1. Background
The use of veno-venous (VV) extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) treatment for respiratory failure has increased exponentially over the last decades [1]. Until 2009, evidence regarding survival rates for VV-ECMO patients was unfavorable, with a relatively low volume of ECMO cases reported worldwide [2,3]. The CESAR trial and data gathered during the H1N1 pandemic highlighted survival benefits for patients treated with VV-ECMO for severe Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) [4,5]. Since 2009, the number of patients treated annually with VV-ECMO increased to 4000 ECMO cases [6]. The mean ECMO treatment duration also increased along with the rising number of ECMO cases. In a large retrospective study of data collected on 2355 patients from the extracorporeal life support organization (ELSO) registry during 2000-2012, the median ECMO support duration was 168 hours (7 days), with a range of 90-306 hours (3.50-12.75 days) [7]. According to the 2016 ELSO registry report, the mean ECMO support duration had increased to 300 hours (~12.50 days) for adults with non-traumatic ARDS [3]. In 2018, 20% of all ECMO runs were defined as prolonged (longer than 14 days) [1]. Since the coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, approximately 15,000 patients with COVID-19-associated ARDS have been treated with VV-ECMO worldwide [6]. The very early reports suggested that ECMO support would be prolonged for these patients
In contrast, until the COVID-19 pandemic, ECMO support lasting less than 14 days was considered short while ECMO treatment lasting longer than 14 days was deemed prolonged [1], though some papers suggested 21 days [11] or 28 days [12] as a definition for prolonged ECMO. Whether certain patient characteristics, lab results, or treatment-related parameters can predict treatment duration, and whether ECMO duration affects prognosis is still unknown. Yet, these questions are of extreme medical and economic significance because ECMO is a highly resource-demanding treatment. Predicting treatment duration and prognosis may aid clinicians in daily decision-making regarding their patients and to better understand the natural history of patients on ECMO.
Overall, information on the outcomes of patients treated with VV ECMO for a prolonged duration is scarce.
2. Methods
In this multicenter retrospective study, we aimed to learn more about this poorly defined group of patients treated with VV ECMO for a prolonged duration.
We conducted a retrospective, multi-center study, based on data collected from the Israeli ECMO registry (originated in 2019).
Data was extracted from the Israeli ECMO registration for all adult patients (>18 years old) with a positive PCR COVID-19 test and respiratory failure who had been treated with VV-ECMO at six ECMO centers. Patients’ records with poor data collection were excluded.
Data collected included: (1) demographic information, comorbidities, and pre-ECMO baseline parameters such as respiratory support modality, prone position, gas exchange data, duration of invasive mechanical ventilation before ECMO cannulation, and treatment with nitric oxide, inotropes, or vasopressors; (2) ECMO-related parameters such as total ECMO duration, maximal blood flow, and maximal gas flow; and (3) ECMO and non-ECMO-related complications such as thrombotic events (e.g., venous or arterial thrombosis, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and ECMO circuit thrombosis necessitating circuit replacement), bleeding defined as requiring treatment with blood products, and infections, including ventilator-associated pneumonia and bacteremia.
Primary outcomes were 180-day mortality and ECMO treatment duration. Secondary outcomes were complication rates parameters that predict ECMO treatment duration and prognosis in prolonged ECMO patients.
The main study aims were to evaluate whether ECMO treatment duration affects prognosis, define risk factors for prolonged ECMO treatment, and evaluate risk factors for poor prognosis of VV-ECMO patients.
This study was conducted according to the amended declaration of Helsinki. Each center’s ethical committee approved the study.
2.1. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were carried out using R software, version 4.3.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Numerical variables are summarized using medians and interquartile range (IQR), while categorical data, including binary variables such as comorbidities, are presented as percentages. Patients are classified based on their ECMO status (connected/disconnected) at specific time points during follow-up; therefore, some patients are included in all groups. A quasi-Poisson regression model was employed to assess the association between pre-ECMO predictors and outcomes. The outcome variable encompassed experiencing death or continued ECMO utilization within 8 weeks (56 days). To investigate whether certain predictors were linked to mortality, Cox regression was performed for specific study groups. Patient survival is presented using Kaplan-Meier plots and comparisons of Kaplan-Meier rates between different groups were executed using bootstrapping analysis. This method involves a resampling technique that generates multiple replications of the original dataset through random sampling with replacement. This approach enables the estimation of sampling variability, facilitating the assessment of significant differences in survival rates among non-mutually exclusive groups. Bootstrapping was employed to determine whether a difference in Kaplan-Meier survival rates significantly deviated from zero. Statistical significance was ascertained using a p-value threshold <0.05.
3. Results
Out of 193 records, 188 from six ECMO centers were included in the study and only five patients were excluded due to missing essential data. Demographics and medical data are shown in
Table 1. Patients’ median age was 50 (IQR 42, 50) years, 69% were male, and the median BMI was 31 kg/m2 (IQR 27, 35). Diabetes and cardiovascular disease were the most common comorbidities (22% and 8.5% of patients, respectively). The median Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score on admission was 8 (IQR 6, 11), and 86% were mechanically ventilated before cannulation, with a median of 2.5 days (IQR 0.5, 5) on mechanical ventilation before cannulation. Fifty-three percent of the patients were treated with nitric oxide, 34% were proned, and 18% required inotrope support before cannulation. The mean ECMO support duration was 29.9 days (IQR 8, 36.7) with a maximal duration of 190 days. Information on survival data was available for 183 patients.
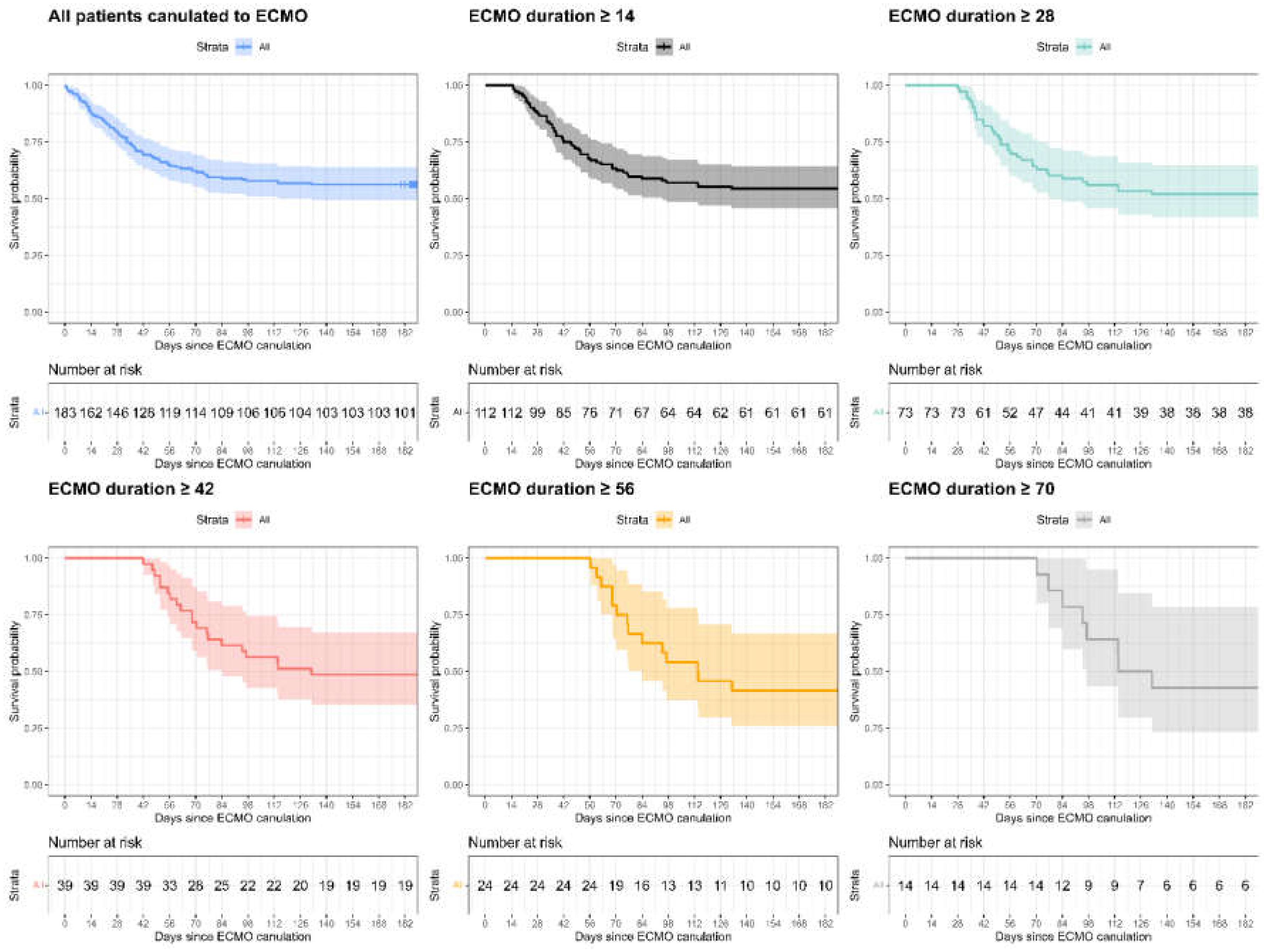
Figure 1 describes the survival rate of patients divided by the time on ECMO. Each plot shows survival rates of up to 180 days from cannulation, for patients who were still alive and on ECMO (i.e., not deceased or decannulated) at a certain time—day 0, 14, 28, 42, 56, and 70 from cannulation. These plots are designed to resemble prospectivity by representing the accumulative data up to the specific day, aiming to aid clinicians in assessing their patients’ outcomes at every point in time.
The overall patients’ survival rates did not change significantly up to 180 days. In a sub-group analysis of patients still on ECMO on day 56, there was a non-significant trend toward reduced survival rate when comparing survival at 90 and 180 days.
Table 2 describes survival rates for 60, 90, and 180 days for all ECMO patients and for patients still on ECMO at 14, 28, 42, and 56 days (i.e., did not die or undergo decannulation). The overall survival rates for 60, 90, and 180 days were 63%, 59%, and 56%, respectively. There was no significant difference in survival for patients who were still alive and on ECMO amongst the different time groups.
We sought to assess different risk factors for mortality and prolonged ECMO treatment.
Table 3 shows a regression model assessing the correlation between several parameters (duration of mechanical ventilation before ECMO cannulation, SOFA score, prone position, and treatment with nitric oxide, vasopressors, or inotropes), and prolonged ECMO treatment. Outcomes were adjusted according to age, gender, and BMI. As shown, every day of mechanical ventilation before cannulation adds an 11% increased risk for prolonged ECMO treatment (p=0.01).
Table 4 shows univariant analyses assessing different parameters and their correlations with mortality. Only age and SOFA score on the day of cannulation were found to correlate significantly with mortality. Risk for mortality was higher by 3% (p=0.001) for every year of age (between 20-74 years old) and by 12% (p=0.006) for each point increase in SOFA score on the day of cannulation.
In addition, patients older than 50 years on the day of cannulation had a higher mortality rate (54% vs. 36%, respectively, p=0.013).
Abbreviations: BMI, Body mass index; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; HR, hazard ratio; CL, confidence limit; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
Table 5 summarizes the incidence of complications and mortality associated with each complication during ECMO treatment. The most abundant complications were infections, bleeding events, and ECMO-related mechanical complications.
Table 6 shows the correlation between specific complications and mortality, with no complications found to correlate significantly to mortality.
4. Discussion
In this retrospective, multicenter study, we aimed to answer two critical questions: (1) does ECMO treatment duration affect prognosis and (2) are there predicting factors for prolonged ECMO duration? These questions are important both medically and economically, as a clinician treating a patient on ECMO for a prolonged time frequently contemplates whether the immense efforts invested in these patients will be worthwhile. Questions on when to discuss lung transplantation or end-of-life treatment frequently arise.
We found no correlation between ECMO duration and survival rates. As shown in
Figure 1 and
Table 2, a patient on the day of ECMO cannulation has a 56% survival rate for 180 days, which remains relatively steady throughout the treatment period. In other words—a patient who is still cannulated on day 14, 28, or 56 has the same chance for survival as they had on the day of cannulation. Hence, we suggest that ECMO duration should not be considered as a single factor when contemplating issues of level of care and end-of-life treatment, as it does not predict treatment failure or higher mortality rates.
In a subgroup analysis of 24 patients still cannulated at 56 days, there was a non-statistically significant trend toward a reduction in survival rate after 90 days from cannulation. Their 90-day survival rate was 62%, which declined to 41% at 180 days, but was not statistically significant. This finding may indicate that days 60 to 90 on ECMO may serve as a landmark for prognostic evaluation (i.e., if the patient is not improving and there are no signs of lung recovery during the 3rd month on ECMO, the possibility of lung transplantation should be discussed. In our cohort, 3 out of 24 patients (12.5%) who were still on ECMO on day 56, underwent lung transplantation after 121, 144, and 189 days, two of whom survived to 6 months. The assumption of the 3rd month of ECMO being an important landmark for prognostic evaluation is supported by Levi et al. who reported on an Israeli series of 20 COVID-19 patients treated with ECMO and listed for lung transplantation. The median duration from hospitalization to listing was 85.5 days. The median duration on the waitlist was 25.5 days. Four patients underwent lung transplantation, while 9 out of the remaining 16 recovered without transplantation after a median of 59 days on ECMO. Seven patients died while waiting for lung transplantation after a median of 101 days on ECMO [13].
Several previous studies issued prolonged ECMO outcomes. Flinspach et al. [14] studied a group of 117 patients in a single center, reporting their outcomes at four different time groups: up to 14, 14-28, 29-50, and above 50 days. Despite an overall relatively low survival of 35%, they did not find a statistically significant difference in mortality rates between the different time groups and concluded that ECMO duration did not increase mortality.
Stern et al. [15] studied a smaller group of 44 ECMO patients, divided between <90 days of ECMO treatment and >90 days, who had remarkable survival rates of overall 82% to hospital discharge. They found a significantly higher mortality in patients treated with ECMO for more than 90 days (62% vs. 90%, respectively). It may be argued that these exceptionally high survival rates at this single-center study may be due to high selectivity, which is also suggested by the young patient age of 40 years, as compared to 50 and 54 years in the current study and Flinspach et al. [14].
In a recent retrospective large-scale study based on the ELSO registry, Abhimanyu et al. analyzed data from 13,681 patients treated with VV ECMO for ARDS [16]. They found that the duration of VV ECMO (per additional day) was significantly associated with reduced survival to hospital discharge in patients supported with VV ECMO for <21 days. However, when the analysis was restricted to patients supported with VV ECMO for > 21 days, duration was not significantly associated with mortality.
We found time on mechanical ventilation before ECMO cannulation to be the only significant risk factor for prolonged ECMO (>56 days), with an 11% higher risk for prolonged ECMO duration for every day of invasive ventilation before ECMO cannulation. These findings support the hypothesis that the sooner VV-ECMO is initiated the better, as supported by Abhimanyu et al., who also found that longer duration of mechanical ventilation before VV ECMO (81 vs. 49 hours, respectively) was associated with prolonged ECMO duration [16].
Time on mechanical ventilation before ECMO cannulation is a well-known prognostic factor for VV-ECMO patients [15,17,18,19]. In the current study, we did not find a significant correlation between duration of ventilation before ECMO and mortality. We assume a possible explanation might be that in our cohort there was a relatively short mean duration between invasive ventilation and ECMO cannulation, a mean of 2.5 days (IQR 0.5-5) as compared to 4 or 7 days in previous studies [17,18,19].
We found that older age and higher SOFA score increased the risk for mortality: 3% for every year (between ages 20-74 years) and 12% for every point of SOFA score. Age older than 50 years was also found to correlate significantly with mortality.
Stern et al. [15], found age and SOFA scores to be significantly higher in patients who required prolonged ECMO duration, but these did not correlate with higher mortality rates.
A high-quality systematic review, including over 17,000 patients [17], also found age to be a statistically significant prognostic factor.
ECMO is a highly invasive treatment that exposes patients to adverse events such as infections, bleeding, and ECMO-related mechanical complications. We found an incidence of approximately 30% for bleeding and 44% for infections. Yet, none of these complications correlated significantly to mortality in our study. In a meta-analysis of 4,800 patients [20], a similar pneumonia rate of 29%-38% was found among COVID-19 ECMO patients. The bacteremia rate was 12%-17%, which is lower than in the current study (38%).
The Israeli ECMO registry lacks the timing for every complication, so we could not assess causality or connection between complications and prolonged ECMO duration. Nonetheless, it is reasonable that the longer the exposure to ECMO the higher the probability for certain ECMO-related complications to occur, such as mechanical complications, bleeding, and infections. Stern et al. [15] found that bleeding and infections were more common after >90 days on ECMO (76.9% vs. 58.1% for bleeding (p=0.31), 84% vs. 51% for pneumonia (p=0.04), and 84% vs. 48% for bacteremia (p=0.026), respectively). We found no correlation between complications and mortality; hence, we suggest that a high incidence of complications should not be regarded as a factor when discussing the level of care or trying to assess prognosis or treatment failure.
Our study is not without limitations. Being a retrospective registry-based study, selection bias is probable. We studied only COVID-19-related ARDS patients so our results cannot be generalized to all VV-ECMO patients, though the comparable results reported by Abhimanyu et al. [16], who studied all ARDS VV ECMO patients, suggest generalizability.
5. Conclusions
In this retrospective multicenter study, we found no correlation between prolonged VV-ECMO treatment in COVID-19-induced ARDS patients and prognosis. This finding may aid clinicians in daily decision-making regarding their patients and to better understand the natural history of patients on ECMO.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.G; methodology, O.G, A.B, N.S and V.N.; formal analysis, O.G, A.B, N.S; investigation, O.G, E.I, D.S, M.M, A.S, Y.K; data curation, A.B; writing—original draft preparation, A.B.; writing—review and editing, O.G; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of: Soroka University Medical Center Helsinki board: Study name “ A retrospective analysis of ECMO use in COVID the Israeli experience”. Approval number SOR-0158-21. Approval date 30.8.2021. Sheba Medical Center Helsinki board: study name: “A retrospective study to describe morbidity and mortality of all COVID ECMO patients in Israel”. Approval number SMC- 8186-21. Rambam Medical Center Helsinki board: Study name “A retrospective study to describe morbidity and mortality of all COVID ECMO patients in Israel”. Approval number 0286-21-RMB-D, approval date 1.5.2021. Wolfson Medical Center Helsinki board: study name: “A retrospective study to describe morbidity and mortality of all COVID ECMO patients in Israel”. Approval number: WOMC-0109-21, Approval date 14.6.2021. Shamir Medical Center Helsinki board: Study name “ Comparing characteristics and outcomes for patients treated with ECMO in Israel” Approval number: RMC-0072-21. Approval date 28.1.2021. Tel-Aviv Sourasky Medical Center Helsinki board: Study name “ Comparing characteristics and outcomes for patients treated with ECMO in Israel” Approval number: TLV0432-2. Approval date 23.11.2023.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Doctor Debby Mir who provided English and scientific editing services.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Abbreviations
ARDS (Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome )
ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation)
ELSO (extracorporeal life support organization)
IQR (interquartile range)
SOFA (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment)
VV (veno-venous)
References
- Posluszny J, Engoren M, Napolitano LM, Rycus PT, Bartlett RH, centers Em. Predicting Survival of Adult Respiratory Failure Patients Receiving Prolonged (>/=14 Days) Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. ASAIO J. 2020;66:825-33.
- Paden ML, Conrad SA, Rycus PT, Thiagarajan RR, Registry E. Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry Report 2012. ASAIO J. 2013;59:202-10.
- Thiagarajan, R.R.; Barbaro, R.P.; Rycus, P.T.; Mcmullan, D.M.; Conrad, S.A.; Fortenberry, J.D.; Paden, M.L. Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry International Report 2016. ASAIO J. 2016, 63, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peek, G.J.; Mugford, M.; Tiruvoipati, R.; Wilson, A.; Allen, E.; Thalanany, M.M.; Hibbert, C.L.; Truesdale, A.; Clemens, F.; Cooper, N.; et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham T, Combes A, Roze H, Chevret S, Mercat A, Roch A, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for pandemic influenza A(H1N1)-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome: a cohort study and propensity-matched analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:276-85.
- ELSO Registry [Internet]. https://www.elso.org/Registry/ELSOLiveRegistryDashboard. Accessed 18 Sept 2024.
- Schmidt, M.; Bailey, M.; Sheldrake, J.; Hodgson, C.; Aubron, C.; Rycus, P.T.; Scheinkestel, C.; Cooper, D.J.; Brodie, D.; Pellegrino, V.; et al. Predicting Survival after Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure. The Respiratory Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Survival Prediction (RESP) Score. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreier, E.; Malfertheiner, M.V.; Dienemann, T.; Fisser, C.; Foltan, M.; Geismann, F.; Graf, B.; Lunz, D.; Maier, L.S.; Müller, T.; et al. ECMO in COVID-19—prolonged therapy needed? A retrospective analysis of outcome and prognostic factors. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Guo Z, Li B, Zhang X, Tian R, Wu W, et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Shanghai, China. ASAIO J. 2020;66:475-81.
- Yang, Y.; Rali, A.S.; Inchaustegui, C.; Alakbarli, J.; Chatterjee, S.; Herlihy, J.P.; George, J.; Shafii, A.; Nair, A.; Simpson, L. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Coronavirus Disease 2019-associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An initial US Experience at a High-volume Centre. Card. Fail. Rev. 2020, 6, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, Z.N.; Dahi, S.; Evans, C.F.; Byrnes, K.A.; Bittle, G.J.; Wehman, B.; Rector, R.P.; McCormick, B.M.; Herr, D.L.; Sanchez, P.G.; et al. Long-Term Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, S.J.; Jung, J.-S.; Hong, S.-B.; Cho, W.H.; Lee, S.-M.; Cho, Y.-J.; Park, S.; Koo, S.-M.; Park, S.Y.; Chang, Y.; et al. Clinical outcomes of patients receiving prolonged extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory support. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, L.; Deri, O.; Huszti, E.; Nachum, E.; Ledot, S.; Shimoni, N.; Saute, M.; Sternik, L.; Kremer, R.; Kassif, Y.; et al. Timing of Lung Transplant Referral in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Lung Injury Supported by ECMO. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flinspach, A.N.; Raimann, F.J.; Bauer, F.; Zacharowski, K.; Ippolito, A.; Booke, H. Therapy and Outcome of Prolonged Veno-Venous ECMO Therapy of Critically Ill ARDS Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, D.R.; Michalak, L.A.; Beckett, A.R.; Tabachnick, D.R.; Tatooles, A.J. Outcomes of patients with COVID-19 supported by venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for greater than 90 days. JTCVS Open 2023, 16, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandel, A.; Fabyan, K.D.; Mendelsohn, S.; Puri, N.; Damuth, E.; Rackley, C.R.; Conrad, S.A.; King, C.S.; Green, A.M. Prevalence and Survival of Prolonged Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Analysis of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, A.; Fernando, S.M.; Rochwerg, B.; Barbaro, R.P.; Hodgson, C.L.; Munshi, L.; MacLaren, G.; Ramanathan, K.; Hough, C.L.; Brochard, L.J.; et al. Prognostic factors associated with mortality among patients receiving venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 11, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Su, L.; Chen, X.; He, H.; Long, Y. Relationship between the Pre-ECMO and ECMO Time and Survival of Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhoul, M.; Keizman, E.; Carmi, U.; Galante, O.; Ilgiyaev, E.; Matan, M.; Słomka, A.; Sviri, S.; Eden, A.; Soroksky, A.; et al. Outcomes of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) for COVID-19 Patients: A Multi-Institutional Analysis. Vaccines 2023, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbaro, R.P.; MacLaren, G.; Boonstra, P.S.; Combes, A.; Agerstrand, C.; Annich, G.; Diaz, R.; Fan, E.; Hryniewicz, K.; Lorusso, R.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: evolving outcomes from the international Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. Lancet 2021, 398, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).