Submitted:
10 November 2024
Posted:
11 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
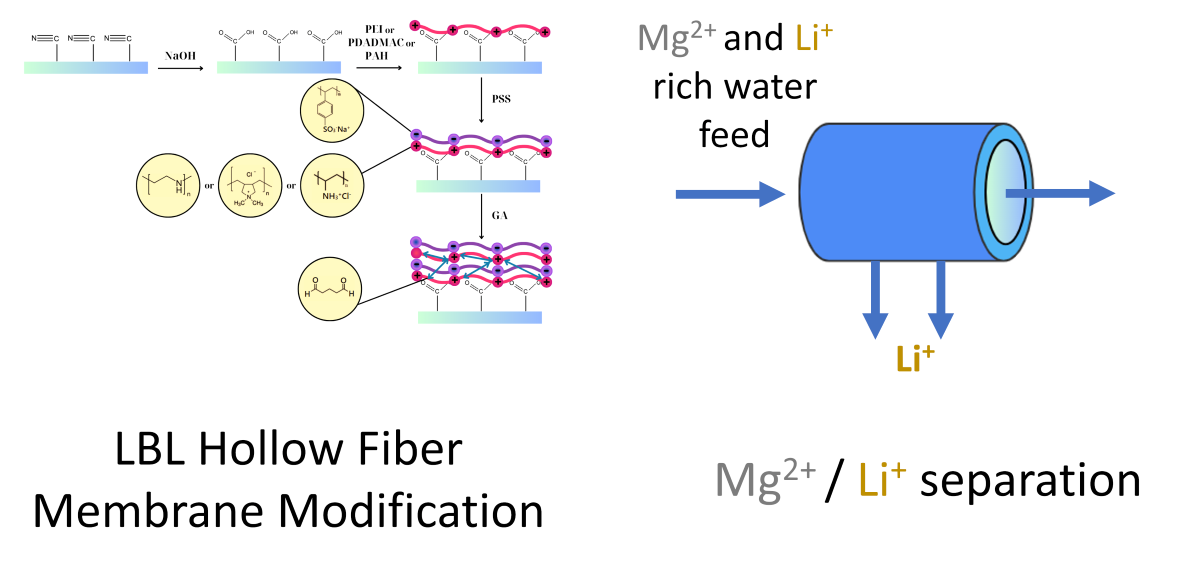
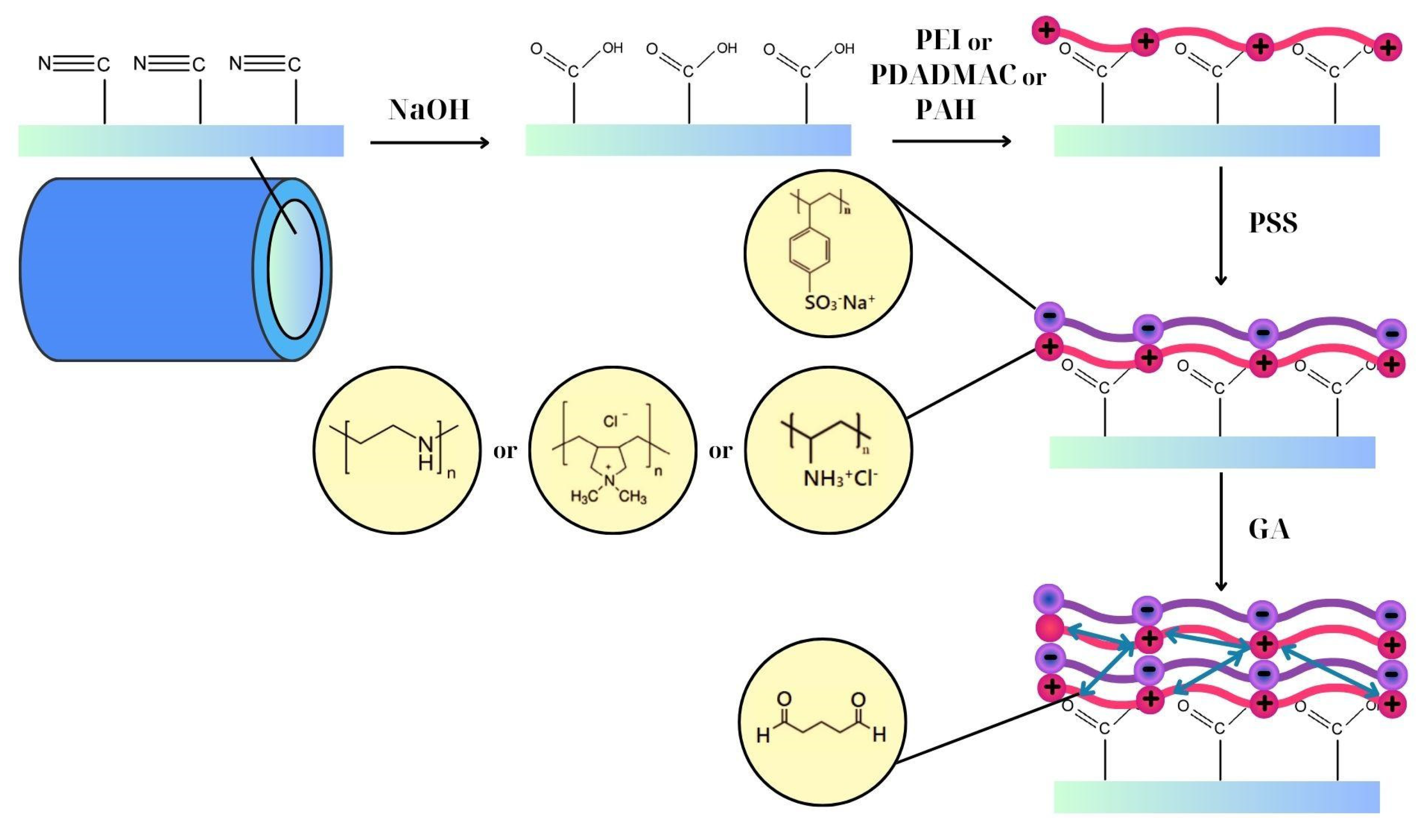
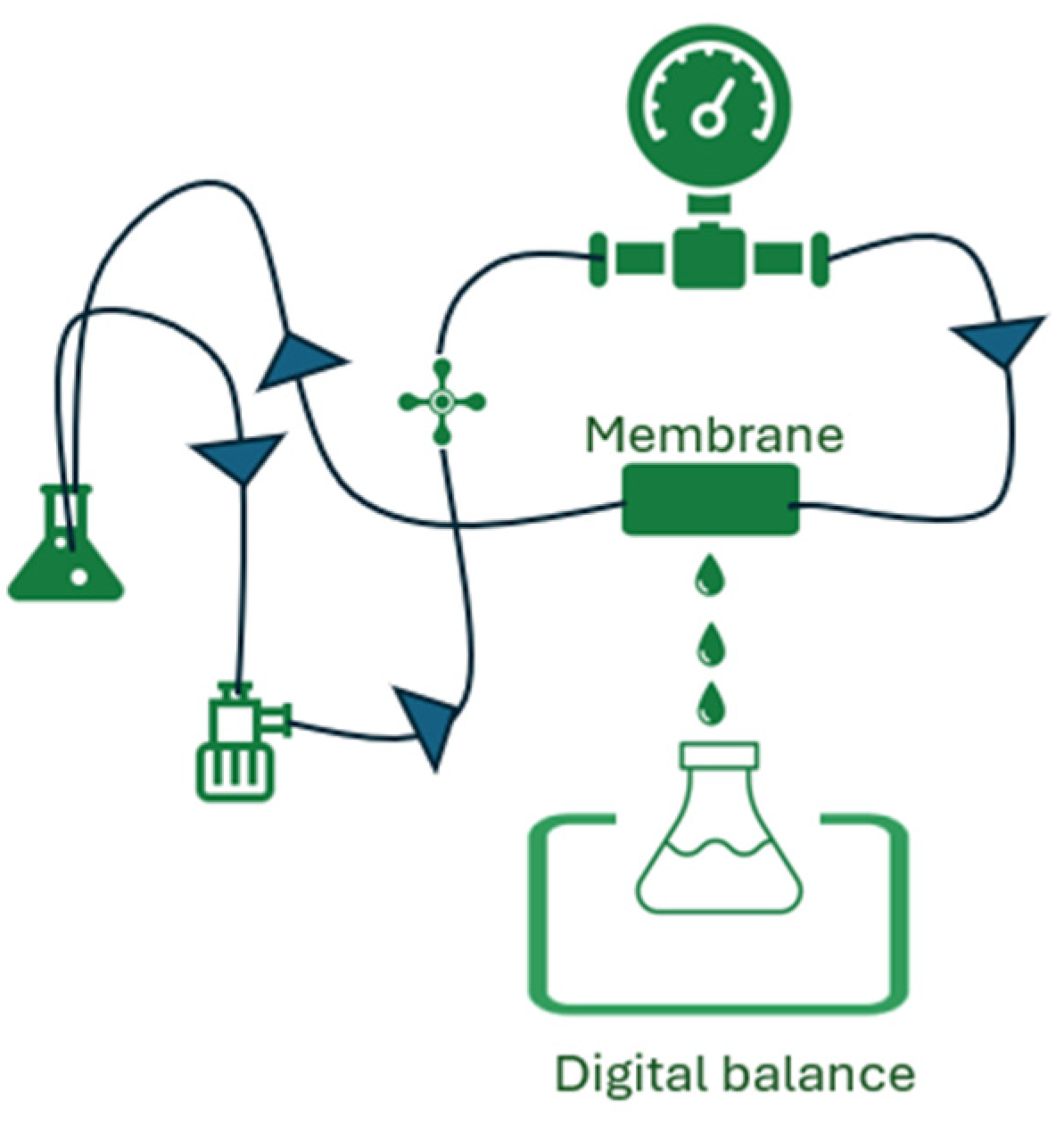
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
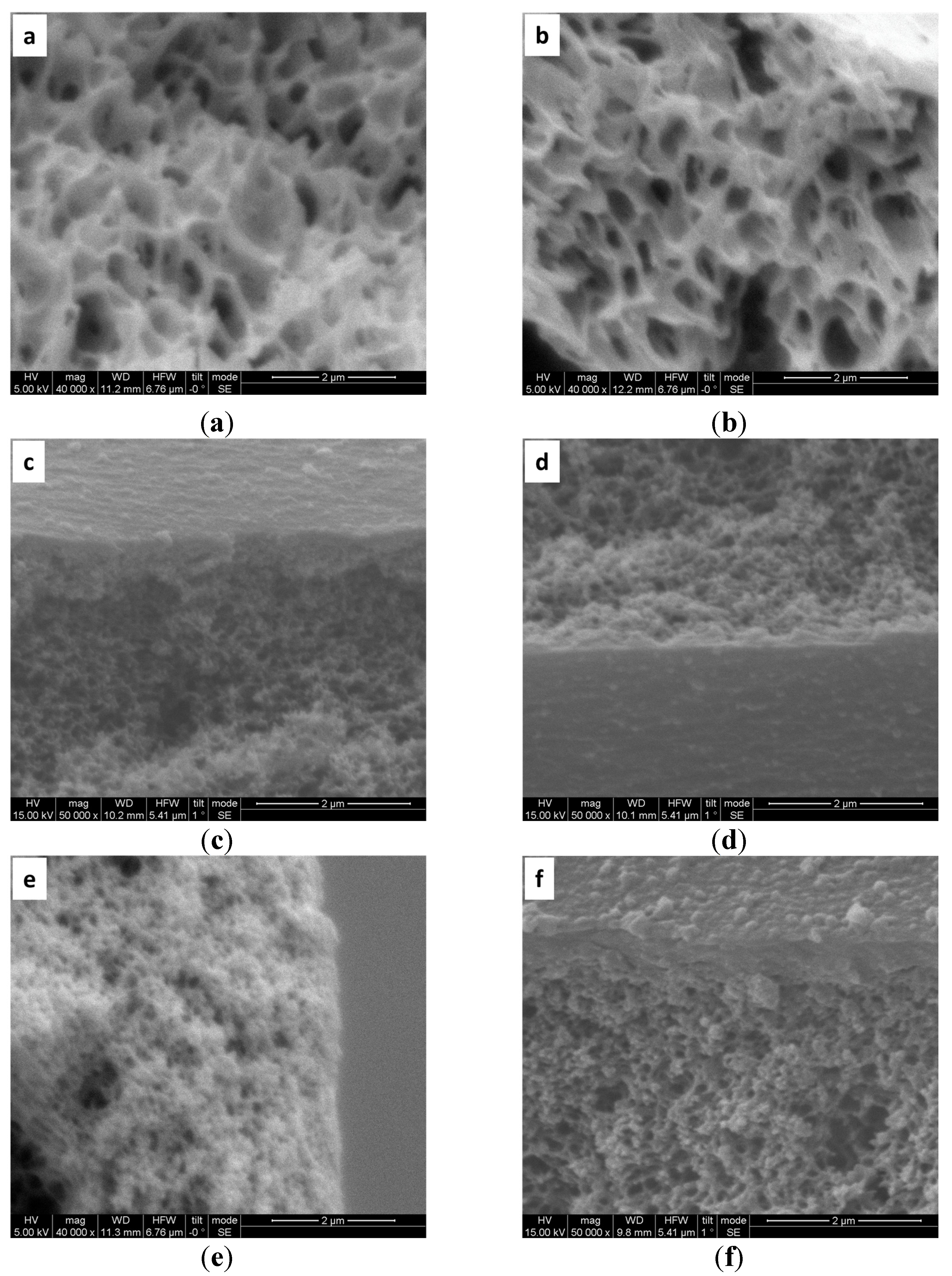
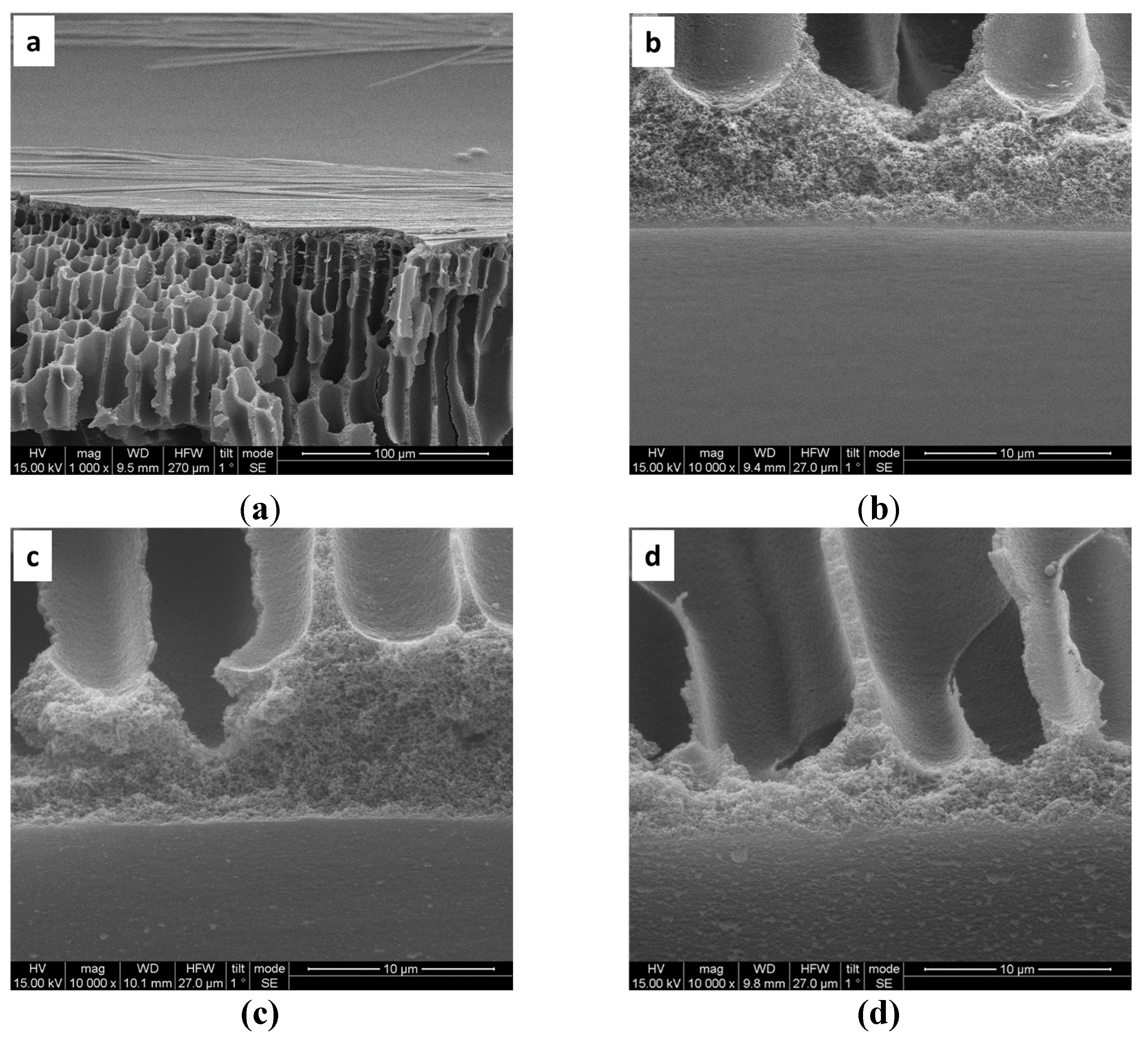
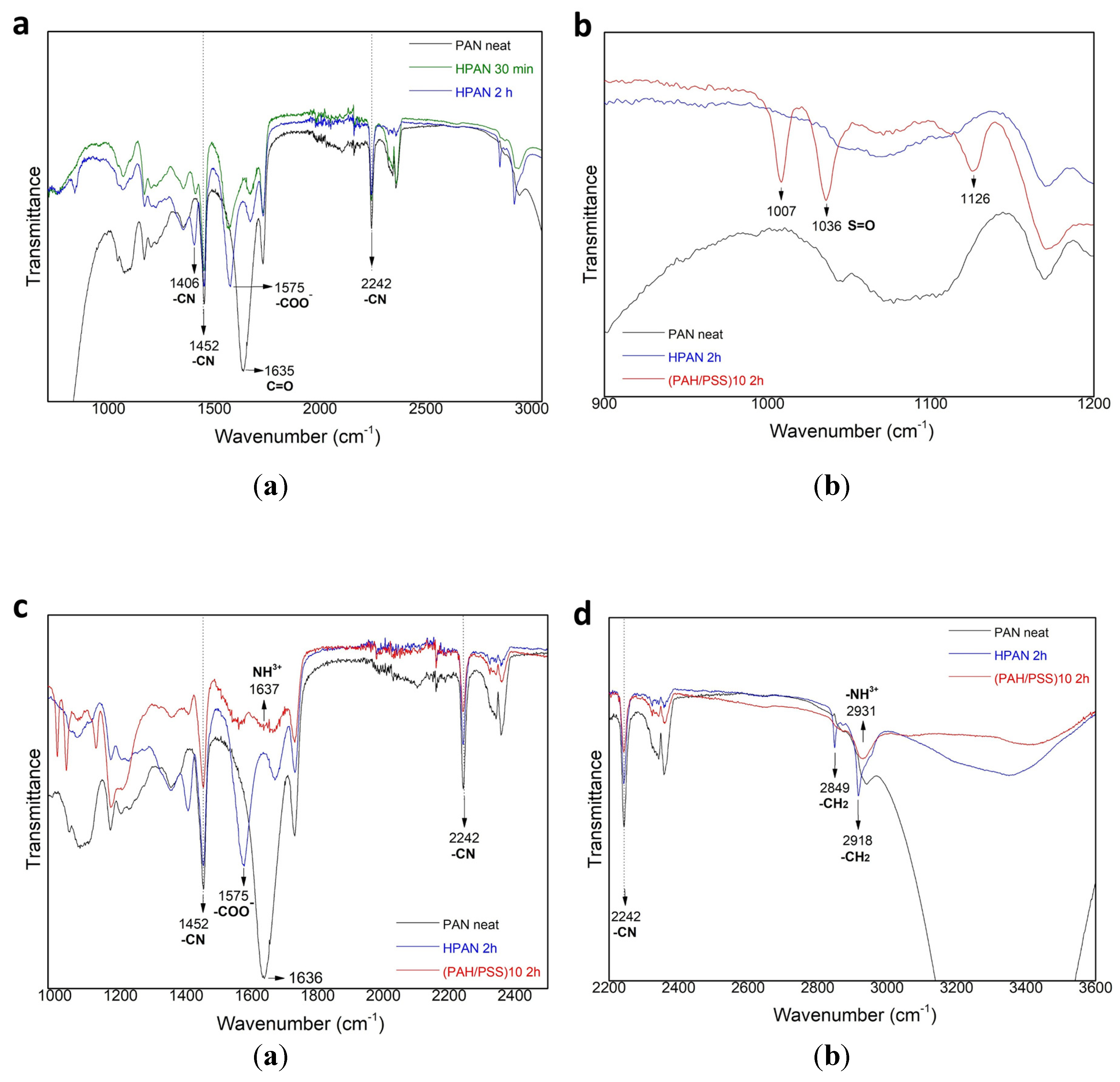
3.1. Characterization of LBL Modified Hollow Fiber Membranes
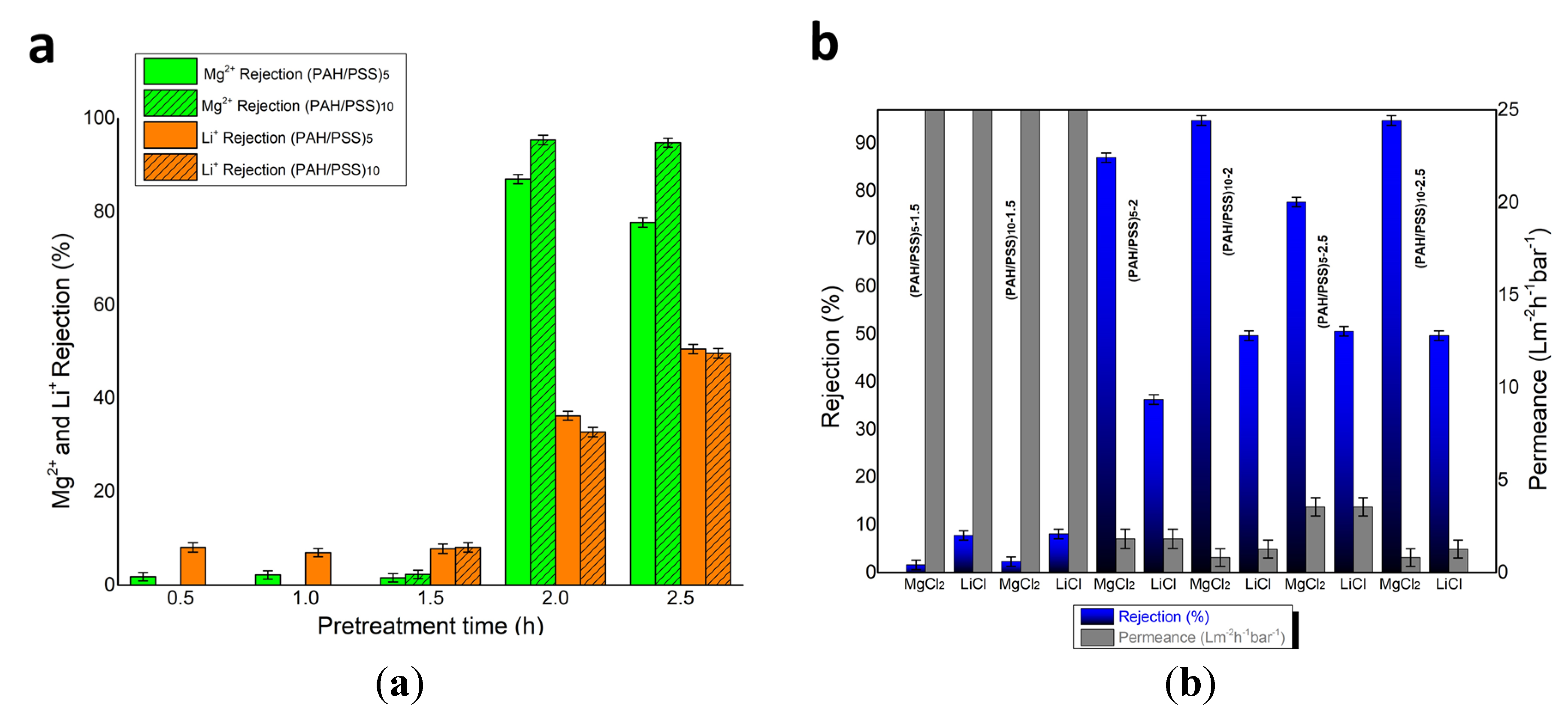
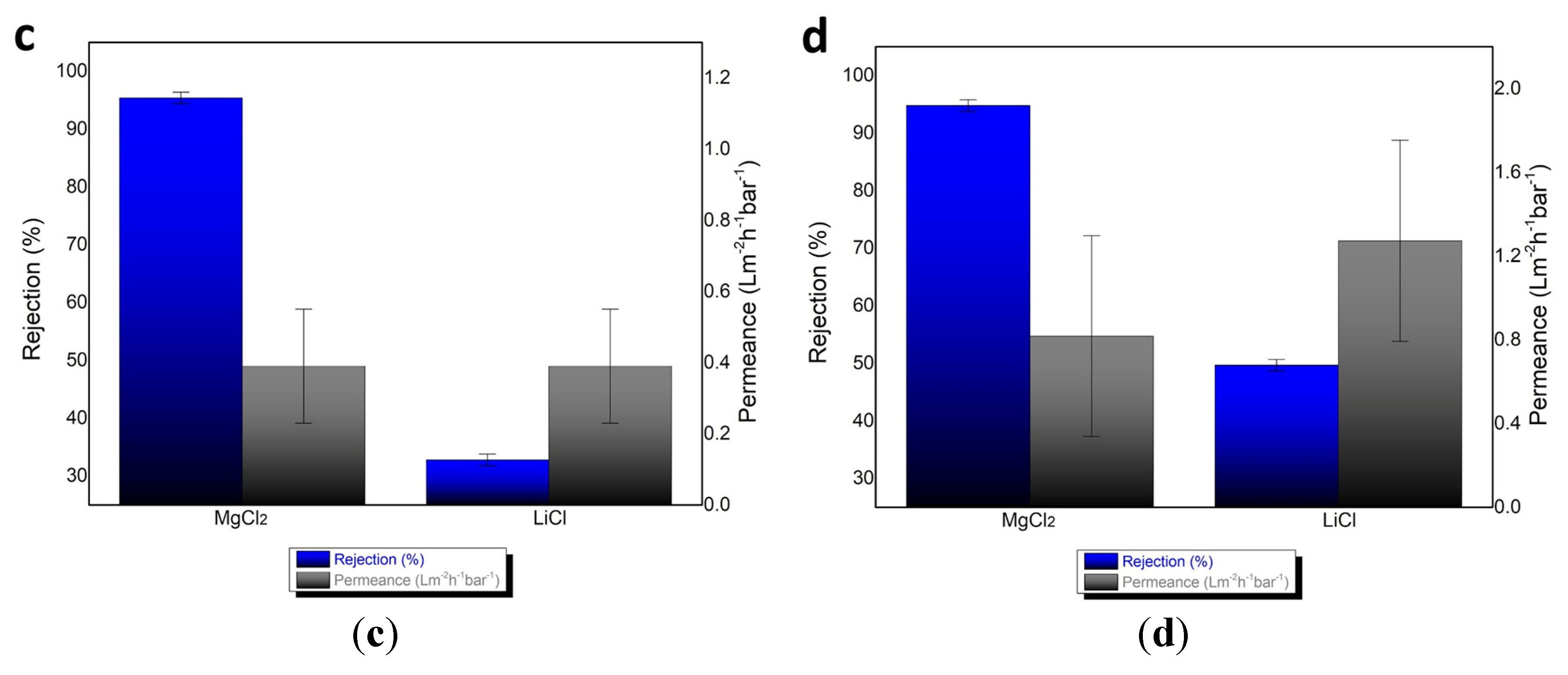
3.2. Separation Performance for Mg2+ and Li+
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, G.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, N.; Yin, S. Based on High Cross-Linked Structure Design to Fabricate PEI-Based Nanofiltration Membranes for Mg2+/Li+ Separation. Journal of Membrane Science 2024, 693, 122351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zeng, G.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Feng, Z.; Tang, B.; Yu, X.; et al. Nanofiltration Membrane Based on a Dual-Reinforcement Strategy of Support and Selective Layers for Efficient Mg2+/Li+ Separation. Separation and Purification Technology 2024, 330, 125254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Guo, F.; Wang, L.; Zhen, H.; Zhang, N.; Yin, S.; Zhou, G.; Ruan, X.; He, G.; Jiang, X. Nanofiltration Membrane with Modified Nano-Gradient Structure and Positive Charge for Li Separation from High Mg/Li Ratio Brine. Desalination 2024, 577, 117394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yan, F.; Li, J.; Mohammad, Y.; He, B. High Performance Li+/Mg2+ Separation Membrane by Grafted Short Chain Amino-Rich Monomers. Journal of Membrane Science 2023, 677, 121634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Wang, N.; Yang, Y.; Shen, M.; An, Q.-F. Positively-Charged Nanofiltration Membrane Constructed by Polyethyleneimine/Layered Double Hydroxide for Mg2+/Li+ Separation. Desalination 2023, 548, 116256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yun, R.; Xiang, X. Recent Advances in Magnesium/Lithium Separation and Lithium Extraction Technologies from Salt Lake Brine. Separation and Purification Technology 2021, 256, 117807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wu, L.-K.; Xu, Z.-L.; Hedar, M.; Luo, L.-H.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Li, H.-X.; Tong, Y.-H.; Xu, S.-J. Efficient Separation of Li+/Mg2+ via Positively Charged TFN Membrane Based on the PEI Interlayer. Chemical Engineering Science 2024, 284, 119523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Cui, W.; Shen, Q.; Yao, Z.; Fang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L. Porous Organic Polymer Interlayers Modulated Nanofiltration Membranes for Ultra-Permselective Li+ /Mg2+ Separation. Journal of Membrane Science 2024, 690, 122207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamble, N.P.; Eugene, E.A.; Phillip, W.A.; Dowling, A.W. Optimal Diafiltration Membrane Cascades Enable Green Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12207–12225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Xu, S.; Wang, R.; Bai, B.; Lin, S.; He, T. Polyelectrolyte-Based Nanofiltration Membranes with Exceptional Performance in Mg2+/Li+ Separation in a Wide Range of Solution Conditions. Journal of Membrane Science 2022, 663, 121027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Dong, C.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Zhao, S.; He, T. Unprecedented Mg2+/Li+ Separation Using Layer-by-Layer Based Nanofiltration Hollow Fiber Membranes. Desalination 2022, 525, 115492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; He, R.; Xu, S.; He, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.-B.; He, T. Layer-by-Layer (LBL) Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes for Seawater Treatment: Ion Rejection. Desalination 2022, 534, 115793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Gong, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. A Poly(Allylamine Hydrochloride)/Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) Microcapsule-Coated Cotton Fabric for Stimulus-Responsive Textiles. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 17731–17738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, C.; Tong, T.; Epsztein, R.; Sun, M.; Verduzco, R.; Ma, J.; Elimelech, M. Selective Removal of Divalent Cations by Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Nanofiltration Membrane: Role of Polyelectrolyte Charge, Ion Size, and Ionic Strength. Journal of Membrane Science 2018, 559, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; Wijeratne, S.; Cheng, C.; Baker, G.L.; Bruening, M.L. Facilitated Ion Transport through Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Films Containing Metal-Binding Ligands. Journal of Membrane Science 2014, 459, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Crosslinked Layer-by-Layer Polyelectrolyte Nanofiltration Hollow Fiber Membrane for Low-Pressure Water Softening with the Presence of SO42− in Feed Water. Journal of Membrane Science 2015, 486, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Pourafshari Chenar, M. Improving Antifouling Performance of PAN Hollow Fiber Membrane Using Surface Modification Method. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 2015, 55, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Bai, R.; Chen, J.P. Behaviors and Mechanisms of Copper Adsorption on Hydrolyzed Polyacrylonitrile Fibers. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2003, 260, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Umar, A.; Chen, Z.; Tian, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Supramolecular Fabrication of Polyelectrolyte-Modified Reduced Graphene Oxide for NO2 Sensing Applications. Ceramics International 2015, 41, 12130–12136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, S.; Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Preparation of Low-Pressure Water Softening Hollow Fiber Membranes by Polyelectrolyte Deposition with Two Bilayers. Desalination 2014, 344, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Yaroshchuk, A.; Bruening, M.L. Electrodialysis through Nafion Membranes Coated with Polyelectrolyte Multilayers Yields >99% Pure Monovalent Ions at High Recoveries. Journal of Membrane Science 2022, 647, 120294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Yaroshchuk, A.; Bruening, M.L. Moderate pH Changes Alter the Fluxes, Selectivities and Limiting Currents in Ion Transport through Polyelectrolyte Multilayers Deposited on Membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 2020, 616, 118570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Enhanced Hollow Fiber Membrane Performance via Semi-Dynamic Layer-by-Layer Polyelectrolyte Inner Surface Deposition for Nanofiltration and Forward Osmosis Applications. Reactive and Functional Polymers 2015, 86, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Zhao, Y.; Fong, H.; Menkhaus, T.J. Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Membranes Modified with Ionically Crosslinked Polyelectrolyte Multilayers for the Separation of Ionic Impurities. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 18376–18389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1st week | 2nd week | 3rd week | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (PAH/PSS)10-2 | (PAH/PSS)10-2.5 | (PAH/PSS)10-2 | (PAH/PSS)10-2.5 | (PAH/PSS)10-2 | (PAH/PSS)10-2.5 | |
| Mg Rejection (%) | 95.40 ±0.9 | 94.8 ±1 | 96.00 ±0.9 | 94.5.2 ±1 | 95.36 ±0.9 | 94.8 ±1 |
| Li Rejection (%) | 32.80 ±0.9 | 49.7 ±1 | 32.80 ±0.9 | 49.6 ±1 | 31.90 ±0.9 | 49.8 ±1 |
| Permeance (LMH/bar) | 0.39 ±0.47 | 1.04 ±0.52 | 0.34 ±0.47 | 1.05 ±0.52 | 0.35 ±0.47 | 1.05 ±0.52 |
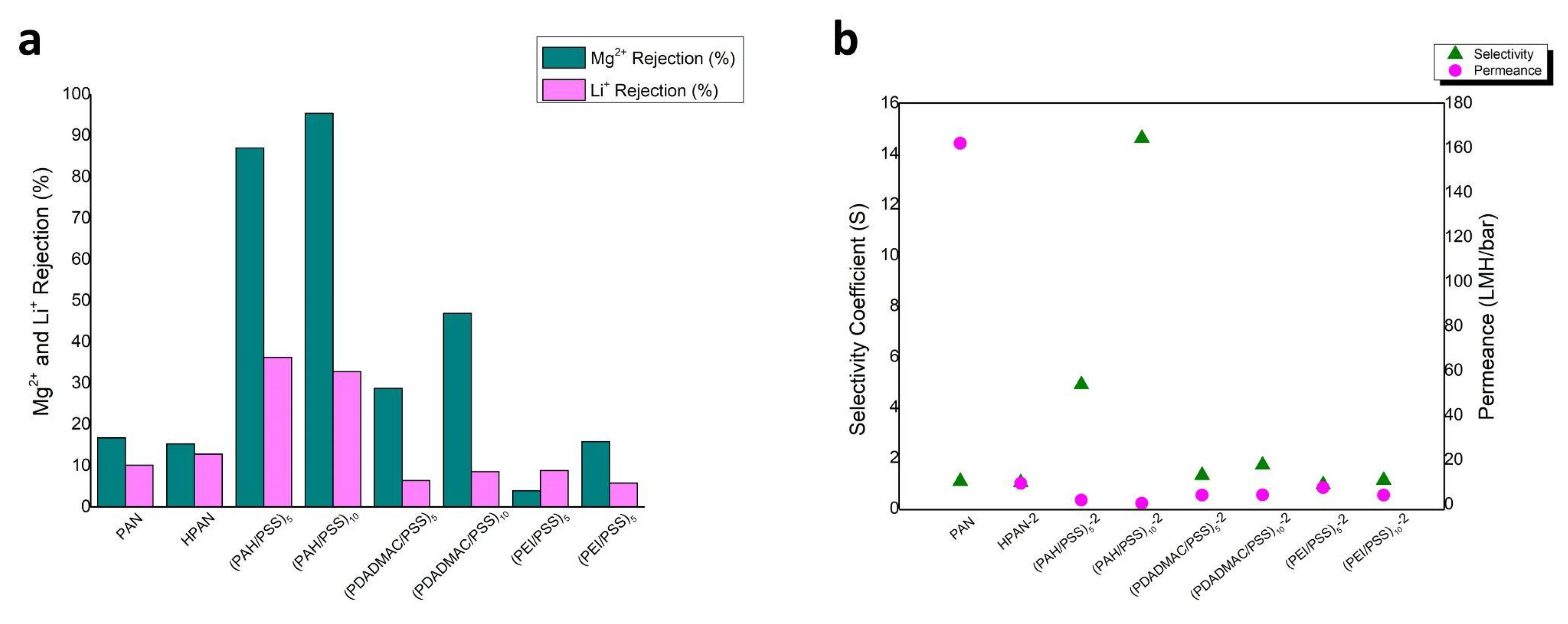
| Sample name | Mg Rejection (%) | Li Rejection (%) | Selectivity Coefficient (S) |
Permeance (LMH/bar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAN | 16.73 ±1 | 10.11 ±1 | 1.079 | 161.91 ±0.51 |
| HPAN-2 | 15.30 ±1.4 | 12.80 ±1.4 | 1.030 | 9.37 ±0.5 |
| (PAH/PSS)5-2 | 87.00 ±1 | 36.30 ±1 | 4.900 | 1.83 ±0.49 |
| (PAH/PSS)10-2 | 95.40 ±0.9 | 32.80 ±0.9 | 14.609 | 0.39 ±0.47 |
| (PDADMAC/PSS)5-2 | 28.74 ±1 | 6.39 ±1 | 1.313 | 4.07 ±0.49 |
| (PDADMAC/PSS)10-2 | 46.95 ±1 | 8.53 ±1 | 1.724 | 4.11 ±0.49 |
| (PEI/PSS)5-2 | 3.97 ±1.1 | 8.83 ±1.1 | 0.949 | 7.46 ±0.5 |
| (PEI/PSS)10-2 | 15.83 ±0.9 | 5.79 ±0.9 | 1.119 | 4.03 ±0.48 |
| Study | Membrane Type | Mg2+ Rejection (%) | Li+ Rejection (%) | Selectivity coefficient | Permeance (LMH/bar) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Study | (PAH/PSS)10 on hydrolyzed PAN hollow fiber | 95.4 | 32.8 | 14.61 | 0.39 | High/average selectivity coefficient. Low permeance. |
| Current Study | (PAH/PSS)5 on hydrolyzed PAN hollow fiber | 87.00 | 36.30 | 4.900 | 1.83 | Average selectivity coefficient. Low/Average permeance. |
| He et al. 2022 | (PSS/PAH)2.5 on PES hollow fiber | 99.1 | 59.4 | 45.11 | 18.4 | High selectivity coefficient. High permeance. |
| Liu et al. 2015 | Crosslinked (PSS/PAH)1.5C on PES hollow fiber | 98.2 | 33.5 (Na+) | 36.94 | 10 | High selectivity coefficient. High permeance. |
| Liu et al. 2015 | (PSS/PAH)2 on PES hollow fiber | 98.1 | 58.6 (Na+) | 21.79 | >10 | High/average selectivity coefficient. High permeance. |
| Liu et al. 2015 | NF 270 | 42.9 | 37.1 (Na+) | 1.10 | >10 | Commercial membrane, low selectivity coefficient. High permeance. |
| Liu et al. 2015 | NF 90 | 96 | 68.6 (Na+) | 7.85 | 6-7 | Commercial membrane, average selectivity coefficient. High/average permeance. |
| Rajesh et al. 2016 | (BPEI/PAA)15 on PAN nanofiber mats coated with CA | 95.3 | 34.1 (Na+) | 14.02 | 5 | Different polyelectrolytes, average selectivity coefficient. High/average permeance. |
| Wang et al. 2024 | B15C5-MX-NF on PES |
89.7 | 21.4 | 7.63 | 10.8 | Different polyelectrolytes, average selectivity coefficient. High permeance. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





