1. Introduction
The carob tree (
Ceratonia siliqua L.) is a typically Mediterranean plant that grows spontaneously in the form of isolated stands [
1]. In Tunisia, the carob tree exhibits significant variability in both its geographical distribution and the genetic diversity of
C. siliqua populations. The tree is well acclimated throughout the Tunisian territory, covering all climatic zones from the north to the south of the country [
2]. Since antiquity, all parts of the carob tree have been exploited due to their rich content of nutritional and bioactive compounds. The bark and leaves have been used in traditional medicine as a laxative, diuretic, anti-diarrheal, and for treating gastroenteritis [
3,
4,
5]. As for the seeds, they are considered the valuable part of the plant (fruit) and are extensively used industrially in Europe to produce the locust bean gum, a food additive (E410) employed as a thickening, stabilizing, or flavoring agent in the food industry and as an active ingredient or carrier molecule in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, textiles, and paints [
6]. The carob pulp, byproduct of the industrial seed processing, is a complex mixture of several phytochemicals. It is very rich in sugars, even more so than sugarcane and sugar beets, and for that reason it is widely used in the preparation of sweet juices and other pastry preparations [
7]. After its roasting process, this pulp serves as a substitute for cocoa in different chocolate-type preparations [
8]. The pulp also serves as a plant matrix rich in macro-elements such as calcium, potassium, magnesium, and phosphorus, in addition to trace elements like iron, zinc, and manganese [
9,
10]. This underused part of the fruit is also recognized as a valuable source of bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols, which exhibit various biological activities [
11]. Phenolic compounds, produced under stressful conditions, represent one of the most abundant group of secondary metabolites in plants. Their chemical structure incorporates one or more aromatic cycles with one or more hydroxyl groups, encompassing simple phenolic molecules of 500 Daltons (e.g. phenolic acids/alcohols) to highly polymerized compounds with molecular weights surpassing 30,000 Daltons (tannins) [
12]. These compounds are widely distributed in fruits and vegetables including the carob pulp, playing a crucial role in determining various organoleptic properties of plant-based foods [
13], and in the prevention and treatment of certain illnesses [
14].
In carob pulp these compounds can be found in different forms (free, bound or soluble) and the main categories found are phenolic acids (mainly 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid), flavonoids ( (+)-catechin, (-)-epigallocatechin, (-)-epigallocatechingallate, (-)-epicatechingallate) and gallotannins [
3]. The antioxidant capacity (AC) is often correlated with the phenolic content of carob extracts, and therefore these compounds are mainly responsible for the bioactivity of the pulp. For that reason, this AC is commonly performed along with the total phenolic content (TPC) and phenolic profile by high performance liquid chromatography. Furthermore, different factors such as the variety and gender of
C. siliqua, the extraction method and/or the process conditions, among others, can affect the polyphenolic profile found in extracts [
7,
11,
15].
In recent years, traditional or conventional extraction techniques (maceration, Soxhlet, etc.), although commonly used as models to compare the efficiencies of alternative extraction methods [
16], are been replaced by advanced innovative and sustainable techniques (accelerated solvent extraction (ASE), microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE), etc.), that produce low consumption of solvent, energy and time [
17], and avoiding phenolic degradation to a greater extent. Furthermore, the promising green solvents, such as natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES), have emerged as a good alternative to replace conventional organic solvents in the fruitful extraction of phenolic compounds from different foods of plant origin [
18]. In this sense, the present work aims for the first time, the comparative study of the conventional
versus innovative green extraction processes of polyphenol compounds from carob pulp of two geographical origins, North and South of Tunisia, using two extraction techniques, one conventional (maceration) and another more innovative and sustainable (UAE), as well as different types of solvents, including organic solvents (ethanol, E) and mixtures (ethanol: water 75:25-E 75 %; and methanol: water 80:20 -M 80 %), commonly used in phenolic extractions, as well as green solvents (water, and the NADES lactic acid (LA): sodium acetate (SA) (3:1), and sucrose (S): citric acid (CA) (1:1)), previously reported in literature as good plant phenolic extractants [
19,
20,
21]. Finally, the results have been assessed by a multivariate chemometric approach.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Standards
Ethanol, methanol, acetonitrile and formic acid of HPLC grade, sodium di-hydrogen phosphate monohydrate, and di-sodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous were acquired from Panreac Applichem ITW Reagents (Darmstadt, Germany). Sodium carbonate anhydrous (Na2CO3) and Folin-Ciocalteu (FC) reagent, were acquired from VWR (Leuven, Belgium). Trolox [(+)-6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchromane-2-carboxylic acid] was purchased from Acros organics (Geel, Belgium). ABTS [2,2´-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt] tablets, potassium persulfate (K2S2O8), DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl), sucrose (S), citric acid (CA), lactic acid (LA), sodium acetate trihydrate (SA), and the reference standards gallic acid (GA; 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid), pyrogallol (benzene-1,2,3-triol), protocatechuic acid (3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid), gentisic acid (2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid), 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid), 4´-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, caffeic acid (3´,4´-dihydroxycinnamic acid), chlorogenic acid (5-caffeoylquinic acid), cryptochlorogenic acid (4-O-caffeoylquinic acid), 3,5-di-caffeoylquinic acid, syringic acid (3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid), p-coumaric acid (4´-hydroxycinnamic acid), ferulic acid (4´-hydroxy-3´-methoxycinnamic acid), sinapic acid (3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid), vanillin (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde), catechin, epicatechin, epigallocatechin, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2, procyanidin C1, quercetin, taxifolin ((2R,3R)-dihydroquercetin), rutin (quercetin 3-rutinoside), hyperoside (quercetin 3-D-galactoside), isoquercitrin (quercetin 3-β-D-glucoside), reynoutrin (quercetin 3-O-xyloside), guaiaverin (quercetin 3-O-α-L-arabinoside), quercitrin (quercetin 3-rhamnoside), apigenin, apigetrin (apigenin 7-O-glucoside), apigenin 7-O-glucuronide, apiin (apigenin-7-(2-O-apiosylglucoside)), vicenin-2 (apigenin 6,8-C-di-β-D-glucopyranoside), luteolin, luteoloside (luteolin 7-O-glucoside), luteolin 7-O-β-D-glucuronide, orientin (luteolin 8-C-β-D-glucopyranoside), eriodictyol (3´,4´,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavanone), naringenin (4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavanone), narirutin (naringenin 7-O-rutinoside), phloretin (dihydronaringenin), phloridzin (phloretin 2-glucoside or dihydronaringenin 2´-glucoside), kaempferol (3,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (Madrid, Spain).
2.2. Plant Material Origin and Processing
Samples of mature carob fruits (Ceratonia siliqua L.) were harvested on August 2023 from two distinct geographic regions in Tunisia: Bousalem in the North (latitude: 34° 36′ N; longitude: 17° 58′ E; altitude: 127 m) and Matmata in the South (latitude: 33° 32′ N; longitude: 10° 58′ E; altitude: 600 m). Bousalem region features a typical Mediterranean climate with a mean annual rainfall of 450 mm, concentrated mainly from November to December. In contrast, Matmata site has a hot and dry climate according to the Köppen-Geiger classification, with an average annual precipitation of 234 mm. The studied samples were randomly harvested from approximately ten carob trees at each site, and around 10 kilograms of pods were collected. The seeds were manually removed, and then the carob pulp from each site was dried at 40 °C for 24 h, ground separately into powder, and stored at -80 °C for further analysis
2.3. Extraction of Bioactive Compounds
Two different extraction techniques were evaluated, the conventional extraction technique maceration (M), and an innovative, environmentally friendly, faster and more efficient technique namely ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE). Furthermore, for each of these techniques different solvents were evaluated, organic solvents commonly used in polyphenol extraction, ethanol, and the mixtures ethanol: water (75:25) and methanol: water (80:20); and the green solvents, water, and the natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) lactic acid: sodium acetate (LA: SA (3:1:)) and citric acid : sucrose (CA: S (1:1)). Both NADES were previously used for the successful extraction of phenolic compounds in plant samples [
19,
21]. To obtain the NADES, the procedure established by Mansinhos et al. [
22] was followed.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the NADES used for phenolic extraction from carob pulp.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the NADES used for phenolic extraction from carob pulp.
| |
Non-conventional green solvents (NADES) |
| |
LA:SA |
CA:S |
|
Components and proportions
|
|
|
|
HBDs
|
Lactic acid |
Citric acid |
|
HBAs
|
Sodium acetate |
Sucrose |
|
HBD: HBA molar ratio
|
3:1 |
1:1 |
|
Ternary component
|
Water |
Water |
|
Amount of water (%)
|
30 |
30 |
|
Characteristics
|
|
|
|
pH
|
3.80 |
1.50 |
|
Appearance
|
Transparent colorless liquid |
Light-yellow semi viscous liquid |
The extraction process was carried out using a concentration of 1 g of dried carob pulp flour/10 mL of solvent. In the case of maceration, the sample was stirred (250 rpm) for 24 hours at room temperature (organic solvents and water) or 50 °C (NADES). In the case of ultrasound-assisted extraction, the process took place in an ultrasonic water bath system (40 kHz) (Ultrasons, JP Selecta, Barcelona, Spain) for 15 minutes under the same temperature conditions of the previous technique. The process was carried out with the carob sample and half of total volume of solvent (1 g/ 5 mL), the supernatant obtained after extraction was separated and the solute was re-extracted with the same volume (5 mL). Then, extracts were centrifuged at 15000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatants obtained from both extractions were pooled to a final volume of 10 mL and finally frozen at -80 °C until HPLC-HRMS analysis.
2.4. Spectrophotometric Analyses
Different spectrophotometric tests based on chemical reactions are commonly used to determine the antioxidant capacity of complex food samples. In this study two methods based on the transfer of one electron (SET) including the total phenolic content (TPC) by Folin-Ciocalteu and Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assays, and a mixture SET and HAT (transfer of a hydrogen atom) test namely 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) method were assessed. The analyses were performed in triplicate using a Synergy HTX MultiMode Microplate Reader (Biotek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA).
2.4.1. TPC by Folin-Ciocalteu Assay
The content of total polyphenols was measured according to the procedure followed by Otles and Yalcin [
23] with slight modifications. Carob extract/blank solution/gallic acid standard solution (10 μL) was mixed with distilled water (175 μL) and Folin-Ciolcalteau reagent (12 μL). The samples were left to stand for 3 min, and then an aqueous sodium carbonate solution (20 %, 30 μL) was added. After 1 hour, the samples were read at 765 nm. The results were expressed as milligrams of gallic acid equivalents per 100 g of dry weight (mg GAE/100 g DW).
2.4.2. TEAC or ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Assay
The AC by TEAC assay was determined according to the procedure of Pereira-Caro et al. [
24]. The absorbance of ABTS radical solution to 0.94-0.97 at 730 nm was adjusted adding methanol to the initial solution of ABTS (3.86 g/L) prepared in aqueous potassium persulfate (2.45 mM). The adjusted ABTS solution (190 μL) was added to each well and the first absorbance was read. Subsequently, the sample/standard solution/blank (10 μL) was added and left in the dark for 15 min. After this, the second absorbance was read. The final absorbance was the difference between the first and second absorbances measured. The results were expressed as milligrams of Trolox equivalents per 100 g of dry weight (mg TE/ 100 g DW).
2.4.3. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Assay
The free radical DPPH scavenging capacity was determined according to the method of Sánchez-Moreno et al. [
25], with slight modifications. The DPPH radical methanol solution (190 μL, 0.35 g/L), previously prepared adjusting the absorbance with methanol to 0.95 at 515 nm, was placed in the different microplate wells and the first reading was done. Then, sample/standard solution/blank (10 μL) was added to each well and the mixture was left to stand in the dark during 50 min. After this time, the microplate was read (second reading). The final absorbance was the difference of the first and the second reading. The results were expressed as milligrams of Trolox equivalents per 100 g of dry weight (mg TE/ 100 g DW).
2.5. Chromatographic Analysis of Polyphenol Compounds by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-HRMS)
The samples (5 µL) were analyzed by direct injection or after dilution (1:4), using a Dionex Ultimate 3000 HPLC system (Thermo Scientific, San José, CA, USA). The analytes from extracts were separated in a reverse phase C18 Kinetex column (150 × 4.6 mm i.d. 5 µm 100 A) (Phenomenex, UK) maintained at 40 °C and using a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min.
The chromatographic conditions using the mobile phases water and acetonitrile, both with 0.1% formic acid, were carried out according to the specifications of Mansinhos et al. [
22]. The mobile phase flow was of 0.2 mL/min directed to an Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, CA, USA) fitted with a heated electrospray ionization probe (HESI) operating in negative ionization mode and scanning the ions in the m/z range from 100 to 1000. The analyses were also based on in-source collision-induced dissociation scans at 25 eV. The capillary temperature was 320 °C, the heater temperature was 150 °C, the sheath gas and the auxiliary gas flow rate were 25 and 5 units, respectively, and the spray voltage was 4.00 kV. Data acquisition and processing were carried out using Xcalibur software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San José, CA, USA). The Exactive Orbitrap was externally calibrated weekly using ready-to-use calibration mixtures (Pierce ESI Negative Ion Calibration Solution and Pierce LQT ESI Positive Ion Calibration Solution, both available from Thermo Fisher Scientific, San José, CA, USA). A quality control (QC) sample was applied to assess and ensure that the analytical process was performed appropriately. The QC sample, a representative pool of identical aliquots of the plant extracts, was injected regularly throughout the run. Targeted identifications of phenolic compounds were achieved by comparing the exact mass and the retention time (RT) with available standards. In the absence of standards, compounds were tentatively identified by comparing the theoretical exact mass of the molecular ion with the measured accurate mass of the molecular ion and searched against Metlin, Phenol Explorer, PubChem and ChemSpider metabolite databases. In addition, these compounds were previously identified in carob pulp [
11,
26,
27,
28,
29]. Metabolites having molecular masses within the pre-specified tolerance (mass difference less than 5 ppm) of the query masses are retrieved from these databases. Additionally, the identification of compounds was carried out following the MSI MS levels previously established by Sumner et al. [
30]. Metabolites classified in level 1 were identified using m/z, RT and/or exact mass of reference standards, while when no reference standards were available these compounds were putatively annotated as level 2 based on their m/z, RT and/or MS/MS from spectral library compounds. The characteristics such as compound name, chemical formula, retention time, theoretical exact mass, delta ppm between experimental and theoretical exact mass, and MSI MI level are summarized in
Supplementary Table S1. Quantification of compounds were carried out by comparing their peak areas against the standard curves obtained with reference solutions. In absence of standard compounds, analytes were quantified by reference to the calibration curve of a closely related parent compound (based on their structures). The linearity of standards was determined and limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) were estimated from the standard deviation of ten determinations of a blank. The different parameters used in quantification of phenolic compounds are summarized in
Supplementary Table S2. All the analyses were performed in duplicate.
2.6. Data Processing and Chemometric Analyses
The experimental data were performed in duplicate and expressed as the mean and standard deviation (SD). Significant differences between results were determined using a one-way or three-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey test with p-values < 0.05 considered significant. The software used was the IBM SPSS Statistics 24.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., 2016, Chicago, Illinois, USA).
Multivariate analysis using principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis heatmap (HCA Heatmap) were employed to assess and identify patterns in the acquired data. Both chemometric tools were generated using the XLSTAT software (Addinsoft, NY, USA) with the HPLC-HRMS and antioxidant capacity results as input variables and all extract samples as scores.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HPLC-HRMS Analysis of Carob Samples
The identification obtained from the HPLC-HRMS analysis concerning the 72 polyphenol compounds identified or putatively identified in 24 (2x2x6) extracts obtained by triplicate from carob pulp of two Tunisian geographical ubications (North and South), and using two extraction techniques (UAE and maceration) and six solvents (conventional: ethanol, ethanol 75%, methanol 80%, and water; non-conventional: LA:SA and CA:S) are reported in
Table S1.
A total of 59 (
Table 2, carob extracts from South Tunisia) and 56 (
Table S3, carob extracts from North Tunisia) compounds were quantified, while the other 13 remaining identified compounds (the phenolic acids 3´,4´-hydroxycinnamic acid, and isochlorogenic acid A; the flavonoids kaempferol, kaempferol 3-gluco-7-rhamnoside, vicenin-2, luteolin 7-O-glucuronide, orientin, quercetin glucuronide, rutin, narirutin, and apiin; the tannin procyanidin C1; and the dihydrochalcone phloretin) presented concentrations for all samples below the detection or quantification limits. Focusing on carob extracts from South of Tunisia, quantified compounds were distributed in phenolic acids, including hydroxycinnamic (5) and hydroxybenzoic (6) acids; phenolic esters (3); flavonoids, distributed in flavan-3-ols (3), flavanones (2), flavonols (7), flavanonols (1) and flavones (5); condensed (2) and hydrolysable (19) tannins; other phenolic (5) compounds, and a miscellaneous (1) compound. Within the family of phenolic acids, the subclass of hydroxybenzoic acids stood out (95.1%-99.7% of phenolic acids), led by 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (93.9-96.7% of total phenolic acids, and 16.9-26.50% of total phenolics), followed by the hydroxycinnamic acids 4´-hydroxy-3´-methoxycinnamic acid (n.d.-0.98% of total phenolics) and 4´-hydroxycinnamic acid (0.07-0.85% of total phenolics). In the case of flavonoids, the highest concentration was found in flavanones, with a notable naringenin content (between 17.65-42.16% of total phenolics), and high contents of the flavonols quercetin glycosides-type, namely quercitrin (quercetin 3-rhamnoside) > isoquercitrin (quercetin 3-
β-D-glucoside ) > hyperoside (quercetin 3-galactoside). Previous works also showed flavonoids as the major constituents of carob pulp. Khelouf et al. [
31] studied the phenolic profile of carob pulp extracts from Ariana (coastal city from the north-eastern of Tunisia) obtained by ethanol-maceration (24 h at room temperature) founding the flavonols isorhamnetin (5.67 mg/ g dry extract (DE), O-methylated flavonol) and quercetin (3.21 mg/ g DE) as the main compounds, and being the concentration of 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid in lower content (0.19 mg/ g DE). In the work of Ioannou et al. [
26], 57% (v/v) acetone-UAE extracts of Cypriot carob showed a different profile, being in this case the flavonol glycoside rutin (0.89 mg /g product) the major compound followed by catechin (0.47 mg/ g product), 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (0.31 mg /g product) and epicatechin (0.11 mg/ g product), and lowest values of quercitrin, myricetin (both 0.03 mg / g product) and quercetin (0.02 mg/g product).
However, most works show that the largest group of phenols are phenolic acids, led by 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid. Thus, Richane et al. [
32] found high concentrations of the mentioned compounds in methanolic extracts of carob pulp from different regions of Tunisia, however, in the following order of concentration, 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (501.26-1628.46 mg/kg of dried residue (D.R.)) > ellagic acid (398.85-940.53 mg/ kg D.R.) > isoquercetrin (264.79-817.61 mg/kg of D.R.) > apigenin (194.66-696.12 mg/kg of D.R.) > naringenin (96.53-362.48 mg/kg of D.R.). On the other hand, methanolic extracts (60 °C, 30 min, UAE) obtained from Cypriot carob fiber (`Tilliria´) [
33], the pulp previously extracted with water, showed 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (1580 μg/ g food) > rutin (286 μg/ g food) > quercetin (40.6 μg/ g food) > myricetin (11.6 μg/ g food) > catechin (9.4 μg/ g food) > 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid (5.6 μg/ g food) as the main components. On the other hand, in other carob extractions obtained with unroasted and roasted (120 °C and 150 °C) carob pulp and using ethanol 45% v/v and maceration from 1-3 weeks [
15], and those obtained with same solvent mixed with commercial roasted carob pulp and extracted using percolation, maceration, infusion or distillation [
34], identified 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid as the main phenolic compound in high quantities in samples.
It was noteworthy the amount of hydrolyzable tannins, mainly galloylhexoside isomers, as well as the benzene-1,2,3-triol content. Papagiannopoulos et al. [
28] also detected high contents of flavonol-glycosides and hydrolysable tannins in commercial samples of carob fiber (carob pulp without sugars) from Germany (unknown plant origin), indicating higher content in the less processed sample (without roasting).
These different profiles and proportions of compounds obtained in carob extracts among literature, even within the same country and from similar sample collection regions, may be due to the variety of carob used, but also largely due to the extraction method used, such as the type of solvent and technique used, the extraction conditions in relation to the extraction time and temperature, the solvent: sample ratio, agitation, etc., among other factors [
7,
35]. Another important factor to take into account in this variability is the great influence of the non-homogenization of the expression of results, since in many cases it refers to the extract and not to the initial sample of origin (the carob pulp), where even in this case there may be modifications when expressing the results if these are expressed based on whether the sample is dry or fresh.
3.1.1. Influence of the Extraction Method (Technique and Solvent) on Phenolic Content
Extraction yields and recovery rates of the phenolic compounds can be enhanced by combining and integrating extraction methods [
16]. Therefore, in this section the influence of different combinations of solvents and techniques used in the extraction of compounds was evaluated. For this aim, within each technique and/or solvent used, factors such as temperatures, times of extraction and solvent-plant ratio (extraction conditions) were set.
Among the factors analyzed, the solvent had a great influence for all the families of compounds studied, while the geographical origin of the plant and the extraction technique did not show significant differences in the extraction of flavanones and flavones, and flavanones and hydrolysable tannins, respectively (
Table 3). Among interactions between main factors, the phenolic content was strongly dependent on those where the solvent was included (significant differences for all families and most of the compounds studied,
Table 3 and
Table S4), in this sense both the graphs and tables presented were evaluated taking into account this result. However, the complex interaction between the factors studied is reflected in the fact that no clear common trend for the different family of compounds studied was found according to the influence of techniques or solvents.
Therefore, for the study of the effect of the technique, fixing the type of solvents studied, it was observed that in the case of the organic solvents, ethanol (100% or 75%) and methanol (80%), in combination with the maceration technique produced significantly higher extractions of flavanones, flavones, total flavonoids, total phenolics and total compounds (
Table 2, South carob extracts). The maceration extraction time (24 h) was quite long for the organic solvents to penetrate and break the cell walls of the raw material, allowing the analytes to dissolve efficiently in the solvents [
36]. This may indicate that some parameters fixed in the UAE technique for these type of solvents, such as the period of time and temperature used, was not sufficient for a good recovery of compounds and it would be necessary to optimize its potential recovery [
37]. Similar trend was observed in the case of extracts obtained with ethanol (75%) and carob from North (
Table S3). Contrary, in the case of the green solvents water and the NADES LA:SA, the UAE technique improve the extraction of certain flavonoids such as flavanones (water), flavonols and flavan-3-ols (LA:SA), total flavonoids (water); condensed (water) and hydrolysable and total (water and LA:SA) tannins and total phenolics and total compounds (water and LA:SA). This could be due to several reasons, including the mechanical and cavitational effects of the ultrasounds, producing disruption of the cellular matrix, reduction in particle size, and mechanical effects, allowing greater penetration of this type of solvents [
38]. On the other hand, it may be due to greater ease of extraction using these solvents, so that with longer extraction time using maceration, their degradation/transformation occurs [
39].
Evaluating the influence of the solvents assessed, the trend was also different depending on the extraction technique. In the extraction of phenolic acids, both in the case of hydroxycinnamic and hydroxybenzoic acids, using maceration (water > ethanol (75%) > methanol (80%) > LA:SA > ethanol > S:CA) or UAE (water > LA:SA > methanol (80%) > ethanol (75%) > ethanol > S:CA), the best extractant was water. Goulas and Georgiou [
27] compared different conventional solvents in combination with UAE for the extraction of phenolics from carob pulp and found that the contents of 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic and 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acids were better extracted with water in comparison to methanol, however acetone-water and acidic acetone extracts presented the best results (almost twice as much as with water). On the other hand, it should be highlighted the green method resulting from the combination of UAE and the NADES LA:SA as the fourth best extractant, while for both techniques the other NADES (CA:S) produced the worst phenolic acid recoveries.
In the case of phenolic esters, there is a drastic decrease in the extraction of compounds from maceration (ethanol (75%) > W > LA:SA > methanol (80%) > ethanol > S:CA) to UAE (ethanol (75%) > ethanol > methanol (80%) > water). In both techniques ethanol (75%) was the solvent that extracted higher contents, but although in the case of maceration it was followed by the NADES LA:SA, for the UAE the conditions used were not adequate for both NADES, showing no extraction of this family of compounds.
In general, the extraction of total flavonoids (maceration, ethanol (75%) ≈ methanol (80%) ≈ water > ethanol ≈ LA:SA > S:CA; UAE, water > ethanol (75%) ≈ LA:SA ≈ methanol (80%) ≥ ethanol ≈ CA:S) was favored by the organic solvents ethanol (75%) and methanol (80%) and the green solvent water in the case of maceration, while in the case of the UAE technique, water was the most appropriate solvent. However, this family showed great variability in the extractability of each subclass of compounds. Thus, in flavan-3-ols LA:SA in combination with UAE followed by ethanol (75%), methanol (80%) or LA:SA using maceration were the most appropriate extracting methods. The highest extraction of flavanones, the most considerable group within the flavonoids, was produced using water-UAE, followed by water and ethanol (75%) with maceration, although producing half the extraction than the first case. Ethanol (75%) (M) ≈ LA:SA (UAE) ≈ methanol (80%) (M) > LASA (M) were the solvents with the best extractions of flavonols. Finally, the best extraction of flavanonols was observed in water (M) > methanol (80%) (M) ≈ water (UAE) ≈ LA:SA (UAE) ≈ ethanol (75%) (M) ≈ LA:SA (M), while flavones were better extracted using ethanol (75%) (M) ≈ methanol (80%) (M) > LA:SA (UAE). A previous study comparing different conventional solvents (water, methanol, acidic acetone and acetone water) in the extraction of phenolics from carob pulp found that those with acetone extracted higher contents of the flavonols quercetin (not detected in water and methanol) and rutin, and the flavan-3-ols catechin (not detected in water and methanol) and epicatechin; however, in the case of the flavonol myricetin higher contents were obtained with water and methanol [
27].
Regarding tannins, those of the subclass of condensates were extracted in greater quantities using methanol (80%) (M) > water (UAE) > ethanol (75%) (UAE) > ethanol (75%) (M) > methanol (80%) (UAE) > water (M), while NADES did not show extracting power. However, in the case of hydrolyzed tannins LA:SA (UAE) was the best extractant, closely followed by ethanol (M), water (UAE) and ethanol (75%) (M). Other identified phenols, highlighting benzene-1,2,3-triol, were extracted in large quantities using water (UAE and M), ethanol (75%) (M) and LA:SA (M and UAE). Finally, galactopyranosyl glucose was adequately extracted with all solvents used, highlighting the NADES CA:S.
3.1.2. Impact of Tunisian Origin on the Profile of Phenolics from Different Carob Extracts
Previous studies have shown that the geographical origin of the plant has a great influence on the phenolic profile obtained, even suggesting that these compounds may be markers of the location where the plant has grown. This has been largely attributed to the climatic variations that may occur in the areas where the plant grows [
29,
32].
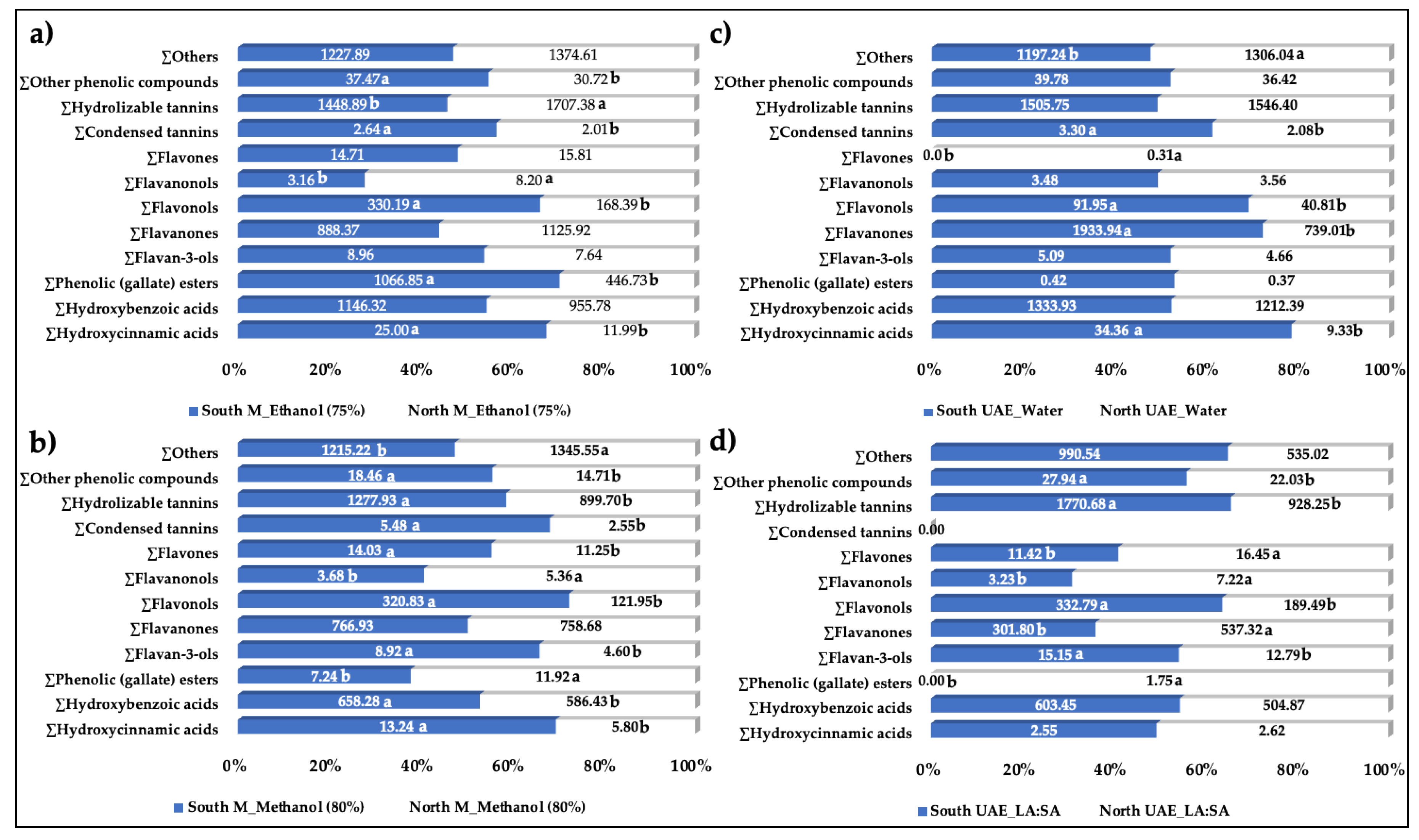
In this research, the phenolic profile of carob pulp flour from two different locations of Tunisia has been evaluated. The results have been compared taking into account four of the best extractants, which have been the combination of the conventional technique maceration with the organic solvents ethanol (75%) (
Figure 1, a) or methanol (80%) (
Figure 1, b), followed by a sustainable technique (UAE) with a green conventional solvent (water,
Figure 1, c) or non-conventional solvent (NADES LA:SA (3:1),
Figure 1, d). The results show appreciable differences among the methods assessed, however with a general common trend. Comparing the phenolics of carob extracts from both regions of Tunisia using the conventional methods, we can observe higher contents of hydroxycinnamic acids, flavonols, condensed tannins and other phenolic compounds in the sample from South. In the case of ethanol (75%) extracts, the southern region (more arid climate) also stands out in its content in hydroxybenzoic acids, flavan-3-ols, flavones and hydrolysable tannins. Scarce literature related to carob pulp has defined the variations in the phenolic profile according to the geographical origin of the samples. However, Richane et al. [
32], evaluating the variations of carob extracts from different Tunisian geographic locations, found that the conventional methanolic (80%) extracts of carob pulp from mean and lower semi-arid, and upper arid climate regions showed in general higher contents of certain phenolic acids, mainly the hydroxybenzoic acids 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic and 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acids, and some flavonoids, the flavone apigenin, and the flavan-3-ols epigallocatechin and epicatechin-3-O-gallate, and the flavonols kaempferol and kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside. Thus, the results are partially shared with the present research.
For the green methods, there is greater equity in the content found between North and South regions, however, the sample from the South of Tunisia continues to be the one that showed higher concentrations of phenolics, such as the flavonoids flavonols and flavanones, the condensed tannins and the hydroxycinnamic acids in UAE-water extracts, while the flavonoids flavan-3-ols and flavonols and the hydrolysable tannins and other phenolic compounds in extracts elaborated using the UAE-LA:SA method.
3.2. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Capacity of Carob Extracts by Folin-Ciocalteu, TEAC and DPPH In Vitro Assays
Phenolics are compounds linked to the antioxidant capacity (AC) of plant extracts and already found in different carob products as the main responsible for this bioactivity [
40]. As can be seen in
Table S5, high correlations were found between the different methods employed for evaluating the AC of compounds present in carob extracts, namely total phenolic content (TPC), the DPPH and TEAC assays. These methods are based on different mechanisms of action by which the natural antioxidant compounds can exert their activity [
41]. Thus, the AC evaluated by these three mentioned methods was highly correlated with different phenolic compounds (
Table S5), and therefore these compounds contribute significantly to this bioactivity. Among the compounds involved in the evaluated bioactivity are the hydroxybenzoic acids 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid; many flavonoids such as the flavan-3-ols catechin, epicatechin and epigallocatechin; the flavanone eriodictyol; the flavonols quercetin, isoquercitrin, guaiaverin, hyperoside, reynoutrin, quercitrin and isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside; the flavones apigenin, apigenin-7-O-glucoside, apigenin-7-O-glucuronide, luteolin, luteolin-7-O-glucoside; the hydrolysable tannins galloyl dihexoside isomer IV, digalloyl hexoside isomer III, trigalloyl hexoside isomers I-V, tetragalloyl hexoside isomer II and pentagalloyl hexoside; and other phenolic, benzene-1,2,3-triol. Among the mentioned compounds, 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, luteolin and apigenin were compounds that have previously been attributed with antioxidant properties in carob pulp extracts [
32].
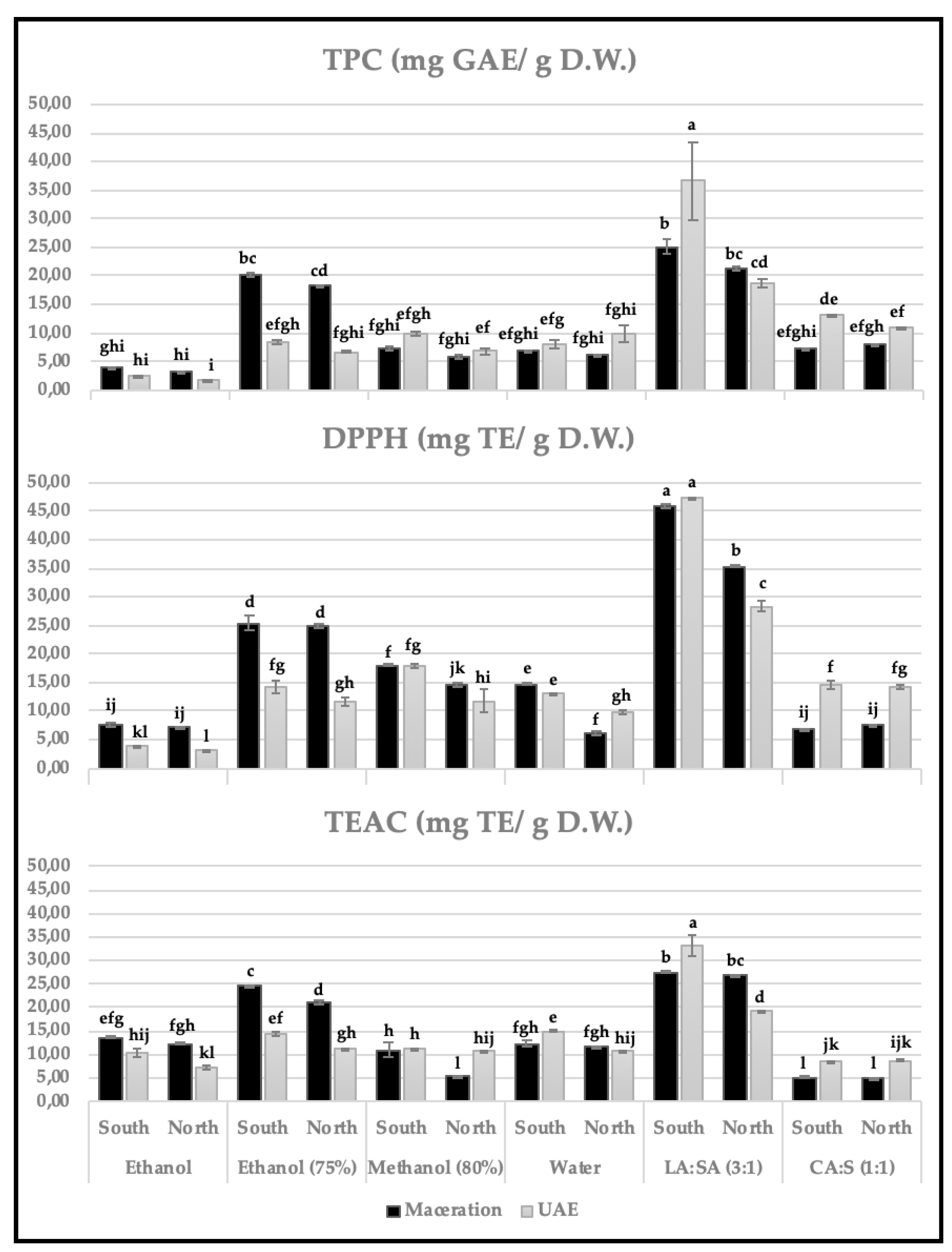
Evaluating the effect of the method (solvent and technique) and plant origin on the AC assessed by the three methods (
Figure 2), similar tendencies were found in the results, with the samples from southern Tunisia extracted with LA:SA-UAE showing the highest antioxidant capacities (TPC, 36.56 mg GAE/ g d.w.; DPPH, 47.24 mg TE/ g d.w.; TEAC, 33.14 mg TE/ g d.w.), closely followed by LA:SA-M (25.04 mg GAE/ g d.w., TPC; 45.71 mg TE/ g d.w., DPPH; and 27.53 mg TE/ g d.w., TEAC). This is an interesting fact regarding the use of this green extract in different industrial applications. These extracts were not those with the highest content of phenolic compounds (
Table 2 and
Table S3), therefore, their higher bioactivity indicates that other compounds may contribute to their ability to neutralize the action of free radicals. Santos-Martín et al. [
20] also found the extracts of leaves of blueberry using LA:SA:W (3:1:2)-UAE, those with higher TPC (135 mg GAE/ g dried blueberry leaves, DBL) and TEAC activity (153 mg TEAC/ g DBL), in comparison to those with the NADES choline chloride: oxalic acid (ChCl:Ox; 1:1) (109 mg GAE/ g DBL, TPC; 137 mg TEAC/ g DBL, TEAC), and the organic solvent methanol 80% (86.9 mg GAE/ g DBL, TPC; 130.1 mg TEAC/ g DBL, TEAC).
Comparing our results with those of previous works found in literature using different solvents and/or techniques for the assessment of the antioxidant potential in carob pulp, lowest values of TPC (Folin-Ciocalteu) were found using UAE-acetone and carob from North of Morocco (20.38 ± 0.124 mg GAE/ g d.m) [
42]. In the work of Samia et al. [
43], comparing between two conventional techniques, ethanol (30%) extracts using maceration (11.65 mg GAE/g DW) showed higher results compare to Soxhlet (9.88 mg GAE/g DW) in the extraction of carob fruits from Grombalia (Northeast of Tunisia). Both values were lower (practically half) than those obtained in the present work with maceration but using a higher ethanol content (75%), 20.12 and 18.27 mg GAE/g d.w for the samples from southern and northern Tunisia, respectively. However, carob pulp from North (Bizerte, sub-humid climate; 13.19 mg GAE/ g D.R.) and medium (Kairouan, upper arid climate, 23.11 mg GAE/ g D.R.) of Tunisia and extracted with methanol 80%-maceration showed higher values (two to three-fold)[
32] than those of the present work extracted with the same technique and solvent (6.4 and 7.3 mg GAE/ g D.W. from North and South of Tunisia, respectively). Due to the great influence of the extraction method used, these differences can probably be mostly justified by the fact that the extraction time used was half an hour compared to 24 hours used in our case. In a short time, the bioactive compounds were probably extracted and subsequently degraded, making it necessary to optimize times and temperatures for each of the technique-solvent combinations used.
Other interesting extracts were those obtained with carob pulp from northern Tunisia by maceration using ethanol (75%). Finally, the worst results presented in CA:S-maceration (TPC, DPPH and TEAC) and ethanol-UAE/maceration (TPC and DPPH) were consistent with those found in the phenolic profile (
Table 2 and
Table S3).
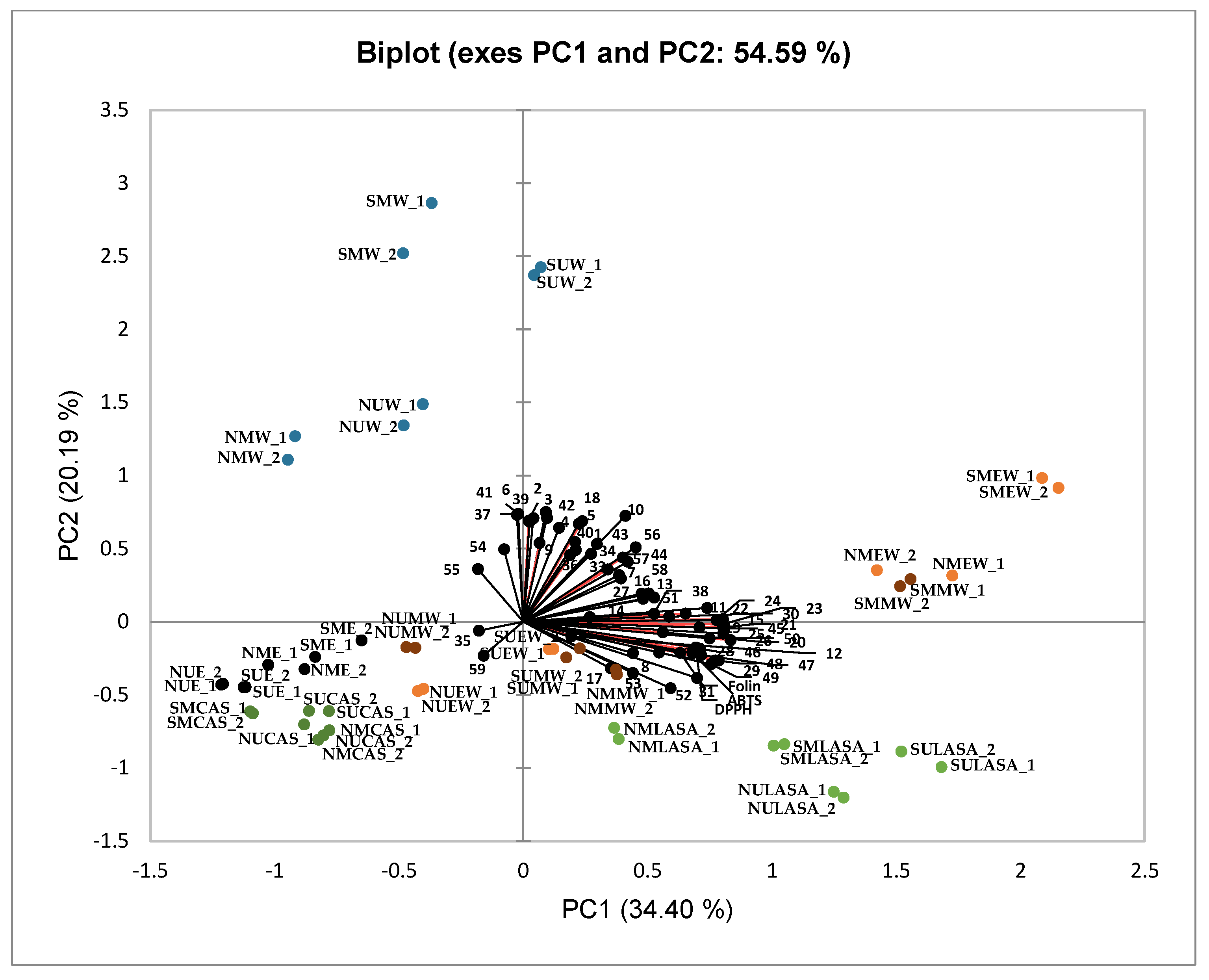
3.3. Chemometric Analysis: Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Heatmap Hierarchical Clustering Analysis (Heatmap HCA)
A principal component analysis (PCA) biplot was performed to describe the characteristics of the original data set and to present the overall similarities and differences among the different carob pulp extracts obtained from two Tunisian ubications (North and South) and using combinations of a convectional technique (maceration) and solvents (ethanol 100% and 75%, methanol 80%) and greener solvents (water, the NADES LA:SA and CA:S) and technique (UAE), and based on the phenolic profile obtained by HPLC-HRMS and biological properties analyzed by TPC, DPPH and TEAC assays (
Figure 3). The first two principal components (PC) accounted for 54.59% of the total variation in the dataset, with PC1 and PC2 explaining 34.40% and 20.19.%, respectively.
The biplot showed a clear differentiation of three groups of carob extracts characterized by presenting the highest phenolic content. One group formed by the extracts obtained with water (regardless of the technique and origin of plant material; SMW, SUW, NUW and NMW) and located in the positive part of PC2 (second quadrant). These aqueous extracts are characterized by higher contents of phenolic acids, both hydroxycinnamic acids and hydroxybenzoic acids, and flavanones specifically the compound naringenin, as well as certain hydrolysable tannins of the galloyl dihexoside-type.
The second group, positioned in the most positive part of PC1 (first quadrant), is composed by the extracts obtained using maceration in combination with ethanol (75%) or methanol (80%) (SMEW, NMEW, and SMMW), while the third group is formed by the extracts combining the NADES LA:SA (3:1) with maceration (SMLASA) and UAE (SULASA and NULASA), samples positioned in the fourth quadrant. The closeness of both groups in graph indicated similar extracting power of polyphenols in plant samples. These second and third groups are characterized by their contents in the subclasses of flavonoids namely flavonols (mainly guaiaverin, reynoutrin, isoquercitrin and isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside) and flavones (apigenin, apigenin 7-O-glucoside, apigenin 7-O-glucuronide, luteolin and luteolin 7-O-glucoside), as well as the hydrolyzed tannins of the digalloyl hexoside and trigalloyl hexoside-types (
Table 2 and
Table S3, and
Figure 3). It is also remarkable the high antioxidant capacity (TPC, TEAC and DPPH assays) of LA:SA extracts. Fu et al. [
44], analyzing the phenolic content of the peels of
Carya cathayensis Sarg, also found a similar extraction profile comparing the alcohol:water solvents and that of LA:SA, and attributing the results obtained to the similarity of the parameters evaluated.
Finally, another clearly defined group of extracts were those obtained with ethanol and the NADES CA:S, positioned in the third quartile of the PCA, which presented the lowest content of phenolic compounds.
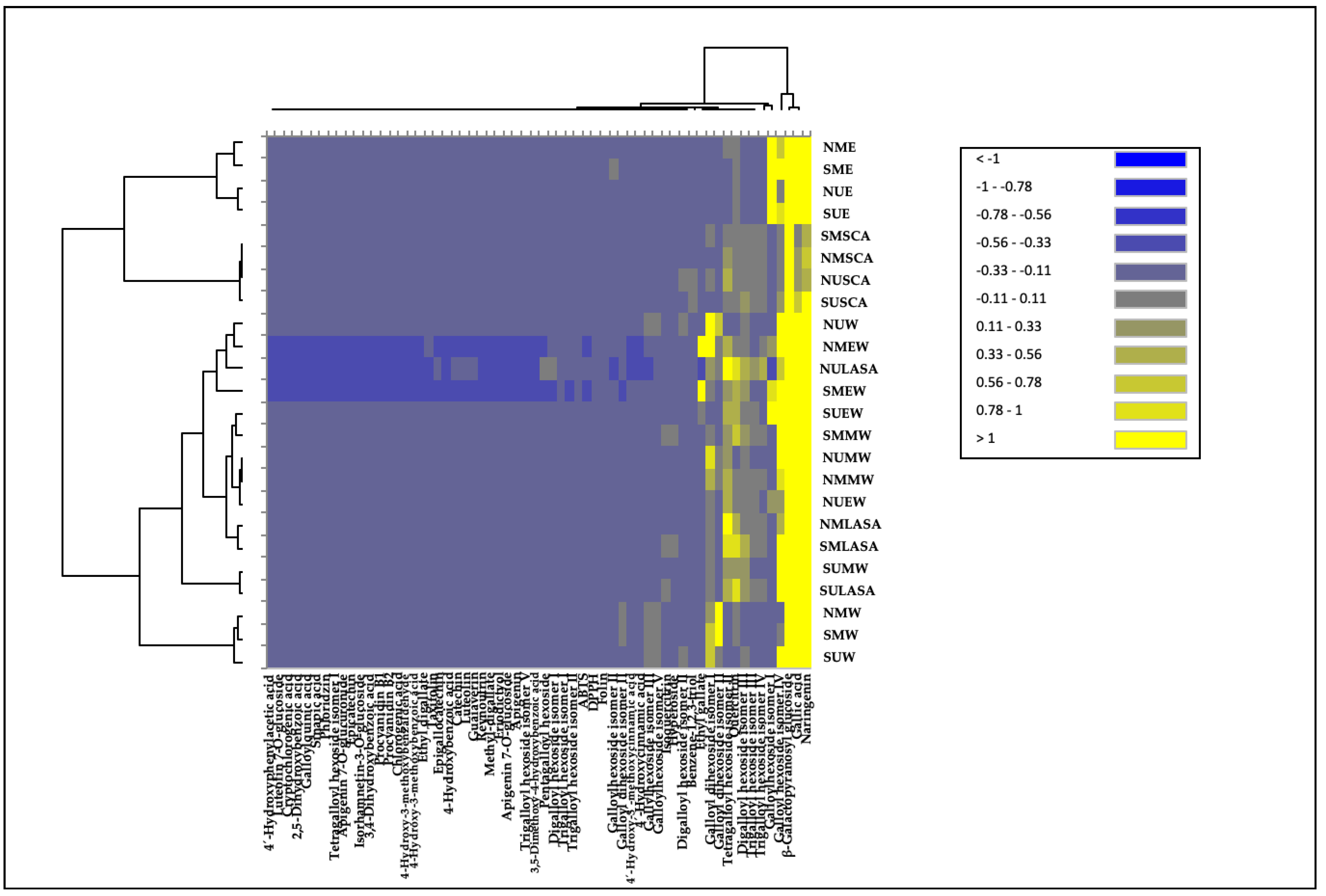
Additionally, the polyphenolic dataset was elaborated by means of unsupervised hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA, produced from the fold-change heat map) in order to group samples according to intrinsic similarities in their phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity. The HCA heat map is reported as
Figure 4, showing a clear differential profile of the extracts obtained with the NADES CA:S and the organic solvent ethanol (samples outlined in the first cluster of HCA), both using maceration or UAE techniques, in comparison to the other carob extracts consisting of samples included in the same second cluster, and being those with the highest contents of bioactive compounds. This fact reveals the different and, according to the heatmap and HPLC-HRMS results (
Table 2 and
Table S3), scarce contents in phenolics and lower antioxidant potential of extracts obtained with these solvents. Within the second cluster, different sub-clusters distributed in different levels can be observed for the remaining extracts according to the chemical profile obtained for each combination of technique and solvent used. Aqueous extracts obtained by maceration from both locations in Tunisia (NMW and SMW) and those obtained by UAE from southern Tunisia (SUW), are clearly differentiated from the rest of the remaining extracts. On the other hand, UAE extracts using methanol (80%) and LA:SA (1:3) from south of Tunisia (SUMW and SULASA, respectively) presented a closer and differentiated profile to aqueous extractions. Combinations of the other organic solvents with water and the solvent NADES LA:SA using different extraction techniques, as well as the water sample from northern Tunisia extracted by UAE were grouped together. Finally, it is important to note that water and LA:SA-UAE extracts, and ethanol (75%)-maceration from Northern Tunisia (NUW, NULASA and NMEW, respectively) and that from the South extracted by ethanol (75%)-maceration (SMEW) are samples close to those with the lowest phenolic content, however, highlighting by a high contents of certain hydrolysable tannins of galloyl dihexoside and tetragalloyl hexoside-types.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, 72 phytochemicals in carob extracts were quantified by HPLC-HRMS, mainly including hydroxycinnamic and hydroxybenzoic acids, phenolic esters, flavan-3-ols, flavanones, flavonols, flavanonols, flavones, condensed and hydrolysable tannins, other phenolic compounds and miscellaneous. Among these compounds, the flavanone naringenin, the hydroxybenzoic acid 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid, the flavonols isoquercitrin, hyperoside and quercitrin, the hydrolysable tannins galloyl, digalloyl and tetragalloyl hexoside isomers, and benzene-1,2,3-triol were the most predominant compounds in the extracts. The green method combinations, water-UAE and LA:SA (3:1)-UAE, were powerful extractants for the evaluated compounds, mainly phenolic acids, flavanones, hydrolysable tannins and other phenolic compounds in the case of water, while in the LA:SA (1:3) extracts, flavan-3-ols, flavonols and hydrolyzable tannins. Both methods are considered good alternatives to conventional combinations (ethanol (75%) or methanol (80%)-maceration) commonly used in the extraction of polyphenols in plant byproducts. In relation to the geographical origin of the samples, using the conventional methods or the sustainable combinations namely water-UAE and LA:SA-UAE, the southern sample showed the highest contents for most families of phenolic compounds determined. The results obtained show high variability in the content of extracted compounds depending on the method used (the technique and mainly the solvent), indicating the need to optimize the extraction method conditions depending on the origin of the raw material and the family of compounds to be extracted. New perspectives on the optimization of other close combinations of green solvents, such as new combinations of HBA and HBD or their proportions, or even additional extraction conditions (e.g. new extraction times, solvent : sample ratio, etc.) would be interesting. In addition, the good results obtained with the green methods assessed provide new insights of these sustainable extracts rich in added-value bioactive compounds for industrial applications, promoting a circular economy of an underused Mediterranean byproduct.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: Extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) of the 72 compounds identified in carob extracts from North and South of Tunisia and using different extraction techniques (maceration or ultrasound-assisted extraction) and solvents (ethanol 100% or 75%, methanol 80%, lactic acid: sodium acetate (3:1) or citric acid: sucrose (1:1)); Table S1: HPLC-HRMS-characteristics of the different compounds identified in carob extracts; Table S2: HPLC-HRMS-parameters for quantification of the different compounds analyzed in carob extracts: slope, intercept and R2 of the calibration curve, and limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) and range of work; Table S3: Phenolic composition (µg/g) determined by HPLC-HRMS of carob extracts from North of Tunisia and obtained using two different techniques (maceration, M; ultrasound-assisted extraction, UAE) and six solvents (ethanol (100% or 75%), methanol (80%), water, lactic acid : sodium acetate (LA:SA, 3:1); citric acid: sucrose (CA:S, 1:1)); Table S4: Three-way ANOVA: influence of the plant origin (North and South of Tunisia), bioactive extraction technique (maceration, ultrasound-assisted extraction, UAE), solvent (ethanol (E), ethanol: water (E:W; 75:25), methanol:water (M:W; 80:20), water (W), lactic acid: sodium acetate (LA:SA; 3:1); sucrose: citric acid (S:CA; 1:1) on the extraction of polyphenol compounds (µg/ g DW) determined by HPLC-HRMS; Table S5: Pearson´s correlations between phenolic compounds and the antioxidant capacity of Ceratonia siliqua L. pulp..
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S., F.S., J.M.M.R., R.R.S.; methodology, C.S., F.S., M.A.E.C., S.C.J., A.M.O., and R. R.S.; software, R.R.S.; validation, R.R.S.; formal analysis, R.R.S.; investigation, C.S., F.S., M.A.E.C., S.C.J., A.M.O., and R.R.S..; resources, R.R.S., F.S., S.B., and J.M.M.R.; data curation, R.R.S..; writing—original draft preparation, C.S., R.R.S..; writing—review and editing, C.S., F.S., J.M.M.R., R.R.S.; visualization, R.R.S.; supervision, F.S., R.R.S.; project administration, R.R.S.; funding acquisition, F.S., S.B., J.M.M.R.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Raquel Rodríguez Solana was supported by the grant RYC2022-036888-I, funded by MCIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by the FSE+.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Martins-Loução, M.A.; Correia, P.J.; Romano, A. Carob: A Mediterranean resource for the future. Plants 2024, 13(9), 1188. [CrossRef]
- Naghmouchi, S.; Khouja, M.L.; Romero, A.; Tous, J.; Boussaid, M. Tunisian carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) populations: Morphological variability of pods and kernel. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 121(2), 125-30. [CrossRef]
- Dahmani, W.; Elaouni, N.; Abousalim, A.; Akissi, Z.L.E.; Legssyer, A.; Ziyyat, A.; Sahpaz, S. Exploring carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.): A comprehensive assessment of its characteristics, ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemical aspects, and pharmacological activities. Plants 2023, 12(18), 3303. [CrossRef]
- Azab, A. Carob (Ceratonia siliqua): health, medicine and chemistry. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2017, 6(10), 456-469. [CrossRef]
- Moumou, M.; Mokhtari, I.; Milenkovic, D.; Amrani, S.; Harnafi, H. Carob ( Ceratonia siliqua L.): A comprehensive review on traditional uses, chemical composition, pharmacological effects and toxicology (2002-2022). J. Biol. Act. Prod. Nat. 2023, 13(3), 179-223. [CrossRef]
- Laaraj, S.; Salmaoui, S.; Addi, M.; El-rhouttais, C.; Tikent, A.; Elbouzidi, A.; Taibi, M.; Hano, C. Noutfia, Y. Elfazazi, K. Carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) seed constituents: A comprehensive review of composition, chemical profile, and diverse applications. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2023, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Solana, R.; Romano, A.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M. Carob pulp: A nutritional and functional by-product worldwide spread in the formulation of different food products and beverages. A review. Processes 2021, 9(7), 1146. [CrossRef]
- Akdeniz, E.; Yakışık, E.; Rasouli Pirouzian, H.; Akkın, S.; Turan, B.; Tipigil, E.; Said Toker, O.; Ozcan, O. Carob powder as cocoa substitute in milk and dark compound chocolate formulation. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58(12), 4558-66. [CrossRef]
- Musa Özcan, M.; Arslan, D.; Gökçalik, H. Some compositional properties and mineral contents of carob ( Ceratonia siliqua ) fruit, flour and syrup. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 58(8), 652-8. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Solana, R.; Carlier, J.D.; Costa, M.C.; Romano, A. Multi-element characterisation of carob, fig and almond liqueurs by MP-AES: Multi-element characterisation of carob, fig and almond liqueurs by MP-AES. J. Inst. Brew. 2018, 124(3), 300-9. [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, I.J.; Christou, A.; Kapnissi-Christodoulou, C.P. Polyphenols in carobs: A review on their composition, antioxidant capacity and cytotoxic effects, and health impact. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 355-74. [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Garg, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Fiorino, M.; Ameen, S.M.; Haddad, M.A.; Al-Hiary, M. Natural polyphenols: chemical classification, definition of classes, subcategories, and structures. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102(5), 1397-400. [CrossRef]
- Bucalossi, G.; Fia, G.; Dinnella, C.; De Toffoli, A.; Canuti, V.; Zanoni, B.; Servili, M.; Pagliarini, E.; Gallina Toschi, T.; Monteleone, E. Functional and sensory properties of phenolic compounds from unripe grapes in vegetable food prototypes. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126291. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Md.M.; Rahaman, Md.S.; Islam, Md.R.; Rahman, F.; Mithi, F.M.; Alqahtani, T.; Almikhlafi, M.A.; Alghamdi, S.Q.; Alruwaili, A.S.; Hossain, Md.S.; Ahmed, M.; Das, R.; Emran, T.B.; Uddin, Md.S. Role of phenolic compounds in human disease: current knowledge and future prospects. Molecules 2021, 27(1), 233. ttps://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010233.
- Rodríguez-Solana, R.; Salgado, J.M.; Pérez-Santín, E.; Romano, A. Effect of carob variety and roasting on the antioxidant capacity, and the phenolic and furanic contents of carob liquors. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99(6), 2697-707. [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Tobón, J.F. Recent advances and comparisons of conventional and alternative extraction techniques of phenolic compounds. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57(12), 4299-315. [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, G.; Prava Jyoti, T.; Chandel, S.; Singh, R. Eco-friendly extraction: innovations, principles, and comparison with traditional methods. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2024, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Redha, A.A. Review on extraction of phenolic compounds from natural sources using green deep eutectic solvents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69(3), 878-912. [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.B.T.; Jadeja, G.C. Microwave-assisted extraction for recovery of polyphenolic antioxidants from ripe mango ( Mangifera indica L.) peel using lactic acid/sodium acetate deep eutectic mixtures. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2020, 26(1), 78-92. [CrossRef]
- Santos-Martín, M.; Cubero-Cardoso, J.; González-Domínguez, R.; Cortés-Triviño, E.; Sayago, A.; Urbano, J.; Fernández-Recamales, A. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from blueberry leaves using natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) for the valorization of agrifood wastes. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 175, 106882. [CrossRef]
- Savi, L.K.; Dias, M.C.G.C.; Carpine, D.; Waszczynskyj, N.; Ribani, R.H.; Haminiuk, C.W.I. Natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) based on citric acid and sucrose as a potential green technology: a comprehensive study of water inclusion and its effect on thermal, physical and rheological properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2019, 54(3), 898-907. [CrossRef]
- Mansinhos, I.; Gonçalves, S.; Rodríguez-Solana, R.; Ordóñez-Díaz, J.L.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Romano, A. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction and natural deep eutectic solvents combination: a green strategy to improve the recovery of phenolic compounds from Lavandula pedunculata subsp. lusitanica (Chaytor) Franco. Antioxidants 2021, 10(4), 582. [CrossRef]
- Otles, S.; Yalcin, B. Phenolic compounds analysis of root, stalk, and leaves of nettle. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Caro, G.; Madrona, A.; Bravo, L.; Espartero, J.L.; Alcudia, F.; Cert, A.; Mateos, R. Antioxidant activity evaluation of alkyl hydroxytyrosyl ethers, a new class of hydroxytyrosol derivatives. Food Chem. 2009, 115(1), 86-91. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Larrauri, J.A.; Saura-Calixto, F. A procedure to measure the antiradical efficiency of polyphenols. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 76(2), 270-6. [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.D.; Savva, I.K.; Christou, A.; Stavrou, I.J.; Kapnissi-Christodoulou, C.P. Phenolic profile, antioxidant activity, and chemometric classification of carob pulp and products. Molecules 2023, 28(5), 2269. [CrossRef]
- Goulas, V.; Georgiou, E. Utilization of carob fruit as sources of phenolic compounds with antioxidant potential: extraction optimization and application in food models. Foods 2019, 9(1), 20. [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulos, M.; Wollseifen, H.R.; Mellenthin, A.; Haber, B.; Galensa, R. Identification and quantification of polyphenols in carob fruits ( Ceratonia siliqua L.) and derived products by HPLC-UV-ESI/MSn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52(12), 3784-91. [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Martinez-Piernas, A.B.; Stavrou, I.J.; Garcia-Reyes, J.F.; Kapnissi-Christodoulou, C.P. HPLC-ESI-HRMS and chemometric analysis of carobs polyphenols – Technological and geographical parameters affecting their phenolic composition. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104744. [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T. W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; Hankemeier, T.; Hardy, N.; Harnly, J.; Higashi, R.; Kopka, J., Lane, A.N.; Lindon, J.C.; Marriot, P.; Nicholls, A.W.; Reily, M.D.; Thaden, J.J., Viant, M.R. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis: chemical analysis working group (CAWG) metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3(3), 211-21. [CrossRef]
- Khelouf, I.; Jabri Karoui, I.; Abderrabba, M. Chemical composition, in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of carob pulp (Ceratonia siliqua L.) from Tunisia. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77(10), 6125-34. [CrossRef]
- Richane, A.; Rim, B.M.; Wided, M.; Riadh, K.; Khaoula, A.; Nizar, M.; Hanen, B.I. Variability of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of ten Ceratonia siliqua L. provenances. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2022, 104, 104486. [CrossRef]
- Goulas, V.; Hadjisolomou, A. Dynamic changes in targeted phenolic compounds and antioxidant potency of carob fruit (Ceratonia siliqua L.) products during in vitro digestion. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 101, 269-75. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Solana, R.; Coelho, N.; Santos-Rufo, A.; Gonçalves, S.; Pérez-Santín, E.; Romano, A. The influence of in vitro gastrointestinal digestion on the chemical composition and antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory capacities of carob liqueurs obtained with different elaboration techniques. Antioxidants, 2019, 8(11), 563. [CrossRef]
- Loullis, A.; Pinakoulaki, E. Carob as cocoa substitute: a review on composition, health benefits and food applications. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244(6), 959-77. [CrossRef]
- Zannou, O.; Pashazadeh, H.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Koca, I.; Galanakis, C.M. Green and highly extraction of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity from kinkeliba (Combretum micranthum G. Don) by natural deep eutectic solvents (NADESs) using maceration, ultrasound-assisted extraction and homogenate-assisted extraction. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15(5), 103752. [CrossRef]
- Papoutsis, K.; Pristijono, P.; Golding, J.B.; Stathopoulos, C.E.; Bowyer, M.C.; Scarlett, C.J.; Vuong, Q.V. Optimizing a sustainable ultrasound-assisted extraction method for the recovery of polyphenols from lemon by-products: comparison with hot water and organic solvent extractions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244(8), 1353-65. [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound: a clean, green extraction technology. TrAC,Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 100-9. [CrossRef]
- Cravotto, G.; Mariatti, F.; Gunjevic, V.; Secondo, M.; Villa, M.; Parolin, J.; Cavaglià, G. Pilot scale cavitational reactors and other enabling technologies to design the industrial recovery of polyphenols from agro-food by-products, a technical and economical overview. Foods 2018, 7(9), 130. [CrossRef]
- Custódio, L.; Fernandes, E.; Escapa, A.L.; Fajardo, A.; Aligué, R.; Alberício, F.; Neng, N.R.; Nogueira, J.M.F.; Romano, A. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of carob tree fruit pulps are strongly influenced by gender and cultivar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59(13), 7005-12. [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical methods used in determining antioxidant activity: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22(7), 3380. [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, F.E.; Silva, J.C.G.E.; Cacciola, F.; Asraoui, F.; Tayeq, H.; Ben Amar, Y.M.; Palma Lovillo, M.; Chouaibi, N.; Brigui, J. Evaluation of different extraction methods on the phenolic profile and the antioxidant potential of Ceratonia siliqua L. pods extracts. Molecules 2022, 27(19), 6163. [CrossRef]
- Samia, O.; Nesrine, M.; Feten, Z.K.; Riadh, K. Tunisian Ceratonia siliqua: phytochemical analysis, antioxidant activity, preparation and characterization of carob emulsion system. European J. Nutr. Food Saf. 2022, 14(2), 41-52. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Belwal, T.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Luo, Z. UPLC-Triple-TOF/MS characterization of phenolic constituents and the influence of natural deep eutectic solvents on extraction of Carya cathayensis Sarg. peels: Composition, extraction mechanism and in vitro biological activities. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131042. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Comparison of polyphenol extraction (µg/g D.W.), determined by HPLC-HRMS, from North and South of Tunisia according to the better solvent-technique methods namely, combinations of maceration-ethanol (75%) (a), maceration-methanol (80%) (b), ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE)-water (c), and the NADES LA:SA (3:1)-UAE (d). In each graph, for each family of compounds, values marked with different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
Figure 1.
Comparison of polyphenol extraction (µg/g D.W.), determined by HPLC-HRMS, from North and South of Tunisia according to the better solvent-technique methods namely, combinations of maceration-ethanol (75%) (a), maceration-methanol (80%) (b), ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE)-water (c), and the NADES LA:SA (3:1)-UAE (d). In each graph, for each family of compounds, values marked with different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
Figure 2.
Antioxidant capacity by total phenolic content (TPC; Folin-Ciocalteu; expressed as mg of gallic acid equivalents/ g of dry weight), Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC, expressed as mg of Trolox equivalents/ g of dry weight) and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH, expressed as mg of Trolox equivalents/ g of dry weight·) in vitro assays. The bioactivity was evaluated in carob (north and south origins) extracts obtained using maceration or ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) techniques and in combination with conventional (ethanol-100% and 75%, methanol-80%, water) or innovative sustainable solvents (lactic acid: sodium acetate, LA: SA (3:1:); citric acid : sucrose, CA: S (1:1)). In each graph, values marked with different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
Figure 2.
Antioxidant capacity by total phenolic content (TPC; Folin-Ciocalteu; expressed as mg of gallic acid equivalents/ g of dry weight), Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC, expressed as mg of Trolox equivalents/ g of dry weight) and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH, expressed as mg of Trolox equivalents/ g of dry weight·) in vitro assays. The bioactivity was evaluated in carob (north and south origins) extracts obtained using maceration or ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) techniques and in combination with conventional (ethanol-100% and 75%, methanol-80%, water) or innovative sustainable solvents (lactic acid: sodium acetate, LA: SA (3:1:); citric acid : sucrose, CA: S (1:1)). In each graph, values marked with different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Score and loading biplot of the first two principal components (PC1 and PC2) of the phenolic content by HPLC-HRMS and biological properties by TPC, DPPH and TEAC assays from North (N) and South (S) of Tunisian carob pulp extracted with maceration (M) or ultrasound-assisted extraction (U) techniques and in combination with ethanol (100%, E; 75%, EW), methanol (80%; MW), water (W), lactic acid: sodium acetate (LASA) or citric acid: sucrose (CAS). The numbers of volatile compounds are those indicated in
Table 2.
Figure 3.
Score and loading biplot of the first two principal components (PC1 and PC2) of the phenolic content by HPLC-HRMS and biological properties by TPC, DPPH and TEAC assays from North (N) and South (S) of Tunisian carob pulp extracted with maceration (M) or ultrasound-assisted extraction (U) techniques and in combination with ethanol (100%, E; 75%, EW), methanol (80%; MW), water (W), lactic acid: sodium acetate (LASA) or citric acid: sucrose (CAS). The numbers of volatile compounds are those indicated in
Table 2.
Figure 4.
Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Heatmap (HCA Heatmap) of the phenolic content by HPLC-HRMS and biological properties by TPC, DPPH and TEAC assays from North (N) and South (S) of Tunisian carob pulp extracted with maceration (M) or ultrasound-assisted extraction (U) techniques and in combination with ethanol (E), ethanol (75%; EW), methanol (80%; MW), water (W), lactic acid: sodium acetate (LASA) or citric acid: sucrose (CAS).
Figure 4.
Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Heatmap (HCA Heatmap) of the phenolic content by HPLC-HRMS and biological properties by TPC, DPPH and TEAC assays from North (N) and South (S) of Tunisian carob pulp extracted with maceration (M) or ultrasound-assisted extraction (U) techniques and in combination with ethanol (E), ethanol (75%; EW), methanol (80%; MW), water (W), lactic acid: sodium acetate (LASA) or citric acid: sucrose (CAS).
Table 2.
Phenolic composition (µg/g) determined by HPLC-HRMS of carob extracts from South of Tunisia and obtained using two different techniques (maceration, M; ultrasound-assisted extraction, UAE) and six solvents (ethanol (100% or 75%), methanol (80%), water, lactic acid : sodium acetate (LA:SA, 3:1); citric acid: sucrose (CA:S, 1:1)).
Table 2.
Phenolic composition (µg/g) determined by HPLC-HRMS of carob extracts from South of Tunisia and obtained using two different techniques (maceration, M; ultrasound-assisted extraction, UAE) and six solvents (ethanol (100% or 75%), methanol (80%), water, lactic acid : sodium acetate (LA:SA, 3:1); citric acid: sucrose (CA:S, 1:1)).
| |
Solvent |
Ethanol |
Ethanol: water (75 %) |
Methanol: water (80 %) |
Water |
LA:SA (3:1) |
CA:S (1:1) |
| |
Extraction technique |
M |
UAE |
M |
UAE |
M |
UAE |
M |
UAE |
M |
UAE |
M |
UAE |
| 1 |
Sinapic acid |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.22 ± 0.03a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.24 ± 0.01a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 2 |
4´-Hydroxy-3´-methoxycinnamic acid |
2.24 ± 0.48d |
1.55 ± 0.13d |
12.20 ± 0.12b |
1.85 ± 0.02d |
5.39 ± 0.28c |
0.74 ± 0.01d |
31.44 ± 2.01a |
6.35 ± 0.01c |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 3 |
4´-Hydroxycinnamic acid |
4.20 ± 0.60de |
1.76 ± 0.11e |
10.66 ± 0.15c |
2.54 ± 0.01de |
5.15 ± 0.07d |
2.10 ± 0.08e |
27.22 ± 2.01a |
21.62 ± 0.08b |
1.42 ± 0.03e |
1.84 ± 0.01e |
3.04 ± 0.45de |
2.12 ± 0.34e |
| 4 |
Cryptochlorogenic acid |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.33 ± 0.06c |
0.38 ± 0.01bc |
0.55 ± 0.12b |
0.24 ± 0.11c |
0.55 ± 0.01b |
1.60 ± 0.06a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 5 |
Chlorogenic acid |
n.d. |
n.d. |
1.58 ± 0.15c |
1.73 ± 0.01bc |
2.16 ± 0.29b |
1.37 ± 0.28c |
2.15 ± 0.01b |
4.79 ± 0.14a |
n.d. |
0.71 ± 0.05d |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| |
∑Hydroxycinnamic acids |
6.43 ± 1.07e |
3.31 ± 0.02e |
25.00 ± 0.45c |
6.51 ± 0.01e |
13.24 ± 1.76d |
4.45 ± 0.32e |
61.60 ± 4.01a |
34.36 ± 0.13b |
1.42 ± 0.03e |
2.55 ± 0.06e |
3.04 ± 0.45e |
2.12 ± 0.34e |
| 6 |
2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
0.12 ± 0.05cd |
n.d. |
0.34 ± 0.08b |
0.12 ± 0.02cd |
0.20 ± 0.01c |
n.d. |
0.93 ± 1.01a |
0.24 ± 0.02bc |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 7 |
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
0.60 ± 0.09fg |
0.39 ± 0.01g |
2.41 ± 0.01ab |
0.85 ± 0.06ef |
2.13 ± 0.06b |
1.10 ± 0.07de |
1.66 ± 6.01c |
2.26 ± 0.01b |
2.60 ± 0.14a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
1.39 ± 0.20cd |
| 8 |
3,5-Dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid |
n.d. |
n.d. |
3.89 ± 0.70c |
1.48 ± 0.38cd |
n.d. |
n.d. |
4.35 ± 0.01c |
1.34 ± 0.08cd |
9.76 ± 0.62b |
24.34 ± 2.18a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 9 |
4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid |
0.81 ± 0.04c |
n.d. |
2.99 ± 0.03b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
4.84 ± 8.01a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 10 |
3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic acid |
418.38 ± 67.60de |
243.48 ± 6.07f |
1130.12 55.26b |
400.35 ± 3.04e |
651.83 ± 67.58c |
551.63 ± 11.73cd |
1181.83 ± 3.01b |
1327.04 ± 17.57a |
537.65 ± 24.56cde |
568.06 ± 34.58c |
86.71 ± 1.55g |
134.53 ± 12.86fg |
| 11 |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
2.93 ± 0.19ef |
1.36 ± 0.02g |
6.57 ± 0.40b |
2.71 ± 0.05ef |
4.13 ± 0.19cd |
2.23 ± 0.18fg |
3.40 ± 9.01de |
3.06 ± 0.10def |
4.74 ± 0.77c |
11.06 ± 0.29a |
n.d. |
1.12 ± 0.26gh |
| |
∑Hydroxybenzoic acids |
422.85 ± 67.97de |
245.24 ± 6.08f |
1146.32 ± 54.90b |
405.51 ± 2.67e |
658.28 ± 67.32c |
554.96 ± 11.98cd |
1197.02 ± 8.01ab |
1333.93 ± 17.56a |
554.74 ± 26.09cd |
603.45 ± 32.69c |
86.71 ± 1.55g |
137.04 ± 12.93fg |
| |
∑Phenolic acids |
429.28 ± 69.04de |
248.55 ± 6.10f |
1171.32 ± 55.35b |
412.02 ± 2.66e |
671.53 ± 69.08c |
559.41 ± 12.30cd |
1258.62 ± 2.01ab |
1368.29 ± 17.43a |
556.17 ± 26.07cde |
606.01 ± 32.75c |
89.75 ± 1.10g |
139.16 ± 12.59fg |
| 12 |
Methyl-digallate |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
3.85 ± 0.14a |
1.12 ± 0.08b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.07 ± 0.10c |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 13 |
Ethylgallate |
4.96 ± 1.05b |
3.47 ± 0.02b |
1066.85 ± 67.69a |
54.19 ± 0.27b |
3.39 ± 1.09b |
n.d. |
18.15 ± 9.01b |
0.42 ± 0.06b |
7.75 ± 0.46b |
n.d. |
2.19 ± 1.58b |
n.d. |
| 14 |
Ethyl digallate |
0.00 ± 0.00b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
1.77 ± 0.05a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| |
∑Phenolic (gallate) esters |
4.96 ± 1.05b |
3.47 ± 0.02b |
1066.85 ± 67.69a |
55.95 ± 0.22b |
7.24 ± 1.23b |
1.12 ± 0.08b |
18.15 ± 9.01b |
0.42 ± 0.06b |
7.82 ± 0.56b |
n.d. |
2.19 ± 1.58b |
n.d. |
| 15 |
Catechin |
1.12 ± 0.00f |
1.30 ± 0.02f |
5.58 ± 0.11b |
3.92 ± 0.07c |
5.38 ± 0.05b |
3.28 ± 0.24d |
2.42 ± 1.01e |
3.20 ± 0.14d |
3.70 ± 0.20cd |
8.22 ± 0.33a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 16 |
Epicatechin |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.60 ± 0.01c |
0.43 ± 0.02d |
0.98 ± 0.01a |
0.47 ± 0.01d |
0.90 ± 0.01ab |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.86 ± 0.00b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 17 |
Epigallocatechin |
0.22 ± 0.02f |
1.24 ± 0.01e |
2.78 ± 0.68c |
1.63 ± 0.06de |
2.56 ± 0.09cd |
1.96 ± 0.01cde |
1.94 ± 2.01cde |
1.90 ± 0.06cde |
4.98 ± 0.18b |
6.08 ± 0.12a |
n.d. |
5.17 ± 0.43ab |
| |
∑Flavan-3-ols |
1.34 ± 0.02d |
2.54 ± 0.04d |
8.96 ± 0.78b |
5.98 ± 0.15c |
8.92 ± 0.02b |
5.71 ± 0.25c |
5.26 ± 3.01c |
5.09 ± 0.20c |
8.68 ± 0.02b |
15.15 ± 0.46a |
n.d. |
5.17 ± 0.43c |
| 18 |
Naringenin |
606.15 ± 163.38cd |
312.55 ± 7.06e |
886.72 ± 3.38b |
574.97 ± 14.03cd |
764.93 ± 163.97bc |
399.47 ± 23.64de |
904.87 ± 1.01b |
1932.79 ± 35.42a |
263.12 ± 23.44e |
299.95 ± 19.94e |
230.98 ± 24.94e |
270.66 ± 40.25e |
| 19 |
Eriodictyol |
1.20 ± 0.37cde |
0.45 ± 0.03f |
1.65 ± 0.02abc |
1.38 ± 0.06bcd |
2.00 ± 0.03a |
0.87 ± 0.02def |
1.02 ± 2.01de |
1.15 ± 0.09cde |
1.23 ± 0.04cde |
1.85 ± 0.10ab |
0.81 ± 0.08ef |
0.84 ± 0.05ef |
| |
∑Flavanones |
607.34 ± 163.75cd |
313.00 ± 7.09e |
888.37 ± 3.36b |
576.35 ± 13.97cd |
766.93 ± 163.00bc |
400.34 ± 23.65de |
905.89 ± 3.01b |
1933.94 ± 35.51a |
264.35 ± 23.40e |
301.80 ± 19.84e |
231.78 ± 25.02e |
271.50 ± 40.20e |
| 20 |
Quercetin |
n.d. |
n.d. |
1.36 ± 0.12a |
n.d. |
0.76 ± 0.02b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.77 ± 0.11b |
1.21 ± 0.45ab |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 21 |
Isoquercitrin |
6.99 ± 2.14e |
6.24 ± 0.02e |
51.36 ± 0.03a |
24.50 ± 0.25c |
50.72 ± 2.71a |
21.86 ± 0.36c |
15.03 ± 9.01d |
15.44 ± 0.28d |
46.82 ± 0.01b |
48.21 ± 0.04ab |
4.89 ± 0.94e |
12.39 ± 1.95d |
| 22 |
Guaiaverin |
n.d. |
n.d. |
8.86 ± 0.12a |
3.75 ± 0.08b |
8.54 ± 0.00a |
3.03 ± 0.01b |
1.08 ± 0.01c |
1.15 ± 0.04c |
3.70 ± 0.26b |
3.52 ± 0.82b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 23 |
Hyperoside |
5.32 ± 1.36ef |
4.52 ± 0.09f |
42.84 ± 1.14ab |
22.36 ± 0.94c |
47.08 ± 1.36a |
17.91 ± 0.12c |
13.16 ± 3.01d |
12.58 ± 0.84d |
39.96 ± 2.42b |
40.07 ± 0.66b |
3.20 ± 0.76f |
9.32 ± 1.66de |
| 24 |
Reynoutrin |
1.02 ± 0.26e |
0.85 ± 0.02e |
8.45 ± 0.32a |
4.27 ± 0.08c |
8.38 ± 0.32a |
3.69 ± 0.20c |
1.95 ± 0.01d |
1.99 ± 0.03d |
6.44 ± 0.14b |
6.43 ± 0.19b |
0.49 ± 0.04e |
1.11 ± 0.10e |
| 25 |
Quercitrin |
53.63 ± 14.58efg |
32.60 ± 1.38g |
216.40 ± 2.74ab |
116.18 ± 5.27c |
204.41 ± 14.66b |
100.29 ± 3.24cd |
78.84 ± 6.01de |
60.79 ± 2.00ef |
199.94 ± 10.27b |
232.66 ± 0.87a |
28.03 ± 3.73g |
48.27 ± 9.72fg |
| 26 |
Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.92 ± 0.04a |
0.37 ± 0.01c |
0.93 ± 0.06a |
0.31 ± 0.02c |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.66 ± 0.10b |
0.68 ± 0.14b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| |
∑Flavonols |
66.95 ± 18.34ef |
44.21 ± 1.47fg |
330.19 ± 1.21a |
171.43 ± 6.63c |
320.83 ± 5.99ab |
147.09 ± 3.70c |
110.06 ± 8.49d |
91.95 ± 3.19de |
298.29 ± 8.48b |
332.79 ± 1.18a |
36.62 ± 5.47g |
71.09 ± 6.21ef |
| 27 |
Taxifolin |
1.16 ± 0.27cd |
0.63 ± 0.02d |
3.16 ± 0.28b |
1.87 ± 0.07c |
3.68 ± 0.05b |
1.66 ± 0.02c |
5.84 ± 1.01a |
3.48 ± 0.05b |
3.04 ± 0.16b |
3.23 ± 0.19b |
0.86 ± 0.04d |
0.79 ± 0.03d |
| |
∑Flavanonols |
1.16 ± 0.27cd |
0.63 ± 0.02d |
3.16 ± 0.28b |
1.87 ± 0.07c |
3.68 ± 0.05b |
1.66 ± 0.02c |
5.84 ± 1.01a |
3.48 ± 0.05b |
3.04 ± 0.16b |
3.23 ± 0.19b |
0.86 ± 0.04d |
0.79 ± 0.03d |
| 28 |
Apigenin |
1.03 ± 0.05f |
n.d. |
3.32 ± 0.03a |
1.67 ± 0.06c |
2.97 ± 0.05b |
1.38 ± 0.06de |
n.d. |
n.d. |
1.21 ± 0.10ef |
1.52 ± 0.19cd |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 29 |
Apigenin 7-O-glucoside |
0.65 ± 0.27d |
0.40 ± 0.00de |
3.40 ± 0.00a |
2.09 ± 0.11c |
3.44 ± 0.03a |
1.61 ± 0.01c |
n.d. |
n.d. |
2.85 ± 0.07b |
2.79 ± 0.16b |
0.32 ± 0.15de |
0.77 ± 0.19d |
| 30 |
Apigenin 7-O-glucuronide |
n.d. |
n.d. |
1.05 ± 0.08a |
0.56 ± 0.00b |
1.18 ± 0.12a |
0.42 ± 0.00b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.48 ± 0.00b |
0.43 ± 0.02b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 31 |
Luteolin |
3.58 ± 0.98c |
1.75 ± 0.14d |
6.37 ± 0.02a |
4.00 ± 0.07c |
5.76 ± 0.07ab |
3.34 ± 0.21c |
0.12 ± 5.01e |
n.d. |
4.35 ± 0.19bc |
5.88 ± 0.61ab |
1.76 ± 0.50d |
1.54 ± 0.39de |
| 32 |
Luteolin 7-O-glucoside |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.57 ± 0.00c |
n.d. |
0.68 ± 0.00bc |
2.37 ± 0.06a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.70 ± 0.07bc |
0.81 ± 0.11b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| |
∑Flavones |
5.26 ± 1.31d |
2.14 ± 0.14ef |
14.71 ± 0.09a |
8.33 ± 0.10c |
14.03 ± 1.14a |
9.12 ± 0.21c |
0.12 ± 2.01ef |
n.d. |
9.59 ± 0.29bc |
11.42 ± 1.09b |
2.08 ± 0.64ef |
2.32 ± 0.59e |
| |
∑Flavonoids |
735.68 ± 198.26d |
395.12 ± 9.78efg |
1461.79 ± 0.18b |
880.13 ± 1.74cd |
1318.79 ± 5.14b |
664.21 ± 30.54def |
1106.01 ± 121.72bc |
2095.24 ± 40.84a |
783.88 ± 5.11de |
897.05 ± 16.95d |
299.38 ± 16.42g |
399.15 ± 24.40fg |
| 33 |
Procyanidin B1 |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.90 ± 0.07d |
2.06 ± 0.02b |
2.72 ± 0.08a |
0.89 ± 0.03d |
0.85 ± 0.01d |
1.30 ± 0.11c |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 34 |
Procyanidin B2 |
1.25 ± 0.02d |
0.65 ± 0.04e |
1.74 ± 0.11bc |
1.00 ± 0.12d |
2.76 ± 0.10a |
1.68 ± 0.11c |
1.21 ± 2.01d |
2.00 ± 0.00b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| |
∑Condensed tannins |
1.25 ± 0.02e |
0.65 ± 0.04f |
2.64 ± 0.04c |
3.05 ± 0.14b |
5.48 ± 0.17a |
2.57 ± 0.09c |
2.06 ± 2.01d |
3.30 ± 0.11b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 35 |
Galloylhexoside isomer I |
1030.84 ± 139.19a |
581.16 ± 10.25b |
351.38 ± 19.76c |
315.24 ± 0.53c |
n.d. |
n.d. |
4.47 ± 8.01d |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 36 |
Galloylhexoside isomer II |
51.38 ± 11.16a |
18.71 ± 0.35b |
58.35 ± 5.26a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
20.74 ± 3.01b |
24.73 ± 0.40b |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 37 |
Galloylhexoside isomer III |
5.13 ± 0.03e |
n.d. |
18.83 ± 0.32c |
n.d. |
13.61 ± 0.62d |
20.44 ± 0.39c |
54.15 ± 1.01b |
92.95 ± 2.16a |
11.74 ± 0.15d |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 38 |
Galloylhexoside isomer IV |
428.61 ± 88.05cd |
167.36 ± 0.15ef |
426.85 ± 0.17cd |
383.01 ± 2.67cd |
727.88 ± 88.01b |
847.20 ± 5.91b |
45.11 ± 6.01f |
545.42 ± 2.22c |
336.25 ± 3.90de |
1155.45 ± 128.77a |
23.08 ± 2.73f |
51.78 ± 1.95f |
| 39 |
Galloylhexoside isomer V |
1.88 ± 0.10gh |
0.97 ± 0.08h |
12.98 ± 0.21de |
5.49 ± 0.36f |
14.28 ± 0.19cd |
12.26 ± 0.08e |
42.72 ± 8.01b |
74.92 ± 0.69a |
12.79 ± 0.24de |
15.07 ± 0.25c |
3.32 ± 0.19g |
1.79 ± 0.07gh |
| 40 |
Galloyl dihexoside isomer I |
5.07 ± 0.70f |
5.37 ± 0.08f |
78.53 ± 2.96cd |
25.20 ± 1.02ef |
83.06 ± 0.25c |
72.14 ± 0.69cd |
203.68 ± 0.01b |
327.89 ± 3.30a |
43.35 ± 1.96de |
80.10 ± 12.36c |
16.80 ± 0.86ef |
11.52 ± 2.74ef |
| 41 |
Galloyl dihexoside isomer II |
2.98 ± 1.00c |
n.d. |
29.14 ± 0.16c |
13.47 ± 0.57c |
24.07 ± 1.32c |
21.17 ± 0.45c |
368.33 ± 9.01a |
124.54 ± 3.80b |
19.94 ± 0.20c |
33.90 ± 1.63c |
0.04 ± 0.06c |
3.94 ± 0.07c |
| 42 |
Galloyl dihexoside isomer III |
1.04 ± 0.20f |
2.32 ± 0.04ef |
9.27 ± 0.02cd |
11.49 ± 0.00c |
8.82 ± 0.59cde |
n.d. |
53.02 ± 0.01a |
43.75 ± 2.97b |
4.47 ± 0.20def |
5.10 ± 0.88cdef |
n.d. |
1.41 ± 0.48f |
| 43 |
Digalloyl hexoside isomer I |
0.94 ± 0.28g |
0.25 ± 0.00g |
24.55 ± 1.64b |
4.27 ± 0.04f |
12.96 ± 0.13c |
11.89 ± 0.78cd |
8.35 ± 9.01e |
46.62 ± 0.92a |
8.97 ± 0.36de |
8.26 ± 1.86e |
1.21 ± 0.28fg |
0.01 ± 0.02g |
| 44 |
Digalloyl hexoside isomer II |
4.32 ± 1.31hi |
2.25 ± 0.10i |
41.63 ± 0.35b |
10.90 ± 0.07fg |
31.27 ± 1.30c |
29.66 ± 0.03c |
13.30 ± 3.01ef |
75.15 ± 0.18a |
19.13 ± 2.61d |
16.35 ± 1.87de |
10.77 ± 0.74fg |
7.62 ± 0.48gh |
| 45 |
Digalloyl hexoside isomer III |
20.08 ± 2.78def |
10.96 ± 0.18f |
131.94 ± 0.04a |
52.29 ± 1.66cde |
115.90 ± 2.02ab |
82.85 ± 1.26bc |
16.00 ± 0.01ef |
76.55 ± 1.22c |
119.42 ± 2.82ab |
134.59 ± 31.15a |
27.36 ± 3.02def |
52.98 ± 5.34cd |
| 46 |
Trigalloyl hexoside isomer I |
0.97 ± 0.34de |
0.55 ± 0.04de |
9.33 ± 0.31a |
3.11 ± 0.23c |
5.72 ± 0.32b |
2.82 ± 0.02c |
n.d. |
4.53 ± 0.14b |
10.01 ± 0.34a |
9.20 ± 0.22a |
1.92 ± 0.93cd |
0.27 ± 0.16e |
| 47 |
Trigalloyl hexoside isomer II |
8.75 ± 0.84ab |
2.02 ± 0.03de |
10.67 ± 0.20a |
2.60 ± 0.18cde |
8.47 ± 6.03ab |
5.81 ± 0.01bc |
n.d. |
4.05 ± 0.02cd |
9.91 ± 1.26a |
10.09 ± 2.66a |
2.37 ± 0.29cde |
1.64 ± 0.48de |
| 48 |
Trigalloyl hexoside isomer III |
12.41 ± 0.16ef |
6.06 ± 0.16ef |
51.09 ± 2.82abc |
43.82 ± 0.89bcd |
49.95 ± 0.68abc |
32.64 ± 1.24d |
1.16 ± 4.01f |
37.49 ± 0.55cd |
52.14 ± 4.84ab |
63.07 ± 9.05a |
17.05 ± 0.57e |
18.89 ± 4.94e |
| 49 |
Trigalloyl hexoside isomer IV |
5.82 ± 1.01e |
4.63 ± 0.14e |
50.56 ± 0.89b |
21.59 ± 0.52cd |
48.13 ± 1.24b |
28.20 ± 0.80c |
0.62 ± 8.01e |
23.90 ± 0.68cd |
47.81 ± 1.56b |
62.87 ± 5.35a |
19.17 ± 1.51d |
16.60 ± 2.82d |
| 50 |
Trigalloyl hexoside isomer V |
0.14 ± 0.09e |
0.12 ± 0.03e |
4.33 ± 0.25a |
1.65 ± 0.10d |
3.39 ± 0.08b |
1.96 ± 0.20cd |
n.d. |
1.62 ± 0.03d |
2.73 ± 0.20bc |
2.04 ± 0.54cd |
0.49 ± 0.26e |
0.12 ± 0.17e |
| 51 |
Tetragalloyl hexoside isomer I |
n.d. |
n.d. |
2.47 ± 0.19a |
0.07 ± 0.01bc |
0.30 ± 0.03b |
0.06 ± 0.03c |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 52 |
Tetragalloyl hexoside isomer II |
23.51 ± 2.65e |
12.16 ± 0.17e |
136.98 ± 4.41abc |
112.07 ± 4.61bc |
126.20 ± 2.75bc |
87.25 ± 7.60cd |
1.92 ± 5.01e |
1.63 ± 0.03e |
189.78 ± 37.14a |
164.10 ± 21.17ab |
41.98 ± 8.83de |
49.96 ± 13.69de |
| 53 |
Pentagalloyl hexoside |
n.d. |
0.29 ± 0.01d |
n.d. |
3.77 ± 0.10bc |
3.95 ± 0.30b |
0.56 ± 0.03d |
n.d. |
n.d. |
7.58 ± 0.35a |
10.48 ± 2.71a |
0.61 ± 0.16cd |
0.14 ± 0.20d |
| |
∑Hydrolyzable tannins |
1603.87 ± 244.58ab |
815.20 ± 9.53e |
1448.89 ± 22.55abc |
1010.04 ± 3.68de |
1277.93 ± 19.36bcd |
1256.91 ± 13.85cd |
833.58 ± 75.73e |
1505.75 ± 7.03abc |
896.02 ± 43.83e |
1770.68 ± 128.27a |
166.18 ± 8.11f |
218.66 ± 27.22f |
| |
∑Tannins |
1605.12 ± 244.60ab |
815.86 ± 9.49e |
1451.53 ± 22.51abc |
1013.09 ± 3.54de |
1283.41 ± 19.19bcd |
1259.49 ± 13.76cd |
835.64 ± 75.87e |
1509.05 ± 7.14abc |
896.02 ± 43.83e |
1770.68 ± 128.27a |
166.18 ± 8.11f |
218.66 ± 27.22f |
| 54 |
4´-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
13.64 ± 0.71a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 55 |
Galloylquinic acid |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.02 ± 0.03 |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 56 |
Benzene-1,2,3-triol |
9.13 ± 0.56fg |
5.70 ± 0.07g |
33.41 ± 0.99b |
8.45 ± 0.05fg |
16.18 ± 0.32de |
15.83 ± 0.54de |
31.79 ± 2.27bc |
38.82 ± 1.58a |
27.15 ± 0.85c |
27.94 ± 1.36c |
13.47 ± 0.52ef |
19.22 ± 2.94d |
| 57 |
Vanillin |
0.75 ± 0.29cd |
n.d. |
3.24 ± 0.19a |
0.66 ± 0.06cde |
1.38 ± 0.00b |
0.39 ± 0.22def |
0.24 ± 0.00ef |
0.97 ± 0.04bc |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| 58 |
Phloridzin |
n.d. |
n.d. |
0.82 ± 0.09a |
n.d. |
0.89 ± 0.05a |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
n.d. |
| |
∑Other phenolic compounds |
9.88 ± 0.86ef |
5.70 ± 0.07f |
37.47 ± 0.88b |
9.12 ± 0.10ef |
18.46 ± 0.37d |
16.22 ± 0.76d |
45.70 ± 3.01a |
39.78 ± 1.63b |
27.15 ± 0.85c |
27.94 ± 1.36c |
13.47 ± 0.52de |
19.22 ± 2.94d |
| 59 |
β-Galactopyranosyl glucose |
794.25 ± 125.57cd |
1027.31 ± 35.37bcd |
1227.89 ± 71.40b |
1104.89 ± 5.04bc |
1215.22 ± 32.10bc |
1064.07 ± 58.52bc |
608.77 ± 20.16d |
1197.24 ± 1.32bc |
1044.71 ± 71.66bc |
990.54 ± 224.82bcd |
2747.06 ± 166.38a |
1265.31 ± 168.79b |
| |
∑Others |
794.25 ± 125.57cd |
1027.31 ± 35.37bcd |
1227.89 ± 71.40b |
1104.89 ± 5.04bc |
1215.22 ± 32.10bc |
1064.07 ± 58.52bc |
608.77 ± 20.16d |
1197.24 ± 1.32bc |
1044.71 ± 71.66bc |
990.54 ± 224.82bcd |
2747.06 ± 166.38a |
1265.31 ± 168.79b |
| |
∑Total phenolics |
2731.29 ± 499.24bcd |
1436.10 ± 11.89e |
4972.55 ± 31.39a |
2254.13 ±0.49d |
3095.02 ± 28.07b |
2400.15 ± 54.21cd |
3185.27 ± 273.52b |
4951.99 ± 26.98a |
2071.09 ± 86.70de |
3069.02 ± 111.98bc |
542.93 ± 12.08f |
727.91 ± 76.87f |
| |
∑Total compounds |
3525.54 ± 624.81bcd |
2463.41 ± 47.25ef |
6200.45 ± 102.79a |
3359.02 ± 5.53cd |
4310.24 ± 4.03b |
3464.23 ± 4.31cd |
3794.04 ± 253.35bcd |
6149.24 ± 28.30a |
3115.81 ± 15.04de |
4059.56 ± 112.84bc |
3289.99 ± 178.46cde |
1993.22 ± 91.92f |
Table 3.
Three-way ANOVA: influence of the plant origin (North and South of Tunisia), extraction technique (maceration, ultrasound-assisted extraction, UAE), and solvent (ethanol (E, 100%; E 75%, 75%), methanol 80% (M, 80%), water (W), lactic acid: sodium acetate (LA:SA; 3:1); citric acid: sucrose (CA:S; 1:1)) on different families of polyphenol compounds (µg/ g DW) determined by HPLC-HRMS in carob pulp.
Table 3.
Three-way ANOVA: influence of the plant origin (North and South of Tunisia), extraction technique (maceration, ultrasound-assisted extraction, UAE), and solvent (ethanol (E, 100%; E 75%, 75%), methanol 80% (M, 80%), water (W), lactic acid: sodium acetate (LA:SA; 3:1); citric acid: sucrose (CA:S; 1:1)) on different families of polyphenol compounds (µg/ g DW) determined by HPLC-HRMS in carob pulp.
| |
|
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
F6 |
F7 |
F8 |
F9 |
F10 |
F11 |
F12 |
F13 |
F14 |
F15 |
F16 |
| Plant origin (A) |
South |
13.67 ± 17.89 |
612.17 ± 404.32 |
625.84 ± 419.13 |
97.35 ± 299.33 |
6.07 ± 3.96 |
621.80 ± 472.54 |
193.09 ± 135.30 |
2.45 ± 1.53 |
6.59 ± 5.19 |
830.00 ± 490.84 |
1.75 ± 1.70 |
1071.10 ± 507.67 |
1072.85 ± 508.36 |
22.51 ± 12.83 |
1190.61 ± 519.75 |
3839.15 ± 1267.51 |
| North |
6.02 ± 6.00 |
511.46 ± 316.62 |
517.48 ± 319.62 |
42.58 ± 125.51 |
4.81 ± 3.68 |
593.57 ± 262.93 |
92.16 ± 65.81 |
4.20 ± 2.43 |
6.46 ± 5.72 |
701.21 ± 292.84 |
0.92 ± 0.94 |
786.30 ± 464.06 |
787.22 ± 464.64 |
17.85 ± 9.16 |
1241.71 ± 612.75 |
3308.06 ± 1115.85 |
| |
P value |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0771 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.5976 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0455 |
<0.0001 |
| Extraction technique (B) |
Maceration |
12.13 ± 16.17 |
557.74 ± 346.97 |
569.87 ± 359.37 |
117.69 ± 298.21 |
4.76 ± 3.55 |
591.00 ± 287.47 |
152.19 ± 126.99 |
3.69 ± 2.45 |
6.75 ± 5.66 |
758.38 ± 356.90 |
1.35 ± 1.54 |
887.05 ± 480.14 |
888.40 ± 481.04 |
19.84 ± 11.82 |
1250.47 ± 701.19 |
3604.66 ± 1227.69 |
| UAE |
6.43 ± 8.87 |
527.17 ± 380.14 |
533.60 ± 387.11 |
7.88 ± 16.65 |
5.76 ± 4.12 |
593.71 ± 456.21 |
119.56 ± 101.66 |
2.60 ± 1.80 |
5.73 ± 5.02 |
727.35 ± 455.94 |
1.24 ± 1.22 |
944.93 ± 514.66 |
946.17 ± 515.19 |
18.69 ± 11.34 |
1155.37 ± 300.21 |
3389.07 ± 1203.15 |
| |
P value |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0798 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0002 |
<0.0001 |
0.1226 |
0.1248 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
Solvent
(C )
|
E |
4.16 ± 1.60 |
325.09 ± 86.37 |
329.24 ± 87.84 |
3.87 ± 1.54 |
1.11 ± 1.02 |
471.85 ± 141.82 |
51.35 ± 18.29 |
1.38 ± 0.75 |
3.11 ± 1.50 |
528.79 ±156.40 |
1.00 ± 0.26 |
884.77 ± 485.20 |
885.77 ± 485.33 |
7.19 ± 2.39 |
892.76 ± 199.34 |
2647.63 ± 615.98 |
| |
E (75%) |
11.93 ± 8.62 |
726.74 ± 355.50 |
738.67 ± 363.40 |
399.37 ± 449.84 |
6.52 ± 2.21 |
831.05 ± 221.44 |
206.79 ± 123.99 |
4.13 ± 2.59 |
12.00 ± 3.79 |
1060.49 ± 286.99 |
2.33 ± 0.60 |
1173.34 ± 481.36 |
1175.67 ± 481.52 |
21.14 ± 14.12 |
1210.73 ± 119.98 |
4606.06 ± 1580.76 |
| |
M (80%) |
6.85 ± 4.02 |
595.94 ± 41.81 |
602.80 ± 45.60 |
5.52 ± 4.70 |
5.38 ± 2.55 |
668.28 ± 166.11 |
181.57 ± 127.07 |
3.47 ± 1.42 |
9.97 ± 3.51 |
868.67 ± 223.93 |
2.83 ± 1.83 |
1104.16 ± 181.29 |
1106.98 ± 182.47 |
16.25 ± 1.54 |
1227.32 ± 115.00 |
3827.55 ± 347.67 |
| |
W |
31.95 ± 20.69 |
1080.06 ± 317.91 |
1112.01 ± 323.92 |
7.22 ± 8.02 |
4.15 ± 1.61 |
1077.98 ± 535.14 |
81.14 ± 38.34 |
5.2 ± 1.97 |
0.14 ± 0.12 |
1168.60 ± 556.79 |
1.86 ± 1.27 |
1098.26 ± 533.52 |
1100.12 ± 534.58 |
35.58 ± 10.11 |
875.20 ± 413.08 |
4298.73 ± 1575.19 |
| |
LA:SA (3:1) |
1.93 ± 0.72 |
539.80 ± 49.24 |
541.73 ± 49.50 |
3.15 ± 3.11 |
11.55 ± 2.77 |
364.51 ± 113.16 |
277.89 ± 93.70 |
4.52 ± 1.80 |
11.48 ± 3.30 |
669.95 ± 96.84 |
0.00 ± 0.00 |
1075.12 ± 441.90 |
1075.12 ± 441.90 |
24.23 ± 3.71 |
935.02 ± 271.69 |
3249.20 ± 550.84 |
| |
CA:S (1:1) |
2.26 ± 0.82 |
103.26 ± 23.51 |
105.51 ± 23.45 |
0.66 ± 1.16 |
3.92 ± 2.45 |
232.45 ± 51.79 |
57.04 ± 13.04 |
1.26 ± 0.66 |
2.46 ± 1.20 |
297.13 ± 54.09 |
0.00 ± 0.00 |
236.54 ± 53.35 |
236.54 ± 53.35 |
16.68 ± 3.89 |
2155.93 ± 679.48 |
2812.44 ± 643.76 |
| |
P value |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
| A x B |
P value |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0033 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0579 |
0.0418 |
0.0007 |
0.0933 |
0.0943 |
<0.0001 |
0.0871 |
0.0963 |
| A x C |
P value |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
| B x C |
P value |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
| A x B x C |
P value |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0012 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
<0.0001 |
0.0001 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).