1. Introduction
Systemic hypertension is generally defined generally as persistently elevated systolic blood pressure, and can be categorized as situation, secondary, or idiopathic hypertension [
1]. In particular, secondary hypertension commands attention in veterinary medicine as it can be related by chronic kidney disease [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7], hyperadrenocorticism [
8,
9,
10,
11], and diabetes [
12,
13,
14,
15], and is often encountered in clinical settings.
Chronically elevated blood pressure is known to cause target organ or tissue damage, especially in the kidney [
4,
17], eye [
18,
19], brain [
17,
20], and vasculature [
21] in dogs. Thus, once a dog is identified as having chronically high blood pressure, antihypertensive treatment needs to be initiated promptly to prevent severe damage to these organs. Extremely serious complications of systemic hypertension such as abdominal aortic aneurysm and dissection are reported rarely in veterinary medicine [
22], although they occur more frequently in human medicine [
25,
26]. Given this disparity in severe complications, it is unsurprising that diagnostic techniques are more well established for human cases of suspected systemic hypertension than veterinary ones. For human patients, abdominal aortic aneurysm is classically diagnosed when aortic diameter exceeds 30 mm [
23] or when the aorta shows 1.5-fold dilation versus its normal size [
24]. Although abdominal aortic aneurisms are rare in canine medicine, image-based evaluations of aortic diameter are of interest as diagnostic techniques for other conditions that may be related to chronically high blood pressure.
Canine systemic hypertension needs to be assessed swiftly, so that target organ damage can be prevented and any underlying disease treated. Currently, the most commonly used blood pressure measurement method in clinical practice is the non-invasive oscillometric technique, or Doppler sphygmomanometry. However, non-invasive blood pressure measurements require technical proficiency and a certain degree of cooperation from the patient to obtain accurate and clinically useful results. The syndrome of “white-coat hypertension”—where blood pressure may be elevated in a hospital setting—is also particularly problematic in small animal medicine. Veterinarians thus need other, reliable diagnostic tests when evaluating systemic hypertension.
Imaging examinations are potentially useful diagnostic tools for such assessments. In human medicine, ultrasonographic abdominal aortic measurements are well established as useful parameters for evaluating diagnosis, therapeutic interventions, and prognosis in patients with high blood pressure [
29,
30,
31]. By contrast, in canine medicine, there is only one report on ultrasonographically determined abdominal aorta-caudal vena cava ratio as a potential index of systemic hypertension [
16].
Abdominal ultrasound is a very convenient and non-invasive technique, but it shares some of the same disadvantages of oscillometry; for example, evaluation can become problematic when the patient is uncooperative. Furthermore, inter-observer reliability can be an issue. Computed tomography (CT) may thus offer some advantages as an imaging modality for measurement of vascular geometry. Dogs are often anesthetized to undergo CT, which can circumvent the issue of non-cooperation with an examiner, although it may be questioned whether anesthesia has some effect on measured parameters. As an imaging modality, CT allows for objective evaluations, and is a suitable method to ascertain the presence of diseases that may cause secondary hypertension, such as cerebral hemorrhage and adrenal tumors because it is a whole-body imaging method.
Based on the advantages of CT and considering the above-mentioned report that ultrasonographically determined Ao/CVC ratio reflects systolic blood pressure, we hypothesized that CT measurements would capture hypertensive changes in abnormal aortic diameter, through any changes relative to the caudal vena cava. If validated as an appropriate tool, CT could be a convenient, objective, and examiner-independent method for detecting systemic hypertension in patients based on aortic measurements. To investigate this hypothesis, we retrospectively evaluated dogs that had undergone oscillometric blood pressure and CT scans at our hospital on the same day, to ascertain any differences in Ao/CVC ratio between hypertensive and normotensive dogs, as the primary endpoint in this study. We also established a new parameter for assessment of aortic geometry, the ratio of the abdominal aorta to the first lumbar vertebra (Ao/L1 ratio), to assure evaluations unaffected by any patient dehydration. To further investigate the use of CT-based aortic geometry in evaluation of systemic hypertension, we evaluated differences in Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratios in cohorts of male and female, and anesthetized and unanesthetized, dogs.
2. Materials and Methods
In this retrospective study, we evaluated data from 32 dogs that underwent CT examinations and blood pressure measurements on the same day, while receiving medical care at Kagoshima University Veterinary Teaching Hospital (Kagoshima, Japan) between February and August 2024. The medical records of each dog were reviewed, and they were designated as a hypertensive or a normotensive dog, by an investigator (NM), a veterinarian affiliated to the Diagnostic Imaging Department of Kagoshima University Veterinary Teaching Hospital. Specifically, a dog was classified as normotensive when its systolic blood pressure was ≤140 mmHg, or hypertensive when its systolic blood pressure exceeded 140 mmHg.
Ethics approval was waived for this retrospective study, because it did not involve any procedures with experimental animals. It was conducted in accordance with the research ethics bylaws of Kagoshima University. The owner of each dog evaluated in this study had given consent to the use of the relevant data in research at the time of medical examinations.
The dogs underwent CT imaging with a dedicated 16-helical sliced CT scanner (Aquilion TSX-201A, Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation, Tochigi, Japan) with or without anesthesia. The anesthesia protocol was determined by the examining veterinarian depending on the patient's condition and temperament. A total of 20 dogs underwent CT scans without anesthesia, and 12 dogs were anesthetized for the procedure. The anesthetics used involved combinations of propofol, dexmedetomidine, butorphanol, and isoflurane; specifically, anesthetized dogs received propofol and isoflurane in 10 cases, and dexmedetomidine and butorphanol in two cases each. Dogs had undergone CT imaging in ventral recumbency in 31 cases and in right lateral recumbency in one case. All images were acquired in DICOM format and were read and measured using the DICOM viewer OsiriX Ver. 5.9. All observations and measurements were performed by two investigators (YI, KY) under the supervision of the other investigator, and senior veterinarian (NM). All images were taken in plain CT with a slice thickness of 1 mm, usually in the soft tissue condition (WL50:WW350), and the window level and width were changed as necessary.
Blood pressure was measured three times by experienced veterinarians and/or nurses using the Doppler method, and the mean of the three measurements was taken as the adopted value. When the animal appeared agitated at the time of measurement, this was recorded in its medical record. The dilation of the abdominal aorta was assessed by the ratio of its diameter to the diameter of the caudal vena cava or the first lumbar vertebra (L1).
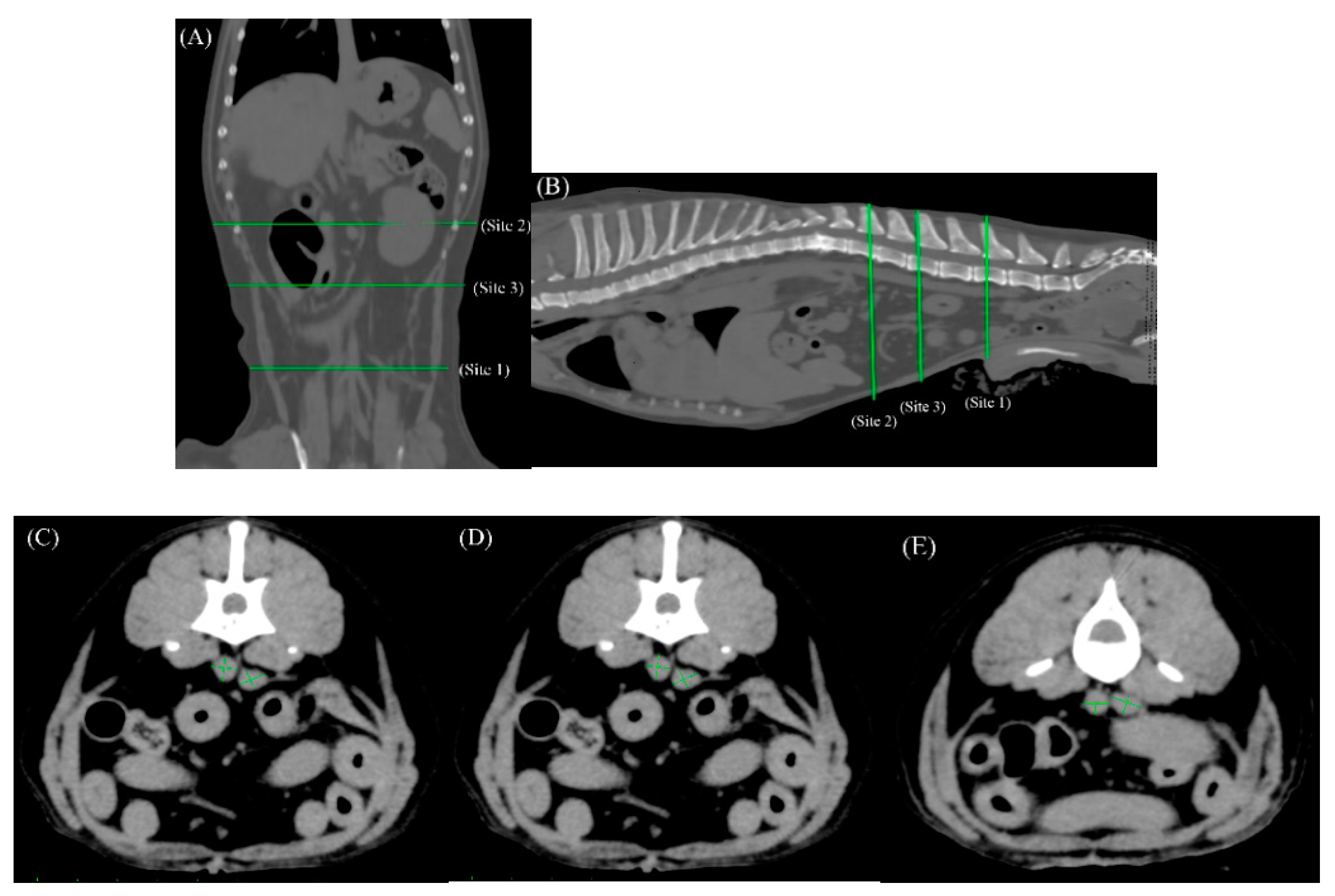
We targeted three sites in the abdomen, for measurement of the diameters of the adjacent aorta and caudal vena (
Figure 1A–E). The first location (Site 1) was selected in reference to the measurement site determined in a similar report on ultrasonographic measurements [
16], cranial to the origin of the bifurcated external iliac anatomy. Blood vessel diameters were measured again in the same manner at two different locations in the same region (Sites 2 and 3), to facilitate analytical checks for any error arising due to a change in measurement site. Site 2 was selected at a cranial point along the abdominal blood vessels, as a site adjacent to the L1 vertebra, and Site 3 was selected as a medial point between Sites 1 and 2.
At each measurement site, two notional, perpendicular lines were drawn through the center of each blood vessel extending to its border, and the longer of the two lines was regarded as its maximal diameter, and its measured length was adopted as the value for evaluation.
Three anatomical sites targeted for measurement of the diameters of the aorta and caudal vena cava in the abdomen are shown in dorsal (A) and sagittal views (B), with Site 1 at a well-defined location in the abdomen cranial to the origin of the bifurcated external iliac artery (C), Site 2 just below the first lumbar vertebra (E), and Site 3 at a medial point between Sites 1 and 2, and separated by at least five slices from them sites (D). The conditions for this image were soft tissue conditions (WL:50WW:300, slice thickness 1mm).
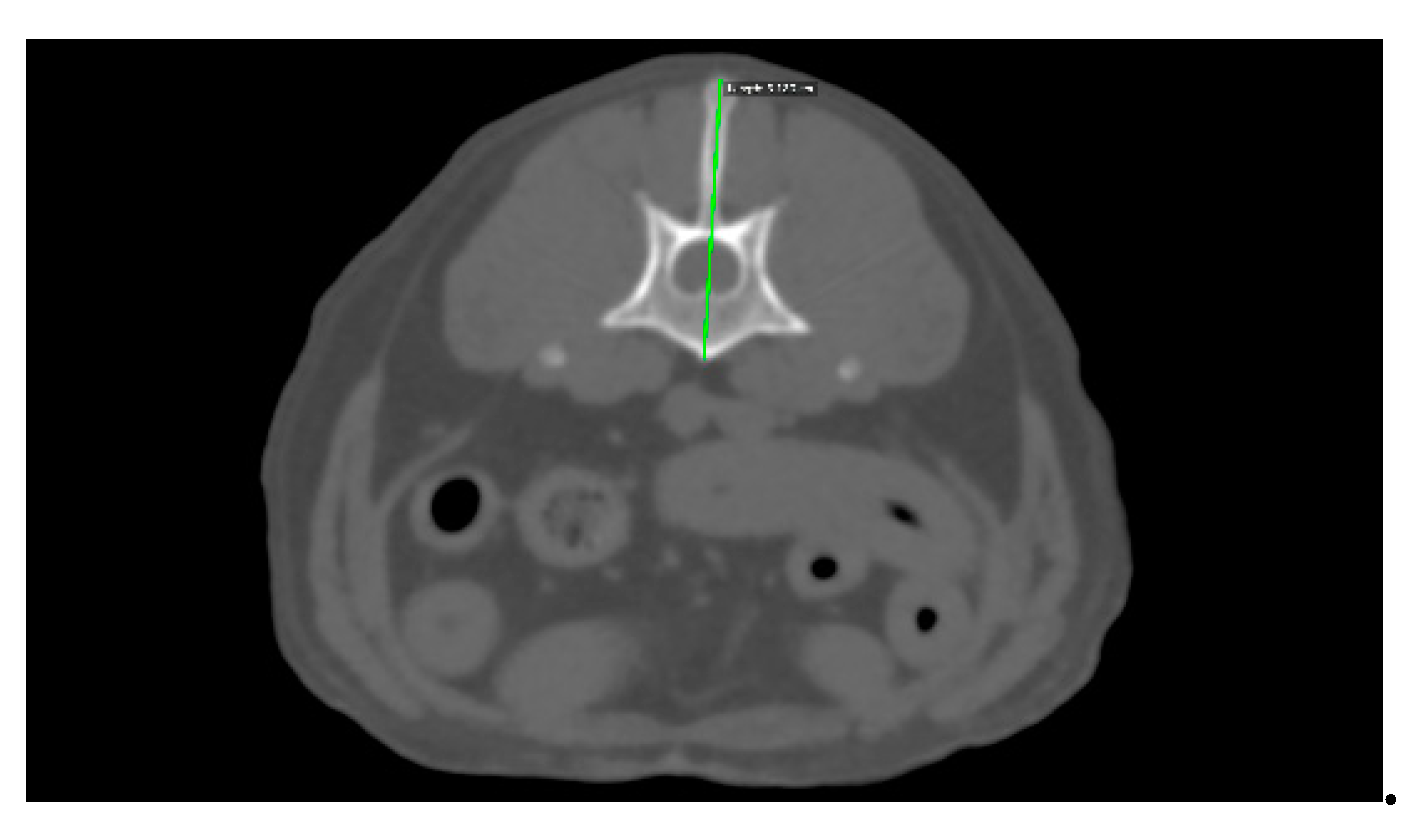
The diameter of the L1 vertebra was measured as a straight line from the longest part of the spinous process to the ventral side of the vertebral body, where it can be clearly observed. The conditions for this image involved a bone window (WL:300WW:1500, slice thickness 1mm) [
Figure 2].
Data were analyzed using the statistical analysis software GraphPad Prism version 10.0.2 for Windows (GraphPad Software, La Jolla California USA,
www.graphpad.com). Data were compared between hypertensive and normotensive dogs, and between males and females, and anesthetized and unanesthetized dogs, using with student's t test, paired t test. Further comparisons of blood vessel diameters and diameter ratios were made between each of the three measurement sites using with . A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
Our study population (n = 32) comprised 14 males and 18 females (mean age: 8.8 years; mean body weight: 6.18 kg).
Eighteen of the 32 dogs were designated as hypertensive, and the other 14 were designated as normotensive.
Hypertensive dogs included eight males and six females (mean age: 8.3 years; mean body weight: 5.8 kg), and they showed a mean systolic blood pressure of 168.7 mmHg (median: 161 mmHg, max: 207 mmHg, min: 142.8 mmHg) [
Table 1]. Among hypotensive dogs, there were four cases of medical conditions known to predispose for secondary hypertension; specifically, cerebral hemorrhage (n = 1), chronic kidney disease (n = 2), and hyperadrenocorticism (n = 1). Other conditions diagnosed for hypertensive dogs included lung tumor (n = 2), liver tumor (n = 1), cervical disc herniation (n = 1), bile duct cystadenoma (n = 1), idiopathic epilepsy (n = 1 ), and perineal hernia (n = 1), with no diagnosis made in the other three cases.
Normotensive dogs included seven males and 11 females (mean age: 9.3 years; mean body weight: 6.51 kg), and showed a mean systolic blood pressure of 125. 3mmHg (max-min: 140 mmHg - 97.2mm Hg) [
Table 1]. No normotensive dog was diagnosed with a condition associated with secondary hypertension.
Table 1.
Clinical and demographic characteristics of hypertensive and normotensive dogs.
Table 1.
Clinical and demographic characteristics of hypertensive and normotensive dogs.
| |
Hypertensive |
Normotensive dogs |
| Population |
N = 14 |
N = 18 |
| Male / Female |
N = 8 / N = 6 |
N = 7 / N = 11 |
| Intact / Neutered |
N = 3 / N = 11 |
N = 4 / N = 14 |
| Mean age (max-min) |
8.3 years (13.8years-1.2years, 95% CI: 8.37-8.23 ) |
9.3years (15.3yeras - 0.5 years, 95%CI: 9.37- 9.23) |
| Mean body weight (man – min) |
5.8kg (12kg-2.5kg, 95%CI: 5.85- 5.75) |
6.51 kg (30.7kg-2.08kg, 95%CI:6.61-6.41) |
| Mean systolic blood pressure (max-min) |
168.7 mmHg (207mmHg-142.8mmHg, 95%CI: 169.1- 168.3) |
125.3mmHg (140mmHg-97.2mmHg,95% CI: 125.5-125.1) |
| Breed |
Chihuahua (n=3)
Toy poodle (3)
Maltese(1)
French bulldog (1)
Scottish terrier poodle (1)
Shih-Tzu(1)
Welsh corgi(1)
Boston terrier(1), Miniature Schnauzer(1)
Shetland sheepdog (1)
|
Toy poodle (6)
Mixed breed (3)
Chihuahua (2)
Shiba-inu (2)
French bulldog (1)
Kaninhen dachshund (1)
Golden retriever (1)
Pomeranian(1)
Schipperke (1), |
Data on the abdominal aorta and caudal vena diameters (measured at three sites in each dog) and the LI diameter are shown in
Table 2
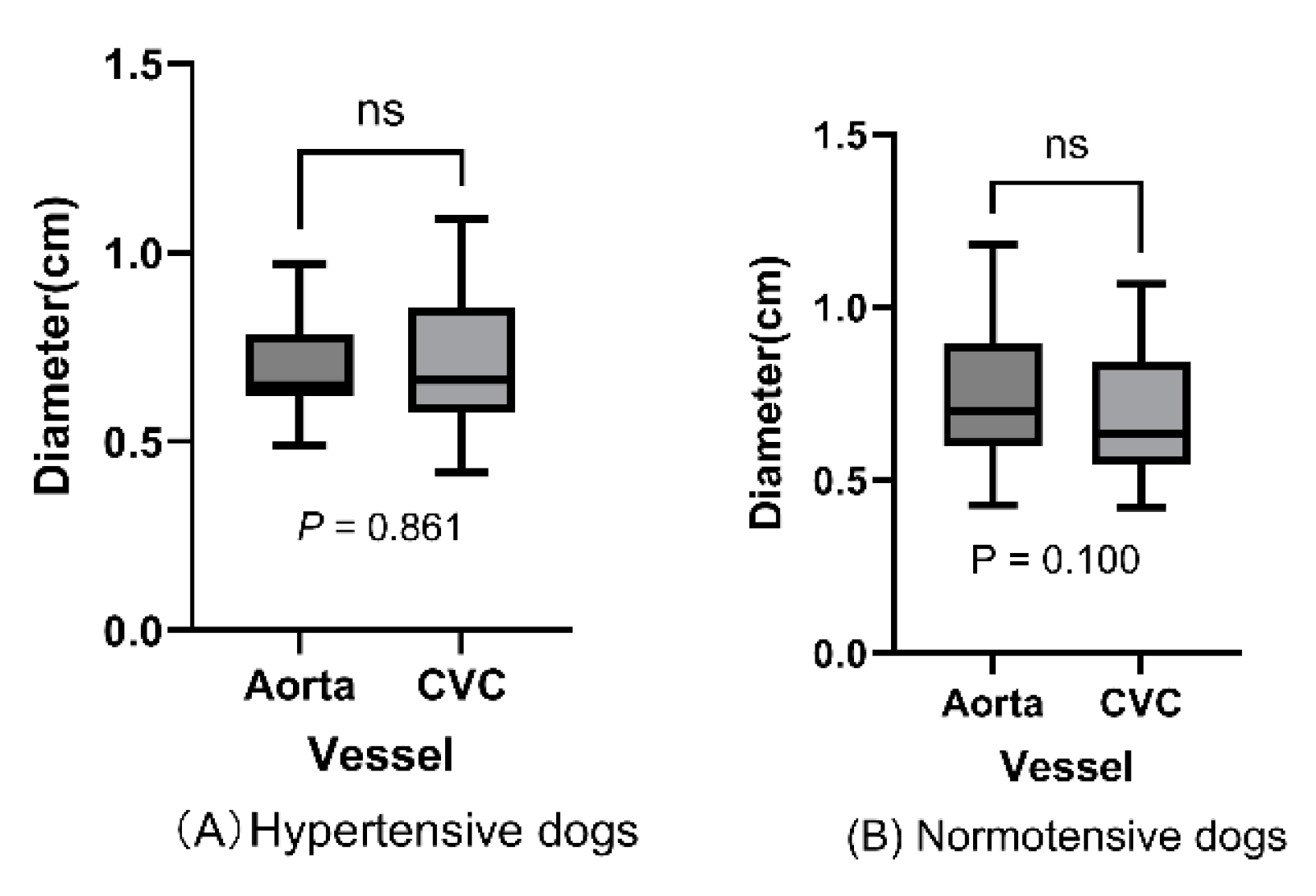
Abdominal aortic diameter did not significantly differ with the caudal vena diameter in hypertensive dogs (0.691 vs. 0.699 cm; p=0.861;
Figure 3A) or normotensive dogs (0.732 vs. 0.685 cm; p=0.100;
Figure 3B).
The distributions of measured abdominal aorta and caudal vena cava diameters are shown for hypertensive dogs (A) and normotensive dogs (B), and indicated no significant difference between blood vessel diameters within either population (hypertensive dogs: P = 0.861; normotensive dogs: P = .100 > 0.5; paired t-test)
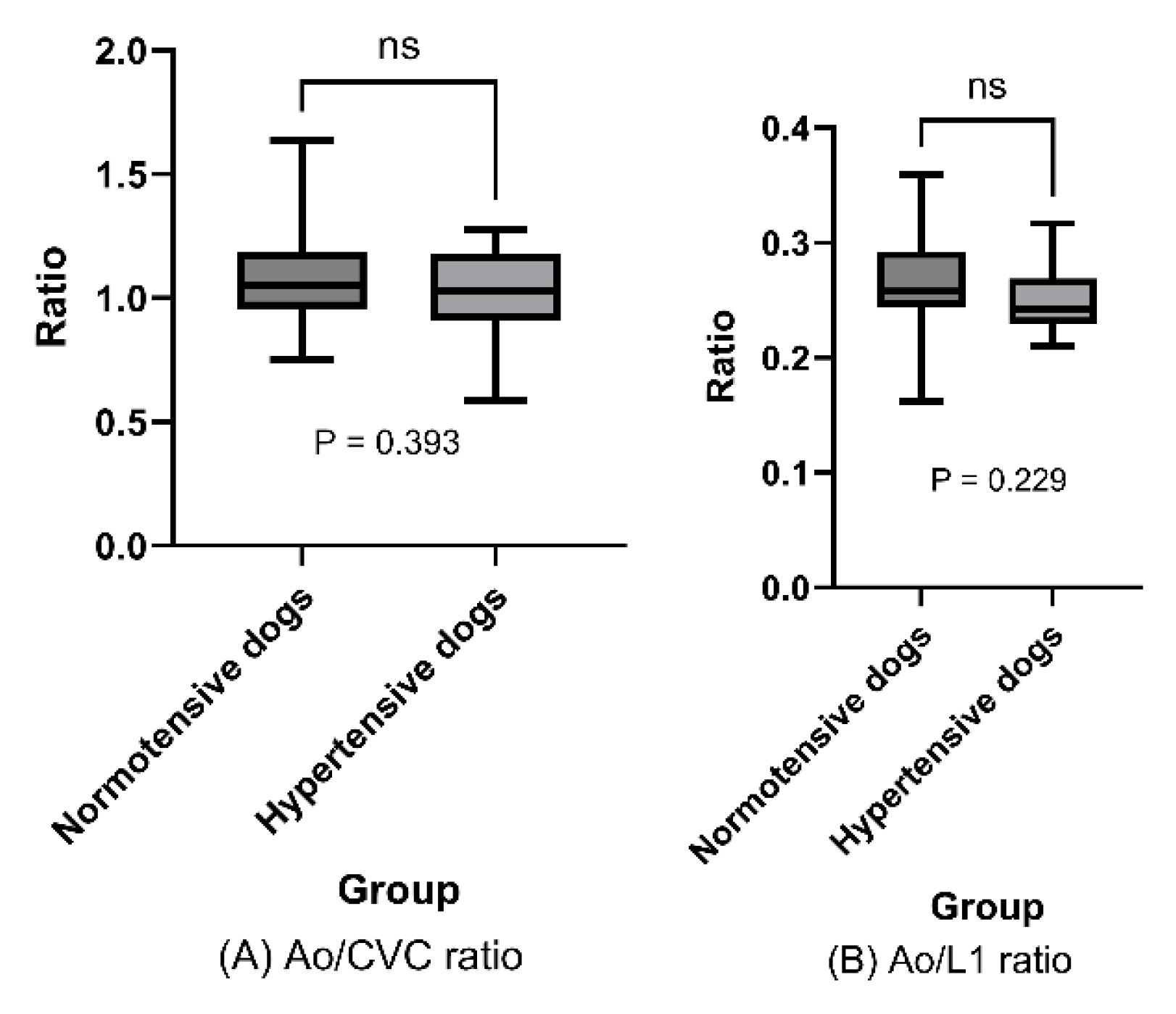
In analysis of the key endpoints, mean Ao/CVC ratio did not differ significantly between hypertensive and normotensive dogs (1.03 [SD: ±0.18] vs. 1.08 [SD: ±0.20]; P=0.393;
Figure 4A). Ao/L1 ratio was also assessed (to mitigate against any effect of dehydration on the results), and showed no significant difference between hypertensive and normotensive dogs (0.250 [SD±0.028] vs. 0.266 [SD±0.041]; P= 0.229;
Figure 4B).
Mean Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratios in hypertensive and normotensive dogs are represented in box plots, and indicated no significant difference between these population groups (Ao/CVC ratio: P = .393; Ao/L1 ratio: P = .229 > .05; t-test).
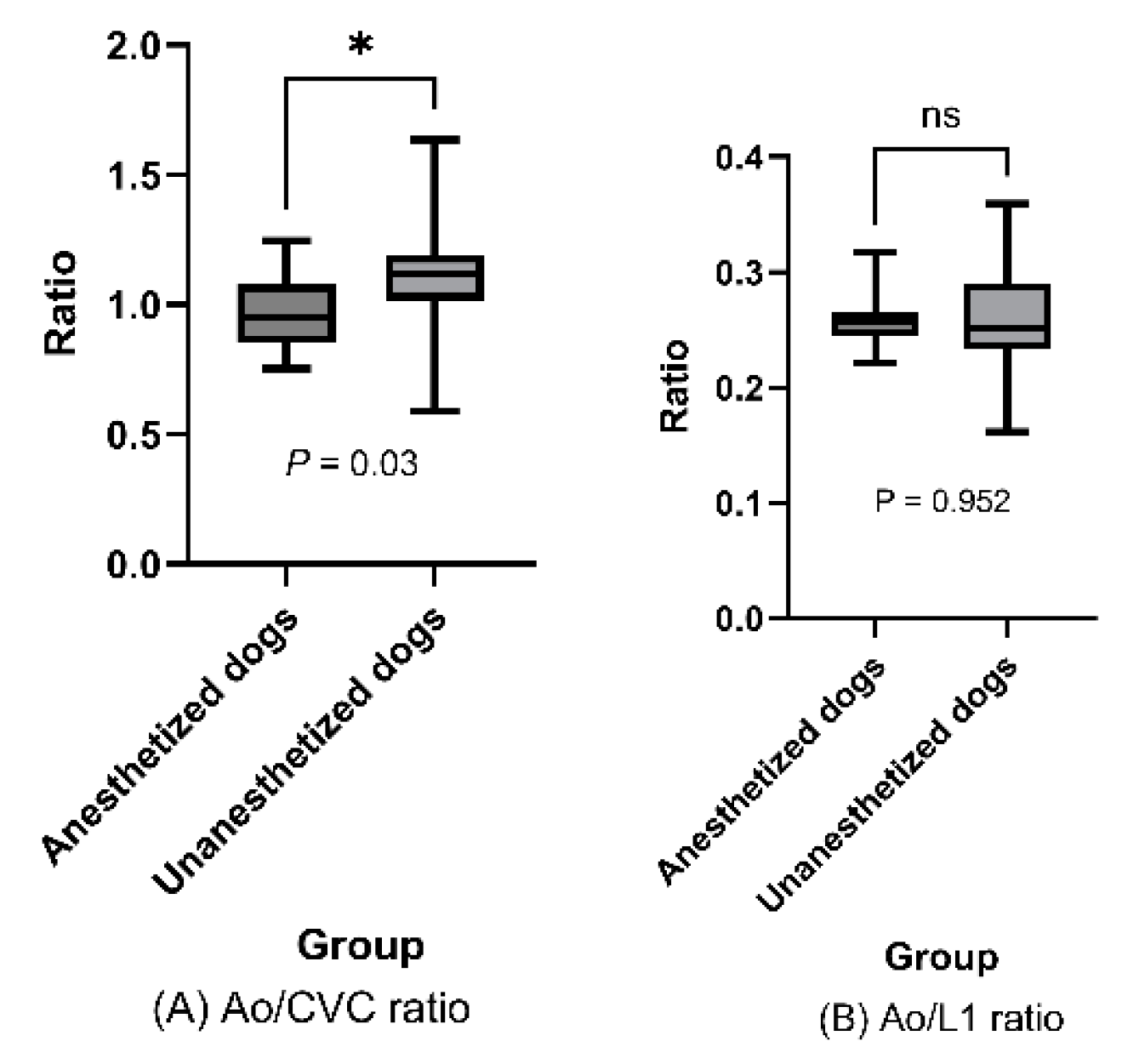
In other evaluations, we investigated other factors that might potentially be associated with blood pressure or vascular changes. Ao/CVC differed significantly between anaesthetized and unanesthetized dogs (0.97 [SD±0.15] vs. 1.11 [SD±0.19], p=0.03,
Figure 5A), but Ao/L1 ratio did not (0.26 [SD±0.02] vs. 0.26 [SD±0.04], p=0.952,
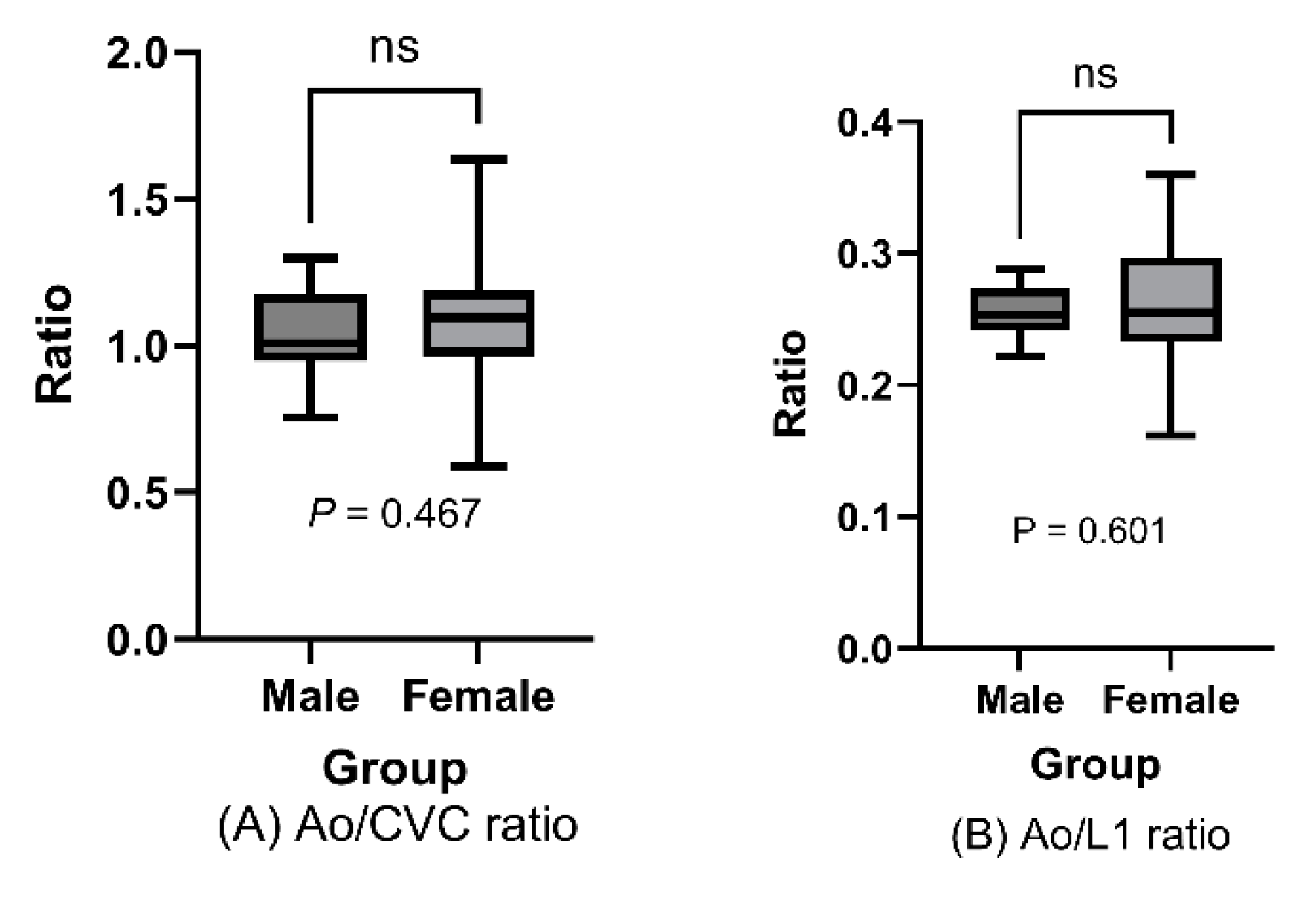
Figure 5B). Furthermore, we found no differences in either ratio between males and females (Ao/CVC ratio [males vs. females]: 1.03 [SD±0.19] vs. 1.08 [SD±0.15], P= 0.467,
Figure 6A; Ao/L1 ratio: 0.255 [SD±0.02] vs. 0.262 [SD±0.05], P= 0.601,
Figure 6B).
Mean Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratios in anesthetized dogs vs. unanesthetized dogs are rep-resented in box plots. Ao/CVC ratio showed a significant difference noted (P = 0.03) [A], but AO/L1 ratio did not P = 0.952 > 0.05) [B]; t-test.
Mean Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratios in male and female dogs are represented in box plots, and indicated no significant differences between sexes (Ao/CVC ratio: P = 0.467; Ao/L1 ratio: P = .0.601 > .05; t-test)
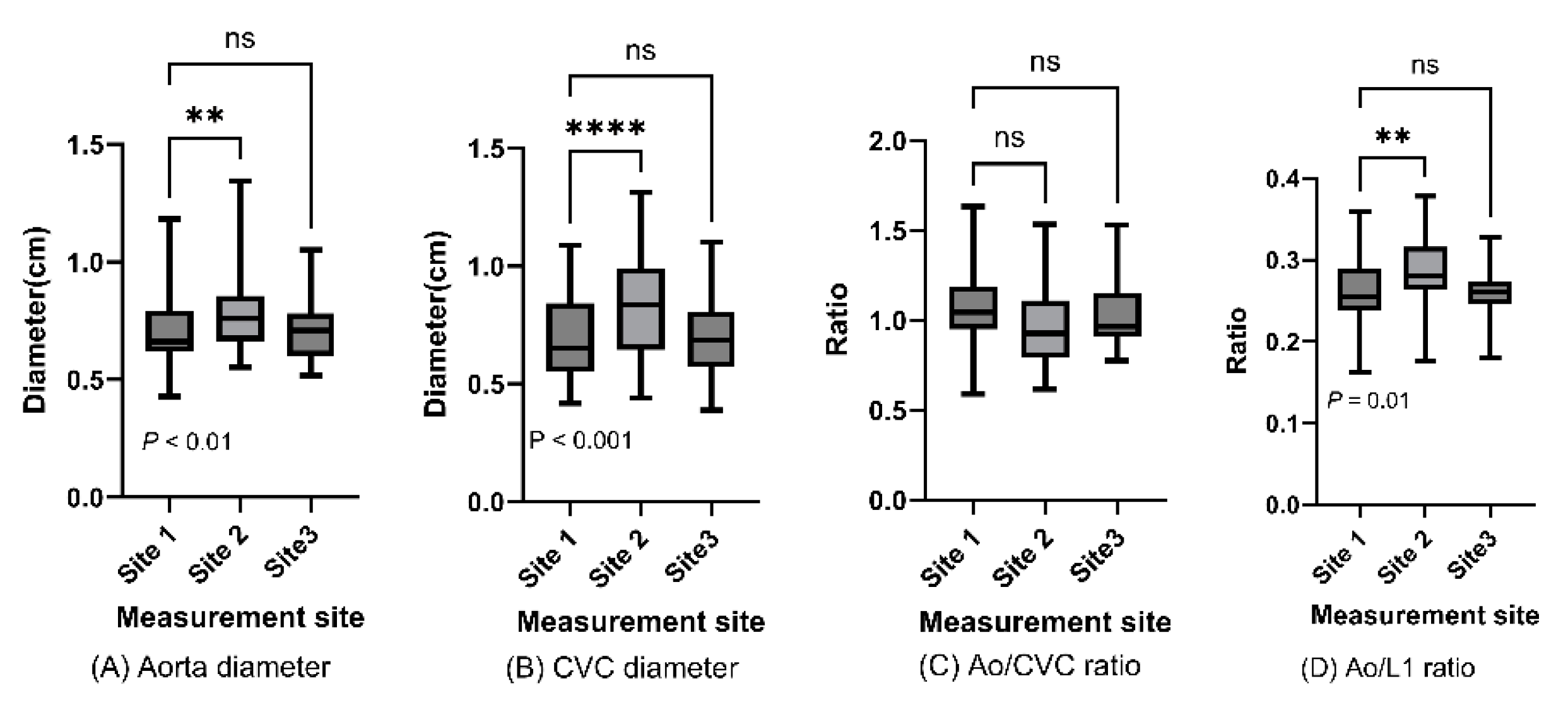
We also evaluated data for each of the three vascular measurement sites (
Figure 1A,B). Abdominal aortic and caudal vena cava diameter differed significantly between Sites 1 and 2, but we found no significant difference for blood vessel diameters at Site 3 or for Ao/CVC or Ao/L1 ratio for any of three measurement sites (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8).
Abdominal aorta and caudal vena cava diameters and Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratios are displayed in box plots for caudal, medial, and cranial measurement sites, and indicated some significant differences between measurement in one-way ANOVA (P < 0.05)
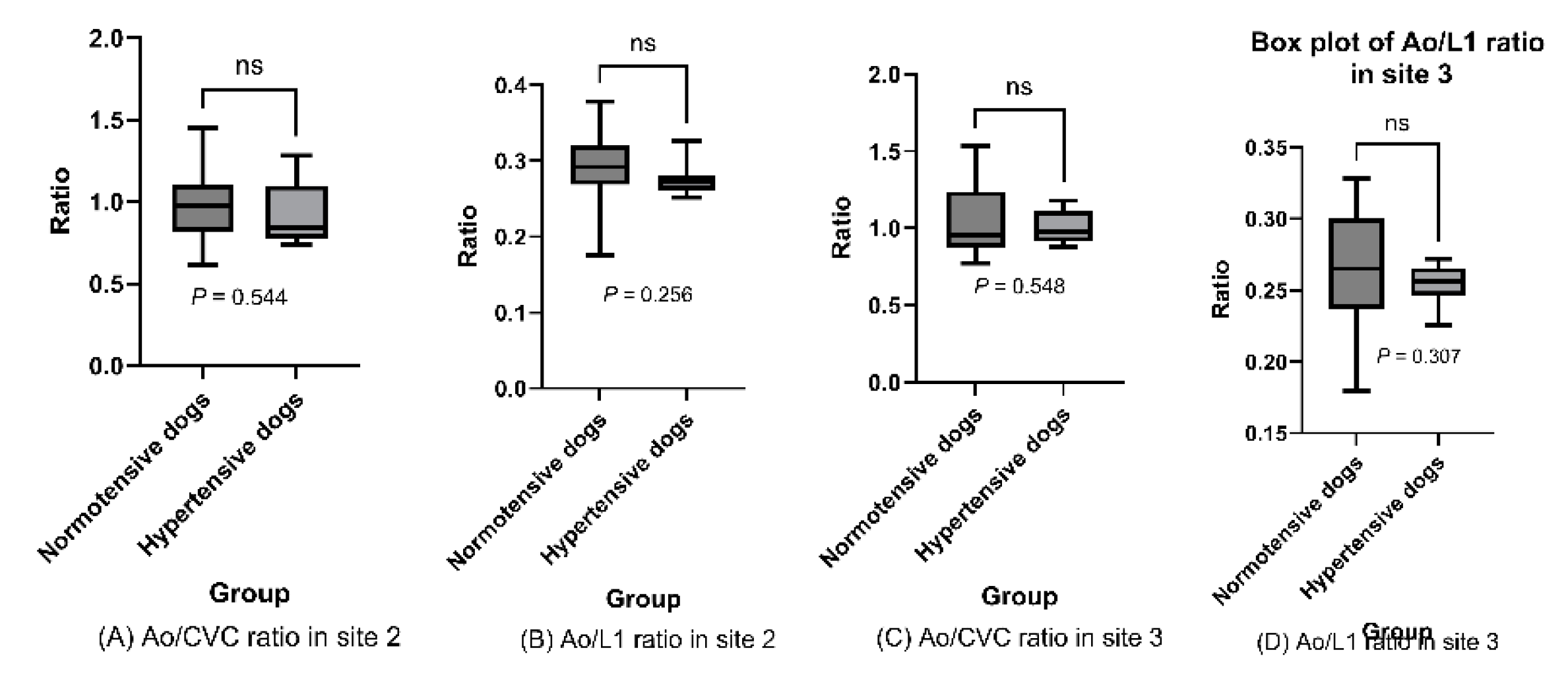
Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratios for two measurement sites are shown in box plots for hypertensive and normotensive dogs, and indicated no significant differences between the two population groups (site 2 [cranial]: P values = 0.544 and 0.256 [for Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratios, respectively]; site 3 [medial]: P values = 0.548 and 0.307 > .05; t-test)
4. Discussion
In this study, we investigated whether enlarged abdominal aortic diameter as measured in CT was associated with hypertension in dogs. Our evaluation was based on the ratios of the abdominal aortic diameter to those of the caudal vena cava and the L1 vertebra. To the authors’ knowledge, it is the first report on the relationship of these parameters with blood pressure, based on CT measurements, in canine medicine.
Based on the study findings, the hypothesis that CT-measured enlargement of the abdominal aortic diameter would reflect hypertension was rejected. We found no significant differences in Ao/CVC ratio between hypertensive and normotensive dogs. Furthermore, Ao/L1 ratio, which we evaluated to remove any possible influence of dehydration on interpretation of study data, also did not significantly differ between hypertensive and normotensive dogs. Our study thus produced no evidence that aorta measurements would be clinically useful for evaluation of hypertension.
Interestingly, the negative results based on CT measurements we report here contrast with a previous report that ultrasonographically measured aortic diameter (based on Ao/CVC ratio) could be indicatative of increased blood pressure [
16]. In that report, hypertensive dogs had shown a mean Ao/CVC ratio of 1.515, yet no hypertensive dog in our study showed an Ao/CVC ratio exceeding 1.280, and the only Ao/CVC ratio in this study exceeding the figure from the ultrasound report (max: 1.634) was in a normotensive dog. We cannot rule out the possibility that positioning of dogs and the concomitant effect of gravity during the imaging examinations may explain some of the discrepancy between our CT report and the previous ultrasound report. In our study, CT measurements were taken with the dog in ventral recumbency in 31/32 cases, whereas ultrasound was performed with the dog in right or left lateral recumbency in the previous study [
16]. Furthermore, in human medicine, ultrasonographically measured blood vessels diameters have been reported to differ depending on whether the patient is in a supine or prone position, or then changes to a standing position [
43]. However, differences in recumbency are unlikely to fully explain any inconsistency between CT and ultrasonography, and we need to consider other possible explanations.
Ultrasound and CT are different modalities, and there are a number of factors that may explain differences in the results obtained with each modality. In veterinary medicine, anesthetic procedures—which may reduce blood pressure—are common at the time of CT imaging, meaning that hypotension is a frequently reported complication in the perioperative period [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42]. By contrast, ultrasound examinations are often performed without anesthesia in dogs, which generally tolerate this procedure well. Measurement conditions are likely to differ with variation in the patient's recumbency during imaging, with or without anesthesia, and differences between measurement sites are possible, as shown by the significant differences in abdominal blood vessel diameters noted for the caudal and cranial measurement sites in this study. Furthermore, according to a report from human medicine, aortic measurements in cases of abdominal aortic aneurysms may differ between CT and ultrasonography [
30]. It is thus plausible that that discrepancies between our CT measurements and previous ultrasonographic measurements may reflect an issue with CT. However, other interpretations, which would allow for CT measurements accurately capturing vascular geometry in this study, are also worthy of consideration.
The abdominal aortic and caudal vena cava diameters reported here do not markedly differ from those reported in previous ultrasonographic studies [
32,
33,
34,
35,
36]. It is true that anesthesia is often used in CT imaging and can affect blood pressure; however, comparisons for the main evaluation endpoints (Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratio) in this study provide some cautionary evidence. Only Ao/CVC ratio showed a significant difference between anesthetized dogs (n=12) and unanesthetized dogs (n=20), whereas Ao/L1 ratio showed none. This suggests that only CVC may be affected by anesthesia, and that evaluation of blood vessels using CVC may be inappropriate [
44]. Differences in vessel diameters and Ao/CVC ratio between the different anatomical measurement sites were detectable in this study, which suggests that CT is sufficiently sensitive to changes in vascular geometry. Furthermore, in ultrasonography, the probe has to be pressed firmly against the body surface to visualize deeper blood vessels, which may result in overestimation of the vessel diameter. Hence, it is possible that our findings may reflect the fact that abdominal aortic diameter was not affected by hypertension in the dogs in this study population. However, the normal ranges of blood vessel diameters, and the response of vasculature to hypertension may vary between dog breeds, and further research in larger, more diverse study populations is needed to establish the generalizability of the results reported here.
The question of whether aortic enlargement is an indicator of hypertension remains somewhat controversial in human medicine. Systemic hypertension has been cited as a risk factor for the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms [
25], but other reports have suggested that the correlation is a weak one, relative to other factors [
5]. Factors having identified associations with aortic aneurysms include smoking, as the most significant risk factor [
45], as well as male gender, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.[
26] Interestingly, there are conflicting reports on the effects of antihypertensive treatment, with some studies suggesting that such treatments may arrest abdominal aortic dilatation [
46], and others that they do not [
47,
48,
49]. So, the issue appears unresolved in human medicine, and may be even more open in veterinary medicine, where abdominal aortic aneurysms or dissections are little reported [
22], and are currently considered to be only a rare complication in recent guidelines for the veterinary profession [
1]. Thus, it is possible that dogs with abdominal aortic aneurysm or its precursor lesions were evaluated in previous studies.
Considering reports on Ao/CVC ratio as a means of assessing fluid responsiveness in hospitalized dogs [
32,
33], it is important to guard against the possibility that hydration status may act as a confounder in these assessments. In this retrospective study, we were unable to establish the hydration status of each dog after the event. However, we established a new parameter, Ao/L1 ratio, to evaluate the ratio of the aorta to a structure with fixed dimensions unaffected by hydration level, and to the authors’ knowledge, this is the first report on the use of this parameter in canine medicine. The Ao/L1 ratio largely tracked the Ao/CVC ratio, in showing no difference between hypertensive and normotensive dogs, suggesting that hydration status had not affected the data in this study, and providing useful evidence for researchers who may consider using this parameter in the future. The single divergence between Ao/CVC and Ao/L1 ratios was shown in anesthetized versus unanesthetized dogs, which raises questions about the effect of anesthetics on the vena cava, as stated above.
In other evaluations, we found no sex difference in Ao/CVC or Ao/L1 ratio in this study, which suggests a contrast with human medicine, where male gender is regarded as a risk factor abdominal aortic aneurysm. We found significant differences in these ratios and vessel diameters between the anatomically different measurement sites, indicating that careful selection of a measurement site is required when comparing blood vessels dimensions using CT.
This study has several limitations. One concerns the relatively small sample size, especially for hypertensive dogs, which makes it difficult to exclude the possibility that “white-coat hypertension” syndrome may have affected the collected data. Additionally, in the majority of cases, it was difficult to establish the underlying disease causing hypertension, meaning that causal relationships could not be established and direct comparisons of patients with different diseases could not be made. Another important limitation concerns the fact that vessel diameters were only measured with CT in this study, and there was no simultaneous measurement using ultrasonography.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we found that abdominal aortic diameter as measured by CT appears not to be affected by systemic hypertension. This result is inconsistent with previous findings in similar studies using ultrasonography. Thus, we suggest that CT measurements of abdominal aortic dilation may not represent a viable approach for assessing cases of suspected systemic hypertension, either because CT as an imaging modality cannot capture such hypertension-related changes, or because aortic diameter is not affected by blood pressure in dogs. Consequently, there is a need for large-scale, simultaneous prospective studies with simultaneous CT and ultrasonographic measurements, to elucidate any potential utility, or the lack of utility, of these imaging modalities for blood pressure assessments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.I. and N.M.; methodology, Y.I. and K.Y.; validation, Y.I., K.Y. and N.M.; formal analysis, Y.I. and N.M..; investigation, Y.I.,K.Y. and N.M; data curation, Y.I.,K.Y. and N.M.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.I.; writing—review and editing, N.M.; visualization, Y.I. and K.Y.; supervision, N.M.; project administration, Y.I. and N.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because it did not involve any procedures with experimental animals. It was conducted in accordance with the research ethics bylaws of Kagoshima University. The owner of each dog evaluated in this study had given consent to the use of data in research at the time of medical examinations.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank all our colleagues at Kagoshima University Veterinary Teaching Hospital for their help in collecting CT images and providing medical care to our patients, our fellow researcher, Nobuhiro Nozaki, for helping with statistical analysis, and Henry Smith (Co-chair of the Veterinary Special Interest Group in the European Medical Writers Association) for helping with the English editing of a draft of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Acierno MJ, Brown S, Coleman AE, et al. ACVIM consensus statement: Guidelines for the identification, evaluation, and management of systemic hypertension in dogs and cats. J Vet Intern Med. 2018;32(6):1803-1822. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez AP, Del-Angel-Caraza J, Quijano-Hernández IA, Barbosa-Mireles MA. Obesity-hypertension and its relation to other diseases in dogs. Vet Res Commun. 2015;39(1):45-51. [CrossRef]
- Bodey, A.R. and Michell, A.R. (1996), Epidemiological study of blood Sressure in omestic dogs. Journal of Small Animal Practice, 37: 116-125. [CrossRef]
- Cortadellas O, del Palacio MJ, Bayón A, Albert A, Talavera J. Systemic hypertension in dogs with leishmaniasis: prevalence and clinical consequences. J Vet Intern Med. 2006;20(4):941-947. [CrossRef]
- O'Neill DG, Elliott J, Church DB, McGreevy PD, Thomson PC, Brodbelt DC. Chronic kidney disease in dogs in UK veterinary practices: prevalence, risk factors, and survival. J Vet Intern Med. 2013;27(4):814-821. [CrossRef]
- Buranakarl, C., Ankanaporn, K., Thammacharoen, S. et al. Relationships Between Degree of Azotaemia and Blood Pressure, Urinary Protein:Creatinine Ratio and Fractional Excretion of Electrolytes in Dogs with Renal Azotaemia. Vet Res Commun 31, 245–257 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Anderson LJ, Fisher EW. The blood pressure in canine interstitial nephritis. Res Vet Sci. 1968;9(4):304-313.
- Lien YH, Hsiang TY, Huang HP. Associations among systemic blood pressure, microalbuminuria and albuminuria in dogs affected with pituitary- and adrenal-dependent hyperadrenocorticism. Acta Vet Scand. 2010;52(1):61. Published 2010 Nov 12. [CrossRef]
- García San José P, Arenas Bermejo C, Clares Moral I, Cuesta Alvaro P, Pérez Alenza MD. Prevalence and risk factors associated with systemic hypertension in dogs with spontaneous hyperadrenocorticism [published correction appears in J Vet Intern Med. 2020 Nov;34(6):3167. doi:1111/jvim.15941]. J Vet Intern Med. 2020;34(5):1768-1778. [CrossRef]
- García San José P, Arenas Bermejo C, Alonso-Miguel D, Clares Moral I, Cuesta-Alvaro P, Pérez Alenza MD. Changes in systolic blood pressure in dogs with pituitary dependent hyperadrenocorticism during the first year of trilostane treatment. J Vet Intern Med. 2021;35(1):130-141. [CrossRef]
- García San José P, Pérez-Alenza MD, Alonso-Miguel D, González Sanz S, Arenas Bermejo C. Prevalence of Systemic Hypertension and Control of Systolic Blood Pressure in a Cohort of 14 Dogs with Adrenal-Dependent Hypercortisolism during the First Year of Trilostane Treatment or after Adrenalectomy. Animals (Basel). 2024;14(3):511. Published 2024 Feb 3. [CrossRef]
- Mazzi A, Fracassi F, Dondi F, Gentilini F, Famigli Bergamini P. Ratio of urinary protein to creatinine and albumin to creatinine in dogs with diabetes mellitus and hyperadrenocorticism. Vet Res Commun. 2008;32 Suppl 1:S299-S301. [CrossRef]
- Struble AL, Feldman EC, Nelson RW, Kass PH. Systemic hypertension and proteinuria in dogs with diabetes mellitus. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1998;213(6):822-825.
- Marynissen SJ, Smets PM, Ghys LF, et al. Long-term follow-up of renal function assessing serum cystatin C in dogs with diabetes mellitus or hyperadrenocorticism. Vet Clin Pathol. 2016;45(2):320-329. [CrossRef]
- Herring IP, Panciera DL, Werre SR. Longitudinal prevalence of hypertension, proteinuria, and retinopathy in dogs with spontaneous diabetes mellitus. J Vet Intern Med. 2014;28(2):488-495. [CrossRef]
- Holland M, Hudson J, Bao Y, Gaillard P. Aortic to caudal vena cava ratio measurements using abdominal ultrasound are increased in dogs with confirmed systemic hypertension. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2020;61(2):206-214. [CrossRef]
- Jacob F, Polzin DJ, Osborne CA, et al. Association between initial systolic blood pressure and risk of developing a uremic crisis or of dying in dogs with chronic renal failure. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2003;222(3):322-329. [CrossRef]
- Violette NP, Ledbetter EC. Punctate retinal hemorrhage and its relation to ocular and systemic disease in dogs: 83 cases. Vet Ophthalmol. 2018;21(3):233-239. [CrossRef]
- Violette NP, Ledbetter EC. Intracorneal stromal hemorrhage in dogs and its associations with ocular and systemic disease: 39 cases. Vet Ophthalmol. 2017;20(1):27-33. [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson K, Nordborg C, Johansson BB. The hemodynamic effect of bilateral carotid artery ligation and the morphometry of the main communicating circuit in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984;121(3):241-247. [CrossRef]
- Misbach C, Gouni V, Tissier R, et al. Echocardiographic and tissue Doppler imaging alterations associated with spontaneous canine systemic hypertension. J Vet Intern Med. 2011;25(5):1025-1035. [CrossRef]
- Waldrop JE, Stoneham AE, Tidwell AS, Jakowski RM, Rozanski EA, Rush JE. Aortic dissection associated with aortic aneurysms and posterior paresis in a dog. J Vet Intern Med. 2003;17(2):223-229.
- McGregor JC, Pollock JG, Anton HC. The Value of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. 1975;20(3). [CrossRef]
- Evans G, Stansby G, Hamilton G. Suggested standards for reporting on arterial aneurysms. 1992;15(2). [CrossRef]
- Sakalihasan N, Limet R, Defawe OD. Abdominal aortic aneurysm. Lancet. 2005;365(9470):1577-1589. [CrossRef]
- Cornuz J, Sidoti Pinto C, Tevaearai H, Egger M. Risk factors for asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysm: systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based screening studies. Eur J Public Health. 2004;14(4):343-349. [CrossRef]
- The Global and Regional Prevalence of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Modelling Analysis. 2022;Publish Ahead of Print. [CrossRef]
- .Zhou A, Leach JR, Zhu C, et al.. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms as a Potential Marker for Disease Progression. Published online February 6, 2023. [CrossRef]
- .Iwakoshi S, Hirai T, Kichikawa K. Updates on Ultrasonography Imaging in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. 2019;12(3). [CrossRef]
- Sprouse LR 2nd, Meier GH 3rd, Lesar CJ, et al. Comparison of abdominal aortic aneurysm diameter measurements obtained with ultrasound and computed tomography: Is there a difference?. J Vasc Surg. 2003;38(3):466-472. [CrossRef]
- Ashton HA, Gao L, Kim LG, Druce PS, Thompson SG, Scott RA. Fifteen-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial of ultrasonographic screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2007;94(6):696-701. [CrossRef]
- Combet-Curt J, Pouzot-Nevoret C, Cambournac M, et al. Ultrasonographic measurement of caudal vena cava to aorta ratio during fluid resuscitation of dogs with spontaneous circulatory shock. J Small Anim Pract. 2023;64(11):669-679. [CrossRef]
- Rabozzi R, Oricco S, Meneghini C, Bucci M, Franci P. Evaluation of the caudal vena cava diameter to abdominal aortic diameter ratio and the caudal vena cava respiratory collapsibility for predicting fluid responsiveness in a heterogeneous population of hospitalized conscious dogs. J Vet Med Sci. 2020;82(3):337-344. [CrossRef]
- Kwak J, Yoon H, Kim J, Kim M, Eom K. Ultrasonographic measurement of caudal vena cava to aorta ratios for determination of volume depletion in normal beagle dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2018;59(2):203-211. [CrossRef]
- Herreria-Bustillo VJ, Fitzgerald E, Humm KR. Caval-aortic ratio and caudal vena cava diameter in dogs before and after blood donation. J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2019;29(6):643-646. [CrossRef]
- Darnis E, Boysen S, Merveille AC, Desquilbet L, Chalhoub S, Gommeren K. Establishment of reference values of the caudal vena cava by fast-ultrasonography through different views in healthy dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2018;32(4):1308-1318. [CrossRef]
- Costa RS, Raisis AL, Hosgood G, Musk GC. Preoperative factors associated with hypotension in young anaesthetised dogs undergoing elective desexing. Aust Vet J. 2015;93(4):99-104. [CrossRef]
- Claeys MA, Gepts E, Camu F. Haemodynamic changes during anaesthesia induced and maintained with propofol. Br J Anaesth. 1988;60(1):3-9. [CrossRef]
- Bijker JB, van Klei WA, Kappen TH, van Wolfswinkel L, Moons KG, Kalkman CJ. Incidence of intraoperative hypotension as a function of the chosen definition: literature definitions applied to a retrospective cohort using automated data collection. Anesthesiology. 2007;107(2):213-220. [CrossRef]
- Flacke WE, Flacke JW, Bloor BC, McIntee DF, Sagan M. Effects of dexmedetomidine on systemic and coronary hemodynamics in the anesthetized dog. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1993;7(1):41-49. [CrossRef]
- Quinn CT. What is the best treatment for hypotension in healthy dogs during anaesthesia maintained with isoflurane?. Aust Vet J. 2024;102(5):264-273. [CrossRef]
- Grubb T, Sager J, Gaynor JS, et al. 2020 AAHA Anesthesia and Monitoring Guidelines for Dogs and Cats. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2020;56(2):59-82. [CrossRef]
- van Zandwijk JK, Simmering JA, Schuurmann RCL, et al. Position- and posture-dependent vascular imaging-a scoping review. Eur Radiol. 2024;34(4):2334-2351. [CrossRef]
- Meneghini C, Rabozzi R, Franci P. Correlation of the ratio of caudal vena cava diameter and aorta diameter with systolic pressure variation in anesthetized dogs. Am J Vet Res. 2016;77(2):137-143. [CrossRef]
- MacSweeney ST, Ellis M, Worrell PC, Greenhalgh RM, Powell JT. Smoking and growth rate of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Lancet. 1994;344(8923):651-652. [CrossRef]
- Gellatly C, Sweeting M, Emin A, et al. Influence of cardiometabolic medications on abdominal aortic aneurysm growth in the UK Aneurysm Growth Study: metformin and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors associated with slower aneurysm growth. Br J Surg. 2024;111(1):znad375. [CrossRef]
- Thomas Manapurathe D, Moxon JV, Krishna SM, et al. Cohort Study Examining the Association of Optimal Blood Pressure Control at Entry With Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:868889. Published 2022 May 3. [CrossRef]
- Golledge J, Pinchbeck J, Tomee SM, et al. Efficacy of Telmisartan to Slow Growth of Small Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(12):1374-1381. [CrossRef]
- Sweeting MJ, Thompson SG, Brown LC, Greenhalgh RM, Powell JT. Use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors is associated with increased growth rate of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52(1):1-4. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).