Section 1. Introduction
The interplay between thermodynamics and brain wave configurations offers a profound lens through which to study the dynamics of neural activity, particularly in processes such as thought, sensation, and motor acts. The brain, as a thermodynamically open system, continuously exchanges energy with its environment, maintaining non-equilibrium states essential for functionality. By framing neural oscillations and brain wave patterns through thermodynamic principles, we can uncover how the brain optimizes its energy use, adapts to environmental demands, and orchestrates cognitive and motor functions over varying time scales.
Section 1.1. Thermodynamic Framework and Neural Systems
Thermodynamics, the science of energy and entropy, provides a foundational framework for understanding the energy demands of biological systems. The brain, which consumes about 20% of the body’s energy at rest despite accounting for only 2% of body weight, exemplifies an energy-intensive system optimized for efficiency (Howarth, Gleeson, & Attwell, 2012). Neural activity, including the maintenance of resting membrane potentials, action potential generation, and synaptic transmission, requires the continuous expenditure of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This energy is predominantly used by ion pumps such as the Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase, which restore ionic gradients disrupted by neural firing.
From a thermodynamic perspective, the brain is an open system operating far from equilibrium, relying on energy inputs to maintain low-entropy states. According to the second law of thermodynamics, entropy in isolated systems increases, leading to disorder. However, the brain counteracts this tendency through constant energy intake and dissipation, enabling organized neural activity and adaptive responses to external stimuli (Engel et al., 2013).
Section 1.2 Brain Waves as Oscillatory Dynamics
Brain wave activity reflects rhythmic oscillations of neural activity and is classified into five major frequency bands: delta (1–4 Hz), theta (4–8 Hz), alpha (8–12 Hz), beta (13–30 Hz), and gamma (30–100 Hz). Each frequency band corresponds to distinct neural states and cognitive functions. For instance, delta waves dominate during deep sleep, theta waves are associated with memory and navigation, alpha waves with relaxed wakefulness, beta waves with active thinking, and gamma waves with high-level information processing and consciousness (Buzsáki, 2006).
Neural oscillations are generated by the dynamics between excitatory and inhibitory neurons, synaptic interactions, and intrinsic cellular properties. These oscillations enable large-scale synchronization across brain regions, improving the efficiency of neural communication and processing. Disruptions in oscillatory patterns are implicated in numerous neurological disorders, including epilepsy, schizophrenia, and Parkinson’s disease, emphasizing the critical role of these dynamics in maintaining normal brain function (Uhlhaas & Singer, 2010).
Section 1.3 Thermodynamic Insights into Neural Oscillations
The application of thermodynamic principles to neural oscillations reveals the energetic underpinnings of brain wave dynamics. The brain can be conceptualized as a system that minimizes free energy—a principle widely supported by the free energy principle in neuroscience. According to this theory, the brain strives to reduce the difference between its internal model of the environment and incoming sensory information, thereby maintaining a state of dynamic equilibrium (Friston, 2010).
In thermodynamic terms, neural oscillations represent modes of energy organization that optimize information processing. Lower-frequency oscillations, such as alpha and theta waves, are associated with energy-efficient, baseline states, while higher-frequency oscillations like gamma waves signify increased energy expenditure required for demanding cognitive tasks (Engel et al., 2013). Synchronization of neural activity within these bands reduces redundancy and enhances signal-to-noise ratios, further conserving energy.
Section 1.4 Temporal Dynamics of Thought, Sensation, and Motor Acts
The temporal dynamics of thought, sensation, and motor acts are inherently tied to the brain’s oscillatory and thermodynamic properties. These processes unfold over distinct time scales, with neural oscillations mediating their execution:
Sensation: Sensory input is processed on millisecond time scales, involving rapid gamma oscillations that integrate sensory information across cortical regions. For example, visual processing engages gamma-band synchronization in the primary visual cortex and higher-order areas (Bosman et al., 2012).
Thought: Cognitive processes, such as problem-solving and decision-making, occur over milliseconds to seconds and are primarily associated with beta oscillations. These oscillations facilitate the coordination of neural circuits responsible for attention and working memory (Siegel, Donner, & Engel, 2012). Patients with Attention Deficit Disorder, for example can be diagnosed by elevated theta/beta rates (Montgomery, 2023)
Motor Acts: Motor planning and execution involve both beta and gamma oscillations, operating on tens to hundreds of milliseconds. Beta oscillations are implicated in maintaining the motor plan, while gamma oscillations contribute to the precision and timing of movements (Kilavik et al., 2013).
These temporal patterns reflect the brain’s ability to dynamically allocate energy to meet the demands of specific tasks. By modulating oscillatory activity, the brain optimizes its energetic efficiency across varying functional states (Montgomery, 2024).
The concept of energy landscapes, borrowed from thermodynamics, provides a useful framework for understanding the brain’s temporal dynamics. An energy landscape represents the potential energy of a system as a function of its state variables. In the context of neural activity, different brain states correspond to distinct attractors on the energy landscape.
Thought Processes: Thought can be viewed as a transition between attractors on the energy landscape, mediated by beta and gamma oscillations. The speed and efficiency of these transitions depend on the energy barriers separating attractors, reflecting the cognitive load of the task at hand (Deco et al., 2013).
Sensation: Sensory input induces shifts in the energy landscape, stabilizing attractors corresponding to the processing of specific stimuli. Gamma oscillations, by rapidly synchronizing activity, facilitate these transitions and ensure efficient sensory integration.
Motor Acts: Motor planning and execution involve transitions through energy states optimized for precision and timing. The interaction between beta and gamma oscillations reflects the trade-off between maintaining a stable motor plan and executing rapid adjustments in response to environmental feedback (Engel & Fries, 2010).
Section 1.5 Implications for Brain Disorders
Disruptions in the thermodynamic and oscillatory dynamics of the brain are associated with various neurological and psychiatric disorders. For instance:
In epilepsy, excessive synchronization of neural activity leads to hyperexcitable states, reflecting maladaptive energy use (Lytton, 2008).
In schizophrenia, altered gamma-band activity is linked to deficits in sensory processing and cognitive function (Uhlhaas & Singer, 2010).
In Parkinson’s disease, abnormal beta oscillations in the motor cortex interfere with movement initiation and coordination (Brown, 2007).
Understanding these disorders through the lens of thermodynamics and oscillatory brain wave dynamics offers new avenues for therapeutic intervention, such as neurostimulation techniques that restore normal oscillatory patterns.
Section 1.6 Summary
The integration of thermodynamic principles with the study of brain wave configurations provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the energetic basis of neural activity. By exploring how neural oscillations optimize energy use across thought, sensation, and motor acts, we can gain deeper insights into the brain’s functional architecture. This interdisciplinary approach bridges neuroscience, physics, and cognitive science, advancing our understanding of both normal brain function and pathological states.
Section 2. Methodology
This methodology formulates a mathematical framework to model the relationship between thermodynamics and brain wave configurations, emphasizing the temporal dynamics of thought, sensation, and motor acts. Using the principles of energy minimization and oscillatory dynamics, we derive a sequence of lemmas that culminate in a proof linking brain wave frequencies to energy optimization in neural activity.
Section 2.1. Definitions and Notation
Let the brain be represented as a system characterized by:
A state space , where each state corresponds to a specific neural configuration.
An energy function , representing the total energy of the system in a given state.
Neural oscillations as a frequency distribution , corresponding to the dominant brain wave frequencies (delta, theta, alpha, beta, gamma).
The brain’s behavior over time is modeled as a trajectory governed by dynamical equations.
- 2.
Energy Dynamics and Oscillations
The brain operates as a system minimizing free energy
, which we define as:
where:
is the total energy of the system.
is the effective thermodynamic temperature.
is the entropy associated with the state .
- 3.
Lemmas
Neural oscillations represent stable attractor states that minimize free energy. Assume a set of oscillatory statessuch that:
These states correspond to local minima of the free energy landscape.
For a dynamical system with state trajectory
, free energy evolves according to:
At equilibrium, , implying that . Local minima satisfy stability conditions , confirming oscillatory states minimize .
Higher-frequency oscillations (e.g., gamma waves) correspond to higher energy states, while lower frequency oscillations (e.g., delta waves) correspond to lower energy states. Define as the oscillation frequency at state :
The oscillatory dynamics are governed by a harmonic approximation around equilibrium states:
where
is an equilibrium state. The oscillation frequency
is proportional to
, linking higher curvature (higher energy) to higher frequencies.
The time required for a state transition
is inversely proportional to the oscillation frequency:
Consider a simple harmonic oscillator:
The solution has a period . The time for half a cycle, corresponding to state transition, is , establishing the inverse relationship.
- 4.
Proof: Energy Optimization Through Oscillations
From Lemma 1, oscillatory states are attractors that minimize free energy . Lemma 2 establishes that oscillation frequency reflects the curvature of the energy landscape, indicating the energy cost of the state. Lemma 3 links time scales to oscillation frequencies, demonstrating that processes such as thought (beta waves), sensation (gamma waves), and motor acts (beta-gamma coupling) operate on time scales inversely proportional to their energy demands.
Combining these results, neural oscillations distribute energy efficiently across processes by aligning temporal dynamics with the curvature of the energy landscape. Lower frequencies (delta, theta) govern slower, energy-conserving processes, while higher frequencies (gamma) enable rapid, energy-intensive functions.
- 5.
Applications and Implications
- 6.
Thought: Beta oscillations ( ) mediate attention and decision-making, requiring moderate energy states.
- 7.
Sensation: Gamma oscillations () integrate sensory input rapidly, demanding high energy.
- 8.
Motor Acts: Beta-gamma coupling supports coordinated movement, balancing energy efficiency and speed.
This mathematical framework provides a rigorous basis for understanding how thermodynamics shapes the temporal dynamics of brain wave configurations in cognitive and motor functions.
Section 2.2. Energy Optimization in Cognition
Cognition, encompassing processes such as attention, memory, decision-making, and problem solving, requires the brain to efficiently allocate and utilize its limited energy resources. Neural oscillations, as dynamic states in the brain’s energy landscape, play a critical role in optimizing energy distribution across cognitive tasks. By leveraging thermodynamic principles and differential equations, we can understand how oscillatory activity supports efficient cognitive functioning.
-
1.
The Brain as an Energy-Optimizing System
The brain consumes a disproportionate amount of the body’s energy, approximately 20% of total metabolic expenditure, despite comprising only of body weight (Howarth, Gleeson, & Attwell, 2012). This energy is primarily used to maintain ionic gradients through -ATPase pumps, supporting neural signaling and synaptic transmission. Cognitive processes impose additional demands, requiring the brain to allocate energy dynamically to regions and networks involved in specific tasks.
From a thermodynamic perspective, the brain operates as an open system minimizing free energy:
where
is the energy of the cognitive state,
is its entropy, and
is the effective thermodynamic temperature. Cognitive tasks, which involve transitioning between attractor states in the energy landscape, require efficient energy utilization to minimize
.
Section 2.1.1. Neural Oscillations as Energy States
Cognition relies on neural oscillations to coordinate activity within and between brain regions.
Oscillations at different frequencies correspond to distinct energy states:
Low-frequency oscillations (e.g., delta, theta) govern baseline, energy-conserving states, such as resting or slow-wave sleep.
High-frequency oscillations (e.g., beta, gamma) support energy-intensive tasks, including attention, working memory, and problem solving (Engel et al., 2013).
The relationship between frequency and energy is captured by the harmonic approximation:
E(x)≈E_0+1/2 x^T ∇^2 E(x_0 )x
where the oscillation frequency ω(x) is proportional to √(∇^2 E(x)). Higher frequencies, such as gamma waves, are associated with steeper curvatures in the energy landscape, reflecting greater energy demands.
Section 2.1.2. Time Scales of Cognitive Processes
Cognitive processes operate over specific time scales, reflecting the brain’s ability to adapt energy expenditure to task demands:
Attention: Beta oscillations ( ω≈13-30” “ Hz ) mediate the maintenance of focus and the filtering of irrelevant information. These oscillations balance energy use, sustaining activity in prefrontal and parietal regions (Siegel, Donner, & Engel, 2012).
Working Memory: Theta-gamma coupling supports the encoding and retrieval of information. Theta waves ( ω≈4-8” “ Hz ) provide a low-frequency scaffold, while gamma waves ( ω>30” “ Hz ) carry high-frequency information, ensuring efficient energy use during memory tasks (Lisman & Jensen, 2013).
Decision-Making: Decision-making involves transitioning between attractors in the energy landscape. The speed of these transitions depends on the curvature of the energy landscape and the oscillatory frequencies governing the process. Beta oscillations stabilize decision states, while gamma oscillations enable rapid transitions under high cognitive loads (Deco et al., 2013).
The temporal dynamics of these processes highlight the brain’s ability to align oscillatory activity with energy demands, optimizing cognitive efficiency.
4. Energy Dissipation and Efficiency
The brain’s energy optimization strategy involves dissipating energy in a controlled manner to prevent metabolic overload while maintaining cognitive performance. This principle is evident in the synchronization of oscillations across networks:
ΔE=∫‖∇Φ(x)‖^2 dx
where Φ(x) represents the potential field governing network activity. Synchronization minimizes redundant activity, reducing ΔE and improving energy efficiency (Friston, 2010).
For instance, large-scale neural networks such as the default mode network (DMN) and task-positive network (TPN) alternate their activity depending on task demands, preventing unnecessary energy expenditure during rest or low-intensity tasks (Fox et al., 2005).
5. Cognitive Load and Energy Barriers
Cognitive tasks vary in their energy requirements based on complexity. Tasks with higher cognitive loads require transitions across higher energy barriers in the landscape:
ΔE_”cognitive load “ ∝∇^2 E(x),
where ∇^2 E(x) reflects the curvature of the energy landscape.
Simple tasks: Involve shallow energy wells, allowing rapid transitions with minimal energy.
Complex tasks: Require navigating steep energy gradients, consuming more energy and involving higher-frequency oscillations.
-
6.
Implications for Cognitive Disorders
Disruptions in energy optimization are linked to cognitive impairments in various neurological and psychiatric disorders:
Schizophrenia: Altered gamma oscillations impair information processing, reflecting inefficient energy use (Uhlhaas & Singer, 2010).
Alzheimer’s Disease: Reduced synchronization in theta and gamma oscillations disrupts memory processes, increasing metabolic inefficiency (Stam, 2010).
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Imbalances in beta-theta coupling lead to difficulties in maintaining focus and regulating attention, reflecting poor energy allocation (Lenz et al., 2008).
Conclusions
Energy optimization in cognition is achieved through the dynamic modulation of neural oscillations, which align frequency-dependent energy states with the demands of cognitive tasks. By minimizing free energy and synchronizing activity across networks, the brain maintains a balance between performance and metabolic efficiency. This thermodynamic framework provides insights into the temporal dynamics of cognition and highlights potential targets for interventions in cognitive disorders.
Section 3. Results
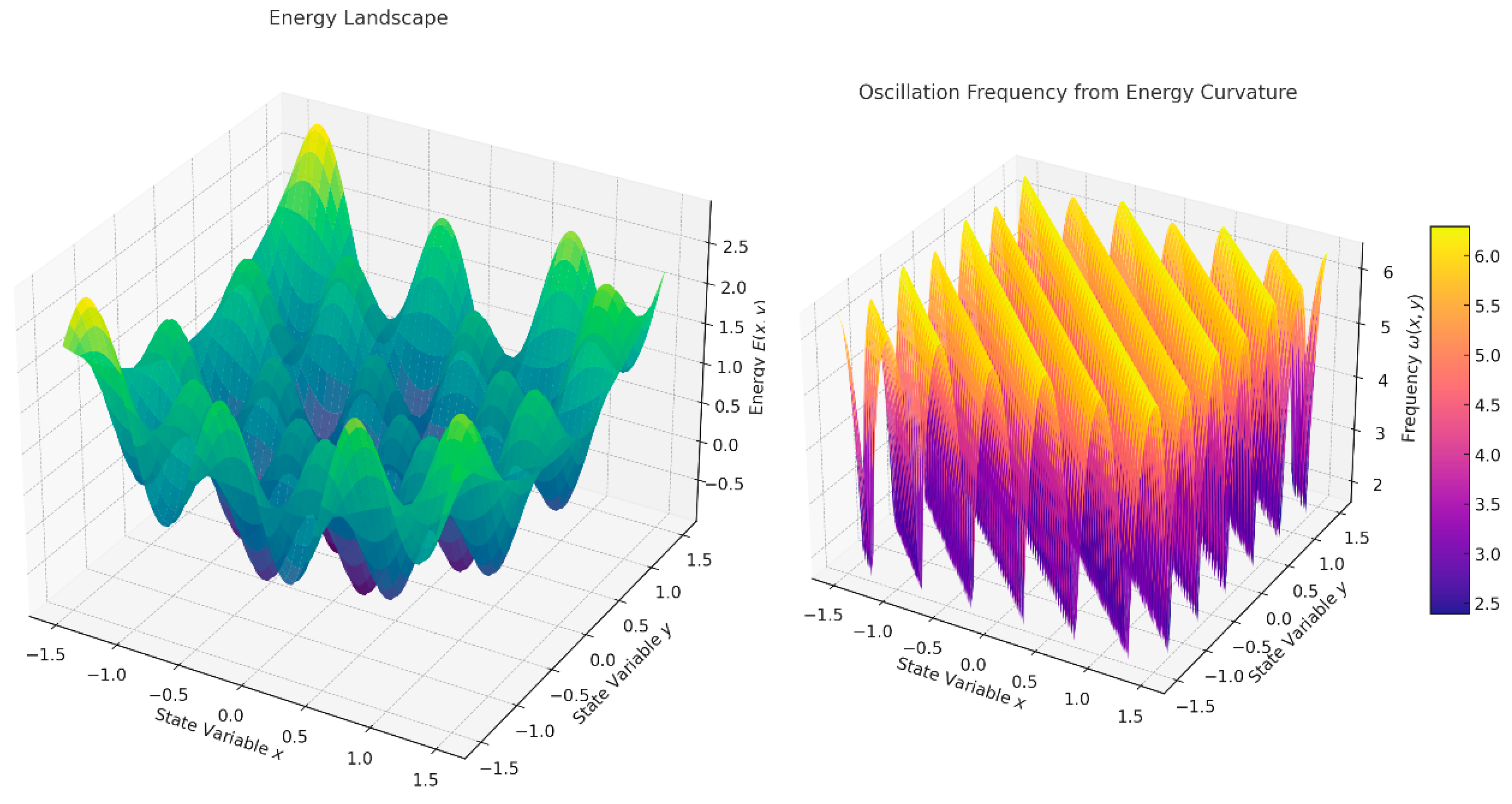
These visualizations capture the relationship between neural oscillations, energy optimization, and the brain’s ability to navigate its energy landscape efficiently during cognitive tasks
Image 1.
The plots illustrate the core concepts from the methodology: Energy Landscape: The left graph shows the energy landscape as a multi-well potential. Peaks and valleys represent energy barriers and attractors in the state space, corresponding to different neural configurations. Cognitive processes, such as transitions between thoughts or decisions, can be visualized as movements across this landscape. Oscillation Frequency: The right graph demonstrates how oscillation frequency (1/ω) depends on the curvature of the energy landscape. Regions with high curvature (steep slopes) correspond to higher frequencies, reflecting greater energy demands (e.g., gamma oscillations).Lower frequencies (e.g., delta or theta oscillations) align with flatter regions, indicating lower energy states.
Image 1.
The plots illustrate the core concepts from the methodology: Energy Landscape: The left graph shows the energy landscape as a multi-well potential. Peaks and valleys represent energy barriers and attractors in the state space, corresponding to different neural configurations. Cognitive processes, such as transitions between thoughts or decisions, can be visualized as movements across this landscape. Oscillation Frequency: The right graph demonstrates how oscillation frequency (1/ω) depends on the curvature of the energy landscape. Regions with high curvature (steep slopes) correspond to higher frequencies, reflecting greater energy demands (e.g., gamma oscillations).Lower frequencies (e.g., delta or theta oscillations) align with flatter regions, indicating lower energy states.
These graphs visually represent the mathematical concepts of the energy landscape and oscillation frequency, highlighting their relevance to neural dynamics, energy optimization, and cognitive processes.
The relationship between frequency and energy is captured by the harmonic approximation:
where the oscillation frequency
is proportional to
. Higher frequencies, such as gamma waves, are associated with steeper curvatures in the energy landscape, reflecting greater energy demands.
Section 3.1. Time Scales of Cognitive Processes
Cognitive processes operate over specific time scales, reflecting the brain’s ability to adapt energy expenditure to task demands:
Attention: Beta oscillations () mediate the maintenance of focus and the filtering of irrelevant information. These oscillations balance energy use, sustaining activity in prefrontal and parietal regions (Siegel, Donner, & Engel, 2012).
Working Memory: Theta-gamma coupling supports the encoding and retrieval of information. Theta waves () provide a low-frequency scaffold, while gamma waves () carry high-frequency information, ensuring efficient energy use during memory tasks (Lisman & Jensen, 2013).
Decision-Making: Decision-making involves transitioning between attractors in the energy landscape. The speed of these transitions depends on the curvature of the energy landscape and the oscillatory frequencies governing the process. Beta oscillations stabilize decision states, while gamma oscillations enable rapid transitions under high cognitive loads (Deco et al., 2013).
The temporal dynamics of these processes highlight the brain’s ability to align oscillatory activity with energy demands, optimizing cognitive efficiency.
- 4.
Energy Dissipation and Efficiency
The brain’s energy optimization strategy involves dissipating energy in a controlled manner to prevent metabolic overload while maintaining cognitive performance. This principle is evident in the synchronization of oscillations across networks:
where
represents the potential field governing network activity. Synchronization minimizes redundant activity, reducing
and improving energy efficiency (Friston, 2010).
For instance, large-scale neural networks such as the default mode network (DMN) and task-positive network (TPN) alternate their activity depending on task demands, preventing unnecessary energy expenditure during rest or low-intensity tasks (Fox et al., 2005).
- 5.
Cognitive Load and Energy Barriers
Cognitive tasks vary in their energy requirements based on complexity. Tasks with higher cognitive loads require transitions across higher energy barriers in the landscape:
where
reflects the curvature of the energy landscape.
Section 3.2. Cognitive and Functional Dynamics:
Cognitive processes (e.g., decision-making) involve navigating the energy landscape, with time scales governed by oscillatory frequencies.
Sensory processing operates in high-frequency regions for rapid integration, while low-frequency regions conserve energy during rest or slow-wave sleep.
Higher energy barriers and frequencies correspond to more complex cognitive demands, whereas simpler or baseline tasks are associated with flatter, low-energy regions.
These graphs provide a comprehensive visualization of how thermodynamics and oscillatory dynamics underpin the brain’s energy-efficient functioning.
Section 4. Discussion
The exploration of brain wave configurations through the lens of thermodynamics offers profound insights into the intricate processes that underlie cognition, sensation, and motor acts. This perspective is not only scientific but also deeply philosophical, touching on questions about the nature of thought, the organization of biological energy, and the role of time in shaping human experience. By understanding neural oscillations as thermodynamic phenomena, we can examine how the brain optimizes energy to support the complex choreography of mental and physical activity.
Section 4.1. Thermodynamic Foundations of Neural Oscillations
The brain, like all living systems, operates as an open thermodynamic system. It constantly exchanges energy and matter with its environment to sustain non-equilibrium states essential for life. The high metabolic demands of the brain—despite its relatively small size, consuming approximately of the body’s resting energy-underscore the need for efficient energy management (Howarth, Gleeson, & Attwell, 2012). Neural oscillations, which are rhythmic patterns of electrical activity, can be understood as the brain’s strategy to organize energy flow, reduce redundancy, and enhance processing efficiency.
From a thermodynamic perspective, oscillatory activity is driven by the brain’s need to minimize free energy. Free energy, defined as , where is the system’s energy, is its entropy, and is the effective temperature, represents the cost of maintaining a given state. Minimizing free energy allows the brain to align its internal states with external environmental demands, thereby reducing uncertainty (Friston, 2010), (Montgomery, 2024a). This process of energy minimization is not purely mechanical; it is deeply intertwined with cognition and the brain’s capacity to predict and interpret sensory inputs.
Section 4.2. Neural Oscillations as Thermodynamic States
Brain waves, classified into frequency bands such as delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma, correspond to distinct energy states. Lower-frequency oscillations, like delta and theta, dominate during states of rest or minimal cognitive demand. These frequencies reflect energy-efficient, stable configurations that conserve resources. Conversely, higher-frequency oscillations, such as gamma, are associated with energy-intensive tasks like sensory integration and decision-making (Engel et al., 2013).
The frequency of neural oscillations can be mathematically linked to the curvature of the brain’s energy landscape:
where
is the oscillation frequency and
represents the curvature of the energy landscape at state
. Regions of high curvature, indicating steep energy gradients, correspond to higher frequencies, while flatter regions align with lower frequencies. This relationship demonstrates how the brain dynamically adjusts its oscillatory activity to meet the energetic demands of different cognitive states.
Section 4.2 Temporal Dynamics and Cognitive Processing
The brain’s ability to allocate energy efficiently is reflected in the temporal dynamics of thought, sensation, and motor acts. Each of these processes operates on specific time scales, which correspond to the frequency bands of neural oscillations. Sensory processing, for example, occurs on millisecond time scales and is mediated by high-frequency gamma waves, which facilitate rapid information integration across cortical areas (Bosman et al., 2012). Thought processes, such as reasoning and decision-making, unfold over milliseconds to seconds, often involving beta oscillations that support the maintenance and manipulation of information in working memory (Siegel, Donner, & Engel, 2012). Motor planning and execution, governed by beta and gamma oscillations, balance the precision and timing required for movement with the stability of motor plans (Kilavik et al., 2013).
The philosophical implications of these temporal dynamics are significant. Time, as experienced subjectively, is shaped by the rhythms of neural oscillations. The distinction between thought, sensation, and action is not merely functional but also temporal. Each process carves out a unique temporal structure within the continuum of experience, mediated by the oscillatory activity of the brain.
Section 4.3 Energy Landscapes and the Organization of Thought
The concept of energy landscapes, borrowed from thermodynamics, offers a compelling framework for understanding how the brain organizes cognitive activity. An energy landscape represents the potential energy associated with different neural configurations. In this framework, cognitive states correspond to attractors—stable regions in the landscape where the brain’s activity tends to settle.
Transitions between cognitive states can be viewed as movements across the energy landscape. The ease or difficulty of these transitions depends on the energy barriers separating attractors. For instance, shifting from one thought to another during a problem-solving task may involve overcoming an energy barrier, the height of which reflects the cognitive load of the task. Beta and gamma oscillations play a critical role in facilitating these transitions by synchronizing activity across neural networks and enabling the efficient allocation of energy (Deco et al., 2013).
This dynamic organization of thought highlights the brain’s ability to balance stability and flexibility. Stability is achieved through the maintenance of attractor states, which provide coherence and continuity to cognitive processes. Flexibility, on the other hand, is ensured by the brain’s capacity to transition between attractors, allowing for adaptation to new information or changing goals.
Section 4.4 Philosophical Reflections on Energy and Cognition
The thermodynamic perspective on brain function invites philosophical reflections on the nature of thought and consciousness. If neural oscillations and energy landscapes shape the temporal dynamics of cognition, what does this imply about the essence of thought? Is thought merely a byproduct of energy optimization, or does it possess an ontological status independent of its physical substrate?
One possible interpretation is that thought represents a dynamic interaction between stability and change, mediated by the brain’s oscillatory activity. The attractors in the energy landscape provide a framework for stability, while the transitions between attractors embody the creativity and adaptability of thought. This duality echoes philosophical notions of being and becoming, suggesting that cognition is both grounded in the physical reality of the brain and transcendent in its capacity to generate new meanings and ideas.
Moreover, the temporal nature of neural oscillations raises questions about the relationship between time and consciousness. If different frequencies correspond to distinct time scales of experience, then consciousness itself may be a composite of these temporal layers. This perspective aligns with the view that consciousness is not a singular phenomenon but a mosaic of interwoven rhythms, each contributing to the richness of subjective experience. It’s important to highlight that, EEG´s in brain death patients are necessarily silent, mwithout any oscillations or activity.
Section 4.5 Implications for Understanding Human Potential
The interplay between thermodynamics and brain wave configurations has practical implications for understanding and enhancing human potential. By modulating neural oscillations through techniques such as neurofeedback or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), it may be possible to optimize cognitive performance, enhance learning, or treat neurological disorders. For example, enhancing gamma oscillations could improve attention and memory, while promoting alpha oscillations might facilitate relaxation and stress reduction (Uhlhaas & Singer, 2010).
Additionally, this framework provides a basis for exploring the limits of human cognition. If thought is constrained by the energy landscape of the brain, then expanding the boundaries of this landscape—through education, training, or technological augmentation—could unlock new levels of creativity and understanding. This idea resonates with philosophical visions of self-transcendence, where the human mind seeks to overcome its limitations and reach for greater heights of knowledge and insight.
Section 5. Conclusions
The integration of thermodynamic principles with the study of brain wave configurations offers a transformative perspective on neural function and cognition. Neural oscillations, as dynamic patterns of energy organization, allow the brain to optimize energy use while maintaining the flexibility required for complex cognitive and motor processes. By minimizing free energy, the brain not only achieves stability in attractor states but also facilitates transitions that support thought, sensation, and action. This balance between stability and adaptability underscores the brain’s remarkable efficiency and capacity for innovation.
Philosophically, this framework suggests that cognition is a dynamic interplay between physical constraints and transcendent possibilities. Thought emerges as a phenomenon shaped by the energy landscape of the brain yet capable of transcending its immediate substrate to create meaning and pursue goals. The temporal nature of neural oscillations further enriches our understanding of consciousness, pointing to its layered and rhythmic construction.
Practically, understanding the relationship between thermodynamics and brain wave dynamics offers pathways to enhance cognitive performance and treat neurological disorders. By harnessing techniques to modulate neural oscillations, we can explore the boundaries of human potential, fostering new levels of creativity, understanding, and well-being.
*The Author claims there are no conflicts of interest.
Section 6. Attachments
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
# Define the energy landscape
def energy_landscape(x, y):
“““Energy landscape modeled as a multi-well potential.”““
return np.sin(2 * np.pi * x) * np.cos(2 * np.pi * y) + 0.5 * (x**2 + y**2)
# Define oscillation frequency as a function of curvature
def oscillation_frequency(x, y):
“““Frequency derived from the curvature of the energy landscape.”““
curvature = np.abs(4 * np.pi**2 * (np.cos(2 * np.pi * x) * np.cos(2 * np.pi * y) -
np.sin(2 * np.pi * x) * np.sin(2 * np.pi * y)) + 1)
return np.sqrt(curvature)
# Generate a grid for visualization
x = np.linspace(-1.5, 1.5, 100)
y = np.linspace(-1.5, 1.5, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z = energy_landscape(X, Y)
Freq = oscillation_frequency(X, Y)
# Plot the energy landscape
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 8))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121, projection=‘3d’)
ax1.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=‘viridis’, alpha=0.9)
ax1.set_title(“Energy Landscape”, fontsize=14)
ax1.set_xlabel(“State Variable $x$”)
ax1.set_ylabel(“State Variable $y$”)
ax1.set_zlabel(“Energy $E(x, y)$”)
# Plot the frequency landscape
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection=‘3d’)
surf = ax2.plot_surface(X, Y, Freq, cmap=‘plasma’, alpha=0.9)
ax2.set_title(“Oscillation Frequency from Energy Curvature”, fontsize=14)
ax2.set_xlabel(“State Variable $x$”)
ax2.set_ylabel(“State Variable $y$”)
ax2.set_zlabel(“Frequency $\\omega(x, y)$”)
fig.colorbar(surf, ax=ax2, shrink=0.5, aspect=10)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
References
- Bosman, C. A., et al. (2012). Attentional stimulus selection through selective synchronization between monkey visual areas. Neuron, 75(5), 875–888.
- Deco, G., Jirsa, V. K., & McIntosh, A. R. (2013). Resting brains never rest: Computational insights into potential cognitive states. Trends in Neurosciences, 36(5), 268–274.
- Engel, A. K., & Fries, P. (2010). Beta-band oscillations: Signaling the status quo? Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 20(2), 156–165.
- Friston, K. (2010). The free-energy principle: A unified brain theory? Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11(2), 127–138.
- Howarth, C., Gleeson, P., & Attwell, D. (2012). Updated energy budgets for neural computation in the neocortex and cerebellum. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 32(7), 1222–1232.
- Kilavik, B. E., Zaepffel, M., Brovelli, A., MacKay, W. A., & Riehle, A. (2013). The ups and downs of beta oscillations in sensorimotor cortex. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 7, 43.
- Montgomery, R. M. (2023). Simulating Topological Changes in Human Brain Networks: A Computational Approach. [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R. M. (2024). Deep Learning for ADHD Diagnosis:Integrating Diverse EEG Biomarkers for Enhanced Predictive. [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R. M. (2024)a. From Neural Cords to Complex Brains The Evolution of the Vertebrate Central Nervous System and Human Cognition. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, M., Donner, T. H., & Engel, A. K. (2012). Spectral fingerprints of large-scale neuronal interactions. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 13(2), 121–134.
- Uhlhaas, P. J., & Singer, W. (2010). Abnormal neural oscillations and synchrony in schizophrenia. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11(2), 100–113.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).