1. Introduction
According to recent reports by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), as of 2023, 56% of the global population, approximately 4.4 billion people, reside in urban areas. This percentage is projected to rise to nearly 70% by 2050, placing enormous pressure on effective policies to ensure sustainable urban development
[1]. To ensure sustainable urban development, it is crucial to implement effective policies and utilize advanced information and communications technologies as demands on urban governance and decision-making increase. Urban data is an indispensable fundamental component for achieving urban informatization and governance
[2]. By integrating Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Building Information Modeling (BIM), Internet of Things (IoT), and other data that describe the physical environment and dynamic characteristics of the city into a unified smart city platform, it is possible to ensures that insights are gleaned from both macro-level urban planning down to micro-level neighbourhood specifics, facilitating a comprehensive grasp of the city's operational landscape
[3,4]. Data aggregated on urban platforms has become an indispensable feature for managing various aspects of urban life, facilitating improved service delivery, resource allocation, and overall urban resilience
[5].
However, the multidisciplinary nature of urban data presents formidable challenges to effective urban governance. Each industry sector imposes its own data schemas, often resulting in compartmentalized data silos. For example, the construction industry primarily focuses on the data management of the entire lifecycle of building projects, while GIS concentrate on the acquisition, storage, analysis, and visualization of spatial data. Simultaneously, IoT devices generate vast amounts of dynamic data in real-time, which are used to monitor and optimize urban infrastructure and public services. Different departments and regions have also developed data standards tailored to specific application contexts, such as City Information Modeling (CIM) [
6], the 3D Realistic Geospatial Scene in China
[7], and the Digital Twin City framework
[8]. Despite being based on GIS data forms and related to cities, these data standards have different domain-specific requirements, and failed to express a unified data structure. Consequently, heterogeneous data formats and diverse standards hinder urban data integration, impeding comprehensive analysis and decision-making
[9]. While significant progress has been made in data integration
[10,11], current studies mainly focus on the specific scenario application of the conversion of different data formats. These methods often lack reusability for new application scenarios and struggle to extract the complex semantics within heterogeneous data. Fundamentally, they did not use urban entities as the core unit of management, making it difficult to construct relationships between entities. Additionally, the format conversion and knowledge modeling of fixed urban data for specific scenarios often require substantial manual effort, which is inefficient and prone to errors. In light of these challenges, establishing an object-oriented knowledge-sharing infrastructure is essential for advancing urban data management and governance.
One method for building bridges between multi-source heterogeneous data is Semantic Web technology. As endorsed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), this technology holds significant promise for facilitating interoperability and the integrated management of spatial semantic information
[12]. In the semantic web paradigm, an object-oriented approach is often used to formalize the concepts and relationships of the real world or specific domains. This is achieved through nodes, properties, and their interconnected edges, collectively referred to as ontology. In urban governance, abstracting multi-source heterogeneous data into urban entities serves as a foundational framework for data integration. This enhances inter-industry collaboration and knowledge sharing within the urban environment
[13]. Ding
[14] described the potential of Semantic Web technology for integrating heterogeneous urban geographic data represented by City Geography Markup Language (CityGML) and OpenStreetMap, and highlighted the value of extending these technologies to other geospatial domains in the future.
This study presents an innovative ontology framework designed for data fusion and urban governance applications, ensuring compatibility with diverse data standards while maintaining the integrity of semantic information. Our principal contributions are threefold: (1) We introduce a scalable ontology framework capable of integrating a variety of data types through the incorporation of components such as the entity, property, and relationship, addressing the critical need for effective data fusion in urban management. (2) We detail a comprehensive design methodology for SMOF components, which is anchored in urban data standards. This ensures an alignment with the data requirements of smart cities, highlighting the importance of standardized data management practices in urban governance. (3) We investigate the practicality and scalability of SMOF through a case study, which underscores the framework's capabilities in knowledge representation and semantic querying, demonstrating its potential to enhance data management and decision-making processes.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 reviews relevant studies on smart city data governance and ontology construction.
Section 3 details the study’s workflow, describing knowledge sources, expression model, construction method, and the basic principles of SMOF.
Section 4 elaborates on the core components in SMOF and examines specific scenarios to verify its usability. Finally, we conclude the paper.
2. Related Work
This study focuses on constructing an ontology-based framework for data integration and governance applications in urban platforms. Relevant aspects of previous research are reviewed in this section
2.1. Data Integration in Smart City
Data integration, a critical component of soft infrastructure, is pivotal for fostering collaborative knowledge development across urban areas [
15]. However, as underscored by Liu [
16], there exists a considerable challenge in the distillation of meaningful insights from the extensive and heterogeneous datasets amassed within the context of data-driven smart cities.
Within the framework of urban governance, a multitude of heterogeneous data sources coexist. Despite the common practice of managing these datasets in isolation [
17], their unified integration is instrumental in achieving a holistic depiction of spatial information, encompassing both indoor and outdoor environments, as well as static and dynamic elements. To achieve the integration of natural resource data and building engineering data that constitute the physical environment of a city, it is often necessary to build bridges between these two types of data. Scholars have conducted research from different perspectives, including the spatial location, geometric description, and domain-specific attributes of heterogeneous data in the fields of GIS and BIM [
18].
In terms of geometric transformation and representation, Zhu [
19] integrated geometric semantics with computer graphics to convert Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) into popular GIS shapefile formats. This method has become mainstream for format conversion but does not explore the complex semantic depth of the data, limiting its potential to enhance urban management and decision-making processes. Ji [
20] implemented the conversion of geometry, semantics, and coordinates between BIM and GIS formats from the perspective of extending related standards, based on ontology technology, and achieved basic semantic applications. In the study of integrating the physical environment of cities with dynamic data, Cheng [
21] proposed a data-centric predictive maintenance framework leveraging BIM and IoT technologies. This framework features an information layer for integrating diverse datasets and an application layer to support predictive maintenance.
Liu explored various data integration solutions for smart cities, including new standards, models, and semantic web technologies [
22]. Their findings indicate that semantic web technologies are particularly effective for integrating urban data resources due to their ability to manage complex data relationships and semantics. Shi [
23] investigated techniques for data integration, such as format conversion using IFC and CityGML, data standard extensions, and ontology-based methods. They observed that while format conversion and standard extensions require extensive manual work, ontology-based approaches provide a more accurate representation of users' conceptual understanding of the real world. These methods are advantageous as they provide a structured means to represent and reason about the complexities inherent in urban data.
In conclusion, adopting holistic and scalable methods for integrating diverse data sources is essential for urban platforms [
24]. Ontology-based approaches effectively harmonize disparate datasets, ensuring robust data storage and connectivity crucial for urban governance.
2.2. Ontology in smart city
Karabulut [
25] have noted that ontologies, with their formal structure, reasoning capabilities, and extensibility, are deemed superior to other knowledge management systems. In the realm of urban studies and the integration of heterogeneous data, ontologies have demonstrated significant utility. Ma [
26] have taken strides by transforming data from OpenStreetMap into urban objects and introducing a semantic connector to foster the establishment of spatial relationships between these objects. Ding [
14,
27] conducted studies on CityGML standard for semantic interoperability and knowledge graph construction involving various geographic and 3D city data. They successfully implemented knowledge graph representation and querying of 3D geographic data. Huang [
28] advanced the field by developing an ontology that integrates data modeling standards from the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), including CityGML, IndoorGML, and SensorThings APIs. Their work provides innovative solutions for smart homes, healthcare, and fire evacuation systems. Beyond the integration of BIM, GIS, and IoT, ontologies have been extensively applied across various smart city sectors, including sustainable development [
29,
30,
31]. Du [
11] proposed an ontology model specifically for urban infrastructure asset management processes, which they validated using a practical decision-support system. Qi [
32] proposed an ontology model that addresses the relationship between urban heat island mitigation techniques, performance indicators, and the urban environment. Hofmeister [
31] addressed the lack of a comprehensive information integration framework in the flood domain by integrating ontologies related to power, rivers, water resources, and infrastructure, thereby supporting risk assessment.
However, De Nicola [
13], in their review of 67 smart city ontologies, underscored the prevailing absence of cross-domain and cross-level coordination and collaboration. They highlighted that research often remains confined to semantic modeling within specific scenarios and domains. Espinoza-Arias [
33] observed that ontologies in urban contexts are challenging to reuse and frequently neglect the integration of underlying data models, a critical component for smart-city platforms. For example, Ghosh [
34] constructed an ontology for sustainable urban transformation by abstracting concepts related to policies, services, and management involved in urban governance into entities; however, this ontology does not encompass specific data. Dunbar [
35] argued that ontologies should serve as a semantic abstraction layer over existing standards and models rather than attempting to replace all current data models. They emphasized that the focus should be on enhancing interoperability and data integration across different domains. Additionally, the W3C advocates for the standardization of data to facilitate seamless integration from a variety of sources and to decouple data from its schema [
23].
Despite advancements, many current ontologies lack flexibility to adapt to various urban scenarios and struggle to interlink redundant and core data standards effectively. This limitation hinders their application and reduces their effectiveness in supporting robust data governance. A semantic model is still needed, centered on core urban governance entities abstracted from multi-source heterogeneous urban data, which proficiently connect redundant and core data standards and adapt to different scenarios.
Our research aims to bridge these gaps by mapping and linking data standards across various disciplines to create a simplified ontology. Future studies will focus on detailed methodology and implementation
3. Methodology
Our methodology, outlined in
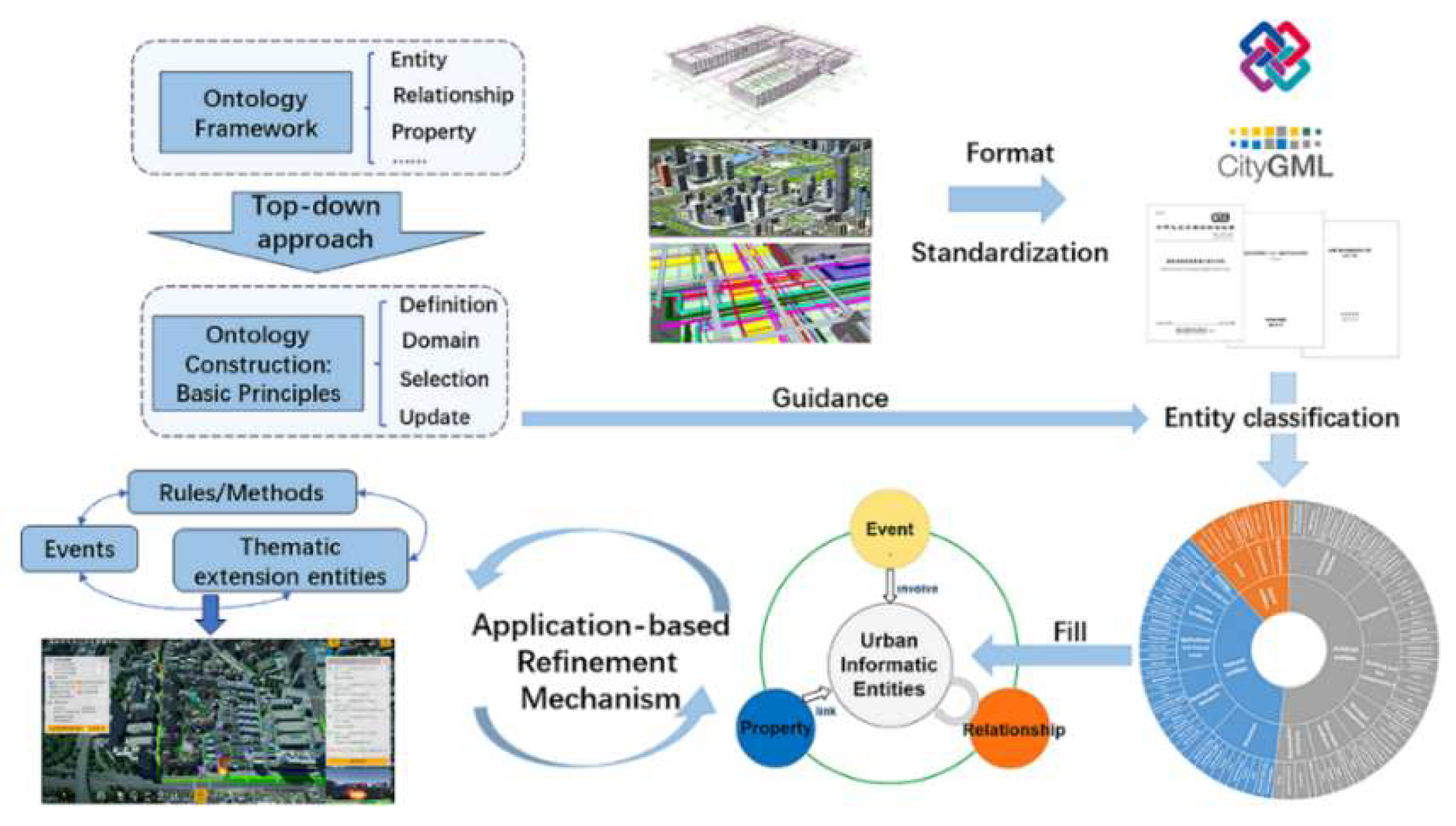
Figure 1, is organized into three stages: framework design, knowledge sourcing, and practical application. Initially, we used an object-oriented and graph-based approach to define the framework's knowledge expression model and construction method. Next, we identified SMOF's knowledge sources and established basic principles to define the fundamental conceptual scope. This involved organizing a hierarchical classification system for entities, constructed as ontologies. Finally, we demonstrated SMOF's practical utility in a specific urban governance scenario, highlighting its capacity for future expansion and continuous refinement.
3.1. Knowledge Structure Design
Based on related research [
36,
37], knowledge categories in this study consist of five parts, as shown in Equation 1.
In Equation 1, SMOF signifies the Smart City Ontology Framework; UIE refers to Urban Informatics Entities and their thematic extensions, which is the most important part in SMOF; UIEP signifies the properties of UIE; UIER is the relationship between UIE; and UIEE refers to events that involve UIE, UIEP; and R/M are based on rules/methods.
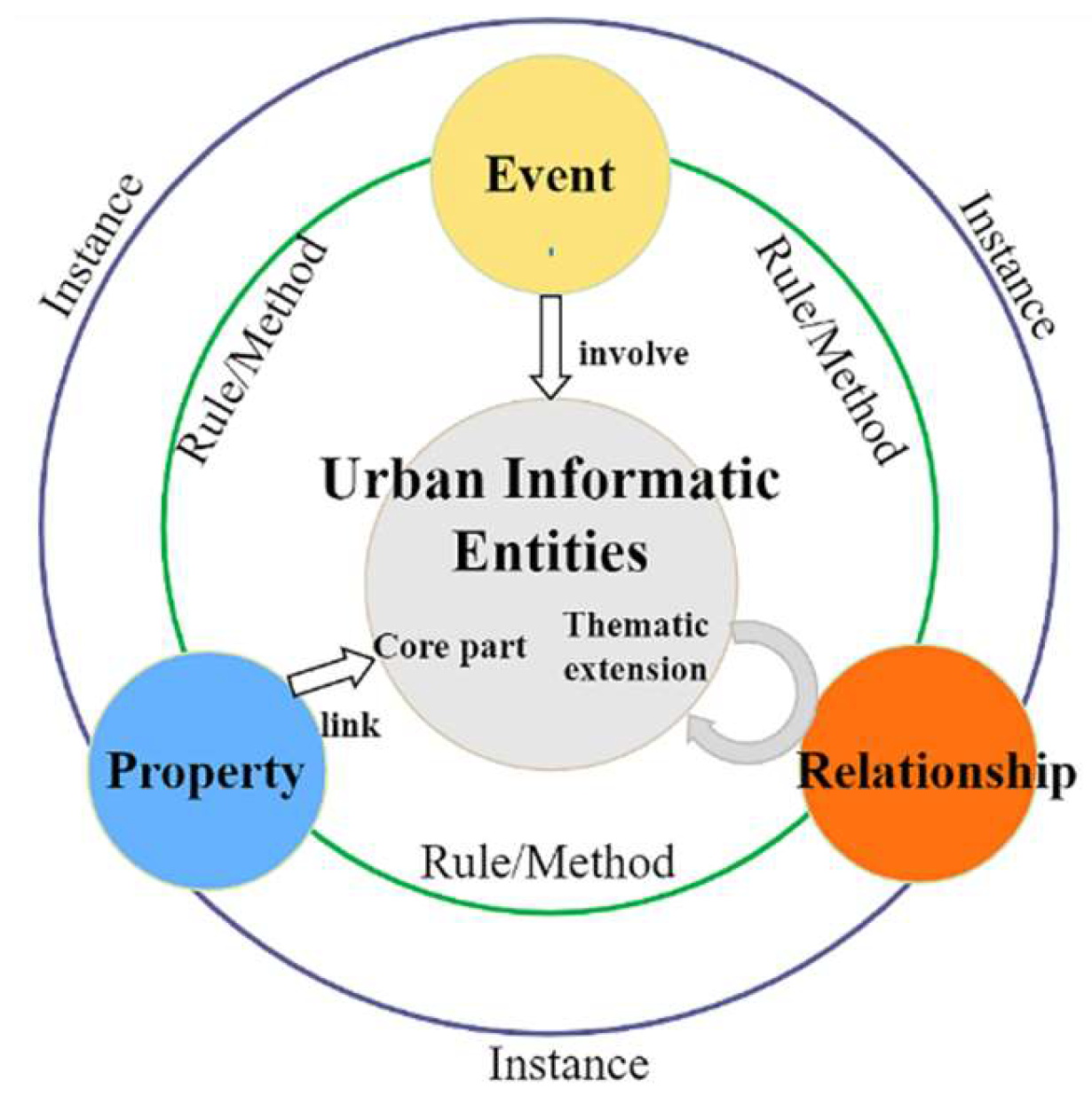
The architectural schema corresponding to Equation 1 is delineated in
Figure 2. At the apex of abstraction, the framework encapsulates five distinct knowledge categories: UIE refers to the collection of objects that objectively exist within the operational fabric of a city, possessing spatiotemporal characteristics and semantic connotations like properties and relationships. UIEs are bifurcated into core and thematic extension entities, which are distinguished by their ubiquity in urban governance applications. Entity relationships represent associations between entities, typically expressed using network graphs. Properties are the basic elements that constitute an entity and are common characteristics of the same type of entity. Events are descriptions of phenomena or actions that involve several entity objects at a specific time and space and cause certain results. When elements meet certain conditions, they trigger events, which usually modify properties and relationships of entities under the guidance of rules and methods, which in turn include multiple rules, i.e., control, and update rules. The results generated by rules also serve as element knowledge that links the entire reasoning process through the conditions and results.
Encompassing this structured knowledge hierarchy is the instance layer, which extracts relevant data from traditional databases and stores it in the graph database to form knowledge graph. The emergence of novel knowledge within this paradigm is fundamentally the result of interactions among the five principal elemental types.
Different elements can transform existing features into SMOF by mapping relationships. Concrete illustrations of this process are elaborated in
Section 4.
3.2. Construction Methods and Knowledge Source
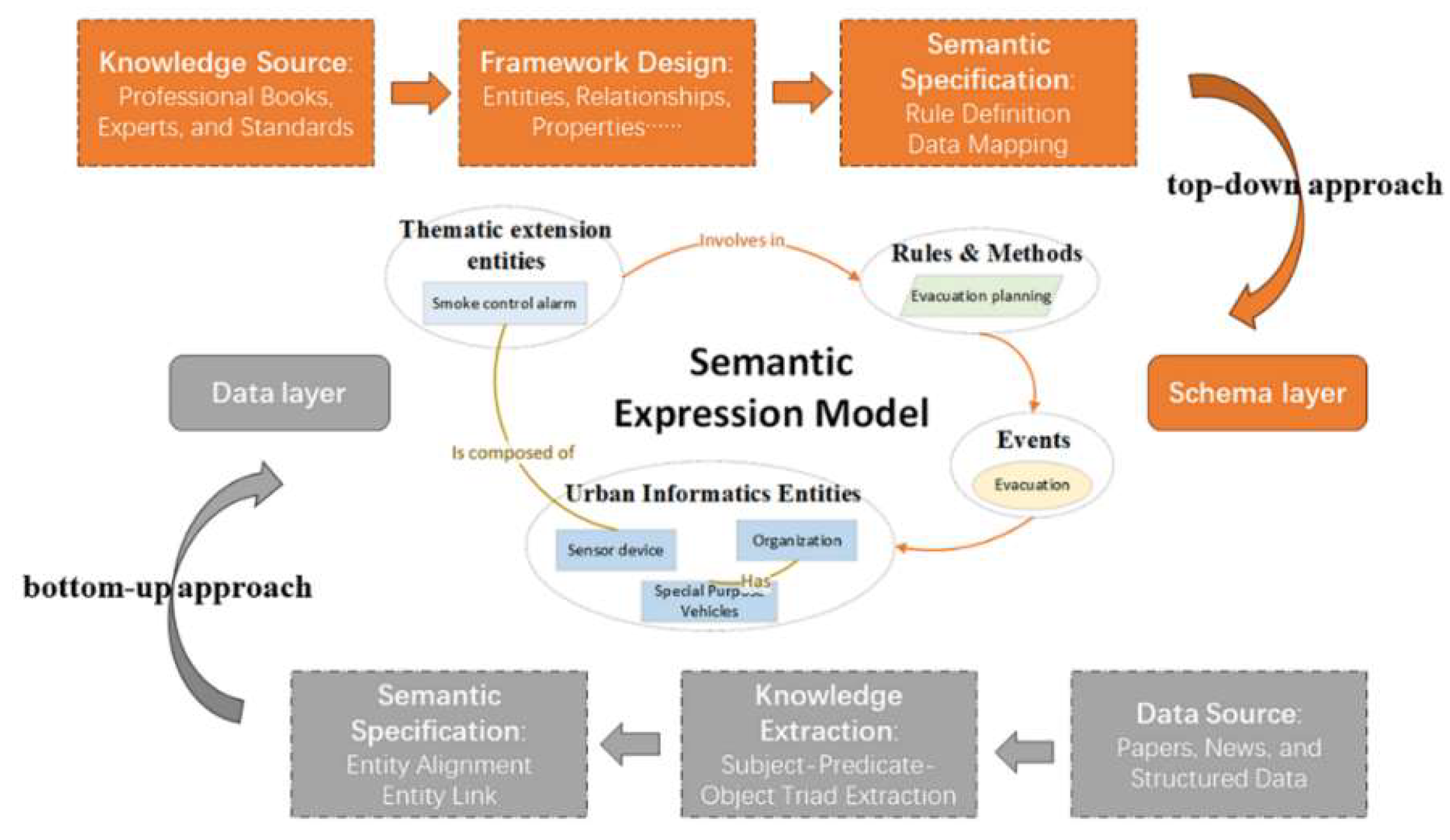
A concrete ontology is developed using a knowledge representation model, as depicted in
Figure 3, illustrating two common ontology construction methods: top-down and bottom-up. The top-down approach starts with expert-derived high-level concepts, necessitating domain-specific knowledge, while the bottom-up approach extracts knowledge from existing data without predefined structures [
11,
38].
Urban governance knowledge was derived from various sources, including standards, professional literature, reports, and news. Among these, standards are especially pivotal due to their provision of rich normative knowledge. Although most urban data standards do not directly describe data objects in the form of ontologies, the hierarchical classification conceptual models constructed to illustrate domain objects can serve as a foundation for creating urban entities [
39]. It is noted that scholars advocate for an ontology creation process rooted in domain expertise rather than solely relying on pre-existing data standards or current datasets [
7]. The urban governance domain presents unique considerations since smart-city platforms’ data storage systems are inherently aligned with specific formatting standards. These standards provide authoritative, comprehensive, and systematic knowledge, which is vital for the robustness and expansion of the knowledge framework.
In light of these considerations, we grounded the ontology in authoritative data standards, using a top-down approach to design SMOF and a bottom-up approach to populate the schema. This dual strategy aims to semantically enrich and connect city datasets, overcome data heterogeneity, and facilitate the development of universal analysis tools. The strategy organized the classification and coding standards of urban objects, abstracting valuable objects into a general part of the UIE based on the object-oriented approach. Universal relationships and properties between entities were established according to relevant standards and data formats, completing the SMOF design. For specific application scenarios, we employed a bottom-up approach to extract instance knowledge from datasets, while delineating events, methods, and rules to ensure the reliability and comprehensiveness of the ontology framework.
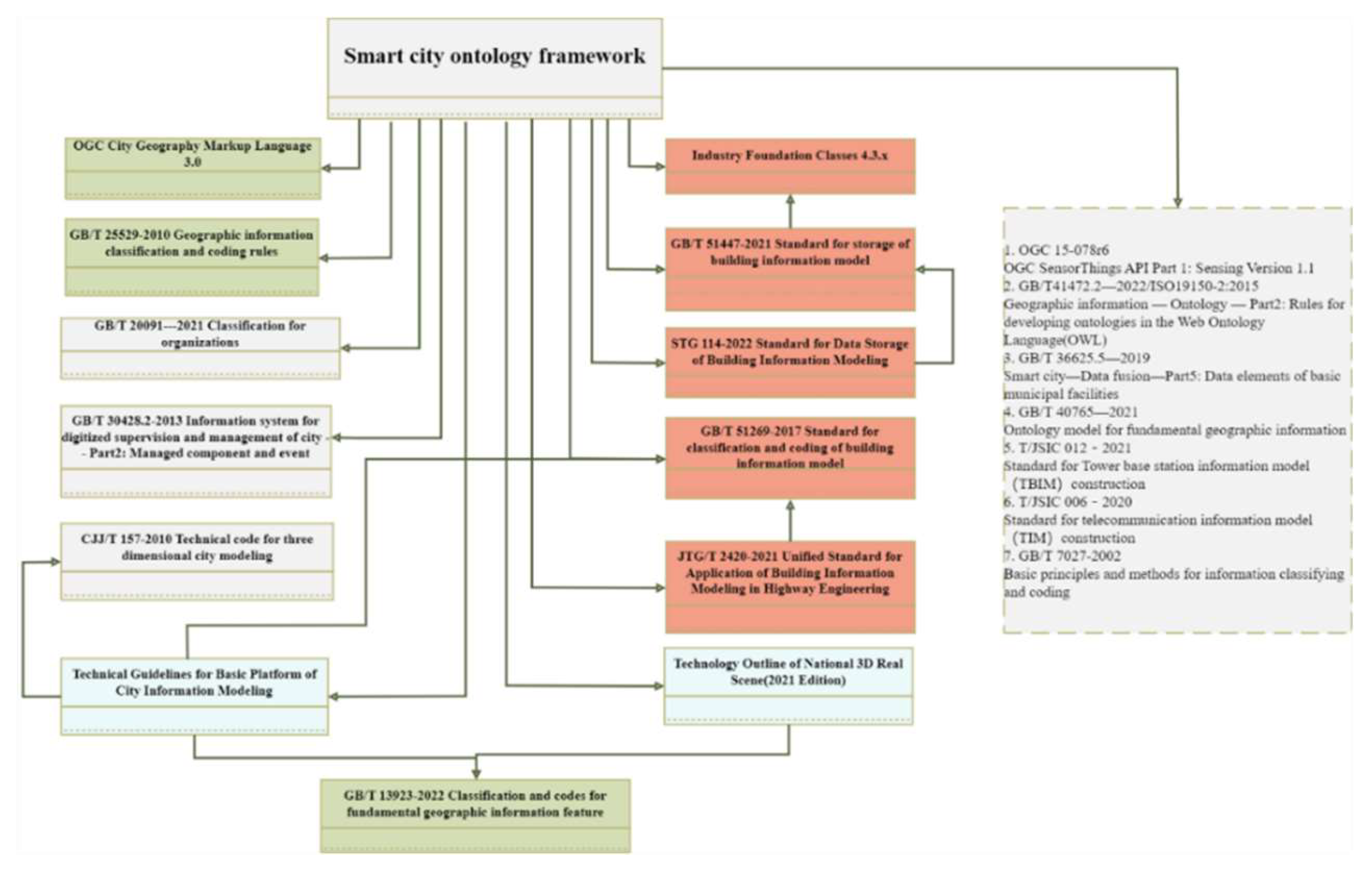
Our study reviewed various urban governance standards, including 3 international standards, 10 national standards, and 7 industry or regional standards, as shown in
Figure 4. The term “use” indicates entities, properties, and relationships from standards that are incorporated into ontology construction after processes like semantic fusion or reference links between standards. “Indirect references” indicate certain classification methods within standards that, although not directly cited, contribute to the framework. Referenced standards include those related to urban governance, 3D modeling, component management, and highway engineering, as well as data storage formats like IFC and CityGML. SMOF can be constructed based on knowledge and reference relationships between relevant standards and specific content, combined with a top-down approach.
3.3Basic Principle
The crux of ontology development lies in the hierarchical categorization of entities. Our work draws inspiration from the foundational UPON model proposed by De Nicola [
40] and its subsequent elucidation [
41]. This scholarly lineage has introduced the 'ability problem,' which is pivotal in delineating the ontology's scope and objectives. It ensures a standardized content framework for ontological development. As demonstrated in
Table 1, this approach necessitates adherence to defined principles governing the ontology's structure. It encompasses entity definitions, their hierarchical classifications, and the methodologies for semantic disambiguation—crucial aspects when constructing the UIE component of SMOF. Building upon the UIE's established classification system, the ontology framework can be expansively developed. This expansion is achieved by strategically employing a top-down methodology that aligns with the rigorous standards.
4. Result
Based on the principles and expression models outlined previously, we developed the framework. Our primary references were the Technical Guidelines for the Basic Platform of City Information Modeling and Industry Foundation Classes 4.3.x, key standards in CIM and BIM fields. These were integrated with GB/T 30428 and GB/T 20091-2021, important for urban governance and organizational classification. We performed semantic integration and resolved ambiguities where these standards overlapped or contained redundant elements.
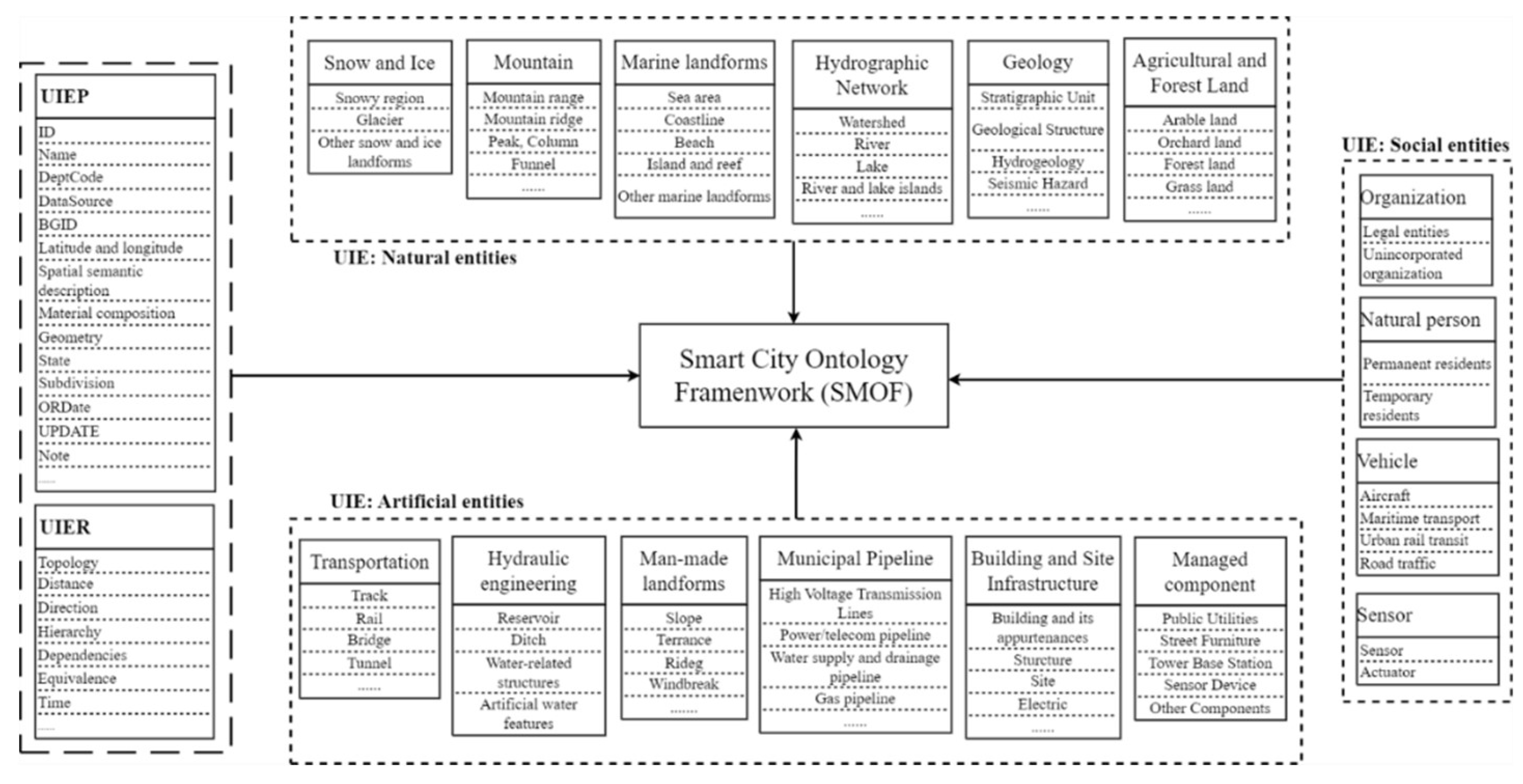
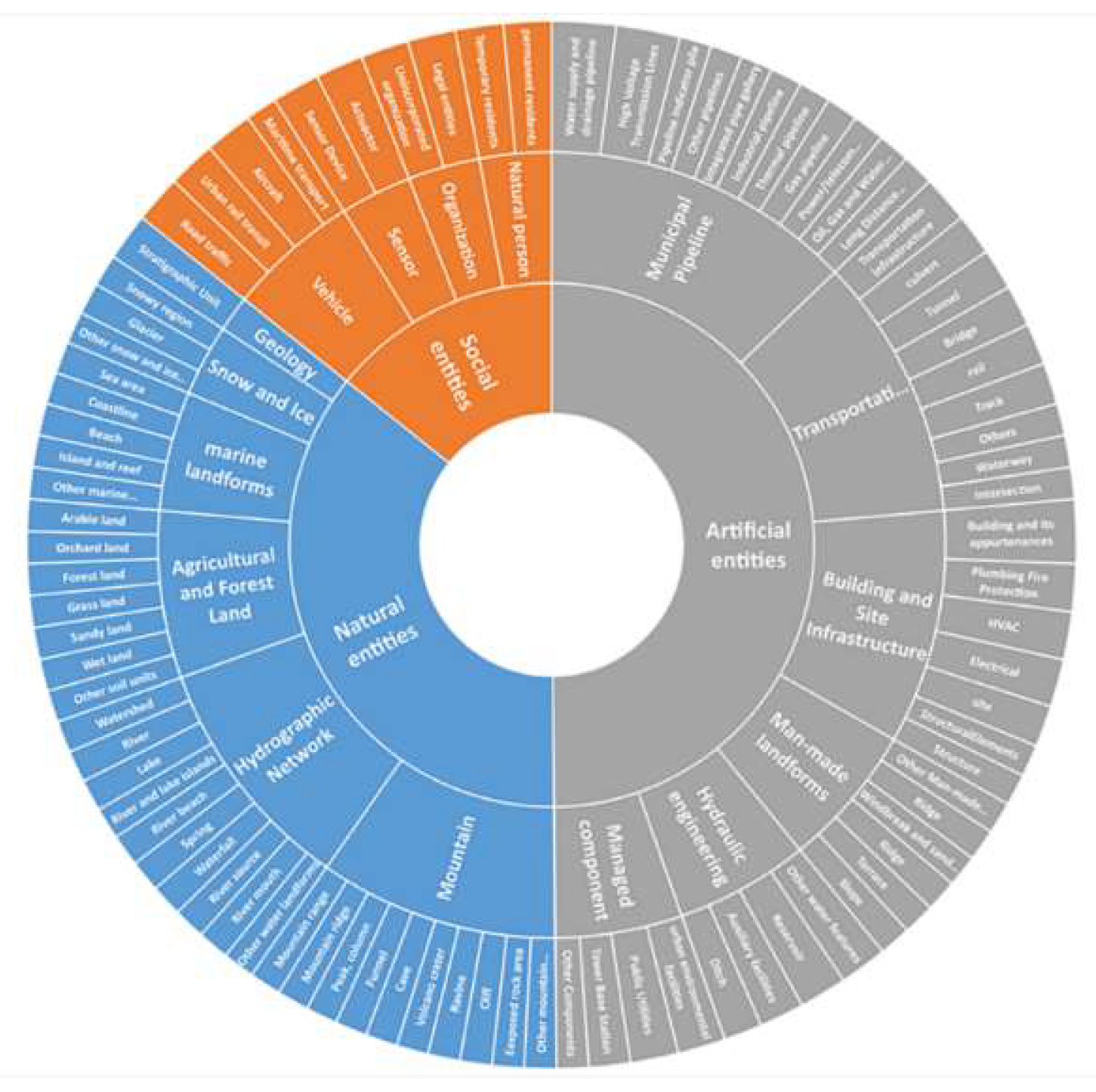
Figure 5 shows the generic core parts (UIE, UIEP, and UIER) of SMOF, divided into three primary categories and 15 large classes using a hierarchical classification method. Generic core properties and relationships were established by comprehensively referring to various standards.
4.1. UIE Classification
In SMOF, UIE is categorized into natural, artificial, and social entities, which are deemed core to the framework. Natural entities are characterized by urban objects that exist naturally or evolve through organic processes, such as mountain ranges or water bodies. In contrast, artificial entities encompass structures or elements that have been crafted or modified through human actions, including buildings and infrastructure components. Social entities, on the other hand, capture the essence of urban dynamics, representing the interactive aspects of urban life, such as individuals and transportation systems, which engage with both the natural and artificial environments. These core concepts are systematically structured and organized into various categories, resulting in the creation of a concept hierarchy depicted in
Figure 6.
For natural entities, classifications align with the Technology Outline of National 3D Real Scene (2021 Edition). Recognizing the escalating significance of underground engineering and resource management, we have expanded our framework to include geological units. This expansion is well-founded on authoritative references, including the JTG/T 2420-2021 Unified Standard for Application of Building Information Modeling in Highway Engineering and the GB/T25529-2010 Geographic Information Classification and Coding Rules. Within our framework, geological units are meticulously classified into strata, rock masses, geological structures, and other relevant categories. These detailed classifications will be developed and articulated to ensure they meet the precise requirements of targeted use cases.
The classification of artificial entities adheres to National 3D Real Scene standards. In the realm of transportation-entity design, we utilized BIM-related standards to classify roads by type, component, and facility, consolidating track types under a unified attribute. For building-related entities, our design encompassed internal functional components such as electrical systems and HVAC, while eliminating repetitive concepts across different standards. Although the GB/T 30428.2-2013 offers a hierarchical classification for urban components, we identified certain redundancies. To address this, we consolidated various kiosk types—ranging from newspaper to telephone and information kiosks—under a generalized "kiosk" category. We also excluded components with minimal management value, such as trench toilet covers and clothing racks. Given the lack of a unified pipeline information model, we adopted a function-based classification system for urban pipelines and introduced new subclasses like civil engineering structures and municipal facilities.
Within our framework, social entities are urban elements with distinctive managerial relevance, separate from static structures. This category includes natural persons, organizations, vehicles, and sensors. Natural persons are bifurcated into permanent and temporary residents. Organizations are typified according to the GB/T 20091-2021 standards. Vehicles, serving as instrumentalities within the urban transport network, are delineated into aircraft, maritime, road, and urban rail transit. Sensors, crucial for urban governance, are recognized as a unique social entity subset. Their semantic characterization is often informed by the SSN ontology endorsed by the W3C, in conjunction with the OGC Sensors API and IFC standards. For the sake of streamlined integration with other ontologies, this research specifically concentrates on actuators and sensors, sidelining controllers, alarms, and observations from the current schema.
4.2. Core Properties and Relationships
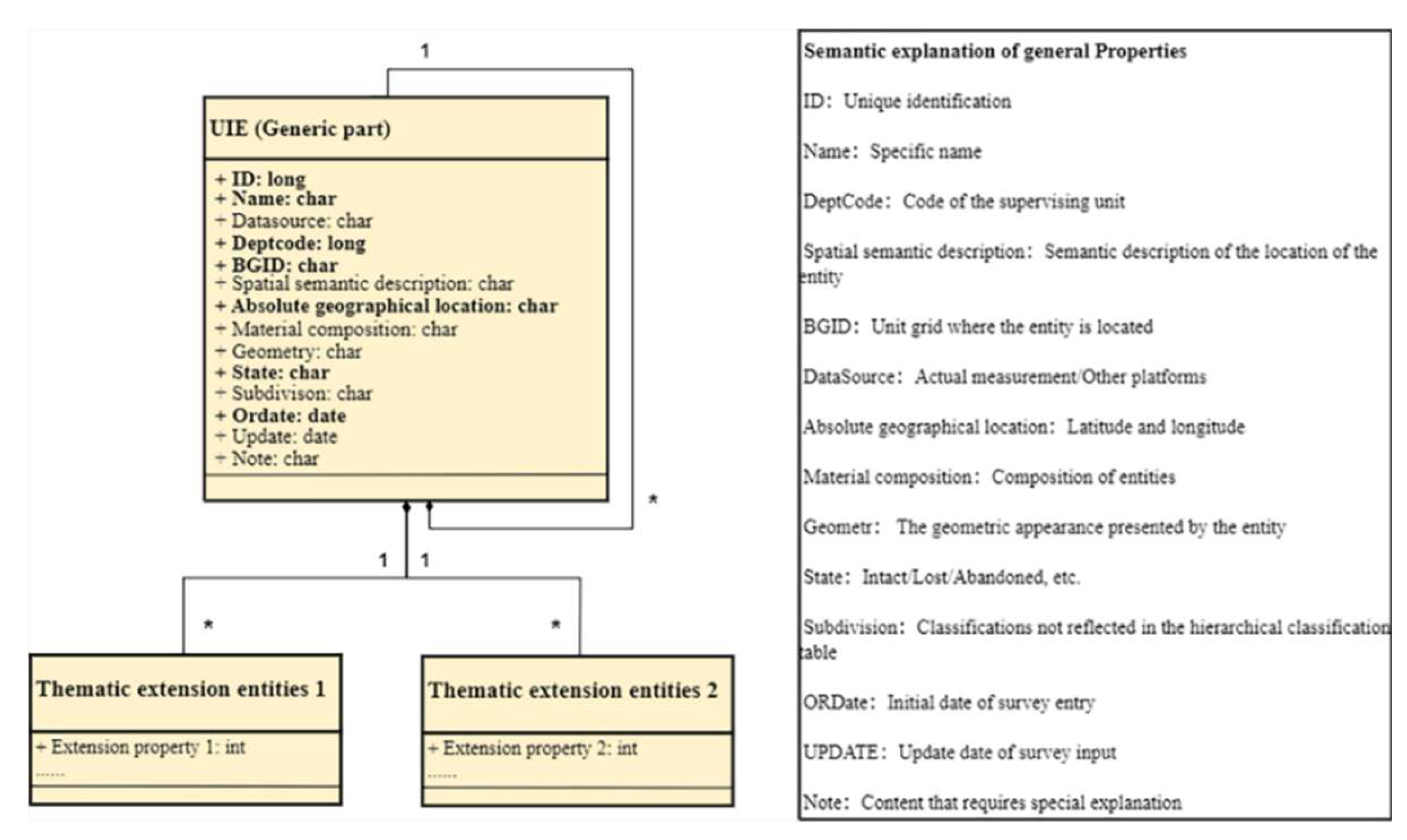
To ensure unified expression and facilitate departmental collaboration, the properties and relationships of UIE need thorough exploration. UIEP is used to describe the knowledge of the internal and external characteristics of an entity, including its specific location, ID, and name, as shown in
Figure 7. This framework encompasses attribute descriptions, data types, and distinguishes mandatory (in bold) from elective information. Although SMOF doesn’t set geometric shapes, visualization and Levels of Detail (LOD) require explicit geometric definitions via asWKT or asGML formats. UIE’s geometric representation uses CityGML formats, like Point, LineString, Surface, and Solid [
23].
The UIER involves the interactions between entities, forming a network of associations that allows for a comprehensive exploration of data characteristics and their interrelationships. In crafting the specifications for these relationships, our approach emphasizes the minimization of core relationship types. This strategy encompasses subordinate relationships with nuanced differences while preserving distinct differentiation among various relationship categories. Drawing from established standards, the UIER encompasses key dimensions of entity interaction, including spatial relationship, belonging, and temporal correlations. A comprehensive list of these core relationships is presented in
Table 2, offering a detailed breakdown of their structural and functional roles within the framework.
4.3. Rules/Methods and Instance Layer
The formulation of knowledge rules and methods arises from fundamental knowledge elements, including triggers and conclusions. These elements are instrumental in defining the Urban Information Events (UIEE) by establishing constraints that link entity properties. This approach transcends traditional data-centric analysis, creating a solid foundation for reasoning and knowledge modeling. The conceptual framework is summarized by the following equation:
The term "SMC" denotes a rule's condition, a logical construct integrating relevant facts, while "SMR" indicates an emergency conclusion or action triggered once the SMC condition is met.
Comprehensive knowledge descriptions depend on specific urban governance scenarios. In ontology, the Semantic Web Rule Language (SWRL) and SPARQL Protocol express rules and methods, with SWRL handling complex logic rules and SPARQL enabling robust RDF data querying.
The instance layer holds tangible objects like buildings and buses, each uniquely identified and property-defined. Detailed rules, methods, and examples are in the case study section, equipping SMOF to meet city administration's dynamic needs.
4.4. Verification and Case Study
Following the construction of SMOF, it is imperative to test both the theoretical understanding and the applied technologies to garner comprehensive practical feedback. Building upon Shuai [
41] work, which encapsulated methodologies for ontology validation, our evaluation of the developed ontology focused on its capacity for modeling and its applicability in real-world scenarios.
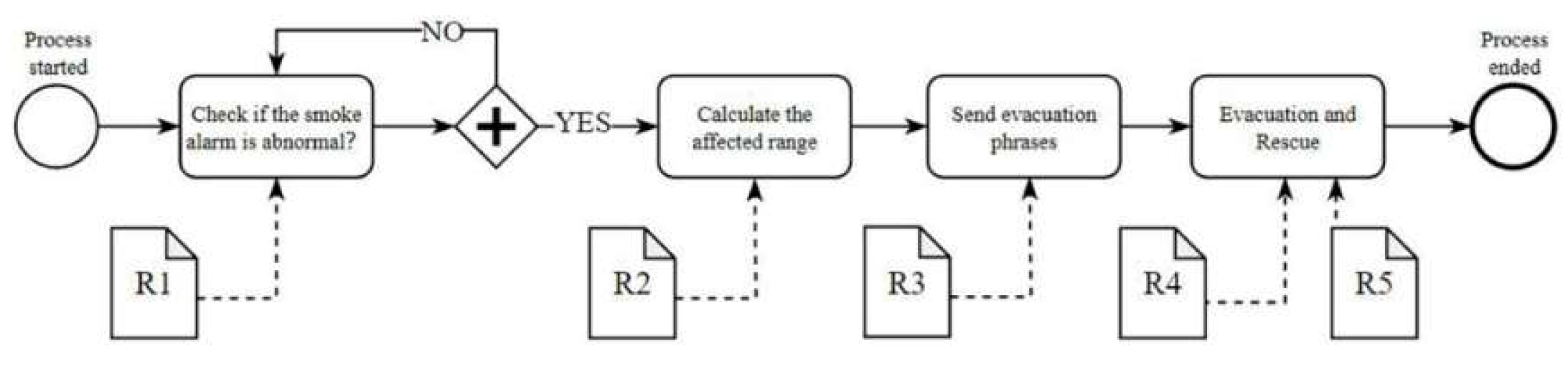
To verify the applicability of SMOF, we chose fire emergency rescue as the specific scenario and utilized the Shenzhen Visual Spatial Digital Platform, deploying the program on the Java platform with Jena to build a semantic-based web application. Effective management of fire emergencies is essential for urban safety, requiring swift responses and effective evacuation plan. However, seamless data exchange and coordinated systems during emergencies present significant challenges. This highlights the urgent need for a sophisticated fire-protection system that can display fire-related information and devise automated response strategies [
42]. The process model for the scenario is illustrated in
Figure 8.
The implementation involves two stages. First, the thematic ontology for fire emergency response is developed using Protégé (
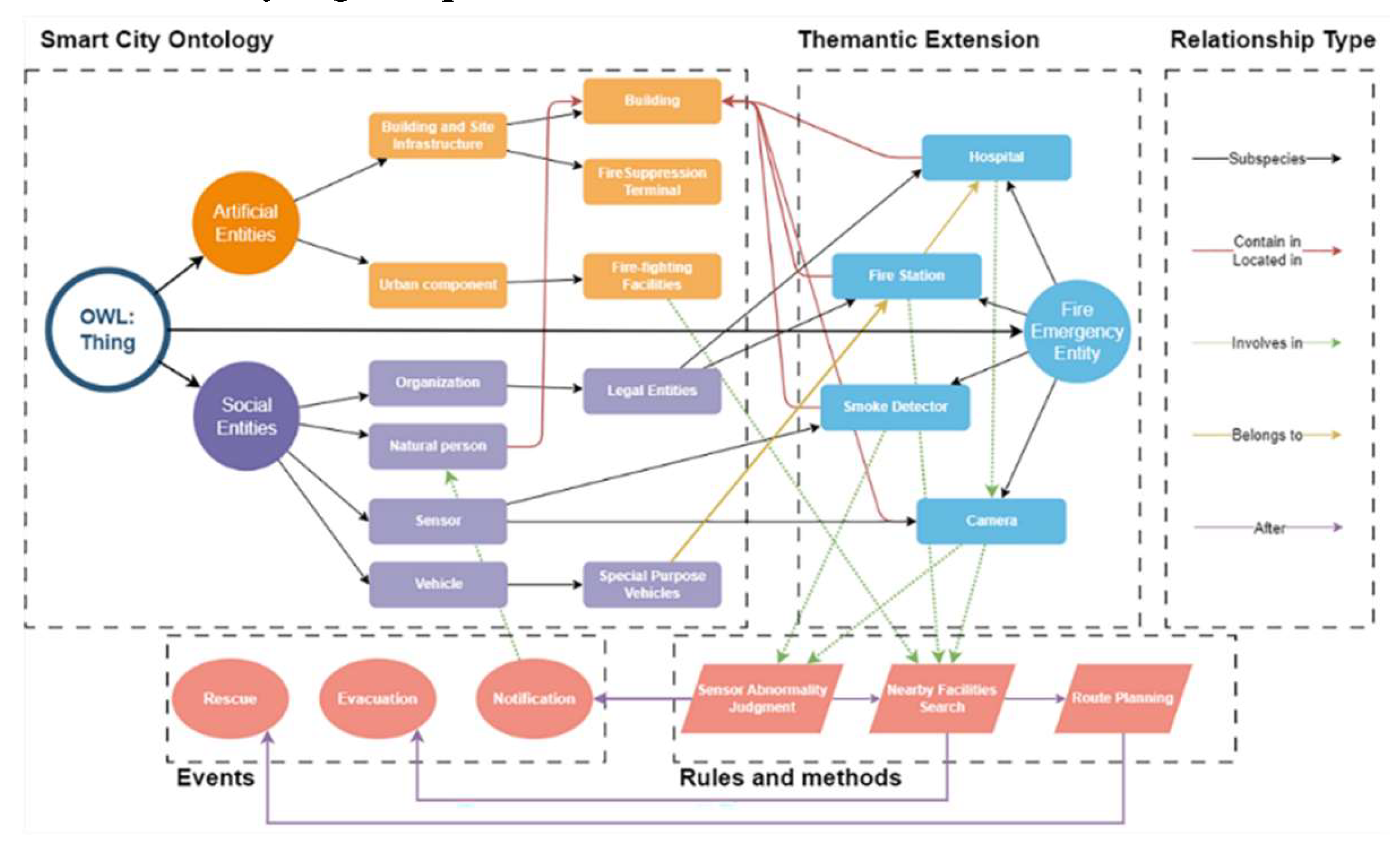
http://protege.stanford.edu/). The resulting knowledge expression diagram is delineated in
Figure 9. This ontology extends to smoke control alarms and cameras by incorporating sensing devices as thematic extension entities. Fire monitoring is executed by tracking the status of these devices, initiating queries for nearby fire protection facilities upon anomaly detection, and notifying hospitals and residents.
The second stage includes instance injection based on mapping rules and querying via SPARQL [
43]. In SMOF, data instantiation refers to the bottom-up extraction of semantics from different data sources and formats and transforming them into the knowledge model, bridging the conceptual and physical representation gap.
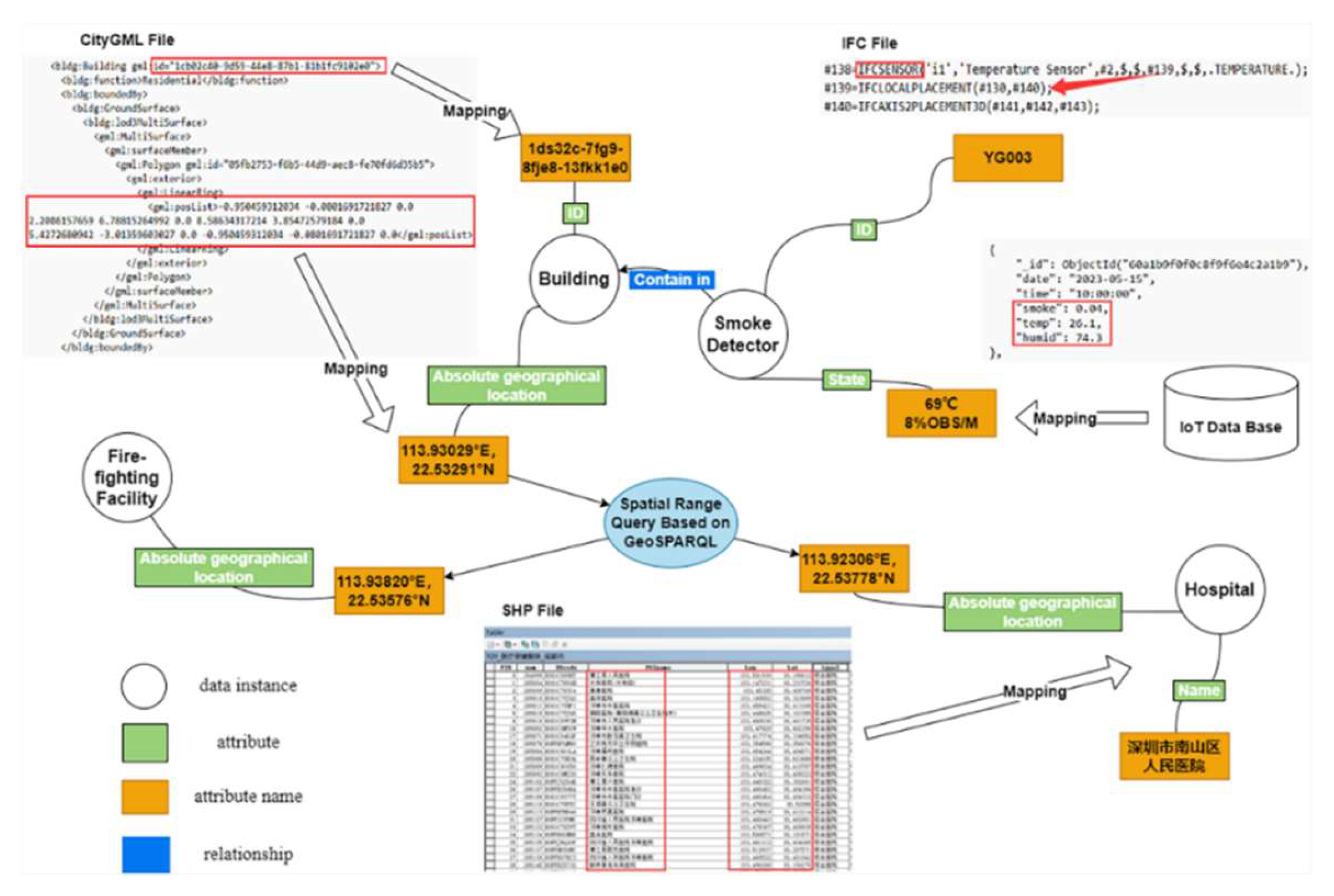
In developing a mapping tool, researchers define input parameters as specific ontology components following the ontology schema. The input data, structured within a schema template, transforms into data instantiations. As depicted in
Figure 10, a simplified data mapping diagram is presented for data instantiation, predominantly utilizing IFC, CityGML, and ShapeFile formats. Tools like Ifcopenshell parse data within the red box, adding semantics to CSV files for transfer to a graph-based database. The convergence of BIM and IoT is facilitated by correlating the GUID of the IFC entity with the ID of an object within the IoT database. By harnessing location coordinates extracted from the IFC, the specific building housing the sensor is pinpointed. Additional details like the building's name are derived from CityGML. Ultimately queries via GeoSPARQL identify nearby firefighting facilities and hospitals.
Graph data structures enable multiple association queries, challenging to achieve with traditional relational data structures. The semantic richness of ontologies facilitates the generation of customized semantic tags, aligning with user-specific requirements and filtering criteria. These needs are elegantly translated into SPARQL queries to extract the pertinent information. SPARQL, a query language designed for graph data structures, operates by querying information through graphical patterns and conditional rules. A selection of SPARQL-based queries is presented in
Table 3. Ontology-based queries simplify processes compared to key-value structures of relational databases, deriving new insights and enhancing data-driven urban planning and management [
23].
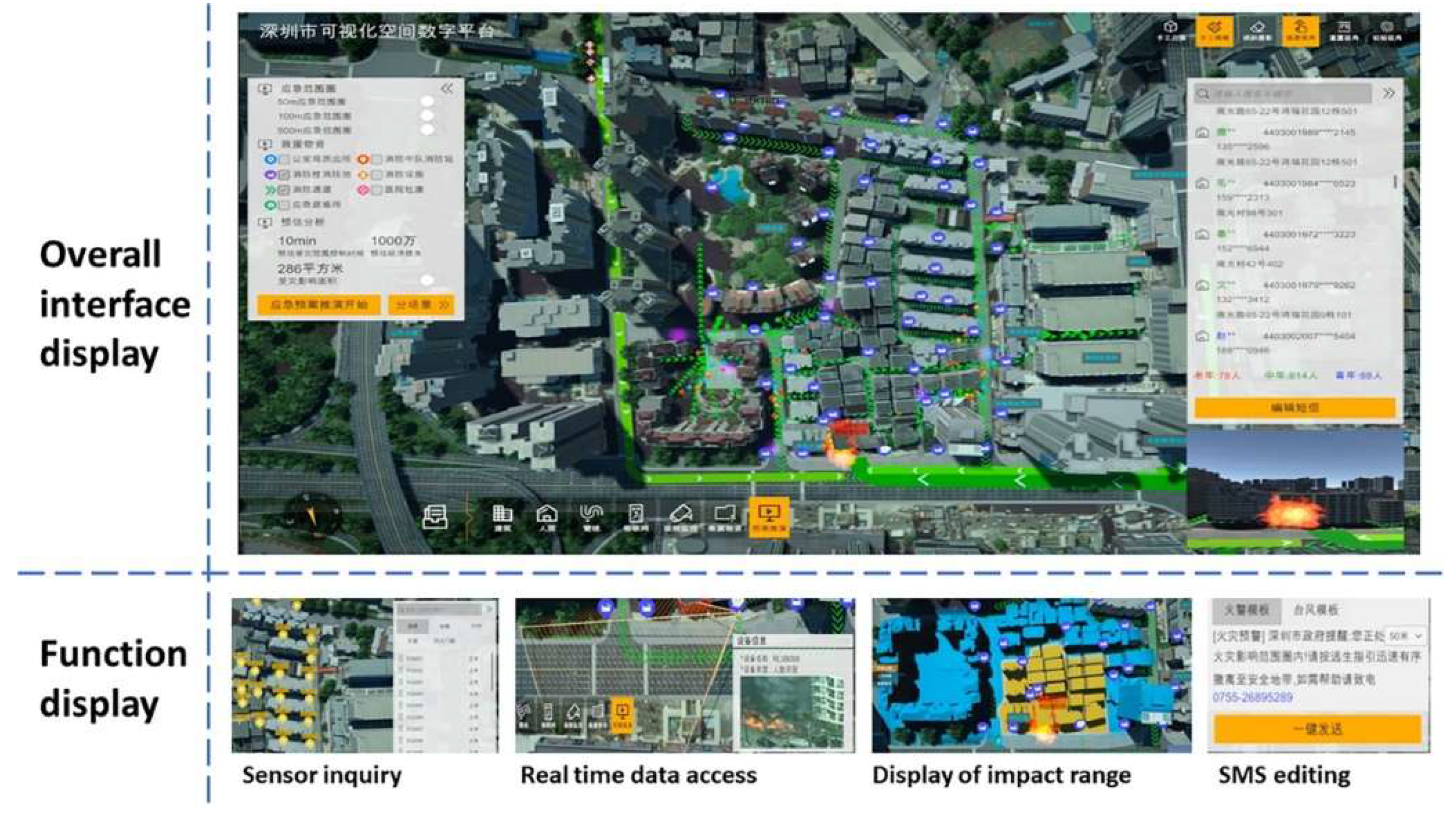
The entire scenario is illustrated in
Figure 11. In this case, functions, such as sensor queries, real-
time data access, and impact range displays, are realized by storing static data, such as BIM, GIS, and dynamic data from sensors into an ontology-based graph database.
5. Discussion
This study proposes a robust solution for the integration of multi-source data and urban governance through an ontology framework. The research contributes to the existing body of knowledge in three principal areas:
Development of an Ontology Framework: Acknowledging the multifaceted nature of urban governance, it is evident that no single ontology can serve all sectors uniformly. We have architected SMOF to assimilate a variety of data types in city platforms, ensuring its scalability through the incorporation of components such as UIE, UIEP, and UIER. The ontology is structured into a general core and thematic extensions, allowing SMOF to support specialized applications while maintaining foundational universality.
Detailed Design of SMOF Components: Given the reliance on industry-specific data formats, SMOF avoids direct abstraction of city objects, anchoring instead on municipal data storage and classification standards. Using a top-down approach, we established principles for ontology construction and meticulously populated the framework. This systematic method minimizes subjectivity and aligns closely with native smart city data, enhancing the framework's applicability and relevance.
Exploration of SMOF's Practicality and Scalability: In a bottom-up application to real-world scenarios, we have validated SMOF's practicality for knowledge representation. We have demonstrated the process by which data from smart city platforms can be effectively mapped to ontology entities and have explored the framework's capabilities for semantic querying. This exploration is crucial in establishing the groundwork for how SMOF can be utilized in practical urban governance scenarios.
As previously noted [
44], the domain of urban governance is replete with various ontologies, and SMOF necessitates comparison with its existing counterparts.
Table 4 presents the domains, references, and core concepts of each ontology. With our framework's foundation in data standards and its focus on thematic extensions, we have concentrated primarily on the connectivity between SMOF and other related ontologies.
The table elucidates that most entities that describe the physical space of a city (e.g., city objects and spaces) can be interconnected using artificial entities. Entities that describe the dynamic operations of a city (such as sensors and individuals) can be correlated to social entities within SMOF. Key performance indicators, topology, and geometry can be associated with corresponding properties, relationships, and rules/methods. This paper provides a general exploration of the connectivity between SMOF and various related ontologies, with the understanding that specific connection interfaces and reusability require further investigation in subsequent stages.
Consolidating the Discussion, the development and preliminary exploration of SMOF represent a significant step forward in addressing the complexities of smart city data.
6. Conclusions
In this research, we have successfully engineered and deployed SMOF, leveraging semantic web technologies and meticulously aligning with a range of international and domestic standards. SMOF is designed to address data utilization challenges in urban governance, particularly those arising from heterogeneous, multi-standard, and multidisciplinary datasets. The knowledge structure was developed by interrogating knowledge sources and capability questions, referencing 20 relevant standards to strengthen the framework's core entities, relationships, and properties. Guided by six foundational principles, SMOF integrates a wide array of data sources, from GIS and BIM foundations to dynamic IoT sensor streams. A representative use case demonstrates SMOF's capability for scenario-specific knowledge representation, mapping diverse data, and executing non-relational semantic queries. This case substantiates the robustness and scalability of ontology-driven methodologies, showcasing their targeted and extensive applicability.
Constructing a comprehensive ontology demands profound domain knowledge and expertise in knowledge engineering. Despite its robustness, the current framework has several limitations: (1) Content Enrichment: The core components of SMOF require further refinement to balance simplicity and comprehensiveness, ensuring the framework remains accessible while capturing the complexities of smart city data. (2) Formal Standardization: This study constructs the framework but doesn't fully address multi-scale representation and geometric aspects. Future work should focus on the 'data-model-knowledge' paradigm [
39] to develop a more granular integration of data scales and geometric information. (3) Data Governance Complexities: While addressing entity mapping and application within the data lifecycle, the study does not fully integrate SMOF with other critical stages like security and data sharing, essential for a holistic approach to smart city data management.
The next phase of our research involves refining SMOF in light of these issues and aligning it more closely with existing urban ontologies. We also aim to expand our research scope to include a diverse range of smart city applications, enhancing the generalizability of our findings. Collaboration with stakeholders from different sectors will ensure that SMOF meets unique domain-specific challenges and opportunities.
Additionally, we advocate for governmental initiatives to establish dedicated entities, such as City Administrative Data Management Bureaus, to streamline and amalgamate data across siloed departmental platforms. This unification is projected to dismantle existing data management and application barriers, fostering inter-sectorial synergy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Xiaolong He and Xi Kuai; methodology, Xi Kuai; software, Xiaolong He; validation, Xiaolong He; formal analysis, Yu Liu; investigation, Zhigang Zhao; resources, Xiaolong He and Xi Kuai; writing—original draft preparation, Xiaolong He; writing—review & editing, Xiaolong He; visualization, Biao He; supervision, Xi Kuai; project administration, Renzhong Guo; funding acquisition, Xi Kuai, Yu Liu. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China [Grant Number 2022YFC3800604]; Guangdong Key Laboratory of Urban Informatics [Grant Number GEMLab—2023003]; Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation [Grant Number 2022A1515010117]; Shenzhen Science and Technology Program [Grant Number 20220810160944001]; and the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Number 41901325].
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process: During the preparation of this work the authors used ChatGPT in order to enhance the readability and language of the manuscript. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
References
- UNFPA. Urbanization. Available online: https://www.unfpa.org/urbanization#readmore-expand (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Javed, A.R.; Shahzad, F.; Rehman, S.U.; Zikria, Y.B.; Razzak, I.; Jalil, Z.; Xu, G. Future Smart Cities: Requirements, Emerging Technologies, Applications, Challenges, and Future Aspects. Cities 2022, 129, 103794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, O.; Liu, H.; Abudayyeh, O.; Houshyar, A.; Almatared, M.; Alhawiti, A. Data Fusion for Smart Civil Infrastructure Management: A Conceptual Digital Twin Framework. Buildings 2023, 13(11), 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Rui, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lu, L.; Li, X. Comprehensive Digital Twin for Infrastructure: A Novel Ontology and Graph-Based Modelling Paradigm. Advanced Engineering Informatics 2024, 62(Part B), 102747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anejionu, O.C.D.; Thakuriah, P.; McHugh, A.; Sun, Y.; McArthur, D.; Mason, P.; Walpole, R. Spatial Urban Data System: A Cloud-Enabled Big Data Infrastructure for Social and Economic Urban Analytics. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 98, 456–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ding, L.; Luo, H.; Ma, L. From Building Information Modeling to City Information Modeling. Journal of Information Technology in Construction (ITcon) 2014, 19, 292–307. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H. Basic Directions and Technological Path for Building 3D Realistic Geospatial Scene in China. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2022, 47(10), 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahat, E.; Hyun, C.T.; Yeom, C. City Digital Twin Potentials: A Review and Research Agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13(6), 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M.F. Elements of an Infrastructure for Big Urban Data. Urban Informatics 2022, 1(1), 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, M. Integration of 3DGIS and BIM and Its Application in Visual Detection of Concealed Facilities. Geo-spatial Information Science 2024, 27(1), 132–141. [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wei, L.; Dimitrova, V.; Magee, D.; Clarke, B.; Collins, R.; Entwisle, D.; et al. City Infrastructure Ontologies. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems 2023, 104, 101991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, P.; Zhang, S.; Lee, Y.C. Semantic Web Technologies in AEC Industry: A Literature Overview. Automation in Construction 2017, 73, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nicola, A.; Villani, M.L. Smart City Ontologies and Their Applications: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13(10), 5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xiao, G.; Pano, A.; Fumagalli, M.; Chen, D.; Feng, Y.; Calvanese, D.; Fan, H.; Meng, L. Integrating 3D City Data through Knowledge Graphs. Geo-spatial Information Science 2024. [CrossRef]
- Israilidis, J.; Odusanya, K.; Mazhar, M.U. Exploring Knowledge Management Perspectives in Smart City Research: A Review and Future Research Agenda. International Journal of Information Management 2021, 56, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y. UrbanKG: An Urban Knowledge Graph System. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology 2023, 14(4), Article 60: 25 pages. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Tan, Y.; Wu, P.; Sutrisna, M.; Cheng, J.; Hampson, K. Trends and Opportunities of BIM-GIS Integration in the Architecture, Engineering and Construction Industry: A Review from a Spatio-temporal Statistical Perspective. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 2017, 6(12), 397. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wright, G.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Li, X.; Liu, R. A State-of-the-Art Review on the Integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Geographic Information System (GIS). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, Z.; Kim, M.J. Integration of BIM and GIS: Geometry from IFC to Shapefile Using Open-Source Technology. Automation in Construction 2019, 102, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, W. An Ontology-Based Rule Mapping Approach for Integrating IFC and CityGML. Transactions in GIS 2024, 28, 675–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.P.; Chen, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, Q. Data-Driven Predictive Maintenance Planning Framework for MEP Components Based on BIM and IoT Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Automation in Construction 2020, 112, 103087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, D.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Tang, L. Construction Method of City-Level Geographic Knowledge Graph Based on Geographic Entity. In International Conference on Geoinformatics and Data Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Pan, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhai, X. An Ontology-Based Methodology to Establish City Information Model of Digital Twin City by Merging BIM, GIS and IoT. Advanced Engineering Informatics 2023, 57, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, M.; Arif, F.; Jan, M.A.; Tan, Z.; Khan, F. Urban Data Management System: Towards Big Data Analytics for Internet of Things Based Smart Urban Environment Using Customized Hadoop. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 96, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, E.; Pileggi, S.F.; Groth, P.; Degeler, V. Ontologies in Digital Twins: A Systematic Literature Review. Future Generation Computer Systems 2024, 153, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Li, X. OSMsc: A Framework for Semantic 3D City Modeling Using OpenStreetMap. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 2024, 38(1), 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xiao, G.; Pano, A.; Stadler, C.; Calvanese, D. Towards the Next Generation of the LinkedGeoData Project Using Virtual Knowledge Graphs. Journal of Web Semantics 2021, 71, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Chiang, Y.-H.; Tsai, F. An Ontology Integrating the Open Standards of City Models and Internet of Things for Smart-City Applications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2022, 9(20), 20444–20457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Song, W. Knowledge Graph Representation of Multi-Source Urban Storm Surge Hazard Information Based on Spatio-Temporal Coding and the Hazard Events Ontology Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Huang, H.; Yang, C. An Ontology-Driven Method for Urban Building Energy Modeling. Sustainable Cities and Society 2024, 106, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Shen, J.; Su, Q.; Liu, S.; Pirasteh, S.; Ishii, K. A Method for Constructing an Urban Waterlogging Emergency Knowledge Graph Based on Spatiotemporal Processes. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Ding, L.; Lim, S. Ontology-Based Knowledge Representation of Urban Heat Island Mitigation Strategies. Sustainable Cities and Society 2020, 52, 101875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Arias, P.; Poveda-Villalón, M.; García-Castro, R.; Corcho, O. Ontological Representation of Smart City Data: From Devices to Cities. Applied Sciences 2018, 9(1), 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.M.; Chandra, A.; Ramaprasad, A. The Ontology of Urban Governance: A Framework for Pathways to Sustainable Urban Transition. Urban Science 2024, 8(2), 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, D.; Hagedorn, T.; Blackburn, M.; Dzielski, J.; Hespelt, S.; Kruse, B.; Verma, D.; Yu, Z. Driving Digital Engineering Integration and Interoperability Through Semantic Integration of Models with Ontologies. arXiv 2022. [CrossRef]
- Gahegan, M.; Pike, W. A Situated Knowledge Representation of Geographical Information. Transactions in GIS 2006, 10(5), 727–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Zhang, X.; Shi, G.; Chen, S.; Huang, Z.; Tang, W. TKRM: A Formal Knowledge Representation Method for Typhoon Events. Sustainability 2020, 12(5), 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Zeng, H.; Liu, M.; Ding, Y.; Ren, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Luo, X.; Zhu, J. Classification and Coding of Entity Features for Digital Twin Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2020, 45(9), 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Luo, Y.; Bao, Y.; Tang, L.; Zeng, S. Integrated Data-Model-Knowledge Representation for Natural Resource Entities. International Journal of Digital Earth 2022, 15(1), 653–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nicola, A.; Missikoff, M.; Navigli, R. A Software Engineering Approach to Ontology Building. Information Systems 2009, 34(2), 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, H.; Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Pirasteh, S.; Han, Z. Construction of User-Adaptive Urban Waterlogging Emergency Scenarios Considering Mapping Concerns. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2024, 131, 103953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.; Pan, Z. Intelligent Control of Building Fire Protection System Using Digital Twins and Semantic Web Technologies. Automation in Construction 2023, 147, 104728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nyerges, T.L.; Nie, G. Modeling and Representation for Earthquake Emergency Response Knowledge: Perspective for Working with Geo-ontology. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 2014a 28(1), 185–205. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, M. A Study on a Spatiotemporal Entity-Based Event Data Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowicz, K.; Haller, A.; Cox, S.J.D.; Le Phuoc, D.; Lefrançois, M. SOSA: A Lightweight Ontology for Sensors, Observations, Samples, and Actuators. Journal of Web Semantics 2019, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, P.; Benigni, M.; Billero, R.; Nesi, P.; Rauch, N. Km4City Ontology Building vs Data Harvesting and Cleaning for Smart-City Services. Journal of Visual Languages and Computing 2014, 25(6), 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, L.; Solanki, M.; den Hartog, F.; Roes, J. Interoperability for Smart Appliances in the IoT World. In The Semantic Web–ISWC 2016. Proceedings, Part II: 15th International Semantic Web Conference, Kobe, Japan, Oct 17–21, 2016; Springer International Publishing: 2016; pp. 21–29.
- Komninos, N.; Bratsas, C.; Kakderi, C.; Tsarchopoulos, P. Smart City Ontologies: Improving the Effectiveness of Smart City Applications. Journal of Smart Cities 2019, 1(1), 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).