Submitted:
02 November 2024
Posted:
05 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material And Methods
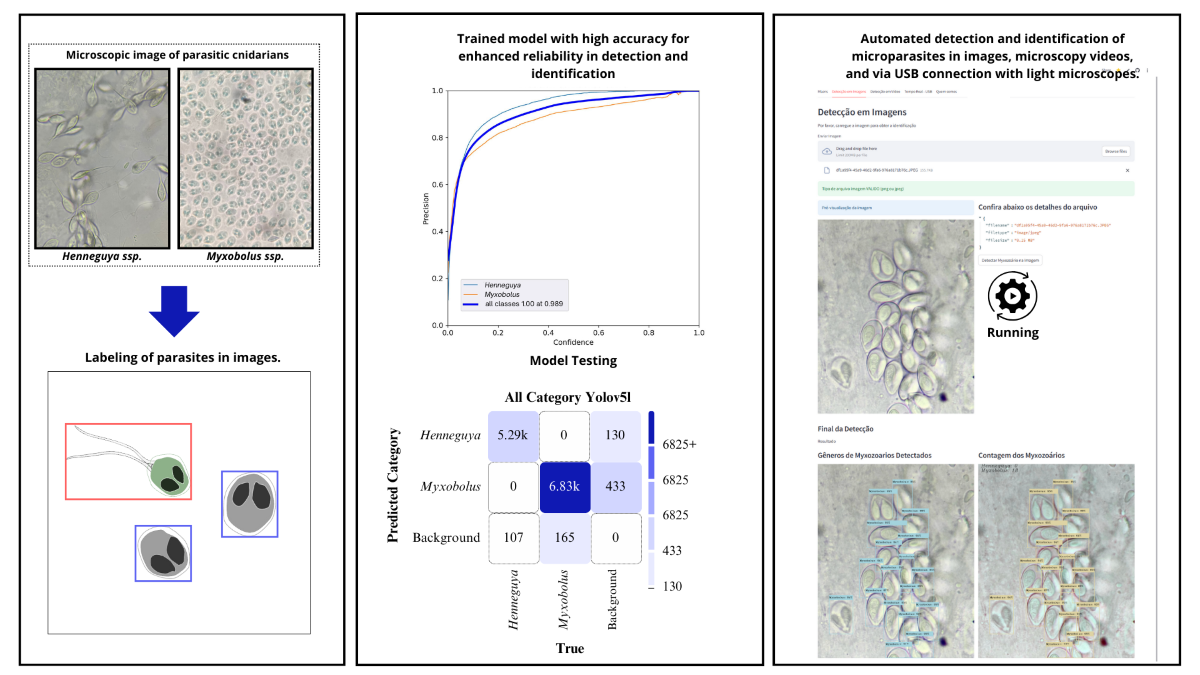
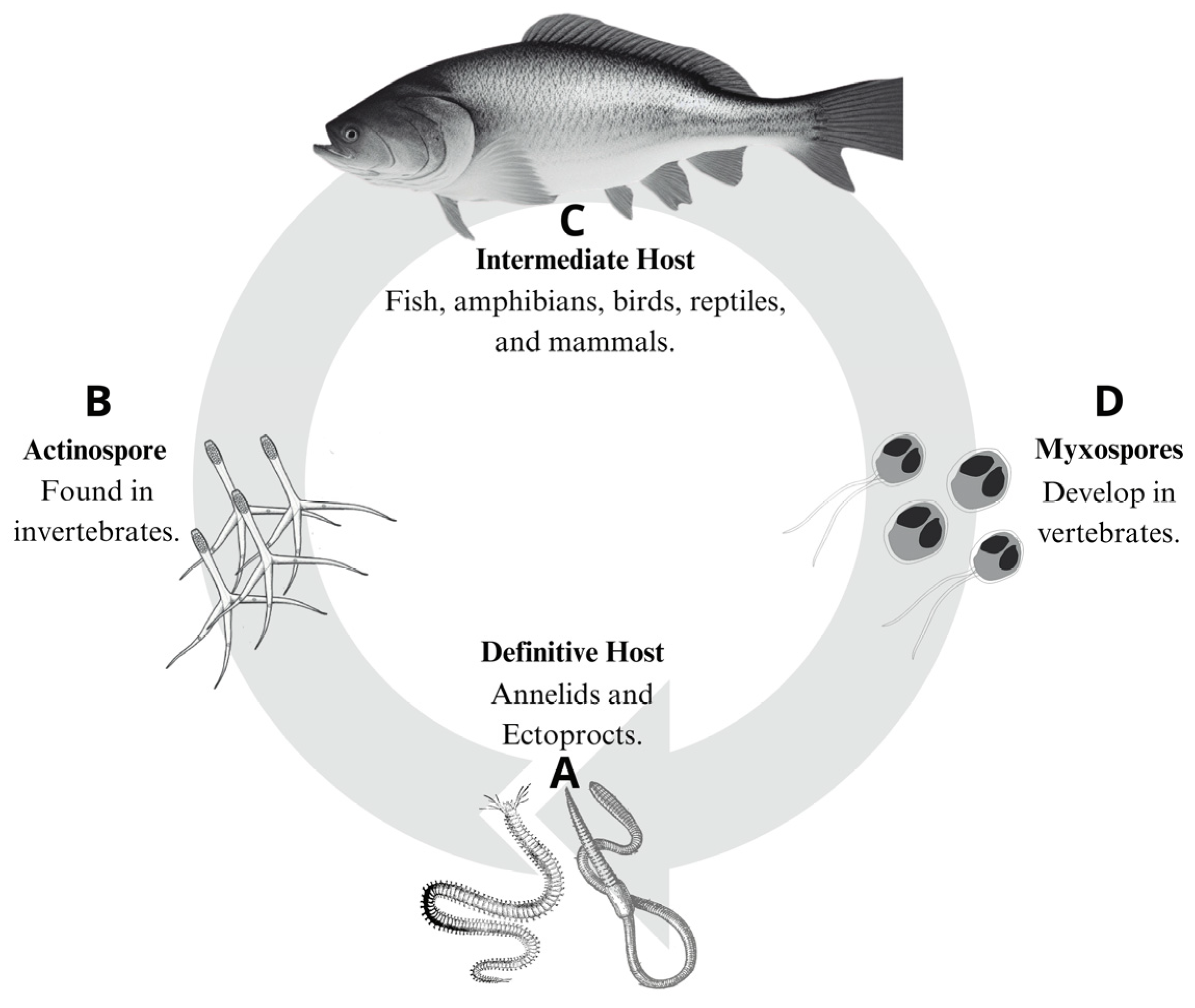
2.1. Cnidaria: Myxozoa
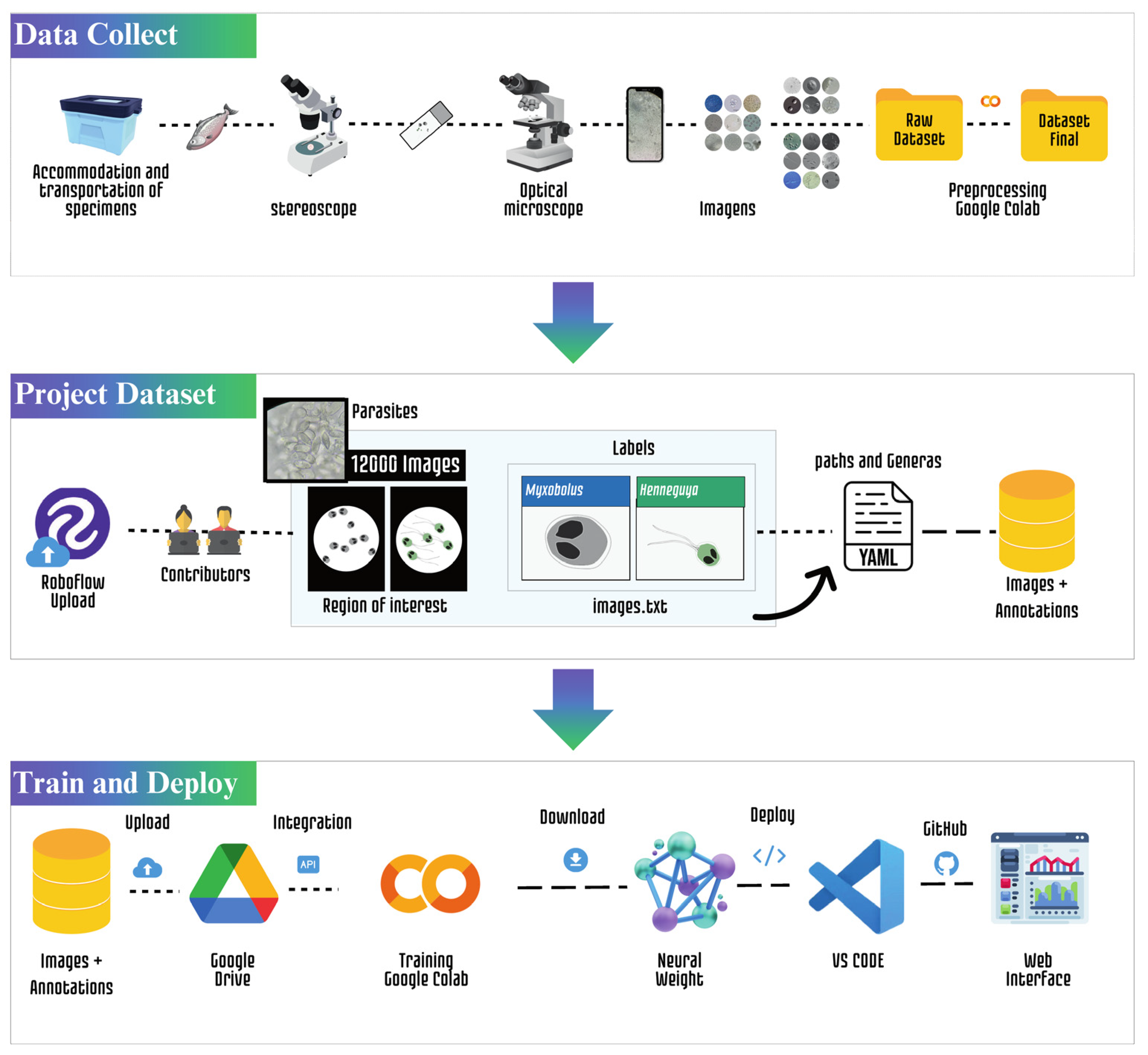
2.2. Data Acquisition
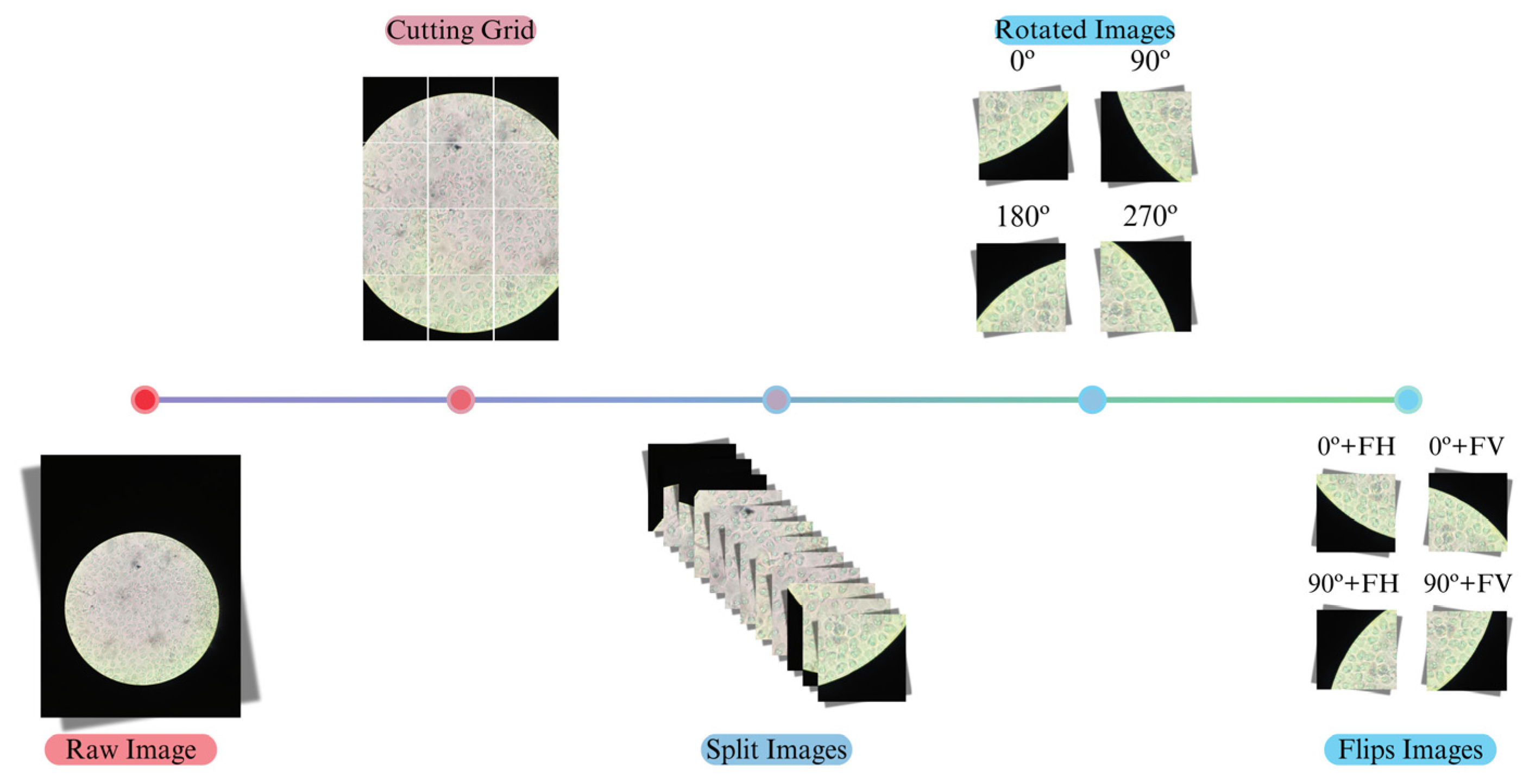
2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Labeling of Myxozoans
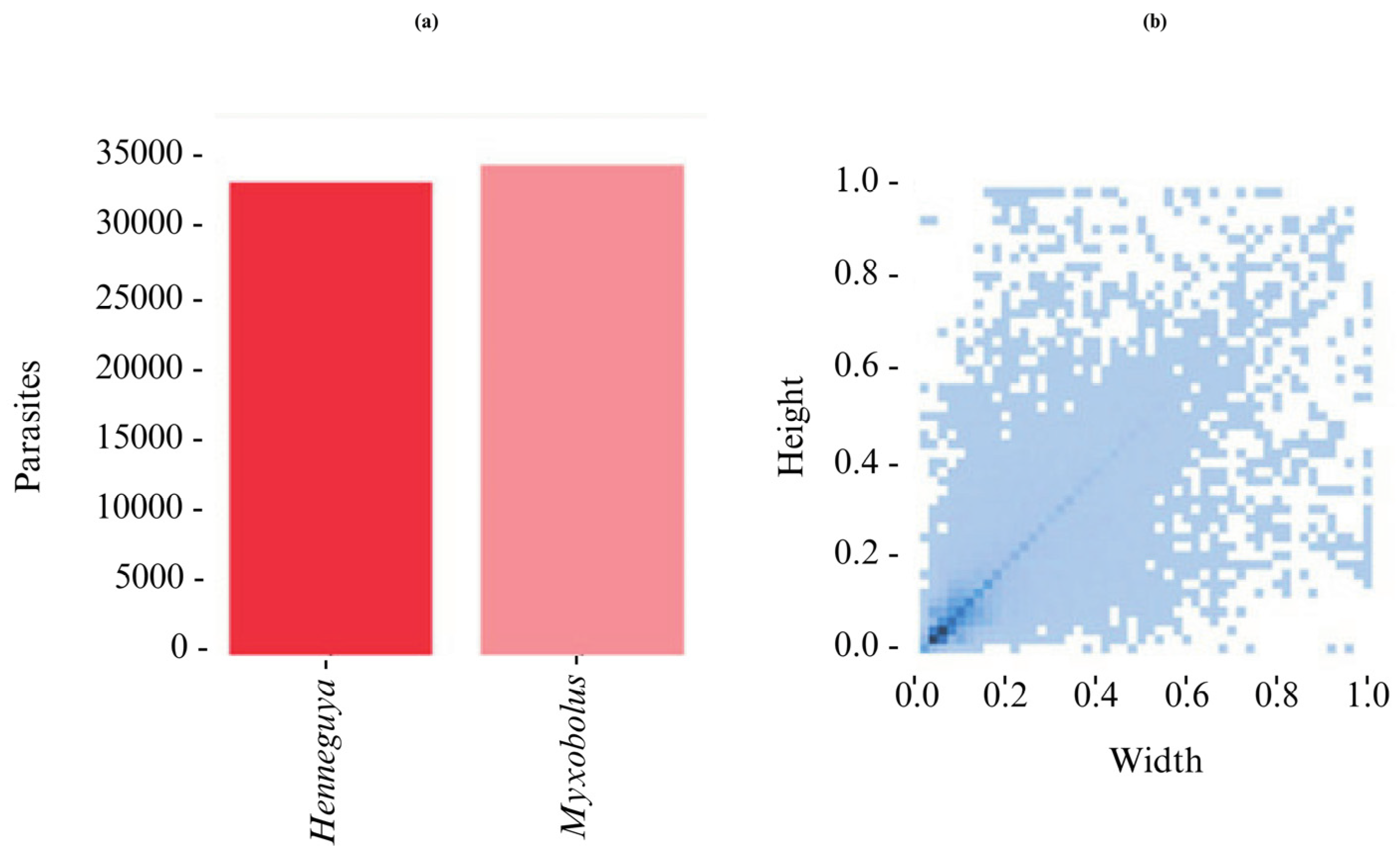
2.4. Quantitative Characteristics of the Dataset
2.5. Experimental Configuration
2.6. YOLOv5
2.5. Evaluation Metrics
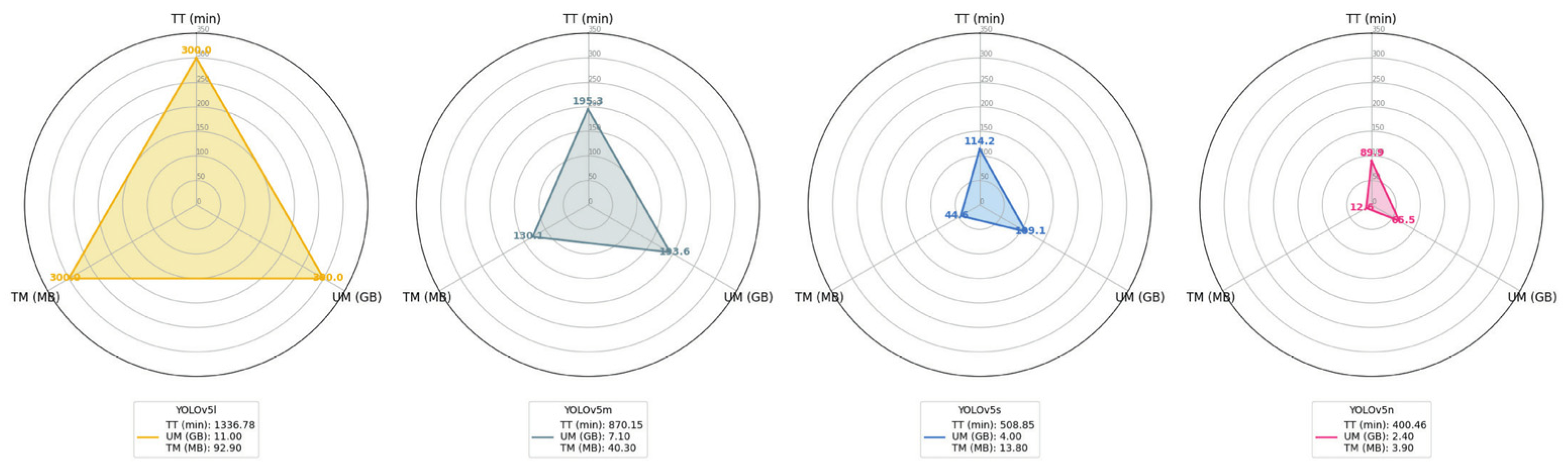
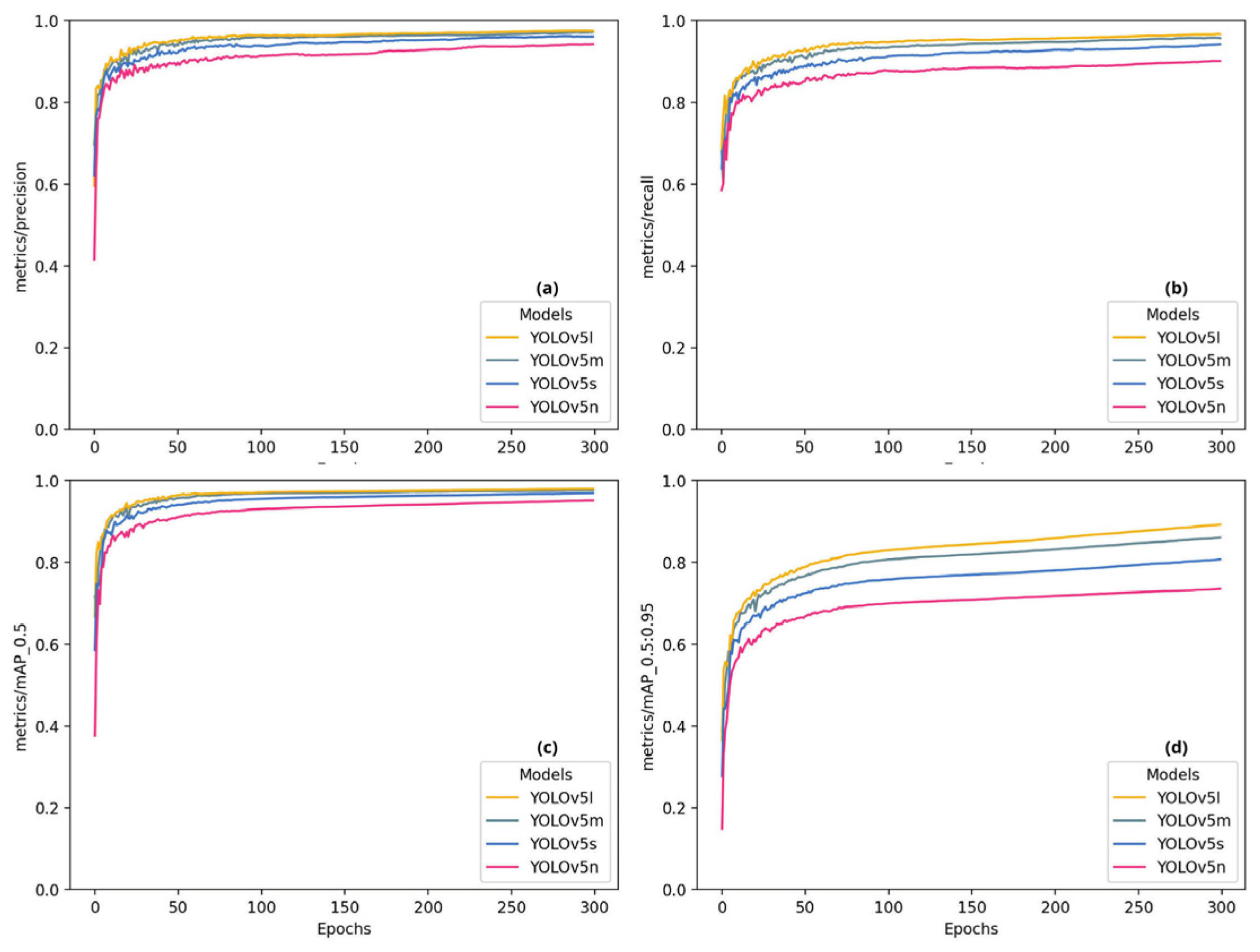
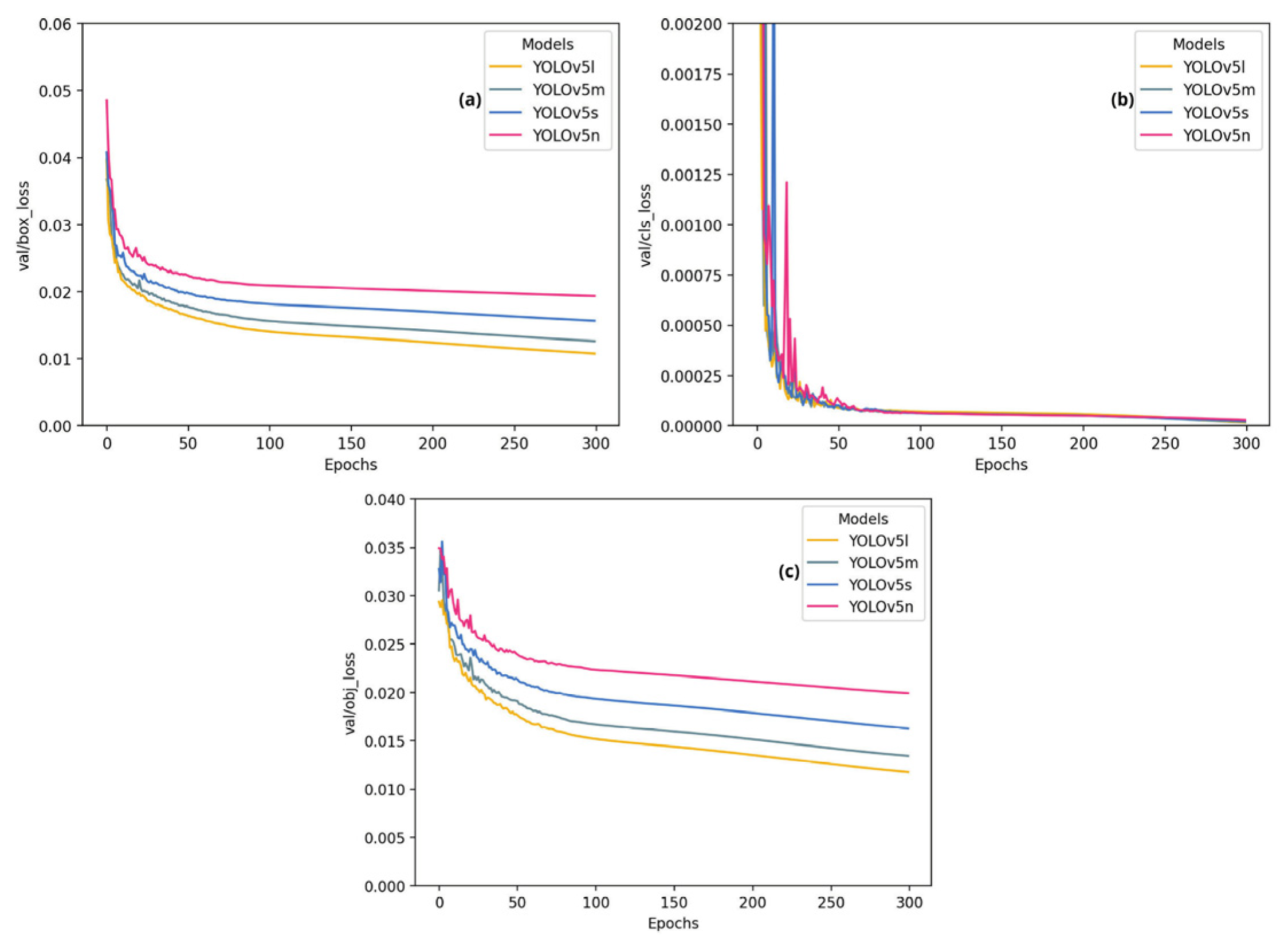
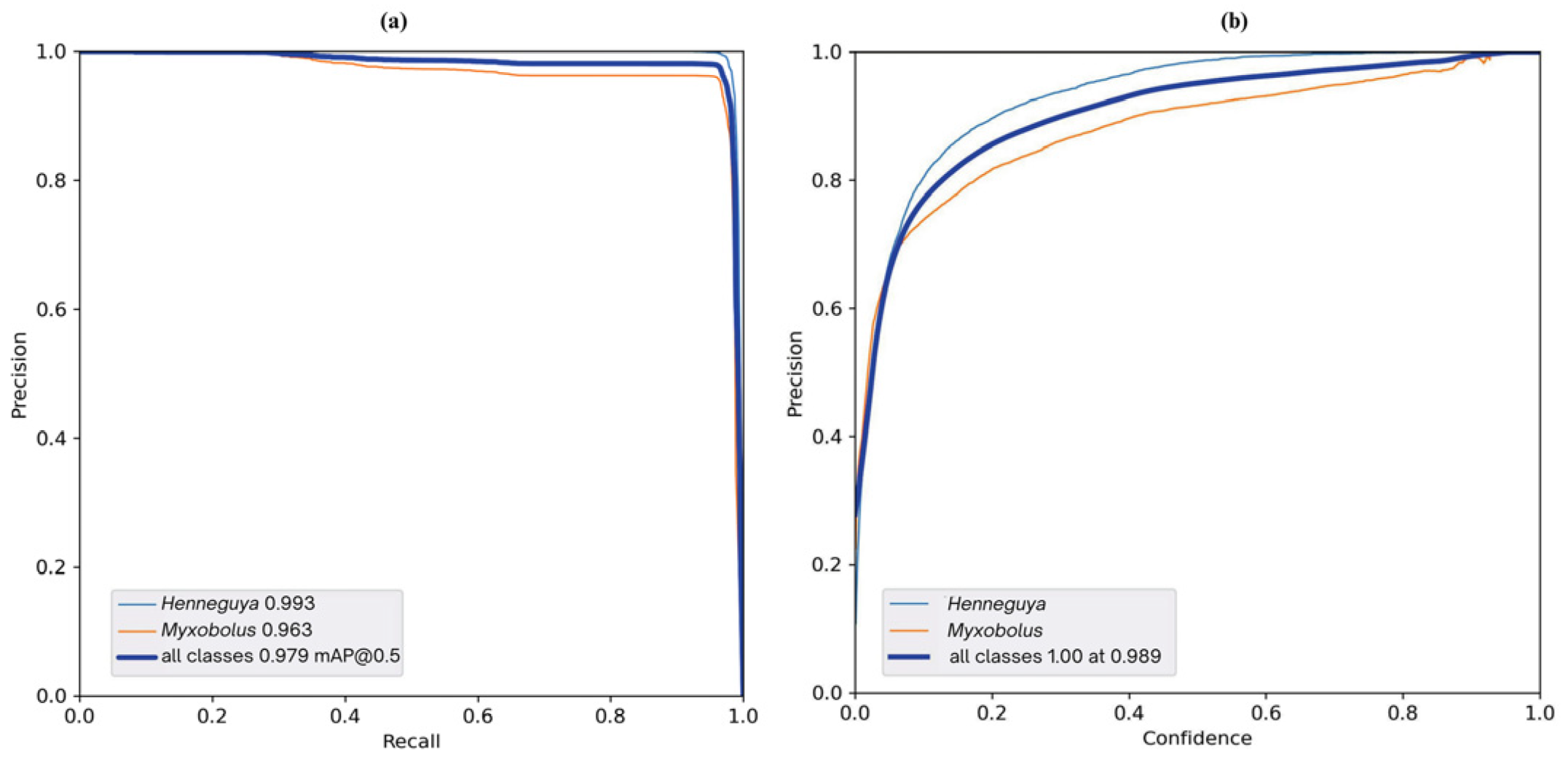
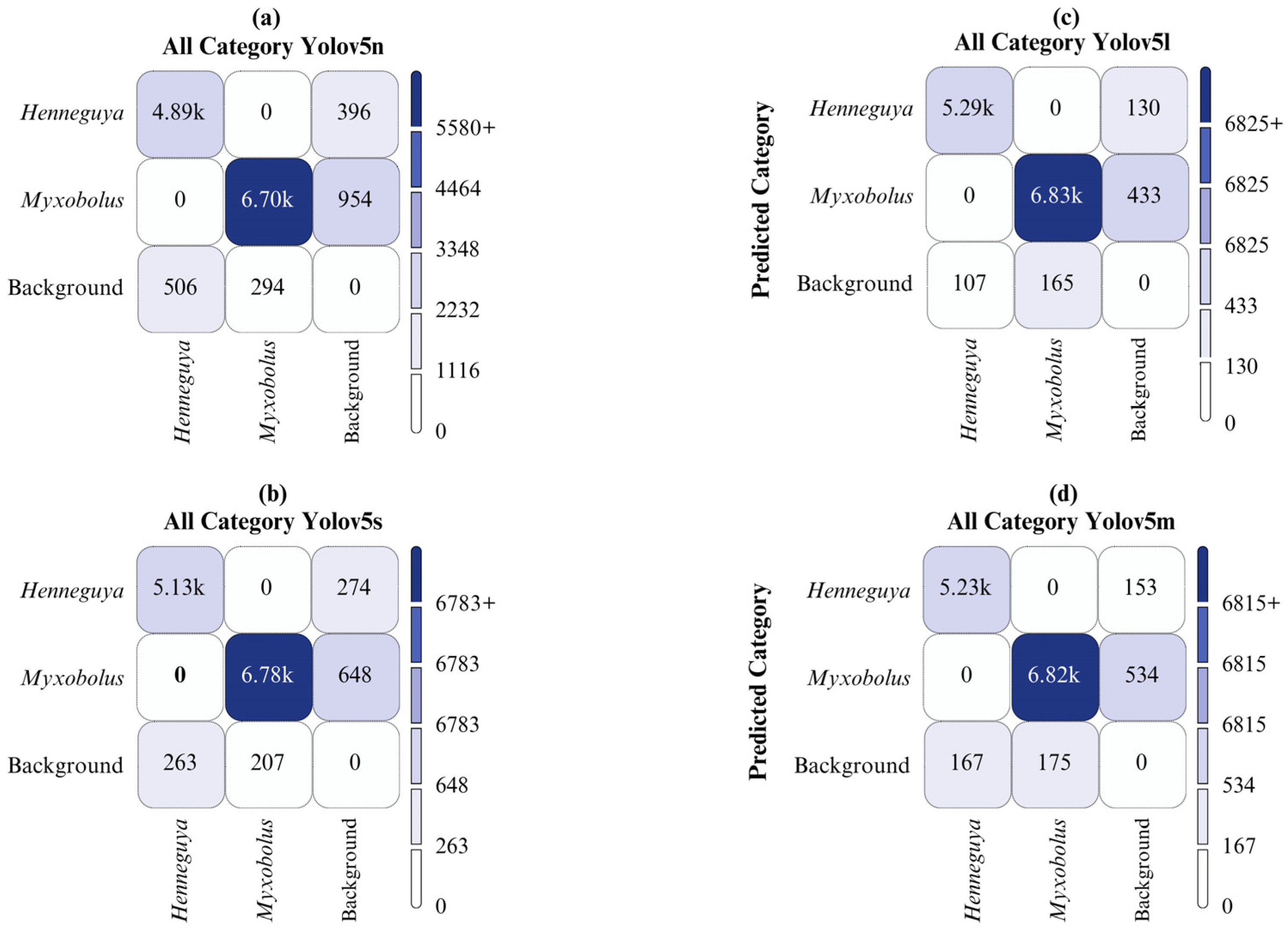
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lom, J.; Dyková, I. Myxozoan genera: definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitologica, 2006, 53(1), 1-36. [CrossRef]
- Fiala, I.; Bartošová-Sojková, P.; Whipps, C.M. Classification and phylogenetics of Myxozoa. In Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development; Okamura, B., Gruhl, A., Bartholomew, J.L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, 2015; pp. 85-110. [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.R.M.; Bartholomew, J.L.; Zhang, J.Y. Mitigating Myxozoan disease impacts on wild fish populations. In Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development; Okamura, B., Gruhl, A., Bartholomew, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Lom, J.; Arthur, J.R. A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. Journal of Fish Diseases, 1989, 12(2), 151-156. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.A.; Videira, M.N.; Bittencourt, L.S.; Araújo, P.G.; Ferreira, R.L.S., et al. Infection of Henneguya sp. on the gills of Metynnis lippincottianus from Curiaú River, in eastern Amazon region (Brazil). Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Parasitology, 2020, 29(3), 003320. [CrossRef]
- Zago, A.C.; Vieira, D.H.M.D.; Franceschini, L.; Silva, R.J. Morphological, ultrastructural, and molecular analysis of a new species of Myxobolus (Cnidaria, Myxosporea) parasitizing Apareiodon piracicabae (Characiformes, Parodontidae) from Brazil. Parasitology International, 2022, 88, 102556. [CrossRef]
- Okamura, B.; Gruhl, A.; Bartholomew, J.L. An Introduction to Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development. In Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development; Okamura, B., Gruhl, A., Bartholomew, J.L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, 2015; pp. xx-xx. [CrossRef]
- Jerônimo, G.T., et al. Fish parasites can reflect environmental quality in fish farms. Reviews in Aquaculture, 2022, 14(3), 1558-1571. [CrossRef]
- Lauringson, M., et al. Spatial and intrahost distribution of myxozoan parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae among Baltic sea trout (Salmo trutta). Journal of Fish Diseases, 2023, 46(10), 1073-1083. [CrossRef]
- Sichman, J.S. Artificial intelligence and society: advances and risks. Estudos Avançados, 2021, 35, 37-50. [CrossRef]
- Li, R. Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change Our Society, Economy, and Culture; Skyhorse Publishing: New York, 2020. ISBN 9781510753006.
- Lee, K.W. Augmenting or Automating? Breathing Life into the Uncertain Promise of Artificial Intelligence [PhD Thesis]. New York University, New York, 2022.
- De Moraes, A.L.Z.; Barbosa, L.V.F.; Del Grossi, V.C.D. Artificial Intelligence and Human Rights: Contributions to a Regulatory Framework in Brazil; Editora Dialética: São Paulo, 2022. ISBN 9786525253725.
- Siqueira-Batista, R., et al. Artificial neural networks and medical education. Revista Brasileira de Educação Médica, 2014, 38, 548-556. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L., et al. Review of image classification algorithms based on convolutional neural networks. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(22), 4712. [CrossRef]
- Yonck, R. Heart of the Machine: Our Future in a World of Artificial Emotional Intelligence; Arcade: New York, 2020. eISBN 9781628727374.
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A. A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50v2. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 2020, 19, 100360. [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, J.P.; Noura, H.; Salman, O.; Chealb, A. Security analysis of drones systems: Attacks, limitations, and recommendations. Internet of Things, 2020, 11, 100218. [CrossRef]
- Noever, D.; Noever, S.E.; Miller, M. Hunting with machine vision. arXiv, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.C.P. Inteligência artificial: riscos, benefícios e uso responsável. Estudos Avançados, 2021, 35, 21–36. [CrossRef]
- Candiotto, K.B.B.; Karasinski, M. Inteligência artificial e os riscos existenciais reais: uma análise das limitações humanas de controle. Filosofia Unisinos, 2022, 23, e23307. [CrossRef]
- Keszthelyi, S.; Pónya, Z.; Csóka, A.; Bázar, G.; Morschhauser, T.; Donkó, T. Non-destructive imaging and spectroscopic techniques to investigate the hidden-lifestyle arthropod pests: a review. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, 2020, 127(3), 283-295. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Arif, T.; Ahamad, G.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Khan, S.; Ali, M.A.M. An efficient and effective framework for intestinal parasite egg detection using YOLOv5. Diagnostics, 2023, 13(18), 2978. [CrossRef]
- Okamura, B.; Hartigan, A.; Naldoni, J. Extensive uncharted biodiversity: the parasite dimension. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 2018, 58(6), 1132-1145. [CrossRef]
- Giribet, G.; Edgecombe, G. The Invertebrate Tree of Life; 2020. [CrossRef]
- Zatti, S.A.; Marinho, A.M.R.; Adriano, E.A., et al. Integrative taxonomy reveals a panmictic population of Henneguya longisporoplasma n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxozoa) in the Amazon Basin. Acta Parasitologica, 2022, 67, 1644-1656. [CrossRef]
- Okamura, B.; Gruhl, A. Myxozoa + Polypodium: a common route to endoparasitism. Trends in Parasitology, 2016, 32(4), 268-271. [CrossRef]
- Eiras, J.C.; Barman, G.D.; Chanda, S., et al. An update of the species of Myxosporea (Cnidaria, Myxozoa) described from Indian fish. Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 2023, 47, 12-36. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Ding, Y. When self-supervised learning meets scene classification: remote sensing scene classification based on a multitask learning framework. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(20), 3276. [CrossRef]
- Bydder, M.; Rahal, A.; Fullerton, G.D.; Cooper, T.G. The magic angle effect: a source of artifacts, a determinant of image contrast, and a technique for imaging. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2007, 25(2), 290-300. [CrossRef]
- Zendehdel, N.; Chen, H.; Leu, M.C. Real-time tool detection in smart manufacturing using you-only-look-once (YOLO) v5. Manufacturing Letters, 2023, 35, 1052-1059. [CrossRef]
- Ghose, P.; Ghose, A.; Sadhukhan, D., et al. Improved polyp detection from colonoscopy images using finetuned YOLO-v5. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2024, 83, 42929-42954. [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Alshouiliy, K.; Agrawal, D.P. Dimensionality reduction for human activity recognition using Google Colab. Information, 2020, 12(1), 6. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G. Small unopened cotton boll counting by detection with MRF-YOLO in the wild. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 204, 107576. [CrossRef]
- Li, R. Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change Our Society, Economy, and Culture; Simon and Schuster: 2020. ISBN 9781510753006.
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T. Lite-YOLOv5: a lightweight deep learning detector for on-board ship detection in large-scene Sentinel-1 SAR images. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4), 1018. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Yan, G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B. Faster and lightweight: an improved YOLOv5 object detector for remote sensing images. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15, 4974. [CrossRef]
- Badgujar, C.M.; Poulose, A.; Gan, H. Agricultural object detection with You Only Look Once (YOLO) algorithm: a bibliometric and systematic literature review. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2024, 223, 109090. [CrossRef]
- Elshahawy, M.; Elnemr, A.; Oproescu, M.; Schiopu, A.G.; Elgarayhi, A.; Elmogy, M.M. Early melanoma detection based on a hybrid YOLOv5 and ResNet technique. Diagnostics, 2023, 13, 2804. [CrossRef]
- Wu, D., et al. Detection of Camellia oleifera fruit in complex scenes via YOLOv7 and data augmentation. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(22), 11318. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, R.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. High-precision seedling detection model based on a multiactivation layer and depth-separable convolution using images acquired by drones. Drones, 2022, 6(6), 152. [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Lang, B.; Song, Z. Ca-YOLO: Model optimization for remote sensing image object detection. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 26438-26450. [CrossRef]
- Isa, I.S.; Rosli, M.S.A.; Yusof, U.K.; Maruzuki, M.I.F.; Sulaiman, S.N. Optimizing the hyperparameter tuning of YOLOv5 for underwater detection. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 52818-52831. [CrossRef]
- Benjumea, A.; Aduen, I.; Cuzzolin, F.; Bradley, A. YOLO-Z: Improving small object detection in YOLOv5 for autonomous vehicles. arXiv, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Z.D., et al. Improved YOLOv5 network for real-time multiscale traffic sign detection. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35, 7853-7865. [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Peng, T.; Cao, H.; Xu, Y.; Wei, X.; Cui, B. Tia-YOLOv5: An improved YOLOv5 network for real-time detection of crop and weed in the field. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13, 1091655. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.; Saad, F.; et al., S.A. Experimental validation of computer-vision methods for the successful detection of endodontic treatment obturation and progression from noisy radiographs. Oral Radiology, 2023, 39, 683-698. [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Pedoeem, J.; Chen, C. YOLO-LITE: A real-time object detection algorithm optimized for non-GPU computers. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data); Seattle, WA, USA, 2018, pp. 2503-2510. [CrossRef]
- Du, J. Understanding of object detection based on CNN family and YOLO. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2018, 1004, 012029. [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; University of Washington, Allen Institute for AI, Facebook AI Research, 2016. Disponível em: http://pjreddie.com/yolo/.
- Tong, K.; Wu, Y. Deep learning-based detection from the perspective of small or tiny objects: A survey. Image and Vision Computing, 2022, 123, 104471. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wei, G.; Yuan, X.; Liang, Y.; Bo, Y. Efficient YOLOv7-Drone: An enhanced object detection approach for drone aerial imagery. Drones, 2023, 7(10), 616. [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Shangguan, H.; Wang, L. PC-Yolo: Enhanced YOLOv5-based defect detection system with improved partial convolution for ham sausage inspection. In Fourth International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Analysis (ICCPA 2024); SPIE, 2024, pp. 451-459. [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Lu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sang, P. LAYN: Lightweight Multi-Scale Attention YOLOv8 Network for Small Object Detection. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 29294-29307. [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Su, Y.; Cao, X., et al. YOLOFM: an improved fire and smoke object detection algorithm based on YOLOv5n. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14, 4543. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Zayed, T.; Abdelkader, E.M. A novel YOLOv8-GAMWise-IoU model for automated detection of bridge surface cracks. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 414, 135025. [CrossRef]
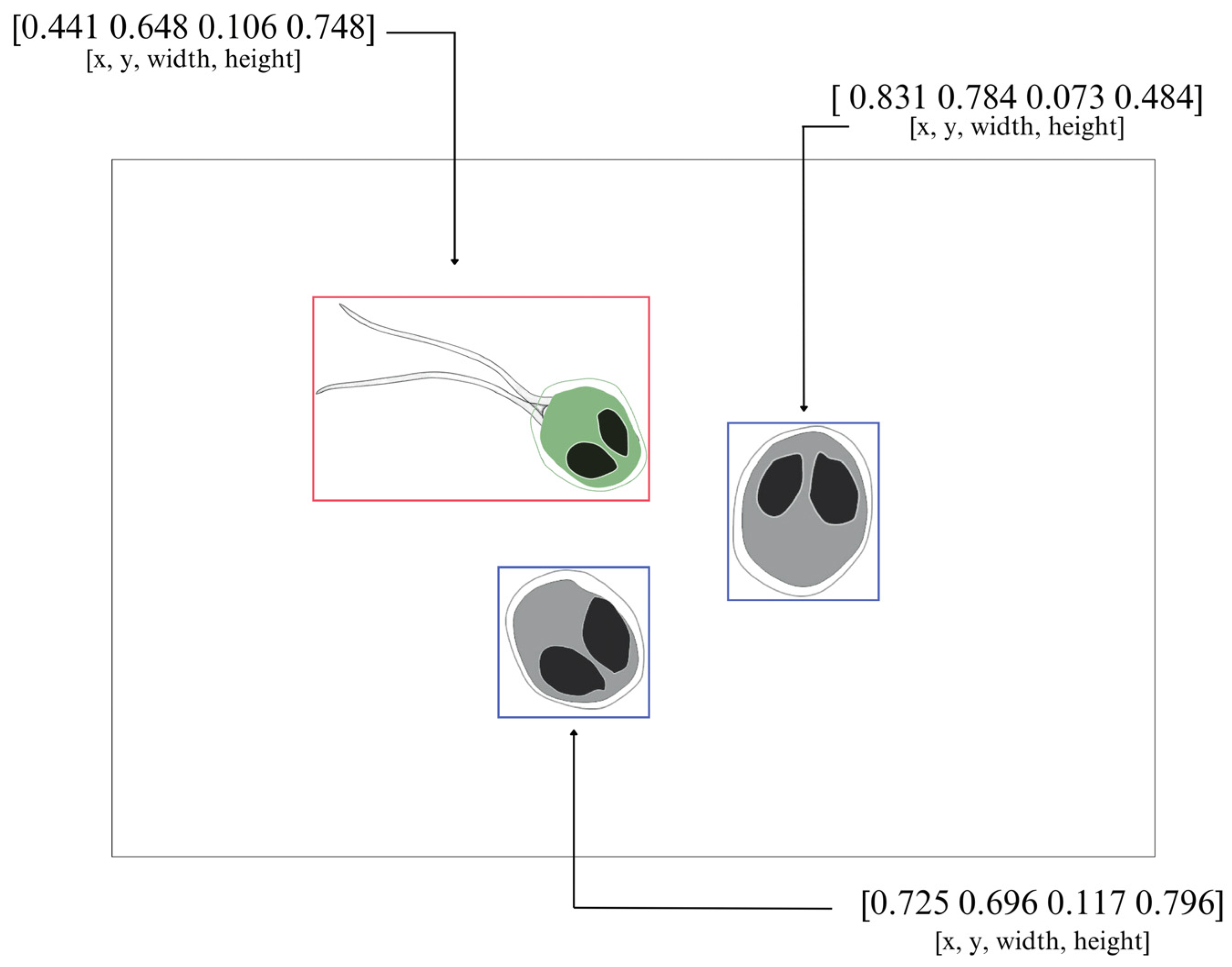

| Genera | X | Y | W | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.72500000 | 0.69609375 | 0.11718750 | 0.79609375 |
| 1 | 0.83125000 | 0.78437500 | 0.07343750 | 0.48437500 |
| 0 | 0.44140625 | 0.64765625 | 0.10625000 | 0.74765625 |
| Category Information Genera Labeled for YOLOv5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henneguya | 0 | Myxobolus | 1 | |
| Model | Genus | Images | Parasites | Precision | Recall | mAP:50 | mAP:50-95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5l | All | 2000 | 12386 | 0.974 | 0.967 | 0.980 | 0.892 |
| Henneguya | 2000 | 5396 | 0.994 | 0.970 | 0.993 | 0.905 | |
| Myxobolus | 2000 | 6990 | 0.954 | 0.965 | 0.966 | 0.879 | |
| YOLOv5m | All | 2000 | 12386 | 0.972 | 0.957 | 0.976 | 0.860 |
| Henneguya | 2000 | 5396 | 0.995 | 0.951 | 0.990 | 0.876 | |
| Myxobolus | 2000 | 6990 | 0.949 | 0.962 | 0.962 | 0.844 | |
| YOLOv5n | All | 2000 | 12386 | 0.928 | 0.895 | 0.943 | 0.727 |
| Henneguya | 2000 | 5396 | 0.976 | 0.852 | 0.947 | 0.74 | |
| Myxobolus | 2000 | 6990 | 0.880 | 0.938 | 0.939 | 0.713 | |
| YOLOv5s | All | 2000 | 12386 | 0.948 | 0.935 | 0.964 | 0.954 |
| Henneguya | 2000 | 5396 | 0.985 | 0.915 | 0.974 | 0.815 | |
| Myxobolus | 2000 | 6990 | 0.911 | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.780 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





