Submitted:
04 November 2024
Posted:
05 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
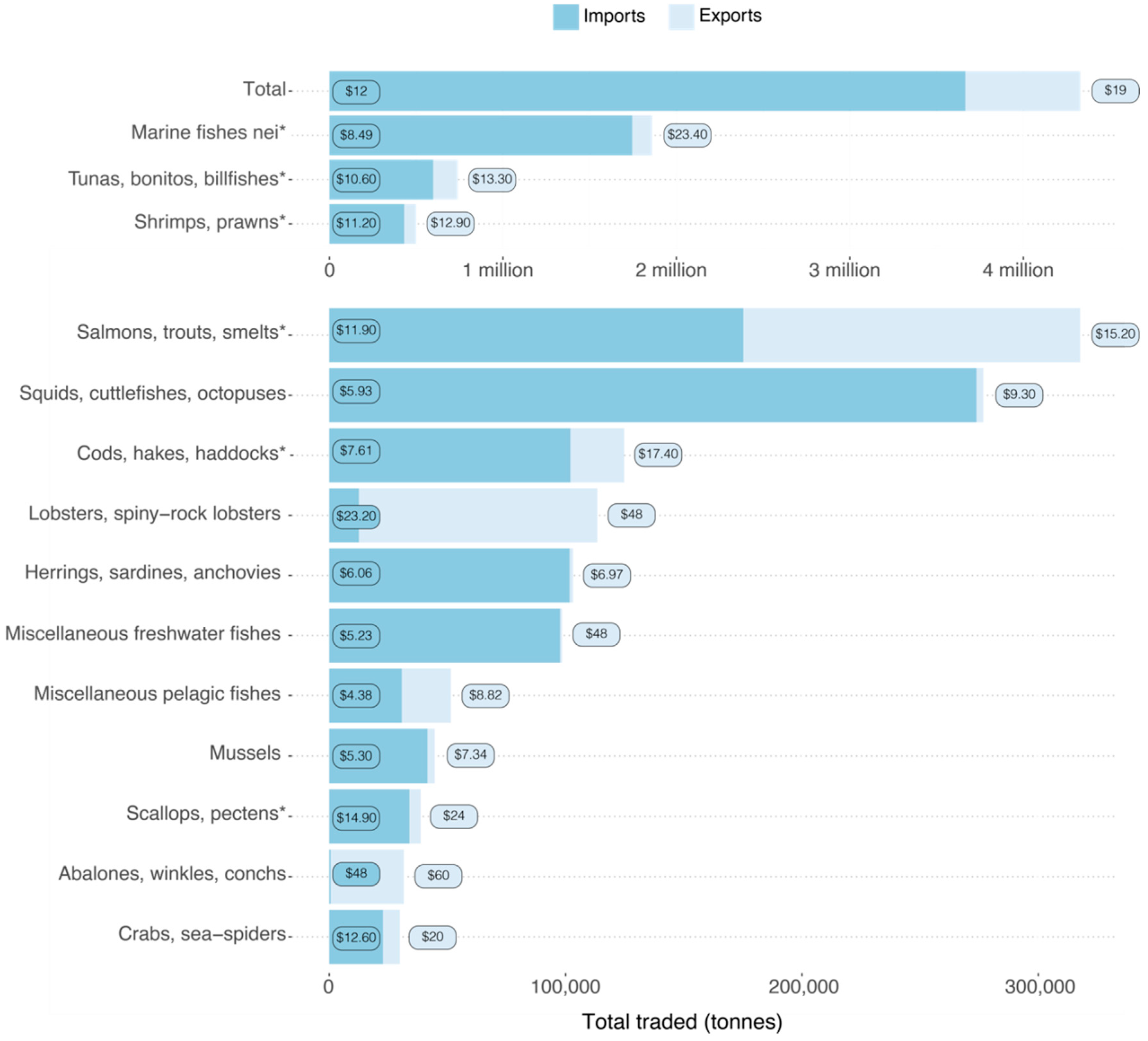
Dependence on seafood imports is growing for many nations, effectively exporting the environmental and social impacts from consuming nations to producers. While countries have commitments to national regulations and global sustainability targets, such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, sustainability standards for imported seafood are lacking. We examine the sustainability implications of high-income countries’ reliance on seafood imports, using Australia as a case study. Australia imports around 60-70% of domestically consumed seafood, with 96.5% imported from 20 countries. Compared to Australia, these countries generally have lower environmental performance, higher vulnerability to slavery, and increased risk of illicit trade in their supply chains. Yet, biophysical limits on wild catch, low demand for underutilized species, social conflict, environmental concerns over aquaculture expansion, and low domestic production, suggest imports will likely remain an important source of seafood for Australian consumers. Other high-income countries in Europe and North America face similar challenges. These countries have a pivotal role in promoting responsible trade. Comprehensive sustainability assessments that integrate environmental and social considerations of production and trade, improved mapping of seafood production activities, and more granular trade data will be critical for informed and effective trade regulations that support sustainability commitments.
Keywords:
Main
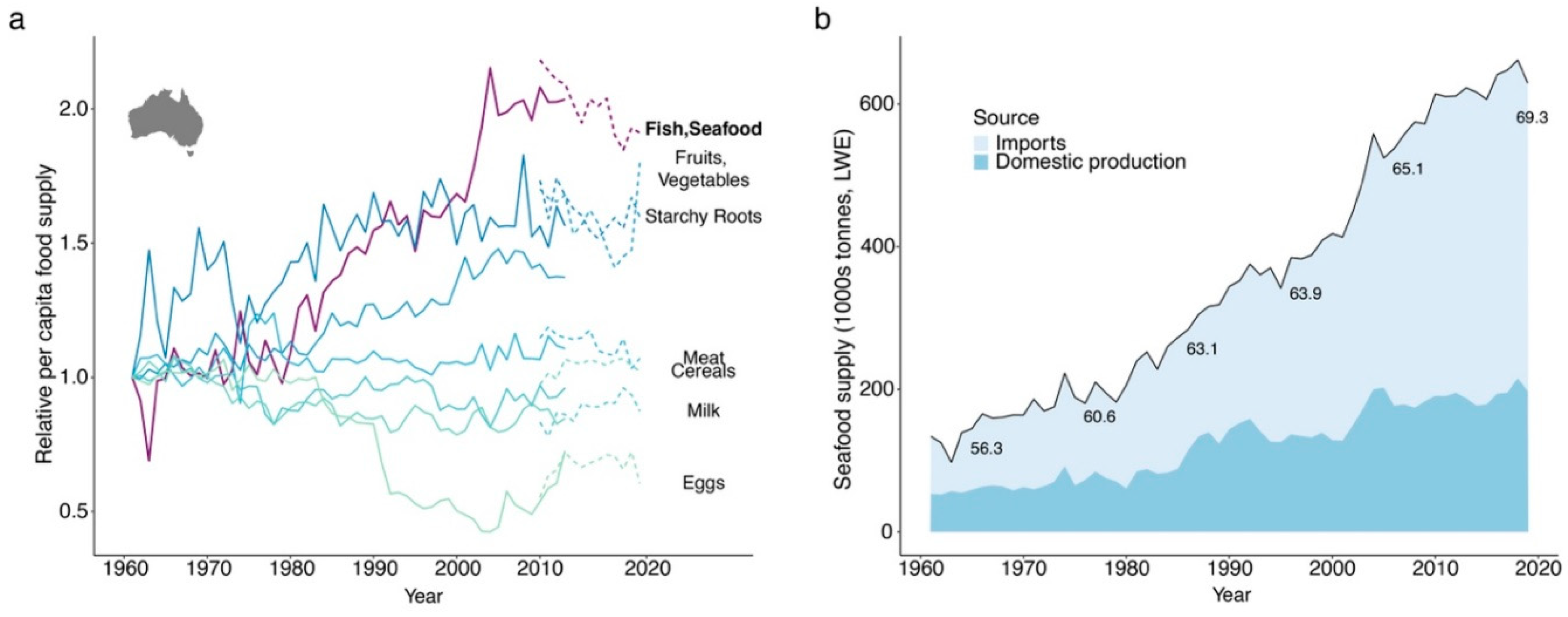
Australia’s Growing Seafood Import Dependence
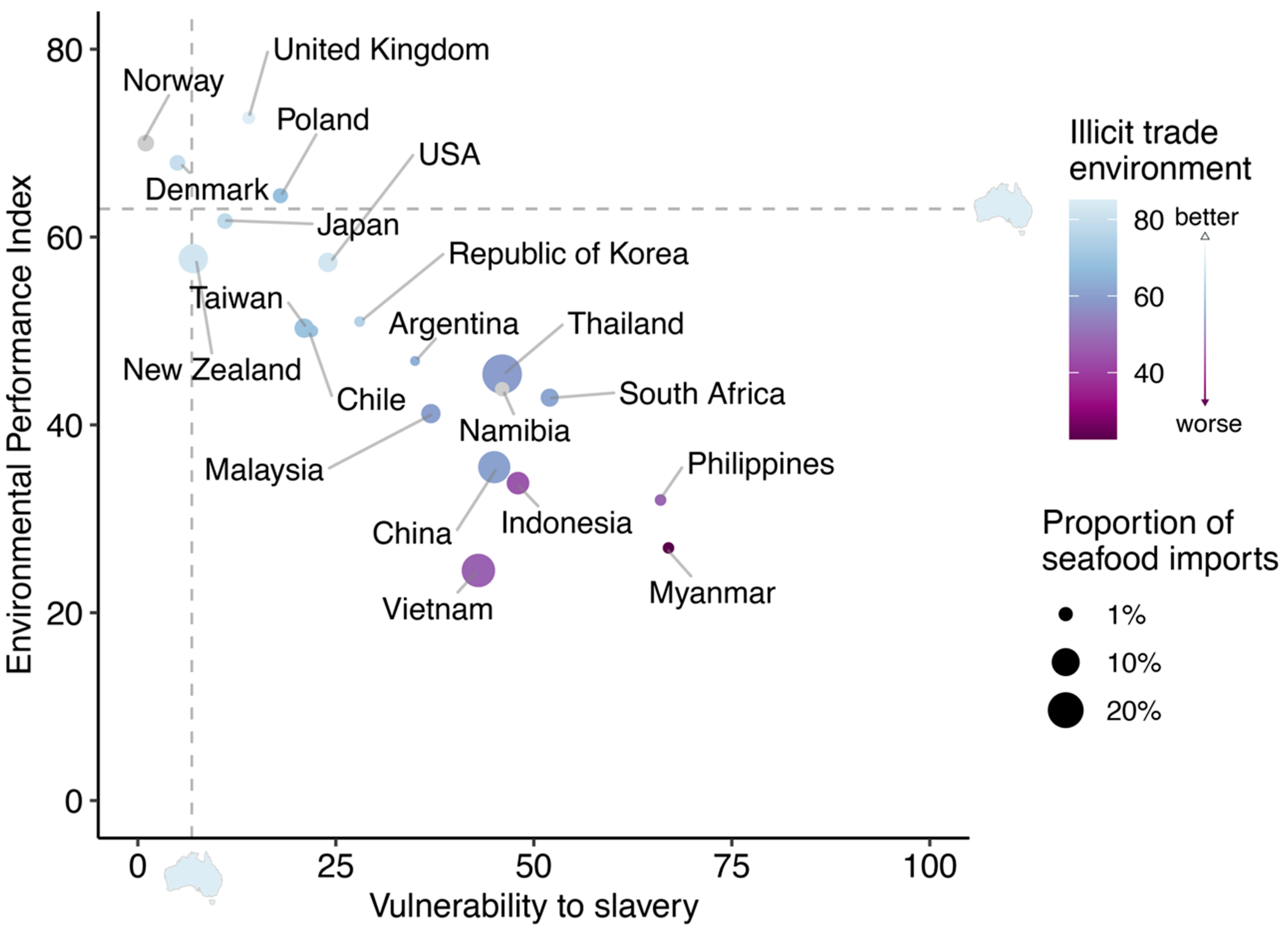
Sustainability Implications of Australia’s Imported Seafood
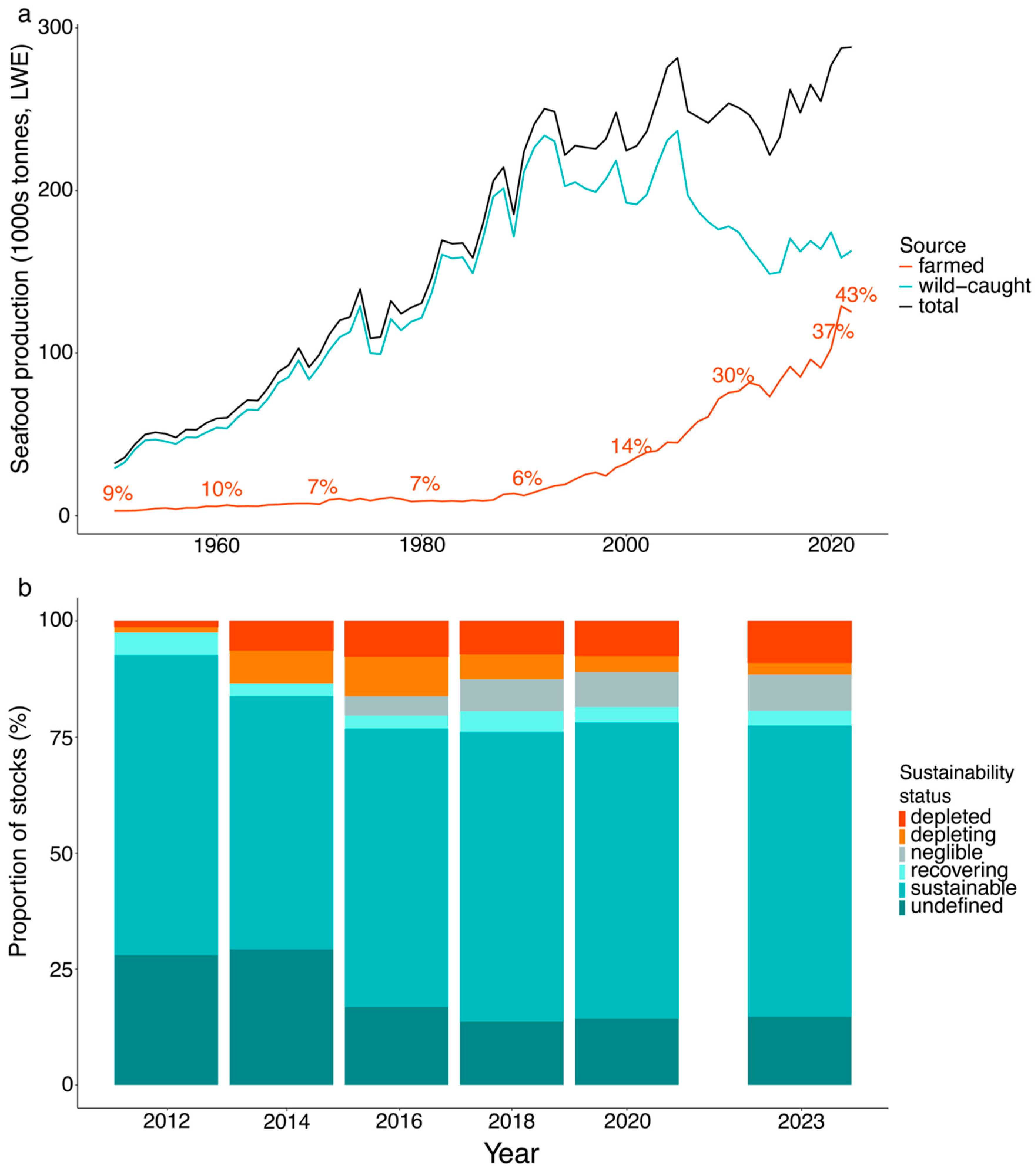
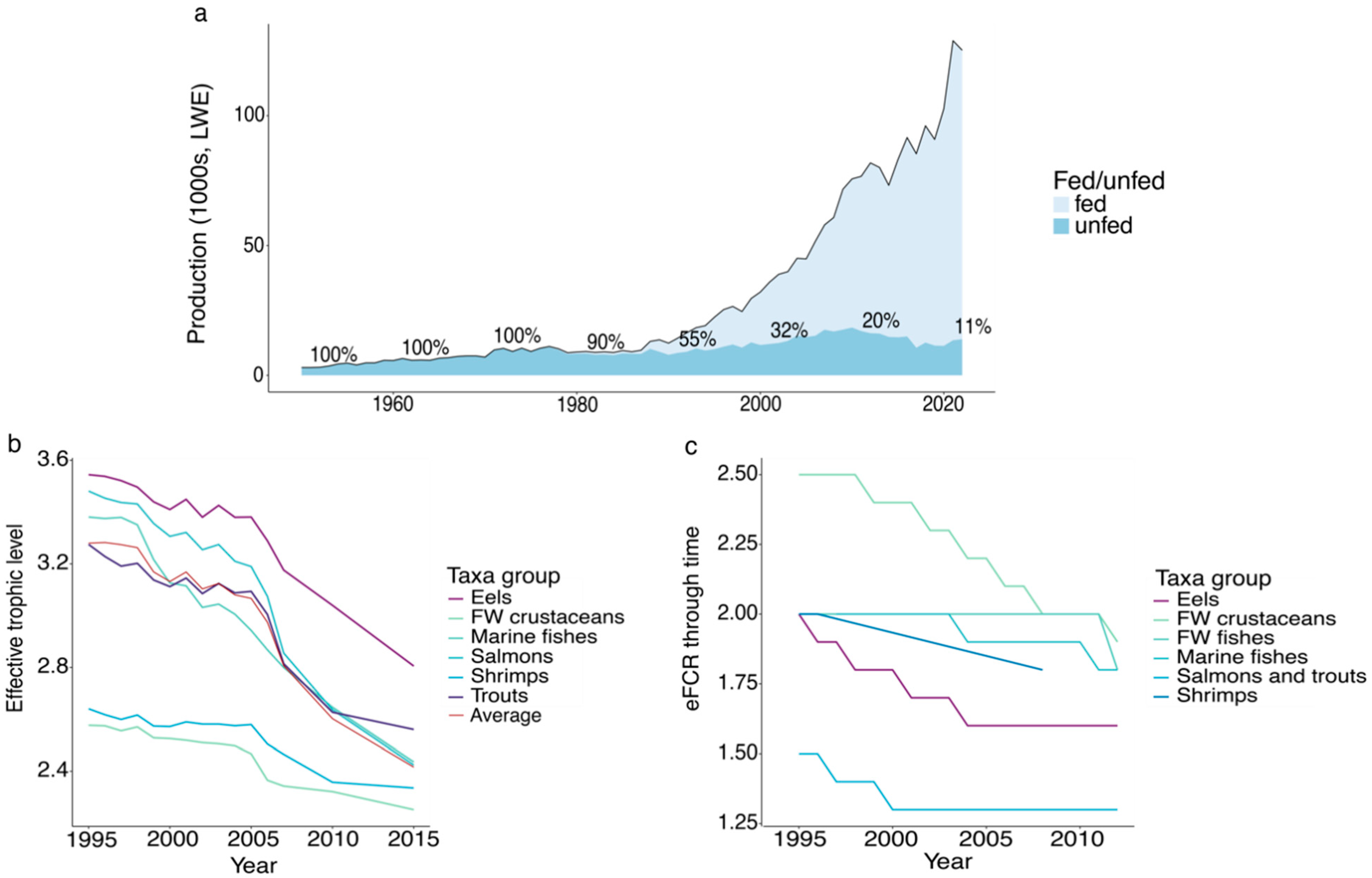
Opportunities to Reduce Import-Reliance for Seafood in Australia
Seafood Sustainability for Import-Reliant Futures
- (1)
- More comprehensive sustainability assessments
- (2)
- Spatially specific data for the location of seafood production
- (3)
- Improving data on international seafood trade
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Disclosure Statement
Data Availability Statement
References
- ABARES (2022). Fisheries Status Reports 2022. Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics . [CrossRef]
- Alder, J., Cullis-Suzuki, S., Karpouzi, V., Kaschner, K., Mondoux, S., Swartz, W., Trujillo, P., Watson, R., & Pauly, D. (2010). Aggregate performance in managing marine ecosystems of 53 maritime countries. Marine Policy, 34(3), 468–476. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J. L., Asche, F., & Garlock, T. (2018). Globalization and commoditization: The transformation of the seafood market. Journal of Commodity Markets, 12, 2–8. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J. L., Asche, F., & Garlock, T. (2019). Economics of Aquaculture Policy and Regulation. Annual Review of Resource Economics, 11(1), 101–123. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K. (2020). Trade Protectionism in Australia: Its Growth and Dismantling. Journal of Economic Surveys, 34(5), 1044–1067. [CrossRef]
- Asche, F., Bellemare, M. F., Roheim, C., Smith, M. D., & Tveteras, S. (2015). Fair Enough? Food Security and the International Trade of Seafood. World Development, 67, 151–160. [CrossRef]
- Asche, F., Roheim, C. A., & Smith, M. D. (2016). Trade intervention: Not a silver bullet to address environmental externalities in global aquaculture. Marine Policy, 69, 194–201. [CrossRef]
- Australian Government Department of Agriculture and Water Resources (2016). Productivity Commission - Inquiry into regulation of the Australian marine fisheries and aquaculture sectors https://www.pc.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0011/199055/sub056-fisheries-aquaculture-attachment.pdf.
- Banks, G. (2005). Structural reform Australian-style: Lessons for others? https://www.pc.gov.au/media-speeches/speeches/cs20050601/cs20050601.pdf.
- Bellmann, C., Tipping, A., & Sumaila, U. R. (2016). Global trade in fish and fishery products: An overview. Marine Policy, 69, 181–188. [CrossRef]
- Belton, B., Bush, S. R., & Little, D. C. (2018). Not just for the wealthy: Rethinking farmed fish consumption in the Global South. Global Food Security, 16, 85–92. [CrossRef]
- Belton, B., Little, D. C., Zhang, W., Edwards, P., Skladany, M., & Thilsted, S. H. (2020). Farming fish in the sea will not nourish the world. Nature Communications, 11(1), Article 1. [CrossRef]
- Belton, B., Reardon, T., & Zilberman, D. (2020). Sustainable commoditization of seafood. Nature Sustainability, 3(9), Article 9. [CrossRef]
- Belton, B., & Thilsted, S. H. (2014). Fisheries in transition: Food and nutrition security implications for the global South. Global Food Security, 3(1), 59–66. [CrossRef]
- Béné, C., Lawton, R., & Allison, E. H. (2010). “Trade Matters in the Fight Against Poverty”: Narratives, Perceptions, and (Lack of) Evidence in the Case of Fish Trade in Africa. World Development, 38(7), 933–954. [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, S, V., Perdana, A., Vivekanand, T. S., Venkatesh, V. G., Cheng, Y., & Shi, Y. (2024). From ocean to table: Examining the potential of Blockchain for responsible sourcing and sustainable seafood supply chains. Production Planning & Control, 0(0), 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Blasco, G. D., Ferraro, D. M., Cottrell, R. S., Halpern, B. S., & Froehlich, H. E. (2020). Substantial Gaps in the Current Fisheries Data Landscape. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2020.612831.
- Brugere, C., Bansal, T., Kruijssen, F., & Williams, M. (2023). Humanizing aquaculture development: Putting social and human concerns at the center of future aquaculture development. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 54(2), 482–526. [CrossRef]
- Bunwaree, P. (2023). The illegality of fishing vessels “going dark” and methods of deterrence. International & Comparative Law Quarterly, 72(1), 179–211. [CrossRef]
- Ching-Pong Poo, M., Wang, T., & Yang, Z. (2024). Global food supply chain resilience assessment: A case in the United Kingdom. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 181, 104018. [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y. I., Wang, C. M., Park, J. C., & Lader, P. F. (2020). Review of cage and containment tank designs for offshore fish farming. Aquaculture, 519, 734928. [CrossRef]
- Clawson, G., Kuempel, C. D., Frazier, M., Blasco, G., Cottrell, R. S., Froehlich, H. E., Metian, M., Nash, K. L., Többen, J., Verstaen, J., Williams, D. R., & Halpern, B. S. (2022). Mapping the spatial distribution of global mariculture production. Aquaculture, 553, 738066. [CrossRef]
- Commonwealth of Australia. (2017). Commonwealth of Australia’s 2017 Foreign Policy White Paper. Commonwealth of Australia. https://www.dfat.gov.au/publications/minisite/2017-foreign-policy-white-paper/fpwhitepaper/foreign-policy-white-paper.html.
- Condie, C. M., Alexander, K. A., Fulton, E. A., Vince, J., & Condie, S. A. (2022). Reducing socio-ecological conflict using social influence modelling. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 22002. [CrossRef]
- Condie, C. M., Vince, J., & Alexander, K. A. (2022). Increasing polarisation in attitudes to aquaculture: Evidence from sequential government inquiries. Marine Policy, 136, 104867. [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, R. S., Blanchard, J. L., Halpern, B. S., Metian, M., & Froehlich, H. E. (2020). Global adoption of novel aquaculture feeds could substantially reduce forage fish demand by 2030. Nature Food, 1(5), Article 5. [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, R. S., Metian, M., Froehlich, H. E., Blanchard, J. L., Sand Jacobsen, N., McIntyre, P. B., Nash, K. L., Williams, D. R., Bouwman, L., Gephart, J. A., Kuempel, C. D., Moran, D. D., Troell, M., & Halpern, B. S. (2021). Time to rethink trophic levels in aquaculture policy. Reviews in Aquaculture, 13(3), 1583–1593. [CrossRef]
- Cundy, M. E., Santana-Garcon, J., McLennan, A. G., Ayad, M. E., Bayer, P. E., Cooper, M., Corrigan, S., Harrison, E., & Wilcox, C. (2023). Seafood label quality and mislabelling rates hamper consumer choices for sustainability in Australia. Scientific Reports, 13(1), Article 1. [CrossRef]
- Curtotti, R., Dylewski, M., Cao, A., & Tuynman, H. (2023). Australian fisheries and aquaculture outlook to 2027–28. [CrossRef]
- DAFF. (2023a). Measures to prevent the importation of illegal, unreported and unregulated seafood: Discussion paper (Rep.). Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry. Canberra. https://haveyoursay.agriculture.gov.au/iuu-seafood-imports.
- DAFF. (2023b). Measures to prevent the importation of illegal, unreported and unregulated seafood: Draft Report (Rep.). Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry. Canberra. https://haveyoursay.agriculture.gov.au/iuu-seafood-imports.
- Davis, K. F., Downs, S., & Gephart, J. A. (2021). Towards food supply chain resilience to environmental shocks. Nature Food, 2(1), Article 1. [CrossRef]
- Department of Agriculture. (2015). Australia’s seafood trade. https://www.agriculture.gov.au/sites/default/files/sitecollectiondocuments/fisheries/aus-seafood-trade.pdf.
- Department of Agriculture and Water Resources. (2017). National Aquaculture Strategy. https://www.agriculture.gov.au/sites/default/files/sitecollectiondocuments/fisheries/aquaculture/national-aquaculture-strategy.pdf.
- Dominguez-Martinez, Rosa Mar and Spijkers, Jessica, Harrison, Emily, and Wilcox, Chris (2023). The Minderoo Foundation's submission to: market-based measures to prevent the importation of illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) seafood. Brisbane, QLD, Australia: The University of Queensland. [CrossRef]
- Dorber, M., Verones, F., Nakaoka, M., & Sudo, K. (2020). Can we locate shrimp aquaculture areas from space? – A case study for Thailand. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 20, 100416. [CrossRef]
- Dorninger, C., Hornborg, A., Abson, D. J., von Wehrden, H., Schaffartzik, A., Giljum, S., Engler, J.-O., Feller, R. L., Hubacek, K., & Wieland, H. (2021). Global patterns of ecologically unequal exchange: Implications for sustainability in the 21st century. Ecological Economics, 179, 106824. [CrossRef]
- Edgar, G. J., Bates, A. E., Krueck, N. C., Baker, S. C., Stuart-Smith, R. D., & Brown, C. J. (2024). Stock assessment models overstate sustainability of the world’s fisheries. Science, 385(6711), 860–865. [CrossRef]
- Edgar, G. J., Ward, T. J., & Stuart-Smith, R. D. (2018). Rapid declines across Australian fishery stocks indicate global sustainability targets will not be achieved without an expanded network of ‘no-fishing’ reserves. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 28(6), 1337–1350. [CrossRef]
- Edgar, G. J., Ward, T. J., & Stuart-Smith, R. D. (2019). Weaknesses in stock assessment modelling and management practices affect fisheries sustainability. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 29(11), 2010–2016. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P., Zhang, W., Belton, B., & Little, D. C. (2019). Misunderstandings, myths and mantras in aquaculture: Its contribution to world food supplies has been systematically over reported. Marine Policy, 106, 103547. [CrossRef]
- Eisenbarth, S. (2022). Do exports of renewable resources lead to resource depletion? Evidence from fisheries. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 112, 102603. [CrossRef]
- English, P. A., Ward, E. J., Rooper, C. N., Forrest, R. E., Rogers, L. A., Hunter, K. L., Edwards, A. M., Connors, B. M., & Anderson, S. C. (2022). Contrasting climate velocity impacts in warm and cool locations show that effects of marine warming are worse in already warmer temperate waters. Fish and Fisheries, 23(1), 239–255. [CrossRef]
- EUMOFA. (2004). Annex 7 - conversion factors by cn-8 code, version 2024 [data retrieved from EUMOFA European Market Observatory for Fisheries and Aquaculture products [online]. Retrieved September, 2024, from https ://www.eumofa.eu/supply-balance-and-other-methodologies].
- European Commission. (2019). MARE - The EU Fish Market 2019 edition is out: Everything you wanted to know about the EU market for fish and seafood. Retrieved September 29, 2022, from https://ec.europa.eu/newsroom/mare/items/664022.
- FAO (2017). Voluntary guidelines for Catch Documentation Schemes. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- FAO (2020) FAO Food Balances (-2013), version 2020. FAOSTAT. license: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Retrieved March 31, 2023, from https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FBS.
- FAO (2024a) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. [CrossRef]
- FAO (2023) FAO Food Balances (2010-), version 2023. FAOSTAT. license: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Retrieved September 26, 2024, from https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FBS.
- FAO. (2024b). FAO Global Fishery and Aquaculture Production Statistics, version 2024.1 (fishtatj) [data retrieved from FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Division [online]. Rome. www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/software/fishstatj/en].
- FAO. (2024c). FAO Global Aquatic Trade Statistics - By partner country, version 2024.1 (fishstatj) [In: FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Division [online]. Rome. www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/software/fishstatj/en].
- FAO. (2024d). FAO Global Aquatic Trade Statistics - All partners aggregated, version 2024.1 (fishstatj) [In: FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Division [online]. Rome. www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/software/fishstatj/en].
- Farmery, A. K., Allison, E. H., Andrew, N. L., Troell, M., Voyer, M., Campbell, B., Eriksson, H., Fabinyi, M., Song, A. M., & Steenbergen, D. (2021). Blind spots in visions of a “blue economy” could undermine the ocean’s contribution to eliminating hunger and malnutrition. One Earth, 4(1), 28–38. [CrossRef]
- Farmery, A. K., Gardner, C., Green, B. S., Jennings, S., & Watson, R. A. (2015). Domestic or imported? An assessment of carbon footprints and sustainability of seafood consumed in Australia. Environmental Science & Policy, 54, 35–43. [CrossRef]
- Farmery, A. K., Gardner, C., Jennings, S., Green, B. S., & Watson, R. A. (2017). Assessing the inclusion of seafood in the sustainable diet literature. Fish and Fisheries, 18(3), 607–618. [CrossRef]
- Fisheries and Aquaculture. (2024). United Nations University. UNU-CPR, 2024-05-01. Retrieved August 13, 2024, from https://unu.edu/cpr/article/fisheries-and-aquaculture.
- Flanders Marine Institute (2023). Maritime Boundaries Geodatabase: Maritime Boundaries and Exclusive Economic Zones (200NM), version 12. Available online at https://www.marineregions.org/. [CrossRef]
- Fleming, A., Hobday, A. J., Farmery, A., van Putten, E. I., Pecl, G. T., Green, B. S., & Lim-Camacho, L. (2014). Climate change risks and adaptation options across Australian seafood supply chains – A preliminary assessment. Climate Risk Management, 1, 39–50. [CrossRef]
- Fong, C. R., Gonzales, C. M., Rennick, M., Lahr, H. J., Gardner, L. D., Halpern, B. S., & Froehlich, H. E. (2022). California aquaculture in the changing food seascape. Aquaculture, 553, 738009. [CrossRef]
- Fong, C. R., Gonzales, C. M., Rennick, M., Lahr, H. J., Gardner, L. D., Halpern, B. S., & Froehlich, H. E. (2024a). Conflict and alignment on aquaculture among Californian communities. Aquaculture, 580, 740230. [CrossRef]
- Fong, C. R., Gonzales, C. M., Rennick, M., Lahr, H. J., Gardner, L. D., Halpern, B. S., & Froehlich, H. E. (2024b). The structure and function of a coastal state aquaculture plan. Aquaculture, 593, 741164. [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, H. E., Couture, J., Falconer, L., Krause, G., Morris, J. A., Perez, M., Stentiford, G. D., Vehviläinen, H., & Halpern, B. S. (2021). Mind the gap between ICES nations’ future seafood consumption and aquaculture production. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 78(1), 468–477. [CrossRef]
- Garlock, T. M., Asche, F., Anderson, J. L., Eggert, H., Anderson, T. M., Che, B., Chávez, C. A., Chu, J., Chukwuone, N., Dey, M. M., Fitzsimmons, K., Flores, J., Guillen, J., Kumar, G., Liu, L., Llorente, I., Nguyen, L., Nielsen, R., Pincinato, R. B. M., … Tveteras, R. (2024). Environmental, economic, and social sustainability in aquaculture: The aquaculture performance indicators. Nature Communications, 15(1), 5274. [CrossRef]
- Gentry, R. R., Froehlich, H. E., Grimm, D., Kareiva, P., Parke, M., Rust, M., Gaines, S. D., & Halpern, B. S. (2017). Mapping the global potential for marine aquaculture. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1(9), Article 9. [CrossRef]
- Gephart, J. A., Agrawal Bejarano, R., Gorospe, K., Godwin, A., Golden, C. D., Naylor, R. L., Nash, K. L., Pace, M. L., & Troell, M. (2024). Globalization of wild capture and farmed aquatic foods. Nature Communications, 15(1), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Gephart, J. A., Froehlich, H. E., & Branch, T. A. (2019). To create sustainable seafood industries, the United States needs a better accounting of imports and exports. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(19), 9142–9146. [CrossRef]
- Gephart, J. A., & Golden, C. D. (2022). Environmental and nutritional double bottom lines in aquaculture. One Earth, 5(4), 324–328. [CrossRef]
- Gephart, J. A., Henriksson, P. J. G., Parker, R. W. R., Shepon, A., Gorospe, K. D., Bergman, K., Eshel, G., Golden, C. D., Halpern, B. S., Hornborg, S., Jonell, M., Metian, M., Mifflin, K., Newton, R., Tyedmers, P., Zhang, W., Ziegler, F., & Troell, M. (2021). Environmental performance of blue foods. Nature, 597(7876), Article 7876. [CrossRef]
- Godar, J., & Gardner, T. (2019). Trade and Land-Use Telecouplings. In C. Friis & J. Ø. Nielsen (Eds.), Telecoupling: Exploring Land-Use Change in a Globalised World (pp. 149–175). Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Golden, C. D., Koehn, J. Z., Shepon, A., Passarelli, S., Free, C. M., Viana, D. F., Matthey, H., Eurich, J. G., Gephart, J. A., Fluet-Chouinard, E., Nyboer, E. A., Lynch, A. J., Kjellevold, M., Bromage, S., Charlebois, P., Barange, M., Vannuccini, S., Cao, L., Kleisner, K. M., … Thilsted, S. H. (2021). Aquatic foods to nourish nations. Nature, 598(7880), Article 7880. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Parrao, C., Shisler, S., Moratti, M., Yavuz, C., Acharya, A., Eyers, J., & Snilstveit, B. (2021). Aquaculture for improving productivity, income, nutrition and women’s empowerment in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 17(4), e1195. [CrossRef]
- Guillen, J., Natale, F., Carvalho, N., Casey, J., Hofherr, J., Druon, J.-N., Fiore, G., Gibin, M., Zanzi, A., & Martinsohn, J. Th. (2019). Global seafood consumption footprint. Ambio, 48(2), 111–122. [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B. S., Frazier, M., Verstaen, J., Rayner, P.-E., Clawson, G., Blanchard, J. L., Cottrell, R. S., Froehlich, H. E., Gephart, J. A., Jacobsen, N. S., Kuempel, C. D., McIntyre, P. B., Metian, M., Moran, D., Nash, K. L., Többen, J., & Williams, D. R. (2022). The environmental footprint of global food production. Nature Sustainability, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E., Ryland, M., & Thomas Travaille, K. (2021). Mending the net: Strengthening Australia's import policies to combat illegal seafood. Minderoo Foundation. https://cdn.minderoo.org/content/uploads/2021/09/29112031/20210917-mending-the-net.pdf.
- Henriksson, P. J. G., Pelletier, N. L., Troell, M., & Tyedmers, P. H. (2013). Life Cycle Assessments and Their Applications to Aquaculture Production Systemslife cycleassessment (LCA)aquaculture production systems. In P. Christou, R. Savin, B. A. Costa-Pierce, I. Misztal, & C. B. A. Whitelaw (Eds.), Sustainable Food Production (pp. 1050–1066). Springer. [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C. C., Levine, A., Agrawal, A., Basurto, X., Breslow, S. J., Carothers, C., Charnley, S., Coulthard, S., Dolsak, N., Donatuto, J., Garcia-Quijano, C., Mascia, M. B., Norman, K., Poe, M. R., Satterfield, T., St. Martin, K., & Levin, P. S. (2016). Engage key social concepts for sustainability. Science, 352(6281), 38–40. [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, R., Amoroso, R. O., Anderson, C. M., Baum, J. K., Branch, T. A., Costello, C., de Moor, C. L., Faraj, A., Hively, D., Jensen, O. P., Kurota, H., Little, L. R., Mace, P., McClanahan, T., Melnychuk, M. C., Minto, C., Osio, G. C., Parma, A. M., Pons, M., … Ye, Y. (2020). Effective fisheries management instrumental in improving fish stock status. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(4), 2218–2224. [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, R., Banobi, J., Hall, S. J., Pucylowski, T., & Walsworth, T. E. (2018). The environmental cost of animal source foods. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 16(6), 329–335. [CrossRef]
- Hornborg, S., van Putten, I., Novaglio, C., Fulton, E. A., Blanchard, J. L., Plagányi, É., Bulman, C., & Sainsbury, K. (2019). Ecosystem-based fisheries management requires broader performance indicators for the human dimension. Marine Policy, 108, 103639. [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, E., Schrobback, P., Pascoe, S., & Curtotti, R. (2021). Market integration between the major domestic fish markets in Australia. Fisheries Research, 243, 106085. [CrossRef]
- Hua, K., Cobcroft, J. M., Cole, A., Condon, K., Jerry, D. R., Mangott, A., Praeger, C., Vucko, M. J., Zeng, C., Zenger, K., & Strugnell, J. M. (2019). The Future of Aquatic Protein: Implications for Protein Sources in Aquaculture Diets. One Earth, 1(3), 316–329. [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, R. D. (2010). Globalizing European Union environmental policy. Journal of European Public Policy, 17(3), 335–349. [CrossRef]
- Kittinger, J. N., Bernard, M., Finkbeiner, E., Murphy, E., Obregon, P., Klinger, D. H., Schoon, M. L., Dooley, K. J., & Gerber, L. R. (2021). Applying a jurisdictional approach to support sustainable seafood. Conservation Science and Practice, 3(5), e386. [CrossRef]
- Kittinger, J. N., Teh, L. C. L., Allison, E. H., Bennett, N. J., Crowder, L. B., Finkbeiner, E. M., Hicks, C., Scarton, C. G., Nakamura, K., Ota, Y., Young, J., Alifano, A., Apel, A., Arbib, A., Bishop, L., Boyle, M., Cisneros-Montemayor, A. M., Hunter, P., Le Cornu, E., … Wilhelm, T. ’Aulani. (2017). Committing to socially responsible seafood. Science, 356(6341), 912–913. [CrossRef]
- Klein, C. J., Kuempel, C. D., Watson, R. A., Teneva, L., Coll, M., & Mora, C. (2022). Global fishing between jurisdictions with unequal fisheries management. Environmental Research Letters, 17(11), 114004. [CrossRef]
- Kuempel, C. D., Frazier, M., Nash, K. L., Jacobsen, N. S., Williams, D. R., Blanchard, J. L., Cottrell, R. S., McIntyre, P. B., Moran, D., Bouwman, L., Froehlich, H. E., Gephart, J. A., Metian, M., Többen, J., & Halpern, B. S. (2020). Integrating Life Cycle and Impact Assessments to Map Food’s Cumulative Environmental Footprint. One Earth, 3(1), 65–78. [CrossRef]
- Larson, S., Stoeckl, N., Fachry, M. E., Dalvi Mustafa, M., Lapong, I., Purnomo, A. H., Rimmer, M. A., & Paul, N. A. (2021). Women’s well-being and household benefits from seaweed farming in Indonesia. Aquaculture, 530, 735711. [CrossRef]
- Laubenstein, T., Smith, T. F., Hobday, A. J., Pecl, G. T., Evans, K., Fulton, E. A., & O’Donnell, T. (2023). Threats to Australia’s oceans and coasts: A systematic review. Ocean & Coastal Management, 231, 106331. [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, F., & Booth, R. (2010, September 29). Modern-day slavery: Horrific conditions on board ships catching fish for Europe. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/law/2010/sep/30/modern-day-slavery-fishing-europe.
- Lester, S. E., Gentry, R. R., Lemoine, H. R., Froehlich, H. E., Gardner, L. D., Rennick, M., Ruff, E. O., & Thompson, K. D. (2022). Diverse state-level marine aquaculture policy in the United States: Opportunities and barriers for industry development. Reviews in Aquaculture, 14(2), 890–906. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S. G., & Boyle, M. (2017). The Expanding Role of Traceability in Seafood: Tools and Key Initiatives. Journal of Food Science, 82(S1), A13–A21. [CrossRef]
- Li, M., Jia, N., Lenzen, M., Malik, A., Wei, L., Jin, Y., & Raubenheimer, D. (2022). Global food-miles account for nearly 20% of total food-systems emissions. Nature Food, 3(6), Article 6. [CrossRef]
- Lim-Camacho, L., Hobday, A. J., Bustamante, R. H., Farmery, A., Fleming, A., Frusher, S., Green, B. S., Norman-López, A., Pecl, G. T., Plagányi, É. E., Schrobback, P., Thebaud, O., Thomas, L., & van Putten, I. (2015). Facing the wave of change: Stakeholder perspectives on climate adaptation for Australian seafood supply chains. Regional Environmental Change, 15(4), 595–606. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Yang, X., Wang, Z., Liu, B., Zhang, J., Liu, X., Meng, D., Gao, K., Zeng, X., Yu, G., Zhang, Q., Cui, Y., Huang, Z., Luo, H., & Zhou, M. (2024). Mapping the fine spatial distribution of global offshore surface seawater mariculture using remote sensing big data. International Journal of Digital Earth, 17(1), 2402418. [CrossRef]
- Long, T., Widjaja, S., Wirajuda, H., & Juwana, S. (2020). Approaches to combatting illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing. Nature Food, 1(7), 389–391. [CrossRef]
- Love, D. C., Fry, J. P., Milli, M. C., & Neff, R. A. (2015). Wasted seafood in the United States: Quantifying loss from production to consumption and moving toward solutions. Global Environmental Change, 35, 116–124. [CrossRef]
- Marchese, D., Reynolds, E., Bates, M. E., Morgan, H., Clark, S. S., & Linkov, I. (2018). Resilience and sustainability: Similarities and differences in environmental management applications. Science of The Total Environment, 613–614, 1275–1283. [CrossRef]
- Marin, C., Adewumi, O. M., Asche, F., Garlock, T. M., Kristofersson, D. M., Lorenzen, K., & Yang, B. (2024). Does seafood trade enhance seafood availability in developing countries? The case of Nigeria. Marine Policy, 161, 106030. [CrossRef]
- Mason, J. G., Eurich, J. G., Lau, J. D., Battista, W., Free, C. M., Mills, K. E., Tokunaga, K., Zhao, L. Z., Dickey-Collas, M., Valle, M., Pecl, G. T., Cinner, J. E., McClanahan, T. R., Allison, E. H., Friedman, W. R., Silva, C., Yáñez, E., Barbieri, M. Á., & Kleisner, K. M. (2022). Attributes of climate resilience in fisheries: From theory to practice. Fish and Fisheries, 23(3), 522–544. [CrossRef]
- Mora, C., Myers, R. A., Coll, M., Libralato, S., Pitcher, T. J., Sumaila, U. R., Zeller, D., Watson, R. A., Gaston, K. J., & Worm, B. (2009). Management Effectiveness of the World’s Marine Fisheries. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K., Bishop, L., Ward, T., Pramod, G., Thomson, D. C., Tungpuchayakul, P., & Srakaew, S. (2018). Seeing slavery in seafood supply chains. Science Advances, 4(7), e1701833. [CrossRef]
- Nash, K. L., MacNeil, M. A., Blanchard, J. L., Cohen, P. J., Farmery, A. K., Graham, N. A. J., Thorne-Lyman, A. L., Watson, R. A., & Hicks, C. C. (2022). Trade and foreign fishing mediate global marine nutrient supply. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 119(22), e2120817119. [CrossRef]
- Newton, R. W., & Little, D. C. (2018). Mapping the impacts of farmed Scottish salmon from a life cycle perspective. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 23(5), 1018–1029. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Thanh, B., Le Van Thuy, T., Nguyen Anh, M., Nguyen Nguyen, M., & Nguyen Hieu, T. (2021). Drivers of agricultural transformation in the coastal areas of the Vietnamese Mekong delta. Environmental Science & Policy, 122, 49–58. [CrossRef]
- Park, J., Van Osdel, J., Turner, J., Farthing, C. M., Miller, N. A., Linder, H. L., Ortuño Crespo, G., Carmine, G., & Kroodsma, D. A. (2023). Tracking elusive and shifting identities of the global fishing fleet. Science Advances, 9(3), eabp8200. [CrossRef]
- Pascoe, S., Schrobback, P., Hoshino, E., & Curtotti, R. (2022). Impact of changes in imports and farmed salmon on wild-caught fish prices in Australia. European Review of Agricultural Economics, jbac003. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y., Sengupta, D., Duan, Y., Chen, C., & Tian, B. (2022). Accurate mapping of Chinese coastal aquaculture ponds using biophysical parameters based on Sentinel-2 time series images. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 181, 113901. [CrossRef]
- Roberson, L. A., Watson, R. A., & Klein, C. J. (2020). Over 90 endangered fish and invertebrates are caught in industrial fisheries. Nature Communications, 11(1), 4764. [CrossRef]
- Roberson, Leslie, Gilles Hosch, Chris Wilcox, Rosa Mar Dominguez Martinez, Glenn Sant, and Carissa Klein (2024)“A New Seafood Import Policy for Nations to Combat Illegal Fishing” Preprints . [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, Anthony, Piddocke, Toby, Ashby, Crispian, Conron, Simon, Hartmann, Klaas, Hesp, Alex, Hone, Patrick, Jacobsen, Ian, Jesson-Kerr, Marlee, Mayfield, Stephen, Stewart, John, Usher, Michael, Woodhams, James and Wright, Daniel (eds) (2024), Status of Australian Fish Stocks Reports 2024, Fisheries Research and Development Corporation, Canberra. https://www.fish.gov.au/.
- Rousseau, Y., Blanchard, J. L., Novaglio, C., Pinnell, K. A., Tittensor, D. P., Watson, R. A., & Ye, Y. (2024). A database of mapped global fishing activity 1950–2017. Scientific Data, 11(1), 48. [CrossRef]
- Saha, C. K. (2024). Governing sociocultural sustainability through standards: Evidence from aquaculture eco-certification schemes. Aquaculture, 578, 740011. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Jerez, P., Karakassis, I., Massa, F., Fezzardi, D., Aguilar-Manjarrez, J., Soto, D., Chapela, R., Avila, P., Macias, J. C., Tomassetti, P., Marino, G., Borg, J. A., Franičević, V., Yucel-Gier, G., Fleming, I. A., Biao, X., Nhhala, H., Hamza, H., Forcada, A., & Dempster, T. (2016). Aquaculture’s struggle for space: The need for coastal spatial planning and the potential benefits of Allocated Zones for Aquaculture (AZAs) to avoid conflict and promote sustainability. Aquaculture Environment Interactions, 8, 41–54. [CrossRef]
- Schrobback, P., Pascoe, S., & Zhang, R. (2019). Market Integration and Demand for Prawns in Australia. Marine Resource Economics, 34(4), 311–329. [CrossRef]
- Selig, E. R., Nakayama, S., Wabnitz, C. C. C., Österblom, H., Spijkers, J., Miller, N. A., Bebbington, J., & Decker Sparks, J. L. (2022). Revealing global risks of labor abuse and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing. Nature Communications, 13(1), Article 1. [CrossRef]
- Shamsuzzoha, A., Marttila, J., & Helo, P. (n.d.). Blockchain-enabled traceability system for the sustainable seafood industry. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 0(0), 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Smith, D. C., Haddon, M., Punt, A. E., Gardner, C., Little, L. R., Mayfield, S., O’Neill, M. F., Saunders, T., Stewart, J., Wise, B., Fulton, E. A., & Conron, S. (2021). Evaluating the potential for an increased and sustainable commercial fisheries production across multiple jurisdictions and diverse fisheries. Marine Policy, 124, 104353. [CrossRef]
- Smith, M. D., Roheim, C. A., Crowder, L. B., Halpern, B. S., Turnipseed, M., Anderson, J. L., Asche, F., Bourillón, L., Guttormsen, A. G., Khan, A., Liguori, L. A., McNevin, A., O’Connor, M. I., Squires, D., Tyedmers, P., Brownstein, C., Carden, K., Klinger, D. H., Sagarin, R., & Selkoe, K. A. (2010). Sustainability and Global Seafood. Science, 327(5967), 784–786. [CrossRef]
- Spillias, S., Cottrell, R. S., Kelly, R., O’Brien, K. R., Adams, J., Bellgrove, A., Kelly, B., Kilpatrick, C., Layton, C., Macleod, C., Roberts, S., Stringer, D., & McDonald-Madden, E. (2022). Expert perceptions of seaweed farming for sustainable development. Journal of Cleaner Production, 368, 133052. [CrossRef]
- Spillias, S., Valin, H., Batka, M., Sperling, F., Havlík, P., Leclère, D., Cottrell, R. S., O’Brien, K. R., & McDonald-Madden, E. (2023). Reducing global land-use pressures with seaweed farming. Nature Sustainability, 6(4), 380–390. [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, R. C., Ruwet, M., Boschetti, F., Fielke, S., Fleming, A., Dominguez-Martinez, R. M., Plagányi, É., Schrobback, P., & Melbourne-Thomas, J. (2023). The socio-ecological resilience and sustainability implications of seafood supply chain disruption. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 33(4), 1129–1154. [CrossRef]
- Sun, W., Hou, T., Chen, C., Yang, G., Chen, B., Meng, X., & Ren, K. (2024). Mapping China’s coastal aquaculture ponds expansion with sentinel-2 images during 2017–2021. International Journal of Digital Earth, 17(1), 2297943. [CrossRef]
- Sutton, T., & Siciliano, A. (2016). Seafood Slavery. Center for American Progress. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/seafood-slavery/.
- Swartz, W., Rashid Sumaila, U., Watson, R., & Pauly, D. (2010). Sourcing seafood for the three major markets: The EU, Japan and the USA. Marine Policy, 34(6), 1366–1373. [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A. G. J., & Metian, M. (2008). Global overview on the use of fish meal and fish oil in industrially compounded aquafeeds: Trends and future prospects. Aquaculture, 285(1), 146–158. [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A. G. J., & Metian, M. (2015). Feed Matters: Satisfying the Feed Demand of Aquaculture. Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture, 23(1), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Teh, L. C. L., Caddell, R., Allison, E. H., Finkbeiner, E. M., Kittinger, J. N., Nakamura, K., & Ota, Y. (2019). The role of human rights in implementing socially responsible seafood. PLOS ONE, 14(1), e0210241. [CrossRef]
- Teh, L. C. L., & Sumaila, U. R. (2013). Contribution of marine fisheries to worldwide employment. Fish and Fisheries, 14(1), 77–88. [CrossRef]
- The Economist Intelligence Unit. (2018). 2018 the global illicit trade environment index [data available from https://impact.economist.com/projects/deliver-change/article/interactive-tool/]. http://illicittradeindex.eiu.com/.
- The Walk Free Foundation. (2023). 2023 global slavery index [data available for download from: www.globalslaveryindex.org]. www.globalslaveryindex.org.
- Tickler, D., Meeuwig, J. J., Bryant, K., David, F., Forrest, J. A. H., Gordon, E., Larsen, J. J., Oh, B., Pauly, D., Sumaila, U. R., & Zeller, D. (2018). Modern slavery and the race to fish. Nature Communications, 9(1), 4643. [CrossRef]
- Tickler, D., Meeuwig, J. J., Palomares, M.-L., Pauly, D., & Zeller, D. (2018). Far from home: Distance patterns of global fishing fleets. Science Advances, 4(8), eaar3279. [CrossRef]
- Tran, T. Q., Vu, H. V., & Nguyen, T. V. (2023). Aquaculture, household income and inequality in Vietnam’s coastal region. Marine Policy, 153, 105634. [CrossRef]
- Troell, M., Costa-Pierce, B., Stead, S., Cottrell, R. S., Brugere, C., Farmery, A. K., Little, D. C., Strand, Å., Pullin, R., Soto, D., Beveridge, M., Salie, K., Dresdner, J., Moraes-Valenti, P., Blanchard, J., James, P., Yossa, R., Allison, E., Devaney, C., & Barg, U. (2023). Perspectives on aquaculture’s contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals for improved human and planetary health. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 54(2), 251–342. [CrossRef]
- Truong, H. H., Hines, B. M., Rombenso, A. N., & Simon, C. J. (2023). Aquaculture nutrition in Australia: Challenges and trends. Animal Production Science. [CrossRef]
- Turchini, G. M., Trushenski, J. T., & Glencross, B. D. (2019). Thoughts for the Future of Aquaculture Nutrition: Realigning Perspectives to Reflect Contemporary Issues Related to Judicious Use of Marine Resources in Aquafeeds. North American Journal of Aquaculture, 81(1), 13–39. [CrossRef]
- Tuynman, H., Dylewski, M., Cao, A., & Curtotti, R. (2024). Australian fisheries and aquaculture outlook to 2028–29. [CrossRef]
- van Putten, I., Koopman, M., Fleming, A., Hobday, A. J., Knuckey, I., & Zhou, S. (2019). Fresh eyes on an old issue: Demand-side barriers to a discard problem. Fisheries Research, 209, 14–23. [CrossRef]
- Walker, B., Crépin, A.-S., Nyström, M., Anderies, J. M., Andersson, E., Elmqvist, T., Queiroz, C., Barrett, S., Bennett, E., Cardenas, J. C., Carpenter, S. R., Chapin, F. S., de Zeeuw, A., Fischer, J., Folke, C., Levin, S., Nyborg, K., Polasky, S., Segerson, K., … Vincent, J. R. (2023). Response diversity as a sustainability strategy. Nature Sustainability, 6(6), Article 6. [CrossRef]
- Ward, T. M., Wolfe, B. W., Grammer, G. L., Ivey, A. R., King, E., Schiller, A., McDonald, K. S., & Dambacher, J. M. (2023). Large sardine resource discovered off south-eastern Australia: Potential risks, challenges and benefits of establishing a new fishery. Marine Policy, 155, 105739. [CrossRef]
- Watson, R. A., Green, B. S., Tracey, S. R., Farmery, A., & Pitcher, T. J. (2016). Provenance of global seafood. Fish and Fisheries, 17(3), 585–595. [CrossRef]
- Watson, R. A., Nichols, R., Lam, V. W. Y., & Sumaila, U. R. (2017). Global seafood trade flows and developing economies: Insights from linking trade and production. Marine Policy, 82, 41–49. [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M. J., Emerson, J. W., Esty, D. C., de Sherbinin, A., & Wendling, Z. A. (2024). 2024 environmental performance index. Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy. New Haven, CT. epi.yale.edu.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




