Submitted:
06 November 2024
Posted:
07 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Detailed profiling results for an initial set of VLM, VLA, and emerging "generalist" models, providing insights into their capabilities and limitations
- Analysis of generalization
- A systematic set of evaluation splits and metrics specifically designed for robotics learning tasks in the widely-used OpenX Dataset
- A general framework for mapping VLMs to other modality classes, with particular emphasis on action spaces
- Open-source software infrastructure for downloading, managing, and utilizing the benchmark data
2. Related Work
General Multimodal Benchmarks
Multimodal Language Model Evaluations
Robotics-Specific Benchmarks
3. Evaluating VLMs and VLAs
3.1. Data
- Scale and Diversity: The large number of trajectories and varied robot embodiments allows for comprehensive assessment of model generalization capabilities.
- Real-World Relevance: Being composed entirely of real robot data rather than simulated interactions, the dataset better reflects the challenges of physical robot deployment.
- Standardization: The consistent RLDS format facilitates systematic evaluation across different robot platforms and task types.
- Cross-Domain Assessment: The inclusion of both manipulation and locomotion tasks enables evaluation of model performance across fundamentally different types of robot control.
3.1.1. Dataset Curation
3.2. Models
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
- Non-Negativity: The metric remains non-negative, ensuring that errors are consistently accounted for without potential cancellation effects from opposing signs.
- Sensitivity to Large Errors: The squared term in MSE emphasizes larger deviations, providing clear indication of significant prediction errors.
- Bias-Variance Trade-off: MSE inherently captures both bias and variance components, offering a comprehensive measure of prediction accuracy.
- Average MSE (AMSE): Computed as the mean MSE across all trajectories in a dataset, AMSE enables direct comparison of model performance across different datasets and architectures.
- Normalized AMSE (NAMSE): Calculated as , this metric normalizes predictions to each model’s prediction range, facilitating more equitable cross-dataset for a single model comparisons by accounting for different scales in model outputs.
- Completion Rate: We assess successful completion by comparing final predicted actions with ground truth final actions. While this serves as an approximate measure of task completion, it provides valuable insights into models’ ability to reach target states across trajectories.
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Profiling Configuration
JAT Configuration
- Image Processing: JAT requires 4-channel images. For 3-channel RGB inputs, we create an RGBA image by duplicating the red channel as the alpha channel. For 2-channel inputs, we duplicate both channels to create a 4-channel representation.
- Observation Processing: For dictionary-type observations, we concatenate all floating-point observations (excluding image and language instruction embeddings) into a single tensor. In cases where no floating-point observations exist, we pass a zero-filled dummy tensor.
- Action Processing: Ground truth actions are processed by concatenating all floating-point actions into a single tensor when the action space is represented as a dictionary.
- Multi-Image Handling: For timesteps with multiple available images, we select the primary image (typically designated with the keyword `image’).
GPT Configuration
-
Prompt Construction: Each prediction is based on a comprehensive prompt including:
- -
- Floating-point observation states with their corresponding keys as descriptors for specific datasets like Berkeley Autolab where there are such observation states available.
- -
- Primary image observation
- -
- Natural language instruction
- -
- Verbal descriptions for each action space dimension
- -
- The official action space statistics if available or statistical information (min, max, mean) for each action dimension.
- -
- Environmental and task descriptions when available
-
Output Processing: To handle GPT’s VLM-native outputs, which may be incompatible with the required floating-point action tensor format, we implemented error handling:
- -
- For incompatible outputs (incorrect tensor sizes, string elements, mixed text-tensor outputs, or non-scalar elements), we generate a random action tensor with values in as a fallback.
- Multi-Image Processing: For timesteps with multiple available images, we select the primary image (typically designated with the keyword `image’).
OpenVLA Configuration
-
Gripper Command Standardization: We implemented several conversion protocols:
- -
- Binary discretization: For to conversion, we threshold at
- -
- Ternary discretization: For to conversion, values map to (closed), to 1 (open), and to 0 (no change)
- -
- Continuous normalization: For to conversion, we apply the formula: . This was used by the authors in [22].
-
Special Cases:
- -
- For the UCSD pick-and-place dataset, we used dataset statistics to scale gripper commands to the appropriate torque space
- -
- For ETH agent affordances, we applied the transformation: , where high and low are the 99th and 1st percentiles respectively
-
Action Space Handling:
- -
- For datasets using velocity, angular velocity, or torque-based action spaces (e.g., ETH agent affordances and UCSD datasets), we note potential compatibility issues with OpenVLA’s position-based predictions
- -
- We exclude `Terminal’ tensors from action spaces, as OpenVLA predicts only XYZ, RPY, and gripper commands
Additional Considerations
4.2. Inference Infrastructure
JAT and GPT Infrastructure
OpenVLA Infrastructure
5. Results & Discussion
| Dataset Name | Registered Dataset Name | In Pretraining | Action Space Type |
| Jaco Play | jaco_play | ✓ | 4D (1 grip, 3 pos) |
| Berkeley Cable Routing | berkeley_cable_routing | ✓ | 7D (3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| NYU Door Opening | nyu_door_opening_surprising_effectiveness | 8D (1 grip, 3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) | |
| VIOLA | viola | ✓ | 8D (1 grip, 3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| Berkeley Autolab UR5 | berkeley_autolab_ur5 | ✓ | 8D (1 grip, 3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| TOTO | toto | ✓ | 7D (3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| Columbia PushT | columbia_cairlab_pusht_real | 8D (1 grip, 3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) | |
| NYU ROT | nyu_rot_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) | |
| Stanford HYDRA | stanford_hydra_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) |
| UCSD Kitchen | ucsd_kitchen_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | 8D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip, 1 term) |
| UCSD Pick Place | ucsd_pick_and_place_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | 4D (3 vel, 1 grip torque) | |
| USC Cloth Sim | usc_cloth_sim_converted_externally_to_rlds | 4D (3 pos, 1 grip) | |
| Tokyo PR2 Fridge | utokyo_pr2_opening_fridge_converted_externally_to_rlds | 8D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip, 1 term) | |
| Tokyo PR2 Tabletop | utokyo_pr2_tabletop_manipulation_converted_externally_to_rlds | 8D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip, 1 term) | |
| UTokyo xArm Pick-Place | utokyo_xarm_pick_and_place_converted_externally_to_rlds | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) | |
| Stanford MaskVIT | stanford_mask_vit_converted_externally_to_rlds | 5D (3 pos, 1 ang, 1 grip) | |
| ETH Agent Affordances | eth_agent_affordances | 6D (3 vel, 3 ang vel) | |
| Imperial Sawyer | imperialcollege_sawyer_wrist_cam | 8D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip, 1 term) | |
| ConqHose | conq_hose_manipulation | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) | |
| Plex RoboSuite | plex_robosuite | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) |
| GPT | OpenVLA | JAT | ||||
| Dataset Name | AMSE | NAMSE | AMSE | NAMSE | AMSE | NAMSE |
| Jaco Play | 0.288 | 0.188 | 0.239 | 0.228 | 1.237 | 0.295 |
| Berkeley Cable Routing | 0.117 | 0.010 | 0.058 | 0.091 | 0.533 | 0.411 |
| NYU Door Opening | 0.094 | 0.046 | 0.121 | 0.304 | 0.008 | 0.061 |
| VIOLA | 0.355 | 0.134 | 0.061 | 0.072 | 0.997 | 0.331 |
| Berkeley Autolab UR5 | 0.074 | 0.049 | 0.142 | 0.249 | 0.040 | 0.073 |
| TOTO | 0.361 | 0.069 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 1.335 | 0.238 |
| Columbia PushT | 0.030 | 0.046 | 0.118 | 0.820 | 0.242 | 0.347 |
| NYU ROT | 0.441 | 0.034 | 0.228 | 0.308 | 0.288 | 0.177 |
| Stanford HYDRA | 0.201 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.054 | 0.728 | 0.147 |
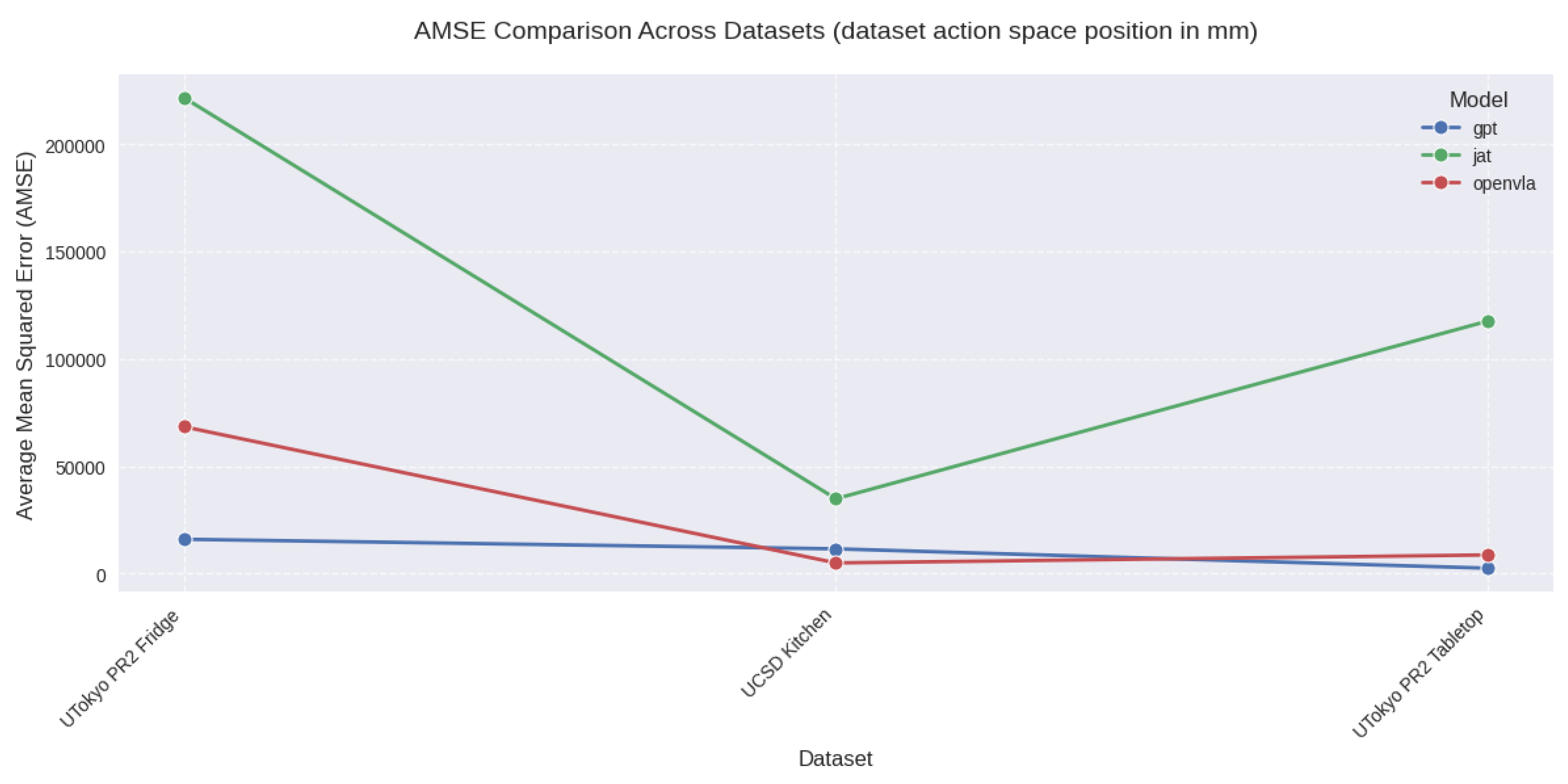
| UCSD Kitchen | 11580.963 | 0.207 | 5018.936 | 0.116 | 34890.635 | 0.353 |
| UCSD Pick Place | 0.650 | 0.086 | 0.535 | 0.175 | 0.614 | 0.210 |
| USC Cloth Sim | 0.223 | 0.260 | 0.234 | 0.305 | 0.109 | 0.375 |
| Tokyo PR2 Fridge | 16035.136 | 0.037 | 68433.175 | 0.159 | 221666.531 | 0.324 |
| Tokyo PR2 Tabletop | 2550.878 | 0.014 | 8728.959 | 0.116 | 117663.493 | 0.364 |
| UTokyo xArm Pick-Place | 0.505 | 0.088 | 1.471 | 0.252 | 2.623 | 0.254 |
| Stanford MaskVIT | 0.645 | 0.120 | 0.163 | 0.184 | 1.060 | 0.571 |
| ETH Agent Affordances | 1.168 | 0.057 | 0.114 | 0.139 | 1.073 | 0.290 |
| Imperial Sawyer | 0.073 | 0.183 | 0.075 | 0.517 | 0.118 | 0.356 |
| ConqHose | 0.127 | 0.024 | 0.084 | 0.264 | 1.373 | 0.178 |
| Plex RoboSuite | 0.471 | 0.067 | 0.280 | 0.206 | 0.950 | 0.142 |
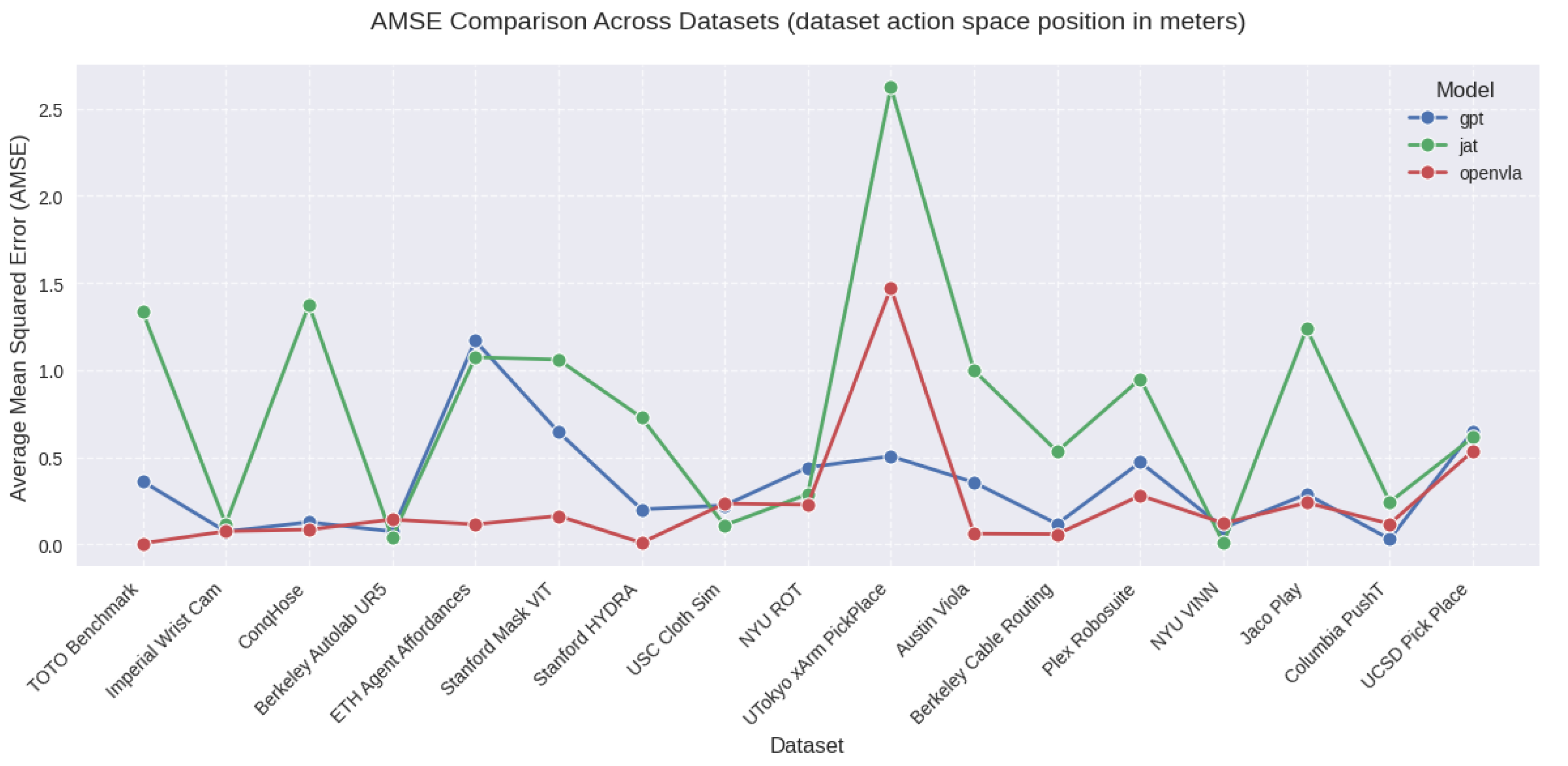
5.1. Average Model Performance Analysis
Overall Performance Patterns
- berkeley_autolab_ur5 (AMSE: 0.074)
- columbia_cairlab_pusht_real (AMSE: 0.030)
- imperialcollege_sawyer_wrist_cam (AMSE: 0.073)
Common Challenges
- Complex manipulation tasks, particularly those involving large movements or multi-step sequences like Kitchen manipulation tasks.
- Tasks requiring significant temporal reasoning or complex action sequences. This follows naturally as the models were assessed in a zero shot fashion.
5.1.1. Model-Specific Analysis
OpenVLA
GPT
JAT
5.1.2. Implications for Future Development
- The variation in performance across robot platforms suggests that more work is needed in developing platform-agnostic control capabilities
- The superior performance of GPT and OpenVLA in their respective strengths suggests that combining their approaches - sophisticated prompt engineering with robotics-specific training - might yield better overall performance
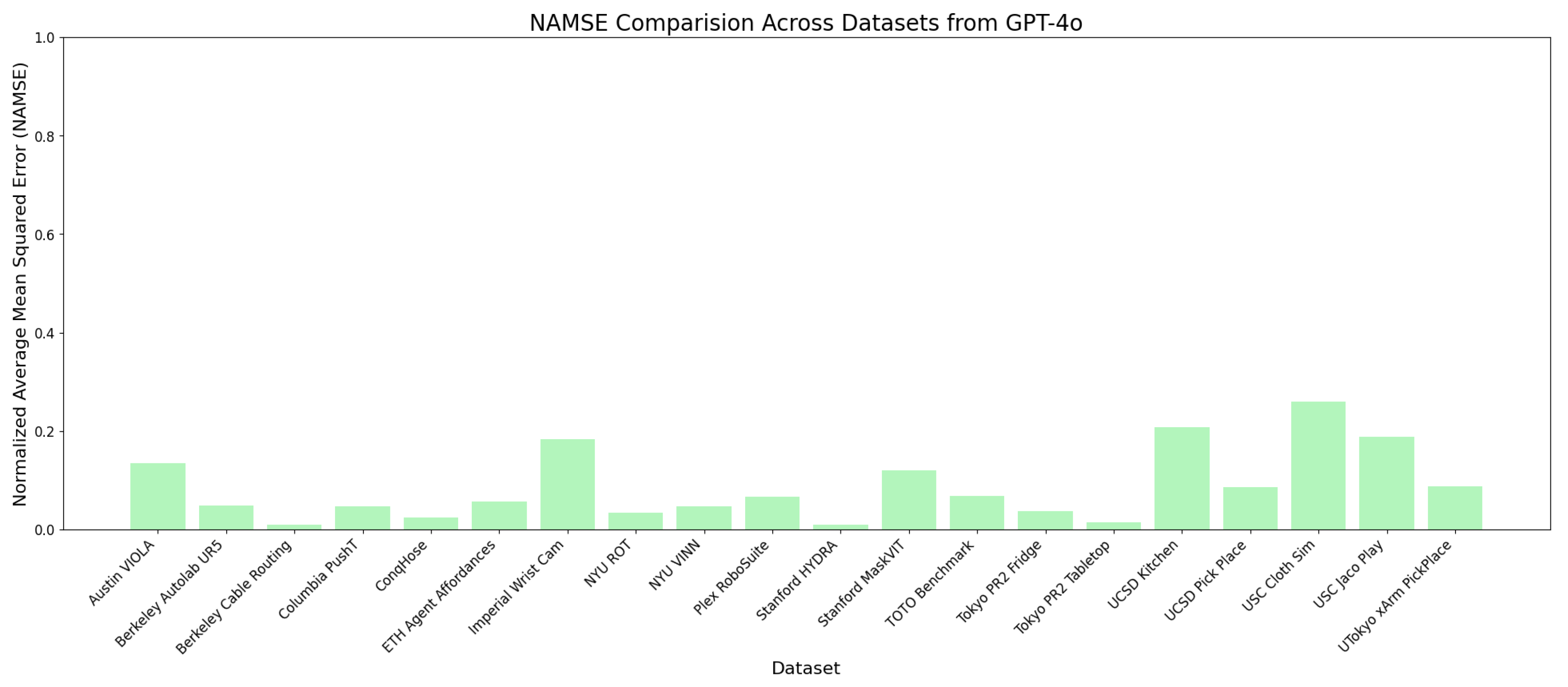
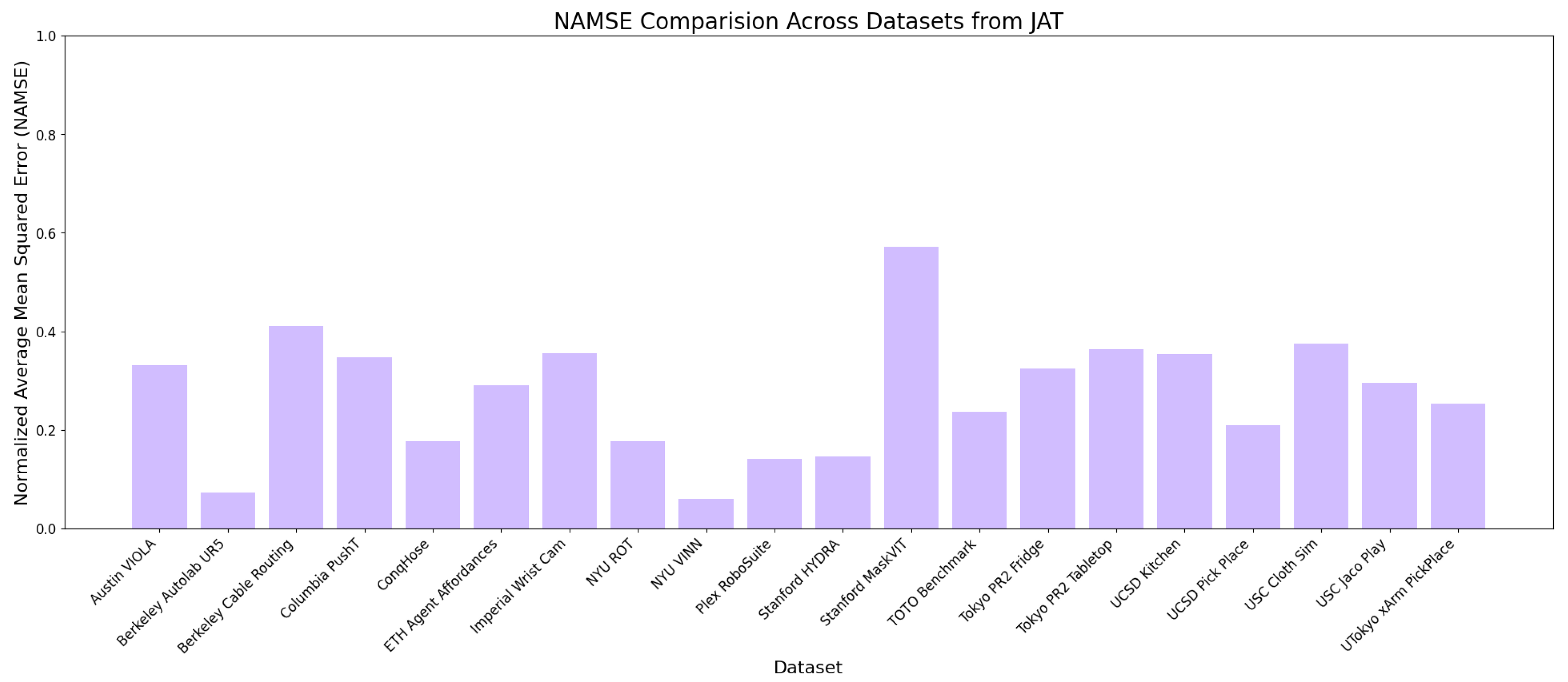
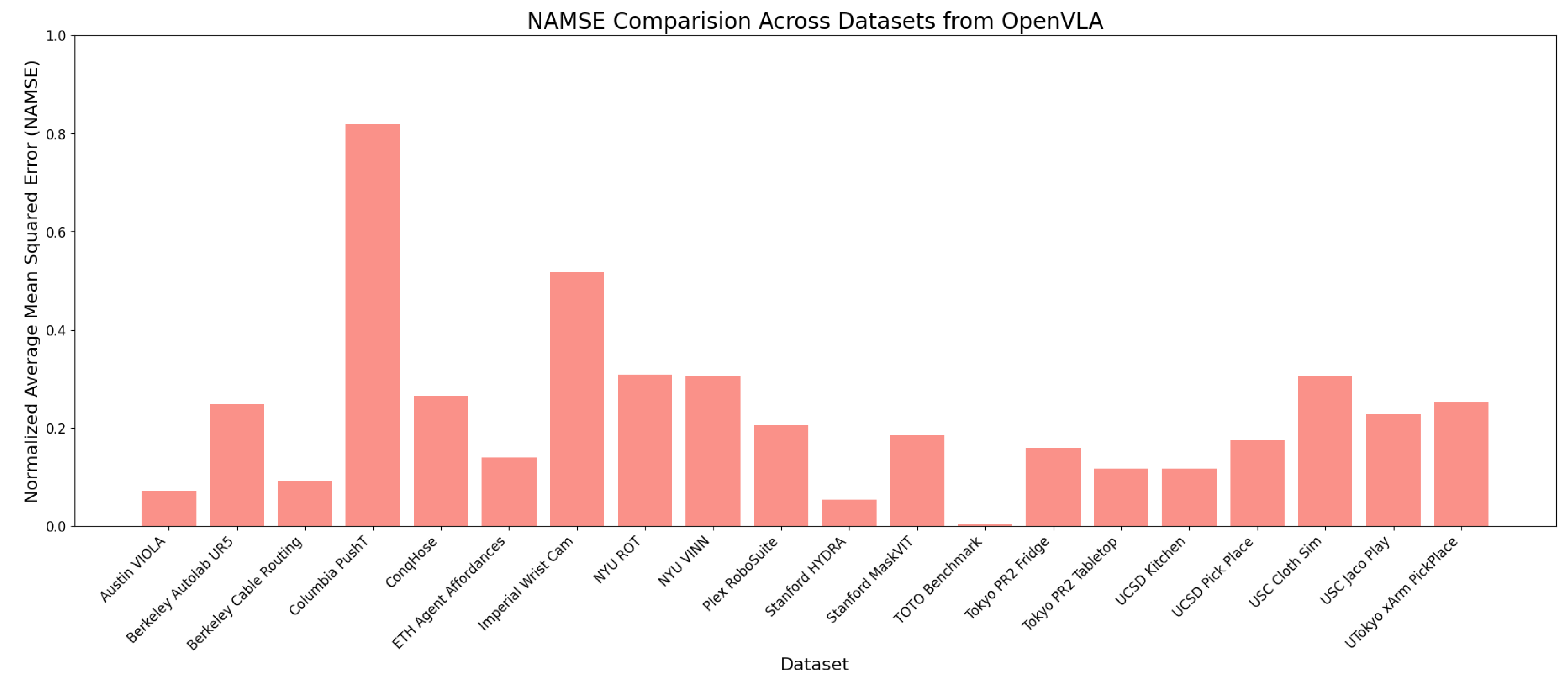
5.2. Normalized Performance Analysis
5.2.1. Model-Specific Performance Patterns
GPT-4o
- Explicit action space statistics (min, max, mean) for each dimension
- Verbal descriptions for each action dimension
- Detailed environment and task descriptions when available
OpenVLA
- Highest normalized error on columbia_cairlab_pusht_real (NAMSE: 0.82)
- Exceptionally strong performance on certain tasks (e.g., toto with NAMSE: 0.003)
- Clear pattern of task-specific performance variations
JAT
- Notable performance spike on ucsd_kitchen_dataset (NAMSE ∼0.57)
- Relatively consistent performance band for similar task types
- Higher baseline NAMSE compared to GPT-4o but more stable than OpenVLA
5.2.2. Cross-Model Insights
Task Difficulty Patterns
- Kitchen manipulation tasks and complex multi-step operations consistently show higher NAMSE
- Simple pick-and-place operations tend to show lower normalized error
- Tasks requiring precise control generally result in higher normalized error
Architectural Implications
- GPT-4o’s consistent normalized performance suggests its architecture and prompting strategy create a more generally robust system
- OpenVLA’s high variation indicates stronger task specialization, possibly due to its training approach and dual visual encoder
- JAT’s moderate but consistent variation suggests a middle ground between specialization and generalization
6. Future Work
- Compositional Generalization: Evaluating how well VLAs can combine learned primitives to solve novel tasks, particularly in scenarios requiring multi-step reasoning or tool use.
- Long Sequence Reliability: Developing metrics to assess the consistency of model behavior over extended sequences, including the ability to maintain goals and adapt to changing conditions.
- Cross-Embodiment Transfer: Further investigating how knowledge transfers between different robot morphologies, potentially leading to more efficient training strategies for new platforms.
- Memory and Long-Term Planning: Assessing models’ capabilities in tasks requiring long-term memory and strategic planning, particularly in multi-phase manipulation tasks.
- Multi-Agent Interaction: Extending the benchmark to scenarios involving multiple agents, evaluating coordination and collaborative manipulation capabilities.
7. Conclusions
Appendix A.
Appendix A.1. Dataset Coverage, Completion Rate, and Additional AMSE Recordings
| Dataset Name | Registered Dataset Name | JAT | GPT | OpenVLA | Action Space Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-1 Robot Action | fractal20220817_data | ✓ | 10D (2 pos for base, 1 ang for base, 1 grip, 3 ang for arm, 3 pos for arm) | ||
| QT-Opt | kuka | ✓ | 10D (2 pos for base, 1 ang for base, 1 grip, 3 ang for arm, 3 pos for arm) | ||
| Berkeley Bridge | bridge | ✓ | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang,1 term) | ||
| Freiburg Franka Play | taco_play | ✓ | – | ||
| USC Jaco Play | jaco_play | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 4D (1 grip, 3 pos) |
| Berkeley Cable Routing | berkeley_cable_routing | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7D (3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| Roboturk | roboturk | ✓ | – | ||
| NYU VINN | nyu_door_opening_surprising_effectiveness | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8D (1 grip, 3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| Austin VIOLA | viola | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8D (1 grip, 3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| Berkeley Autolab UR5 | berkeley_autolab_ur5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8D (1 grip, 3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| TOTO Benchmark | toto | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7D (3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| Language Table | language_table | ✓ | 2D | ||
| Columbia PushT | columbia_cairlab_pusht_real | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8D (1 grip, 3 ang, 3 pos, 1 term) |
| NYU ROT | nyu_rot_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) |
| Stanford HYDRA | stanford_hydra_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) |
| NYU Franka Play | nyu_franka_play_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| Maniskill | maniskill_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| Furniture Bench | furniture_bench_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | 8D (3 pos, 4 quat, 1 grip) | ||
| CMU Franka Exploration | cmu_franka_exploration_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| UCSD Kitchen | ucsd_kitchen_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip, 1 term) |
| UCSD Pick Place | ucsd_pick_and_place_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 4D (3 vel, 1 grip torque) |
| Austin Sirius | austin_sirius_dataset_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| BC-Z | bc_z | ✓ | 61D (30 pos, 30 ang, 1 grip) | ||
| USC Cloth Sim | usc_cloth_sim_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 4D (3 pos, 1 grip) |
| Tokyo PR2 Fridge | utokyo_pr2_opening_fridge_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip, 1 term) |
| Tokyo PR2 Tabletop | utokyo_pr2_tabletop_manipulation_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip, 1 term) |
| Saytap | utokyo_saytap_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| UTokyo xArm PickPlace | utokyo_xarm_pick_and_place_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) |
| UTokyo xArm Bimanual | utokyo_xarm_bimanual_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | 14D (dual arm 7D control) | |
| Berkeley MVP Data | berkeley_mvp_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| Berkeley RPT Data | berkeley_rpt_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| KAIST Nonprehensile | kaist_nonprehensile_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | 20D (3 pos, 3 ang, 7 gain coeff, 7 damping ratio coeff) | |
| Stanford MaskVIT | stanford_mask_vit_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 5D (3 pos, 1 ang, 1 grip) |
| LSMO Dataset | tokyo_u_lsmo_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| ConqHose | conq_hose_manipulation | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip) |
| ETH Agent Affordances | eth_agent_affordances | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 6D (3 vel, 3 ang vel) |
| Imperial Wrist Cam | imperialcollege_sawyer_wrist_cam | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8D (3 pos, 3 ang, 1 grip, 1 term) |
| Plex RoboSuite | plex_robosuite | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7D (6 pose, 1 grip) |
| DLR Sara Grid Clamp Dataset | dlr_sara_grid_clamp_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| DLR Sara Pour Dataset | dlr_sara_pour_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| DLR Wheelchair Shared Control | dlr_edan_shared_control_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| ASU TableTop Manipulationl | asu_table_top_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| CMU Franka Pick-Insert Data | iamlab_cmu_pickup_insert_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| Austin Mutex | utaustin_mutex | ✓ | – | ||
| Stanford Robocook | stanford_robocook_converted_externally_to_rlds | ✓ | – | ||
| CMU Play Fusion | cmu_play_fusion | ✓ | – | ||
| CMU Stretch | cmu_stretch | ✓ | – | ||
| RECON | berkeley_gnm_recon | ✓ | – | ||
| CoryHall | berkeley_gnm_cory_hall | ✓ | – | ||
| SACSoN | berkeley_gnm_sac_son | ✓ | – | ||
| DobbE | dobbe | ✓ | – | ||
| IO-AI Office PicknPlace | io_ai_tech | ✓ | – | ||
| RoboSet | robo_set | ✓ | – |
| Dataset Name | GPT | OpenVLA | JAT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jaco Play | 0.917% | 29.358% | 0.000% |
| Berkeley Cable Routing | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| NYU Door Opening | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| VIOLA | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| Berkeley Autolab UR5 | 1.923% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| TOTO | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| Columbia PushT | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| NYU ROT | 7.143% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| Stanford HYDRA | 0.833% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| UCSD Kitchen | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| UCSD Pick Place | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| USC Cloth Sim | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| Tokyo PR2 Fridge | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| Tokyo PR2 Tabletop | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| UTokyo xArm Pick-Place | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| Stanford MaskVIT | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| ETH Agent Affordances | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| Imperial Sawyer | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| ConqHose | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
| Plex RoboSuite | 0.000% | 0.000% | 0.000% |
References
- Brohan, A.; Brown, N.; Carbajal, J.; Chebotar, Y.; Chen, X.; Choromanski, K.; Ding, T.; Driess, D.; Dubey, A.; Finn, C. ; others. Rt-2: Vision-language-action models transfer web knowledge to robotic control. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2307.15818 2023.
- Walke, H.R.; Black, K.; Zhao, T.Z.; Vuong, Q.; Zheng, C.; Hansen-Estruch, P.; He, A.W.; Myers, V.; Kim, M.J.; Du, M. ; others. Bridgedata v2: A dataset for robot learning at scale. Conference on Robot Learning. PMLR, 2023, pp. 1723–1736.
- Brohan, A.; Brown, N.; Carbajal, J.; Chebotar, Y.; Dabis, J.; Finn, C.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Hausman, K.; Herzog, A.; Hsu, J. ; others. Rt-1: Robotics transformer for real-world control at scale. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2212.06817 2022.
- Chi, C.; Xu, Z.; Feng, S.; Cousineau, E.; Du, Y.; Burchfiel, B.; Tedrake, R.; Song, S. Diffusion policy: Visuomotor policy learning via action diffusion. The International Journal of Robotics Research 2023, 02783649241273668. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, A.; Lee, L.; Xiao, T.; Finn, C. Decomposing the generalization gap in imitation learning for visual robotic manipulation. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2024, pp. 3153–3160.
- Team, O.M.; Ghosh, D.; Walke, H.; Pertsch, K.; Black, K.; Mees, O.; Dasari, S.; Hejna, J.; Kreiman, T.; Xu, C. ; others. Octo: An open-source generalist robot policy. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2405.12213 2024.
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y. ; others. Segment anything. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 4015–4026.
- Minderer, M.; Gritsenko, A.; Stone, A.; Neumann, M.; Weissenborn, D.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Mahendran, A.; Arnab, A.; Dehghani, M.; Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhai, X.; Kipf, T.; Houlsby, N. Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformer. 2022; arXiv:cs.CV/2205.06230. [Google Scholar]
- Alayrac, J.B.; Miech, A.; Laptev, I.; Sivic, J.; others. Multi-Task Learning of Object States and State-Modifying Actions from Web Videos. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Driess, D.; Xia, F.; Sajjadi, M.S.; Lynch, C.; Chowdhery, A.; Ichter, B.; Wahid, A.; Tompson, J.; Vuong, Q.; Yu, T. ; others. Palm-e: An embodied multimodal language model. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2303.03378 2023.
- Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, L.; Lin, K.; Gan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. Git: A generative image-to-text transformer for vision and language. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2205.14100 2022.
- Chen, M.; Tworek, J.; Jun, H.; Yuan, Q.; Pinto, H.P.D.O.; Kaplan, J.; Edwards, H.; Burda, Y.; Joseph, N.; Brockman, G. ; others. Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2107.03374 2021.
- Kaplan, J.; McCandlish, S.; Henighan, T.; Brown, T.B.; Chess, B.; Child, R.; Gray, S.; Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Amodei, D. Scaling laws for neural language models. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2001.08361 2020.
- Hoffmann, J.; Borgeaud, S.; Mensch, A.; Buchatskaya, E.; Cai, T.; Rutherford, E.; Casas, D.d.L.; Hendricks, L.A.; Welbl, J.; Clark, A. ; others. Training compute-optimal large language models. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2203.15556 2022.
- Sutton, R. The bitter lesson. Incomplete Ideas (blog) 2019, 13, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Collaboration, O.X.E.; O’Neill, A.; Rehman, A.; Gupta, A.; Maddukuri, A.; Gupta, A.; Padalkar, A.; Lee, A.; Pooley, A.; Gupta, A.; Mandlekar, A.; Jain, A.; Tung, A.; Bewley, A.; Herzog, A.; Irpan, A.; Khazatsky, A.; Rai, A.; Gupta, A.; Wang, A.; Kolobov, A.; Singh, A.; Garg, A.; Kembhavi, A.; Xie, A.; Brohan, A.; Raffin, A.; Sharma, A.; Yavary, A.; Jain, A.; Balakrishna, A.; Wahid, A.; Burgess-Limerick, B.; Kim, B.; Schölkopf, B.; Wulfe, B.; Ichter, B.; Lu, C.; Xu, C.; Le, C.; Finn, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, C.; Chi, C.; Huang, C.; Chan, C.; Agia, C.; Pan, C.; Fu, C.; Devin, C.; Xu, D.; Morton, D.; Driess, D.; Chen, D.; Pathak, D.; Shah, D.; Büchler, D.; Jayaraman, D.; Kalashnikov, D.; Sadigh, D.; Johns, E.; Foster, E.; Liu, F.; Ceola, F.; Xia, F.; Zhao, F.; Frujeri, F.V.; Stulp, F.; Zhou, G.; Sukhatme, G.S.; Salhotra, G.; Yan, G.; Feng, G.; Schiavi, G.; Berseth, G.; Kahn, G.; Yang, G.; Wang, G.; Su, H.; Fang, H.S.; Shi, H.; Bao, H.; Amor, H.B.; Christensen, H.I.; Furuta, H.; Bharadhwaj, H.; Walke, H.; Fang, H.; Ha, H.; Mordatch, I.; Radosavovic, I.; Leal, I.; Liang, J.; Abou-Chakra, J.; Kim, J.; Drake, J.; Peters, J.; Schneider, J.; Hsu, J.; Vakil, J.; Bohg, J.; Bingham, J.; Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Hu, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Sun, J.; Luo, J.; Gu, J.; Tan, J.; Oh, J.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Malik, J.; Silvério, J.; Hejna, J.; Booher, J.; Tompson, J.; Yang, J.; Salvador, J.; Lim, J.J.; Han, J.; Wang, K.; Rao, K.; Pertsch, K.; Hausman, K.; Go, K.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Goldberg, K.; Byrne, K.; Oslund, K.; Kawaharazuka, K.; Black, K.; Lin, K.; Zhang, K.; Ehsani, K.; Lekkala, K.; Ellis, K.; Rana, K.; Srinivasan, K.; Fang, K.; Singh, K.P.; Zeng, K.H.; Hatch, K.; Hsu, K.; Itti, L.; Chen, L.Y.; Pinto, L.; Fei-Fei, L.; Tan, L.; Fan, L.J.; Ott, L.; Lee, L.; Weihs, L.; Chen, M.; Lepert, M.; Memmel, M.; Tomizuka, M.; Itkina, M.; Castro, M.G.; Spero, M.; Du, M.; Ahn, M.; Yip, M.C.; Zhang, M.; Ding, M.; Heo, M.; Srirama, M.K.; Sharma, M.; Kim, M.J.; Kanazawa, N.; Hansen, N.; Heess, N.; Joshi, N.J.; Suenderhauf, N.; Liu, N.; Palo, N.D.; Shafiullah, N.M.M.; Mees, O.; Kroemer, O.; Bastani, O.; Sanketi, P.R.; Miller, P.T.; Yin, P.; Wohlhart, P.; Xu, P.; Fagan, P.D.; Mitrano, P.; Sermanet, P.; Abbeel, P.; Sundaresan, P.; Chen, Q.; Vuong, Q.; Rafailov, R.; Tian, R.; Doshi, R.; Mart’in-Mart’in, R.; Baijal, R.; Scalise, R.; Hendrix, R.; Lin, R.; Qian, R.; Zhang, R.; Mendonca, R.; Shah, R.; Hoque, R.; Julian, R.; Bustamante, S.; Kirmani, S.; Levine, S.; Lin, S.; Moore, S.; Bahl, S.; Dass, S.; Sonawani, S.; Tulsiani, S.; Song, S.; Xu, S.; Haldar, S.; Karamcheti, S.; Adebola, S.; Guist, S.; Nasiriany, S.; Schaal, S.; Welker, S.; Tian, S.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Dasari, S.; Belkhale, S.; Park, S.; Nair, S.; Mirchandani, S.; Osa, T.; Gupta, T.; Harada, T.; Matsushima, T.; Xiao, T.; Kollar, T.; Yu, T.; Ding, T.; Davchev, T.; Zhao, T.Z.; Armstrong, T.; Darrell, T.; Chung, T.; Jain, V.; Kumar, V.; Vanhoucke, V.; Zhan, W.; Zhou, W.; Burgard, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Geng, X.; Liu, X.; Liangwei, X.; Li, X.; Pang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Chebotar, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bisk, Y.; Dou, Y.; Cho, Y.; Lee, Y.; Cui, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Iwasawa, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cui, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Lin, Z. Open X-Embodiment: Robotic Learning Datasets and RT-X Models. https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.08864, 2023.
- Khazatsky, A.; Pertsch, K.; Nair, S.; Balakrishna, A.; Dasari, S.; Karamcheti, S.; Nasiriany, S.; Srirama, M.K.; Chen, L.Y.; Ellis, K. ; others. Droid: A large-scale in-the-wild robot manipulation dataset. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2403.12945 2024.
- Shridhar, M.; Manuelli, L.; Fox, D. Cliport: What and where pathways for robotic manipulation. Conference on robot learning. PMLR, 2022, pp. 894–906.
- Nair, S.; Rajeswaran, A.; Kumar, V.; Finn, C.; Gupta, A. R3m: A universal visual representation for robot manipulation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2203.12601 2022.
- Karamcheti, S.; Nair, S.; Chen, A.S.; Kollar, T.; Finn, C.; Sadigh, D.; Liang, P. Language-driven representation learning for robotics. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2302.12766 2023.
- Stone, A.; Xiao, T.; Lu, Y.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Lee, K.H.; Vuong, Q.; Wohlhart, P.; Kirmani, S.; Zitkovich, B.; Xia, F. ; others. Open-world object manipulation using pre-trained vision-language models. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2303.00905 2023.
- Kim, M.J.; Pertsch, K.; Karamcheti, S.; Xiao, T.; Balakrishna, A.; Nair, S.; Rafailov, R.; Foster, E.; Lam, G.; Sanketi, P. ; others. OpenVLA: An Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Model. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2406.09246 2024.
- Marcu, A.M.; Chen, L.; Hünermann, J.; Karnsund, A.; Hanotte, B.; Chidananda, P.; Nair, S.; Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Shotton, J.; Arani, E.; Sinavski, O. LingoQA: Visual Question Answering for Autonomous Driving. 2024; arXiv:cs.RO/2312.14115]. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.P.; Lyu, Y.; Fan, X.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, P.; Lee, M.A.; Zhu, Y.; others. Multibench: Multiscale benchmarks for multimodal representation learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2021, 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, T.; Liu, R.; Zhang, G.; Stevens, S.; Jiang, D.; Ren, W.; Sun, Y. ; others. Mmmu: A massive multi-discipline multimodal understanding and reasoning benchmark for expert agi. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024, pp. 9556–9567.
- Antol, S.; Agrawal, A.; Lu, J.; Mitchell, M.; Batra, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Parikh, D. Vqa: Visual question answering. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2015, pp. 2425–2433.
- Marino, K.; Rastegari, M.; Farhadi, A.; Mottaghi, R. Ok-vqa: A visual question answering benchmark requiring external knowledge. Proceedings of the IEEE/cvf conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 3195–3204.
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer, 2014, pp. 740–755.
- Hudson, D.A.; Manning, C.D. Gqa: A new dataset for real-world visual reasoning and compositional question answering. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 6700–6709.
- Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.X.; Wen, J.R. Evaluating object hallucination in large vision-language models. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2305.10355 2023.
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, G.; Shi, P.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H.; Ye, Q.; Yan, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J. ; others. Evaluation and analysis of hallucination in large vision-language models. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2308.15126 2023.
- Yin, Z.; Wang, J.; Cao, J.; Shi, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; Sheng, L.; Bai, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z. ; others. LAMM: Language-Assisted Multi-Modal Instruction-Tuning Dataset. Framework, and Benchmark, 2023; 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Shao, W.; Zhang, K.; Gao, P.; Liu, S.; Lei, M.; Meng, F.; Huang, S.; Qiao, Y.; Luo, P. Lvlm-ehub: A comprehensive evaluation benchmark for large vision-language models. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2306.09265 2023.
- Ge, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, X.; Shan, Y. Planting a seed of vision in large language model. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2307.08041 2023.
- Zhang, Y.Z.B.L.S.; Wang, W.Z.Y.Y.J.; Chen, C.H.Z.L.K.; Liu, D.L.Y.; Duan, H. Mmbench: Is your multi-modal model an all-around player. arXiv preprint 2023, arXiv:2307.06281 2023, 222. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Mm-vet: Evaluating large multimodal models for integrated capabilities. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2308.02490 2023.
- Lu, P.; Bansal, H.; Xia, T.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Hajishirzi, H.; Cheng, H.; Chang, K.W.; Galley, M.; Gao, J. Mathvista: Evaluating mathematical reasoning of foundation models in visual contexts. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2310.02255 2023.
- Mialon, G.; Fourrier, C.; Swift, C.; Wolf, T.; LeCun, Y.; Scialom, T. Gaia: a benchmark for general ai assistants. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2311.12983 2023.
- Pumacay, W.; Singh, I.; Duan, J.; Krishna, R.; Thomason, J.; Fox, D. The colosseum: A benchmark for evaluating generalization for robotic manipulation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2402.08191 2024.
- Xing, E.; Gupta, A.; Powers, S.; Dean, V. Kitchenshift: Evaluating zero-shot generalization of imitation-based policy learning under domain shifts. NeurIPS 2021 Workshop on Distribution Shifts: Connecting Methods and Applications, 2021.
- James, S.; Ma, Z.; Arrojo, D.R.; Davison, A.J. RLBench: The Robot Learning Benchmark & Learning Environment. arXiv e-prints, art. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1909.12271 2019.
- Huang, J.; Ping, W.; Xu, P.; Shoeybi, M.; Chang, K.C.C.; Catanzaro, B. Raven: In-context learning with retrieval augmented encoder-decoder language models. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2308.07922 2023.
- Heo, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, D.; Lim, J.J. Furniturebench: Reproducible real-world benchmark for long-horizon complex manipulation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2305.12821 2023.
- Liu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, C.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Stone, P. Libero: Benchmarking knowledge transfer for lifelong robot learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Xu, C.; Liu, F.; Tan, L.; Lin, Z.; Wu, J.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. FMB: A functional manipulation benchmark for generalizable robotic learning. The International Journal of Robotics Research 2023, 02783649241276017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Landeghem, J.; Tito, R. ; Borchmann,.; Pietruszka, M.; Joziak, P.; Powalski, R.; Jurkiewicz, D.; Coustaty, M.; Anckaert, B.; Valveny, E.; others. Document understanding dataset and evaluation (dude). Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 19528–19540.
- Deitke, M.; VanderBilt, E.; Herrasti, A.; Weihs, L.; Ehsani, K.; Salvador, J.; Han, W.; Kolve, E.; Kembhavi, A.; Mottaghi, R. ProcTHOR: Large-Scale Embodied AI Using Procedural Generation. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 5982–5994. [Google Scholar]
- Gallouédec, Q.; Beeching, E.; Romac, C.; Dellandréa, E. Jack of All Trades, Master of Some, a Multi-Purpose Transformer Agent. 2024; arXiv:cs.AI/2402.09844]. [Google Scholar]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S. ; others. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2303.08774 2023.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




