1. Introduction
Enzyme-catalyzed processes are becoming more important in large-scale industries such as the environment, pharmaceutical, and food industries. However, the use of free enzymes often has limitations, such as low stability and difficulties in recovery and reuse, thereby increasing the cost. Enzyme immobilization can improve the stability of enzymes under reaction conditions such as high acidity/alkalinity, high temperatures, or high contents of organic solvents. It can also facilitate the separation and reuse of enzymes from reaction solutions [
1].
Silica (SiO
2) is a low-cost and earth-abundant matrix that is one of the most widely used supports for enzyme immobilization. Because of its physical stability, biocompatibility, electrical conductivity, and chemical inertness, silica can be used not only as a matrix for biocatalysts and biosensors but also as a carrier for drug delivery systems and cosmetic additives [
2,
3,
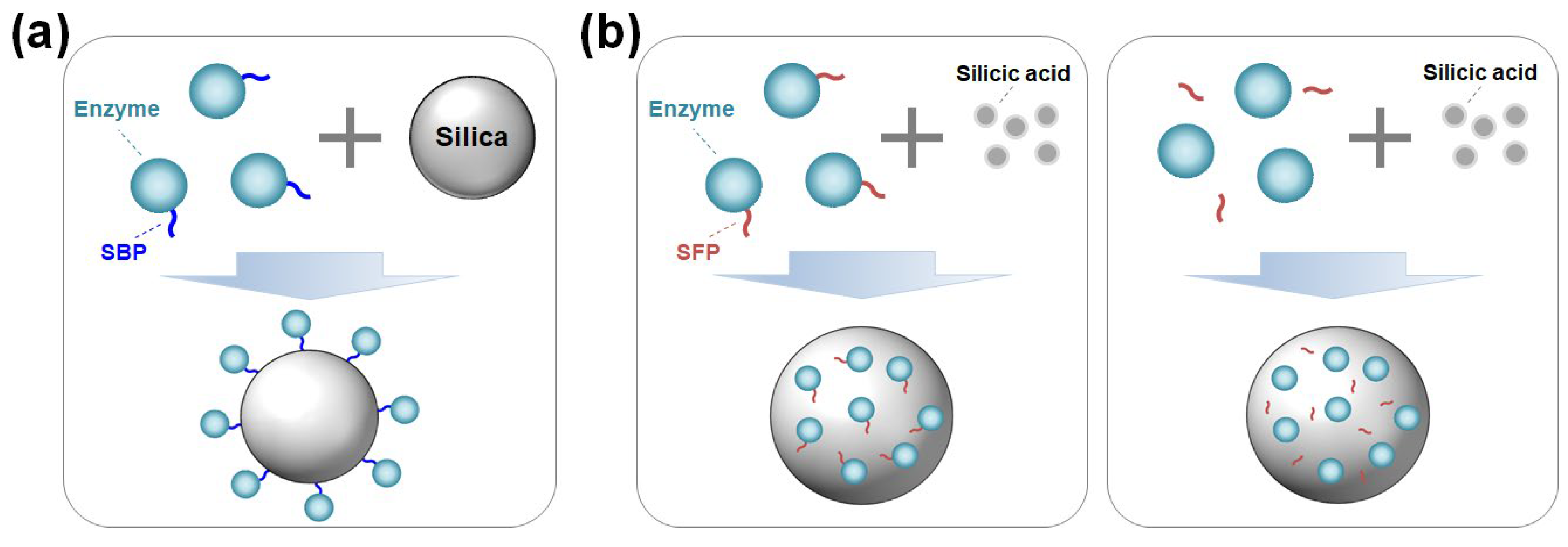
4]. Recently, many studies have been conducted on silica-binding proteins/peptides (SBPs) and silica-forming proteins/peptides (SFPs). SBPs are important tools that can be used to anchor target enzymes with a controlled orientation, in the form of fusion protein, on the surface of silica owing to their strong affinity to the silica surface (
Figure 1a) [
5]. SFPs have the ability to synthesize silica from silica precursors (e.g. orthosilicic acid) by polymerizing precursors and inducing the aggregation of silica particles [
6,
7]. In this biomimetic process, target enzymes, either in the form of being genetically fused or physically blended with an SFP, can be encapsulated in situ in the synthesized silica particles under neutral pH and room temperature conditions in a short time (
Figure 1b). In general, though with some exceptions, both SBPs and SFPs are characterized by having a high isoelectric point (pI) value with a high content of positively charged amino acids (Lys, Arg, His). SFPs are generally considered SBPs, but not vice versa [
8], implying that a more elaborate sequence design is required to confer silica-forming functionality.
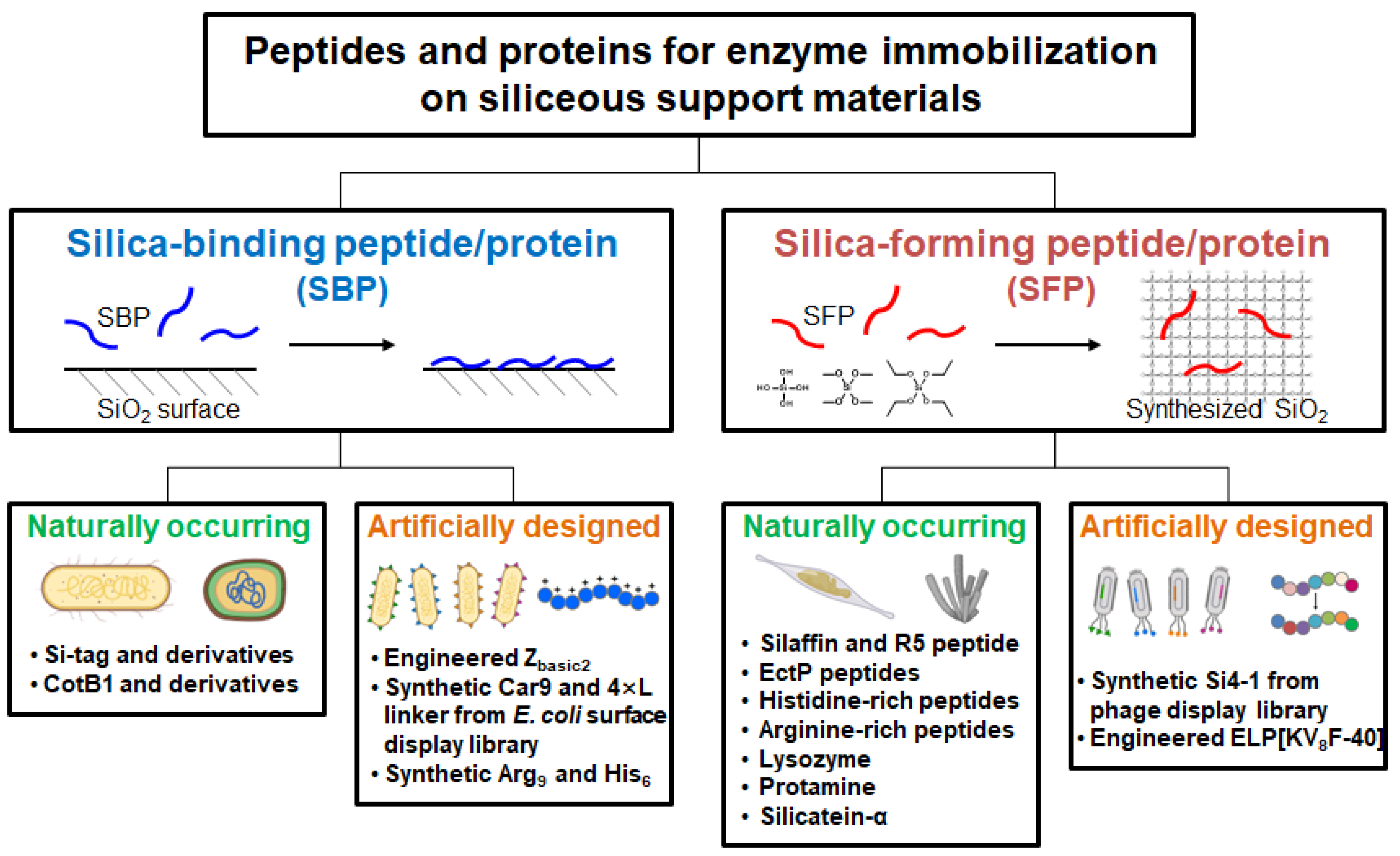
In this review, SBPs and SFPs relevant to enzyme technologies are categorized into naturally occurring and artificially engineered ones, and their distinct features, including the working mechanisms, are summarized (
Figure 2). This review may guide choosing proper SBPs or SFPs for effectively immobilizing enzymes on siliceous materials.
2. Silica-binding proteins/peptides (SBPs)
2.1. How SBPs work
The silanol groups (Si-OH) are exposed on the surface of silica, and the silanols (p
Ka ≒ 7) are deprotonated to be silanolates (Si-O
-) depending on the pH [
9]. Proteins or peptides rich in positively charged residues can bind to and be adsorbed onto the negatively charged surface of silica via ionic interactions. Accordingly, cationic SBPs with a high pI can bind to the silica surface via ionic interactions. When the pH is lowered and the silica surface approaches the point of zero charge (pzc), cationic SBPs can be adsorbed primarily via nonionic interactions such as van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonds [
10,
11]. Because enzymes are generally expected to be immobilized and utilized near neutral pH, SBPs widely used as a strong binder for enzyme immobilization are mostly cationic.
In addition, SBPs that are mainly composed of non-polar amino acids, such as the S2 peptide with the sequence AFILPTG, prefer hydrophobic interactions with the silica surface [
10]. These interactions are strengthened when the silica surface gets closer to the pzc. On the contrary, when the silica surface is more negatively charged, a higher concentration is required for the adsorption of those hydrophobic SBPs to occur [
10,
11].
Collectively, the contribution of each interaction to the binding of a SBP to the silica surface may vary depending on pH, pI of the SBP, and amino acid composition of the SBP [
11]. The amino acid sequences and the pI values of various SBPs are summarized in
Table 1.
2.2. Naturally occurring SBPs
2.2.1. Si-tag and its derivatives
The Si-tag is the other name of
Escherichia coli L2, a ribosomal protein with 273 amino acids. This SBP has been discovered by bioprospecting
E. coli proteins that can strongly bind to silica under 1 M NaCl conditions where ionic interactions are generally suppressed [
12]. The binding is strong with a dissociation constant (
Kd) of 0.7 nM and is virtually irreversible without salt and detergent. The positively charged, intrinsically disordered N-terminal (1-60) and C-terminal (203-273) domains are cooperatively required for the strong silica binding, while the central domain (61-202) is not responsible for the silica binding ability of Si-tag [
12]. Accordingly, a shortened version (L2NC) of the Si-tag has been created by removing the central domain and directly fusing the N-terminal region with the C-terminal region [
13]. The Si-tag contains 63 positively charged residues, crucial for strongly binding to silica via ionic interactions. In addition, the efficient binding of Si-tag can occur even under high salt and denaturing conditions. This can be explained by conformational adaptation of the intrinsically disordered regions of Si-tag at the binding interface by which not only ionic interactions between cationic side chains and silanol groups but also hydrophobic interactions between apolar side chains and hydrophobic siloxane sites are optimized [
14].
Kim et al. studied the immobilization of L2NC-fused carbonic anhydrase (CA) on diatomaceous earth for carbon dioxide (CO
2) capture applications [
13]. The thermal stability of the enzyme was improved by the self-immobilization of the enzyme in multilayers at a high packing density. Intriguingly, the immobilization system showed a phenomenon of activity−stability trade-off according to the amount of enzyme loading, providing a unique model for studying the effect of macromolecular crowding on surface-immobilized enzymes. In another study by Zurier and Goddard, the N-terminal domain (1-60) of Si-tag was fused to a polyethylene terephthalate (PET)-degrading enzyme (PETase), which was then immobilized in mesoporous silica nanoparticles [
15]. The immobilized PETase showed improved thermal stability, leading to better PET degradation performance in unbuffered, simulated wastewater conditions. These studies demonstrate that enzyme immobilization on siliceous materials via the shortened versions of Si-tag can be a simple and effective way to develop highly stabilized biocatalysts for environmental bioremediation.
Similar to the L2NC, the rplB protein, a homolog of Si-tag originating from
Mannheimia succiniciproducens, was redesigned by removing the central domain and linking the N-terminal domain and the C-terminal domain [
16]. The resulting SBP was used to immobilize avian influenza (AI) antigen on a silica surface in a nanogap field-effect transistor biosensor without surface modification. The biosensor was successful in the electrical detection of an anti-AI antibody in a label-free manner [
16].
2.2.2. CotB1 derivatives
CotB1 is a spore coat protein from
Bacillus cereus with 171 amino acids involved in biosilicification in and around the spore coat layer [
17]. The zwitterionic C-terminal region (142-171) of CotB1 is essential for the
Bacillus biosilicification [
17], of which the 14 amino acid-length cationic peptide (CotB1p) at the outermost C-terminus showed a strong affinity for silica particles [
18]. CotB1 and CotB1p, with a
Kd of 2.09 nM and 1.24 nM at pH 8.0, respectively, were employed as fusion tags for affinity purification of target proteins. Furthermore, a half-length CotB1p (SB7 tag) was successfully developed as an affinity tag for silica [
19]. However, unlike the Si-tag, the binding of CotB1 derivatives was inhibited at high ionic strength, implying that ionic interaction between the negatively charged silica surface and the cationic residues at the C-terminal region of CotB1 is the primary driving force for the strong binding.
Müller et al. tried to immobilize an engineered hydrolase on silica materials via the fusion of CotB1p peptide for efficient enzymatic inactivation of the antibiotics Florfenicol. However, the tagging with the CotB1p resulted in a low yield of target enzyme and severely impaired growth of
E. coli host cells [
20]. On the other hand, the tagging with the Si-tag, despite the large size, did not impair cell growth or protein expression [
20].
2.3. Artificially engineered SBPs
2.3.1. Zbasic2
The Z
basic2 protein is an engineered arginine-rich variant of the Z domain, a 7-kDa three-helix bundle derived from the B domain of
Staphylococcus aureus protein A [
21,
22]. Originally, the Z
basic2 was developed as a general purification tag for ion exchange chromatography, but it was later found that the Z
basic2 can also tightly bind to silica surfaces. The binding force of Z
basic2 to silica is affected by pH and ionic strength, suggesting a principal role of ionic interaction in the strong binding. An enzyme fused with the Z
basic2 can be directly immobilized on porous glass from a cleared lysate with excellent binding selectivity and a high loading capacity (> 30 mg protein/g support) [
23]. The binding is thought to be mediated by a positively charged surface patch located across two helices of Z
basic2, which allows an oriented immobilization of the Z
basic2-tethered enzyme with full retention of biological activity [
23]. Bolivar et al. achieved oriented co-immobilization of two enzymes (
d-amino-acid oxidase and catalase) fused with the Z
basic2 on mesoporous silica [
24]. The heterogeneous catalyst was recyclable and stable during the oxidation of
d-methionine into its α-keto acid form.
2.3.2. Car9 peptide
The Car9 peptide was identified from disulfide-constrained, random 12-mer peptide libraries constructed using an
E. coli flagellar display system as a binder to graphite materials [
25]. Later, it was shown to bind to silica with a high affinity. Both the disulfide-constrained form (i.e., loop form) and the linear form of Car9 were effective for silica binding. Although the
Kd (~1 μM) of Car9 seems relatively high compared to those of other strong silica binders, the binding of Car9 to silica was not disrupted even by applying high ionic strength (5 M NaCl). This suggests that similar to the case of Si-tag, the strong binding involves not only ionic interaction but also hydrophobic interaction between the phenylalanine residues and siloxane groups. Indeed, free lysine and arginine were effective for competitively releasing Car9 from silica because their side chains have both cationic and hydrophobic characteristics. The Car9 exhibits a high affinity for silica beads through the above two types of interactions and enables efficient capture of Car9-bound proteins [
25].
The Car9 tag could be added to the N or C terminus of a target protein, and the loading of the Car9-tagged protein was enhanced when using small-sized silica gel with large pores as the binding matrix [
26]. Using an optimized small-scale purification kit, Car9-tagged proteins could be recovered from the silica matrix with high purity at a low cost within minutes [
26]. This technology was extended to using silica spin columns and 96-well borosilicate plates as cheap binding matrices [
27].
2.3.3. Poly(amino acid)
The nonaarginine (Arg
9) tag has been originally known as a protein transduction domain for cellular uptake of small molecule drugs or proteins [
28]. This versatile tag can also be used as a purification tag for cation exchange chromatography and an SBP for enzyme immobilization onto glass slides and silica resins [
29]. However, the Arg
9 tag is not frequently used in protein engineering because it may affect the tertiary structure of a protein [
30]. Although the Arg
9 tag at the C terminus of a target protein can be removed by treating carboxypeptidase B that digests C-terminal arginine and lysine residues, the cleavage yield and specificity are generally low [
30].
Histidine-containing motifs play a critical role in silica binding (and silica synthesis also; See below), as are frequently found in SBPs [
8,
31]. The imidazole groups form hydrogen bonds with silanol and siloxide groups on silica surfaces [
11]. Indeed, the hexahistidine tag (His
6), the most widely used tag for protein purification by immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC), displays an affinity to silica particles [
32]. A His
6-tagged EGFP protein could be purified from
E. coli lysate with a purity of up to 96% using silica as a solid-phase matrix, while the untagged counterpart could not bind to the matrices. Double tagging with N-terminal His
6 and C-terminal SBPs such as Car9 or CotB1p improved the binding strength [
5,
32], which would be advantageous for enzyme immobilization. The binding improvement was achieved by the synergetic contribution of His
6 and SBPs [
5].
2.3.4. Linker peptide
The four repeating, linker peptide (VKTQATSREEPPRLPSKHRPG)
4VKTQTAS (4×L) was discovered as a zeolite (aluminosilicate minerals)-binding peptide through
E. coli cell surface display, and this cationic peptide was later found to be a strong binder toward other silica-containing materials [
33,
34]. The 4×L fused to a
Streptococcus protein G was immobilized onto a silica surface with a vertical orientation, showing a
Kd of 34.77 nM [
35]. A binding test with a series of shorter derivatives showed that the 3×L was the minimally repeating peptide capable of complete binding to zeolite or silica. Similar to the Si-tag, more than 76% of the residues in the linker peptide tend to promote structural disorder, conferring structural flexibility and plasticity required for the strong binding to silica by conformational adaptation [
33].
Lu et al. fused the 4×L peptide to a thermostable β-glucosidase, an enzyme used to biotransform icariin to baohuoside I, a flavonoid compound with various pharmacological activities [
36]. They purified the fusion protein directly from the cell lysate and immobilized it onto Na-Y zeolite in a single step. The immobilized enzyme showed a catalytic efficiency 61% higher than that of the free enzyme, and the stability was also improved at high temperatures and in organic solvents. In another study, Care et al. utilized the 4×L peptide for the immobilization of three thermostable hemicellulases (β-glucosidase, β-xylanase, and β-mannanase) onto Na-Y zeolite [
37]. All three enzymes could be immobilized with the simultaneous formation of cross-linked enzyme aggregate (CLEA), making a stabilized, multiple-enzyme biocatalytic module for the hydrolysis of various hemicellulosic polysaccharides.
3. Silica-forming proteins/peptides (SFPs)
3.1. How SFPs work
Silica synthesis involves the process of polycondensation (polymerization) of silicic acid precursors. Silica polycondensation by SFPs is catalyzed by multiple cationic side chains on the SFPs (
Figure 2a) [
38,
39]. Positively charged residues act as acid-base catalysts that promote the formation of siloxane bonds. A deprotonated amine accepts a proton from a silicic acid to form a reactive silanolate. A water molecule is released from a second silicic acid by a nucleophilic attack of the silanolate on the second silicic acid, facilitated by a nearby protonated amine group as a proton donor. In addition, a positively charged residue can be more polarized and activated by a closely located, negatively charged residue, leading to an improved silicic acid polycondensation by the charge relay effect [
40]. This effect is particularly pronounced when the basic and acidic residues are alternatingly positioned.
In most cases, orthosilicic acid, obtained by the hydrolysis of silicon alkoxides such as tetramethyl orthosilicate (TMOS) and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), is used as the precursor for the silica synthesis by SFPs. However, some SFPs can directly utilize silicon alkoxides as the precursor. Silicatein-α is the most well-known example of this type of SFP [
41]. The ‘enzyme’ silicatein-α can catalyze the hydrolysis of silicon alkoxide molecules and the polycondensation of the resulting silicic acids. The active site residues Ser26 and His165 in the silicatein-α play crucial roles in both reactions. The activity of silicatein is abolished upon thermal denaturation, suggesting its dependence on the protein’s native three-dimensional structure. Biomimetic synthesis of silica directly from TEOS was also demonstrated using synthetic block copolypeptides [
42], implying that both catalytic functionalities might be implemented on a relatively small peptide that does not have a defined three-dimensional structure. The proposed mechanisms of silicatein actions can be found elsewhere [
43,
44].
The catalytic acceleration of silicic acid condensation is insufficient for synthesizing particulate silica, and the precipitation (flocculation) process is required to obtain silica particles. The same SFPs can also serve as flocculating agents by providing plentiful cationic and hydroxyl-containing residues that interact with the anionic surface of small oligomeric/colloidal silica via ionic interactions and hydrogen bonds [
45,
46,
47]. During this process, SFPs are stoichiometrically consumed following the amount of silica synthesis and become entrapped within the synthesized silica particles. This consequence forms the basis of enzyme immobilization in biomimetic silica using SFPs. The amino acid sequences and the pI values of various SFPs are summarized in
Table 2.
3.2. Naturally occurring SFPs
3.2.1. Silaffin-derived R5 peptide
Silaffin is a family of cell wall peptides originating from the diatom
Cylindrotheca fusiformis and is involved in the biosilica formation in diatom cell walls in vivo [
46,
48]. The representative silaffin, silaffin-1A
1 (SSKKSGSYSGSKGSK), is one of the in vivo endoproteolytic products of the silaffin precursor polypeptide sil1p. The polypeptide backbone of silaffin-1A
1 is highly cationic due to the high Lys content and the lack of acidic residues. However, the extensive posttranslational modifications with long-chain polyamines (on Lys residues) and phosphates (on Ser residues) eventually render the native silaffin-1A
1 uniquely zwitterionic, allowing supramolecular assembly of the peptides via electrostatic interactions as an essential prerequisite for silica formation [
48,
49,
50].
The R5 peptide (SSKKSGSYSGSKGSKRRIL) is one of the repeat sequences of the sil1p [
46]. Unlike the native silaffin-1A
1 capable of precipitating silica under a wide range of pH conditions, the synthetic R5 peptide shows silica precipitation activity only at pH > 6 due to the lack of long-chain polyamine modifications [
46,
51]. Since the first demonstration of enzyme immobilization in biomimetic silica support [
52], undoubtedly, the R5 peptide has been the most widely used SFP due to its high efficiency in silica synthesis despite its relatively short length [
2,
4,
53]. The genetic fusion of the R5 peptide to a target enzyme provides benefits over the blending (coprecipitation) method in that the peptide can be easily produced in a microbial host at a low cost, and a higher immobilization yield can be attained, particularly when the concentration of the R5-fused enzyme is high [
54].
In a recent study, the addition of metal cations such as Na
+ and Cs
+ during the immobilization of the R5-fused bovine CA (bCA) was shown to increase the silica synthesis with high packing density, leading to an 11- to 18-fold increase in the stability of the immobilized bCA-R5 compared to the counterpart without the cation addition [
55]. Whether the cation addition was effective for the further stabilization of the R5-fused enzyme was determined by both the pH condition and the enzyme's surface electrostatic nature, suggesting unique interactions among all the components (cation, silica, and R5-fused enzyme) during the immobilization reaction. In another study, Lee et al. fabricated an ultrathin (~1.5 nm) and mesoporous silica layer on triblock copolymer-based micelle nanoparticles that were functionalized with the R5 peptide and a CA enzyme [
56]. The synthesis of the silica shell was performed under a TMOS-water biphasic system. The immobilized enzyme was highly stabilized and showed no mass transfer limitation for the catalytic activity.
Integral membrane proteins (IMPs) are highly aggregation-prone and unstable in solution, impeding further studies and handling of these recalcitrant proteins. Designed amphiphilic β-strand peptides such as BP-1 can associate with IMPs and stabilize them in a detergent-free buffer [
57]. Bialas and Becker employed an R5 peptide-fused BP-1 peptide to further stabilize an integral membrane diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) via biomimetic silica encapsulation [
58]. The stability of encapsulated DGK was improved against protease attack and extremely low pH.
3.2.2. EctP peptides
Yeo et al. performed the BLAST search using the silaffin R5 peptide sequence as a query and identified SFP candidates (EctP1 and EctP2) from the brown algae
Ectocarpus siliculosus [
59]. The EctP peptides exhibited better abilities for silica synthesis than the R5 peptide; particularly, the EctP1 was superior at the relatively low pH 6, at which the R5 peptide rarely showed silicification activity.
3.2.3. Histidine-rich Kpt peptide and glassin
Inspired by His-rich peptides screened from the phage display library [
8], Nguyen et al. performed the BLAST search using the Si3-8 (Kps peptide) sequence as a query. As a potential SFP, the Kpt peptide (KPTHHHHHHDG) was discovered from the marine bacterium
Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3 [
60]. Compared to the R5 peptide, the Kpt peptide performed better at the relatively high pH 8. Obviously, the natural Kpt sequence contains the His
6 sequence, which gives the peptide dual functionalities as both an SFP and a purification tag.
The glassin is a 23-kDa, His-rich protein from the marine sponge
Euplectella aspergillum [
61]. When hydrolyzed TMOS was used as the silica precursor, the glassin showed silica-precipitating activity even after heat denaturation. However, this activity has not been exploited for enzyme encapsulation in bioinspired silica.
3.2.4. Lysozyme
Lysozyme is an antibacterial enzyme that hydrolyzes and degrades bacterial cell walls, leading to the lytic death of bacterial cells. As a highly basic protein containing a high content of hydroxyl group, lysozyme can direct the formation of silica along with the encapsulation of the active lysozyme to create highly stabilized, antibacterial nanocomposite materials [
62]. The immobilized lysozyme was shown to be firmly trapped inside the silica by steric effects [
63]. Although it is currently uncertain how the entrapped enzyme could physically access the bacterial cell wall components for the lytic action, a detailed structural study on the lysozyme-silica composite suggested that the presence of surface-accessible lysozyme was responsible for the observed antibacterial activity [
64]. Because additional enzymes can be simultaneously immobilized during the silica synthesis, lysozyme-mediated silica synthesis offers an economical and efficient method for fabricating versatile nanocomposites equipped with antibacterial activity.
3.2.5. Protamine
Protamines are a group of small DNA-binding peptides found in sperms, contributing to the condensation and stabilization of the spermatid genome [
65]. Notably, protamines are strongly cationic with high contents of Arg, suggesting possible use as SFPs. For example, salmon protamine comprises 32 residues (excluding the first Met), of which 21 (66%) are Arg. Salmon protamine was first used as an SFP to fabricate an alginate/protamine/silica hybrid capsule [
66]. The enzyme β-glucuronidase was pre-encapsulated within the liquid-core alginate, and then the anionic surface was coated with the cationic protamine by which biomimetic microscale silica shell was subsequently formed from sodium silicate solution. The silica shell effectively prevented the shrinking or swelling of the core alginate capsule, and the catalytic activity and recycling stability of the encapsulated enzyme were significantly improved after the biomimetic silicification. In a subsequent study, biomimetic layer-by-layer mineralization was demonstrated using the protamine for biocatalytic nanoscale coatings of silica or titania [
67]. Protamine-conjugated glucose oxidase was stably incorporated into a desired layer, exhibiting higher catalytic activity when located closer to the outer surface. Although protamine was successfully used as an effective SFP, enzyme encapsulation in a genetically fused form has not yet been proven.
3.2.6. Arginine-rich peptides
In addition to protamines, other arginine-rich SFPs have been discovered. The Salp1 peptide was derived from a siliceous choanoflagellate [
68]. Unlike the R5 peptide, a wet silica gel was fabricated when using Salp1 unless the ionic strength of the silicifying solution sufficiently increased. Notably, the release of the entrapped GFP-Salp1 from the silica matrix was much slower than the GFP-R5. This was attributed to two Cys residues in the Salp1 that can form intermolecular disulfide bonds, resulting in a more stable encapsulation. The different release profiles of different SFPs might be exploited for the controlled release of multiple proteins, e.g., in a drug delivery system.
Min et al. found multiple arginine-rich peptides, all showing silicifying activity [
69]. Among them, the 22-residue RSGH peptide, which has the duplicated sequence from the 11-residue peptide from
Equus caballus, was a more efficient SFP than the R5 peptide under acidic (pH 5 and pH 6) conditions [
69]. Similarly, the 23-residue Wa-RSG peptide from
Winogradskyella arenosi worked as well at pH 6 as it did at pH 7 [
70]. These peptides were adsorbed onto the surface of yeast or bacterial cells, respectively, and the cells were encapsulated in silica shells, resulting in improved tolerance to dehydration and UV-C irradiation [
69,
70].
3.2.7. Silicatein
Silicatein filaments were first discovered in silica spicules of the marine sponge
Tethya aurantia. The filaments consist of three different silicatein subunits designated as α, β, and γ, of which silicatein-α comprises 70% of the mass of the filaments. Unlike the above-mentioned other SFPs, the silicateins were found to be able to catalyze silica polymerization directly from the non-hydrolyzed, silicon alkoxide precursors TEOS or TMOS at neutral pH [
41,
44], as described in
Section 3.1. The silicatein-α has not been used widely as an SFP for enzyme immobilization because of the relatively large size (23.3 kDa), low expression level in bacterial hosts, and inherent poor solubility [
71]. Nonetheless, a recent study showed that interfacial silica was formed on chitosan gel using silicatein fused with a solubility-enhancing protein and a chitin-binding domain, and the stability and reusability of horseradish peroxidase encapsulated in the chitosan gel was improved [
72].
3.3. Artificially engineered SFPs
3.3.1. Synthetic peptides from phage display biopanning
Among approximately 10
9 random dodecapeptides from a combinatorial M13 phage display library, silica-binding peptides were screened via biopanning on amorphous silica [
8]. Several peptides capable of silica binding were selected after multiple rounds of panning, among which His-rich Si4-1 and Arg-rich Si4-10 peptides had particularly strong binding affinity to silica surfaces. Interestingly, some of the selected SBPs also showed silica-precipitating activity, and the highest activity was observed when using the strongest SBP, Si4-1. Notably, no silica precipitate was visible when the Si4-10 was used, implying that silica-binding ability is not a sufficient requisite for silica-forming activity. Despite the short length (12-mer), these peptides have not been used as SFPs for enzyme encapsulation due to the relatively weak silica-forming activity compared to that of the R5 peptide. Instead, studies were reported where the Si4-1 [
73,
74,
75] and the Si4-10 [
76] were used as SBPs for enzyme immobilization.
3.3.2. Elastin-like polypeptide
Elastin-like polypeptides (ELP) are nature-inspired, artificial polypeptides with a repeated sequence of VPGXG motif, where the “X” is any amino acid except for proline [
77]. ELPs undergo a thermally responsive, reversible phase separation, making them attractive materials for protein purification and nanoassembly. Previously, ELPs fused with the R5 peptide were constructed to fabricate hybrid nanoparticles with the self-assembled core ELP micelles coated by silica shells [
78,
79]. Later, Lin et al. endowed an ELP with the silica-forming ability by incorporating Lys, Val, and Phe at the “X” sites of the 40 repeated pentapeptides in the ratio of 1:8:1 [
80]. The resulting cationic ELP[KV
8F-40] as an SFP was then fused with the enzyme xylanase, and the fusion protein was highly purified by the inverse transition cycling method. The self-assembled xylanase-ELP[KV
8F-40] was efficiently encapsulated within a biomimetic silica matrix, showing a high immobilization yield and improved stability. In other studies by the same group, the ELP[KV
8F-40] was also utilized for the immobilization of a cutinase in silica or magnetic-silica nanoparticles toward enhanced PET biodegradation with improved thermal stability and reusability [
81,
82].
4. Conclusions and outlook
In this review, various SBPs and SFPs are summarized, providing customizable options for enzyme immobilization on siliceous materials under different optimal conditions. Various case studies demonstrate the practical applications of these SBPs and SFPs in enzyme immobilization. While SBPs allow a facile immobilization of enzymes on the surface of silica and a high retention of enzymatic activity after immobilization, surface-exposed enzymes are generally susceptible to external physical and chemical stresses. In contrast, the SFP-mediated silica encapsulation provides a more stable niche for enzymes. The reduction in enzymatic activity due to mass transfer limitations following encapsulation can be alleviated by reducing the silica thickness and/or controlling the silica morphology to achieve a high surface-to-volume ratio. Expanding the understanding of the underlying mechanisms of silica binding and formation will lead to designing new SBPs and SFPs that are more efficient and controllable, thereby broadening their functionalities and applications.
Author Contributions
G.T.L. read the references and wrote the first draft of the manuscript; G.T.L. and B.H.J. discussed the references; B.H.J. developed the concept and outline of the manuscript and thoroughly revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Ministry of Science & ICT (RS-2024-00355356, 2021R1A5A8029490, RS-2023-00301974, RS-2024-00413668, and RS-2023-00235511) and by the Korea Basic Science Institute (National Research Facilities and Equipment Center) grant funded by the Ministry of Education (2022R1A6C101B724).
References
- Hartmann, M.; Kostrov, X. Immobilization of enzymes on porous silicas – benefits and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6277–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, B.H.; Kim, C.S.; Jo, Y.K.; Cheong, H.; Cha, H.J. Recent developments and applications of bioinspired silicification. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.R.; Neto, T.; Pedrosa, S.S.; Sousa, S.C.; Azevedo-Silva, J.; Tavares-Valente, D.; Mendes, A.; Pintado, M.E.; Fernandes, J.C.; Oliveira, A.L.S.; et al. Biogenic silica microparticles as a new and sustainable cosmetic ingredient: Assessment of performance and quality parameters. Colloid Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2023, 226, 113305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Pack, S.P. Biomimetic and bioinspired silicifications: Recent advances for biomaterial design and applications. Acta Biomater. 2021, 120, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Steer, D.L.; Song, H.; He, L. Superior binding of proteins on a silica surface: Physical insight into the synergetic contribution of polyhistidine and a silica-binding peptide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.K.M.; Ki, M.R.; Son, R.G.; Kim, K.H.; Hong, J.; Pack, S.P. Synthesis of sub-50 nm bio-inspired silica particles using a C-terminal-modified ferritin template with a silica-forming peptide. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 101, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, M.; Sakashita, S.; Hamada, Y.; Usui, K. Peptides for silica precipitation: Amino acid sequences for directing mineralization. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.R.; Brott, L.L.; Clarson, S.J.; Stone, M.O. Silica-precipitating peptides isolated from a combinatorial phage display peptide library. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2002, 2, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Chen, J.L.; Li, E.; Hu, C.G.; Luo, S.Z.; He, C.Z. Ultrahigh adhesion force between silica-binding peptide SB7 and glass substrate studied by single-molecule force spectroscopy and molecular dynamic simulation. Front. Chem. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, V.; Perry, C.C. Peptide adsorption on silica nanoparticles: Evidence of hydrophobic interactions. ACS nano 2012, 6, 6356–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, S.V.; Emami, F.S.; Berry, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Naik, R.R.; Deschaume, O.; Heinz, H.; Perry, C.C. Chemistry of aqueous silica nanoparticle surfaces and the mechanism of selective peptide adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6244–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Nomura, K.; Hata, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Asami, Y.; Kuroda, A. The Si-tag for immobilizing proteins on a silica surface. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 96, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Joo, K.I.; Jo, B.H.; Cha, H.J. Stability-controllable self-immobilization of carbonic anhydrase fused with a silica-binding tag onto diatom biosilica for enzymatic CO2 capture and utilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27055–27063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Kuroda, A. Why does the silica-binding protein "Si-tag" bind strongly to silica surfaces? Implications of conformational adaptation of the intrinsically disordered polypeptide to solid surfaces. Colloid Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2011, 86, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurier, H.S.; Goddard, J.M. Directed immobilization of PETase on mesoporous silica enables sustained depolymerase activity in synthetic wastewater conditions. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4981–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Park, T.J.; Ahn, J.H.; Huang, X.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, Y.K. Nanogap field-effect transistor biosensors for electrical detection of avian influenza. Small 2009, 5, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, K.; Ikeda, T.; Matsuyama, S.; Abdelhamid, M.A.; Tanaka, T.; Ishida, T.; Hirota, R.; Kuroda, A. The C-terminal zwitterionic sequence of CotB1 is essential for biosilicification of the Bacillus cereus spore coat. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Motomura, K.; Ikeda, T.; Ishida, T.; Hirota, R.; Kuroda, A. Affinity purification of recombinant proteins using a novel silica-binding peptide as a fusion tag. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5677–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.; Ikeda, T.; Motomura, K.; Tanaka, T.; Ishida, T.; Hirota, R.; Kuroda, A. Application of volcanic ash particles for protein affinity purification with a minimized silica-binding tag. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 122, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.M.; Nedielkov, R.; Arndt, K.M. Strategies for enzymatic inactivation of the veterinary antibiotic florfenicol. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, B.; Moks, T.; Jansson, B.; Abrahmsen, L.; Elmblad, A.; Holmgren, E.; Henrichson, C.; Jones, T.A.; Uhlen, M. A synthetic IgG-binding domain based on staphylococcal protein A. Protein eng. 1987, 1, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedhammar, M.; Hober, S. Zbasic—A novel purification tag for efficient protein recovery. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1161, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolivar, J.M.; Nidetzky, B. Positively charged mini-protein Zbasic2 as a highly efficient silica binding module: Opportunities for enzyme immobilization on unmodified silica supports. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10040–10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolivar, J.M.; Gascon, V.; Marquez-Alvarez, C.; Blanco, R.M.; Nidetzky, B. Oriented coimmobilization of oxidase and catalase on tailor-made ordered mesoporous silica. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5065–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, B.L.; Baneyx, F. A cleavable silica-binding affinity tag for rapid and inexpensive protein purification. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Rodriguez, J.; Coyle, B.L.; Samuelson, A.; Aravagiri, K.; Baneyx, F. Affinity purification of Car9-tagged proteins on silica matrices: Optimization of a rapid and inexpensive protein purification technology. Protein Expr. Purif. 2017, 135, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Bailey, M.J.; Look, J.; Baneyx, F. Affinity purification of Car9-tagged proteins on silica-derivatized spin columns and 96-well plates. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 170, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wender, P.A.; Mitchell, D.J.; Pattabiraman, K.; Pelkey, E.T.; Steinman, L.; Rothbard, J.B. The design, synthesis, and evaluation of molecules that enable or enhance cellular uptake: Peptoid molecular transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2000, 97, 13003–13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. M., F.; R.T., R. Polyarginine as a multifunctional fusion tag. Protein sci. 2005, 14, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.L.; Britton, Z.T.; Robinson, A.S. Recombinant protein expression and purification: A comprehensive review of affinity tags and microbial applications. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eteshola, E.; Brillson, L.J.; Lee, S.C. Selection and characteristics of peptides that bind thermally grown silicon dioxide films. Biomol. Eng. 2005, 22, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, A.I.; Domingues, L.; Aguiar, T.Q. Bare silica as an alternative matrix for affinity purification/immobilization of His-tagged proteins. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunna, A.; Chi, F.; Bergquist, P.L. A linker peptide with high affinity towards silica-containing materials. New biotech. 2013, 30, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, S.; Wendelbo, R.; Brown, S. Surface-specific zeolite-binding proteins. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.; Elgundi, Z.; Care, A.; S, C.G.; M, S.L.; Rodger, A.; Sunna, A. Elucidating the binding mechanism of a novel silica-binding peptide. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zou, K.; Guo, B.; Pei, J.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, L. One-step purification and immobilization of thermostable β-glucosidase on Na-Y zeolite based on the linker and its application in the efficient production of baohuoside I from icariin. Bioorganic chem. 2022, 121, 105690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Care, A.; Petroll, K.; Gibson, E.S.Y.; Bergquist, P.L.; Sunna, A. Solid-binding peptides for immobilisation of thermostable enzymes to hydrolyse biomass polysaccharides. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, C.C.; Becker, C.F.W. A sequence-function analysis of the silica precipitating silaffin R5 peptide. J. Pept. Sci. 2014, 20, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, C.C.; Becker, C.F.W. Silaffins in silica biomineralization and biomimetic silica precipitation. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5297–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, T.; Nonoyama, T.; Hirao, K.; Kato, K. Influence of the charge relay effect on the silanol condensation reaction as a model for silica biomineralization. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13154–13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Cha, J.; Stucky, G.D.; Morse, D.E. Silicatein α: Cathepsin L-like protein in sponge biosilica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1998, 95, 6234–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.N.; Stucky, G.D.; Morse, D.E.; Deming, T.J. Biomimetic synthesis of ordered silica structures mediated by block copolypeptides. Nature 2000, 403, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, H.C.; Wiens, M.; Schlossmacher, U.; Brandt, D.; Müller, W.E.G. Silicatein-mediated polycondensation of orthosilicic acid: Modeling of a catalytic mechanism involving ring formation. Silicon 2012, 4, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.N.; Shimizu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Christiansen, S.C.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D.; Morse, D.E. Silicatein filaments and subunits from a marine sponge direct the polymerization of silica and silicones in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradin, T.; Durupthy, O.; Livage, J. Interactions of amino-containing peptides with sodium silicate and colloidal silica: A biomimetic approach of silicification. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2331–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroger, N.; Deutzmann, R.; Sumper, M. Polycationic peptides from diatom biosilica that direct silica nanosphere formation. Science 1999, 286, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, S.V.; Clarson, S.J.; Perry, C.C. On the role(s) of additives in bioinspired silicification. Chem. Commun. 2005, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumper, M.; Kröger, N. Silica formation in diatoms: The function of long-chain polyamines and silaffins. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroger, N.; Lorenz, S.; Brunner, E.; Sumper, M. Self-assembly of highly phosphorylated silaffins and their function in biosilica morphogenesis. Science 2002, 298, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, F.; Brandis, D.; Potzl, C.; Epasto, L.M.; Reichinger, D.; Obrist, D.; Peterlik, H.; Polyansky, A.; Zagrovic, B.; Daus, F.; et al. An atomistic view on the mechanism of diatom peptide-guided biomimetic silica formation. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2401239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, L.; Crump, M.P.; Williams, C.; Booth, P.J.; Mann, S.; Perriman, A.W.; Curnow, P. Structure and function of the silicifying peptide R5. J. Mat. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckarift, H.R.; Spain, J.C.; Naik, R.R.; Stone, M.O. Enzyme immobilization in a biomimetic silica support. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancor, L.; Luckarift, H.R. Bioinspired enzyme encapsulation for biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, B.H.; Seo, J.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Baek, K.; Choi, Y.S.; Pack, S.P.; Oh, S.H.; Cha, H.J. Bioinspired silica nanocomposite with autoencapsulated carbonic anhydrase as a robust biocatalyst for CO2 sequestration. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 4332–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.T.; Jo, B.H. Cation-assisted stabilization of carbonic anhydrase one-step in situ loaded in diatom-inspired silica nanospheres for potential applications in CO2 capture and utilization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Kim, K.R.; Kim, J.H.; Jo, B.H.; Song, Y.H.; Seo, J.H.; Heo, H.R.; Kim, C.S. Bioinspired synthesis of micelle-templated ultrathin silica-layered mesoporous nanoparticles with enhanced mass transfer and stability for biocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.C.; Lee, S.C.; Moeller, A.; Roy, R.S.; Siu, F.Y.; Zimmermann, J.; Stevens, R.C.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B.; Zhang, Q.H. Engineered nanostructured β-sheet peptides protect membrane proteins. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialas, F.; Becker, C.F.W. Biomimetic silica encapsulation of lipid nanodiscs and β-sheet-stabilized diacylglycerol kinase. Bioconjugate Chem. 2021, 32, 1742–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, K.B.; Ki, M.R.; Park, K.S.; Pack, S.P. Novel silica-forming peptides derived from Ectocarpus siliculosus. Process Biochem. 2017, 58, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, K.M.N.; Ki, M.R.; Son, R.G.; Kim, K.H.; Hong, J.; Pack, S.P. A dual-functional peptide, Kpt from Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3 for protein purification and silica precipitation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 163, 107726. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, K.; Amano, T.; Bari, M.R.; Weaver, J.C.; Arima, J.; Mori, N. Glassin, a histidine-rich protein from the siliceous skeletal system of the marine sponge Euplectella, directs silica polycondensation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11449–11454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckarift, H.R.; Dickerson, M.B.; Sandhage, K.H.; Spain, J.C. Rapid, room-temperature synthesis of antibacterial bionanocomposites of lysozyme with amorphous silica or titania. Small 2006, 2, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, F.; Gigli, L.; Ferraro, G.; Cavallo, A.; Michaelis, V.K.; Goobes, G.; Fratini, E.; Ravera, E. Lysozyme is sterically trapped within the silica cage in bioinspired silica–lysozyme composites: A multi-technique understanding of elusive protein–material interactions. Langmuir 2022, 38, 8030–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, M.B.; Luckarift, H.R.; Urban, V.S.; O'Neill, H.; Johnson, G.R. Protein localization in silica nanospheres derived via biomimetic mineralization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruseska, I.; Fresacher, K.; Petschacher, C.; Zimmer, A. Use of protamine in nanopharmaceuticals—A review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Z. Protamine-templated biomimetic hybrid capsules: Efficient and stable carrier for enzyme encapsulation. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, N.R.; Shian, S.; Sandhage, K.H.; Kroger, N. Biocatalytic nanoscale coatings through biomimetic layer-by-layer mineralization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4243–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Yeo, K.B.; Ki, M.R.; Pack, S.P. Self-encapsulation and controlled release of recombinant proteins using novel silica-forming peptides as fusion linkers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.H.; Yeo, K.B.; Ki, M.R.; Jun, S.H.; Pack, S.P. Novel silica forming peptide, RSGH, from Equus caballus: Its unique biosilica formation under acidic conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 153, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.H.; Shin, J.W.; Ki, M.R.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Pack, S.P. Bio-inspired formation of silica particles using the silica-forming peptides found by silica-binding motif sequence, RRSSGGRR. Process Biochem. 2021, 111, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigil, T.N.; Rowson, M.J.C.; Frost, A.J.; Berger, B.W. Understanding the relationships between solubility, stability, and activity of silicatein. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godigamuwa, K.; Nakashima, K.; Tsujitani, S.; Naota, R.; Maulidin, I.; Kawasaki, S. Interfacial biosilica coating of chitosan gel using fusion silicatein to fabricate robust hybrid material for biomolecular applications. J. Mat. Chem. B 2023, 11, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.K.; Zawadzka, A.M.; Deobald, L.A.; Crawford, R.L.; Paszczynski, A.J. Novel method for immobilization of enzymes to magnetic nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Lata, J.P.; Lee, Y.; Hernández, J.C.C.; Nishimura, N.; Schaffer, C.B.; Mukai, C.; Nelson, J.L.; Brangman, S.A.; Agrawal, Y.; et al. Use of tethered enzymes as a platform technology for rapid analyte detection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.W.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, G.M. Simple and efficient enzymatic procedure for p-coumaric acid synthesis: Complete bioconversion and biocatalyst recycling under alkaline condition. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 188, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fraser, K.; Zha, J.; Dordick, J.S. Flexible peptide linkers enhance the antimicrobial activity of surface-immobilized bacteriolytic enzymes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 36746–36756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, D.E.; Chilkoti, A. Purification of recombinant proteins by fusion with thermally-responsive polypeptides. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Chilkoti, A.; Lopez, G.P. Self-assembled hybrid elastin-like polypeptide/silica nanoparticles enable triggered drug release. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6178–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; MacEwan, S.R.; Chilkoti, A.; López, G.P. Bio-inspired synthesis of hybrid silica nanoparticles templated from elastin-like polypeptide micelles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12038–12044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jin, W.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, G. Programmable stimuli-responsive polypeptides for biomimetic synthesis of silica nanocomposites and enzyme self-immobilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 1156–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, G.Z.; Chen, Y.X.; Yi, Z.W.; Jin, W.H.; Zhang, G.Y. A versatile tag for simple preparation of cutinase towards enhanced biodegradation of polyethylene terephthalate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Z.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y.X.; Mao, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, R.F.; Zhang, G.Y. Magnetic silica-coated cutinase immobilized via ELPs biomimetic mineralization for efficient nano-PET degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).