1. Introduction
Corrosion is defined as degradation of materials, with consequent diminution of their properties, due to deteriorative interactions with environments to which they are exposed [
1]. The environments that are usually exposed in the pipelines that can enhance the corrosion rate are corrosive media such as dissolved H
2S, Cl
2, O
2, and CO
2. Another environment faced by pipelines in petroleum industries is organic acid condition. The presence of organic acid increases the solubility of corrosion product films, leading to the reduction of protective corrosion products. The presence of these acids will increase the hydrogen concentration and the acidic environment that favors the corrosion attack towards the metal surface. Among all organic acids, acetic acid is the most abundant, produced by the reaction between hydrocarbon in crude oil, water molecules, and chemical used to enhance the oil recovery process [
2,
3].
The common corrosion control compounds used in the petroleum industry are corrosion-resistant alloys (CRAs), protective coatings, corrosion inhibitors, and cathodic protection. The CRAs and corrosion inhibitors strategies are good for reducing internal corrosion caused by corrosive fluids, which internally degrade processing equipment and pipelines. Of all the corrosion control strategies, corrosion inhibitors are highly considered as an economical and effective way of mitigating internal corrosion [
4]. A review by Xiong et al. [
5] has stated that the surfactant molecules can perform as corrosion inhibitors due to their high affinity to adsorb over the interface, resulting in a higher potential in resolving corrosion issues over metal surfaces. Verma et al. [
6] also stated that the corrosion inhibition performance of surfactants is based on the surfactant molecules’ adsorption capacity over the metal surface’s reactive sites. Quaternary ammonium surfactant is a surfactant compound that contains a hydrophilic head (N
+) and a hydrophobic tail (alkyl chain) that is an excellent corrosion inhibitor due to its properties that could be adsorbed on the metal surface and form a protective layer [
7]. The strong adsorption of nitrogen atoms from the quaternary ammonium surfactant molecules on the metal surface leads to the formation of adsorption film that separates the metal from the corrosive medium [
8]. In 2021, Abdellaoie et al. [
9] found that quaternary ammonium surfactant, namely, 12-(2,3-dioxoindolin-1-yl)-N,N,N-trimethyldodecanammonium bromide has a higher inhibition efficiency (95.9 %) at concentration of 1.0 mM in the presence of 1.0 M HCl at temperature 298 K. Besides, Alnajjar et al. [
10] synthesized, N,N-dimethyl-N-(3-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonamido)propyl)dodecan-1-aminium iodide, another quaternary ammonium surfactant, and found that this surfactant was able to increase the inhibition efficiency up to 98.6 % in the presence of 15 % HCl solution.
Adsorption is the critical aspect for the inhibition activities of the surfactant molecule towards metal surface. A review by Numin et al. in 2022 revealed that an in-depth study on the adsorption properties of the surfactant molecules towards the metal surface gave a better explanation on the inhibition mechanism of the corrosion system [
11]. Other than that, in 2019, Gao et al. studied the effect of the alkyl chain of quaternary ammonium cationic surfactants on corrosion inhibition in HCl solution, experimentally. They found that the dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (DTAC) performed the best with the highest inhibition efficiency of >90 % [
7]. However, the in-depth study on the adsorption mechanism of quaternary ammonium cationic surfactants by computer simulation methods is limited. The previous researchers only focused on the strong acidic condition such as HCl, sulphuric acid (H
2SO
4), and phosphoric acid (H
3PO
4), and there is a lack of studies in acetic acid (CH
3COOH) condition which is more applicable in the petrochemical industries’ pipelines. Thus, this study focuses on the in-depth study of the adsorption mechanism of the quaternary ammonium surfactants with different alkyl chain lengths (C10, C12, C14, C16, and C18) towards the metal surface, Fe (110) in the presence of both HCl and acetic acid via DFT calculation and MD simulation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculation
DFT calculation provides relatively fast and reliable electronic properties to predict the performance of corrosion inhibitors and can theoretically analyze the structure of electrons [
12]. The compound’s electronic properties determine the adsorption properties of the ammonium surfactant cationic CIs towards the metal surface. The DFT calculation is performed by using Tmolex software. The structures of ammonium surfactant CI with a different alkyl chain length C10, C12, C14, C16, and C18 were optimized by using hybrid functional B3LYP [
13,
14] in a non-aqueous or vacuum environment with def-SV(P).h basis set [
15,
16]. The input file was generated by inserting the ground-state calculation under the DFT setting, and the parameters derived from the DFT calculation were visualized and calculated by the Tmolex program.
The output parameters calculated include the highest occupied molecular orbital energy (
) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy (
). Then, both HOMO and LUMO energy were used to calculate the other inhibition parameters of ammonium surfactant cationic CI molecules such as band-gap energy (
), number of transferred electron (
), electronegativity (
), hardness (
), softness (
), ionization potential (
) and electron affinity (
). The derived output parameters, equation, description, and reference are tabulated in
Table 1.
2.2. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
MD simulation has been used to investigate the molecular level interaction of corrosion inhibitors on the corrosion system with the presence of acetic acid. MD simulation can provide the molecular orientation of CI molecules on the metal surface, strength of adsorption, and aggregation of CI molecules in different concentrations [
23]. The initial coordinates of C10, C12, C14, C16, and C18 CI molecules were submitted to the Automated Topology Builder (ATB) and Repository Version 3.0 server to obtain the optimized geometry chemical and topology file. The metal surface used in this simulation was Fe (110) because it is a densely packed surface and, therefore, the most stable [
24]. In the adsorption energy (E
ads), and binding energy (E
bind) calculation, each CI molecule filled the centre of the box with a size of 51.60, 51.60, 77.40 Å. The Fe (110), and the acidic medium were added into the box that contained H
3O
+, Cl-, H
2O, and acetic acid molecules.
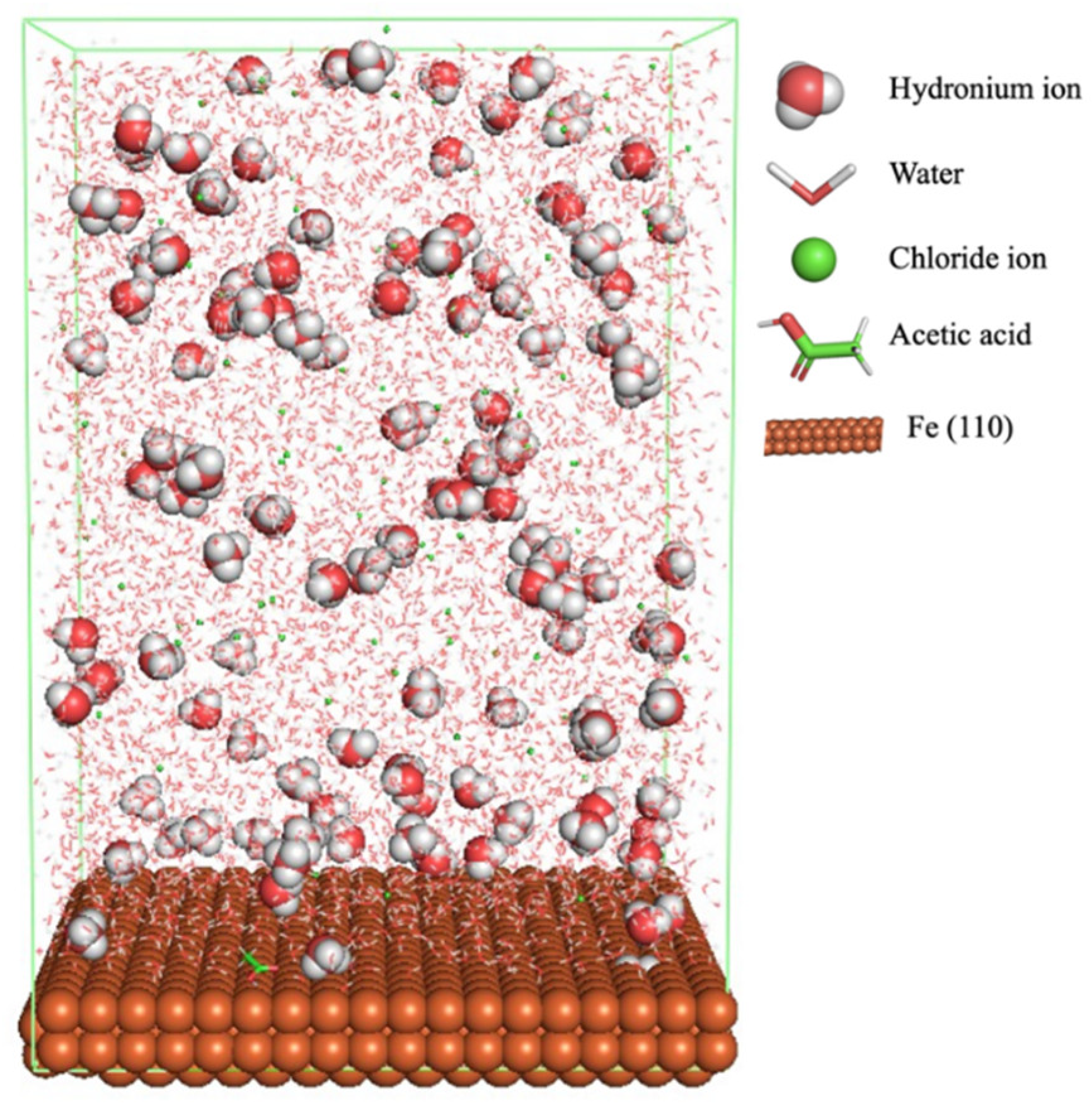
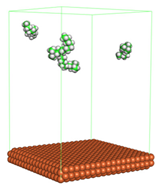
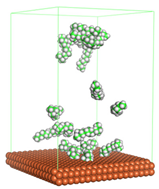
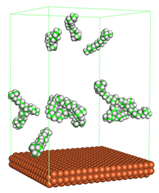
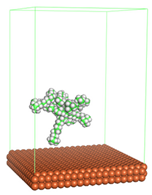
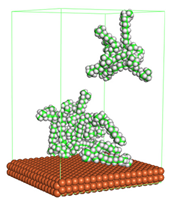
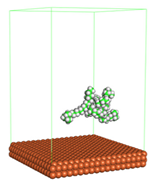
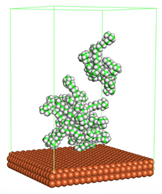
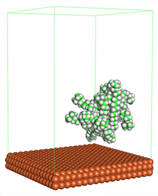
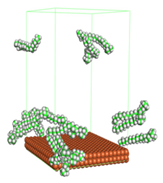
Figure 1 shows the corrosion system without the presence of a CI molecule. For molecular aggregation analysis, the systems were constructed at five different concentrations of CI molecules (0.04, 0.08 0.12, 0.16 and 0.20 M).
After the system preparation, the MD simulation started with energy minimization using the steepest descent and conjugate gradient methods for 5000 steps. This is to resolve the atomic collisions, bond distortions, other unfavorable interactions, and overall energy of the system, resulting in a more stable initial structure for the simulation. Then, the simulation proceeded with the canonical (NVT) and isothermal (NPT) ensemble for 5 ns each. The NVT is to establish the proper orientation in the system’s temperature for the calculation of adsorption energy, and the molecular aggregation of the molecules at different temperatures is investigated after the NPT ensemble. Periodic boundary condition (PBC) was applied in all directions (x, y, z) with 2.0 fs time steps. Electrostatic interaction was calculated using Particle Mesh Ewald (PME) [
25] with a grid spacing of 0.12 nm and fourth-order interpolation. The Coulomb and Lennard interactions were summed up to 1.2 nm. The neighbor search of 1.2 nm was updated every five steps. The bond lengths for solute as well as organic solvent molecules were constrained with Linear Constraint Solver (LINCS) [
26], while for all water molecules, SETTLE algorithm was used [
27]. The GROMACS software package 4.5 with the GROMOS molecular force field was used throughout this simulation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculation
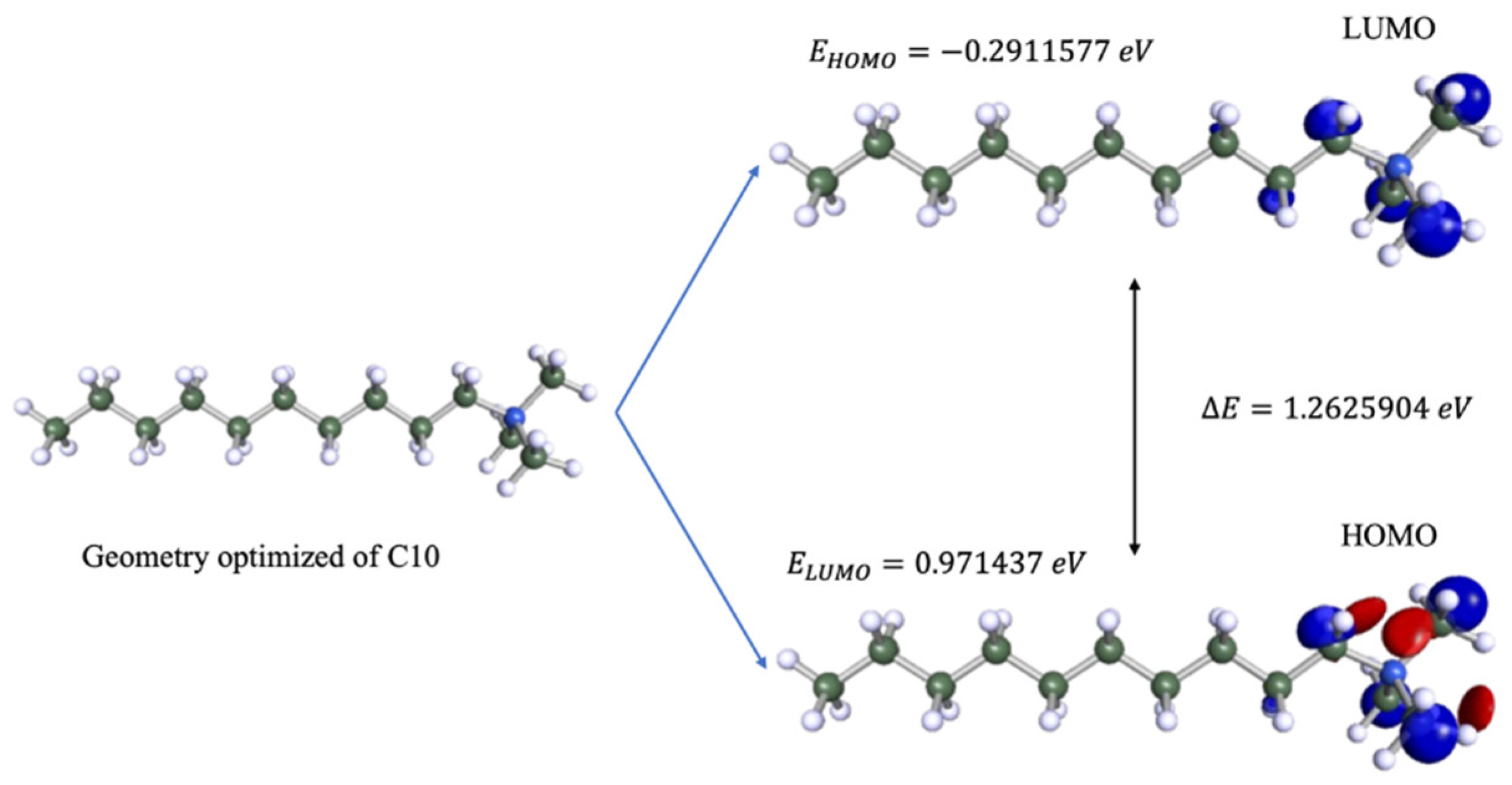
The DFT calculation can be used to explain the adsorption properties of CI molecules towards the metal surface. HOMO represents the groups from CI molecules that are capable of donating electrons to the empty
3d orbital of iron (Fe) atom on the metal surface. At the same time, LUMO represents groups that can accept electrons from the metal surface throughout back-donation [
28,
29]. The optimized structure, HOMO, and LUMO of all CI molecules are illustrated in
Table 2. The table shows that LUMO is distributed at the alpha carbon of the quaternary ammonium groups of CI molecules, while the HOMO is distributed at both the alpha carbon and quaternary ammonium groups. The quaternary ammonium compounds are known to be good electrolytes due to their structure that consists of both polar (N
+) and non-polar (alkyl) terminuses that increase its ability to be adsorbed at the surface [
30].
Table 2 also exhibits that quaternary ammonium groups at all CI molecules can donate electrons to the empty
3d orbital of the Fe atom where the HOMO is concentrated at that region. At the same time, for some molecules such as C10, C14, and C16, the carbon atom next to the quaternary ammonium group behaves as a LUMO region where it can accept electrons from the Fe atom through the back-donation mechanism that can increase the adsorption properties of the CI molecules on the Fe metal surface. The cationic nature of the nitrogen atom within the quaternary ammonium group of the surfactant molecules leads to physisorption, a type of adsorption governed by charge interactions. This interaction, between the N atom and the chloride anion (Cl
-) on the Fe surface, effectively prevents the Cl
- ions from the acid from attacking the metal surface, thereby inhibiting the iron oxidation reaction at the anode [
31]. However, the study by Abdellaoui et al. in 2021 demonstrated that the adsorption of quaternary ammonium surfactants onto metal surfaces can involve both physisorption and chemisorption or called mixed inhibitor [
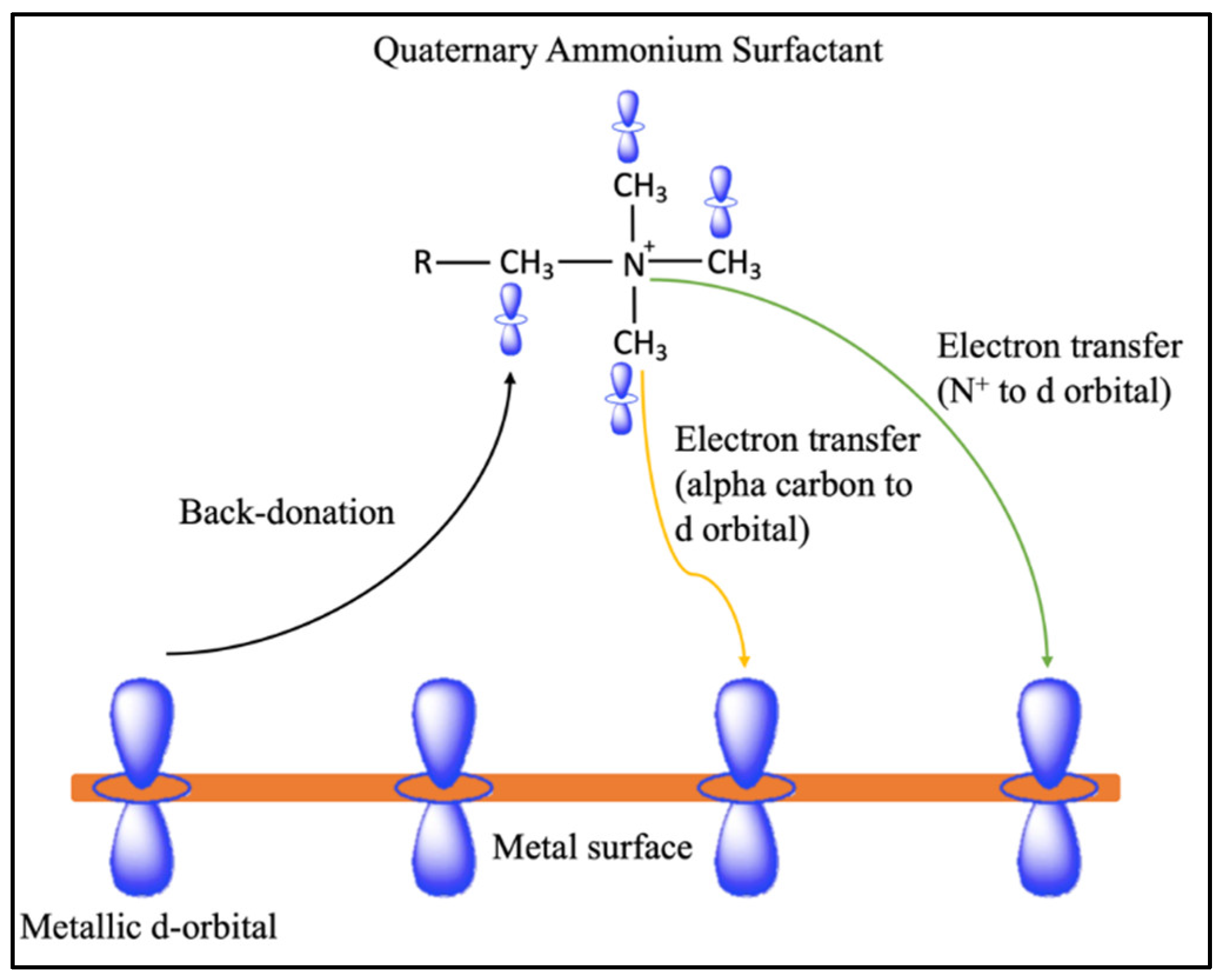
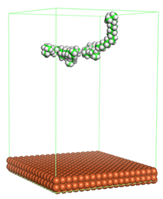
32]. Chemisorption occurs through the formation of covalent bonds, with electron transfer from the alpha carbon of the quaternary ammonium surfactant to the vacant
d-orbital of the metal surface. Alternatively, a back-donation mechanism can transfer electrons from the metal d-orbital to the carbon adjacent to the quaternary ammonium surfactant region (
Figure 2).
The output parameters derived from the DFT calculation are tabulated in
Table 3. The adsorption ability as a donor-acceptor contributor of CI molecules is depicted by the energy of HOMO (
) and LUMO (
). The higher value of
implies the higher donor ability, while the higher value of
represents the acceptor ability of the CI molecules. The band gap energy,
is the difference between LUMO energy and HOMO energy, where the lower
value for all CI molecules (1.26 eV) indicates the higher reactivity of the CI molecules as a donor-acceptor contributor. The identical band gap energy values observed among all quaternary ammonium surfactant CI molecules with varying alkyl chain lengths indicated that the reactivity of these molecules is primarily determined by their reactive HOMO and LUMO regions. This finding is attributed to the quantum chemical DFT calculations, which were performed on individual CI molecules without considering any solvent effects. Consequently, the alkyl chain length exerts a minimal influence on the band gap energy. However, the alkyl chain can play a crucial role in molecular adsorption by providing steric hindrance and protecting the reactive region from interactions with other molecules. This aspect will be explored further in the subsequent section on MD simulation methods. The illustration of the HOMO, LUMO, and
for the C10 molecule is shown in
Figure 3.
A study by Han et al. [
33] has proven experimentally that the CI molecule with the lowest
value gave the highest efficiency as a corrosion inhibitor compared to CI molecules that have a higher
value. The HOMO and LUMO energy values also affect the electronegativity (
), hardness (
η), and softness (σ) of the CI molecules. All CI molecules have a low
value, which indicates the higher ability of the molecules to donate electrons. The low value of
η and high σ value also shows the higher reactivity of the CI molecules in the electron transfer process [
34]. The final output parameter is the number of transferred electrons from CI molecules (
). The positive value of
indicates that the major electron transfer process is from CI molecules to the iron metal surfaces [
35,
36]. The electron-donating ability of these CI molecules is due to the HOMO that is distributed at the alpha carbon regions of the molecules, representing the ability to donate electrons compared to the LUMO that is only circulated at the next carbon from the alpha carbon. DFT calculations have shown that quaternary ammonium surfactant CI molecules can act as both nucleophiles and electrophiles. These molecules can donate electrons to metal surfaces and receive electrons through back-donation, forming coordination bonds via chemisorption. Moreover, the cationic nature of nitrogen allows for physisorption through charge interaction with the metal surface [
7]. The length of the alkyl group attached to the quaternary ammonium surfactants does not significantly influence the electron-donating ability of the CI molecules, as indicated by the minimal variation in the DFT-derived parameters. To assess the impact of alkyl chain length on corrosion inhibition efficiency, the polarity and solubility of the compounds must also be considered. Due to the inverse relationship between alkyl chain length and both polarity and solubility, shorter alkyl chains generally correlate with improved corrosion inhibition performance [
37]. The effects of polarity and solubility will be further explored in the MD simulation analysis with the presence of the corrosion solution.
3.2. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
3.2.1. Adsorption Properties of CI Molecules
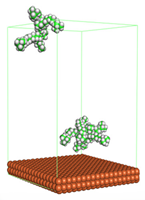
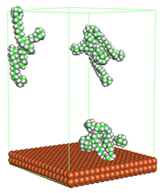
The MD simulation was used to study the adsorption behaviour and the interaction of CI molecules (C10, C12, C14, C16, and C18) towards the Fe (110) metal surface in the presence of 1.0 M HCl and 500 ppm acetic acid solution. The addition of HCl and acetic acid solution is to increase the corrosion attack towards the metal surface.
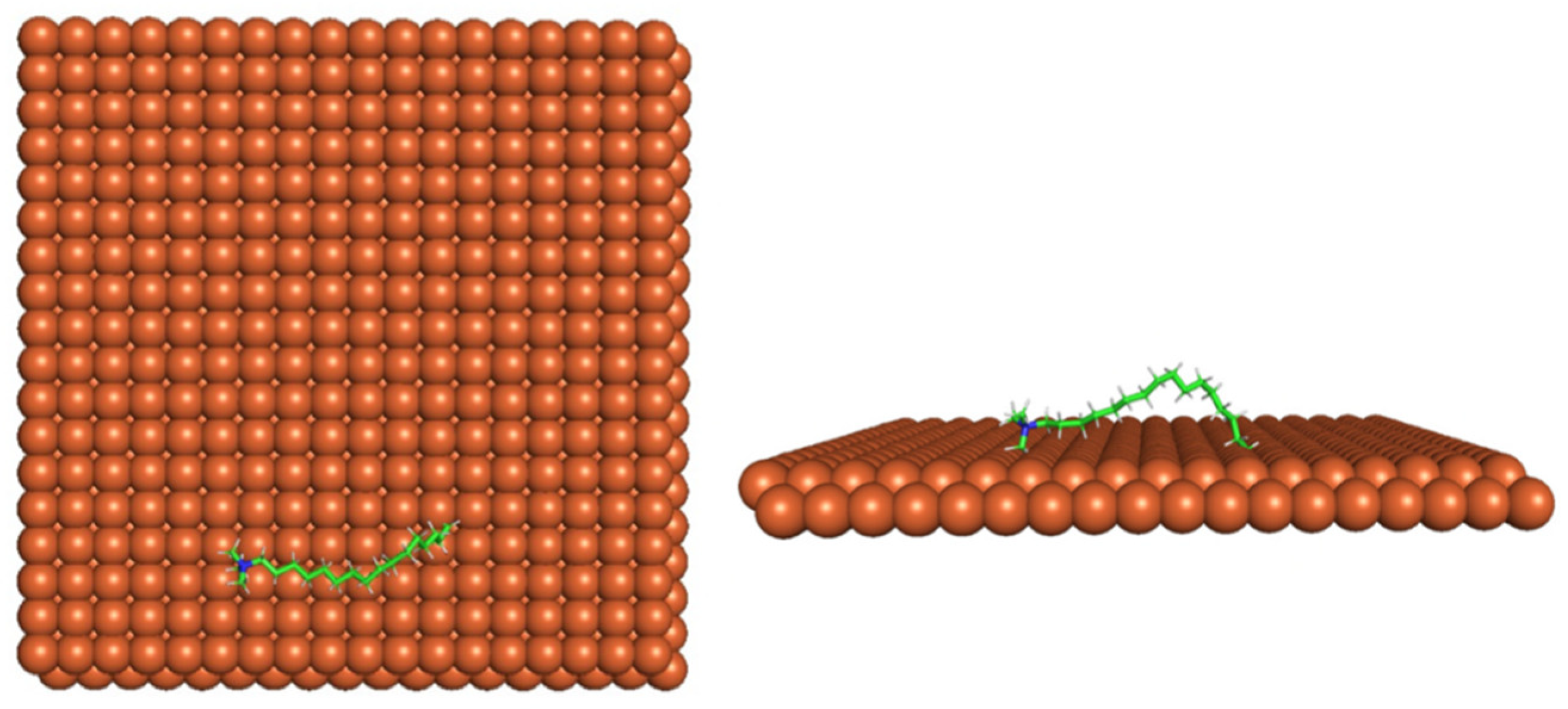
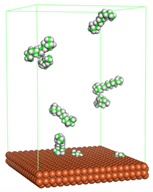
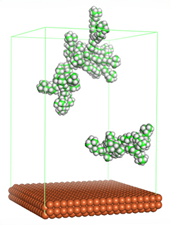
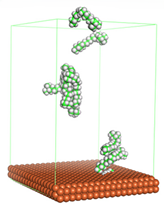
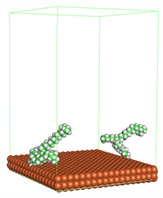
Figure 4 shows the top and side view of CI molecule on the Fe (110) surface after MD simulation. The molecules behaved as a planar orientation on the Fe (110) surface which is more favorable towards the inhibition due to the mechanism of CI that should form a film formation to cover the metal surface from the corrosion attack. The CI with planar orientation will cover more surface than the horizontal orientation. Besides, horizontal orientation also will reduce the adsorption strength of its reactive site due to the hydrophobic part that will undergo force of interaction with the bulk corrosion solution [
38]. Theoretically, in the horizontal orientation, longer alkyl chains on CI molecules experience greater shear forces, which can disrupt the adsorption of the CI molecules’ reactive regions to the metal surface.
Figure 4 demonstrates the adsorption of the quaternary ammonium group onto the metal surface, accompanied by charge interactions and electron transfer between the reactive region of the CI molecules and the metal. This observation aligns with the DFT calculation results, which identified the quaternary ammonium and alpha carbon regions as the HOMO with a high electron-donating capacity. On the other hand, the hydrophobic side of the surfactant molecules is also attached to the metal surface due to the electron back donation from the Fe atom to the alkyl group of the CI molecule [
39]. According to El Defrawy et al. in 2019, the back-donation ability of the CI molecules is directly proportional with the hardness (
η), as defined in the following Equation 1 [
40]:
where
is the band-gap energy for back-donation mechanism. The
value is tabulated in
Table 4 and shows that the values of
η > 0 and
< 0 implies that back-donation from the metal to CI molecule are energetically favoured [
41,
42]. C12, C14, C16, and C18 have the highest back donation ability with the same
value of -0.1574837 eV, compared to the C10 CI molecule with a
value of -0.1578238 eV. As the LUMO region resides within the alkyl groups, increasing the alkyl chain length by two carbons beyond the shortest inhibitor, C10, to C12, enhances back-donation capability. C12 represents the optimal value for back-donation, with the corresponding value remaining relatively constant up to C18. Back-donation is also called the back bonding mechanism, where the carbon atom in the CI molecule can accept electrons back from the metal to strengthen the bond between the metal and the carbon of the CI molecule [
43]. The results show that the quaternary ammonium CI with a longer alkyl chain length provides a site for the back donation mechanism from the Fe metal.
3.2.2. Adsorption Energy
Three different systems were constructed, and the energy of all systems was calculated to find the adsorption energy at seven different temperatures (303, 313, 323, 333, 343, 353, and 363 K). The systems include the corrosion system with CI molecules, corrosion system without CI molecules, and CI molecules only. Equation 2 was used to calculate the adsorption energy (
) [
34].
where the
is the energy for corrosion a system with CI molecules,
is the energy for corrosion system without CI molecules, and
is the energy of the system with CI molecules only.
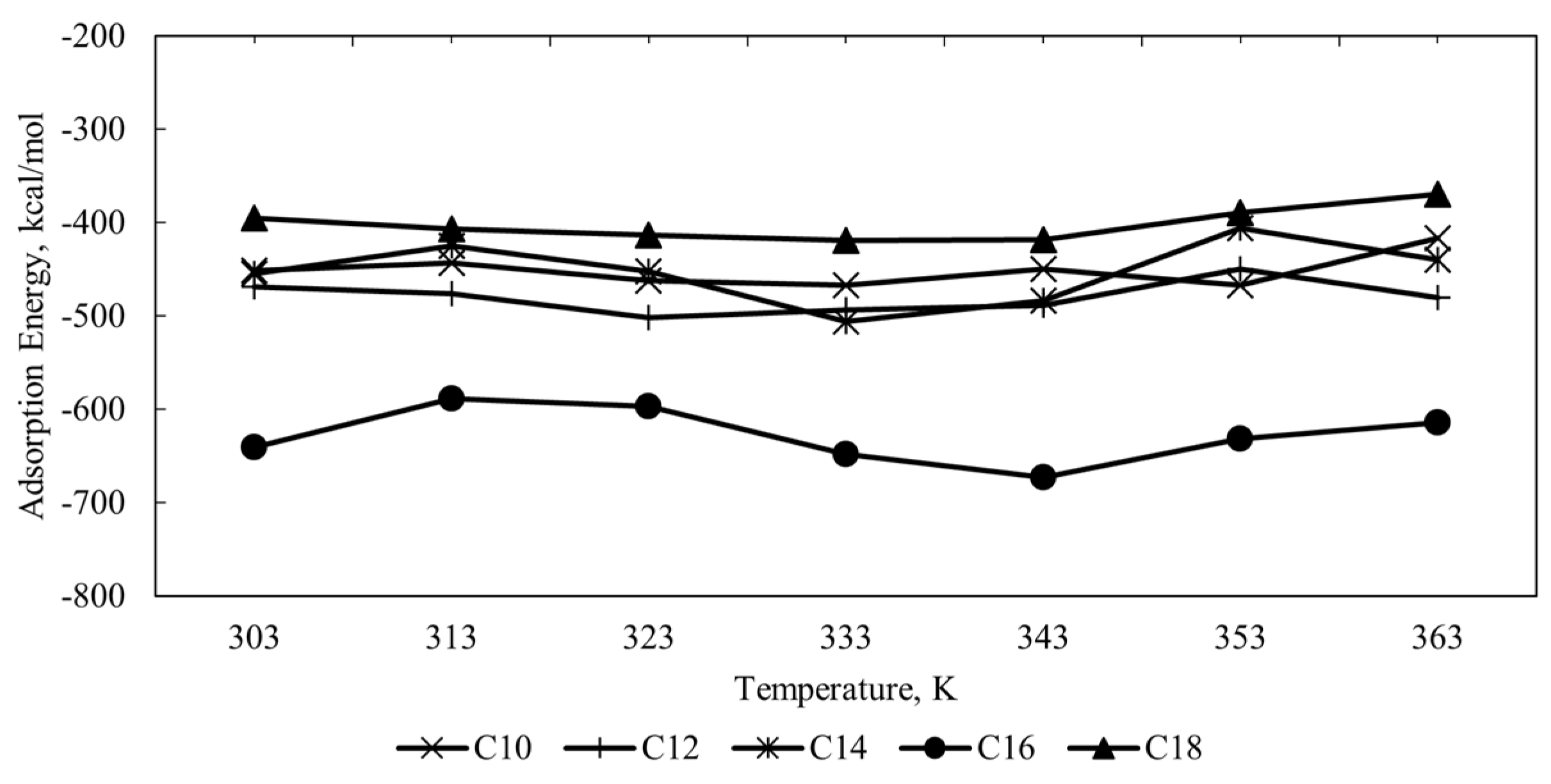
Figure 5 shows the plot of calculated adsorption energy for all CI molecules in the acidic corrosion system at different temperatures. The negative value of adsorption energy for all systems indicates the spontaneity of the adsorption process between CI molecules and Fe (110) metal surface. The higher the negative value of adsorption energy denotes, the stronger the adsorption [
23]. Another energy parameter that can describe the inhibition of CI molecules is binding energy (
). The
value can be translated from the adsorption energy and can be calculated using Equation 3:
The
and
values for all molecules at temperature 323 K were tabulated in
Table 5 where the
value for all molecules is positive, indicating its tendency to the adsorption process. The order of binding energy for all molecules are C16 > C12 > C10 > C14 > C18. Binding energy is referred to the attraction forces between the CI molecules and the metal surfaces. For the quaternary ammonium surfactant CI molecules, the attraction forces mainly happen due to the ionic properties of the hydrophilic head and the hydrophobic interaction of the hydrophobic tail in the bulk solution of the corrosion system [
38,
44]. The results show that CI molecules’ adsorption and binding energy values vary with different alkyl chain length. Among all the CI molecules, C18, with the longest alkyl chain, exhibits the weakest adsorption strength. Conversely, C16, with the second-longest alkyl chain, demonstrates the strongest adsorption strength, adsorption magnitude, and binding energy. The alkyl chain length significantly influences the adsorption strength of CI molecules onto the Fe (110) metal surface, with longer chains generally leading to stronger adsorption. Extended alkyl chains effectively shield the positively charged nitrogen and alpha carbon of the quaternary ammonium surfactant from the shear and flow effects of the bulk corrosion solution. This is attributed to the increased number of carbon atoms in longer chains, which can interact through van der Waals forces, promoting aggregation among the alkyl chains rather than their interaction with the surface. Additionally, the greater conformational freedom of longer chains can hinder their ability to adopt the specific conformations required for strong adsorption. Furthermore, longer alkyl chains can create steric hindrance, limiting the molecules’ proximity to the metal surface and reducing the effective contact area, thereby decreasing adsorption strength. The longer the alkyl chain length, the more hydrophobic group that extends away from the interface towards the solution and provides further protection by forming an array of hydrophobic tails, resulting in the change of electrochemical behaviour of the metal [
45,
46]. Hence, the binding energy between the reactive regions (HOMO and LUMO) of the corrosion inhibitor molecule with the Fe metal surface increases as the alkyl chain length increases.
However, there are some cases where adding alkyl chain length reduces the adsorption strength of the reactive site of the CI molecule towards the metal surface. The decrease in adsorption may be due to the shear and the flow effect experienced by the extended hydrophobic alkyl chain from the bulk solution. The results show a fluctuation of the adsorption strength as the alkyl chain length extended. So, the optimum value of the alkyl chain length is needed to be explicitly investigated due to the variation effect of the adsorption strength on the alkyl chain length of the quaternary ammonium surfactant CI molecules on the Fe (110) metal surface where in this case the highest adsorption is C16, followed by C12, C10, C14, and C18 molecules.
3.2.3. Molecular Aggregation
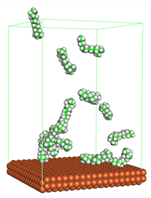
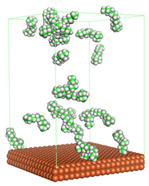
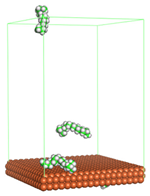
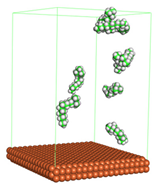
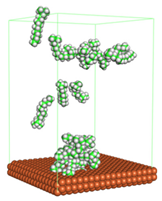
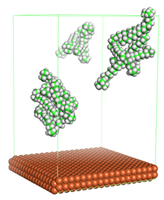
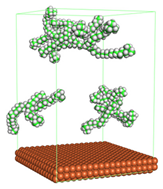
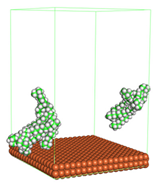
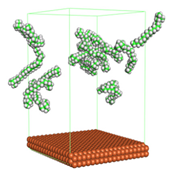
In the molecular aggregation analysis, five systems were constructed via MD simulation for each CI molecule in different concentrations (0.04, 0.08, 0.12, 0.16, and 0.20 M) in the presence of 1.0 M HCl, 500 ppm acetic acid, and temperature 333 K. The system does not consist of a Fe (110) metal surface to investigate the molecular aggregation of the CI molecules at different concentrations in the bulk solution consisting of corrosion particles. The constructed system is shown in
Figure 6. The molecular behaviour of the CI molecules was analyzed based on their diffusion towards the bulk solution or corrosion particles. The diffusion coefficient is defined as the quantity of a substance diffusing from one region to another, passing through each unit of cross-section per unit of time when the volume-concentration gradient is unity. Einstein diffusion Equations 4 and 5 [
47,
48] was used to calculate the diffusion coefficient.
where
is time,
is the position vector of a molecule at time
, and
N is the amount of diffusion molecules. The mean square displacement was derived from the MD simulation, and the limiting slope of the MSD as a function of time can be used to explain the diffusion coefficient of a molecule [
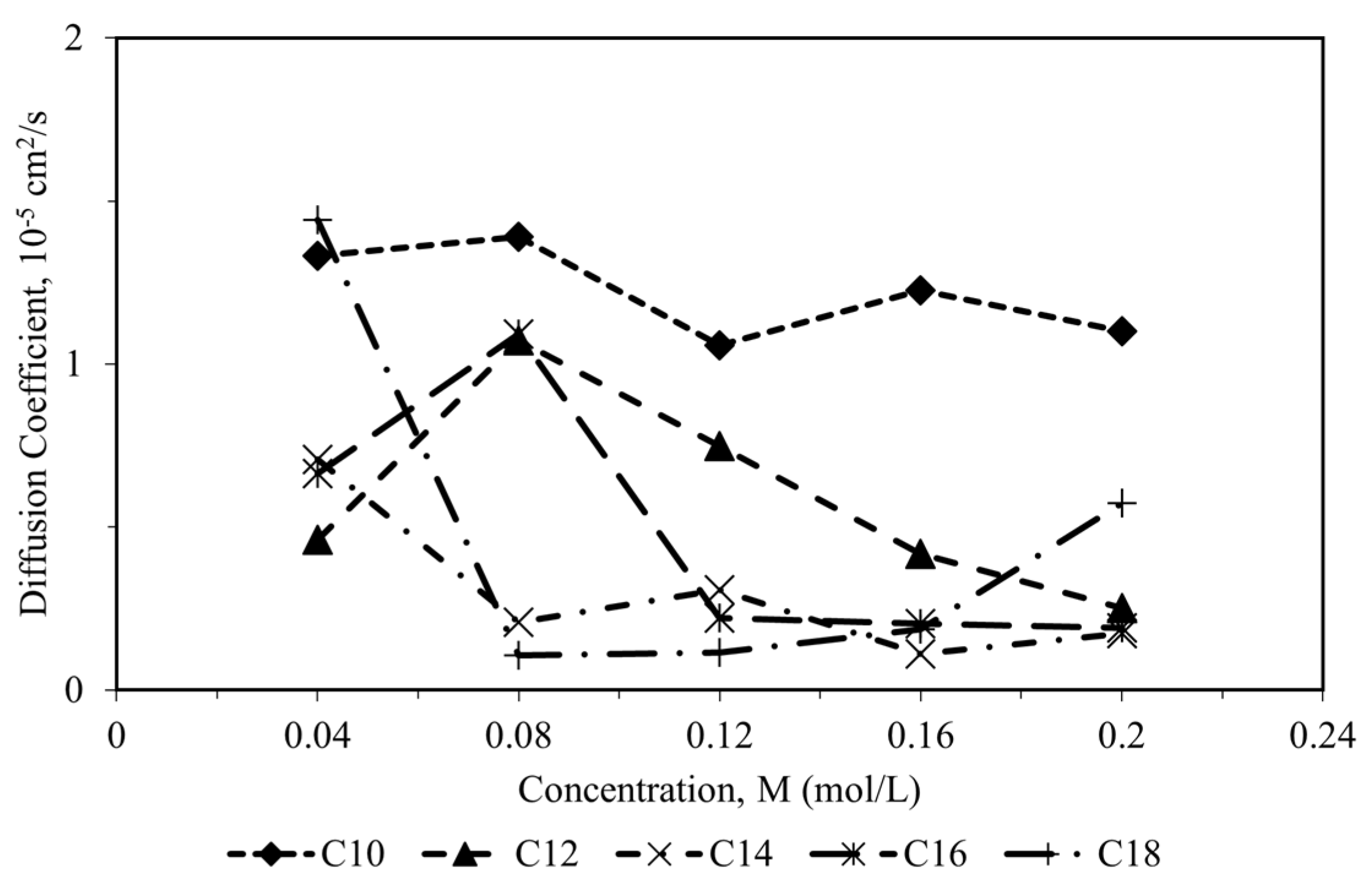
49]. Based on
Figure 7, the diffusion coefficient of CI molecules towards the corrosion particles decreases as the alkyl chain increases. As the alkyl chain length of surfactant molecules increases, their hydrophobicity rises, hindering their diffusion towards polar corrosion particles. This creates a diffusion barrier between the inhibitor molecule and the corrosion particles, enhancing the adsorption of the surfactant onto the metal surface and strengthening the metal-inhibitor interaction [
50]. As stated by Obot et al. [
49], the low diffusion coefficient of CI molecules also indicates that the CI molecules have a promising inhibitive capacity against the corrosion particles’ diffusion. They had proved that the CI molecules with the lowest coefficient diffusion of the corrosive particles have the highest inhibition efficiency, which agrees with the experimental data.
The diffusion coefficient of all CI molecules correlated with the aggregation of the molecules in the corrosion system. The decrease in diffusion of CI molecules was due to the rapid aggregation that leads to cluster formation [
24,52]. According to Sharma et al. [52], the CI molecules that form a cluster aggregation have weaker adsorption at the metal surface than CI molecules that are randomly scattered in the corrosion particles.
Table 6 shows the cluster aggregation of all CI molecules at different concentrations. The C10 molecules with the shortest alkyl chain length behave randomly scattered in the bulk solution corrosion particles from low to high concentrations. Although the C10 CI molecules were randomly scattered in the corrosion particles, the diffusion coefficient showed that the molecule has a strong interaction with the corrosion particles with a high diffusion coefficient value. These properties can disturb its inhibition ability by reducing its surface activities and affecting the adsorption strength (low magnitude of adsorption and binding energy) of the CI molecule towards the metal surface. For the C12 molecule, the molecules were randomly scattered at low concentrations (0.04 and 0.08 M), and the cluster aggregation started to form at a concentration of 0.12 M. The ability of the C12 molecules to be randomly scattered in the bulk solution corrosion particles favored the inhibition efficiency towards the metal surface. The low diffusion coefficient also contributes to better surface activities and increases adsorption strength towards the metal surface. On the other hand, the molecules with a longer alkyl chain (C14, C16, and C18) formed a cluster aggregation at all concentrations, which does not favor the inhibition efficiency. Based on the results from MD simulation, C12 surfactant molecules have the most promising inhibition properties with high negative value of adsorption energy, high binding energy, low diffusion with the corrosion particles and randomly scattered at low concentration. The results by MD simulation were at an excellent agreement with the experimental results studied by Gao et al. [
7] in 2019, where the dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (DTAC) surfactant molecules with 12 alkyl chain had the highest inhibition efficiency compared to its significant type surfactants with different chain length.
4. Conclusions
The DFT calculation and MD simulation methods successfully investigated the adsorption properties of all quaternary ammonium surfactants CI molecules with different chain lengths throughout this study. All CI molecules show a high reactive adsorption centre with lower band-gap energy at 1.26 eV in the DFT calculation. The region of reactive adsorption centre for all CI molecules is focused on the molecules’ ammonium group (N+). The values of other parameters derived in the DFT calculation also showed the reactive center’s ability to donate and accept electrons on the metal surface. The inhibition efficiency ranking for all CI molecules based on adsorption energy and binding energy are C16 > C12 > C10 > C14 > C18, where C16 had the highest negative value of adsorption energy and highest binding energy value. However, the C16 molecules formed a cluster even at low concentration in the molecular aggregation analysis. Thus, the C12 ammonium surfactants gave the most promising corrosion inhibitor compared to its significant surfactants with different chain lengths based on the MD simulation method analysis. It showed high adsorption and binding energy after C16 molecules, and it behaved in a randomly scattered form in the molecular aggregation analysis. The excellent agreement between the computer simulation data with the experimental results from the literature and the success in analyzing the inhibition efficiency of all ammonium CI molecules proves the validity of using computer modelling in this application. Therefore, the CI activities and adsorption properties analysis based on computer modelling can be helpful for a future reference on the development of a new CI molecule.
Author Contributions
Jumbri, K.: Conceptualization, Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Project administration. Numin, M.S.: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing - Original draft. Kee, K.E.: Conceptualization, Resources. Hassan, A.: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing - Original draft. Borhan, N.: Conceptualization, Resources. Daud, N.M.R.: Writing – review & editing. Nor, A.M.: Writing – review & editing. Suhor, F.: Writing – review & editing. Dzulkifli, N.N.: Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
This research was funded by the Yayasan Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS-Fundamental Research Grant (YUTP-FRG) grant number 015LC0-409.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS for sponsoring this work under Yayasan Universiti Teknologi Petronas-Fundamental Research Grant (YUTP-FRG).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Zehra, S.; Mobin, M.; Aslam, J. 1 - An overview of the corrosion chemistry. In Environmentally Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitors, Washington, DC, Elsevier, 2022, 3-23.
- Chafale, A.; Kapley, A. Biosurfactants as microbial bioactive compounds in microbial enhanced oil recovery. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 352, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Liu, Q.; Lv, J.; Peng, B. Review on microbial enhanced oil recovery: Mechanisms, modeling and field trials. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2020, 192, 107350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurapati, Y. A molecular dynamics study to understand behavior of corrosion inhibitors in bulk aqueous phase and near metal-water interface, Ohio University: Russ College of Engineering and Technology, 2018.
- Xiong, Y.; Cao, M. Application of surfactants in corrosion inhibition of metals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 101830, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A.; Rhee, K.Y. Hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity consideration of organic surfactant compounds: Effect of alkyl chain length on corrosion protection. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 306, 102723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minlan G.; Lei, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Effect of the alkyl chain of quaternary ammonium cationic surfactants on corrosion inhibition in hydrochloric acid solution. C. r., Chim. 2019, 22, 355-362.
- Deyab, M.A.; Ashmawy, A.M.; Nessim, M.I.; Mohsen, Q. New Gemini surfactants based on alkyl benzenaminium: Synthesis and links to application of corrosion protection. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellaoui, O.; Skalli, M.K.; Haoudi, A.; Kandri Rodi, Y.; Arrousse, N.; Taleb, M.; Ghibate, R.; Senhaji, O. Study of the inhibition of corrosion of mild steel in a 1M HCl solution by a new quaternary ammonium surfactant. Mor. J. Chem. 2021, 9(1), 044–056. [Google Scholar]
- Alnajjar, A.O.; Abd El-Lateef, H.M. A novel approach to investigate the synergistic inhibition effect of nickel phosphate nanoparticles with quaternary ammonium surfactant on the Q235-mild steel corrosion: Surface morphology, electrochemical-computational modeling outlines. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numin, M.S.; Hassan, A.; Jumbri, K.; Eng, K. K.; Borhan, N.; Nik M. Daud, N.M.R.; M Nor A, A.; Suhor, F.; Abdul Wahab, R. A recent review on theoretical studies of Gemini surfactant corrosion inhibitors. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, vol. 368, p. 120649.
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Cao, G. Molecular dynamics simulation and DFT calculation of “green” scale and corrosion inhibitor. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 188, 110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional theory. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98(7), 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density functional calculations of molecular bond energies. J. Chem. Phys. 1986, 84(8), 4524–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, C.; Thomas, K.; Huniar, U.; Hellweg, A.; Rubner, O.; Schroer, A. Schroer. Software news and updates TmoleX-a graphical user interface for TURBOMOLE. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 2967-2970.
- Obot, I.B.; Macdonald, D.D.; Gasem, Z.M. Density functional theory (DFT) as a powerful tool for designing new organic corrosion inhibitors. Part 1: An overview. Corros. Sci. 2015, 99, 1-30.
- Dewar, M.J.S.; Thiel, W. Ground states of molecules. 38. The MNDO method. Approximations and parameters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99(15), 4899–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.G. Absolute electronegativity and hardness: Application to inorganic chemistry. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27(4), 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez-Roman, J.H.; Padilla-Campos, L.; Paez, M.A.; Zagal, J.H.; Rubio, M.A.; Rangel, C.M.; Costamagna, J.; Cardenas-Jiron, G. The influence of aniline and its derivatives on the corrosion behaviour of copper in acid solution: A theoretical approach. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2005, 757(1-3), 1-7.
- Sastri, V.S.; Perumareddi. J.R. Molecular orbital theoretical studies of some organic corrosion inhibitors. Corros. Sci. 1997, 53, 617-622.
- Lukovits, I.; Kalman, E.; Zucchi, F. Corrosion inhibitors—correlation between electronic structure and efficiency. Corrosion 2001, 57(1), 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, N.I.N.; Sobri, S.; Yusof, Y.N.; Kassim, N.K. An overview of molecular dynamic simulation for corrosion inhibition of ferrous metals. Metals 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, N.; Jumbri, K.; Kassim, M.A.; Wahab, R.A.; Rahman, M.B.A. Density functional theory and molecular dynamics simulation studies of bio-based fatty hydrazide-corrosion inhibitors on Fe (110) in acidic media. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 118321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B. P-LINCS: A parallel linear constraint solver for molecular simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Kollman, P.A. Settle: An analytical version of the SHAKE and RATTLE algorithm for rigid water models. J. Comput. Chem. 1992, 13(8), 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokalj, A. On the alleged importance of the molecular electron-donating ability and the HOMO–LUMO gap in corrosion inhibition studies. Corros. Sci. 2021, 180, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunyemi, B.T.; Latona, D.F. , Ayinde, A.A.; Adejoro, I.A. Theoretical investigation to corrosion inhibition efficiency of some chloroquine derivatives using density functional theory. Adv. J. Chem. A. 2020, 3(4), 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ullah, S.; Hu, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, B. The surface adsorption, aggregate structure and antibacterial activity of Gemini quaternary ammonium surfactants with carboxylic counterions. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, B.; Deng, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. Nitrate on localized corrosion of carbon steel and stainless steel in aqueous solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 369, 137660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellaoui, O.; Skalli, M.K.; Haoudi, A.; Rodi, Y.L.; Arrousse, N.; Taleb, M.; Ghibate, R.; Senhaji, O. Study of the inhibition of corrosion of mild steel in a 1M HCl solution by a new quaternary ammonium surfactant. Mor. J. Chem. 2021, 9(1), 044–056. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadani, A.; Kataria, H.; Singh, S. Synthesis, characterization and comparative evaluation of phenoxy ring containing long chain gemini imidazolium and pyridinium amphiphiles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361(1), 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Ma, X. Efficiency of Gemini surfactant containing semi-rigid spacer as microbial corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in simulated seawater. Bioelectrochem. 2021, 140, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakiet, M.; Tedim, J.; Kowalczyk, I.; Brycki, B. Functionalised novel Gemini surfactants as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 50 mM NaCl: Experimental and theoretical insights. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 580, 123699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, B.; Xiang, J.; Chen, X.; Gu, T.; Liu, H. The performance and mechanism of bifunctional biocide sodium pyrithione against sulfate reducing bacteria in X80 carbon steel corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2019, 150, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Ebenso, E.E.; Quraishi, M.A. Molecular structural aspects of organic corrosion inhibitors: Influence of -CN and -NO2 substituents on designing of potential corrosion inhibitors for aqueous media. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 316, 113874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazouti, A.; Errahmany, N.; Rbaa, M.; Galai, M.; Rouifi, Z.; Touir, R.; Zarrouk, A.; Kaya, S.; Touhami, M.E.; Ibrahimi, B.E.; Erkan, S. Effect of hydrocarbon chain length for acid corrosion inhibition of mild steel by three 8-(n-bromo-R-alkoxy)quinoline derivatives: Experimental and theoretical investigations. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1244, 130976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.; Guesmi, N.E.; Al-Gorair, A.S.; El-Sayed, R.; Meshabi, A.; Sobhi, M. Enhancing the anticorrosion performance of mild steel in sulfuric acid using synthetic non-ionic surfactants: practical and theoretical studies. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2021, 14(2), 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defrawy, A.E.; Abdallah, M.; Al-Fahemi, J. Electrochemical and theoretical investigation for some pyrazolone derivatives as inhibitors for the corrosion of c-steel in 0.5 M hydrochloric acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, R.S.A.; Al-Bagawi, A.H.; Shehata, A.H.; Shamroukh, A.H.; Abdallah, M. Corrosion inhibition and adsorption properties of some heterocyclic derivatives on C-steel surface in HCl. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2020, 51, 1-11.
- Alfakeer, M.; Abdallah, M.; Fawzy, A. Corrosion Inhibition effect of expired ampicillin and flucloxacillin drugs for mild steel in aqueous acidic medium. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 3283–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulechfar, C.; Ferkous, H.; Delimi, A.; Berredjem, M.; Kahlouche, A.; Madaci, A.; Djellali, S.; Boufas, S.; Djedouani, A.; Errachid, A.; Khan, A.A.; Boublia, A.; Lemaoui, T.; Benguerba, Y. Corrosion inhibition of Schiff base and their metal complexes with [Mn (II), Co (II) and Zn (II)]: Experimental and quantum chemical studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 378, 121637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Seyeux, A.; Zanna, S.; Pailleret, A.; Nesic, S.; Marcus, P. Adsorption mechanism of quaternary ammonium corrosion inhibitor on carbon steel surface using ToF-SIMS and XPS. Corros. Sci. 2023, 213, 110952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, J.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ali, S.A.; Aljeaban, N.A. Pyrrolidine-based quaternary ammonium salts containing propargyl and hydrophobic C-12 and C-16 alkyl chains as corrosion inhibitors in aqueous acidic media. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, G.; Verma, C.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Barsoum, I.; Alfantazi, A. Corrosion inhibition of P110 carbon steel useful for casing and tubing applications in 3.5% NaCl solution using quaternary ammonium-based copolymers. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 402, 124691.
- Babarao, R.; Jiang, J. Diffusion and separation of CO2 and CH4 in silicalite, C168 Schwarzite, and IRMOF-1: A comparative study from molecular dynamics simulation. Langmuir 2008, 24(10), 5474–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, L.; Pozuelo, J.; Lo ́ pez-Gonza ́ lez, M.; Fang, J.; Riande, E. Simulation and experimental studies on proton diffusion in polyelectrolytes based on sulfonated naphthalenic copolyimides. Macromolecules 2009, 42(17), 6572–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Bahraq, A.A.; Alamri, A.H. Density functional theory and molecular dynamics simulation of the corrosive particle diffusion in pyrimidine and its derivatives films. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 210, 111428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Vashisht, H.; Alrefaee, S.H.; Jain, R.; Kumar, S.; Kaya, S.; Guo, L.; Verma, C. Decyltriphenylphosphonium bromide containing hydrophobic alkyl chain as a potential corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in sulfuric acid: Theoretical and experimental studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ko, X.; Kurapati, Y.; Singh, H.; Nesic, S. Adsorption Behavior of organic corrosion inhibitors on metal surfaces—some new insights from molecular simulations. Corrosion 2019, 75(1), 90-105, 2019.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).