Submitted:
30 October 2024
Posted:
31 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.3. Experimental Content
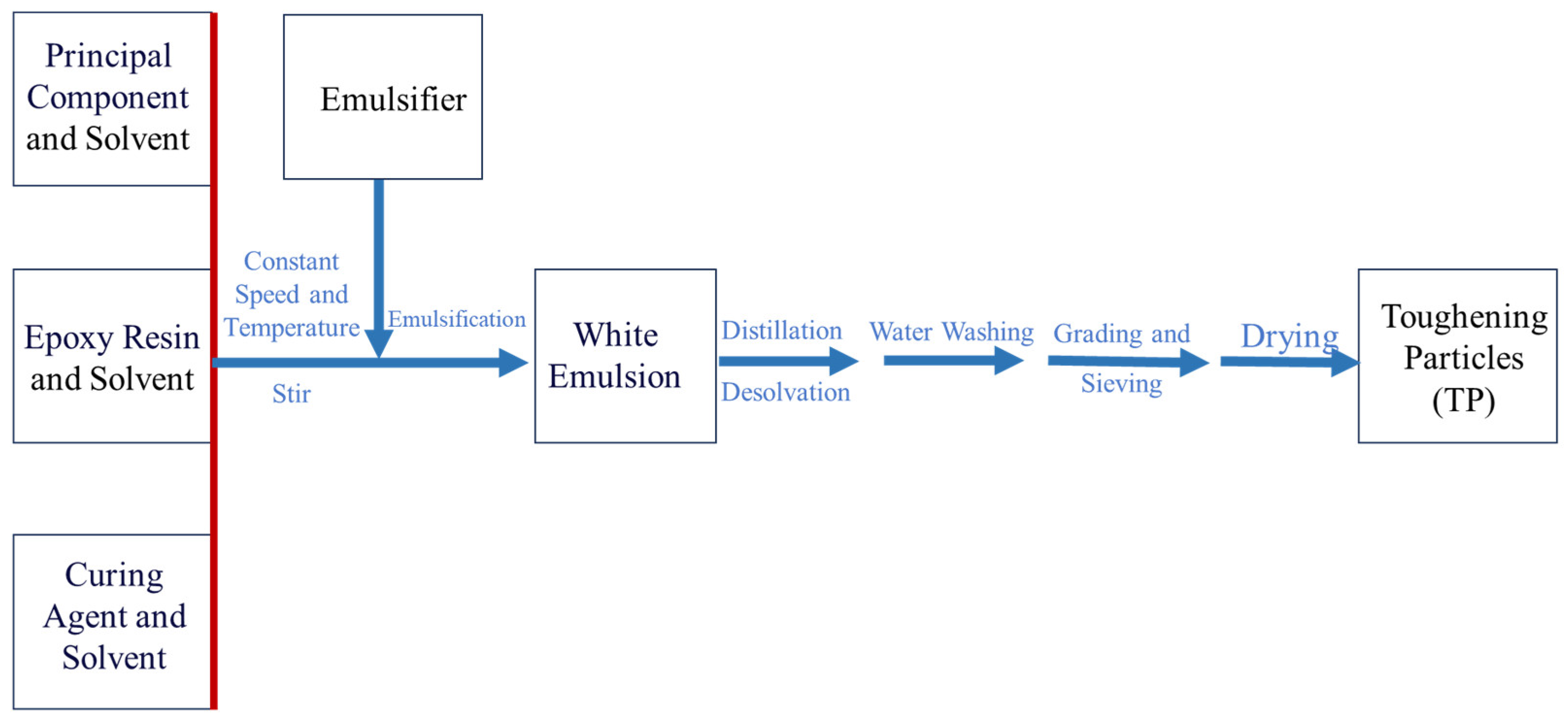
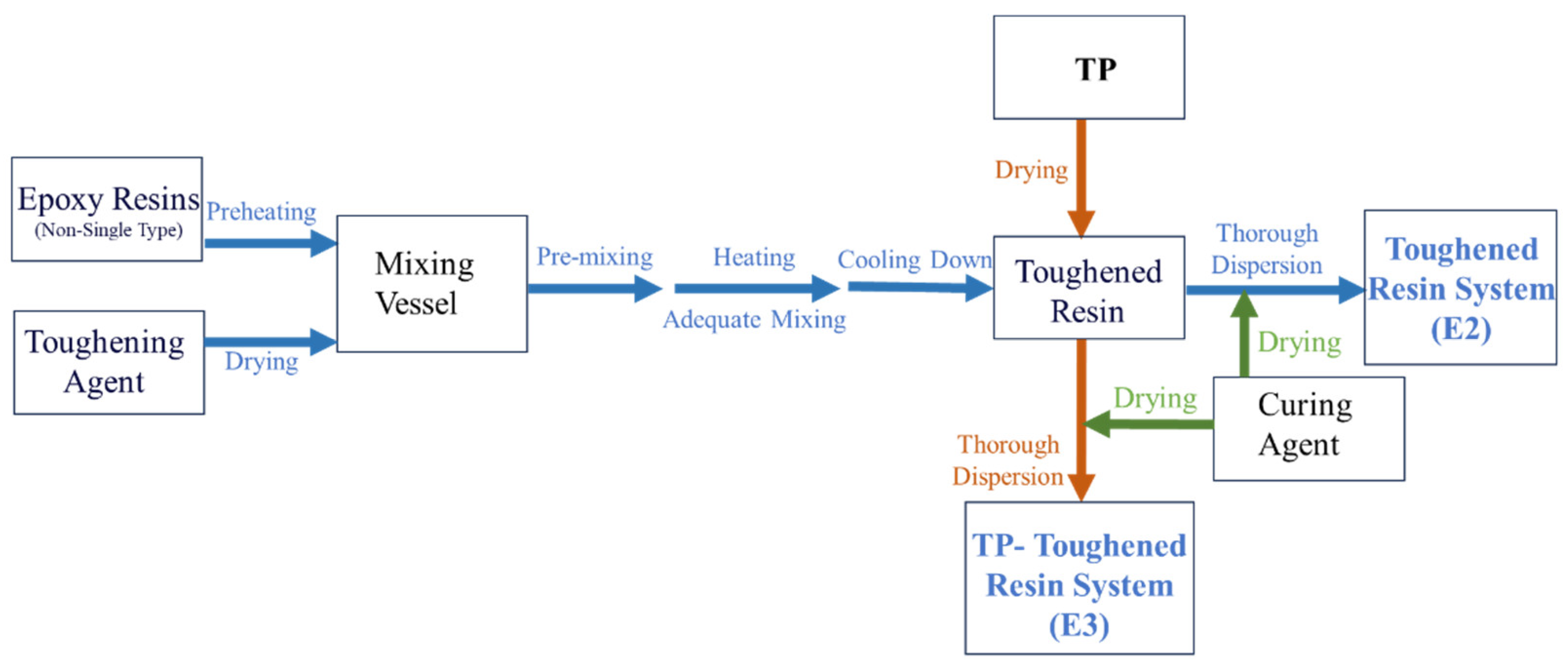
2.4. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Resin Properties
3.1.1. Mechanical Properties of the Resins
| E1 | E1-CV/% | E2 | E2-CV/% | E3 | E3-CV/% | |
| Tensile strength/MPa | 80.76 | 4.10 | 78.25 | 7.16 | 85.27 | 6.30 |
| Young’s modulus/GPa | 3.3 | 4.63 | 3.24 | 6.23 | 2.86 | 8.20 |
| Elongation at break/% | 3.15 | 12.28 | 3.29 | 11.74 | 4.58 | 14.38 |
| Bending strength/MPa | 136.38 | 5.29 | 156.12 | 4.06 | 145.42 | 1.00 |
| Bending modulus/GPa | 3.31 | 3.08 | 3.28 | 2.77 | 2.90 | 1.40 |
| Impact strength/kJ/m2 | 19.84 | 12.41 | 22.23 | 8.90 | 41.68 | 9.48 |
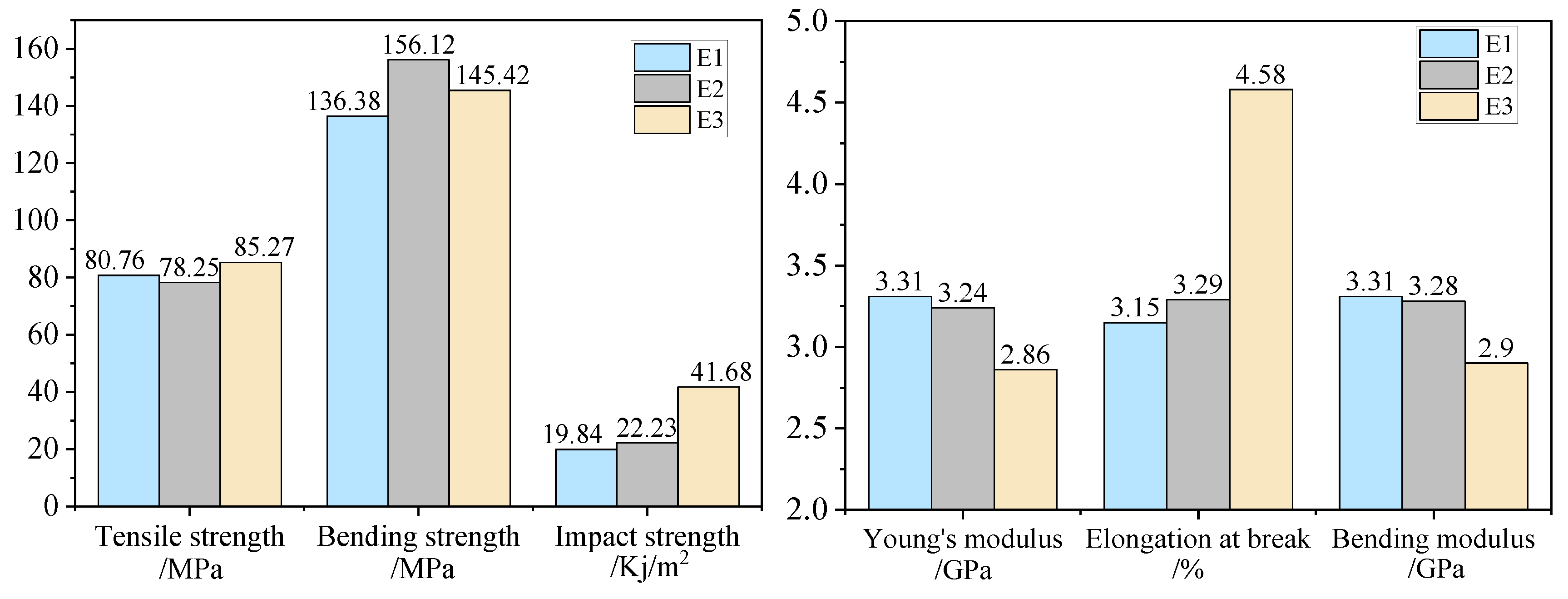
3.1.2. Thermodynamic Properties of the Resins
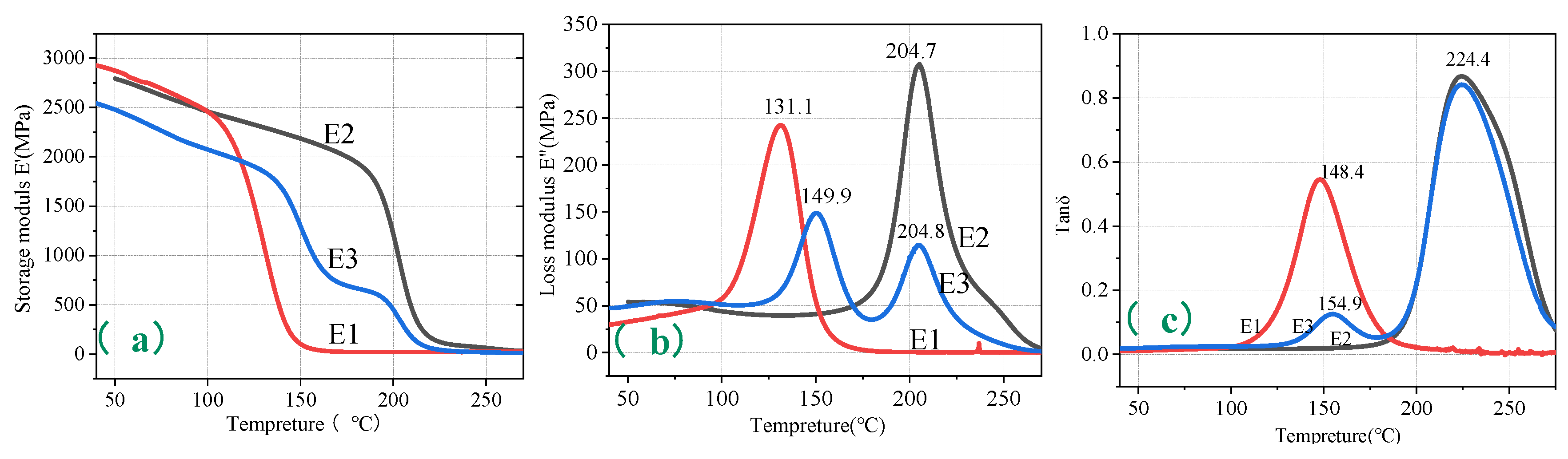
| The onset temperature of the E´ curve | The peak temperature of the E" curve | The peak temperature of the Tanδ curve | |
| E1 | 128.0 | 131.1 | 148.4 |
| E2 | 197.9 | 204.7 | 224.4 |
| E3 | 141.4 | 149.9 | 154.9 |
| 200.8 | 204.8 | 224.4 |
3.2. Effect of Toughened Matrix Resin on the Compressive Properties of Carbon Fiber Composites
3.2.1. Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber
| Linear density mg/m | Density g/cm3 |
Sizing agent content /% | Tensile strength/MPa | Young's modulus/GPa | |
| Test value | 453 | 1.7796 | 1.12 | 6089 | 297 |
| CV/% | 1.1 | 2.4 | 1.7 | 3.9 | 0.7 |
3.2.2. Mechanical Properties Analysis of Carbon Fiber Composites
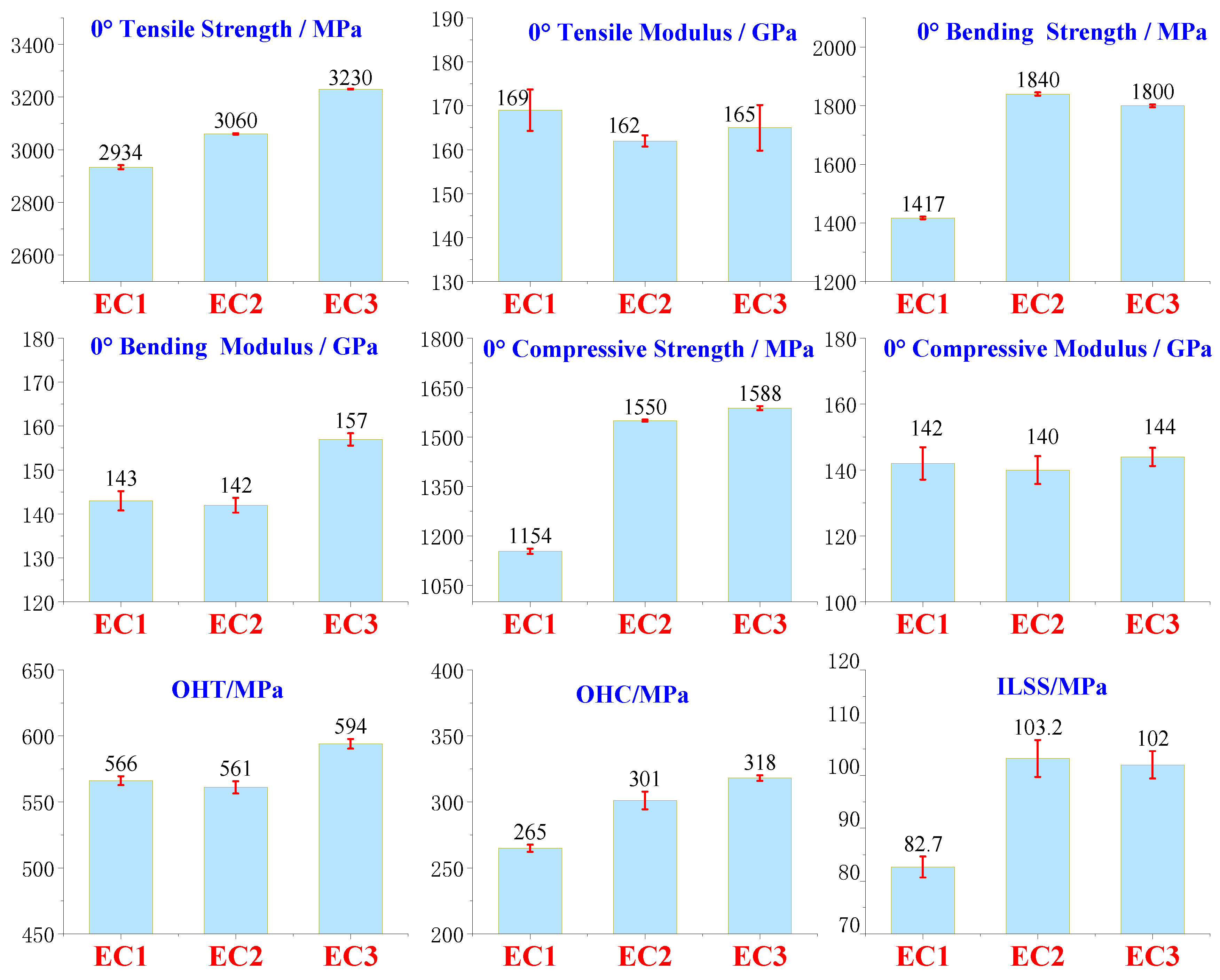
| EC1 | EC2 | EC3 | EC1-CV/% | EC2-CV/% | EC3-CV/% | |
| 0° Tensile Strength / MPa | 2934 | 3060 | 3230 | 7.6 | 2.1 | 1.5 |
| 0° Tensile Modulus / GPa | 169 | 162 | 165 | 4.7 | 1.3 | 5.2 |
| 0° Flexural Strength / MPa | 1417 | 1840 | 1800 | 4.2 | 5.6 | 4.7 |
| 0° Flexural Modulus / GPa | 143 | 142 | 157 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 1.4 |
| ILSS-RTD/MPa | 82.7 | 103.2 | 102.0 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| 0° Compressive Strength / MPa | 1154 | 1550 | 1588 | 7.8 | 3.3 | 6.0 |
| 0° Compressive Modulus / GPa | 142 | 140 | 144 | 4.9 | 4.2 | 2.8 |
| OHT / MPa | 566 | 561 | 594 | 3.4 | 4.7 | 3.7 |
| OHC / MPa | 265 | 301 | 318 | 2.7 | 6.7 | 2.1 |
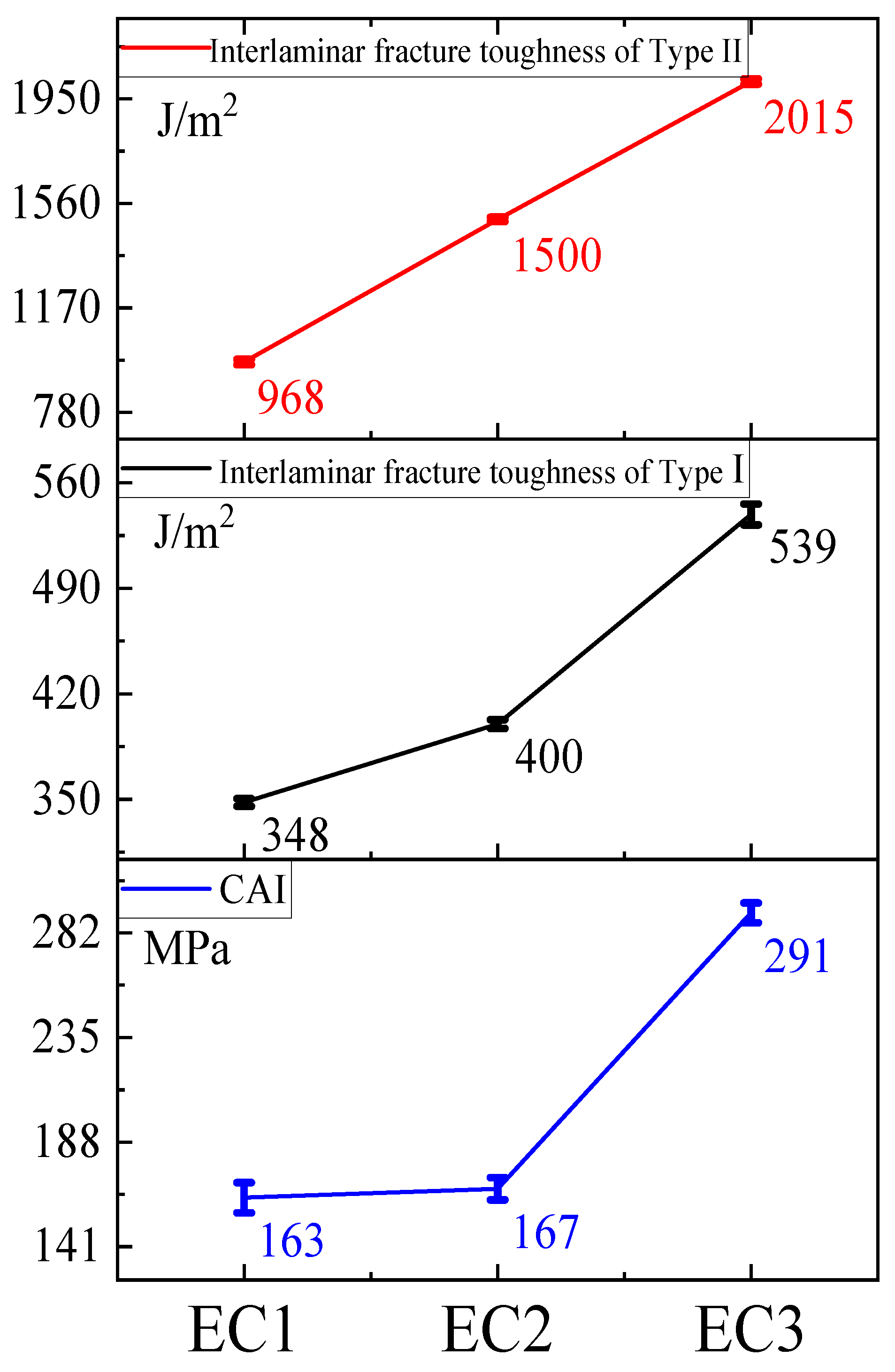
| CAI / MPa | 163 | 167 | 291 | 6.8 | 5.0 | 4.4 |
| GⅠC /J/m2 | 348 | 400 | 539 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 6.9 |
| GⅡC/J/m2 | 968 | 1200 | 2015 | 10.1 | 8.3 | 9.5 |
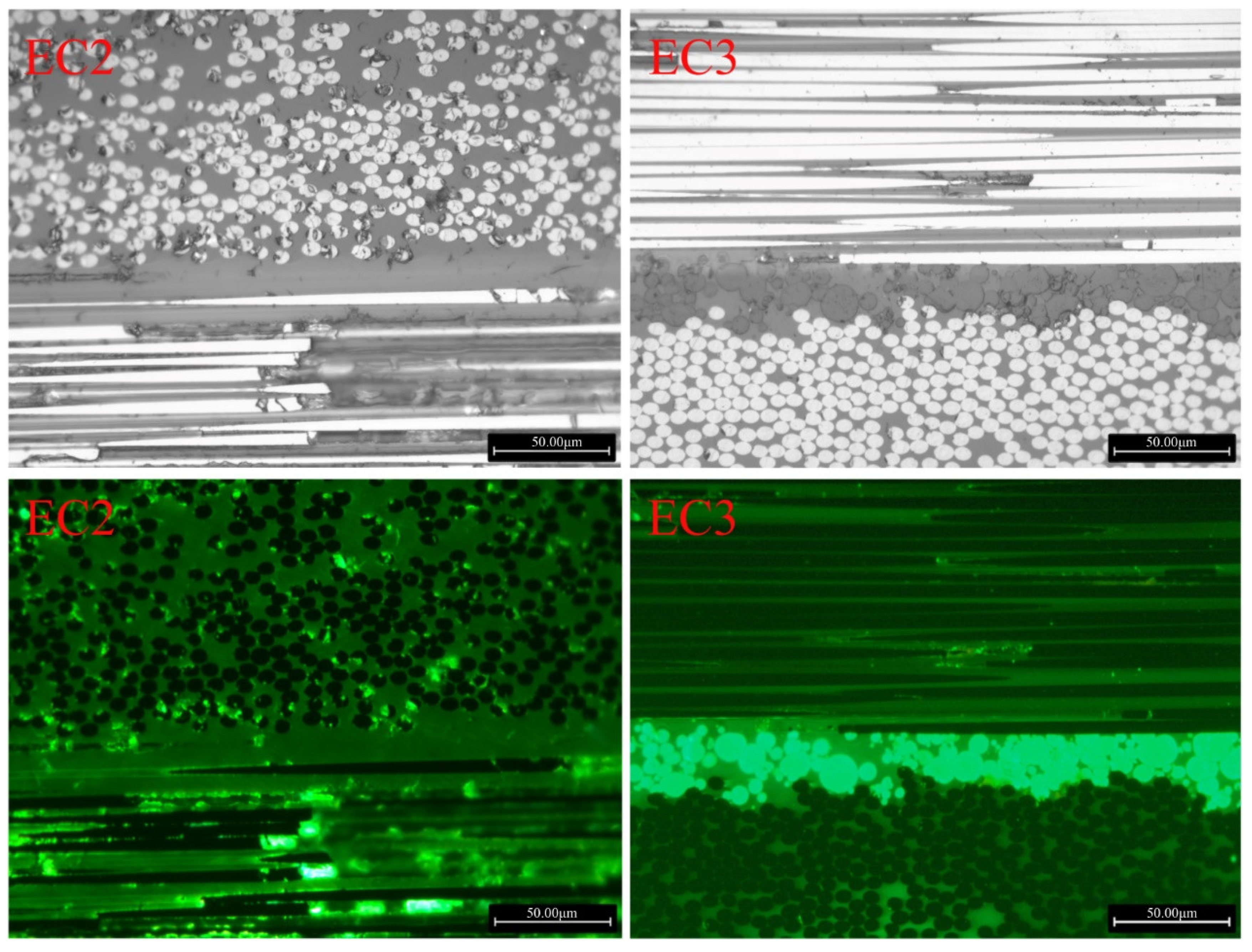
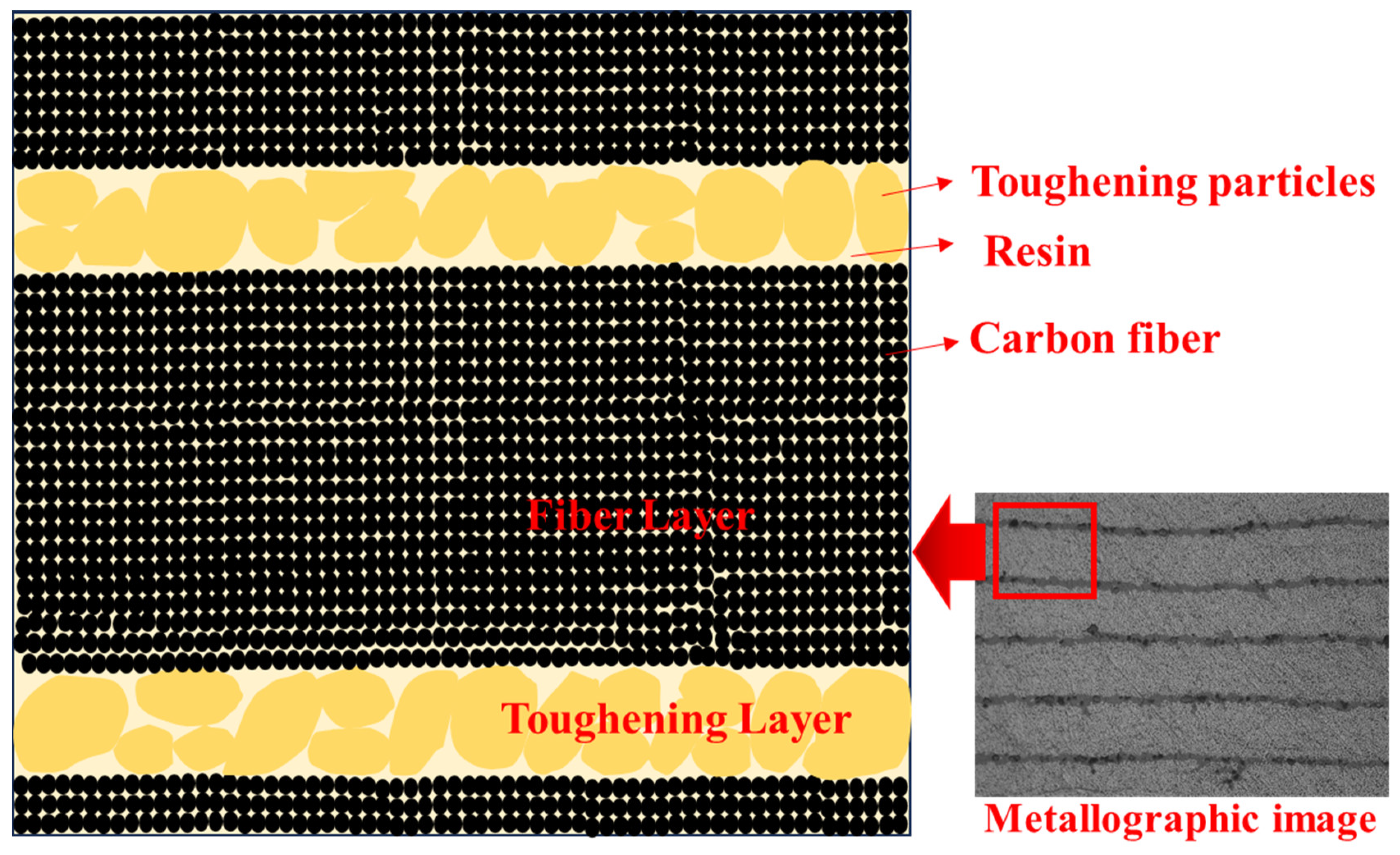
3.2.3. Microstructural State of Particle Toughened Carbon Fiber Composites
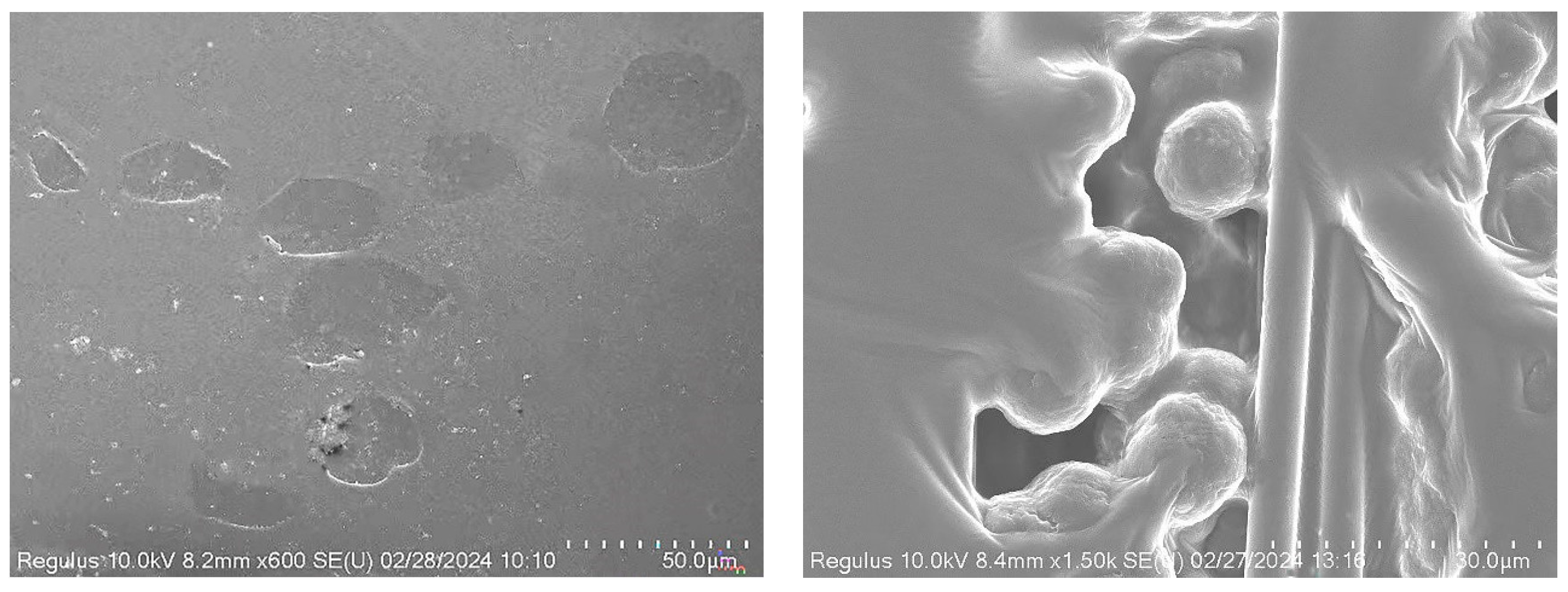
3.2.4. Mechanism of Particle Toughening and Compression Failure Morphology
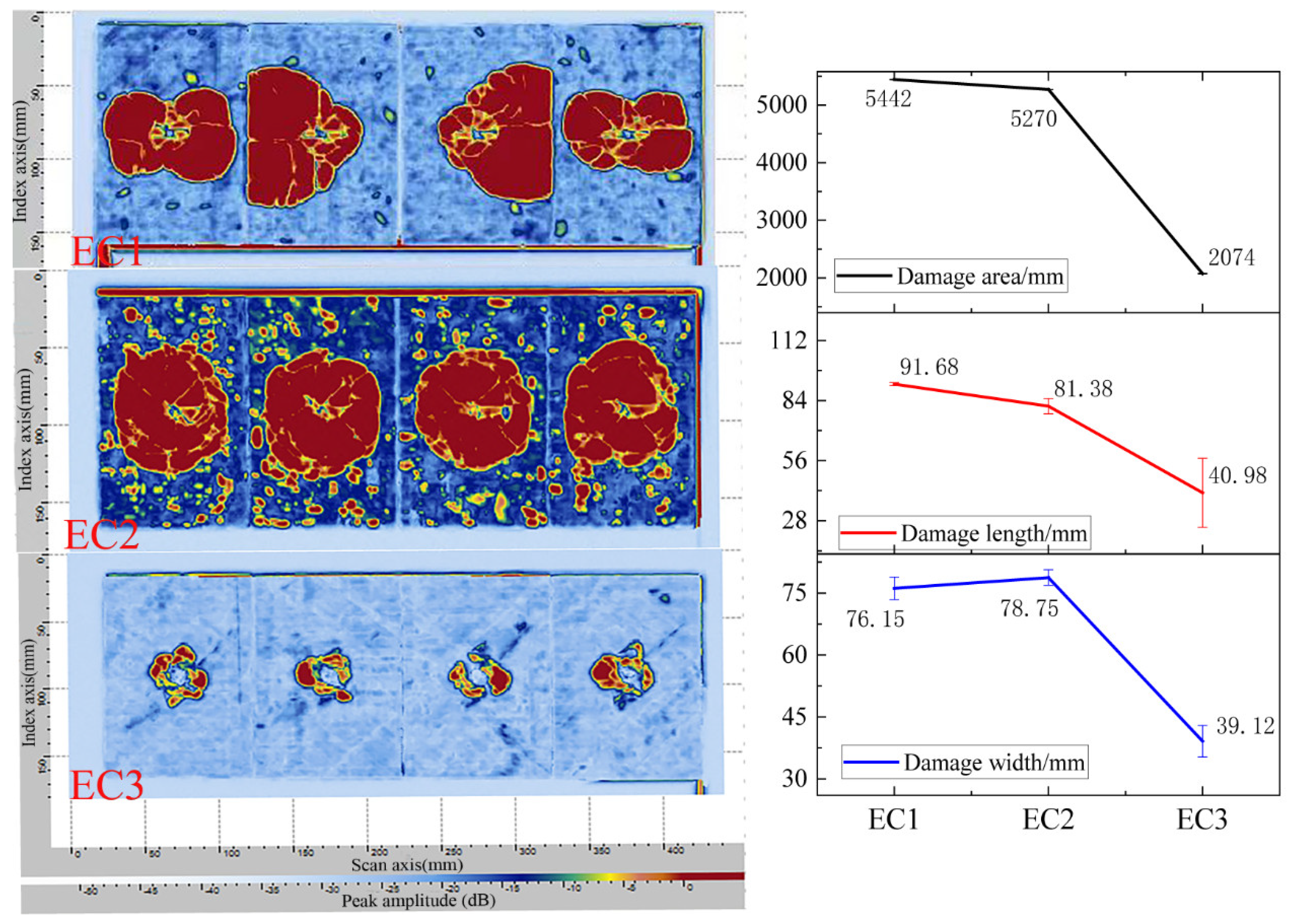
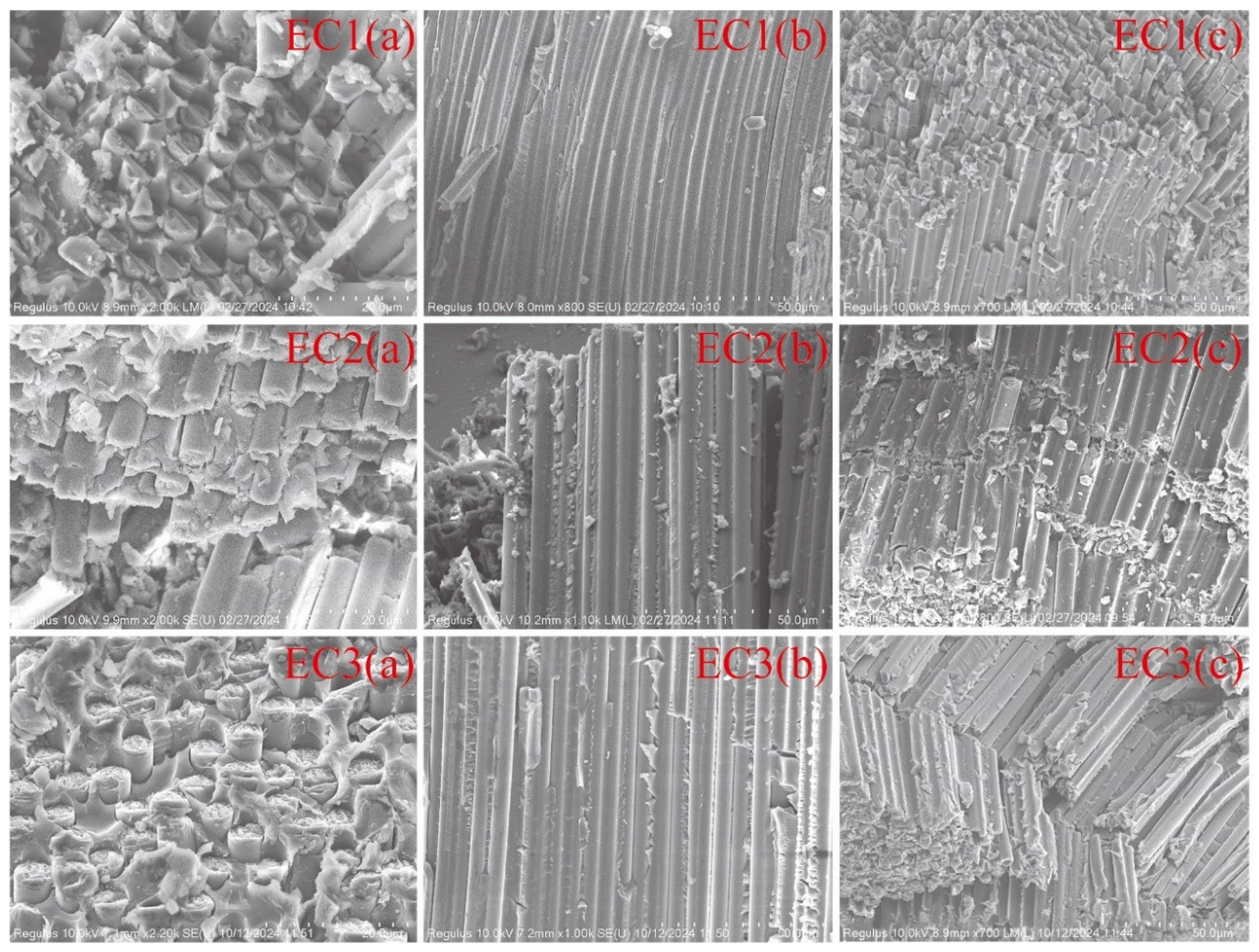
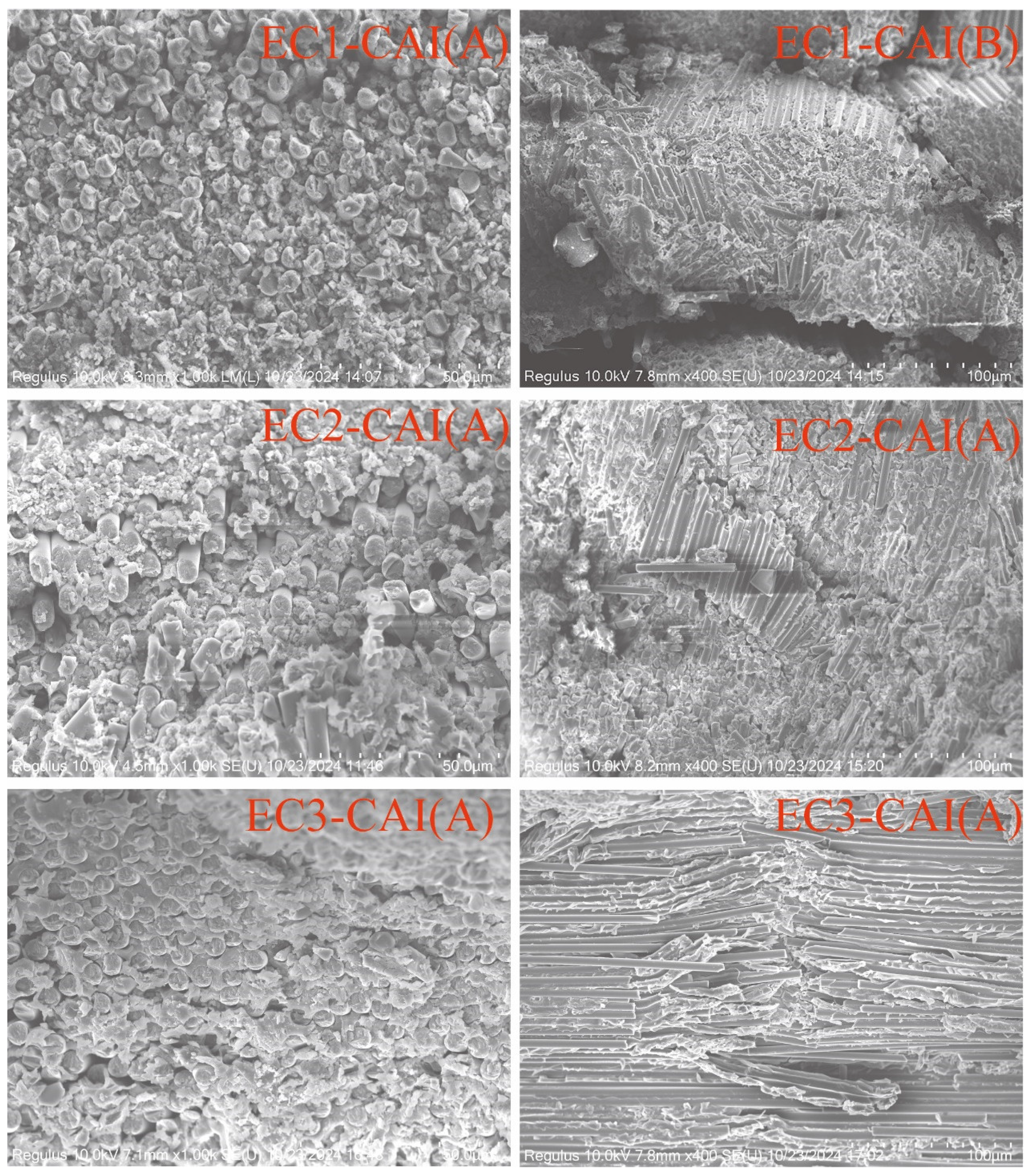
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He Fu. Carbon Fibers and Graphite Fibers. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press. 2010.
- LIU Liuxin, LU Xiaoying, WU Ying, LI Shuanhong, WU Jinyu, YUAN Wenjing, GAO Yuan. Progress in interface modification and application of carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2024, 52(9): 70-81 . [CrossRef]
- N. Domun , H. Hadavinia , T. Zhang, T. Sainsbury , G. H. Liaghat and S. Vahid .Improving the fracture toughness and the strength of epoxy using nanomaterials-a review of the current status[J]. (Review Article) Nanoscale, 2015,7, 10294-10329. [CrossRef]
- China National Building Materials Group: With the Ambition of Serving the Country's Great Interests, Boldly Shouldering the Country's Important Responsibilities, and Forging the Country's Premium Materials [J]. China Building Materials, 2024, (10): 32-36.
- Zheng Yaping. Research on High-Modulus Resin Matrix and High-Compressive Strength Composites [D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2001.
- Liu Bangxiong. Research on the Damaged Mechanism in Low-velocity Impact and Compressive Residual Strength of Stitched Carbon Fiber Composite Laminates [D]. Nanchang University,2024. [CrossRef]
- Tian Jing. Studies on Low-velocity Impact Damage of Stitched Composite Laminates [D]. Studies on Low-velocity Impact Damage of Stitched Composite Laminates,2008.
- YAO Jiawei, FENG Ruixuan, NIU Yifan, et al. Research progress of the interleaved thermoset composites by carbon nanomaterials/thermoplastic resin[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(2): 528-543. [CrossRef]
- Latif Zeeshan,Ali Mumtaz,Lee Eui-JongZubair ZakariyaLee Kang HoonTornabene Francesco.Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Nano-Carbon-Reinforced Polymeric Nanocomposites: A Review[J].journal of composites science,2023,7(10).
- JIANG Cai, CHE Zhe, XING Fei, et al. Research progress on interlaminar property of carbon nanotube-continuous fiber reinforced resin matrix composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(3): 863-883.
- Hsieh T H , Kinloch A J , Masania K ,et al.The toughness of epoxy polymers and fibre composites modified with rubber microparticles and silica nanoparticles[J].Journal of Materials Science, 2010, 45(5):1193-1210. [CrossRef]
- Xiao Tian.The study of core-shell toughened multi-functional epoxy resin and its carbon fiber composite[D].Beijing University of Chemical Technology,2012. [CrossRef]
- Phong N T , Gabr M H , Anh L H ,et al.Improved fracture toughness and fatigue life of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composite due to incorporation of rubber nanoparticles[J].Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 48(17):6039-6047. [CrossRef]
- A K L K , B G P S , A P A L ,et al.Improved fracture toughness of carbon fiber composite functionalized with multi walled carbon nanotubes[J].Carbon, 2008, 46( 15):2026-2033. [CrossRef]
- P,Karapappas,A,et al.Enhanced Fracture Properties of Carbon Reinforced Composites by the Addition of Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes[J].Journal of Composite Materials, 2009, 43(9). [CrossRef]
- Elisa B , Eslam S , Usama K ,et al.Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of CFRP Laminates Incorporating Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes[J].Polymers, 2015, 7(6):1020-1045. [CrossRef]
- ZHAO Hongchen, OU Yunfu, WU Longqiang, et al. Preparation and toughening mechanism of glass fiber/epoxy composites toughened by carbon nanotube sprayed layers[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(5): 2364-2373. [CrossRef]
- WU Longqiang, OU Yunfu, MAO Dongsheng, et al. Interlaminar properties and toughening mechanisms of aligned carbon nanotube fiber veil interleaved carbon fiber/epoxy composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(10): 5611-5620. [CrossRef]
- Yang Z X, Chai Z H, Jin Z H, et al. Analysis of impact resistance of graphite reinforced carbon fiber composites[J]. Plastics Science and Technology, 2023, 51(8): 48-53. [CrossRef]
- Hu Tao, Zhao Donglin, Cheng Xingwang, et al. Study on the Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Graphene Oxide Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 45(06): 29-33. [CrossRef]
- Kim Seong-Hwang,Park Soo-Jin.Effect of graphene oxide/graphitic nanofiber nanohybrids on interfacial properties and fracture toughness of carbon fibers-reinforced epoxy matrix composites[J].Composites, Part B. Engineering,2021,227(15):109387.1-109387.9.
- DAI Shaowei, ZHOU Yujing, LI Weidong, et al. Interlaminar toughening of carbon fiber/epoxy composites with graphene oxide-carbon nanotube composite film[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(7): 3862-3873. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia V , Gomez J , Cristiano F ,et al.Industrial manufacturing and characterization of multiscale CFRP laminates made from prepregs containing graphene-related materials[J].Materials Research Express, 2020. [CrossRef]
- ] Zeng Qingyang. Study on the Interlaminar Toughening of Carbon Fiber Composites through Synergistic Effects of Micro- and Nano-particles [D]. Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2018. DOI: CNKI:CDMD:2.1018.323795.
- Yibiao Wan, Jiamei Lai, Peixi He, et al. Effect of Modification with Inorganic Micro- and Nano-particles on the Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber Composites [J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Junshuai. Preparation and Properties of Nano-clay/Carbon Modified Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composites [D]. Hefei University of Technology, 2018. DOI: CNKI:CDMD:2.1018.222616.
- Mingyan Zhang, Mingchuan Li, Chengzhi Zhou, et al. Effect of Montmorillonite and Carbon Nanotubes on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Epoxy Composites [J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2015, 31(6): 116-121.
- Wang Zhenyu, Li Jianhua, Guo Huijun, et al. In-situ Synthesis of Nano-SiO2 Reinforced Anionic Polyester-based Sizing Agent and Its Effect on the Interlaminar Shear Strength of Carbon Fiber Composites [J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 7. [CrossRef]
- Jiang Zhenyu, Zhang Hui, Liu Sheng, et al. Improved Interfacial Bonding of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Matrix Modified by Wel-l Dispersed Nano-SiO2 Particles, 2007, 22(3): 8. [CrossRef]
- Fang Yixin, Chen Wei, Jiang Zhenyu, et al. Compressive Performance of Multi-phase Reinforced Epoxy Composites with Carbon Fibers and Nano SiO₂ [J]. Acta Materialiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(6): 1343-1352.
- Chen Yonglong. Study on Preparation and Properties of Nano-SiO2 and Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy-Bismaleimide Composites [D]. Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2015.
- Zhang Yingchen, Zou Jing, Wu Hongyan, et al. Method for Surface Modification of Carbon Fibers Coated with Nano-Silicon Dioxide by Plasma Treatment [P]. Shanghai, China: CN200810202621.2, Published on August 31, 2011.
- Liu Baiyang. The Study of Preparation and Reinforcing Effect of Silica Nanoparticle-MWCNT Hybrid Reinforcement on CFRP [D]. Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2013.
- Zheng Nan. A Study on Nano-Phase Interlaminar Toughening of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites [D]. Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017.
- LIU Xin, CHEN Duo, HE Huiyong, et al. Synergistic toughening of thermoplastic particles-inorganic particles to carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(8): 1904-1910. [CrossRef]
- YAO Jiawei, LIU Mengyao, NIU Yifan. Mechanical properties of PEK-C interlayer toughened carbon fiber/epoxy composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(5): 1083-1091. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, W.; Dai, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Long, L.; Zhou, Z. Hierarchical Interfacial Construction by Grafting Cellulose Nanocrystals onto Carbon Fiber for Improving the Mechanical Performance of Epoxy Composites. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1537. [CrossRef]
- Ning Na. Core/Shell Nanoparticles – Their Synthesis and Use for Epoxy Resin and Carbon Fiber Composite Toughening [D]. Donghua University, 2022.
- Liu Dawei. Study on the Mechanism of Micro/Nanoparticle Synergistic Reinforcement and Toughening in Carbon Fiber Composites [D]. Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2016. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





