Submitted:
08 November 2024
Posted:
08 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
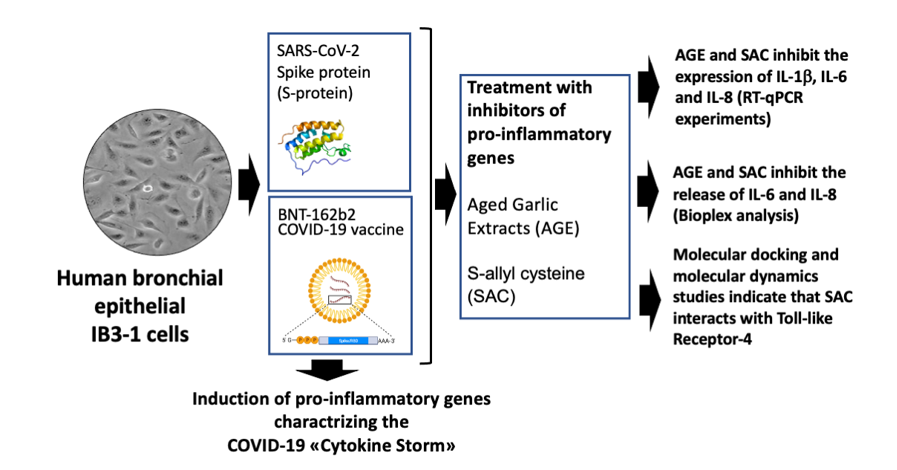
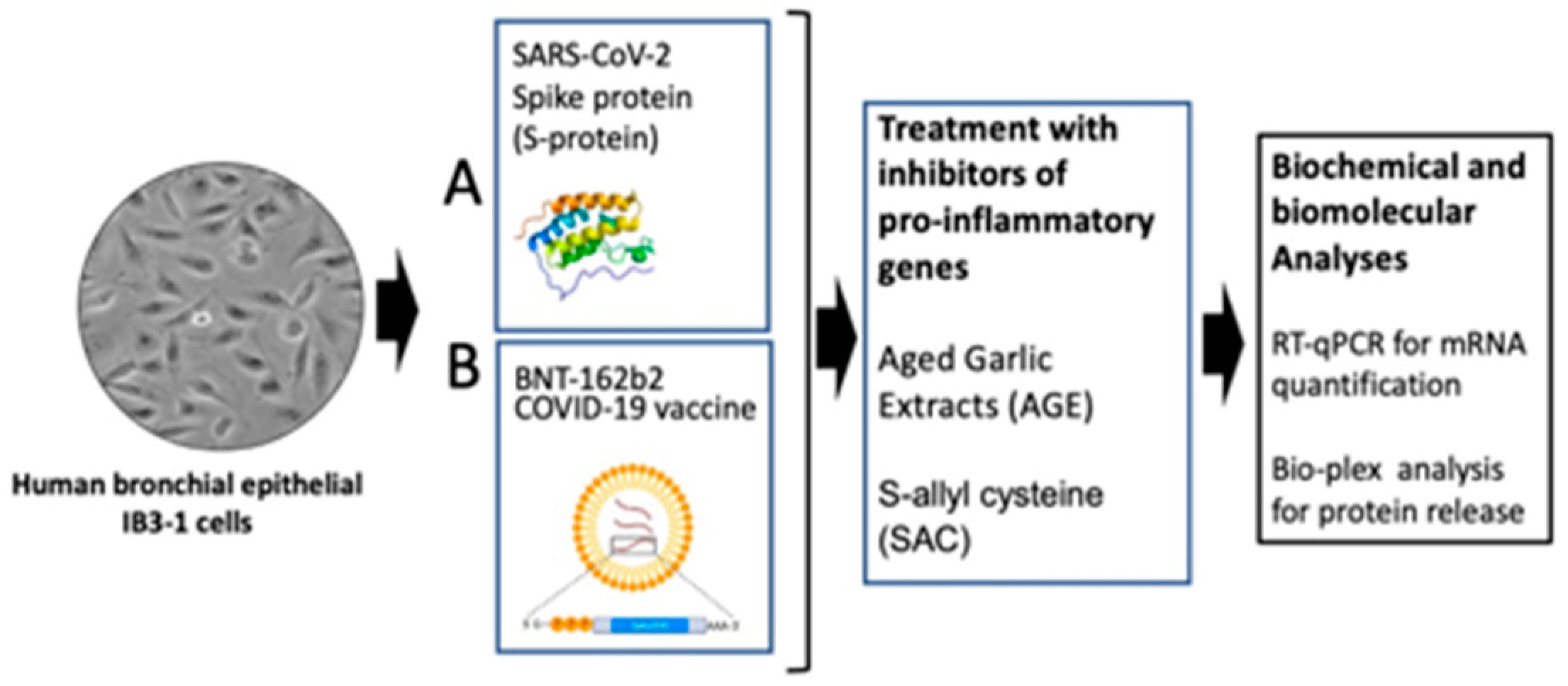
2.1. The Experimental Model System: Induction of Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Bronchial Epithelial IB3-1 Cells After Exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and the COVID-19 BNT162b2 Vaccine
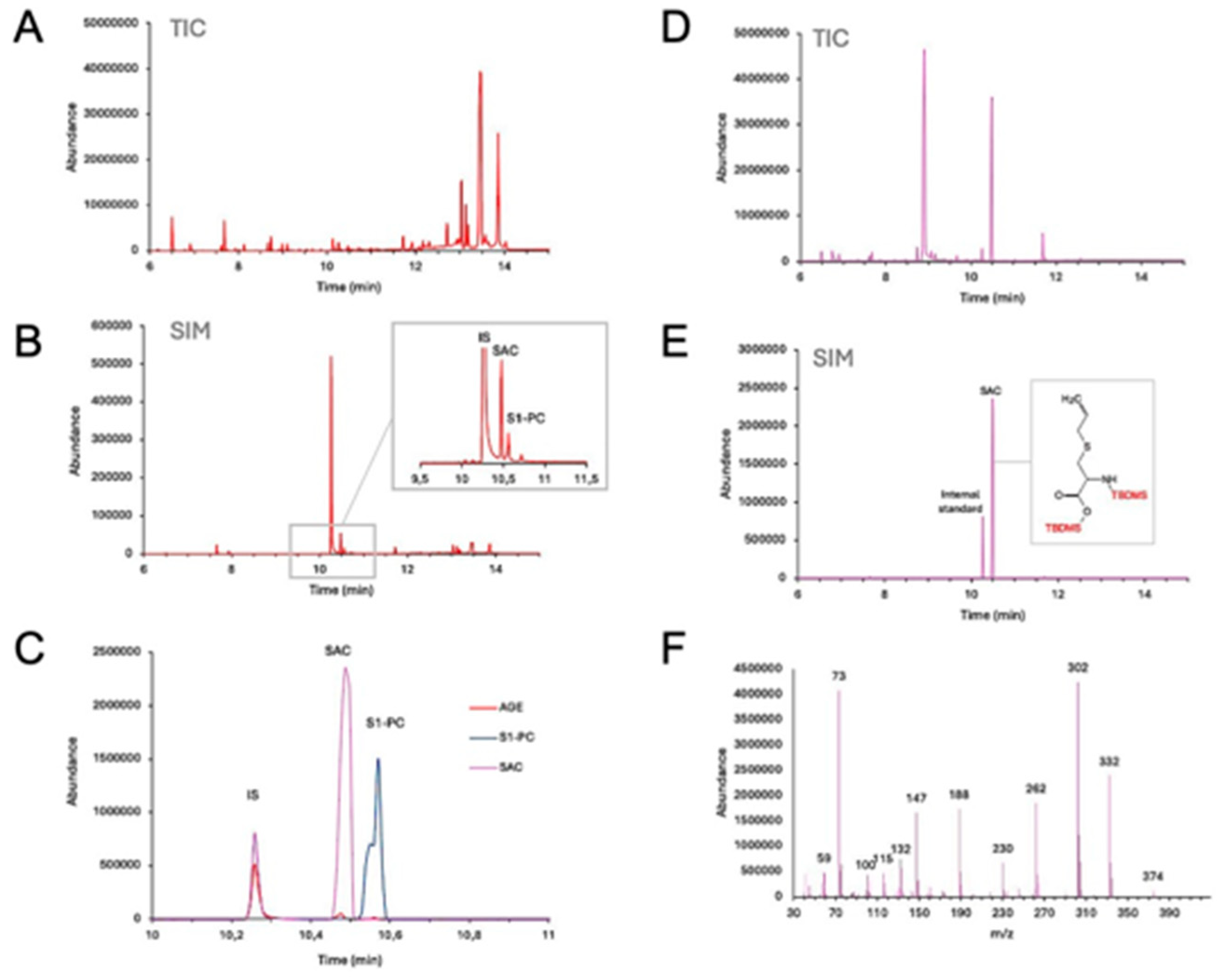
2.2. GC-MS Analysis of AGE and SAC
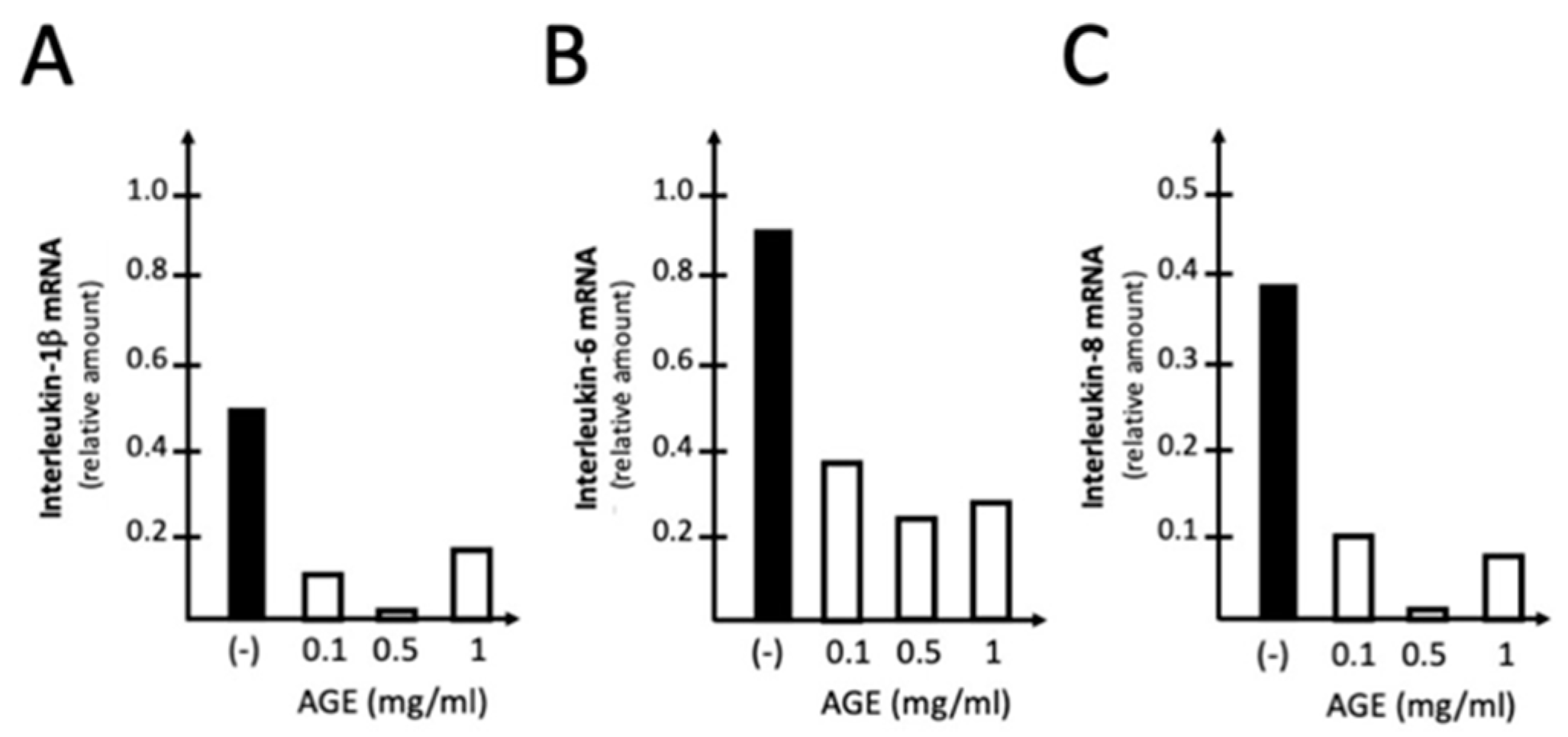
2.3. The Treatment of IB3-1 Cells with AGE Reverses Upregulation of Pro-Inflammatory Genes Induced by SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
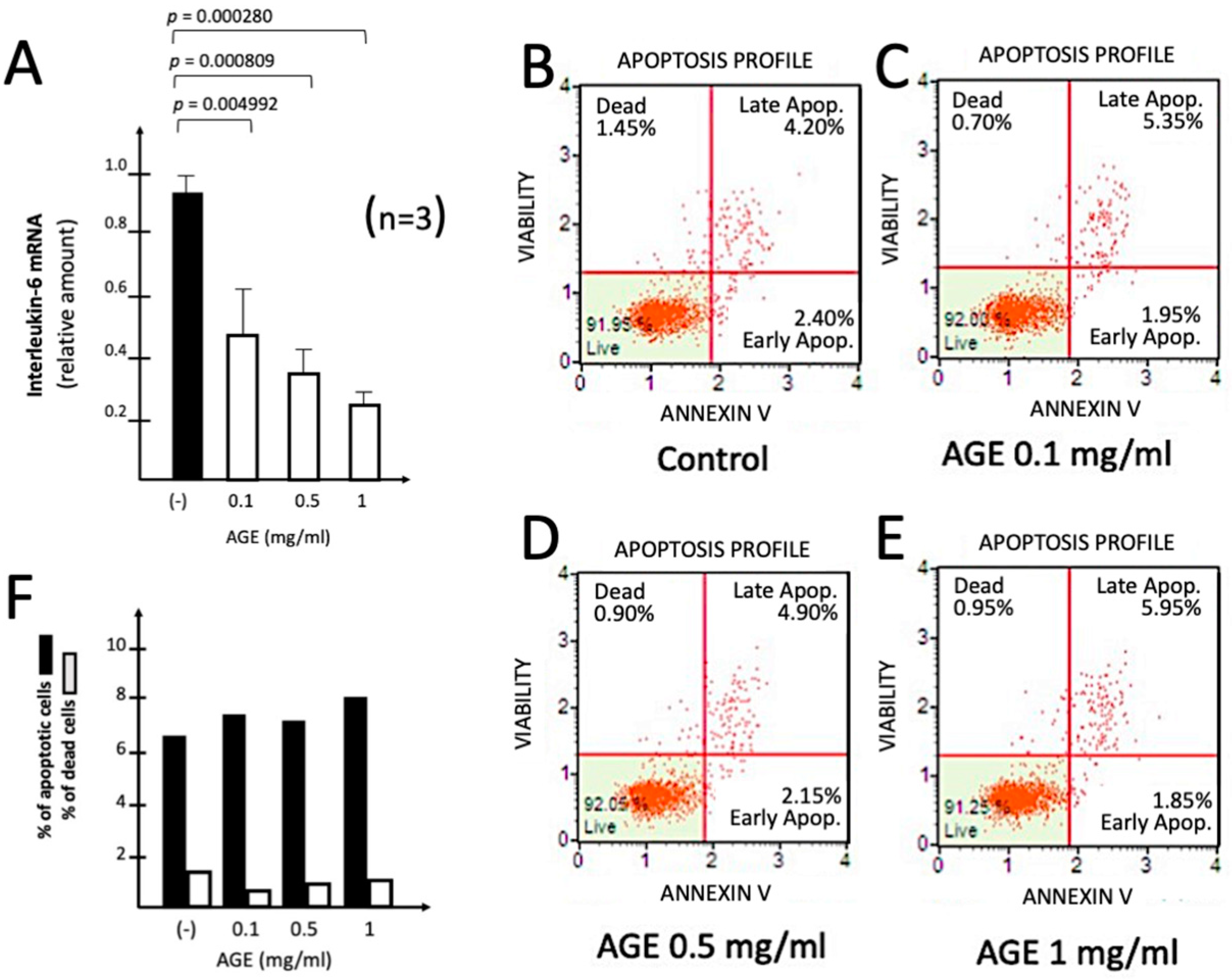
2.4. Effects of AGE on Toxicity and Apoptosis
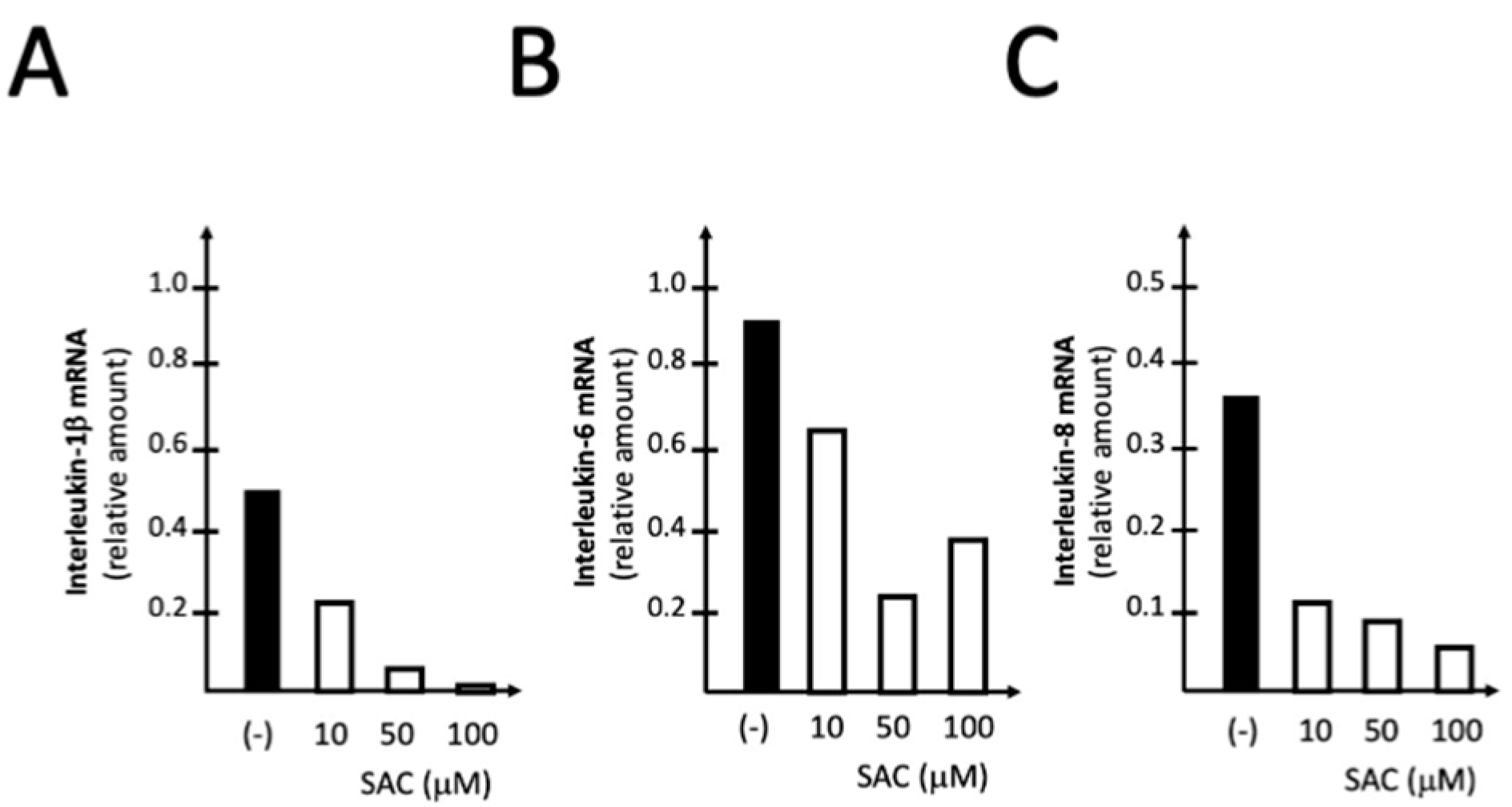
2.5. The Treatment of IB3-1 Cells with S-allyl-cysteine (SAC) Inhibits the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Genes Induced by SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
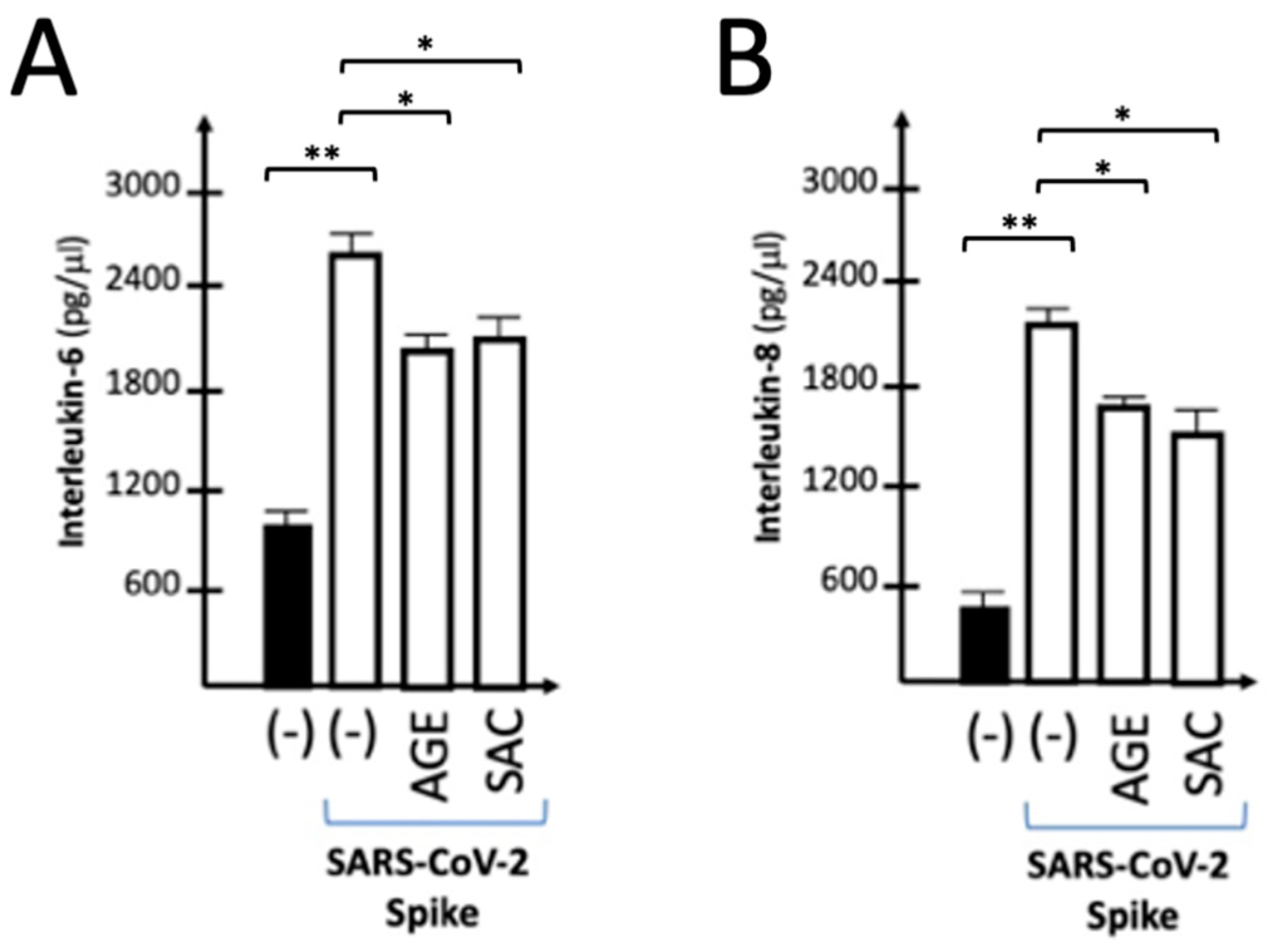
2.6. Effects of AGE and SAC on the Release of IL-6 and IL-8 by IB3-1 Cells Induced to Express Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 S-Protein
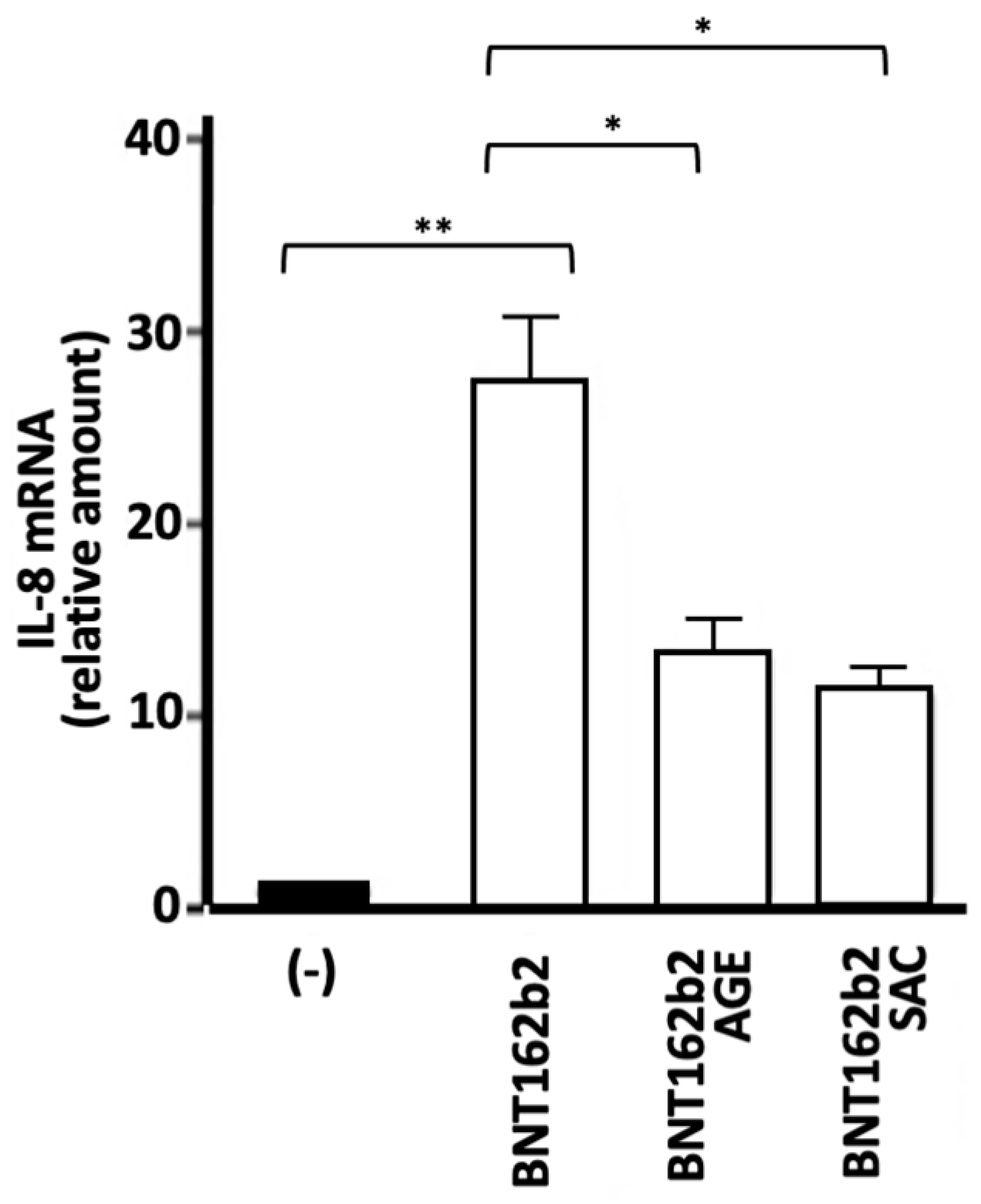
2.7. Effects of AGE and SAC on the Expression of Proinflammatory Genes Induced by the BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine
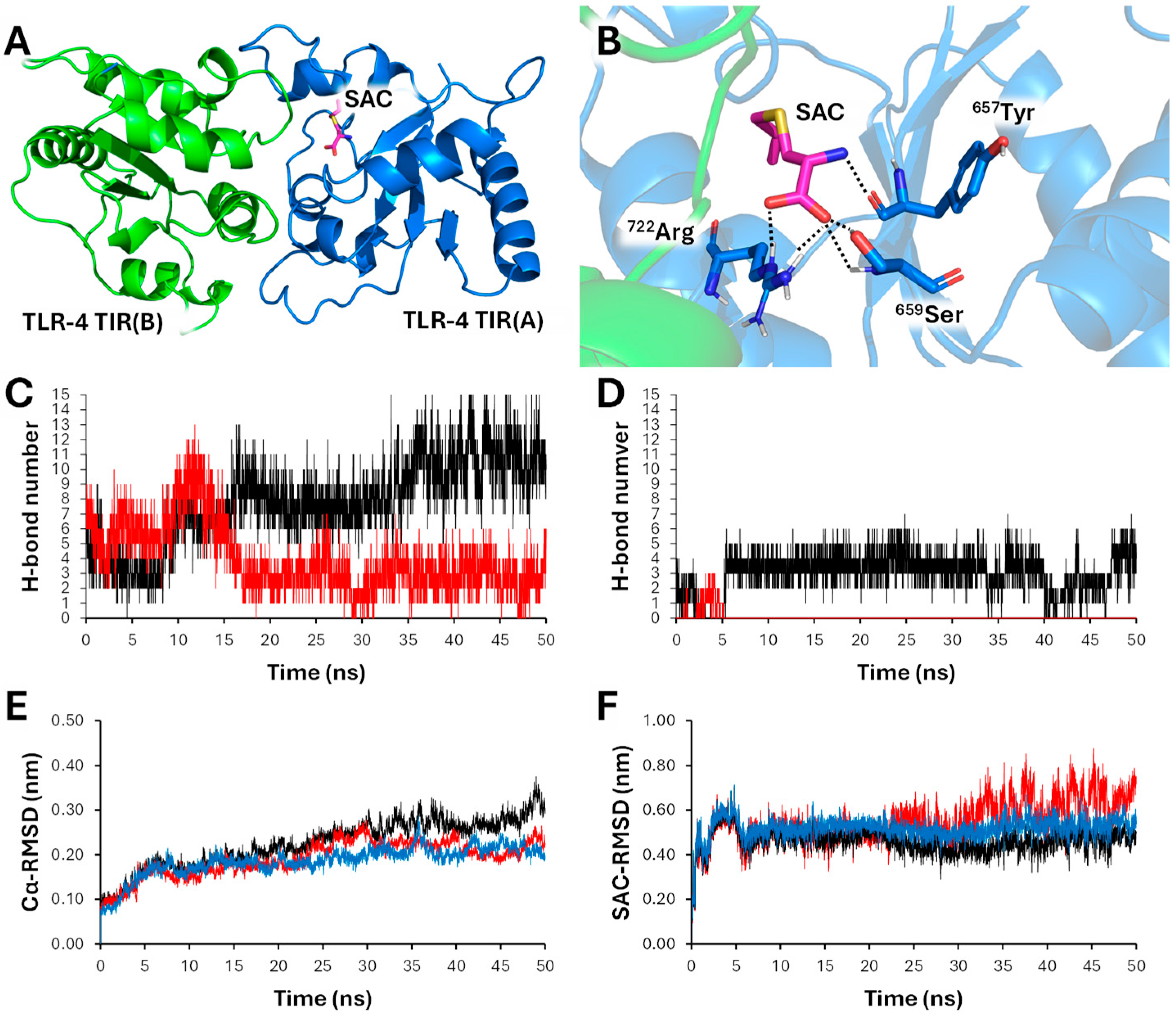
2.8. S-allyl-cysteine (SAC) Efficiently Interacts with Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4): Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Analyses
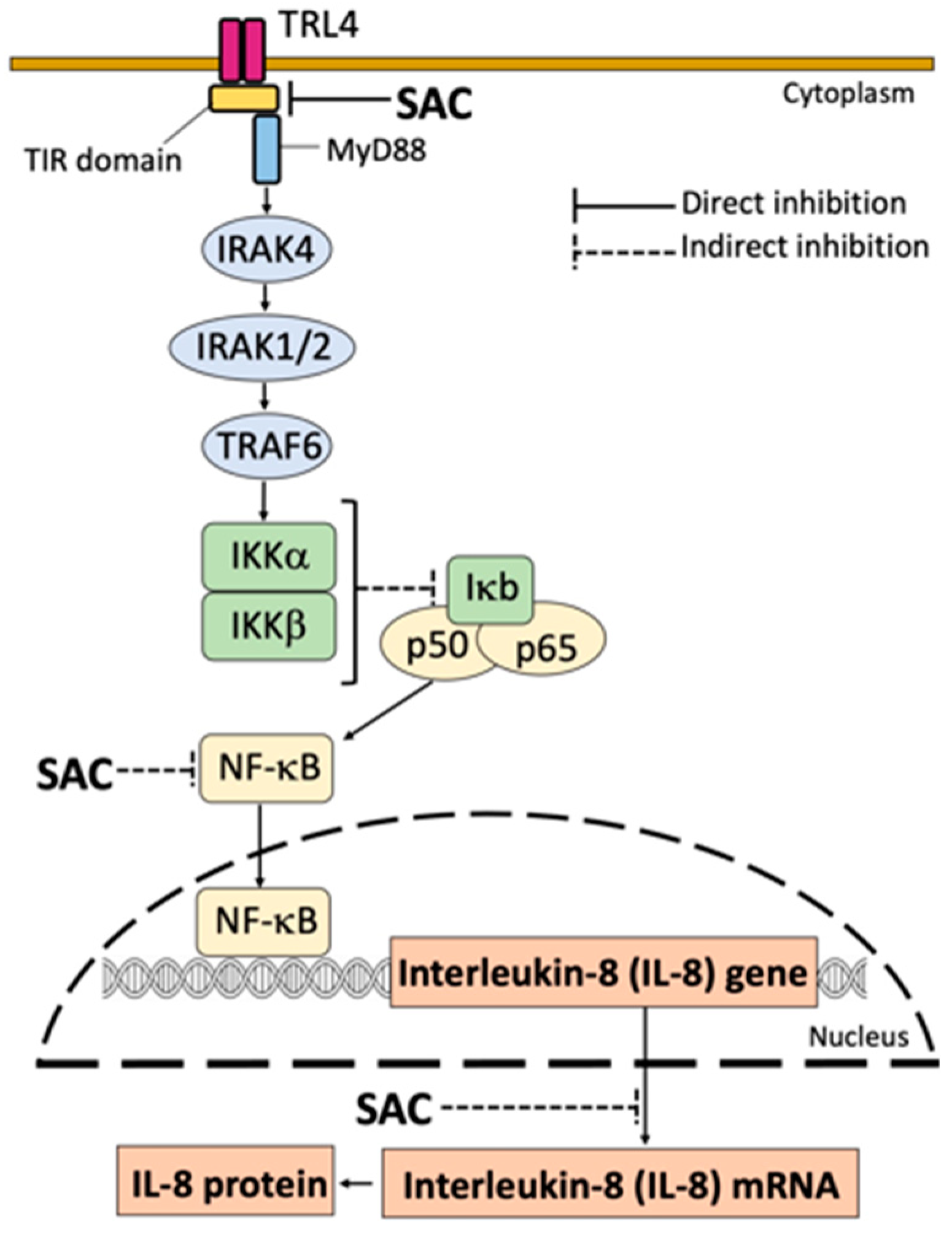
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. AGE Extraction and Chemical Characterization
4.3. Cell Culture Conditions
4.4. Stimulation of Cells with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
4.5. Treatment of IB3-1 Cells with the BNT162b2 Vaccine
4.6. RNA Extraction
4.7. Quantitative Analyses of mRNAs
4.8. Analysis of Cytokines, Chemokines and Growth Factors
4.9. Effects on Cellular Viability and Apoptosis
4.10. Computational Studies
4.11. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hahn, G. History, folk medicine, and legendary uses of garlic. In: Koch HP, Lawson LD, editors. Garlic: The Science and Therapeutic Application of Allium Sativum L and Related Species. Baltimore, Md, USA: Williams & Wilkins; 1996. pp. 1–24.
- Tudu, C.K.; Dutta, T.; Ghorai, M.; Biswas, P.; Samanta, D.; Oleksak, P.; Jha, N.K.; Kumar, M.; Radha Proćków, J.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Dey, A. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of garlic (Allium sativum), a storehouse of diverse phytochemicals: A review of research from the last decade focusing on health and nutritional implications. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 949554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giang, T.V.; Hoa, L.N.M.; Hien, T.T.; Cuong, Q.D.; Cap, N.T.; Lam Vuong, N.; Thach, P.N. Traditional Vietnamese Medicine Containing Garlic Extract for Patients With Non-severe COVID-19: A Phase-II, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Cureus 2023, 15, e42484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vahl E, Svanberg I. Traditional uses and practices of edible cultivated Allium species (fam. Amaryllidaceae) in Sweden. J. Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2022, 18, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; García-Recio, E.; Ruiz, C.; De Luna-Bertos, E.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J. Biological properties and therapeutic applications of garlic and its components. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marni, R.; Kundrapu, D.B.; Chakraborti, A.; Malla, R. Insight into drug sensitizing effect of diallyl disulfide and diallyl trisulfide from Allium sativum L. on paclitaxel-resistant triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 29, 115452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollahosseini, M.; Hosseini-Marnani, E.; Panjeshahin, A.; Panbehkar-Jouybari, M.; Gheflati, A.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials related to the effects of garlic supplementation on platelet aggregation. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 4041–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tang, X.; Wang, W.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Xu, H.; Li, N.; Liu, C. Evaluating the hypolipidemic effect of garlic essential oil encapsulated in a novel double-layer delivery system. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024, 237, 113835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yin, F.; Fu, L.; Ma, Y.; Ye, L.; Huang, Y.; Fan, W.; Gao, W.; Cai, Y.; Mou, X. Garlic-derived exosome-like nanovesicles as a hepatoprotective agent alleviating acute liver failure by inhibiting CCR2/CCR5 signaling and inflammation. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 154, 213592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkubo, S.; Dalla Via, L.; Grancara, S.; Kanamori, Y.; García-Argáez, A.N.; Canettieri, G.; Arcari, P.; Toninello, A.; Agostinelli, E. The antioxidant, aged garlic extract, exerts cytotoxic effects on wild-type and multidrug-resistant human cancer cells by altering mitochondrial permeability. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, Y.; Via, L.D.; Macone, A.; Canettieri, G.; Greco, A.; Toninello, A.; Agostinelli, E. Aged garlic extract and its constituent, S-allyl-L-cysteine, induce the apoptosis of neuroblastoma cancer cells due to mitochondrial membrane depolarization. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, J.; Ide, N.; Nagae, S.; Moriguchi, T.; Matsuura, H.; Itakura, Y. Antioxidant and radical scavenging effects of aged garlic extract and its constituents. Planta Medica 1994, 60, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, J.C.E.; Castro-Boqué, E.; García-Carrasco, A.; Morán-Valero, M.I.; González-Hedström, D.; Bermúdez-López, M.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Espinel, A.E.; Portero-Otín, M. Antihypertensive Effects of an Optimized Aged Garlic Extract in Subjects with Grade I Hypertension and Antihypertensive Drug Therapy: A Randomized, Triple-Blind Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, F.; Jia, G.; Liu, R. Aged black garlic extract inhibits the growth of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells by downregulating MCL-1 expression through the ROS-JNK pathway. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0286454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; MK; Mitra, A. ; Zaky, M.Y.; Pathak, S.; Banerjee, A. A Review on the Efficacy of Plant-derived Bio-active Compounds Curcumin and Aged Garlic Extract in Modulating Cancer and Age-related Diseases. Curr. Rev. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. 2024, 19, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, N.; He, Z.; Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Deng, S.; Xie, L. Diallyl trisulfide inhibits osteosarcoma 143B cell migration, invasion and EMT by inducing autophagy. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.T.; Taka, E.; Messeha, S.; Flores-Rozas, H.; Reed, S.L.; Redmond, B.V.; Soliman, K.F.A.; Kanga, K.J.W.; Darling-Reed, S.F. The Garlic Compound, Diallyl Trisulfide, Attenuates Benzo[a]Pyrene-Induced Precancerous Effect through Its Antioxidant Effect, AhR Inhibition, and Increased DNA Repair in Human Breast Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2024, 16, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentke-Imiolek A, Szlęzak D, Zarzycka M, Wróbel M, Bronowicka-Adamska P. S-Allyl-L-Cysteine Affects Cell Proliferation and Expression of H2S-Synthetizing Enzymes in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 188.
- Burke, H.; Freeman, A.; Cellura, D.C.; Stuart, B.L.; Brendish, N.J.; Poole, S.; Borca, F.; Phan, H.T.T.; Sheard, N.; Williams, S.; Spalluto, C.M.; Staples, K.J.; Clark, T.W.; Wilkinson, T.M.A. Inflammatory phenotyping predicts clinical outcome in COVID-19. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z. , Yu, H., Chen, H., Qi, W., Chen, L., Chen, G., Yan, W., Chen, T., Ning, Q., Han, M., Wu, D., Longitudinal changes of inflammatory parameters and their correlation with disease severity and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 from Wuhan, China. Crit. Care. 2020, 24, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; Marron, T.U.; Xie, H.; Patel, M.; Tuballes, K.; Van Oekelen, O.; Rahman, A.; Kovatch, P.; Aberg, J.A.; Schadt, E.; Jagannath, S.; Mazumdar, M.; Charney, A.W.; Firpo-Betancourt, A.; Mendu, D.R.; Jhang, J.; Reich, D.; Sigel, K.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Feldmann, M.; Parekh, S.; Merad, M.; Gnjatic, S. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soy, M. , Keser, G., Atagündüz, P., Tabak, F., Atagündüz, I., Kayhan, S., 2020. Cytokine in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascarella, G. , Strumia, A., Piliego, C., Bruno, F., Del Buono, R., Costa, F., Scarlata, S., Agrò, F.E. COVID-19 diagnosis and management: a comprehensive review. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Tinello, C.; Vatrella, A.; De Sarro, G.; Pelaia, G. Lung under attack by COVID-19-induced cytokine storm: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620933508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, M.Z. , Bujko, K., Ciechanowicz, A., Sielatycka, K., Cymer, M., Marlicz, W., Kucia, M. SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor ACE2 is expressed on very small CD45(-) precursors of hematopoietic and endothelial cells and in response to virus Spike protein activates the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 17, 266–277. [Google Scholar]
- Soumagne, T.; Winiszewski, H.; Besch, G.; Mahr, N.; Senot, T.; Costa, P.; Grillet, F.; Behr, J.; Mouhat, B.; Mourey, G.; Fournel, A.; Meneveau, N.; Samain, E.; Capellier, G.; Piton, G.; Pili-Floury, S. Pulmonary embolism among critically ill patients with ARDS due to COVID-19. Respir. Med. Res. 2020, 78, 100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasselli, G.; Tonetti, T.; Protti, A.; Langer, T.; Girardis, M.; Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.; Carrafiello, G.; Carsana, L.; Rizzuto, C.; Zanella, A.; Scaravilli, V.; Pizzilli, G.; Grieco, D.L.; Di Meglio, L.; de Pascale, G.; Lanza, E.; Monteduro, F.; Zompatori, M.; Filippini, C.; Locatelli, F.; Cecconi, M.; Fumagalli, R.; Nava, S.; Vincent, J.L.; Antonelli, M.; Slutsky, A.S.; Pesenti, A.; Ranieri, V.M. Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicentre prospective observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A.; Leligdowicz, A.; Liu, K.D. Biological mechanisms of COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasonov, E.; Samsonov, M. The role of Interleukin 6 inhibitors in therapy of severe COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreakos, E.; Papadaki, M.; Serhan, C.N. Dexamethasone, pro-resolving lipid mediators and resolution of inflammation in COVID-19. Allergy 2021, 76, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Simone, G. , Mancusi, C., 2020. Finding the right time for anti-inflammatory therapy in COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 247–248. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Yosri, N.; El-Mallah, M.F.; Ghonaim, R.; Guo, Z.; Musharraf, S.G.; Du, M.; Khatib, A.; Xiao, J.; Saeed, A.; El-Seedi, H.H.R.; Zhao, C.; Efferth, T.; El-Seedi, H.R. Screening for natural and derived bio-active compounds in preclinical and clinical studies: One of the frontlines of fighting the coronaviruses pandemic. Phytomedicine 2021, 85, 153311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, T.; Khafizova, G.; Sokornova, S. In search of herbal anti-SARS-Cov2 compounds. Front. Plant. Sci. 2020, 11, 589998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adem, Ş.; Eyupoglu, V.; Sarfraz, I.; Rasul, A.; Zahoor, A.F.; Ali, M.; Abdalla, M.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Elfiky, A.A. Caffeic acid derivatives (CAFDs) as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2: CAFDs-based functional foods as a potential alternative approach to combat COVID-19. Phytomedicine 2021, 85, 153310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwa, W.; Kumar, R.; Thompson, D.; Lyerly, W.; Moore, R.; Reid, T.E.; Lowe, H.; Toyang, N. Potential of flavonoid-inspired phytomedicines against COVID-19. Molecules 2020, 25, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzobo, K. , Chiririwa, H., Dandara, C., Dzobo, W., Coronavirus Disease-2019 treatment strategies targeting interleukin-6 signaling and herbal medicine. OMICS 2020, 25, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Vilekar, P.; Yang, S.P.; Gupta, M.; Oh, M.I.; Meek, A.; Doyle, L.; Villar, L.; Brennecke, A.; Liyanage, I.; Reed, M.; Barden, C.; Weaver, D.F. Small molecule therapeutics for COVID-19: repurposing of inhaled furosemide. Peer J. 2020, 8, e9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; D'Aversa, E.; Papi, C.; Gambari, L.; Grigolo, B.; Borgatti, M.; Finotti, A.; Gambari, R. Sulforaphane inhibits the expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 induced in bronchial epithelial IB3-1 cells by exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein. Phytomedicine 2021, 87, 153583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; d'Aversa, E.; Breveglieri, G.; Borgatti, M.; Finotti, A.; Gambari, R. In vitro induction of interleukin-8 by SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein is inhibited in bronchial epithelial IB3-1 cells by a miR-93-5p agomiR. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurlo, M.; Gasparello, J.; Verona, M.; Papi, C.; Cosenza, L.C.; Finotti, A.; Marzaro, G.; Gambari, R. The anti-SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine suppresses mithramycin-induced erythroid differentiation and expression of embryo-fetal globin genes in human erythroleukemia K562 cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 2023, 433, 113853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, L.C.; Marzaro, G.; Zurlo, M.; Gasparello, J.; Zuccato, C.; Finotti, A.; Gambari, R. Inhibitory effects of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and BNT162b2 vaccine on erythropoietin-induced globin gene expression in erythroid precursor cells from patients with β-thalassemia. Exp. Hematol. 2024, 129, 104128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; Gambari, L.; Papi, C.; Rozzi, A.; Manicardi, A.; Corradini, R.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. High Levels of Apoptosis Are Induced in the Human Colon Cancer HT-29 Cell Line by Co-Administration of Sulforaphane and a Peptide Nucleic Acid Targeting miR-15b-5p. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparello, J.; Papi, C.; Zurlo, M.; Gambari, L.; Rozzi, A.; Manicardi, A.; Corradini, R.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. Treatment of Human Glioblastoma U251 Cells with Sulforaphane and a Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) Targeting miR-15b-5p: Synergistic Effects on Induction of Apoptosis. Molecules 2022, 27, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colín-González, A.L.; Santana, R.A.; Silva-Islas, C.A.; Chánez-Cárdenas, M.E.; Santamaría, A.; Maldonado, P.D. The antioxidant mechanisms underlying the aged garlic extract- and S-allylcysteine-induced protection. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012, 2012, 907162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penolazzi, L.; Lambertini, E.; Tavanti, E.; Torreggiani, E.; Vesce, F.; Gambari, R.; Piva, R. Evaluation of chemokine and cytokine profiles in osteoblast progenitors from umbilical cord blood stem cells by BIO-PLEX technology. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 320–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzaro, G.; Lampronti, I.; D'Aversa, E.; Sacchetti, G.; Miolo, G.; Vaccarin, C.; Cabrini, G.; Dechecchi, M.C.; Gambari, R.; Chilin, A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel trimethylangelicin analogues targeting nuclear factor kB (NF-kB). Eur J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, R.; Brognara, E.; Fabbri, E.; Finotti, A.; Borgatti, M.; Lampronti, I.; Marzaro, G.; Chilin, A.; Lee, K.K.; Kok, S.H.; Chui, C.H.; Gambari, R. Corilagin Induces High Levels of Apoptosis in the Temozolomide-Resistant T98G Glioma Cell Line. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; Marzaro, G.; Papi, C.; Gentili, V.; Rizzo, R.; Zurlo, M.; Scapoli, C.; Finotti, A.; Gambari, R. Effects of Sulforaphane on SARS-CoV-2 infection and NF-κB dependent expression of genes involved in the COVID-19 'cytokine storm'. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 52, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiel, L.A.; Fitzpatrick, L.E. Toll-like Receptor 2-Dependent NF-κB/AP-1 Activation by Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Adsorbed on Polymeric Surfaces. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3792–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V. Toll-like receptors in sepsis-associated cytokine storm and their endogenous negative regulators as future immunomodulatory targets. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang H, Wang HY, Wang JW, Lou DY, Niu N, Li GH, Qu P. NF-κB inhibitor on Toll-like receptor 4 signal-induced expression of angiotensinogen and AT1a receptor in neonatal rat left ventricular myocytes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 3875–3882. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Wu, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Wu, L.; Zou, H.; Lu, L. Interleukin-6 blocking therapy for COVID-19: From immune pathogenesis to clinical outcomes. Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2022, 3, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavioli, E.; Landoni, G.; Piemonti, L.; Grossi, P.; Toya, S.; Minnella, E.; Allegretti, M.; Mantelli, F. A Phase 2 Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Reparixin in Hospitalized Adult Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Am J Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Gritti, G.; Raimondi, F.; Bottazzi, B.; Ripamonti, D.; Riva, I.; Landi, F.; Alborghetti, L.; Frigeni, M.; Damiani, M.; Micò, C.; Fagiuoli, S.; Lorini, F.L.; Gandini, L.; Novelli, L.; Morgan, J.P.; Owens, B.M.J.; Kanhai, K.J.K.; Reljanovic, G.T.; Rizzi, M.; Di Marco, F.; Mantovani, A.; Rambaldi, A. Siltuximab downregulates interleukin-8 and pentraxin 3 to improve ventilatory status and survival in severe COVID-19. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2710–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.I. , Abdelmoneim, A.H., Mahmoud, E.M., Makhawi, A.M., 2020. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19 patients, its impact on organs and potential treatment by QTY Code-Designed Detergent-Free Chemokine Receptors. Mediators Inflamm. 2020; 8198963. [Google Scholar]
- Brasier, A. The nuclear factor-kappaB-interleukin-6 signalling pathway mediating vascular inflammation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 86, 211–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libermann, T.A.; Baltiore, D. Activation of Interleukin-6 Gene Expression through the NF-KB Transcription Factor. Mol. & Cell Biol. 1990; 2327–2334. [Google Scholar]
- Bezzerri, V.; Borgatti, M.; Finotti, A.; Tamanini, A.; Gambari, R.; Cabrini, G. Mapping the transcriptional machinery of the IL-8 gene in human bronchial epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6069–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Martín, E.; Ruiz, J.; Pérez-Palacios, T.; Silva, A.; Antequera, T. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the determination of free amino acids as their dimethyl-tert-butylsilyl (TBDMS) derivatives in animal source food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2456–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; Lomazzi, M.; Papi, C.; D'Aversa, E.; Sansone, F.; Casnati, A.; Donofrio, G.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. Efficient Delivery of MicroRNA and AntimiRNA Molecules Using an Argininocalix [4]arene Macrocycle. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2019, 18, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.C.; Kwon, H.K.; Batool, M.; Choi, S. Computational Insight Into the Structural Organization of Full-Length Toll-Like Receptor 4 Dimer in a Model Phospholipid Bilayer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: an advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf.Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindahl E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bonomi M, Branduardi D, Bussi G, Camilloni C, Provasi D, Raiteri P, Donadio D, Marinelli F, Pietrucci F, Broglia R, Parrinello M. PLUMED: A portable plugin for free-energy calculations with molecular dynamics. Computer Physics Comm. 2009, 180, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang J, MacKerell AD. CHARMM36 all-atom additive protein force field: Validation based on comparison to NMR data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




