INTRODUCTION
The field of nanotechnology has shown great promise and has numerous applications in a variety of areas, such as electronics, environmental remediation, agriculture, and more (Sun et al., 2019). This technology has led to the development of nanomaterials characterized by the high surface area (1-100 nanometers) with unique properties making them attractive in various applications (Biomedicals, energy solar cell, cosmetics and environmental remediation) (Dimkpa, & Bindraban, 2018). Research has revealed that there are different types of nanomaterials, including carbon-based nanomaterials, composite nanomaterials, metal oxide nanoparticles, biological nanomaterials and metal oxide nanoparticles, to name a few (Tymoszuk, A., & Wojnarowicz. 2020).
Metal oxide nanoparticles have attracted significant attention recently due to their unique physicochemical properties and wide range application in various field (Ahmad et al., 2022). Amongst these metal oxide nanoparticles, Zinc oxide (ZnO-NPs) and Copper oxide nanocomposites (CuO-NPs) have gained significant attention due to their unique physicochemical properties, such as antimicrobial activity, photocatalytic behavior, oxidative potential and have shown promising results in agricultural and environmental contexts (Bhushan et al 2019) and (Rashid et al., 2020). Their synthesis and application have been recently studied. Studies have shown that the stoichiometric ratio of ZnO-NPs and CuO-NPs can significantly influence their physicochemical properties and consequently, their biological interactions (Faizan et al., 2020) and (Sangeetha et al., 2019). However, despite the tremendous application of these nanomaterials, there is growing concern about their potential impact on the environment and living organisms (Singh et al., 2019).
The onion (Allium cepa L.) is widely used as a bioindicator in environmental studies due to its sensitivity to pollutants, making it an ideal model for evaluating the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of nanomaterials (Leme et al., 2019). There are inadequate comprehensive studies on the cytotoxic effects of these nanomaterials on plants, especially at the cellular and genetic levels, which poses a significant gap in understanding their ecological implications (Fadholly et al., 2019). This study addresses the need for detailed research into the impact of the combined effect of CuO/ZnO nanocomposites on the growth and cellular integrity of Allium cepa L roots.
METHODOLOGY
The reagent used such as Hydrochloric acid, Acetic acid, Ethanol, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), Copper acetate dihydrate (Cu(CH3COO)2.2H2O), Zinc acetate dihydrate (Zn(CH3COO)2.2H2O and Thiobarbituric acid (TBA) were sourced from Department of Biochemistry laboratory Federal University, Otuoke, Bayelsa State. The Allium cepa L bulb was purchased from Otuoke market, Otuoke, Bayelsa state and taken to the laboratory for further analysis.
Synthesis of CuO Nanocomposites on Allium Cepa L
Analytically pure copper acetate dihydrate (Cu(CH3COO)2.2H2O) at 0.1M was dissolves in 100mL distilled water. The mixture was swirl constantly until the copper acetate is completely dissolved. Add 0.2M NaOH solution to the mixture dropwise, stirring vigorously and using a hot plate to keep the temperature between 60 to 70 oC for 2 hrs. The solution's pH was raised to 10 in order to guarantee full precipitate formation. The sample was Centrifuged at 4000 – 5000rpm for about 10 – 15 mins, the supernatant was discarded, the resulting CuO-NP precipitate was twice cleaned with distilled water and oven-dried at 80 oC for 12 hrs (Lung et al., 2021).
Synthesis of ZnO Nanocomposites on Allium Cepa L
0.1 mg of analytically pure Zinc acetate dihydrate (Zn(CH3COO)2.2H2O) was dissolved in 100ml distilled water. Using a magnetically stirrer the mixture continually stirred until the zinc acetate is completely dissolved. 0.2 M NaOH was added to the mixture was placed a hot plate, carefully stir the mixture while adding 0.2 NaOH solution dropwise. Keep the temperature between 60 and 70 oC. The solution's pH was raised to 10 in order to guarantee full precipitate formation. Centrifugation was used to collect the precipitate, which was produced, for 10 to 15 minutes at 4000-5000 rpm. After discarding the supernatant, the resultant ZnO-NP precipitate was twice cleaned with distilled water and oven-dried for 12 hrs at 80 oC (Das and Srivastava, 2017).
Preparation of ZnO/CuO50/50 Nanoparticles (1:1)
Dissolve of 0.05 M of analytically pure Zinc acetate dihydrate Zn(CH3COO)2.2H2O and 0.05 M copper acetate dihydrate Cu(CH3COO)2.5H2O in 100 mL distilled water stir the solution continuously with magnetic stirred until the zinc acetate is fully dissolved. To the solution add 0.2 NaOH solution drop wise and stir rigorously maintaining a temperature of 60-70oC using a hot plate 2 -3 h. The pH of the solution was adjusted 10 to ensure complete precipitate formation. The resulting precipitate was collected through centrifugation at 4000-5000 rpm for 10-15 min to collect CuO/ZnO NPs. The supernatant was discard and the CuO/ZnO precipitate was washed twice then oven dried at 80 oC 12 h (Hajji et al., 2023) and (Memon et al., 2020).
Characterization of Nanocomposite
The CuO, ZnO and CuO/ZnO nanocomposite was characterized using SEM and XRD. This is to ascertain the surface morphology, phase composition and crystallography of the nanoparticle (Sakib et al., 2019) and (Memon et al., 2020).
Cytological Study
A mixture of acetic acid: ethanol (1: 3) was prepared and 2 cm3 was measured into a screw top test tube containing 2.00g CuO treated Allium cepa L and allowed to stay for another 24 h at room temperature. The root of the Allium cepa L was stained with a mixture of 2% aceto-orcein and 1M HCl (9:1) and allowed for 4 h at room temperature. A drop of 45% acetic acid was added to single stained root tip and squashed on a glass slide. The resulting sample was observed under Olympus microscope. Digital image was taken for further analysis of different anomalies of the chromosomes and cell division stages (Ahmed et al., 2018). Same procedure was repeated for ZnO and ZnO/CuO treated Alllium cepa L respectively.
Mitotic Index Analysis and Chromosome Abbrration Assay
Four Allium cepa root samples treated with various concentrations of ZnO, CuO and ZnO/CuO NPs were considered. About 300 cells were taken into consideration and the mean was taken from four slides (Ahmed et al., 2018) and (Baskar et al., 2018).
The mitotic index was calculated using the formular
SOD Assay
The SOD assay of the root samples of different treatments was investigated using Das et al., (2000). 1.4 mL of the reaction mixture which includes 1.1 mL of 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.4, 0.04 mL of 1% Triton-X 100, 0.075 mL of 20 mM L-methionine, 0.1 mL of 50 mM EDTA and 0.075 mL of 10 mM hydroxylamine hydrochloride were added to 100 µL of the sample extract and incubated at 30°C for 5 min. Finally, 80 µL of 50 M ribo-flavin was added and the tubes were exposed to 200 W fluorescent lamps for 10 min. 1 mL of Greiss reagent was added and the absorbance of the colored sample was measured at 543 nm (Das and Srivastava, 2017).
Lipid Peroxidation
This was carried out as per Heath and Packer (1968), by measuring the amount of MDA formed due to Thiobarbituric acid (TBA) reaction. 0.5g of root samples were powdered using a mortar and pestle. 5mL of 1% TCA (10 mL g-1 F.W.) was added to it and then centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 min. 1 mL of supernatant was taken in a separate test tube and 4 mL of 0.5% TBA was added and heated to 95°C for 30 min. It was then cooled in ice-cold water and again centrifuged at 5,000 rpm for 5 min. Absorbance was measured at 532 nm in a spectrophotometer. 1% TBA in 20% TCA was taken as blank (Deng et al,. 2016). Finally, MDA content was calculated using an extinction coefficient of 155 mM cm-1 and the results were expressed in µmol MDA g-1 fresh weight.
RESULT
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
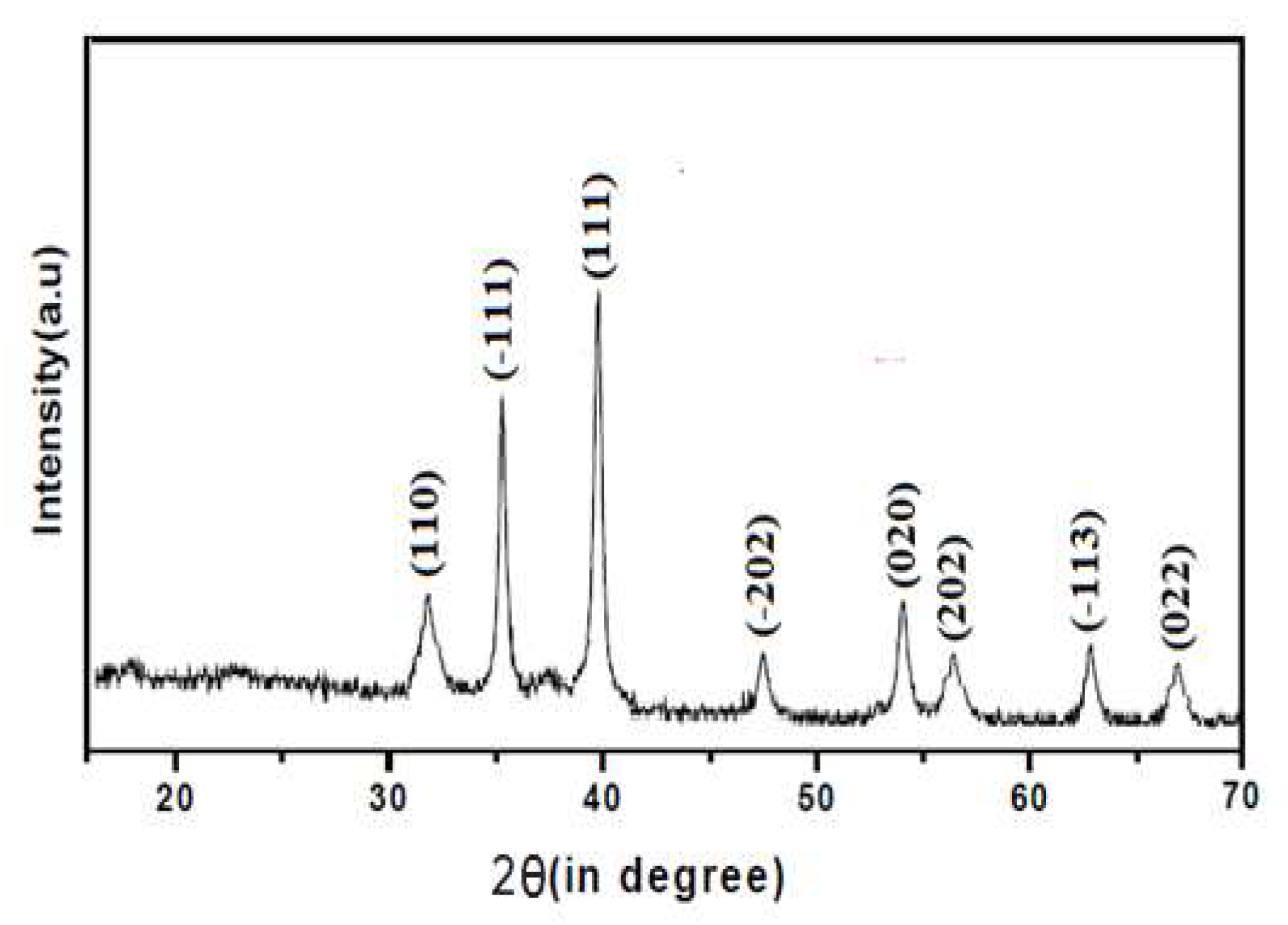
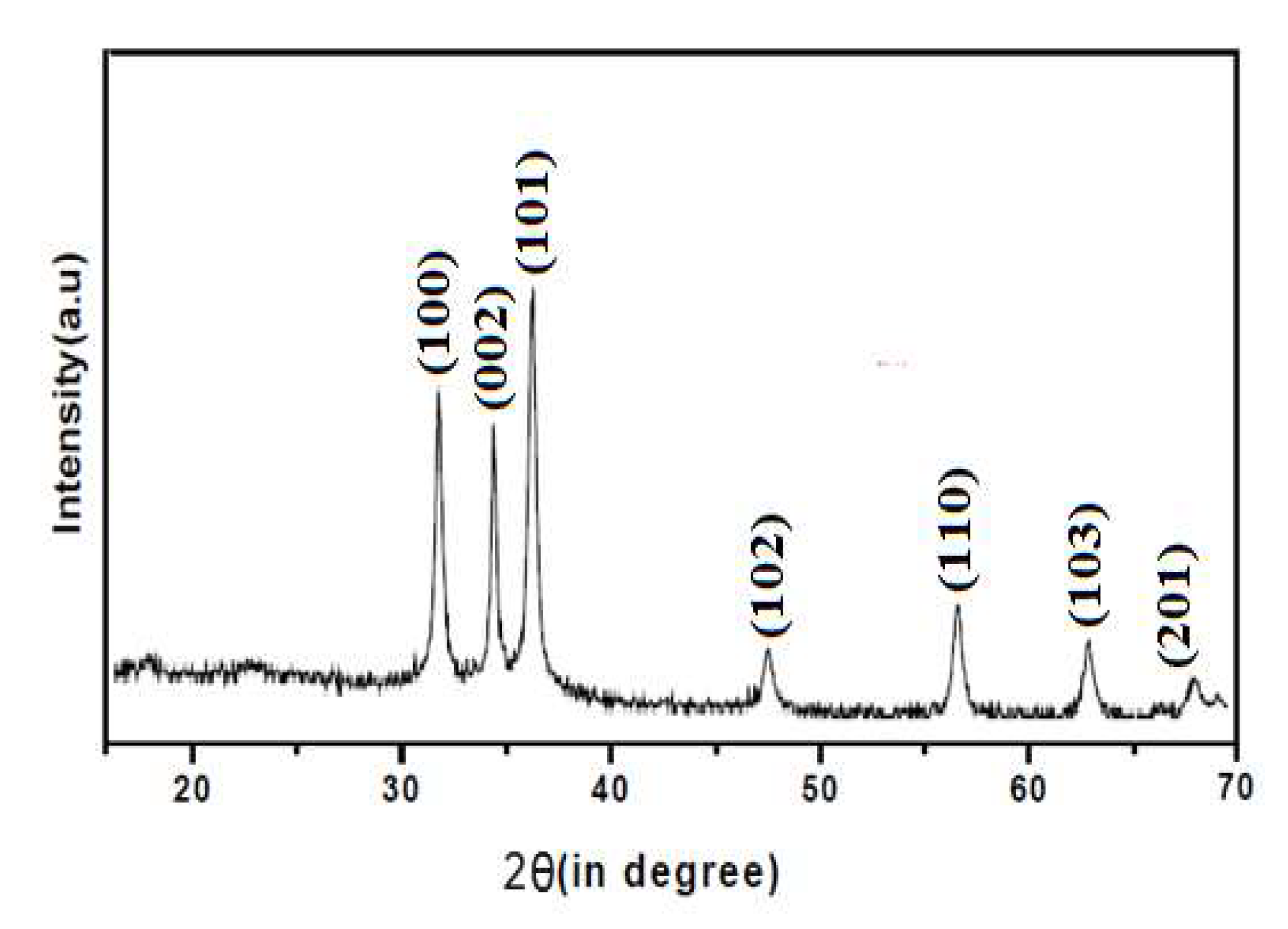
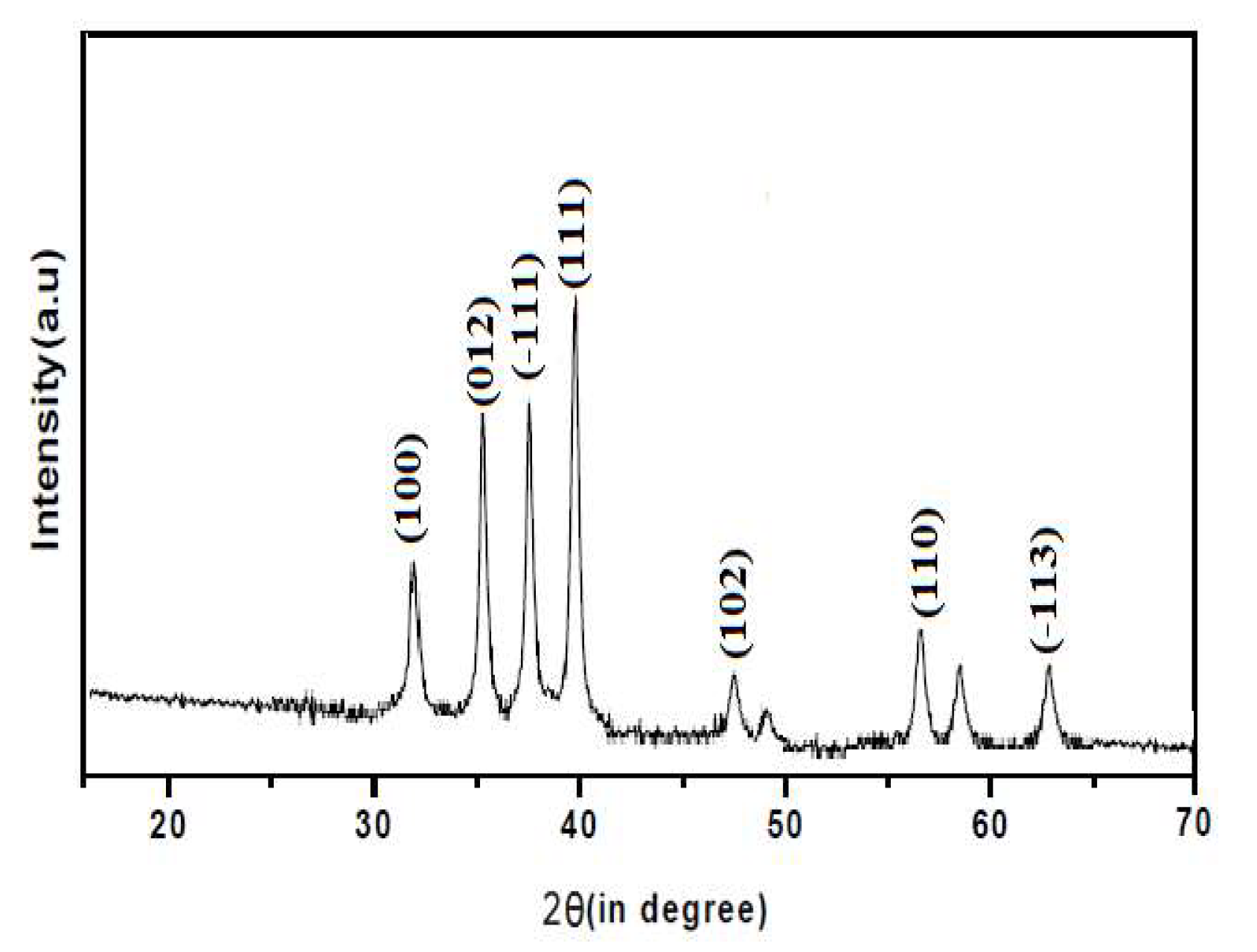
The synthesized CuO, ZnO and CuO/ZnO nanoparticles were confirmed by the characteristic peaks observed in the XRD images seen in
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 respectively. All the peaks were hexagonal and approximately close to the data report by (Kumari
et al., 2017). Diffraction lines were observed at 2θ angle which shows sharp peaks 36.20
o and 38.50
0 for CuO-NP indexed at -111 and 111 respectively, sharp peaks at angle 32.50
o and 37.05
o for ZnO-NPs indexed at 100 and 101 respectively while sharp peaks at angle 32.50
o, 35.50
o, 35.75
o and 39.50
o for CuO/ZnO-NPs indexed at 100, 012, -111 and 111 respectively. The average estimated particle size of CuO was 12.87nm, for ZnO was 13.76nm and for CuO/ZnO-NPs was 13.35nm as estimated using Scherer equation (Bokuniaeva & Vorokh. 2019). The data obtain from the synthesis of CuO-NPs and ZnO-NPs reveals an approximate similarity in the peak obtained with the result from the studies by Morales-Mendoza et al. (2022).
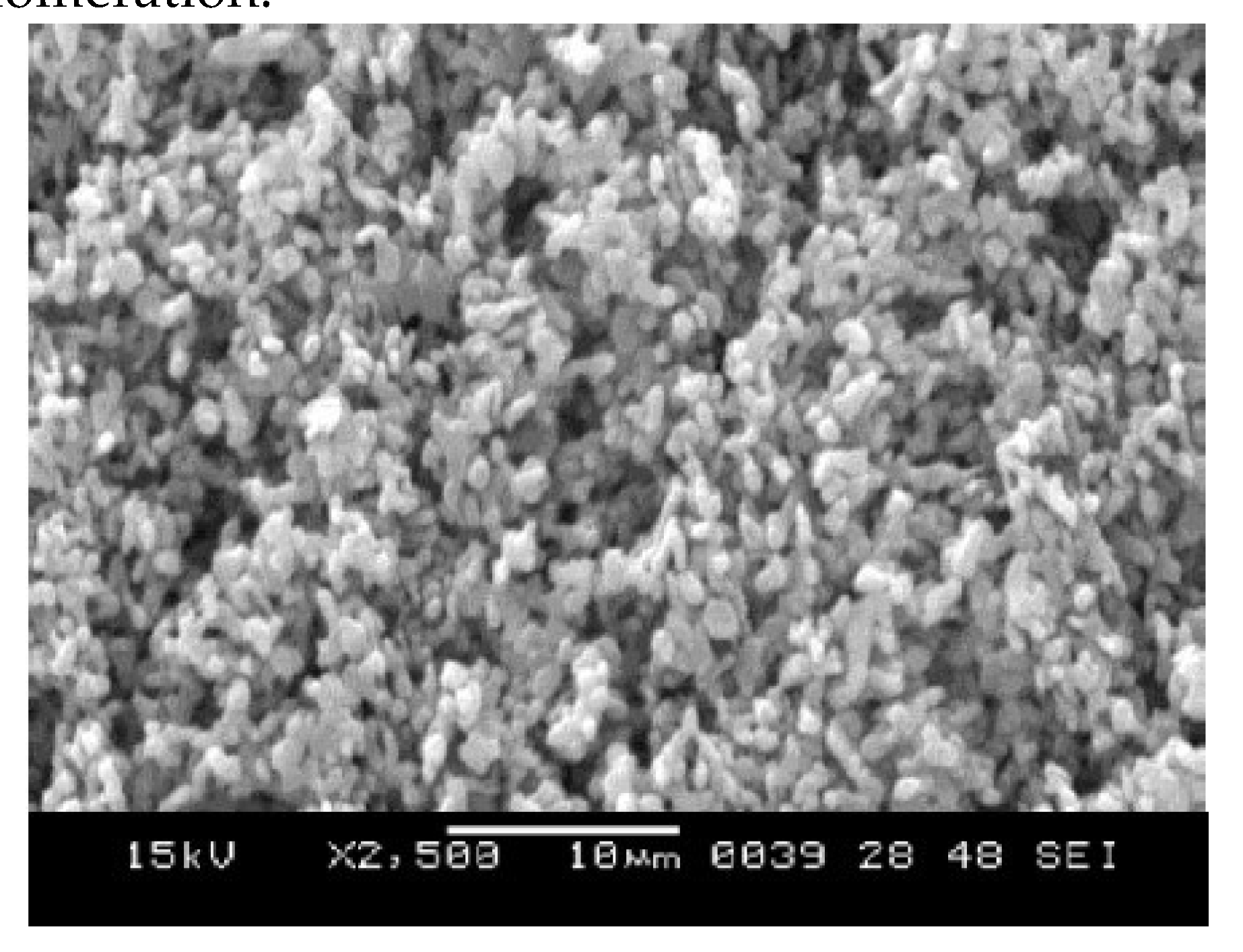
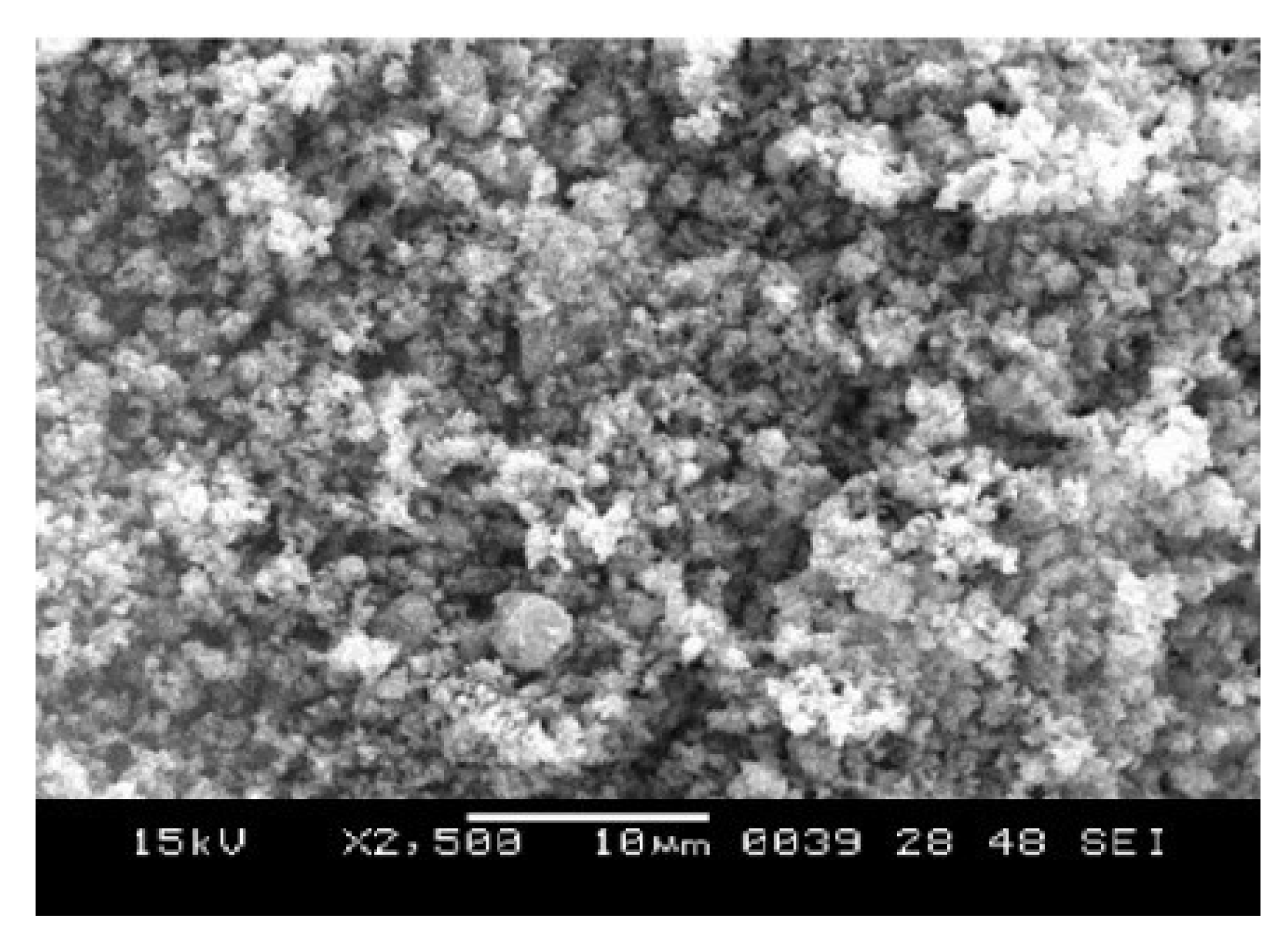
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
The SEM micrograph of CuO, ZnO and CuO/ZnO synthesized nanoparticle respectively are revealed in
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5 respectively. The SEM image of CuO synthesized nanoparticle gives a clear image of highly densed packed structure of CuO nanoparticle with an irregular and granular morphology. The granular structure suggest that CuO nanoparticle may not have uniform shape possibly ranging from spherical to irregular form. The SEM image also showed agglomeration and cluster of the CuO-NP rather than being well dispersed. This information is similar to the study reported by was reported by Wang
et al., (2020).
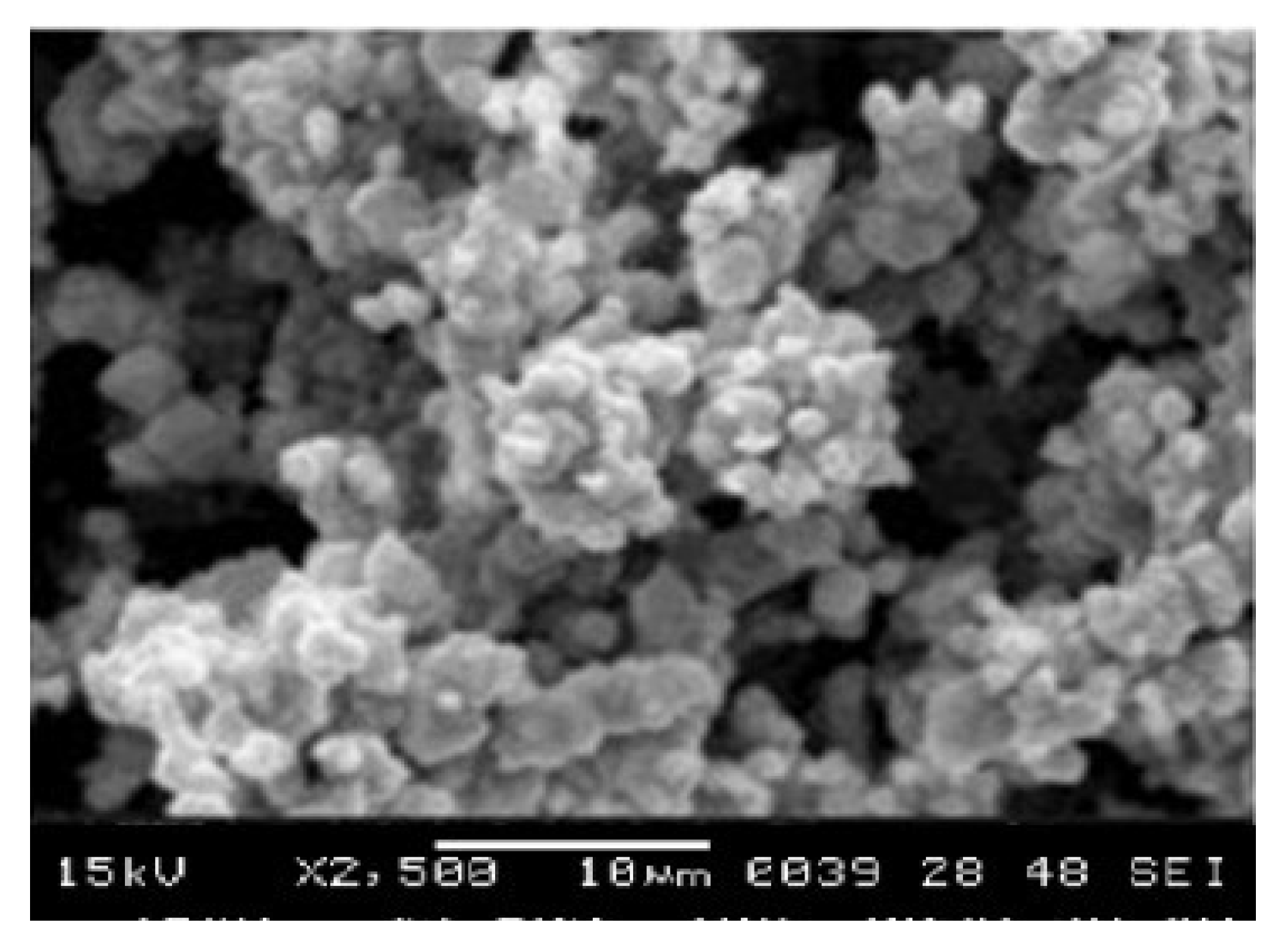
The SEM image of synthesized ZnO nanopartiles reveals densely packed structure with irregular and granular morphology which suggest the nanoparticle may not have a well defined shape. The SEM image also reveals a degree of agglomeration with the ZnO nanoparticle clustering together. Similar SEM image was report by Pandey and Kumar (2018). Their study suggested that the agglomeration may be due to use of insufficient surfactant or stabilizing agent during synthesis.
The SEM image of CuO/ZnO synthesized nanoparticle reveals a cauliflower like morphology which suggest that the synthesis process may have led to hierarchical structure formation of the nanoparticle. Similar study was reported by Morales-Mendoza et al. (2023). The image also revealed the CuO/ZnO nanoparticles (CuO/ZnO-NPs) are tightly packed which suggest significant agglomeration.
Cytotoxicity Study
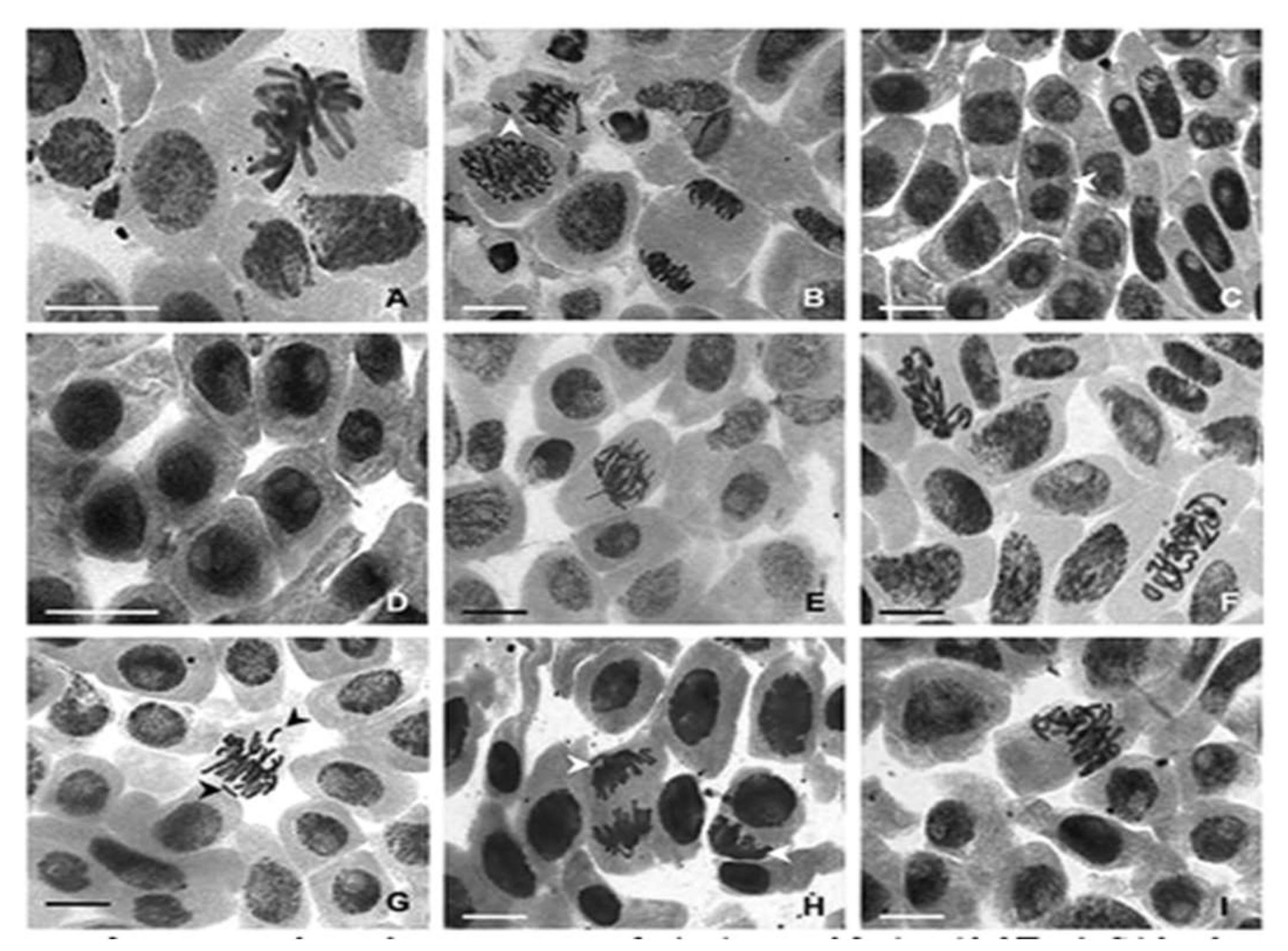
Figure 7 shows the chromosomal aberration of nanocomposite treated
Allium cepe L. Image A reveals normal metaphase where cell are aligned at the metaphase plate. Image B reveals lagging resulting in anueloidy, which suggest abnormal chromosome numbers. Image C reveals the cell shows chromosome stickiness possibly due to toxic effect of the nanoparticle. Image D reveals disorganized chromosomes possibly suggesting chromosome condensation. Image E shows no noticeable aberration. Image F shows abnormal condensation of chromosomes which may be due to high concentration of the nanoparticle. Image G reveals chromosomal bridge during anaphase suggesting chromosome are incorrectly connested. Image H reveals an early anaphase separation and division of the nuclear material. Image I reveals chromosomes separation from each set of chromosomes. Oscar
et al., 2023 reported similar result in their studied of the toxicological effects of pure and amine-functionalized ZnO nanorods on Daphnia magna and Lactuca sativa.
Chromosomal Aberration
Table 1, 2 and 3 showed the native
Allium cepa L root tip exhibit no chromosomal aberration as the number of separating cell was recorded at 107, while the laggard, stickness and abnormality percentage showed no effect. However at 100v/v CuO-NP, ZnO-NPs and CuO/ZnO-NP concentration, the number of cell separation reduced to 14, 19 and 21 respectively, while the laggard value was 4, 3 and 5 respectively, the stickiness value was record at 7, 9 and 11 while the abnormality concentration values were 72.50%, 69.10% and 72.50% respectively indicating some chromosomal mutilation. At 80v/v CuO-NP, ZnO-NPs and CuO/ZnO-NPs concentration the number of cell division reduced to 36, 31 and 38 respectively, while the laggard value was recorded at 11, 14 and 19 respectively, the stickiness value was 21, 19 and 24 while the abnormality concentration was calculated to be 56.20%, 61.20% and 74.25% respectively suggesting several chromosomal damage. At 40v/v CuO-NP, ZnO-NPs and CuO/ZnO-NP concentration the number of cell division reduced to 71, 79 and 82 respectively, while the laggard cells was 18, 17 and 23 respectively, the stickiness value was 17, 21 and 22 while the abnormality concentration values were 51.50%, 54.50% and 53.10% respectively. At 20v/v CuO-NP, ZnO-NPs and CuO/ZnO-NP concentration the number of cell division increased to 91, 102 and 122 respectively, while the laggard cells was 11, 21 and 32 respectively, the stickiness was 7, 9 and 17 while the abnormality percentage values is 17.60%, 21.00% and 22.16% respectively. The data indicate a dose dependant relationship between the concentration of nanocomposite and the occurrence of chromosomal aberrations. Approximately similar result was reported in the study by Ganyata et al. (2020) and Sabeen
et al., (2020).
The
Table 1,
Table 2 and
Table 3 Shows the effect of expose of
Allium cepa L to various concentration of CuO-NPs, ZnO-NPs and CuO/ZnO-NPs respectively
Mitotic Index Analysis
Table 4 shows the mitotic index analysis of
Allium cepa L root tissue. The mitotic index measure the cell population undergoing mitosis. The table shows a decrease in mitotic index for Sample X from 9.090 at 100v/v concentration to 7.692 at 20v/v concentration. It also shows that ZnO-NP induced the highest cell division at 80v/v concentration (12). Similarly, the mitotic indexes for sample Y decrease with varying conc. with a peak at 80v/v concentration (15.167) and lowest at 20v/v concentration (9.677). Sample Z showed a fluctuation in the mitotic index, with a peak 17.697 at 80 v/v concentration which indicates that this concentration promotes the highest cell division for sample Z.
Table 4 reveals the Mitotic Index Analysis of Allium Cepa Root Tissue
SOD Assay for CuO, ZnO and CuO/ZnO Treated Allium CEPA L ROOT TIPS
The SOD assay measures the activity of the enzyme superoxide dismutase, which play a significant role in protecting the cells from oxidative damage by catalyzing the dismutation of superoxide radicals into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide.
Table 5 reveals that SOD activity in the control group is 3.50. This value signifies that natural SOD activity level in the native
Allium cepa L root tissue. Any increase or decrease in the SOD activity typically indicates the nanoparticle effect on oxidative stress and cellular defense response.
Table 5 also reveals that sample A at 100v/v CuO-NPs concentration, The SOD activity is 2.20 which is lower than the control. This implies that at full concentration, CuO-NPs reduces oxidative stress resulting in lower SOD activity. At 80v/v CuO-NP concentration on sample A, the SOD activity increase to 2.4 which is lower than the control. This result signifies a reduced trend in oxidative stress. At 40v/v CuO-NP concentration in sample A, the SOD activity increase to 3.40 close to the control. This implies oxidative stress is being induced by the CuO-NP on the plant cell. At 20v/v concentration, the SOD activity increased to 3.90 which implies that at low CuO-NP concentration, there is increased induced stress on the plane cell.
Similarly,
Table 5 also shows that at 100v/v ZnO-NP concentration, the SOD activity in sample B is 2.80. This suggests a reduced oxidative stress at full concentration. At 80v/v ZnO-NP concentration on sample B, the SOD activity increased to 3.60 suggesting increased induced stress or enzyme inhibition. At 40v/v ZnO-NP concentration in sample B, the SOD activity increased to 4.00. This trend suggests an increased induced oxidative stress with decrease in ZnO-NP concentration.
Finally,
Table 5 revealed that at 100v/v CuO/ZnO-NP concentration in sample C, the SOD activity is 2.60. This suggests that the nanocomposite reduces oxidative stress on the plant cell at full concentration. At 80v/v CuO/ZnO-NP a slight increase in the SOD activity (2.80) was identified however lower than the control. This shows that the composite begins to induce more stress as concentration decreases. At 40v/v and 20v/v CuO/ZnO-NP concentrantion in sample C respectively, the composite induced the most oxidative stress of 4.00 and 4.50 repectively leading to the maximum upregulation of SOD activity. Similarly, a concentration dependent effect was also reported in a study by Shi and Huang. (2023)
Lipid Peroxidation
The MDA assay measures lipid peroxidation which indicates oxidative stress in cells. Higher MDA levels suggest higher oxidative stress, leading to damaged cell.
Table 6 reveals the MDA assay analysis of
Allium cepa L root tissue. The table showed that the MDA level in the control sample (Native
Allium cepa L) is 1.2 nmol/g. This value shows the natural level of lipid peroxidation without any nanoparticle treatment. However, an increase or decrease in the MDA level indicates the effect of the nanoparticle on oxidative stress on the
Allium cepa L plant cell.
The table 6 also revealed that at 100v/v concentration of sample X, the MDA level is 0.8 which is lower than the control, indicating a protective effect against oxidative stress. Similarly, at 80v/v and 40v/v the MDA level (1.00) is identical and lower than the control. While at lower concentration 20v/v the MDA level is 1.2 which is similar to the control, which indicates similar oxidative damage as seen in control.
The table 6 further revealed that at 100v/v concentration of sample Y, MDA level is 1.0, which is slightly lower than the control, offering some protection against oxidative stress. At 80v/v concentration, the MDA level decrease to 0.8, which indicates a stronger protective effect than 100v/v. While at 40v/v and 20v/v concentration respectively, the MDA level is 0.9 which is still below the control but higher then at 80v/v concentration (0.8). This suggests that 80v/v sample Y concentration offers the optimum protection against oxidative stress. This means that further decrease in the concentration will diminish the protective effect.
The table 6 finally showed that at 100% concentration of sample Z, the MDA level is 1.10, which is lower than the control but higher than sample X and Y. At 80v/v concentration, the MDA level is 1.3, which is higher than the control. This indicates that the composite induces oxidative stress which suggests that the composite interacts in a way that exacerbates lipid peroxidative. At 40v/v concentration, the MDA level decreased to 0.85, again below the control level. Similarly, at 20v/v the MDA level is 1.0 which is below the control. This result shows that the MDA level is optimum at 40v/v sample Z concentration (0.85). Approximately similar information was reported by Gantayatvet al., (2020) where they studied the oxidative damage of iron nanoparticle on Allium cepa L root meristems.
CONCLUSIONS
The SEM images of the synthesized CuO-NPs and ZnO-NPs appeared to have irregular, and granular particle shapes. The image appear to have irregular particle sizes and affirmed by the XDR average particle size of 12.78nm and 13.76nm. The synthesized CuO/ZnO-NPs revealed a flower like shape with an average particle size of 13.35nm as estimated from the XRD analysis. The chromosomal aberration of the untreat Allium cepa L showed the several phase of cell division (Porphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase), however the nanoparticle treat Allium cepa L root sample exhibit chromosomal anomalies which suggest the effect of nanocomposite in retarding Allium cepa L chromosome division and multiplication. The study also suggest that at higher concentration (100v/v and 80v/v) CuO/ZnO-NPs exhibited higher chromosomal damage as indicated by the higher abnormality percentage of 81.10% and 74.25% respectively with reduced number of cell division of 21% and 38% respectively. The study suggests that different concentration have varying effects on the mitotic activities of Allium cepa L root cell. Sample Y and Z responded similarly, with peak activity (17.697) at 40v/v. The lowest concentrations (20v/v) exhibited the reduced mitotic activities across all sample.
References
- Ahmad, A. , Hashmi, S. S., Palma, J. M., & Corpas, F. J. Influence of metallic, metallic oxide, and organic nanoparticles on plant physiology. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, B. , Shahid, M., Khan, M. S., &Musarrat, J. Chromosomal aberrations, cell suppression and oxidative stress generation induced by metal oxide nanoparticles in onion (Allium cepa) bulb. Metallomics 2018, 10, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baskar, V. , Nayeem, S., Kuppuraj, S. P., Muthu, T., &Ramalingam, S. Assessment of the effects of metal oxide nanoparticles on the growth, physiology and metabolic responses in in vitro grown eggplant (Solanummelongena). 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bhushan, B. , Pal, A. K., Narang, J., & Kumar, R. A comprehensive review of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their applications in agriculture. Journal of Nanotechnology 2019, 18, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokuniaeva, A. O. , & Vorokh, A. S. (2019, December). Estimation of particle size using the Debye equation and the Scherrer formula for polyphasic TiO2 powder. In journal of physics: Conference series (Vol. 1410, No. 1, p. 012057). IOP Publishing.
- Das, S. , & Srivastava, V. C. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO/CuOnanocomposite by electrochemical method. materials science in semiconductor processing 2017, 57, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F. , Wang, S., & Xin, H. Toxicity of CuO nanoparticles to structure and metabolic activity of Allium cepa root tips. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 2016, 97, 702–708. [Google Scholar]
- Dimkpa, C. O. , &Bindraban, P. S. Nanofertilizers: new products for the industry? Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2018, 66, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar]
- Fadholly, A. , Ansori, A. N., Jayanti, S., Proboningrat, A., Kusala, M. K., Putri, N., & Sudjarwo, S. A. Cytotoxic effect of Allium cepa L. extract on human colon cancer (WiDr) cells: in vitro study. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 2019, 12, 3483–3486. [Google Scholar]
- Faizan, M. , Hayat, S., &Pichtel, J. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on crop plants: A perspective analysis. Sustainable agriculture reviews 41: nanotechnology for plant growth and development 2020, 83-99.
- Gantayat, S. , Nayak, S. P., Badamali, S. K., Pradhan, C., & Das, A. B. Analysis on cytotoxicity and oxidative damage of iron nano-composite on Allium cepa L. root meristems. Cytologia 2020, 85, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Hajji, M. , Ajili, M., Jebbari, N., & Kamoun, N. T. Photocatalytic performance and solar cell applications of coupled semiconductor CuO–ZnO sprayed thin films: Coupling effect between oxides. Optical Materials 2023, 140, 113798. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, M. , Khan, S. S., Pakrashi, S., Mukherjee, A., & Chandrasekaran, N. Cytogenetic and genotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on root cells of Allium cepa. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2017, 190, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, D. M. , & Marin-Morales, M. A. Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: A review on its application. Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research 2019, 682, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, I. , Opriş, O., Soran, M. L., Culicov, O., Ciorîță, A., Stegarescu, A.,...&Pârvu, M. The impact assessment of CuO nanoparticles on the composition and ultrastructure of Triticumaestivum L. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 6739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Memon, S. A. , Xu, L., Wang, H., & Xu, J. Synthesis, characterization, and application of ZnO/CuO nanocomposites. Materials 2020, 13, 1385. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Mendoza, J. E. , Herrera-Pérez, G., Fuentes-Cobas, L., Hermida-Montero, L. A., Pariona, N., & Paraguay-Delgado, F. Synthesis, structural and optical properties of Cu doped ZnO and CuO–ZnO composite nanoparticles. Nano-Structures &Nano-Objects 2023, 34, 100967. [Google Scholar]
- Oscar, B. V. C. , Melegari, S. P., Vicentini, D. S., Simioni, C., Ouriques, L. C., Puerari, R. C., & Matias, W. G. Toxicological effects of pure and amine-functionalized ZnO nanorods on Daphnia magna and Lactuca sativa. Environmental Science: Nano 2023, 10, 1190–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, P. , & Kumar, S. Genotoxicity assessment of zinc oxide nanoparticles usingAlliumcepa assay. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2018, 25, 8893–8902. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M. , Bhattacharjee, R., & Dutta, P. Synthesis, characterization, and applications of ZnO-CuOnanocomposites: A review. Materials Today Chemistry 2020, 18, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeen, M. , Mahmood, Q., Bhatti, Z. A., Irshad, M., Bilal, M., Hayat, M. T., & Shahid, N. Allium cepa assay based comparative study of selected vegetables and the chromosomal aberrations due to heavy metal accumulation. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2020, 27, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Sakib, A. A. M. , Masum, S. M., Hoinkis, J., Islam, R., & Molla, M. A. I. Synthesis of CuO/ZnO nanocomposites and their application in photodegradation of toxic textile dye. Journal of Composites Science 2019, 3, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Sangeetha, J. , Saraswathi, R., &Arumugam, P. Influence of ZnO-CuOnanocompositeon growth, yield and quality of Abelmoschusesculentus (L.) Moench. Applied Nanoscience 2019, 6, 365–375. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y. , & Huang, Y. (2023). Physiological, biochemical, and molecular performance of crop plants exposed to metal-oxide nanoparticles. In Engineered nanomaterials for sustainable agricultural production, soil improvement and stress management (pp. 25-69). Academic Press.
- Singh, R. , Kumar, A., & Singh, N. Nanotechnology for enhancing food security in India: Opportunities, challenges, and policy concerns. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2019, 16, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z. , Xiong, T., Zhang, T., Wang, N., Chen, D., & Li, S. Influences of zinc oxide nanoparticles on Allium cepa root cells and the primary cause of phytotoxicity. Ecotoxicology 2019, 28, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tymoszuk, A. , & Wojnarowicz, J. Zinc oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles impact on in vitro germination and seedling growth in Allium cepa L. Materials 2020, 13, 2784. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. , Ren, Y., He, J., Zhang, L., Wang, X., & Cui, Z. Impact of copper oxide nanoparticles on the germination, seedling growth, and physiological responses in Brassica pekinensis L. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2020, 27, 31505–31515. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).