Submitted:
05 November 2024
Posted:
06 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Background: Ukrainian refugees fleeing the conflict between Russia and Ukraine may face significant challenges to their physical, psycho-emotional, social, and spiritual wellbeing. Aim: To identify the health needs of Ukrainian refugees seen in primary care facilities in Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain. Methods: A mixed-methods design was employed. Quantitative data were obtained through a descriptive analysis of health records, while qualitative data were collected via focus group interviews and thematic analysis of testimonies. Results: The sample comprised 59 individuals (45.4% of all patients seen). Eight participants from five family groups took part in the focus group. The typical profile of a Ukrainian refugee in the Canary Islands is female (79.7%), relatively young, with a high socio-cultural background, generally in good health, travelling alone or with her minor children. The main reasons for consultation were routine health check-ups and control blood tests. The NANDA-I nursing diagnoses indicated a need for psycho-emotional care, with the most prevalent being Risk for Relocation Stress Syndrome (27.1%); Interrupted Family Processes, Disturbed sleep pattern, Risk for Impaired Resilience (13.6% each); and Anxiety (11.9%). Participants rated the healthcare system positively, but language barriers and long waiting times for access to specific services were noted as limitations. Their needs did not significantly differ from those of the local population. Conclusions: This study underscores the need for a tailored approach to refugee care, considering their unique circumstances and needs. Early provision of information about available healthcare services and protocols can facilitate access, manage expectations, and aid decision-making.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Setting and Participants
- −
- Individuals aged 16 years or older.
- −
- Fulfilment of the temporary protection criteria as outlined by the Spanish Order PCM/170/2022 of 9 March, publishing the Agreement of the Council of Ministers of 8 March 2022, which extends temporary protection under Council Implementing Decision (EU) 2022/382 of 4 March 2022 to those affected by the conflict in Ukraine seeking refuge in Spain.
- −
- Availability of an interpreter to ensure effective communication if the participant could not speak Spanish.
- −
- Refusal to provide informed consent.
- −
- Individuals with cognitive disabilities who were unable to understand the information sheet or give informed consent, and who were not accompanied by a legal guardian or representative.
- −
- Individuals relocated to other areas of residence, outside the Puerto de La Cruz basic health district.
2.3. Variables
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample description
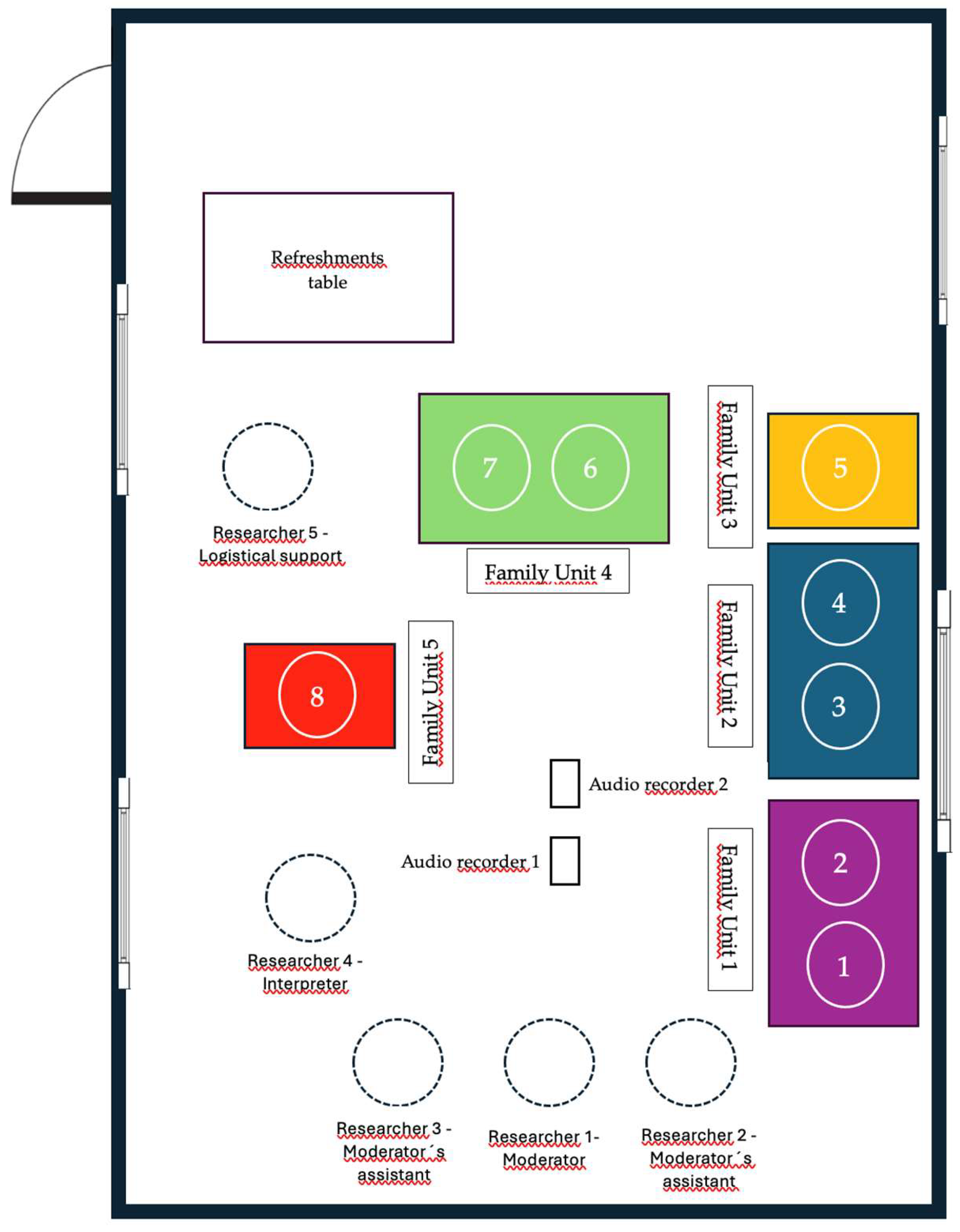
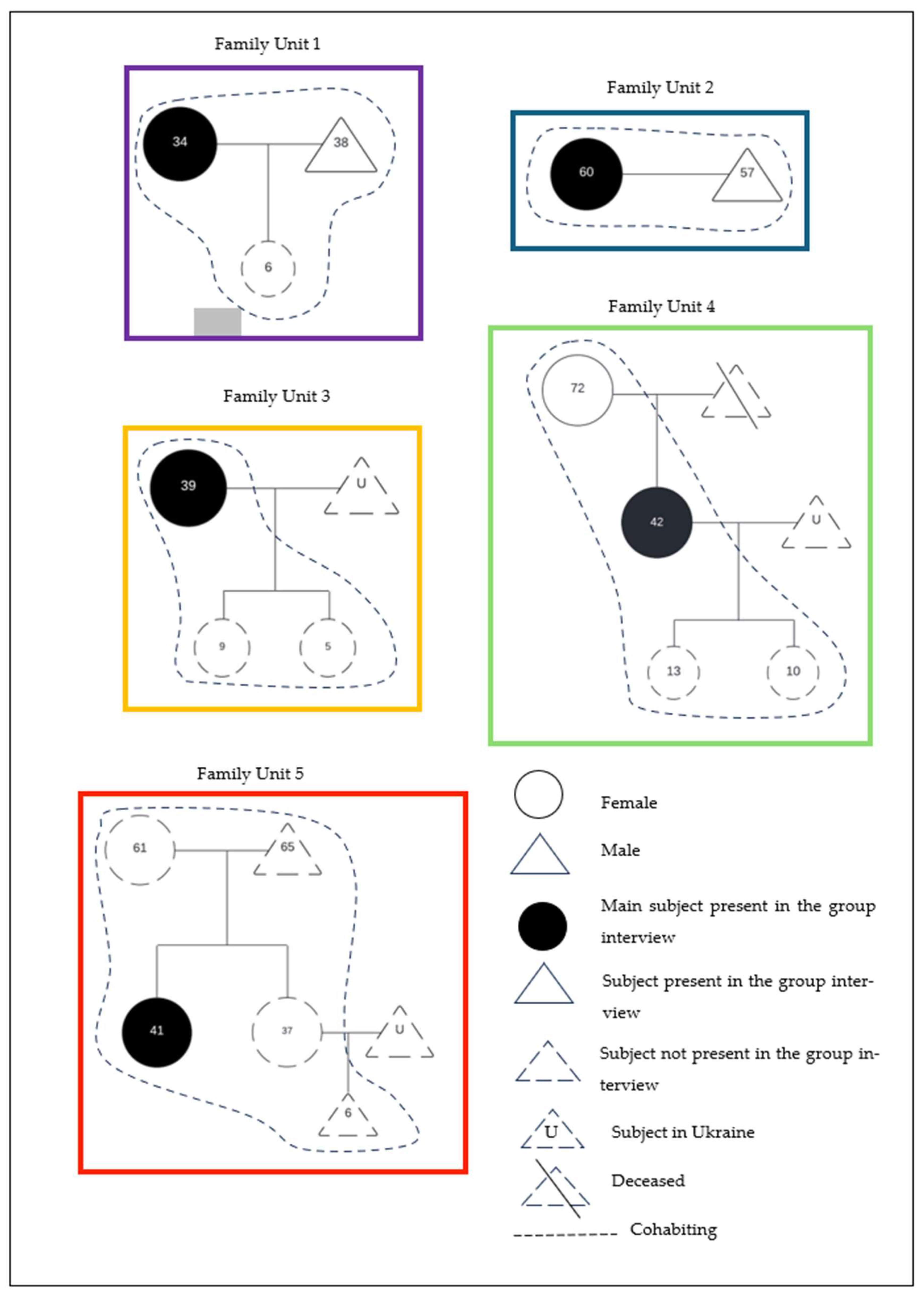
3.2. Focus Group Results
3.2.1. Genogram and Family Context
3.2.2. Discourse analysis
3.2.2.1. Social integration and community support
3.2.2.2. Healthcare
3.2.2.3 Access to medication and services
3.2.2.4 Perception of healthcare professionals
3.2.2.5. Perception of physical and emotional wellbeing
3.2.2.6. Mental health
3.2.2.7. Perception of the care received in emergency services
3.2.2.8. Main demands
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Public Involvement Statement
Guidelines and Standards Statement
Use of Artificial Intelligence
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Questions included in the focus group interview guide
- −
- How long have you been in Spain as a refugee?
- −
- What circumstances led you to leave your home country?
- −
- Do you have any medical history or pre-existing health conditions that we should be aware of?
- −
- What type of health insurance coverage do you have or wish to obtain in Spain?
- −
- What was your access to healthcare like in Ukraine before coming to Spain?
- −
- How do you feel in terms of your physical and emotional health at the moment?
- −
- How has your experience with the Spanish healthcare system been so far? What aspects have you found most positive or negative?
- −
- Have you encountered difficulties accessing healthcare services in your host location? If so, what kind?
- −
- What has been your experience with the healthcare system in Ukraine, and how do you feel about the quality of the healthcare system in Spain?
- −
- Have you received the vaccinations recommended by Spanish health authorities?
- −
- Do you need information about the available vaccines and their importance for your health?
- −
- We understand that traumatic experiences can impact mental health. Have you experienced any emotional or mental difficulties since your arrival that you relate to the conflict or the relocation process?
- −
- Would you like to speak with a mental health professional to receive emotional support?
- −
- Do you have any family members or children under your care? Do they need specific medical care or services?
- −
- How are you managing your family’s health in these circumstances?
- −
- Have you experienced any urgent or serious health problems? If so, what kind?
- −
- Have you followed any health promotion or disease prevention programmes?
- −
- Do you need any specific medications or treatments at this time?
- −
- Are you aware of the available medical services and resources in Tenerife?
- −
- Do you need information on where to find nearby healthcare services?
- −
- Do you feel comfortable communicating in Spanish, or do you require the support of an interpreter?
- −
- Have you encountered any difficulties related to language or communication when seeking healthcare in Spain?
- −
- Do you have a support network in Spain?
- −
- Do you need information about organisations or groups that can provide social and community support?
- −
- What role has the Ukrainian immigrant community played in your adaptation and access to healthcare services in Spain?
- −
- What measures do you think could improve the experience of immigrants in the Spanish healthcare system?
- −
- Is there anything else you would like to share or ask regarding your health and wellbeing in Spain?
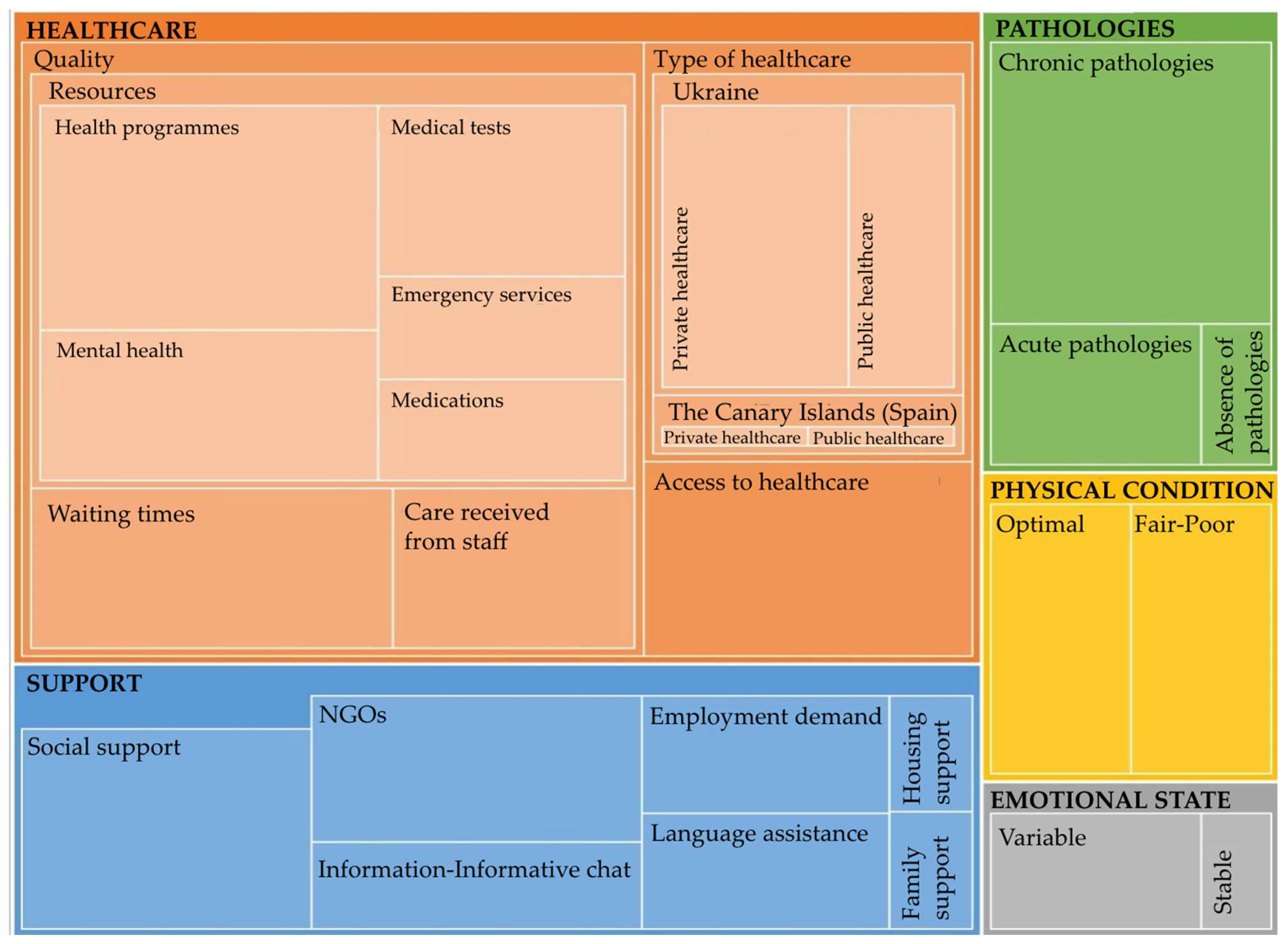
Appendix B. Codebook
| Category | Description | No. of references |
| SUPPORT | Types of support received (social, family, NGOs, etc.) | 23 |
| Family support | Support received from family members | 1 |
| Social support | Support received from people in their environment who are not family members | 6 |
| Housing assistance | Receives some form of help or access to housing | 1 |
| Language assistance | Support or assistance received to facilitate communication | 3 |
| Employment demand | Current employment and job applications | 3 |
| Information/Informative chat | Means of accessing information on aid requests, NGOs, etc. | 3 |
| NGOs | Aid received from NGOs (The Red Cross and the Spanish Commission for Refugee Assistance, CEAR) | 5 |
| HEALTHCARE | Assessment of variables related to the healthcare received | 55 |
| Access to healthcare | Type of health coverage and use of healthcare services | 6 |
| Quality | Evaluation of the healthcare received | 36 |
| Care received from staff | Evaluation of the care provided by healthcare staff | 4 |
| Resources | Assessment of the resources used | 26 |
| Medications | Assessment of access to prescribed medications | 3 |
| Health programmes | Assessment of access to and use of health programmes (paediatrics, dentistry, gynaecology, vaccinations, etc.) | 9 |
| Medical tests | Types of medical tests they had access to | 5 |
| Mental health | Access to and/or demand for mental health services | 6 |
| Emergency services | Evaluation of emergency services | 3 |
| Waiting times | Waiting times for healthcare services | 6 |
| Type of healthcare | Public or private healthcare | 13 |
| The Canary Islands (Spain) | Public or private healthcare received in the Canary Islands | 2 |
| Private healthcare | Use of private healthcare resources | 1 |
| Public healthcare | Use of public healthcare resources | 1 |
| Ukraine | Public or private healthcare received in Ukraine | 11 |
| Private healthcare | Use of private healthcare resources | 7 |
| Public healthcare | Use of public healthcare resources | 4 |
| EMOTIONAL STATE | Evaluation of emotional state due to displacement caused by the war | 4 |
| Stable | No difficulty regulating emotions related to displacement | 1 |
| Variable | Difficulty regulating emotions related to displacement | 3 |
| PHYSICAL CONDITION | 8 | |
| Optimal | Describes physical state as optimal | 4 |
| Fair/Poor | Describes physical state as fair or poor | 4 |
| PATHOLOGIES | Pathologies reported by participants | 12 |
| Absence of pathologies | Reports no illnesses | 1 |
| Acute pathologies | Reports having experienced an acute pathology during their stay in the Canary Islands | 3 |
| Chronic pathologies | Reports having a chronic condition | 8 |
References
- Portal de datos operacionales – Situación de los refugiados de Ucrania. [Internet]. Ginebra: Oficina del Alto Comisionado de las Naciones Unidas para los Derechos Humanos; [citado 1 de marzo de 2024]. Disponible en: https://data.unhcr.org/en/situations/ukraine.
- Directiva 2001/55/CE del Consejo, de 20 de julio de 2001, relativa a las normas mínimas para la concesión de protección temporal en caso de afluencia masiva de personas desplazadas y a medidas de fomento de un esfuerzo equitativo entre los Estados miembros para acoger a dichas personas y asumir las consecuencias de su acogida. [Internet]. Boletín Oficial del Estado, nº 212 (7 de agosto de 2001); [citado 1 de junio de 2024]. Disponible en: https://www.boe.es/buscar/doc.php?id=DOUE-L-2001-81926.
- Decisión de Ejecución (UE) 2022/382 del Consejo de 4 de marzo de 2022 por la que se constata la existencia de una afluencia masiva de personas desplazadas procedentes de Ucrania en el sentido del artículo 5 de la Directiva 2001/55/CE y con el efecto de que se inicie la protección temporal. [Internet]. Boletín Oficial del Estado, nº 71 (4 de marzo de 2022); [citado 1 de junio de 2024]. Disponible en: https://www.boe.es/buscar/doc.php?id=DOUE-L-2022-80366.
- Levy BS, Sidel VW. Documenting the effects of armed conflict on population health. Annual review of public health [Internet]. 2016 [citado 3 de junio de 2024];37:205-18. [CrossRef]
- Wandschneider L, Namer Y, Davidovitch N, Nitzan D, Otok R, Chambaud HL, et al. El papel de las Escuelas de Salud Pública en tiempos de Guerra: Declaración de ASPHER sobre la Guerra contra Ucrania. Public Health Review [Internet]. 2022 [citado3 de junio de 2024];43:1604880. Disponible en: https://www.aspher.org/download/1047/declaracion_de_aspher_sobre_la_guerra_contra_ucrania_es.pdf.
- Junta Permanente de la semFYC, & Responsables y vocalía. Todas las personas tienen derecho a la paz, a la integración y a la cobertura universal de salud. Aten Primaria [Internet]. 2015 [citado3 de junio de 2024]; 47(10):611-2. [CrossRef]
- Asamblea Mundial de la Salud 72. Promoción de la salud de refugiados y migrantes: proyecto de plan de acción mundial, 2019-2023: informe del Director General [Internet]. 2019 [citado 4 de junio de 2024]. Disponible en: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/328691.
- Fuertes C, Martín Laso MA. El inmigrante en la consulta de atención primaria. Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra [Internet]. 2006 [citado 4 de junio de 2024]; 29:9-25. Disponible en: https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1137-66272006000200002.
- Rodríguez J, De La Torre A, Miranda CT. La salud mental en situaciones de conflicto armado. Biomédica [Internet]. 2002 [citado 4 de junio de 2024];22(0):337. [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei J, Baeriswyl-Cottin R, Framorando D, Kasina F, Premand N, Eytan A, et al. What are the barriers to access to mental healthcare and the primary needs of asylum seekers? A survey of mental health caregivers and primary care workers. BMC Psychiatry [Internet]. 2016 [citado 4 de junio de 2024];16(1):336. [CrossRef]
- Bartelson AR, Sutherland MA. Experiences of trauma and implications for nurses caring for undocumented immigrant women and refugee women. Nursing for Women’s Health [Internet]. 2018 [citado 4 de junio de 2024];22(5):411-6. [CrossRef]
- Marchetti F, Preziosi J, Zambri F, Tambascia G, Di Nolfi A, Scardetta P, et al. Health needs and perception of health care quality among Asylum Seekers and Refugees in an Italian local health authority: A qualitative study. Front Public Health [Internet]. 12 de abril de 2023 [citado 4 de junio de 2024];11. Disponible en: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/public-health/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1125125/full.
- Langlois EV, Haines A, Tomson G, Ghaffar A. Refugees: towards better access to health-care services. Lancet [Internet]. 23 de enero de 2016 [citado 23 de junio de 2024];387(10016):319-21. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5603273/.
- Stiegler N, Padmanabhanunni A, Pretorius TB, Bouchard JP. Psychotraumatology of the war in Ukraine: The question of the psychological care of victims who are refugees or who remain in Ukraine. Psychotraumatologie de la guerre en Ukraine : la question de la prise en charge psychologique des victimes re ́fugie ́es ou reste ́es en Ukraine [Internet]. 2023 [citado 23 de julio de 2024]; Disponible en: https://repository.uwc.ac.za:443/xmlui/handle/10566/8702.
- Ekblad S, Gramatik O, Suprun Y. Increasing perceived health and mental health literacy among separated refugee Ukrainian families with urgent needs occasioned by invasion—a group intervention study with participatory methodology in Sweden. Front Public Health [Internet]. 9 de mayo de 2024 [citado 26 de julio de 2024];12. Disponible en: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/public-health/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1356605/full.
- Goto R, Pinchuk I, Kolodezhny O, Pimenova N, Skokauskas N. Mental health services in Ukraine during the early phases of the 2022 Russian invasion. Br J Psychiatry [Internet]. [citado 12 de agosto de 2024];222(2):82-7. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10964280/.
- Su Z, McDonnell D, Cheshmehzangi A, Ahmad J, Šegalo S, Pereira da Veiga C, et al. Public health crises and Ukrainian refugees. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity [Internet]. 1 de julio de 2022 [citado 12 de agosto de 2024];103:243-5. Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0889159122001283.
- Devi S. Russia–Ukraine tensions hampering health-care access. The Lancet [Internet]. 18 de diciembre de 2021 [citado 12 de agosto de 2024];398(10318):2222. Disponible en: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02791-4/abstract.
- Zaliska O, Oleshchuk O, Forman R, Mossialos E. Health impacts of the Russian invasion in Ukraine: need for global health action. The Lancet [Internet]. 16 de abril de 2022 [citado 12 de agosto de 2024];399(10334):1450-2. Disponible en: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(22)00615-8/abstract.
- Cana R. ¿Por qué aumentan las llegadas de personas migrantes a Canarias? [Internet]. CEAR. 2023 [citado 12 de agosto de 2024]. Disponible en: https://www.cear.es/emergencia-aumento-llegadas-canarias/.
- Rosario CR del, Díaz SN, Carlos PG de, Palmero IR, Mahtani VM, Rodríguez MAH, et al. Características de la asistencia sanitaria a la llegada de inmigrantes africanos a las Islas Canarias. Emergencias: Revista de la Sociedad Española de Medicina de Urgencias y Emergencias [Internet]. 2008 [citado 16 de agosto de 2024];20(6):411-8. Disponible en: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=2775564.
- Godenau D, Buraschi D, Zapata-Hernández VM. Evolución reciente de la inmigración marítima irregular en Canarias [Internet]. Observatorio de la Inmigración de Tenerife. Departamento de Geografía e Historia. Universidad de La Laguna. Tenerife; 2020 [citado 16 de agosto de 2024]. Disponible en: https://riull.ull.es/xmlui/bitstream/handle/915/22207/OBITenFacts%20_08__%282020%29_ESP.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y.
- Kardas P, Babicki M, Krawczyk J, Mastalerz-Migas A. War in Ukraine and the challenges it brings to the Polish healthcare system. The Lancet Regional Health – Europe [Internet]. 1 de abril de 2022 [citado 16 de agosto de 2024];15. Disponible en: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanepe/article/PIIS2666-7762(22)00058-8/fulltext.
- Brenes F. Global Health Issues Among Refugee and Immigrant Populations. Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services [Internet]. noviembre de 2020 [citado 18 de agosto de 2024];58(11):4-4. Disponible en: https://journals.healio.com/doi/abs/10.3928/02793695-20200921-02.
- Maillet L, Champagne G, Déry J, Goudet A, Charest S, Abou-Malham S, et al. Implementation of an intersectoral outreach and community nursing care intervention with refugees in Quebec: A protocol study. Journal of Advanced Nursing [Internet]. 2021 [citado 12 de agosto de 2024];77(11):4586-97. Disponible en: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jan.15022.
- Gabrielsson S, Karim H, Looi GME. Learning your limits: Nurses’ experiences of caring for young unaccompanied refugees in acute psychiatric care. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing [Internet]. 2022 [citado 18 de agosto de 2024];31(2):369-78. Disponible en: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/inm.12965.
- Ministerio de Sanidad y Política Social. Orden SAS/1729/2010, de 17 de junio, por la que se aprueba y publica el programa formativo de la especialidad de Enfermería Familiar y Comunitaria [Internet]. Sec. 3, Orden SAS/1729/2010 jun 29, 2010 p. 57217-50. Disponible en: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/o/2010/06/17/sas1729.
- Sánchez Gómez MB, Novo Muñoz MM, Rodríguez Gómez JÁ, Sierra López A, Aguirre Jaime A, Duarte Clíments G, et al. Competencias de enfermeras especialistas en enfermería familiar y comunitaria. Análisis para su desarrollo actual y futuro. Ene [Internet]. 2019 [citado 18 de agosto de 2024];13(3). Disponible en: https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S1988-348X2019000300005&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es.
- ISTAC | Población según sexos. Municipios por islas de Canarias y años | Banco de datos [Internet]. [citado 23 de julio de 2024]. Disponible en: https://www3.gobiernodecanarias.org/istac/statistical-visualizer/visualizer/data.html?resourceType=dataset&agencyId=ISTAC&resourceId=E30245A_000002&version=~latest#visualization/table.
- Onwuegbuzie AJ, Dickinson WB, Leech NL, Zoran AG. Un marco cualitativo para la recolección y análisis de datos en la investigación basada en grupos focales. Paradigmas: Una Revista Disciplinar de Investigación [Internet]. 2011 [citado 19 de agosto de 2024];3(2):127-57. Disponible en: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=3798215.
- Baumgartner TA, Strong CH, Hensley LD. Conducting and Reading Research in Health and Human Performance. McGraw-Hill; 2001. 456 p.
- Langford BE, Schoenfeld G, Izzo G. Nominal grouping sessions vs focus groups. Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal [Internet]. 1 de enero de 2002 [citado 19 de agosto de 2024];5(1):58-70. [CrossRef]
- Herdman TH, Kamitsuru S, Lopes C. NANDA International Nursing Diagnoses: Definitions and Classification, 2021-2023. Thieme Medical Publishers, Incorporated; 2021. 592 p.
- Gordon M. Manual de Diagnóstico de Enfermería. McGraw-Hill Interamericana de España S.L.; 2007. 432 p.
- Martínez JA. Introducción histórica a la antropología del parentesco. Editorial Universitaria Ramon Areces; 2008. 729 p.
- Vignier N, Halley des Fontaines V, Billette de Villemeur A, Cazenave-Roblot F, Hoen B, Chauvin F, et al. Public health issues and health rendezvous for migrants from conflict zones in Ukraine: A French practice guideline. Infect Dis Now [Internet]. junio de 2022 [citado 19 de agosto de 2024];52(4):193-201. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9040487/.
- Lewtak K, Kanecki K, Tyszko P, Goryński P, Bogdan M, Nitsch-Osuch A. Ukraine war refugees-threats and new challenges for healthcare in Poland. Journal of Hospital Infection [Internet]. 2022 [citado 19 de agosto de 2024];125:37-43. Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0195670122001104.
- Lee ACK, Khaw FM, Lindman AES, Juszczyk G. Ukraine refugee crisis: evolving needs and challenges. Public Health [Internet]. 1 de abril de 2023 [citado 19 de agosto de 2024];217:41-5. Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0033350623000252.
- Rolke K, Walter J, Weckbecker K, Münster E, Tillmann J. Identifying gaps in healthcare: a qualitative study of Ukrainian refugee experiences in the German system, uncovering differences, information and support needs. BMC Health Serv Res [Internet]. 4 de mayo de 2024 [citado 22 de agosto de 2024];24(1):585. [CrossRef]
- Kulhánová I, Lustigová M, Drbohlav D, Leontiyeva Y, Dzúrová D. Determinants of self-rated health among highly educated Ukrainian women refugees in Czechia: analysis based on cross-sectional study in 2022. BMC Women’s Health [Internet]. 1 de abril de 2024 [citado 22 de agosto de 2024];24(1):206. [CrossRef]
- Pandey A, Wells CR, Stadnytskyi V, Moghadas SM, Marathe MV, Sah P, et al. Disease burden among Ukrainians forcibly displaced by the 2022 Russian invasion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences [Internet]. 21 de febrero de 2023 [citado 22 de agosto de 2024];120(8):e2215424120. Disponible en: https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.2215424120.
- Dirección General de Salud Pública. Atención sanitaria para desplazados de Ucrania [Internet]. Eapaña: Secretara de Estado de Sanidad; 202. [citado 25 de agosto de 2024]. Disponible en: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/gabinetePrensa/ucrania/docs/Guia_de_actuacion_desplazados-Ucrania_21.03.2022.pdf.
- Ekblad S, Gramatik O, Suprun Y. Increasing perceived health and mental health literacy among separated refugee Ukrainian families with urgent needs occasioned by invasion—a group intervention study with participatory methodology in Sweden. Front Public Health [Internet]. 9 de mayo de 2024 [citado 25 de jagosto de 2024];12. Disponible en: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/public-health/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1356605/full.
- Eriksen A, Shuftan N, Litvinova Y. Health systems in action: Ukraine. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe on behalf of the European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies. 2021; Organización Mundial de la Salud. Diabetes Ucrania 2016 perfil de país [Internet];2016. [citado 25 de agosto de 2024]. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/es/publications/m/item/diabetes-ukr-country-profile-ukraine-2016.
- Spörlein C, Kristen C. Why We Should Care About Regional Origins: Educational Selectivity Among Refugees and Labor Migrants in Western Europe. Front Sociol [Internet]. 7 de mayo de 2019 [citado 25 de agosto de 2024];4. Disponible en: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/sociology/articles/10.3389/fsoc.2019.00039/full.
- Tillmann J, Weckbecker K, Wiesheu P, Bleckwenn M, Deutsch T, Münster E. [Primary care of Ukrainian refugees]. ZFA (Stuttgart). 2023;99(1):28-33.
- Biesiada A, Mastalerz-Migas A, Babicki M. Response to provide key health services to Ukrainian refugees: The overview and implementation studies. Social Science & Medicine [Internet]. 1 de octubre de 2023 [citado 25 de agosto de 2024]; 334:116221. Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277953623005786.
- Greene-Cramer B, Summers A, Lopes-Cardozo B, Husain F, Couture A, Bilukha O. Noncommunicable disease burden among conflict-affected adults in Ukraine: A cross-sectional study of prevalence, risk factors, and effect of conflict on severity of disease and access to care. PLOS ONE [Internet]. 21 de abril de 2020 [citado 26 de agosto de 2024];15(4):e0231899. Disponible en: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0231899.
- Organización Mundial de la Salud. Diabetes Ukraine 2016 country profile [Internet]; 2016.[citado 26 de agosto de 2024]. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/diabetes-ukr-country-profile-ukraine-2016.
- Organización Mundial de la Salud. Ukraine Public Health Situation Analysis (PHSA) - Short form [Internet]; 2022. [citado 27 de agosto de 2024]. Disponible en: https://healthcluster.who.int/publications/m/item/ukraine-public-health-situation-analysis-(phsa)---short-form.
- Comité Asesor de Vacunas e Inmunizaciones. Las vacunaciones en Ucrania [Internet]. España: Asociación Española de Pediatría; 2022[citado 7 de agosto de 2024]. Disponible en: https://vacunasaep.org/profesionales/noticias/Ucrania-situacion-de-las-vacunaciones.
- Limone P, Toto GA, Messina G. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine war on stress and anxiety in students: A systematic review. Front Psychiatry [Internet]. 25 de noviembre de 2022 [citado 27 de agosto de 2024];13. Disponible en: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1081013/full.
- Rizzi D, Ciuffo G, Landoni M, Mangiagalli M, Ionio C. Psychological and environmental factors influencing resilience among Ukrainian refugees and internally displaced persons: a systematic review of coping strategies and risk and protective factors. Front Psychol [Internet]. 9 de octubre de 2023 [citado 27 de agosto de 2024];14. Disponible en: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1266125/full.
- Seleznova V, Pinchuk I, Feldman I, Virchenko V, Wang B, Skokauskas N. The battle for mental well-being in Ukraine: mental health crisis and economic aspects of mental health services in wartime. Int J Ment Health Syst [Internet]. 25 de septiembre de 2023 [citado 27 de agosto de 2024];17(1):28. [CrossRef]
- Zabłocka-Żytka L, Lavdas M. The stress of war. Recommendations for the protection of mental health and wellbeing for both Ukrainian refugees as well as Poles supporting them. Psychiatr Pol [Internet]. 1 de agosto de 2023 [citado 27 de agosto de 2024];57(4):729-46. [CrossRef]
- Dobson J. Men wage war, women and children pay the price. BMJ [Internet]. 10 de marzo de 2022 [citado 27 de agosto de 2024];376:o634. [CrossRef]
- Hodes M. Thinking about young refugees’ mental health following the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry [Internet]. 1 de enero de 2023 [citado 28 de agosto de 2024];28(1):3-14. Disponible en: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/13591045221125639.
- Charlson F, Ommeren M van, Flaxman A, Cornett J, Whiteford H, Saxena S. New WHO prevalence estimates of mental disorders in conflict settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet [Internet]. 20 de julio de 2019 [citado 28 de agosto de 2024];394(10194):240-8. Disponible en: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(19)30934-1/fulltext?banner_id=overwv.
- Boiko DI, Shyrai PO, Mats OV, Karpik ZI, Rahman MdH, Khan AA, et al. Mental health and sleep disturbances among Ukrainian refugees in the context of Russian-Ukrainian war: A preliminary result from online-survey. Sleep Medicine [Internet]. 1 de enero de 2024 [citado 28 de Agosto de 2024];113:342-8. Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S138994572301568X?via%3Dihub.
- Roberts B, Makhashvili N, Javakhishvili J, Karachevskyy A, Kharchenko N, Shpiker M, et al. Mental health care utilisation among internally displaced persons in Ukraine: results from a nation-wide survey. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences [Internet]. febrero de 2019 [citado 28 de agos de 2024];28(1):100-11. Disponible en: https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/epidemiology-and-psychiatric-sciences/article/abs/mental-health-care-utilisation-among-internally-displaced-persons-in-ukraine-results-from-a-nationwide-survey/88702459BFCBFF4D88A49ED5400E3C88.
- Jou YC, Pace-Schott EF. Call to action: addressing sleep disturbances, a hallmark symptom of PTSD, for refugees, asylum seekers and internally displaced persons. Sleep Health [Internet]. diciembre de 2022 [citado 28 de agosto de 2024];8(6):593-600. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9757843/.
- Buchcik J, Kovach V, Adedeji A. Mental health outcomes and quality of life of Ukrainian refugees in Germany. Health Qual Life Outcomes [Internet]. 9 de marzo de 2023 [citado 28 de agosto de 2024];21:23. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9996949/.
- Turrini G, Purgato M, Ballette F, Nosè M, Ostuzzi G, Barbui C. Common mental disorders in asylum seekers and refugees: umbrella review of prevalence and intervention studies. International Journal of Mental Health Systems [Internet]. 25 de agosto de 2017[citado 28 de Agosto de 2014]];11(1):51. Disponible en: https://ijmhs.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13033-017-0156-0.
- Jain N, Prasad S, Czárth ZC, Chodnekar SY, Mohan S, Savchenko E, et al. War Psychiatry: Identifying and Managing the Neuropsychiatric Consequences of Armed Conflicts. J Prim Care Community Health [Internet]. 20 de junio de 2022 [citado 28 de agosto de 2024];13:21501319221106625. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9218442/.
- Anjum G, Aziz M, Hamid HK. Life and mental health in limbo of the Ukraine war: How can helpers assist civilians, asylum seekers and refugees affected by the war? Front Psychol [Internet]. 17 de febrero de 2023 [citado 28 de agosto de 2024];14. Disponible en: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1129299/full.
- Morreel S, Verhoeven V, Bastiaens H, Monten K, van Olmen J. Experiences and observations from a care point for displaced Ukrainians: a community case study in Antwerp, Belgium. Front Public Health [Internet]. 26 de junio de 2024 [citado 28 de agosto de 2024];12. Disponible en: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/public-health/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1349364/full.
| Variable | Category | n (%) | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of family members (up to second-degree relatives) remaining in Ukraine | 0 | 3 (5.1) | 2.2 (1.3) |
| 1 | 7 (11.9) | ||
| 2 | 15 (25.4) | ||
| 3 | 7 (11.9) | ||
| 4 | 4 (6.8) | ||
| 5 | 2 (3.9) | ||
| NR | 21 (35.6) | ||
| Relationship of family members (up to second-degree relatives) remaining in Ukraine | Partner (male) + son | 6 (10.2) | |
| Partner (male) | 3 (5.1) | ||
| Partner (male) + son + father + mother | 2 (3.4) | ||
| Partner (male) + son + mother | 2 (3.4) | ||
| Partner (male) + father + mother | 2 (3.4) | ||
| Partner (male) + mother | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Partner (male) + father + mother + sister | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Partner (male) + grandparents | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Father + mother | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Son | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Son + mother | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Son + grandson | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Daughter + granddaughter | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Son + grandsons | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Daughter + sister | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Mother | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Mother + sister | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Father + mother + grandparents | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Father + mother + brother | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Father + mother + brother + grandparents | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Father + brother | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Brother | 1 (1.7) | ||
| NR | 22 (37.3) | ||
| Number of family members (up to second-degree relatives) accompanying the participant | 0 | 12 (20.3) | 1.5 (1.2) |
| 1 | 16 (27.1) | ||
| 2 | 15 (25.4) | ||
| 3 | 7 (11.9) | ||
| 4 | 4 (6.8) | ||
| NR | 5 (8.5) | ||
| Relationship of family members (up to second-degree relatives) accompanying the participant to Tenerife | Partner (male) | 5 (8.5) | |
| Partner (female) | 3 (5.1) | ||
| Partner (male) + daughter | 2 (3.4) | ||
| Partner (female) + daughter | 2 (3.4) | ||
| Partner (male) + daughter + son | 2 (3.4) | ||
| Partner (male) + mother + daughter | 2 (3.4) | ||
| Partner + children (>2) | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Son | 4 (6.8) | ||
| Children (>2) | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Daughter + sister | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Son + sister | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Daughter + son + sister | 4 (6.8) | ||
| Daughter + grandsons | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Father + mother + sister | 5 (8.5) | ||
| Mother + sister | 8 (13.6) | ||
| Mother | 4 (6.8) | ||
| Sister | 2 (3.4) | ||
| Granddaughter | 2 (3.4) | ||
| NR | 1 (1.7) |
| Reasons for consultation | Total n (%) |
Sex | Pearson’s chi-squared |
p-value | |
| Women n (%) |
Men n (%) |
||||
| General health check-up | 53(89.8) | 43(72.9) | 10(16.9) | 0.70 | 0.40 |
| Request for blood tests | 31(52.5) | 25(42.4) | 6(10.2) | 0.04 | 0.84 |
| Request for regular medication | 25(42.4) | 17(28.8) | 8(13.6) | 3.64 | 0.06 |
| Consultation for an acute health issue and initiation of treatment if necessary | 24(40.7) | 21(35.6) | 3(5.1) | 1.53 | 0.21 |
| Referral for assessment by a specialist other than family medicine | 16(27.1) | 13(22.0) | 3(5.1) | 0.03 | 0.85 |
| Health conditions (ICD-11) | n (%) | NANDA-I nursing diagnoses | n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | 8 (13.6) | Readiness for enhanced health self-management | 25 (42.4) |
| Tobacco abuse | 8 (13.6) | Risk for Relocation Stress Syndrome | 16 (27.1) |
| Hypothyroidism | 6 (10.2) | Discomfort | 10 (16.9) |
| Iron deficiency anaemia | 3 (5.1) | Interrupted Family Processes | 8 (13.6) |
| Anxiety | 3 (5.1) | Risk for Impaired Resilience | 8 (13.6) |
| Osteoarthritis | 3 (5.1) | Disturbed sleep pattern | 8 (13.6) |
| Dyslipidaemia | 3 (5.1) | Anxiety | 7 (11.9) |
| Dyspepsia | 3 (5.1) | Acute Pain | 3 (5.1) |
| Gastritis | 3 (5.1) | Risk for Injury | 3 (5.1) |
| Haemorrhoids | 3 (5.1) | Impaired Skin Integrity | 2 (3.4) |
| Menorrhagia | 3 (5.1) | Readiness for Enhanced Coping | 2 (3.4) |
| Thyroid nodule | 3 (5.1) | Insomnia | 2 (3.4) |
| Fatigue | 2 (3.4) | Relocation Stress Syndrome | 2 (3.4) |
| Tension-type headache | 2 (3.4) | Fear | 2 (3.4) |
| Insomnia | 2 (3.4) | Compromised Family Coping | 1 (1.7) |
| Chronic venous insufficiency | 2 (3.4) | Deficient Knowledge | 1 (1.7) |
| Fibroid uterus | 2 (3.4) | Sleep Deprivation | 1 (1.7) |
| Adjustment disorder | 2 (3.4) | Readiness for Enhanced Sleep | 1 (1.7) |
| Alcohol abuse | 1 (1.7) | Constipation | 1 (1.7) |
| Angioedema | 1 (1.7) | Fatigue | 1 (1.7) |
| Asthenia | 1 (1.7) | Ineffective Health Self-Management | 1 (1,7) |
| Panic attack | 1 (1.7) | Ineffective Family Health Self-Management | 1 (1.7) |
| Cerebral atherosclerosis | 1 (1.7) | Risk for Loneliness | 1 (1.7) |
| Basal cell carcinoma | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Cataract | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Cystocele | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Dementia | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Depression | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Intervertebral disc displacement | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Encephalopathy | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Endometriosis | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Chronic kidney disease | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Epilepsy | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Schizophrenia | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Phaeochromocytoma | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Subcutaneous fibromatosis | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Fibroadenoma of breast | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Impaired fasting glucose | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Pain in knee joint | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Gunshot exit wound | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Hepatitis B | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Hyperplasia of prostate | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Hypoacusis | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Acute myocardial infarction | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Heart failure | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Acute kidney failure | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Fibrocystic disease of breast | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Melasma | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Chronic pancreatitis | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Paraesthesia of skin | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Chronic pyelonephritis | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Psoriasis | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Ovarian cyst | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Allergic rhinitis | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Meniscal tear | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Thymoma | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Congenital malformations of gallbladder | 1 (1.7) | ||
| Vertigo | 1 (1.7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





