Submitted:
08 November 2024
Posted:
08 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
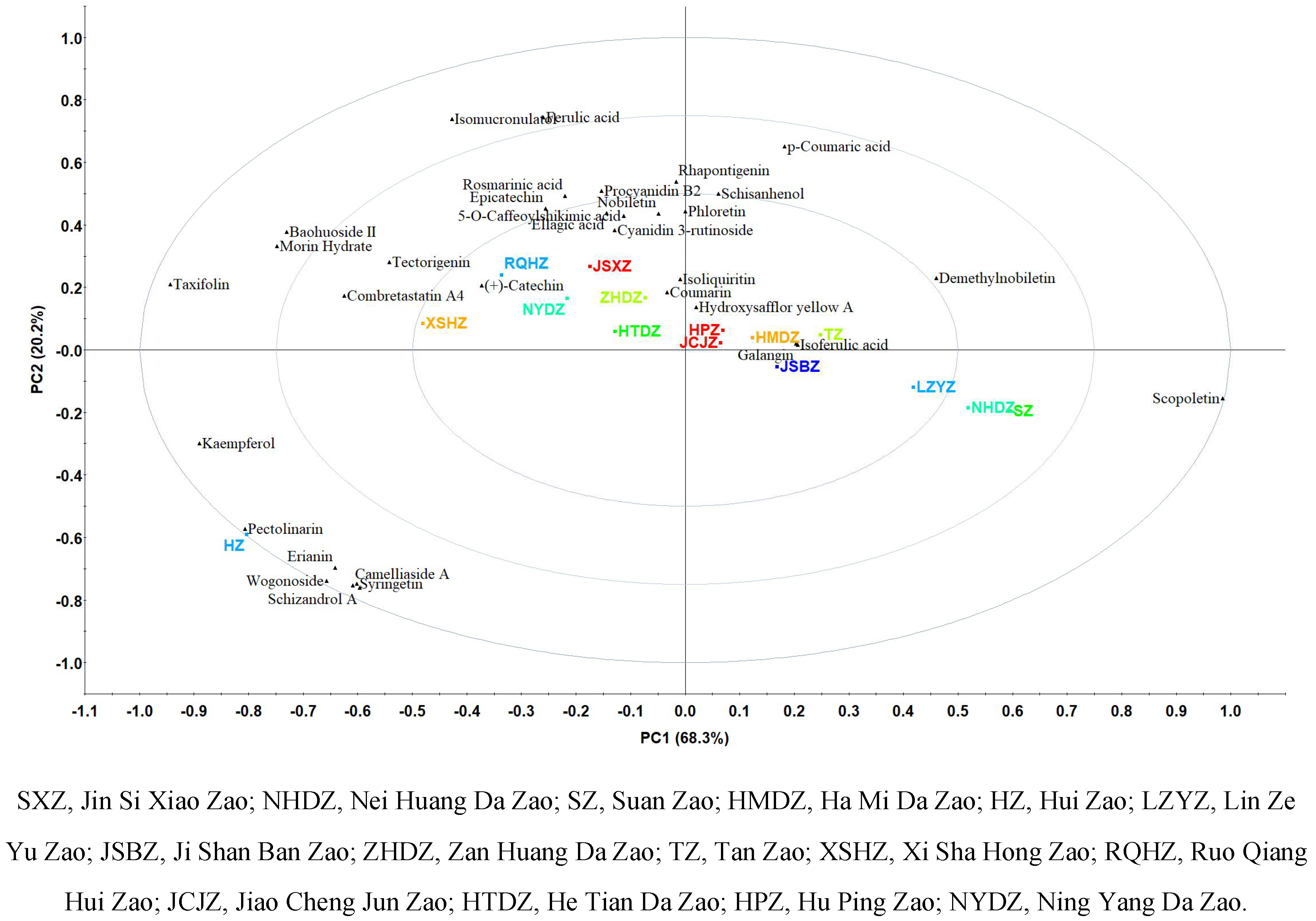
Jujube is the homology of medicine and food, and polyphenols are key compounds that determined the functional effects of jujubes. In this study, characteristic polyphenols in 15 varieties of Chinese jujubes were investigated based on untargeted metabolomics. Result showed a total of 79 characteristic polyphenols were identified in 15 varieties of Chinese jujube, and 55 characteristic polyphenols such as syringetin, spinosin and kaempferol were reported for the first time. Scopoletin (63.94% in LZYZ), pectolinarin (22.63% in HZ) and taxifolin (19.69% in HZ) contributed great and presented significant (p<0.05) differences in 15 varieties of Chinese jujubes. HZ can be characterized by pectolinarin, erianin and wogonoside. While, XSHZ, NYDZ and RQHZ with similar polyphenol profile were characterized by (+)-catechin, combretastatin A4 and tectorigenin. JSBZ, HMDZ, TZ, JCJZ and HPZ had similar polyphenol profile of galangin, isoferulic acid and hydroxysafflor yellow A. In conclusion, metabolomics is critical to grasp the fully nutritional components of jujubes, and the differences of polyphenol profiles and characteristic individual polyphenol of 15 varieties of Chinese jujubes can be well analyzed by principal component analysis (PCA).Jujube is the homology of medicine and food, and polyphenols are key compounds that determined the functional effects of jujubes. In this study, characteristic polyphenols in 15 varieties of Chinese jujubes were investigated based on untargeted metabolomics. Result showed a total of 79 characteristic polyphenols were identified in 15 varieties of Chinese jujube, and 55 characteristic polyphenols such as syringetin, spinosin and kaempferol were reported for the first time. Scopoletin (63.94% in LZYZ), pectolinarin (22.63% in HZ) and taxifolin (19.69% in HZ) contributed great and presented significant (p<0.05) differences in 15 varieties of Chinese jujubes. HZ can be characterized by pectolinarin, erianin and wogonoside. While, XSHZ, NYDZ and RQHZ with similar polyphenol profile were characterized by (+)-catechin, combretastatin A4 and tectorigenin. JSBZ, HMDZ, TZ, JCJZ and HPZ had similar polyphenol profile of galangin, isoferulic acid and hydroxysafflor yellow A. In conclusion, metabolomics is critical to grasp the fully nutritional components of jujubes, and the differences of polyphenol profiles and characteristic individual polyphenol of 15 varieties of Chinese jujubes can be well analyzed by principal component analysis (PCA).
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
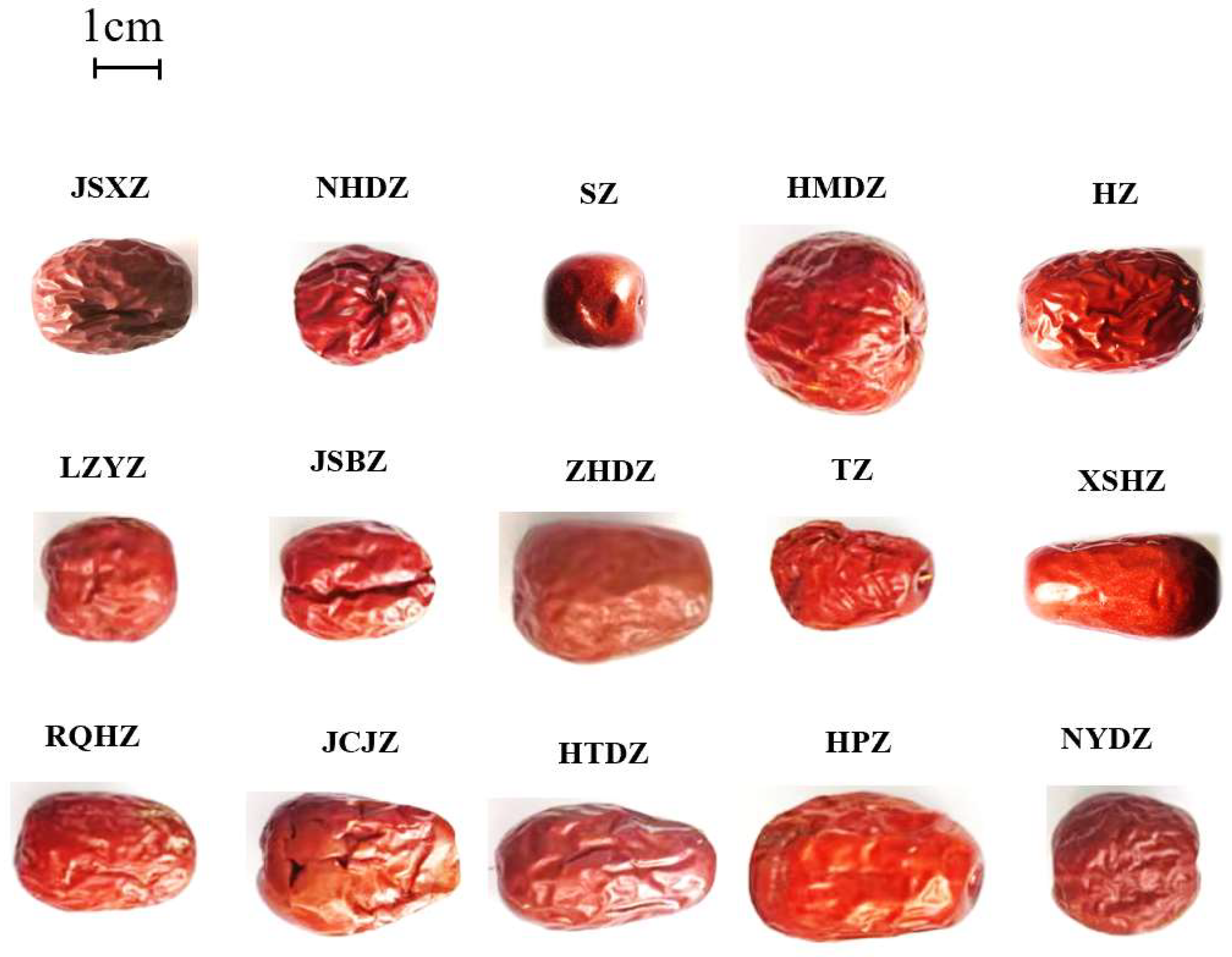
2.Plant Material
2.Metabolite Extraction
2.LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.Metabolite Identification
2.Data Preprocessing
Results and Discussion
3.Identification of Characteristic Polyphenols in 15 Chinese Jujubes
3.Content of Characteristic Polyphenols in 15 Chinese Jujubes
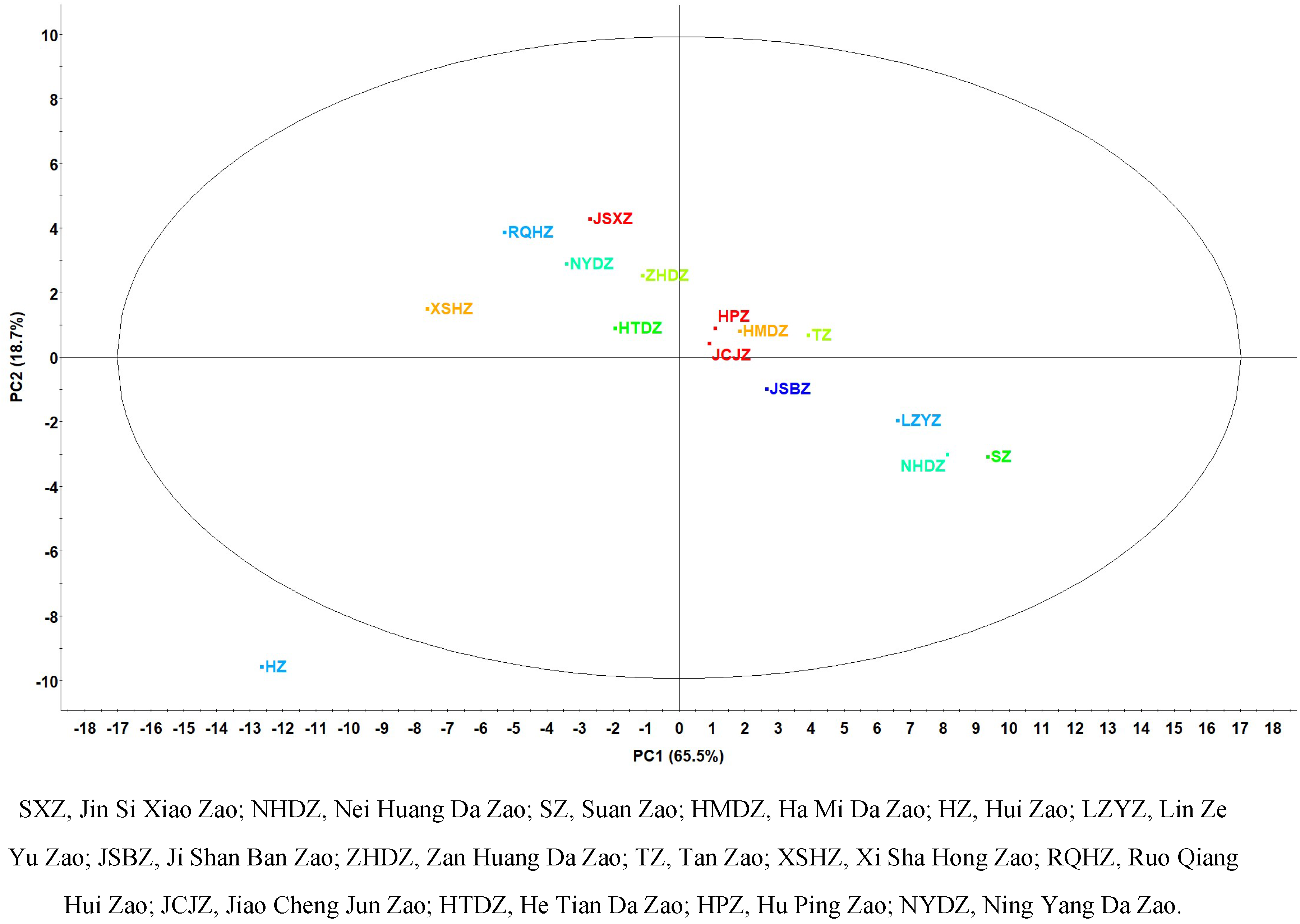
3.PCA of 15 Commercial Chinese jujubes
Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest statement
References
- Zhu, J.; Lu, Y.; He, Q. Recent advances on bioactive compounds, health benefits, and potential applications of jujube (Ziziphus Jujuba Mill.): A perspective of by-products valorization. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2024, 145, 104368. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, P. Artificial autopolyploidization in jujube. Scientia Horticulturae 2023, 314, 111916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, A.; Karim, N.; Shishir, M.; Bao, T.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W. Jujube fruit: A potential nutritious fruit for the development of functional food products. Journal of Functional Foods 2020, 75, 104205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z. Preparation, characterization and in vitro digestion of jujube polysaccharide microcapsules. Food and Bioproducts Processing 2024, 145, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Lao, F.; Shi, X.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J. Effects of cold plasma, high hydrostatic pressure, ultrasound, and high-pressure carbon dioxide pretreatments on the quality characteristics of vacuum freeze-dried jujube slices. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry 2022, 90, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Effects of five extraction methods on total content, composition, and stability of flavonoids in jujube. Food Chemistry: X 2022, 14, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Kou, X.; Wu, C.; Fan, G.; Li, T.; Dou, J.; et al. Cocktail enzyme-assisted alkaline extraction and identification of jujube peel pigments. Food Chemistry, 2021, 357, 129747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Han, J.; Fu, L.; Shang, H.; Yang, L. Assessment of characteristics aroma of heat pump drying (HPD) jujube based on HS-SPME/GC-MS and e-nose. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2022, 110, 104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Pu, Y.; Xu, Y.; He, X.; Cao, J.; et al. Anti-diabetic and anti-obesity: Efficacy evaluation and exploitation of polyphenols in fruits and vegetables. Food Research International 2022, 157, 111202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, D.; Almeida, L.; Dinis, T. Dietary polyphenols: A novel strategy to modulate microbiota-gut-brain axis. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2018, 78, 224–233. [Google Scholar]
- Mahamoud, R.; Bowman, D.; Ward, W.; Mangal, V. Assessing the stability of polyphenol content in red rooibos herbal tea using traditional methods and high-resolution mass spectrometry: Implications for studying dietary interventions in preclinical rodent studies. Food Chemistry 2024, 448, 139068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, M. Reactions of plant polyphenols in foods: Impact of molecular structure. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 112, 241–251. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Fu, C.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; et al. Combining bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity profiling provide insights into assessment of geographical features of Chinese jujube. Food Bioscience 2022, 46, 101573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; et al. Partial compression increases acidity, but decreases phenolics in jujube fruit: Evidence from targeted metabolomics. Food Research International 2023, 164, 112388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; You, F.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C. Comprehensive assessment of phenolic compounds and antioxidant performance in the developmental process of jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.). Journal of Functional Foods 2017, 36, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, Q.; Venkitasamy, C.; Chai, H.; Gao, H.; et al. Changes in phenolic compounds and their antioxidant capacities in jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Miller) during three edible maturity stages. LWT – Food Science and Technology 2016, 66, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q. Phenolic compounds and its antioxidant activities in ethanolic extracts from seven cultivars of Chinese jujube. Food Science and Human Wellness 2014, 3, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafabadi, N.; Sahari, M.; Barzegar, M.; Esfahani, Z. Effect of processing conditions (conventional heating, microwave, chilling, and freezing) on the stability of some bioactive compounds of jujube fruit. Applied Food Research 2023, 3, 100293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Kan, C.; et al. Quantitative assessment of bioactive compounds and the antioxidant activity of 15 jujube cultivars. Food Chemistry 2105, 173, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, X.; Yue, M.; Zhu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X. Advances and perspectives in chemical isotope labeling-based mass spectrometry methods for metabolome and exposome analysis. Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2023, 162, 117022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Hajinia, F.; Kharazmi, M.; Jafari, S. FoodOmics as a promising strategy to study the effects of sourdough on human health and nutrition, as well as product quality and safety; back to the future. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2023, 136, 24–47. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Tang, Y. Effect of extrusion temperature on characteristic amino acids, fatty acids, organic acids, and phenolics of white quinoa based on metabolomics. Food Research International 2023, 169, 112761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.; Ali, V.; Khajuria, M.; Faiz, S.; Gairola, S.; Vyas, D. GC-MS based metabolomic approach to understand nutraceutical potential of Cannabis seeds from two different environments. Food Chemistry 2021, 339, 128076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Peng, J. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of characteristic sugars in three colored quinoas based on untargeted and targeted metabolomics. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2024, 126, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otify, A.; Ibrahim, R.; Abib, B.; Laub, A.; Wessjohann, L.; et al. Unveiling metabolome heterogeneity and new chemicals in 7 tomato varieties via multiplex approach of UHPLC-MS/MS, GC-MS, and UV-Vis in relation to antioxidant effects as analyzed using molecular networking and chemometrics. Food Chemistry 2023, 417, 135866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Xiao, H.; Lv, X.; et al. Analytical opportunities and challenges for data handling with chemometrics strategies from LC-MS based food metabolomics. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2024, 143, 104298. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, C.; Ni, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. Integrate analysis of metabolome and transcriptome of three Fragaria × ananassa cultivars to stablish the non-volatile compounds of strawberry flavor. LWT – Food Science and Technology 2024, 198, 116043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Hou, X.; Han, M.; Qiu, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Discrimination and polyphenol compositions of green teas with seasonal variations based on UPLC-QTOF/MS combined with chemometrics. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2022, 105, 104267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ahsan, M.; Adil, M.; Chen, X.; Nazir, M.; et al. Identification of the gene network modules highly associated with the synthesis of phenolics compounds in barley by transcriptome and metabolome analysis. Food Chemistry 2020, 323, 126862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Characterization of fatty acids, amino acids and organic acids in three colored quinoas based on untargeted and targeted metabolomics. LWT-Food Science and Technology 2021, 140, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, P.; Qi, L.; Lin, S. Identification of changes in volatile compounds in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during seasonings soaking using HS-GC-IMS. LWT – Food Science and Technology 2022, 154, 112695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, D.; Jiang, J.; Li, X. Comprehensive analysis of antibacterial and anti-hepatoma activity of metabolites from jujube fruit. Food Bioscience 2022, 47, 101511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Cao, W.; Xu, J.; Peng, L. Cyclodextrin-assisted liquid-solid extraction for determination of the composition of jujube fruit using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection and quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chemistry 2016, 213, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasfiyati, A.; Antika, L.; Dewi, R.; Septama, A.; Sabarudin, A.; Ernawati, T. An experimental design approach for the optimization of scopoletin extraction from Morinda citrifolia L. using accelerated solvent extraction. Talanta 2022, 238, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, C.; Xu, B. An insight into the health-promoting effects of taxifolin (dihydroquercetin). Phytochemistry 2019, 166, 112066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashno, M.; Gholipour, P.; Salehi, I.; Komaki, A.; Rashidi, K.; Khoshnam, S.; et al. p-Coumaric acid mitigates passive avoidance memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity impairments in aluminum chloride-induced Alzheimer’s disease rat model. Journal of Functional Foods 2022, 94, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Peng, W.; Qi, W.; Zhang, J.; Song, G.; Pang, S.; et al. Ferulic acid combined with different dietary fibers improve glucose metabolism and intestinal barrier function by regulating gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice. Journal of Function Foods 2024, 112, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirasunthorn, N.; Jantho, T.; Ubolsaard, T. Catechin detection in tea samples based on catechin-induced conformation changes in papain. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2024, 132, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, K.; Bu, D.; Wu, Z. Epicatechin attenuates lead (Pb)-induced cognitive impairment in mice: regulation on Nrf2 signaling pathway, and interference on the interaction between Pb with albumin. Food Science and Human Wellness 2024, 13, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X.; Sun, R.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Lin, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. Novel application of HS-GC-IMS with PCA for characteristic fingerprints and flavor compound variations in NFC Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) juice during storage. LWT – Food Science and Technology 2022, 167, 113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Sun, J.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Yao, L.; Sun, M.; et al. Geographical differentiation of Molixiang table grapes grown in China based on volatile compounds analysis by HS-GC-IMS coupled with PCA and sensory evaluation of the grapes. Food Chemistry: X 2022, 15, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compounds | Relative content (%) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JSXZ | NHDZ | SZ | HMDZ | HZ | LZYZ | JSBZ | ZHDZ | TZ | XSHZ | RQHZ | JCJZ | HTDZ | HPZ | NYDZ | |
| Phloretin | 1.08±0.02h | 0.50±0.01c | 0.56±0.01d | 0.85±0.03fg | 0.27±0.01b | 0.31±0.00c | 0.10±0.00a | 0.79±0.01f | 0.70±0.02e | 0.89±0.01g | 0.25±0.01b | 1.10±0.03h | 0.61±0.02d | 1.05±0.01h | 0.52±0.00c |
| Ellagic acid | 1.28±0.04j | 0.12±0.00b | 0.21±0.01cd | 0.29±0.01f | 0.10±0.00a | 0.23±0.00de | 0.10±0.00a | 0.18±0.01c | 0.13±0.01b | 0.25±0.01e | 0.30±0.00f | 0.65±0.02h | 1.24±0.04j | 0.83±0.04i | 0.35±0.01g |
| p-Coumaric acid | 10.67±0.35j | 3.68±0.11d | 4.14±0.15e | 5.29±0.09f | 0.31±0.02a | 3.83±0.12de | 5.35±0.20f | 6.95±0.19h | 10.40±0.33j | 3.26±0.14c | 7.32±0.17h | 6.06±0.08g | 8.12±0.26i | 10.30±0.41j | 2.77±0.05b |
| Pectolinarin * | 1.62±0.02c | 0.46±0.01a | 0.48±0.00a | 1.63±0.03c | 22.63±0.72i | 0.85±0.03b | 2.88±0.10d | 1.56±0.02c | 0.89±0.03b | 9.27±0.38h | 4.71±0.21f | 3.79±0.05e | 7.22±0.09g | 3.80±0.04e | 4.03±0.12e |
| Baohuoside II * | 3.05±0.07h | 2.11±0.03d | 0.62±0.01a | 2.37±0.02ef | 3.00±0.04h | 0.98±0.01b | 2.31±0.00e | 2.97±0.05h | 1.26±0.04c | 4.59±0.15i | 5.81±0.19j | 2.50±0.03fg | 2.69±0.05g | 2.16±0.01d | 2.57±0.04g |
| Syringetin * | 0.31±0.00j | 0.02±0.00a | 0.08±0.01f | 0.11±0.00h | 7.04±0.18k | 0.02±0.00a | 0.03±0.00b | 0.08±0.00f | 0.04±0.00c | 0.09±0.00g | 0.10±0.00h | 0.07±0.00e | 0.12±0.00i | 0.06±0.00d | 0.07±0.00e |
| Coumarin | 0.45±0.01f | 0.20±0.00d | 0.16±0.01bc | 0.15±0.00b | 0.08±0.00a | 0.49±0.02g | 0.29±0.00e | 0.40±0.01e | 0.15±0.01a | 0.17±0.00c | 0.17±0.01c | 0.85±0.02h | 3.00±0.12j | 1.35±0.03i | 0.44±0.01ef |
| Morin Hydrate * | 1.64±0.04h | 0.35±0.01a | 0.32±0.01a | 1.39±0.03g | 1.38±0.02g | 0.41±0.01b | 0.65±0.02d | 1.01±0.01e | 0.51±0.01c | 1.64±0.05h | 1.43±0.02g | 1.78±0.03h | 1.34±0.01g | 1.09±0.02ef | 1.10±0.00f |
| Hydroxysafflor yellow A * |
0.12±0.00i | 0.02±0.00a | 0.03±0.00b | 1.10±0.02j | 0.05±0.00d | 0.04±0.00c | 0.02±0.00a | 0.10±0.00g | 0.05±0.00d | 0.08±0.00f | 0.11±0.00h | 0.07±0.00e | 0.08±0.00f | 0.07±0.00e | 0.11±0.00h |
| Taxifolin | 15.86±0.85f | 4.75±0.32a | 4.64±0.21a | 11.78±0.47de | 19.69±0.73g | 6.67±0.59b | 10.38±0.48cd | 13.34±0.62e | 9.60±0.52c | 15.72±0.83f | 17.96±0.91fg | 10.92±0.35cd | 13.32±0.27e | 11.16±0.44d | 0.15±0.00e |
| Combretastatin A4 * | 4.10±0.12cd | 2.39±0.09b | 0.90±0.03a | 3.76±0.17c | 6.10±0.25g | 2.42±0.16b | 5.62±0.28fg | 7.81±0.19h | 2.40±0.05b | 16.25±0.63i | 4.73±0.11e | 4.31±0.06d | 5.30±0.03f | 5.74±0.14fg | 0.06±0.00c |
| 5-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid * | 3.42±0.12m | 0.08±0.00a | 1.42±0.03k | 0.26±0.00g | 0.17±0.01c | 0.98±0.01j | 0.13±0.00b | 0.88±0.02i | 0.13±0.00b | 0.33±0.01h | 3.03±0.04l | 0.21±0.00e | 0.18±0.01cd | 0.20±0.00de | 0.29±0.00h |
| Rosmarinic acid | 0.78±0.01f | 0.15±0.00b | 0.60±0.01e | 0.60±0.01e | 0.13±0.00a | 0.36±0.01d | 0.29±0.01c | 5.09±0.12m | 1.35±0.03j | 2.04±0.02l | 1.66±0.02k | 0.98±0.03h | 1.13±0.01i | 0.90±0.00g | 0.05±0.00d |
| Nobiletin | 1.09±0.02jk | 0.43±0.01ef | 0.16±0.00b | 1.11±0.05k | 0.27±0.01d | 0.25±0.01d | 0.05±0.01a | 0.22±0.01c | 1.04±0.03j | 0.45±0.01f | 0.58±0.01h | 0.68±0.02i | 0.40±0.01e | 0.45±0.01f | 0.03±0.00c |
| Isomucronulatol * | 1.02±0.02h | 0.22±0.00b | 0.22±0.00b | 0.66±0.01f | 0.20±0.00a | 0.25±0.01c | 0.20±0.00a | 0.83±0.02g | 0.52±0.02d | 1.14±0.03i | 0.64±0.01f | 0.58±0.01e | 0.49±0.01d | 0.83±0.02g | 0.03±0.00c |
| Erianin * | 0.20±0.00g | 0.12±0.00g | 0.03±0.00a | 0.07±0.00d | 1.08±0.02h | 0.03±0.00a | 0.10±0.00f | 0.07±0.00d | 0.06±0.00c | 0.15±0.00e | 0.09±0.00e | 0.22±0.01g | 0.12±0.00g | 0.17±0.01f | 0.06±0.00e |
| Wogonoside * | 0.04±0.00a | 0.18±0.00h | 0.05±0.00b | 0.14±0.00g | 7.26±0.28n | 0.08±0.00c | 0.12±0.00f | 0.15±0.01g | 0.11±0.00e | 1.42±0.05m | 0.09±0.00d | 0.28±0.01k | 0.34±0.00l | 0.20±0.00i | 0.03±0.00c |
| Scopoletin | 26.26±0.73d | 72.60±1.04k | 76.96±0.98k | 47.48±1.16h | 5.88±0.17a | 63.94±0.55j | 53.50±0.70i | 34.90±1.01f | 52.02±1.37hi | 15.68±0.52b | 20.44±0.77c | 43.46±1.12gh | 30.00±0.27e | 42.73±0.85g | 0.03±0.00c |
| Camelliaside A * | 0.08±0.00e | 0.08±0.00e | 0.02±0.00a | 0.03±0.00b | 3.28±0.12h | 0.02±0.00a | 0.04±0.00c | 0.03±0.00b | 0.05±0.00d | 0.15±0.00g | 0.11±0.00f | 0.08±0.00e | 0.05±0.00d | 0.05±0.00d | 18.82±0.62g |
| Isoliquiritin * | 0.72±0.01g | 0.74±0.02g | 0.25±0.01c | 0.23±0.01c | 0.01±0.00a | 0.73±0.01g | 0.50±0.02e | 0.82±0.02h | 0.32±0.01d | 0.11±0.01b | 0.96±0.02i | 1.79±0.04j | 5.13±0.34l | 2.29±0.18k | 4.55±0.09de |
| Galangin * | 0.74±0.02h | 0.26±0.01d | 0.14±0.00a | 0.14±0.00a | 0.26±0.00d | 2.71±0.05k | 0.14±0.00a | 0.37±0.01f | 1.22±0.03i | 0.18±0.00c | 0.33±0.00e | 0.56±0.02g | 2.31±0.05j | 0.41±0.01f | 0.24±0.00f |
| Ferulic acid | 4.31±0.07j | 0.73±0.02c | 0.59±0.01b | 2.95±0.08i | 0.18±0.00a | 1.31±0.04e | 1.60±0.03f | 1.41±0.02e | 0.92±0.02d | 2.89±0.07i | 2.60±0.05h | 2.38±0.04h | 1.61±0.05 | 1.87±0.02g | 1.41±0.02j |
| Isoferulic acid * | 0.74±0.01j | 0.27±0.01e | 0.14±0.00a | 0.15±0.01ab | 0.27±0.01e | 2.71±0.06m | 0.21±0.01d | 0.37±0.00g | 1.22±0.03k | 0.18±0.00c | 0.34±0.01f | 0.56±0.01i | 2.31±0.05l | 0.40±0.01h | 0.49±0.00g |
| Demethylnobiletin * | 0.47±0.01d | 0.96±0.02h | 0.89±0.01g | 0.96±0.01h | 0.02±0.00a | 1.11±0.03i | 0.29±0.00c | 1.21±0.01j | 0.65±0.02e | 1.10±0.02i | 0.13±0.00b | 0.81±0.01f | 0.43±0.01d | 0.80±0.02f | 0.66±0.02j |
| Kaempferol * | 0.90±0.01h | 0.34±0.01c | 0.18±0.00a | 0.44±0.02d | 2.10±0.05k | 0.33±0.01c | 0.70±0.01f | 0.84±0.02h | 0.44±0.01d | 1.03±0.02i | 1.21±0.02j | 0.52±0.01e | 0.54±0.02e | 0.29±0.01b | 0.56±0.01h |
| (+)-Catechin | 0.06±0.00d | 0.05±0.00c | 0.02±0.00a | 0.05±0.00c | 0.05±0.00c | 0.02±0.00a | 0.02±0.00a | 0.36±0.01f | 0.05±0.00c | 1.08±0.02g | 0.07±0.00d | 0.37±0.00f | 0.04±0.00b | 0.05±0.00c | 0.78±0.01g |
| Tectorigenin * | 3.37±0.05g | 1.74±0.02cd | 0.75±0.02a | 1.97±0.05e | 2.68±0.07f | 1.34±0.01b | 5.40±0.04j | 2.72±0.10f | 1.38±0.06b | 5.04±0.06i | 4.60±0.03h | 1.87±0.02de | 1.82±0.02d | 1.61±0.03c | 0.05±0.00b |
| Rhapontigenin * | 1.07±0.03k | 0.52±0.01h | 0.17±0.00b | 0.58±0.01i | 0.01±0.00a | 0.24±0.00c | 0.35±0.01e | 0.31±0.00d | 0.39±0.01f | 0.46±0.01g | 0.82±0.02j | 1.47±0.03l | 0.31±0.00d | 0.50±0.01gh | 0.14±0.00f |
| Epicatechin | 2.05±0.06j | 0.31±0.00b | 0.12±0.00a | 2.21±0.04j | 0.43±0.01d | 0.50±0.01e | 3.34±0.07k | 0.55±0.01f | 1.13±0.03h | 1.21±0.02h | 5.49±0.11l | 0.83±0.02g | 0.40±0.01d | 0.35±0.00c | 0.62±0.01f |
| Schisanhenol * | 1.28±0.03j | 0.70±0.00f | 0.77±0.01gh | 0.99±0.02i | 0.04±0.00a | 0.81±0.02h | 0.29±0.00c | 0.62±0.01e | 0.23±0.00b | 0.50±0.02d | 0.74±0.01fg | 0.60±0.01e | 0.63±0.02e | 0.52±0.01d | 0.58±0.02j |
| Schizandrol A * | 0.04±0.00b | 0.05±0.00c | 0.03±0.00a | 0.04±0.00b | 6.96±0.11j | 0.05±0.00c | 0.08±0.00e | 0.08±0.00e | 0.07±0.00d | 0.15±0.00i | 0.04±0.00b | 0.10±0.00g | 0.09±0.00f | 0.07±0.00d | 0.67±0.02l |
| Procyanidin B2 | 1.76±0.02d | 0.27±0.00b | 1.15±0.02c | 2.63±0.05g | 0.15±0.00a | 2.29±0.04f | 0.27±0.00b | 7.06±0.16j | 5.62±0.08i | 1.98±0.04e | 4.64±0.11h | 1.91±0.06e | 2.39±0.07fg | 2.00±0.03e | 0.21±0.01fg |
| Cyanidin 3-rutinoside * | 1.70±0.03j | 0.07±0.00a | 0.22±0.00g | 0.16±0.00f | 0.13±0.00d | 0.24±0.00h | 0.12±0.00c | 0.13±0.00d | 0.08±0.00b | 0.14±0.00e | 0.24±0.00h | 0.26±0.00i | 0.27±0.01i | 0.27±0.00i | 0.10±0.00f |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




