1. Introduction
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is transmitted from person to person through inhalation of respiratory droplets from patients and direct contact with infected secretions.[
1] It can cause two diseases: varicella and herpes zoster. In temperate climates where vaccination is not practiced, infection with VZV approaches 100% by the age of forty.[
1] There is no animal reservoir, and humans are the only natural host for varicella. After infection, immunity to these diseases appears to persist for life, and second attacks are rare.
Before 1995, there was no varicella vaccine available in Guangzhou, China, and no effective drugs for prevention or treatment, so the disease was endemic. Varicella was designated as a local compulsory notifiable infectious disease in Guangzhou after 1995, managed as a Class C infectious disease, requiring cases to be reported within 24 hours of diagnosis. Simple measures should be taken to prevent the disease, such as home quarantine for patients in school or kindergarten until no new lesions (macules, papules, etc.) appear on the skin and mucous membranes within 24 hours, and health monitoring for two weeks for their close contacts, etc.
Except for the varicella vaccine licensed in South Korea, all VZV vaccines available worldwide are based on the Oka strain.[
1] The varicella vaccine was introduced in Guangzhou, China, in 1999, and it was paid for by the vaccinee or their guardian. School-aged children are at high risk of varicella. The number of varicella outbreaks ranks first among infectious disease outbreaks.[
2] The highly contagious nature of varicella in schools prompted the government to implement control measures in 2012: emergency vaccination for susceptible children once a varicella outbreak was identified in a school.[
3] Even after emergency vaccination for each outbreak, the annual number of varicella outbreaks in schools remained stubbornly high. Guangdong province introduced a two-dose immunization program for children to prevent the disease in 2017.[
4] Children aged 12-24 months receive the first dose of the varicella vaccine, and children aged 4-6 years receive the second dose. Until now, the varicella vaccine has not been included in Guangzhou's immunization program. They are classified as category 2 vaccines, paid for by the vaccinee or their guardian, and not mandatory for children.
Since the implementation of the two-dose varicella immunization program, the incidence of varicella has dropped dramatically in Guangzhou, from 818.67/100,000 per year (2014-2019) to 251.12/100,000 per year (2020-2023). The number of reported varicella outbreaks dropped from 14.5 to 4.25 per year. The high-risk group shifted from children aged 1-14 to children under 1 year old.[
5]
Antibody levels against infectious diseases, ascertained through serosurveillance, are influenced by vaccination and historical exposure to infection, serving as a biomarker for individual immune competence against specific pathogens and a metric for assessing the efficacy of vaccines within the immunized population. Surveillance of immunity levels against vaccine-preventable diseases is a mandated duty of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as prescribed by the Vaccine Administration Law of the People's Republic of China. An annual seroepidemiological assessment is conducted to evaluate the humoral immune response to vaccine-preventable communicable diseases among the healthy population in Guangzhou, China.
According to the actual situations, we tested immunoglobulin G (IgG) against varicella to determine the current individual immune status in healthy people, to identify the vulnerable groups to varicella, to evaluate the durability of varicella antibody persistence after vaccination, and to provide evidence for adjusting the current varicella immunization schedule in China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
Annual monitoring of population immunity levels in healthy individuals within communities was conducted in Guangzhou. One or more communities from each district were selected using simple random sampling. Based on the calculation formula for a cross-sectional study, the minimum number of subjects required was determined to be 1155, with an expected diphtheria antibody seroprevalence of 50%, a precision of 0.05, an allowable error of 0.05, and a design effect of 3. There are 11 districts in Guangzhou, and approximately 1100 subjects were enrolled in each district. Each district recruited at least 8 subjects in each age group (0-5 months, 6-11 months, and 1, 2, 3, 4 years); at least 6 subjects in the age groups 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10-19, and 20-29 years; and at least 5 subjects in the age groups 30-59 and ≥60 years.
Participants' venous blood, demographic information (age, sex, address, household registration, date of birth, and date of sampling), and history of varicella were collected by community staff from July to December.
Varicella vaccine vaccination history (doses, vaccination dates) was collected from the Guangdong Vaccine Circulation and Vaccination Management Information System by matching participants' names, sexes, dates of birth, and addresses. The Vaccination Management Information System has been operational since 1997. Considering the year the information system was developed and potential subjects' recall bias, we only collected vaccination information for children under 19 years old from the Information System.
Inclusion Criteria: Participants were included if they had no fever (axillary temperature ≤ 37.1°C), no acute disease, were neither outpatients nor hospital inpatients, and had no symptoms of respiratory infection, and had resided in their community for at least three months. Subjects or their guardians who were willing to participate in this surveillance voluntarily were also included.
2.2. Serologic Evaluations
Blood samples were centrifuged at 3500×g for 15 minutes, and sera were transferred into 2 mL cryotubes under sterile conditions. Serum samples were stored at −80°C at the Guangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention (GZCDC). Before testing, sera were allowed to stand for 1 hour and processed when they reached room temperature. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; Virion/Serion, Würzburg, Germany) was used to quantitatively measure varicella IgG titers. The assay was performed by GZCDC from February to July each year, according to the manufacturer's instructions, and optical density was measured at wavelengths of 405 and 620 nm using a spectrophotometer. Results were expressed in milli-International Units (mIU/mL).
According to the manufacturer's instructions, antibodies against varicella were defined as <50 mIU/mL as negative, ≥50 mIU/mL and <100 mIU/mL as equivocal, and ≥100 mIU/mL as positive. Seroprotection was defined with a cut-off value of 100 mIU/mL for antibodies against varicella.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Data processing and analysis were performed using R version 4.3.0, along with the Storm Statistical Platform (
www.medsta.cn/software). The varicella antibody concentration was recorded as geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) and analyzed in logarithmic form. Two-sample t-tests (or Wilcoxon two-sample tests), one-way ANOVA (or Kruskal-Wallis tests), or χ2 tests were used to compare the differences in varicella antibody concentration or demographic information between groups within the same doses. Mann-Kendall's test was used to test the trend of antibodies by age group and varicella vaccine doses. Multivariate regression analysis with a stepwise method examined the association between log-transformed varicella antibody concentration and various groups.
2.4. Ethical Considerations
The Ethics Committee of the Guangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention reviewed and approved the study protocol (Identification code: GZCDC-ECHR-2023P0037). Participants or their guardians were informed that their participation was voluntary.
3. Results
A total of 3300 subjects were enrolled from 2020 to 2022 in the study, ranging in age from newborn to 87 years old, with a median age of 5 and an average age of 10.37 years. The ratio of male to female subjects was 1.03:1. The ratio of local residents to migrant residents was 3.72:1. Over 80% (2712/3300) of the subjects were aged between 0-14 years, with 93.22% (2528/2712) having definite varicella vaccine dose records and vaccination dates. Additionally, 2.3% of the subjects had a history of varicella.
3.1. Varicella Antibody Levels
The overall varicella IgG-specific antibody levels were 171.2 mIU/mL (95% CI: 158.9, 184.4), and there was a statistically significant increase with age, from 56.2 mIU/mL at 0 years to 610.5 mIU/mL at 50 years and above. Females exhibited higher varicella IgG-specific antibody levels than males. Local residents had higher varicella IgG-specific antibody levels than non-local residents. Subjects born before 1995 had the highest antibody levels compared to others. The central urban area had significantly lower varicella IgG-specific antibody levels compared to the suburban and outer suburban areas.
Varicella IgG-specific antibody levels showed a statistically significant increase in subjects who received varicella vaccinations, from 0 doses (46.5 mIU/mL) to 2 doses (340.2 mIU/mL), Subjects with a history of varicella exhibited higher antibody levels compared to those without such a history.
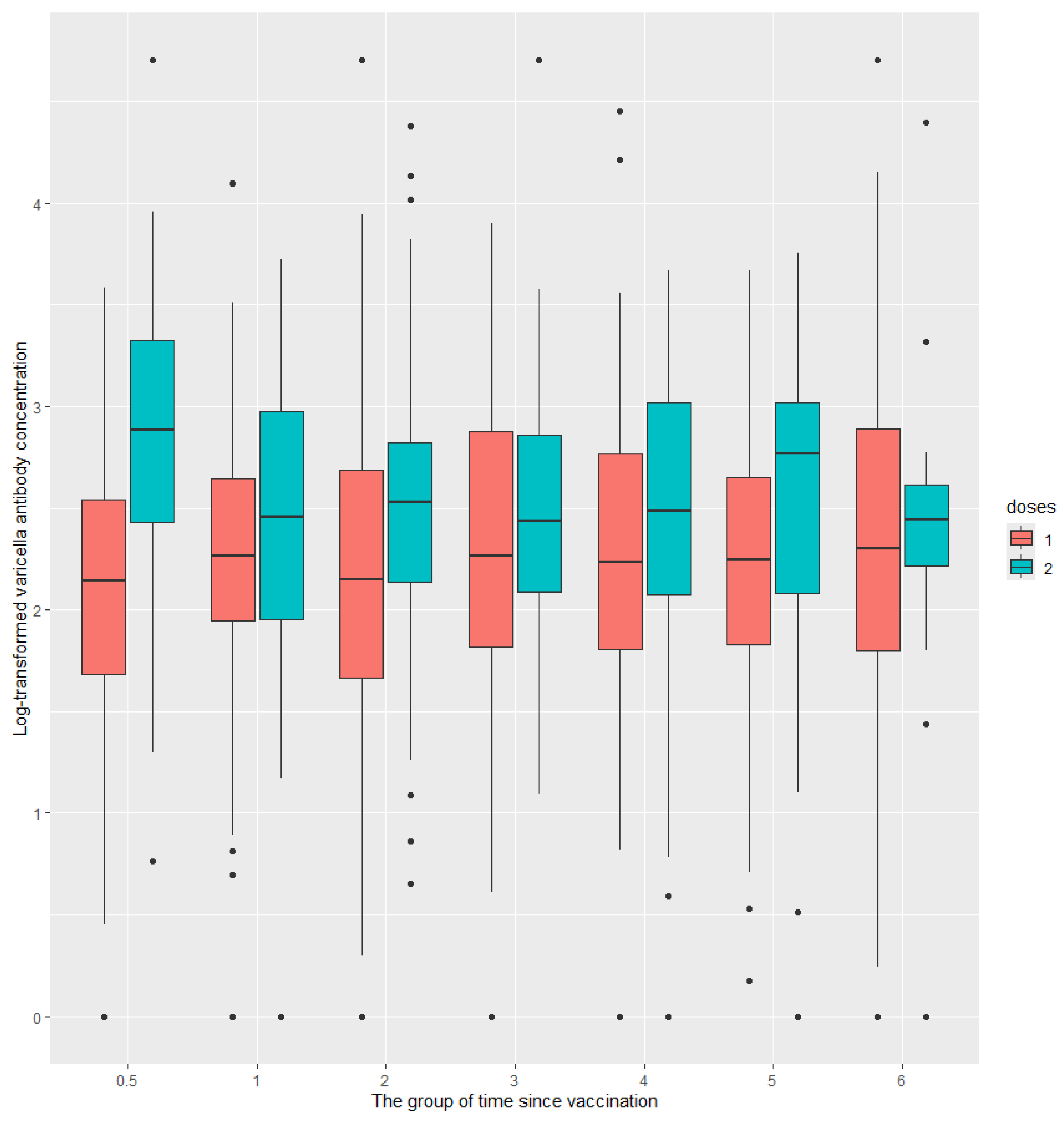
There were significant differences in antibody levels among different groups based on time since vaccination for subjects who received 1 dose (P<0.05) or 2 doses (P<0.001). (
Table 1)
The varicella IgG-specific antibody levels for women of childbearing age were 443.2 mIU/mL (95% CI: 349.5, 562.0), which were significantly higher than those of other women.
Differences in varicella IgG-specific antibody levels among groups defined by age, household, sex, area, and vaccine doses were all statistically significant (P<0.001).
3.2. Varicella Antibody Positive Rate
The overall positive rate of varicella antibodies was 67.00% (95% CI: 65.37, 68.60), which showed a statistically significant increase from 42.47% in the age group 0 years to 95.98% in the age group 51 years and above (p<0.05,
Table 1), with the lowest rates observed in infants (0 years). Females had a higher positive rate for varicella antibodies than males. The central urban area had a lower positive rate for varicella antibodies compared to the suburban and outer suburban areas. The positive rate for varicella antibodies showed a statistically significant increase with the number of doses of the varicella-containing vaccine (DCV) received, from 40.75% with 0 doses to 83.38% with 2 doses.
Differences in the positive rate for varicella antibodies among groups defined by age, household, sex, area, and vaccine doses were all statistically significant (p<0.001).
In the multivariable regression analyses adjusted with a stepwise method, several factors were significantly associated with varicella IgG-specific antibody levels (
Table 2). These factors included area, sex, household registration, dose of varicella vaccine, and history of varicella.
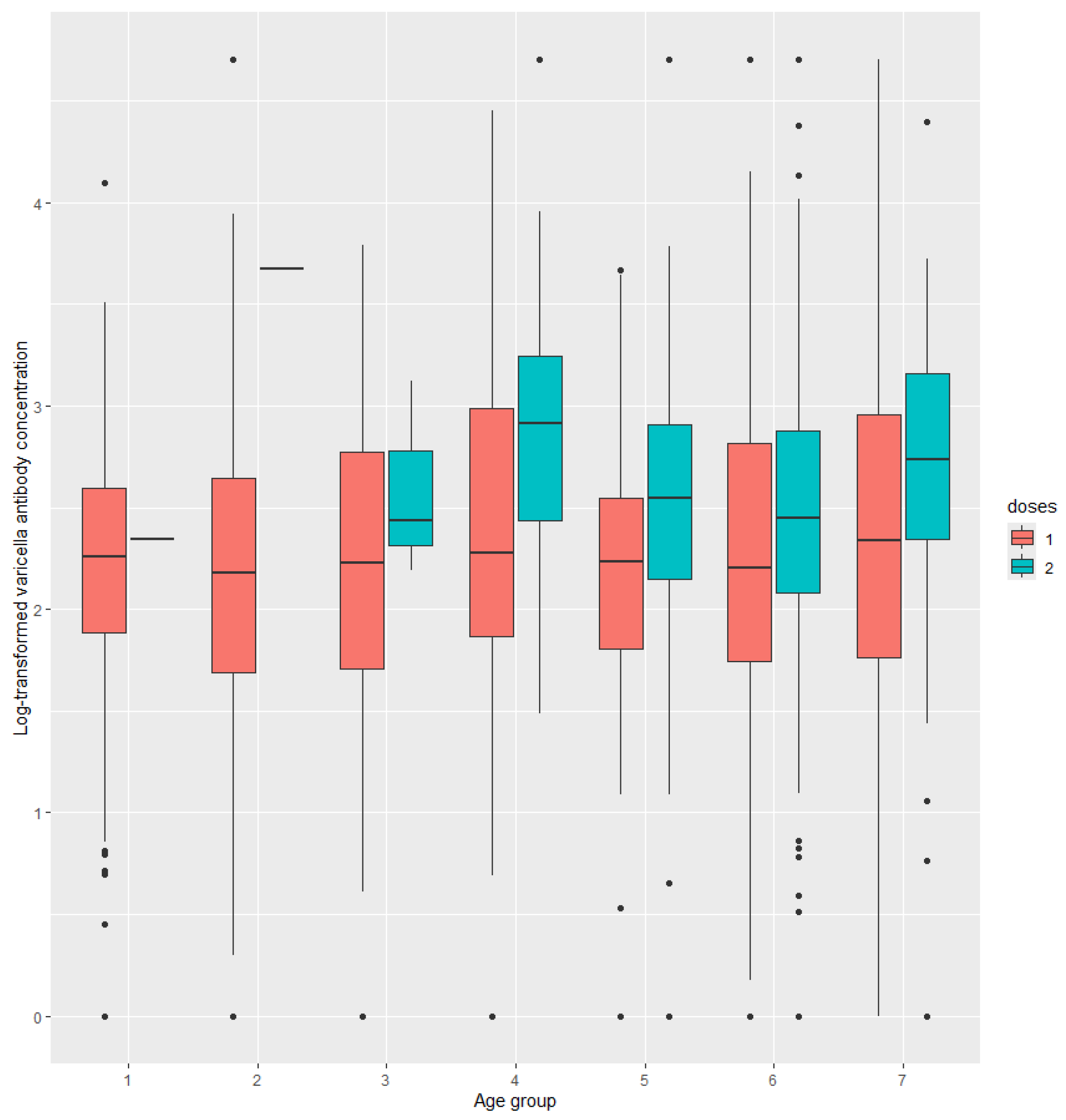
In subjects who received two doses of the varicella vaccine, varicella antibody levels declined significantly over time since the second dose vaccination, from 705.2 mIU/mL at half a year post-vaccination to 194.0 mIU/mL at six years post-vaccination. Additionally, varicella antibody levels decreased significantly as subjects aged. In contrast, no such significant differences were observed in subjects who received only one dose of the varicella vaccine (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2).
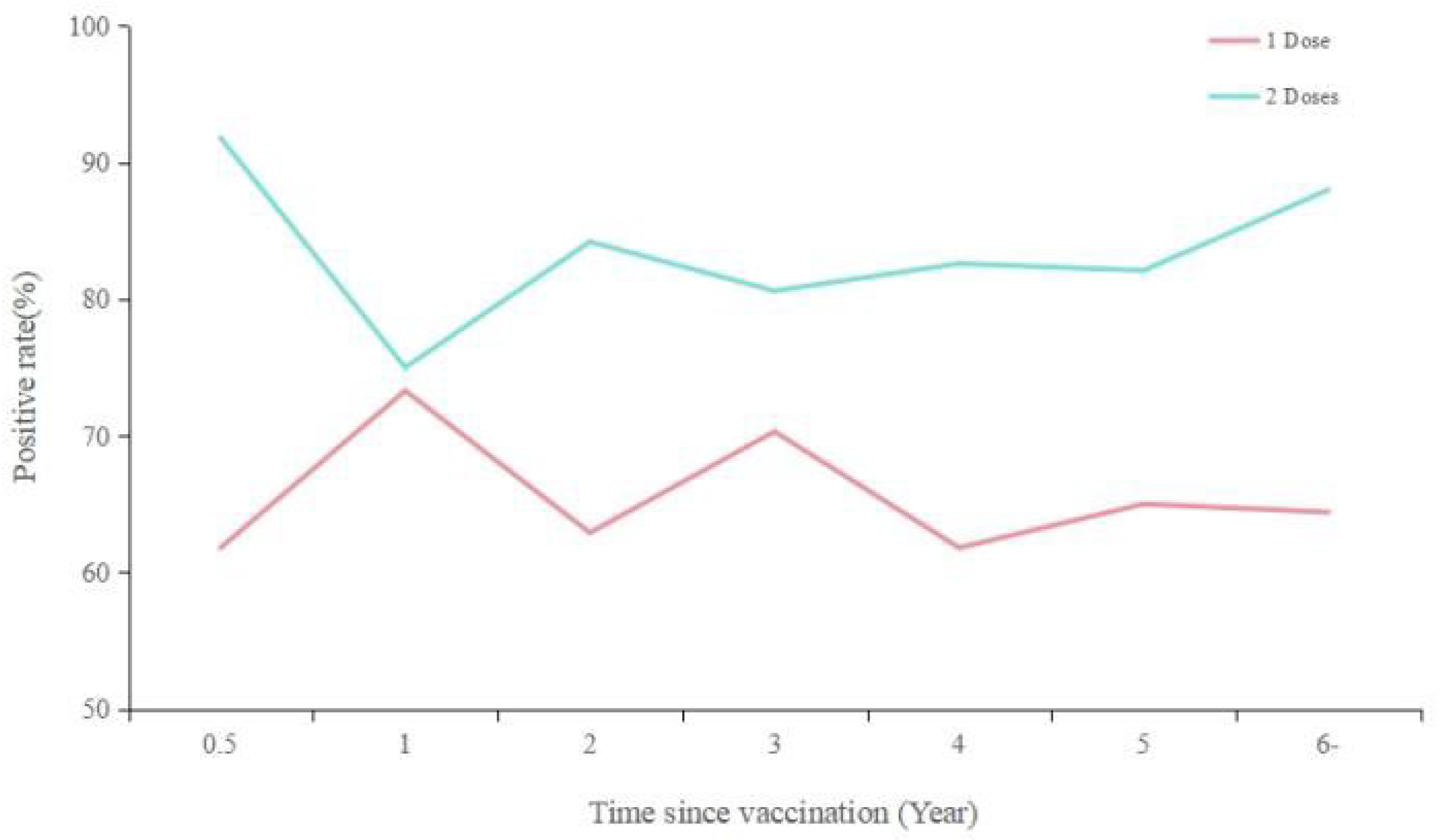
The positive rate of varicella antibodies after vaccination was higher for those who received two doses compared to one dose, with rates remaining in the range of 80-90% for two doses and 60-70% for one dose years after vaccination, without a significant downward trend (
Figure 3).
4. Discussion
The results of community-based serosurveillance indicated that varicella antibody concentration and positivity rate were decreased by age and increased by doses. The varicella antibody levels and positivity rate for women of childbearing age were significantly higher than other women. In the multivariable models, area, sex, household register, dose of varicella vaccine, history of varicella were significantly associated with VZV antibody concentration.
Varicella antibody levels varied place to place. Compare with this study, Zhejiang 2015[
6] and Jiangxi 2017[
7]’s studies issued a similar varicella positive rate (62.99%, 63,27%). Liaonin 2020[
8] and Sichuan 2022[
9] have the lower positive rate (48.94%, 40.80%), while United States 2009-2010[
10] reported a much higher seroprevalence (across all age groups, from 97.1% to .9%). The different seroprevalence probably because of different varicella vaccination strategy and levels of varicella morbidity. The high varicella seroprevalence across all age in US, could be attributed to the successful implementation of routine varicella vaccination in the US starting in 1996. By 2008, 1-dose varicella vaccination coverage among children aged 19–35 months reached 91%.[
10]
In concordance with Beijing 2017 and Liaonin 2020[
8], the seropositivity trend significantly increased with age, from 56.2% for 0y to 98.6% to 40-49y. This is mainly because of natural infection with VZV and implementation of varicella vaccine immunization. In our study, the varicella antibody positive rate for subjects who had a history of varicella was much higher than those hadn’t(92.2% v.s. 56.7%). The same was observed in our birth cohort, seroprevalence decreased from subjects born in the natural infectious stage (before 1995) to subjects born in the promotion of the vaccination stage (after 1999) (92.1% v.s. 63.8%).
Females were associated with higher antibody levels and a higher rate of seropositivity. An analysis of the differences in the history of varicella and vaccination between males and females was conducted. No significant difference was found in the history of varicella vaccination. It is noteworthy that the attack rates of varicella for females were approximately twice those of males (3.7% vs. 1.7%, p=0.001, Supplemental Table S1). This could be a probable cause. However, a varicella epidemiology study in Guangzhou reached the opposite conclusion, showing that the varicella morbidity for males was higher than for females from 2005 to 2017, 143.9/100,000 per year vs. 116.6/100,000 per year[
11]. To determine if sampling bias exists, further studies are required to elucidate this intriguing paradox.
Vaccination helped to improve the immunity level. The seropositivity of subjects who received 2 doses, 1 dose, and 0 dose of vaccine was 83.4%, 65.3% and 40.7%, respectively. Higher the other researches in China, Zhejiang 2015[
6], Sichuan 2022[
9]. Varicella antibody among different age or after vaccination for different doses was analyzed in this study. Subjects who received 2 doses vaccine had a higher GMC than those 1 dose at any time since vaccination, and at any age.
Although antibody titers may diminish over time following vaccination, they remain above the positive threshold (≥50 mIU/mL) even six years post-vaccination, with levels of 194.0 mIU/mL observed for a single dose and 198.8 mIU/mL for two doses. The seropositivity rate for individuals who received one or two doses of the vaccine did not exhibit a significant decline over time. The long-term maintenance of antibodies in healthy individuals after varicella vaccination has also been corroborated in a 14-year prospective study that evaluated the vaccine's efficacy[
12,
13]. A comparable study conducted in less developed areas of Guangdong, China, revealed a rapid increase in antibody levels among teenagers and adults after vaccination, albeit with a lower vaccination coverage[
4]. These investigations were conducted in settings where the wild-type varicella-zoster virus (VZV) was still circulating. The persistence or increase in antibody titers over time could potentially be attributed to external boosting effects due to exposure to the wild-type virus, which complicates the interpretation of these findings.
The varicella antibody levels were significantly higher in suburban and outer suburban areas compared to the central urban area. This disparity was found to be partially associated with the underlying vaccination rates across these regions, rather than the history of varicella infection (P>0.05). The proportion of varicella vaccine uptake was notably lower in the central urban area as compared to the other two areas, with rates of 67.3% in the central urban area versus 70.7% in the suburban area and 69.5% in the outer suburban area (p=0.001, see Supplemental Table S2 for detailed data). The lower varicella vaccine uptake in central urban areas is a complex issue that involves multiple factors. Firstly, there may be differences in access to healthcare services, with suburban and outer suburban areas potentially having better access to vaccination centers or more proactive outreach programs. Secondly, , urban areas often have higher population densities and more diverse communities, which can make it logistically more challenging to implement and maintain vaccination programs effectively.
The administration of two doses of varicella vaccine is recommended for both children and adults to achieve optimal protection against varicella[
14]. According to the World Health Organization's position paper[
1], a single-dose vaccine has a median effectiveness of 83% against varicella. While one dose is sufficient to reduce mortality and severe morbidity from varicella, it does not fully prevent limited virus circulation and outbreaks. The two-dose regimen significantly decreases the number of cases and outbreaks, offering superior protection with a median effectiveness of 95% against all grades of severity of varicella.
We recognize that the demographic composition of our study sample introduces certain limitations in the generalizability of our findings. The sample is predominantly composed of children, with a notable underrepresentation of adults and the elderly. Specifically, individuals within the age range of 10-59 years and those over 60 years account for only 17.7% and 4.5% of our sample, respectively. This distribution significantly deviates from the actual demographic composition in Guangzhou, which may undermine the reliability of our study's outcomes when applied to adult and elderly populations. Consequently, the results obtained for these age groups may not be reproducible, and our conclusions should not be extrapolated indiscriminately to older cohorts. To address this, it is essential to refine the design of immunity level surveillance by deliberately increasing the sample size of adults and older adults, thereby ensuring a more representative and robust dataset that can accurately reflect the immunity levels across different age demographics.
Secondly, due to the developmental timeline of our information system and the inherent risk of recall bias, we were unable to collect vaccination records for a subset of subjects under the age of 19 (7.3%) and individuals over 18 years old. Adults who are too old to have their records in the system and children who are part of the transient population living in Guangzhou present a challenge; if they did not receive vaccines in Guangzhou, it is unlikely that their vaccination files from other cities would be accessible, leading to a lack of vaccination records in our system. This absence of records may be more prevalent among those who are unvaccinated, potentially introducing a positive bias to our results.
Thirdly, the reliance on subjects' memory for the collection of varicella history could introduce recall bias. Individuals who have been infected with VZV may be more inclined to accurately recall a history of varicella, while those without the disease may provide more ambiguous responses. This differential recall could lead to an overestimation of the associations between exposures and diseases, further complicating the interpretation of our findings.
5. Conclusions
In our study, we observed a variance in varicella antibody levels that were influenced by age, vaccination dosage and history of varicella infection. The immunogenicity conferred by vaccination was not only enhanced but also persisted for a minimum of six years. It is hence recommended that both children and adults receive two doses of the varicella vaccine to achieve optimal disease prevention. Extensive clinical validation and scientific studies over three decades have substantiated that routine varicella vaccination in children significantly reduces the incidence, hospitalization, and mortality rates associated with varicellaa[
15,
16,
17,
18]. Notably, a substantial reduction in disease burden has been observed across all age groups, including adults and infants who are not eligible for vaccination[
19,
20]. Recently, an increasing number of provinces and cities in China, such as Qingdao, Tianjin, Suzhou, Shanghai, Beijing, and Shenzhen, have incorporated varicella vaccination into their local immunization programs, achieving high vaccination rates[
21]. The inclusion of varicella vaccine in Guangzhou's routine immunization programs should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of the disease burden and the economic viability of vaccination strategies, taking into account the under-reporting of varicella cases and the broader implications for public health and economic savings.
Author Contributions
Qing He: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing. Pinting Zhu: Methodology. Yang Xu: Methodology. Yilan Li: Resources, Project administration. Lei Luo: Conceptualization, Supervision.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by research grants from the Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (2024A03J0419, 2024A03J0422).
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Varicella and herpes zoster vaccines: WHO position paper, June 2014. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2014, 89, 265–287.
- He, Q.; Li, M.X.; Xu, J.X.; et al. Epidemiological analysis on varicella outbreaks in schools in Guangzhou from 2013 to 2018. Practical Preventive Medicine 2021, 28, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T. Varicella emergency vaccination seemed instrumental in declining chickenpox incident in Guangzhou, Southern China. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2013, 55, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liang, C.; Huang, X.; et al. Vaccination against Varicella Zoster Virus Infection in Less Developed Regions of Guangdong, China: A Cross-Sectional Serosurveillance Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, S.; Yang, Y.Y.; Fu, C. Public's early response to the novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. Emerg Microbes Infect 2020, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhu, S.; Pang, Z.; et al. Antibody levels against varicella-zoster virus among a healthy population in Jinhua city of Zhejiang province, 2015. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization 2016, 22, 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; et al. Antibody levels against laricella-zoster lirus among a lealthy lopulation in Jiangxi province, 2017. Experimental and Laboratory Medicine 2018, 36, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Fang, X.; Ren, L.; et al. Antibody levels against varicella-zoster virus among a healthy population in Liaoning Province. Chinese Journal of Biologicals 2023, 36, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, K.; et al. Antibody levels against varicella-zoster virus among children aged 0-11 in Sicuan province. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization 2023, 29, 554–558. [Google Scholar]
- Lebo, E.J.; Kruszon-Moran, D.M.; Marin, M.; et al. Seroprevalence of measles, mumps, rubella and varicella antibodies in the United States population, 2009-2010. Open Forum Infect Dis 2015, 2, ofv6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, Q.; Ni, L.; et al. Analysis of the epidemiological characteristics and trend of varicella, Guangzhou, 2005-2017. Modern Preventive Medicine 2018, 45, 3470–3474. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, R.; Ray, P.; Tran, T.N.; et al. Long-term effectiveness of varicella vaccine: A 14-Year, prospective cohort study. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1389–e1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macartney, K. Long-term protection against varicella with two-dose combination measles-mumps-rubella-varicella vaccine. Lancet Infect Dis 2019, 19, 222–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Lu, L.; Liu, Y. Expert consensus of varicella vaccine immunization in China. Capital Journal of Public Health 2023, 17, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Varela, F.H.; Pinto, L.A.; Scotta, M.C. Global impact of varicella vaccination programs. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2019, 15, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, E.D.; Marin, M. The Effectiveness of Varicella Vaccine: 25 Years of Postlicensure Experience in the United States. J Infect Dis 2022, 226 (Suppl 4), S425–S430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.; Leung, J.; Anderson, T.C.; et al. Monitoring Varicella Vaccine Impact on Varicella Incidence in the United States: Surveillance Challenges and Changing Epidemiology, 1995-2019. J Infect Dis 2022, 226 (Suppl 4), S392–S399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.; Marti, M.; Kambhampati, A.; et al. Global Varicella Vaccine Effectiveness: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Lu, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Impact of Varicella Immunization and Public Health and Social Measures on Varicella Incidence: Insights from Surveillance Data in Shanghai, 2013-2022. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawaskar, M.; Gil-Rojas, Y.; Irene, P.C.; et al. The impact of universal varicella vaccination on the clinical burden of varicella in Colombia: A National database Analysis, 2008-2019. Vaccine 2022, 40, 5095–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, C.; et al. National and provincial burden of varicella disease and cost-effectiveness of childhood varicella vaccination in China from 2019 to 2049: A modelling analysis. Lancet Reg Health West Pac 2023, 32, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).