al., 2013 |
| H2R | Female and male rats | Gastric mucosa | Pylorus ligation gastric ulcer model, acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), gallic acid, H2R antagonist (Famotidine) | H2 antagonist partially restored SOD, GSH, CAT, GPx, and reduced MDA. | Asokkumar et al., 2014 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Brain microinjections of histamine, H1R antagonist (Tripolidine), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 activation reduced MDA and restored SOD activity. | Qiao et al., 2015 |
| H2R | Male rats | Kidney | Glycerol kidney injury model, L-carnitine, H2R antagonist (Cimetidine) | H2 antagonist normalized NO and glutathione, reduced cytochrome p450. | Estaphan et al., 2015 |
| H2R | BALB/c mice | Liver extracts | Catalase activity, H2O2, H2R antagonist (Cimetidine) | H2 antagonist inhibited catalase and lowered optimal temperature. | Jahangirvand et al., 2016 |
| H2R | Male rats | Heart | Oxidative stress inductor (Doxorubicin), ACE inhibitor (Captopril), H2R antagonist (Famotidine) | H2 inhibition corrected lipid peroxidation and nitrite/nitrate ratio, partially restored SOD. | Kondru et al., 2018 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastrintestinal tract | Dicofenac enterophaty induced model, adenosine receptor antagonist (Quercetin), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist worsened diclofenac-induced MDA increase. | Singh et al., 2017 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Water- immersion restraint stress ulcer model, Thymoquinone, H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist corrected TBARS, GSH, SOD, and CAT in ulcers. | Ahmad et al., 2017 |
| H2R | Transgenic mice Kras/NoxKO | Myeloid cells | H2R agonist (N-methylhistamine) and H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 activation inhibited superoxide and reduced ROS in Kras mice. | Aydin et al., 2019 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Ethanol gastric injutry model, plant extract (Pulicaria crispa), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist partially restored GSH and SOD in ulcers. | Fahmi et al., 2019 |
| H2R | Male rats | Small intestine | Indomethacin small intestine lesion model, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, β-Carotene, sodium selene, H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist partially restored GSH, CAT, GPx, and increased SOD; no MDA effect. | Turkyilmaz et al., 2019 |
| H2R | Male rats | Bone marrow and intestinal tissue | Irradiation, H2R antagonist (Cimetidine) | H2 antagonist corrected MDA, GSH, and SOD levels. | Estaphan et al., 2020 |
| H2R | Female and male mice | Brain | Brain ischemia/reperfusion model, L-carnosine, H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist blocked L-carnosine effects on TBARS, GSH, and MPO in brain ischemia. | Virdi et al., 2020 |
| H2R | Male rats | Testis | Testicular ischemia model, H2R antagonist (Famotidine) | H2 antagonist normalized NO and SOD; MDA and GPx were unaffected. | Tanriverdi et al., 2021 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric tissue | Indomethacin gastric ulcer model, water immersion stress model, plant extract (Elaeagnus conferta Roxb.), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist partially restored CAT, GSH, SOD, and reduced MDA. | Gupta et al., 2021 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Ethanol gastric injutry model, plant extract (E. persicus), H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist restored CAT, GSH, and reduced ROS and MDA. | Beiranvand et al., 2021 |
| H2R | Female swiss mice | Tumor tissue | Breast tumor model, vitamin C, H2R antagonist (Cimetidine) | H2 antagonist partially restored tumor GSH, SOD, and reduced MDA. | Ibrahim et al., 2022 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Indomethacin gastric lesion model, Topiramate, H2R antagonist (Ranitidine) | H2 antagonist restored SOD, CAT, GPx activities, GSH, and reduced MDA. | Jafari et al., 2022 |
| H2R | Male rats | Gastric mucosa | Indomethacin gastric ulcer model, plant extract (Malus domestica Borkh), H2R antagonist (Famotidine) | H2 antagonist partially restored GSH, GPx, and reduced MDA. | Mahmoud et al., 2023 |
| H2R | Rats | Gastric tissue | Indomethacin gastric ulcer model, Felodipine, H2R antagonist (Famotidine) | H2 antagonist corrected MDA, GSH, and catalase levels. | Akbaş et al., 2023 |
6. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Sies H, Jones DP. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) as Pleiotropic Physiological Signalling Agents. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jul;21(7):363-383. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, VI. Free radicals, Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Stress and its Classification. Chem Biol Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue C, Li X, Liu G, Liu W. Evaluation of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain on the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Cytotoxicity in HaCaT Cells Induced by Nanosized Titanium Dioxide Under UVA Irradiation. Int J Toxicol. 2016, 35, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iatsenko I, Boquete JP, Lemaitre B. Microbiota-Derived Lactate Activates Production of Reactive Oxygen Species by the Intestinal NADPH Oxidase Nox and Shortens Drosophila Lifespan. Immunity, 49. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorov DB, Juhaszova M, Sollott SJ. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS Release. Physiol Rev, 94. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang J, Wang X, Vikash V, Ye Q, Wu D, Liu Y, Dong W. ROS and ROS-Mediated Cellular Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 4350. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scialò F, Fernández-Ayala DJ, Sanz A. Role of Mitochondrial Reverse Electron Transport in ROS Signaling: Potential Roles in Health and Disease. Front Physiol. 2017, 8, 428. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kenawi A, Ruffell B. Inflammation, ROS, and Mutagenesis. Cancer Cell, 32. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen NH, Tran GB, Nguyen CT. Anti-Oxidative Effects of Superoxide Dismutase 3 on inflammatory Diseases. J Mol Med (Berl), 98. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee SG, Woo HA, Kil IS, Bae SH. Peroxiredoxin Functions as a Peroxidase and a regulator and sensor of local peroxides. J Biol Chem. 2012, 287, 4403–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Couto N, Wood J, Barber J. The Role of Glutathione Reductase and Related Enzymes on Cellular Redox Homoeostasis Network. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016, 95, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regoli D, Marceau F, Barabé J. De Novo Formation of Vascular Receptors for Bradykinin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978, 56, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeb-Lundberg LM, Marceau F, Müller-Esterl W, Pettibone DJ, Zuraw BL. International Union of Pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the Kinin Receptor Family: from Molecular Mechanisms to Pathophysiological Consequences. Pharmacol Rev, 57. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewald DA, Pang IH, Sternweis PC, Miller RJ. Differential G Protein-Mediated Coupling of Neurotransmitter Receptors to Ca2+ Channels in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons In Vitro. Neuron. 1989, 2, 1185-1193. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin CE, Faussner A, Robinson HE, Chakravarty S, Kyle DJ, Bathon JM, Proud D. Stable Expression of the Human Kinin B1 Receptor in Chinese Hamster Ovary cCells. Characterization of Ligand Binding and Effector Pathways. J Biol Chem. 1997, 272, 11420–11425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignjatovic T, Stanisavljevic S, Brovkovych V, Skidgel RA, Erdös EG. Kinin B1 ReceptorsStimulate Nitric Oxide Production in Endothelial Cells: Signaling Pathways Activated by Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Peptide Lgands. Mol Pharmacol, 1310; 66. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangam EB, Jemima EA, Singh H, Baig MS, Khan M, Mathias CB, Church MK, Saluja R. The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets. Front Immunol. 1873. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco ACCC, Yoshikawa FSY, Pietrobon AJ, Sato MN. Role of Histamine in Modulating the Immune Response and Inflammation. Mediators Inflamm, 9: 2018, 2018. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borriello F, Iannone R, Marone G. Histamine Release from Mast Cells and Basophils. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017, 241, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, P. The Basics of Histamine Biology. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, S: Suppl). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons ME, Ganellin CR. Histamine and its Receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2006, 147 (Suppl 1), S127–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Delemasure S, Blaes N, Richard C, Couture R, Bader M, Dutartre P, Girolami JP, Connat JL, Rochette L. Antioxidant/Oxidant Status and Cardiac Function in Bradykinin B(1)- and B(2)-Receptor Null Mice. Physiol Res, 62. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu C, Li B, Sun Y, Ma G, Yao Y. Bradykinin Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence of Endothelial Progenitor Cells through the B2R/AKT/RB and B2R/EGFR/RB Signal Pathways. Oncotarget. 2467. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres LS, Berger M, Durli ICLO, Kuhl CP, Terraciano PB, Garcez TNA, Dos Santos BG, Guimarães JA, Passos EP, Cirne-Lima EO. Kallikrein-Kinin System and Oxidative Stress in Cisplatin-Induced Ovarian Toxicity. Reprod Toxicol, 93. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrela GR, Wasinski F, Bacurau RF, Malheiros DM, Câmara NO, Araújo RC. Kinin B2 Receptor Deletion and Blockage Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Renal Injury. Int Immunopharmacol. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrela GR, Wasinski F, Gregnani MF, Freitas-Lima LC, Arruda AC, Morais RL, Malheiros DM, Camara NOS, Pesquero JB, Bader M, Barros CC, Araújo RC. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Protects Against Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity by Modulating Kinin B1 Receptor Expression and Aminopeptidase P Activity in Mice. Front Mol Biosci, 7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira APO, Rodrigues FS, Della-Pace ID, Mota BC, Oliveira SM, de Campos Velho Gewehr C, Bobinski F, de Oliveira CV, Brum JS, Oliveira MS, Furian AF, de Barros CS, dos Santos AR, Ferreira J, Fighera MR, Royes LF. HOE-140, an Antagonist of B2 Receptor, Protects Against Memory Deficits and Brain Damage Induced by Moderate Lateral Fuid Percussion Injury in Mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 1935. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang WC, Chien CT, Lin WW, Lin SL, Chen YM, Lai CF, Wu KD, Chao J, Tsai TJ. Early Activation of Bradykinin B2 Receptor Aggravates Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Renal Damage in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. 2006; 41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bledsoe G, Crickman S, Mao J, Xia CF, Murakami H, Chao L, Chao J. Kallikrein/Kinin Protects Against Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Inhibition of Inflammation and Apoptosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard J, Buléon M, Cellier E, Renaud I, Pecher C, Praddaude F, Conti M, Tack I, Girolami JP. ACE Inhibitor Reduces Growth Factor Receptor Expression and Signaling but also Albuminuria through B2-Kinin Glomerular Receptor Activation in Diabetic Rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 1083. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffa MA, Kobeissy F, Al Hariri M, Chalhoub H, Eid A, Ziyadeh FN, Jaffa AA. Global Renal Gene Expression Profiling Analysis in B2-Kinin Receptor Null Mice: Impact of Diabetes. PLoS One, 4471; 7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bledsoe G, Shen B, Yao Y, Zhang JJ, Chao L, Chao J. Reversal of Renal Fibrosis, Inflammation, and Glomerular Hypertrophy by Kallikrein Gene Delivery. Hum Gene Ther, 17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bledsoe G, Shen B, Yao YY, Hagiwara M, Mizell B, Teuton M, Grass D, Chao L, Chao J. Role of Tissue Kallikrein in Prevention and Recovery of Gentamicin-Induced Renal injury. Toxicol Sci. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiarowska-Sendo A, Kozik A, Guevara-Lora I. Influence of Bradykinin B2 Receptor and Dopamine D2 Receptor on the Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Response, and Apoptotic Process in Human Endothelial Cells. PLoS One, 0206; 13. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasunari K, Maeda K, Watanabe T, Nakamura M, Asada A, Yoshikawa J. Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Temocaprilat Prevents High Glucose-Mediated Suppression of Human Aortic Endothelial Cell Proliferation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du YM, Du BH, Yang J, Zang S, Wang XP, Mao X, Zhang W, Jiang LP. Effect of Bradykinin on Rats with Thromboangiitis Obliterans through PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 1016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeseburg H, Iusuf D, van der Harst P, van Gilst WH, Henning RH, Roks AJ. Bradykinin Protects Against Oxidative Stress-Induced Endothelial Cell Senescence. Hypertension, 53. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita TRR, Miguel-Dos-Santos R, Jesus ICG, de Almeida GKM, Fernandes VA, Gomes AAL, Guatimosim S, Martins-Silva L, Ferreira AJ, Capettini LDSA, Pesquero JL, Lauton-Santos S. Ablation of B1- and B2-Kinin Receptors Causes Cardiac Dysfunction through Redox-Nitroso Unbalance. Life Sci. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao YY, Yin H, Shen B, Chao L, Chao J. Tissue Kallikrein Infusion Prevents Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis, Inflammation and Ventricular Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction. Regul Pept. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng W, Xu X, Zhao G, Zhao J, Dong R, Ma B, Zhang Y, Long G, Wang DW, Tu L. Increased Age-Related Cardiac Dysfunction in Bradykinin B2 Receptor-Deficient Mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 71. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong R, Xu X, Li G, Feng W, Zhao G, Zhao J, Wang DW, Tu L. Bradykinin Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Cardiomyocytes Senescence via Regulating Redox State. PLoS One, 7703; 8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi N, Honda T, Yoshida K, Nakano S, Ohno T, Tsubokou Y, Matsuoka H. Critical Role of Bradykinin-eNOS and Oxidative Stress-LOX-1 Pathway in Cardiovascular Remodeling Under Chronic Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition. Atherosclerosis. 2006, 187, 92-100. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida K, Kobayashi N, Ohno T, Fukushima H, Matsuoka H. Cardioprotective Effect of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antagonist Associated with Bradykinin-Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase and Oxidative Stress in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Rats. J Hypertens, 1633; 25. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li HJ, Yin H, Yao YY, Shen B, Bader M, Chao L, Chao J. Tissue Kallikrein Protects Against Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy through Kinin B2 Receptor and Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3beta Activation. Cardiovasc Res. 2007, 73, 130-142. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu L, Guo L, Xie TT, Xin HL. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme is Involved in the Cardiac Hypertrophy Induced by Sinoaortic Denervation in Rats. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2015, 24, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari R, Maulik M, Manchanda SC, Maulik SK. Protective Effect of Bradykinin Antagonist Hoe-140 During In Vivo Myocardial Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury in the Cat. Regul Pept. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin H, Chao L, Chao J. Nitric Oxide Mediates Cardiac Protection of Tissue Kallikrein by Reducing Inflammation and Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion. Life Sci, 82. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cargnoni A, Comini L, Bernocchi P, Bachetti T, Ceconi C, Curello S, Ferrari R. Role of Bradykinin and eNOS in the Anti-Ischaemic Effect of Trandolapril. Br J Pharmacol. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu Y, Fu C, Li B, Liu C, He Z, Li XE, Wang A, Ma G, Yao Y. Bradykinin Protects Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells from High-Glucose-Induced Senescence through B2 Receptor-Mediated Activation of the Akt/eNOS Signalling Pathway. J Diabetes Res, 2021. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akash MSH, Rehman K, Liaqat A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha: Role in Development of Insulin Resistance and Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 105-110. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza DG, Pinho V, Pesquero JL, Lomez ES, Poole S, Juliano L, Correa A Jr, de A Castro MS, Teixeira MM. Role of the Bradykinin B2 Receptor for the Local and Systemic Inflammatory Response that Follows Severe Reperfusion Injury. Br J Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Basuli D, Parekh RU, White A, Thayyil A, Sriramula S. Kinin B1 Receptor Mediates Renal Injury and Remodeling in Hypertension. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022, 8, 780834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Westermann D, Walther T, Savvatis K, Escher F, Sobirey M, Riad A, Bader M, Schultheiss HP, Tschöpe C. Gene Deletion of the Kinin Receptor B1 Attenuates Cardiac Inflammation and Fibrosis During the Development of Experimental Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Diabetes. 2009, 58, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Catanzaro O, Capponi JA, Michieli J, Labal E, Di Martino I, Sirois P. Bradykinin B₁ antagonism inhibits oxidative stress and restores Na+K+ ATPase activity in diabetic rat peripheral nervous system. Peptides, 44. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanzaro OL, Capponi JA, Di Martino I, Labal ES, Sirois P. Oxidative Stress in the Optic Nerve and Cortical Visual Area of Steptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats: Blockade with a Selective Bradykinin B1 Receptor Antagonist. Neuropeptides. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouliot M, Talbot S, Sénécal J, Dotigny F, Vaucher E, Couture R. Ocular Application of the Kinin B1 Receptor Antagonist LF22-0542 Inhibits Retinal Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Rats. PLoS One, 3386; 7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh RU, Robidoux J, Sriramula S. Kinin B1 Receptor Blockade Prevents Angiotensin II-induced Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Primary Hypothalamic Neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 40. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theobald D, Sriramula S. Kinin B1 Receptor Mediates Bidirectional Interaction between Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 2023 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Haddad Y, Couture R. Kininase 1 As a Preclinical Therapeutic Target for Kinin B1 Receptor in Insulin Resistance. Front Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yasunari K, Maeda K, Watanabe T, Nakamura M, Asada A, Yoshikawa J. Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Temocaprilat Prevents High Glucose-Mediated Suppression of Human Aortic Endothelial Cell Proliferation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2003, 42 (Suppl 1):S55-560. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias JP, Ismael MA, Pilon M, de Champlain J, Ferrari B, Carayon P, Couture R. The Kinin B1 Receptor Antagonist SSR240612 Reverses Tactile and Cold allodynia in an Experimental Rat Model of Insulin Resistance. Br J Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 280–287. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dias JP, Talbot S, Sénécal J, Carayon P, Couture R. Kinin B1 Receptor Enhances the Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model of Insulin Resistance: Outcome in Hypertension, Allodynia and Metabolic Complications. PLoS One, 1262; 5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceau F, Sabourin T, Houle S, Fortin JP, Petitclerc E, Molinaro G, Adam A. Kinin Receptors: Functional Aspects. Int Immunopharmacol. 2002, 214, 1729-1739. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csiszar A, Wang M, Lakatta EG, Ungvari Z. Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction During Aging: Role of NF-kappaB. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1333. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmaier, AH. The Kallikrein-Kinin and the Renin-Angiotensin Systems Have a Multilayered iInteraction. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003, 285, R1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duka A, Kintsurashvili E, Duka I, Ona D, Hopkins TA, Bader M, Gavras I, Gavras H. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition After Experimental Myocardial Infarct: Role of the Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors. Hypertension, 1352; 51. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribuot C, Godin D, Couture R, Regoli D, Nadeau R. In Vivo B2-Receptor-Mediated Negative Chronotropic Effect of Bradykinin in Canine Sinus Node. Am J Physiol. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapenna D, De Gioia S, Mezzetti A, Grossi L, Festi D, Marzio L, Cuccurullo F. H2-Receptor Antagonists are Scavengers of Oxygen Radicals. Eur J Clin Invest, 24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedrzycki G, Wolszczak-Biedrzycka B, Dorf J, Michalak D, Żendzian-Piotrowska M, Zalewska A, Maciejczyk M. Antioxidant and Anti-Glycation Potential of H2 Receptor Antagonists-In Vitro Studies and a Systematic Literature Review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanriverdi HI, Şenel U, Gevrek F, Akbaş A. Protective Effect of Famotidine on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Following Testicular Torsion in Rats. J Pediatr Urol, 17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim SSA, El-Aal SAA, Reda AM, Achy SE, Shahine Y. Anti-Neoplastic Action of Cimetidine/Vitamin C on Histamine and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Ehrlich Breast Cancer. Sci Rep, 1151. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estaphan S, Eissa H, Elattar S, Rashed L, Farouk M. A Study on the Effect of Cimetidine and L-Carnitine on Myoglobinuric Acute Kidney Injury in Male Rats. Injury, 1223; 46. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estaphan S, Abdel-Malek R, Rashed L, Mohamed EA. Cimetidine a Promising Radio-Protective Agent Through Modulating Bax/Bcl2 Ratio: An In Vivo Study in Male Rats. J Cell Physiol, 8495. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin E, Hallner A, Grauers Wiktorin H, Staffas A, Hellstrand K, Martner A. NOX2 Inhibition Reduces Oxidative Stress and Prolongs Survival in Murine KRAS-Induced Myeloproliferative Disease. Oncogene, 1534; 38. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoyama T, Fukuda S, Liu Q, Fukuda Y, Nakaji S, Sugawara K. Characteristics of Attenuating Effects of Rebamipide, an Anti-Ulcer Agent, on Oxidative Burst of Human Neutrophils. J Pharmacol Sci, 91. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potnuri AG, Allakonda L, Saheera S. Involvement of Histamine 2 Receptor in Alpha 1 Adrenoceptor Mediated Cardiac Hypertrophy and Oxidative Stress in H9c2 Cardio Myoblasts. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021, 14, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondru SK, Potnuri AG, Allakonda L, Konduri P. Histamine 2 Receptor Antagonism Elicits Protection Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rodent Model. Mol Cell Biochem. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang L, Yao K, Fan Y, He P, Wang X, Hu W, Chen Z. Carnosine Protects Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Against Rotenone-Induced Oxidative Stress Injury Through Histamine H₁ and H₂ Receptors In Vitro. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virdi JK, Bhanot A, Jaggi AS, Agarwal N. Investigation on Beneficial Role of L-Carnosine in Neuroprotective Mechanism of Ischemic Postconditioning in Mice: Possible Role of Histidine Histamine pathway. Int J Neurosci. 2020, 130, 983-998. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estaphan S, Abdel-Malek R, Rashed L, Mohamed EA. Cimetidine a Promising Radio-Protective Agent Through Modulating Bax/Bcl2 Ratio: An In Vivo Study in Male Rats. J Cell Physiol, 8495. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh DP, Borse SP, Nivsarkar M. Overcoming the Exacerbating Effects of Ranitidine on NSAID-Induced Small Intestinal Toxicity With Quercetin: Providing a Complete GI Solution. Chem Biol Interact. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkyilmaz IB, Arda Pirincci P, Bolkent S, Yanardag R. The Effects of Vitamins and Selenium Mixture or Ranitidine Against Small Intestinal Injury Induced by Indomethacin in Adult Rats. J Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12808. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangirvand M, Minai-Tehrani D, Yazdi F, Minai-Tehrani A, Razmi N. Binding of Cimetidine to Balb/C Mouse Liver Catalase; Kinetics and Conformational Studies. Curr Clin Pharmacol, 11. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mahdy NA, El-Sisi AE, Dewidar BI, El-Desouky KI. Histamine Protects Against the Acute Phase of Experimentally-Induced Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion. J Immunotoxico, ,10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaafa KM, Badawy MM, Hamza AA. The Protective Effects of Ascorbic Acid, Cimetidine, and Nifedipine on Diethyldithiocarbamate-Induced Hepatic Toxicity in Albino Rats. Drug Chem Toxicol, 34. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh TY, Lee JS, Ahn BO, Cho H, Kim WB, Kim YB, Surh YJ, Cho SW, Hahm KB. Oxidative Damages are Critical in Pathogenesis of Reflux Esophagitis: Implication of in its Treatment. Free Radic Biol Med, 30. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee JS, Oh TY, Ahn BO, Cho H, Kim WB, Kim YB, Surh YJ, Kim HJ, Hahm KB. Involvement of Oxidative Stress in Experimentally Induced Reflux Esophagitis and Barrett's Esophagus: Clue for the Chemoprevention of Esophageal Carcinoma by Antioxidants. Mutat Res. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh TY, Lee JS, Ahn BO, Cho H, Kim WB, Kim YB, Surh YJ, Cho SW, Lee KM, Hahm KB. Oxidative Stress is More Important Than Acid in the Pathogenesis of Reflux Oesophagitis in Rats. Gut. 2001, 49, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim HK, Kim MG, Leem KH. Extrusion Process of Acanthopanax Senticosus Leaves Enhances the Gastroprotective Effect of Compound 48/80 on Acute Gastric Mucosal Lesion in Rats. J Tradit Chin Med, 36. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao X, Tang X, Zhang J, Chen K, Zhang Y, Wang C, Fei S, Zhu J, Zhu S, Liu Z, Li T, Lv S, Liang Y. Protective Effect of Histamine Microinjected Into the Cerebellar Fastigial Nucleus on Stress-Induced Gastric Mucosal Damage in Rats. Am J Transl Res, 2015; 2, 1648–1659.
- Ahmad SS, Najmi AK, Kaundal M, Akhtar M. Gastroprotective Effect of Thymoquinone on Water Immersion Restraint Stress Induced Ulceration in Rats. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2017, 67, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud MF, Abdo W, Nabil M, Drissi B, El-Shazly AM, Abdelfattah MAO, Sobeh M. Apple (Malus domestica Borkh) lLeaves Attenuate Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Rats. Biomed Pharmacother, 1143. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbaş N, Süleyman B, Mammadov R, Gülaboğlu M, Akbaş EM, Süleyman H. Effect of Felodipine on Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcers in Rats. Exp Anim, 72. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari A, Andishfar N, Esmaeilzadeh Z, Khezri MR, Ghasemnejad-Berenji M. Gastroprotective Effect of Topiramate on Indomethacin-Induced Peptic Ulcer in Rats: Biochemical and Histological Analyses. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakaya K, Hanci V, Bektas S, Can M, Ucan HB, Emre AU, Tascilar O, Ozkocak Turan I, Comert M, Irkorucu O, Karadeniz Cakmak G. Mitigation of Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Mucosal Lesions by a Potent Specific Type V Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor. World J Gastroenterol, 5091; 15. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji Y, Oyeyemi WA, Shittu ST, Bolarinwa AF. Gastro-Protective Effect of Methanol Extract of Ficus Asperifolia Bark on Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Rats. Niger J Physiol Sci, 26. [PubMed]
- Hernández-Muñoz R, Montiel-Ruíz C, Vázquez-Martínez O. Gastric Mucosal Cell Proliferation in Ethanol-Induced Chronic Mucosal Injury is Related to Oxidative Stress and Lipid Peroxidation in Rats. Lab Invest, 1161; 80. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiranvand M, Bahramikia S, Dezfoulian O. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Anti-Ulcerogenic Effects of Eremurus Persicus (Jaub & Spach) Boiss Leaf Hydroalcoholic Extract on Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Rats. Inflammopharmacology, 1503. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmi AA, Abdur-Rahman M, Aboul Naser AF, Hamed MA, Abd-Alla HI, Nasr MI. Pulicaria Crispa Mitigates Gastric Ulcer Induced by Ethanol in Rats: Role of Treatment and Auto Healing. Biomarkers. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadirci E, Suleyman H, Aksoy H, Halici Z, Ozgen U, Koc A, Ozturk N. Effects of Onosma Armeniacum Rroot Extract on Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress in Stomach Tissue of Rats. Chem Biol Interact. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeepkumar Singh L, Kundu P, Ganguly K, Mishra A, Swarnakar S. Novel Role of Famotidine in Downregulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 During Protection of Ethanol-Induced Acute Gastric Ulcer. Free Radic Biol Med, 43. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alirezaei M, Dezfoulian O, Neamati S, Rashidipour M, Tanideh N, Kheradmand A. Oleuropein Prevents Eethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcers Via Elevation of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Rats. J Physiol Biochem, 68. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta M, Gulati M, Kapoor B, Kumar B, Kumar R, Kumar R, Khurana N, Gupta R, Singh N. Anti-Ulcerogenic Effect of Methanolic Extract of Elaeagnus Conferta Roxb. Seeds in Wistar Rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 1141. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaleye MT, Akinmoladun AC. Comparative Gastroprotective Effect of Post-Treatment with Low Doses of Rutin and Cimetidine in Rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol, 27. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kath RK, Gupta RK. Antioxidant Activity of Hydroalcoholic Leaf Extract of Ocimum Sanctum in Animal Models of Peptic Ulcer. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006, 50, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olaleye SB, Farombi EO. Attenuation of Indomethacin- and HCl/Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Gastric Mucosa Damage in Rats by Kolaviron, a Natural Biflavonoid of Garcinia Kola Seed. Phytother Res, 20. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornai M, Colucci R, Antonioli L, Ghisu N, Tuccori M, Blandizzi C, Del Tacca M. Effects of Pantoprazole on Ulcer Healing Delay Associated with NSAID Treatment. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009, 379, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokkumar K, Sen S, Umamaheswari M, Sivashanmugam AT, Subhadradevi V. Synergistic Effect of the Combination of Gallic acid and Famotidine in Protection of Rat Gastric Mucosa. Pharmacol Rep. 2014, 66, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsy M, Ashour O, Amin E, Rofaeil R. Gastroprotective Effects of Telmisartan on Experimentally-Induced Gastric Ulcers in Rats. Pharmazie, 1: 64, 590-594. PMID, 1982; 64.
- Panula, P. Histamine Receptors, Agonists, and Antagonists in Health and Disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021, 180, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira-Machado JA, Lima e Silva FC, Cunha EP, Calsolari MR, Costa DC, Perilo CS, Horta BC, Ferreira IC, Chaves MM. Modulation of the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by cAMP-Elevating Agents in Granulocytes from Diabetic Patients: an Akt/PKB-Dependent Phenomenon. Diabetes Metab, 32. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Román AL, Rodríguez-Flores KL, Hernández-Mora VM, Ruiz-García E, Prospero-García O, Guijosa A, Molina A, Morales-Mulia M, Aschner M, Santamaría A, Ortega-Gómez A. Examining the Role of Histaminergic, Orexinergic, and Cannabinergic Systems in Redox Regulation in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Mini Rev Med Chem, 1806. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





