1. Introduction
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, accounting for 1,796,144 deaths according to GLOBOCAN 2020.[
1] The majority of all lung cancers are Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), and the outcomes for NSCLC are not better compared to other solid organ malignancies. A study conducted in West Sumatra by Ermayanti et al. in 2021 revealed that the majority of lung cancers were adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.[
2] Despite extensive use of systemic therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, the prognosis for NSCLC patients remains poor.[
3]
Cancer is a systemic disease, characterized by prolonged inflammation, which is one of the hallmarks of cancer. Tumor immunology has traditionally focused on the local immune response in the tumor microenvironment. However, an effective anti-tumor immune response cannot occur without continuous communication with the periphery. The immune response to cancer should involve all immune cell lineages throughout the peripheral immune system, in addition to the tumor microenvironment.[
4]
Several inflammation-related biomarkers based on systemic inflammatory cells, such as the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), have proven prognostic value in various types of cancers, including lung cancer.[
3] These predictors are based solely on two inflammatory cell types, whereas the Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII), a novel non-invasive biomarker based on three peripheral blood parameters (platelet, neutrophil, and lymphocyte counts), can comprehensively reflect the balance of the host immune status and inflammation. It has been shown to be a more objective marker with better predictive value for prognosis.[
5]
The prognostic value of SII was first reported by Hu et al., demonstrating its strong prognostic indicator for poor outcomes in 133 hepatocellular carcinoma patients.[
6] SII levels can represent the conditions of lymphocytes, neutrophils, and platelets and may be a robust parameter reflecting the host immune response.[
3] A meta-analysis by Zhang et al., including 7 studies with a total of 2786 cases examining the relationship between SII and Overall Survival (OS) in lung cancer, revealed that high SII significantly correlated with poor OS in lung cancer patients. Patients with high SII had shorter OS compared to the low SII group, suggesting that SII can serve as a promising prognostic factor for lung cancer patients.[
5] This study conducted to investigate the prognostic value of the SII in Advanced stage NSCLC patients, receiving platinum-based chemotherapy, marking the first application of SII in Indonesia, specifically within the West Sumatra population.
2. Materials and Methods
This is an analytical observational study with a retrospective cohort design. All advanced-stage NSCLC patients who had received a minimum of three cycles of chemotherapy from January 2020 to December 2022, at Dr. M Djamil Hospital Padang were included in this study. Patients with a history of previous radiotherapy and targeted therapy, primary malignancy in other organs, chronic systemic inflammatory conditions such as autoimmune diseases, hematological disorders, congestive heart failure, a history of hemodialysis, cardiopulmonary bypass, corticosteroid use, and metabolic disorders (uremia, acidosis, and gout) are excluded from this study.
Patient characteristic including age, sex, smoking status, pathologic, TNM staging, chemotherapy regiment, and one year survival were collected by medical record. The SII calculated by: platelet counts x neutrophil counts/ lymphocyte count. The survival duration is defined as the period (measured in months) from the initiation of therapy until the patient either decease or passes the observation phase. The last follow-up was in December 2023. Survival is categorized into two group: one with a survival period of less than one year and the other with a duration equal to or exceeding one year. The SII optimal cut-off values for one year survival were obtained by a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. The research protocol of this study obtained ethical approval from the medical ethics committee of our institution.
3. Results
This study enrolled a total of 65 participants, comprising 53 male (81.53%) and 12 female (18.47%).
Table 1 presents the comprehensive characteristics of advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients in each survival group from 2020 to 2022. The Median age of the participants was 58 years ranging from 25 to 74 years, with the most patients in the group <60 years (64.61%). The Majority of patients was smoker/ former smoker (81.54%). According to histopathological findings, squamous cell carcinoma is the most predominant type (47.69%). Stage distribution was as follows: stage IIIb included 5 patients (7.69%), stage IIIc had 2 patients (3.08%), stage IVa had 40 patients (61.54%) and stage IVb involved 18 patients (27.69%). Most patients in this study received carboplatin + paclitaxel chemotherapy regimen (89.24%). This study demonstrated that chemotherapy regimen were associated with one-year survival (p<0.05).
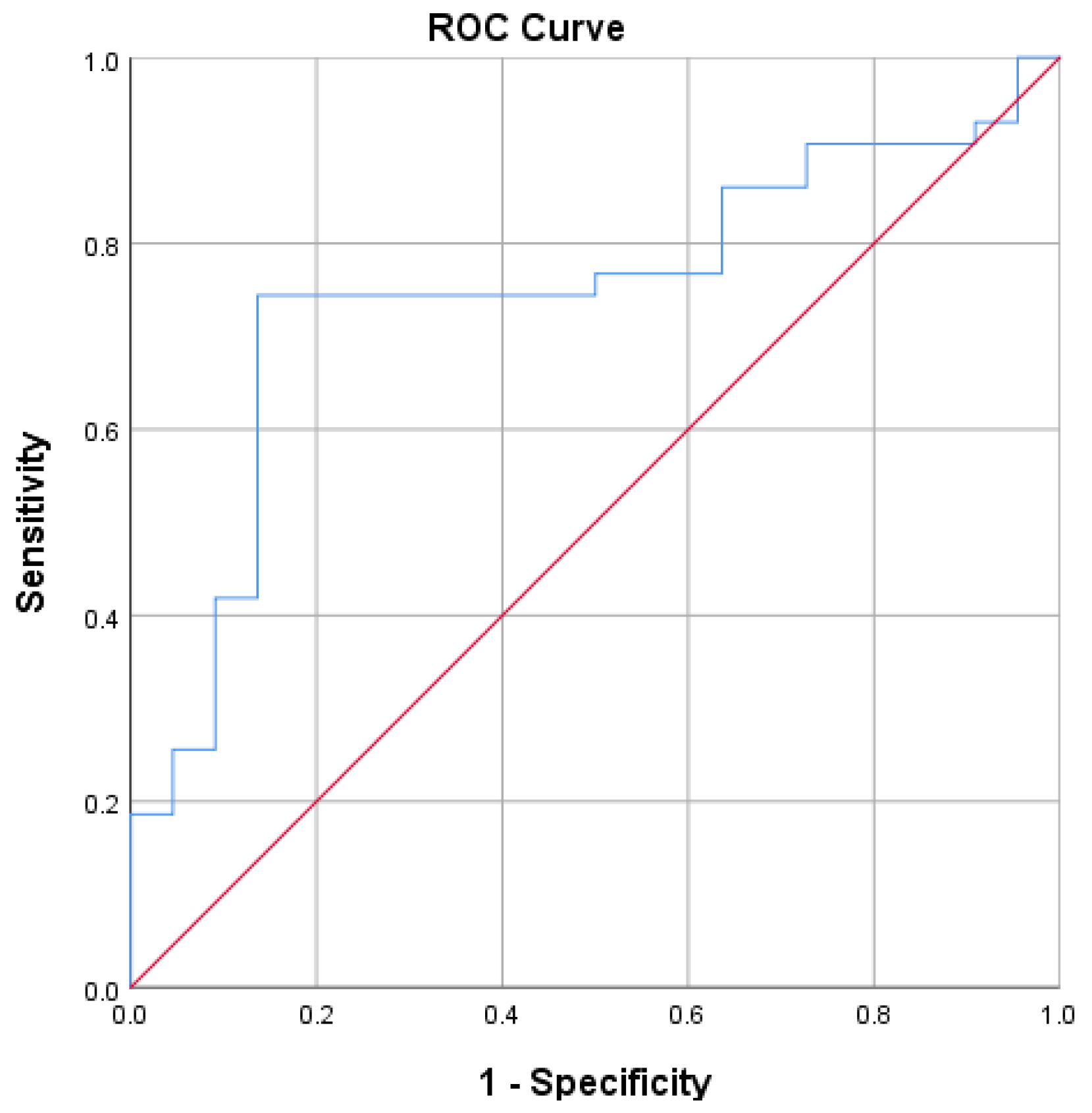
The average Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) in the group with less than one-year survival is higher compared to other groups (3,414.95 x 109/L vs 1,517.95 x 109/L). The data suggests that individuals with higher SII values are more likely to experience a survival duration of less than one year. The statistical analysis underscores a meaningful relationship between the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and the one-year survival rate (p: 0.01; 95%CI: 455.63-3338.36), highlighting the potential utility of SII as a prognostic indicator in this context. The results emphasize the strength of the predictive model, with a remarkable Area Under the Curve (AUC) value of 0.745 (95% CI 0.62-0.87). According to the ROC analysis, the ideal cutoff for SII to forecast one year survival was determined to be 1760.00 x 109/L with sensitivity 74% and specificity 81%.
Figure 1.
The ROC curve of SII for One Year Survival.
Figure 1.
The ROC curve of SII for One Year Survival.
4. Discussion
Our study specifically investigated the prognostic value of the one-year survival of SII in NSCLC patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. The majority of our patients were male, aged 25-74 years, with a significant proportion under 60 years. In contrast, a study by Ermayanti et al. in West Sumatra found that while the majority of lung cancer patients were also male (77.8%), females tended to be younger and predominantly non-smokers, with distinct histopathological profiles and disease characteristics.[
2] Supporting our findings, Marco Galvez-Nino’s research in Lima, Peru, highlighted that lung cancer in patients aged 40 or younger exhibited different clinical and pathological features compared to older patients, with a higher incidence in females and a predominant histological type of adenocarcinoma. Both studies corroborate our observation of a significant number of younger patients with advanced stages of NSCLC.[
7] These findings collectively emphasize the critical importance of considering age and gender in the epidemiological and prognostic assessment of lung cancer.
Findings revealed that among the subtypes of NSCLC, squamous cell carcinoma was the most common, occuring 31 patients (47.70%), followed by adenocarcinoma in 25 patients (38.50%). This differs from other studies in West Sumatra, which found a higher prevalence of adenocarcinoma (55.0%) in females and squamous cell carcinoma (41.1%) in males, and AlQudah et al. in Jordan, where adenocarcinoma accounted for over half of the cases across both sexes.[
2,
8] These discrepancies can be attributed to the exclusion of some adenocarcinoma patients in our study who had previously received targeted therapy or radiotherapy. This exclusion likely skewed our histological distribution towards squamous cell carcinoma, highlighting the impact of prior treatment on histopathological reporting in lung cancer research.
In our study, the majority of patients with advanced-stage NSCLC were diagnosed at stage IVa, representing 61.5% of the study, which underscores the prevalent issue of late-stage diagnosis. This finding aligns with R. Soo's review, which reports a similar trend with 71.3% of NSCLC patients being diagnosed at metastatic stage IV across Southeast Asia. Several factors contribute to this delayed diagnosis, including limited access to healthcare facilities, lack of early screening programs, and the often asymptomatic nature of early-stage lung cancer. Furthermore, socioeconomic barriers and the limited availability of molecular testing and targeted therapies in certain regions exacerbate this issue, delaying the initiation of appropriate treatment. Both studies highlight the critical need for improved early detection strategies and equitable access to advanced diagnostic and therapeutic modalities to enhance survival outcomes for NSCLC patients in Southeast Asia.[
9]
This study demonstrated that the majority of patients (89.20%) received the carboplatin + paclitaxel chemotherapy regimen, with statistical analysis revealing a significant relationship between the chemotherapy regimen and one year survival (p = 0.021). In comparison, the first study by V. Georgoulias et al. assessed the efficacy of docetaxel/cisplatin versus gemcitabine/docetaxel, finding similar objective response rates between the two groups but noting that gemcitabine/docetaxel had a more favorable toxicity profile.[
10] The second study by Giannicola D’Addario et al. conducted a meta-analysis comparing platinum-based versus non-platinum-based chemotherapy, concluding that platinum-based regimens significantly increased response rates and 1-year survival, albeit with higher toxicity.[
11] Together, these findings underscore that while different chemotherapy regimens, including those based on platinum agents, can influence overall survival rates and response, they also vary considerably in their toxicity profiles.
The majority of patients had a survival of less than one year (22 out of 65 patients), highlighting a poor prognosis for advanced-stage NSCLC patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. This finding aligns with Agus Setyawan U et al, where one-year survival rates were very low among 54 wild-type adenocarcinoma lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, with only 12.5% of patients receiving carboplatin/pemetrexed and 6.7% of patients receiving carboplatin/paclitaxel surviving one year.[
12] In contrast, Soeroso NN et al emphasizes the importance of genetic mutations in survival rates. Patients with EGFR mutations had a median overall survival of 15 months compared to 8 months for those without the mutations, while TP53 mutations were associated with a lower overall survival of 7 months compared to 9 months for non-mutations.[
13] This comparison underscores the critical need for improving early detection, diagnosis, and treatment strategies to enhance survival outcomes in advanced NSCLC patients.
This study demonstrated that the average SII in patients with less than one-year survival was significantly higher compared to other groups (3,414.95 x 10
9/L vs 1,517.95 x 10
9/L), indicating that elevated SII values are associated with shorter survival durations. This finding is consistent with results from other studies investigating the prognostic value of SII in NSCLC. For instance, a study on stage III NSCLC patients undergoing curative intent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) found that a low SII (<1,266) at diagnosis was independently associated with improved OS, disease-specific survival (DSS), and progression-free survival (PFS), highlighting the potential of SII as an effective prognostic indicator.[
14] Similarly, research on resected NSCLC patients demonstrated that pre-operative inflammatory status, including high SII values (≥808.9), strongly influences long-term prognosis, with higher SII correlating with more invasive disease stages and poorer survival outcomes.[
15] These studies collectively emphasize the importance of SII as a valuable biomarker for predicting survival in NSCLC patients, underscoring the need for its integration into clinical practice to enhance patient stratification and treatment planning.
The Area Under the Curve showed for the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) was 0.866, which is statistically significant (95% CI 0.782-0.950). The optimal threshold for SII in predicting chemotherapy response was identified as 1931.50 x 10^9/L, with a sensitivity of 76.7% and specificity of 74.3%. We found that 36 patients (55.38%) had high SII (≥1931.50), while 29 patients had low SII. This finding aligns with the meta-analysis by Wang et al., which indicated that high SII before therapy is an indicator of poor overall survival (OS), a predictor of progression-free survival (PFS), and poor cancer-specific survival (CSS) in NSCLC patients.[
16] Additionally, Wei Guo et al.'s study supports our results by demonstrating that SII, along with neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), correlates with OS in NSCLC patients. The SII was found to be an independent prognostic factor for OS, with a higher prognostic value compared to NLR and PLR. Furthermore, SII retained its prognostic significance in the lung adenocarcinoma subgroup.[
17] These studies collectively affirm the utility of SII as a superior prognostic marker for NSCLC patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Afriani Afriani and Sabrina Ermayanti; methodology, Afriani Afriani; software, Afriani Afriani; validation, Afriani Afriani, Sabrina Ermayanti and Dimas Firdaus; formal analysis, Afriani Afriani; investigation, Afriani Afriani; resources, Afriani Afriani; data curation, Afriani Afriani; writing—original draft preparation, Afriani Afriani; writing—review and editing, Afriani Afriani; visualization, Dimas Firdaus; supervision, Sabrina Ermayanti; project administration, Dimas Firdaus. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Health Research Ethics Committee of M. Djamil Hospital, Padang (LB.02.02/5.7/414/2023 – July, 27th 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the collaborative efforts of the medical team, as well as the support from Dr. M Djamil General Hospital. No source of funding was used to assist in the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. The Global Cancer Observatory. GLOBOCAN.
- Ermayanti, S.; Afriani, A.; Nikmawati, S.; Russilawati, R.; Medison, I.; Suyastri, S. Gender Disparities in Their Effects on Characteristics and Prognostics of Lung Cancer Patients in Pulmonary Ward of Dr. M Djamil Hospital, Padang. J. Respirologi Indones. 2021, 41, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, F. Clinical impact of the systemic immune-inflammation index in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 668–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiam-Galvez, K.J.; Allen, B.M.; Spitzer, M.H. Systemic immunity in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Yang, X. Systemic immune-inflammation index is a promising noninvasive marker to predict survival of lung cancer. Medicine 2019, 98, e13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.-R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.-F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.-M.; Qiu, S.-J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Predicts Prognosis of Patients after Curative Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez-Nino, M.; Ruiz, R.; Pinto, J.A.; Roque, K.; Mantilla, R.; Raez, L.E.; Mas, L. Lung Cancer in the Young. Lung 2019, 198, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqudah, M.A.; Alfaqih, M.A.; Hamouri, S.; Al-Shaikh, A.F.; Haddad, H.K.; Al-Quran, W.Y.; Alebbini, M.M.; Amer, N.B.; Al-Smadi, H.I.; Alzoubi, K.H. Epidemiology and histopathological classification of lung cancer: A study from Jordan, retrospective observational study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 65, 102330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soo, R.; Mery, L.; Bardot, A.; Kanesvaran, R.; Keong, T.; Pongnikorn, D.; Prasongsook, N.; Hutajulu, S.; Irawan, C.; Ab Manan, A.; et al. Diagnostic work-up and systemic treatment for advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer in four Southeast Asian countries. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgoulias, V.; Papadakis, E.; Alexopoulos, A.; Tsiafaki, X.; Rapti, A.; Veslemes, M.; Palamidas, P.; Vlachonikolis, I. Platinum-based and non-platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet 2001, 357, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Addario, G.; Pintilie, M.; Leighl, N.B.; Feld, R.; Cerny, T.; Shepherd, F.A. Platinum-Based Versus Non-Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of the Published Literature. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2926–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyawan, U.A.; Yudhanto, H.S.; Madarina, A. One Year Survival of Wild-Type Adenocarcinoma Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy at dr. Saiful Anwar Hospital, Malang. Respir. Sci. 2022, 2, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeroso, N.N.; Ananda, F.R.; Sitanggang, J.S.; Vinolina, N.S. The role of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in determining survival rates of lung cancer patients in the population of North Sumatra, Indonesia. F1000Research 2022, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keit, E.; Coutu, B.; Zhen, W.; Zhang, C.; Lin, C.; Bennion, N.; Ganti, A.K.; Ernani, V.; Baine, M. Systemic inflammation is associated with inferior disease control and survival in stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 227–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzella, A.; Maiolino, E.; Maisonneuve, P.; Loi, M.; Alifano, M. Systemic Inflammation and Lung Cancer: Is It a Real Paradigm? Prognostic Value of Inflammatory Indexes in Patients with Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Che, G. Prognostic value of the pretreatment systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 433–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Cai, S.; Zhang, F.; Shao, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tan, F.; Gao, S.; He, J. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) is useful to predict survival outcomes in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Table 1.
Characteristics of Patients in Survival Group.
Table 1.
Characteristics of Patients in Survival Group.
| Characteristic |
Patients (n,%) |
Survival |
p |
<1 Year
n=43 |
≥1 Year
n=22 |
| Age |
|
| |
<60 |
42 (64.61%) |
27 |
15 |
0.66 |
| |
≥60 |
23 (35.39%) |
16 |
7 |
| Sex |
|
| |
Male |
53 (81.53%) |
36 |
17 |
0.52 |
| Smoking status |
|
| |
Never smoker |
12 (18.46%) |
7 |
5 |
0.52 |
| |
Smoker/ Former Smoker |
53 (81.54%) |
36 |
17 |
| Histopathology |
|
| |
Adenocarcinoma |
25 (38.46%) |
15 |
10 |
0.68 |
| |
Squamous cell |
31 (47.69%) |
22 |
9 |
| |
Adenosquamous |
9 (13.84%) |
6 |
3 |
| TNM Staging |
|
| |
IIIb |
5 (7.69%) |
4 |
1 |
0.68 |
| |
IIIc |
2 (3.08%) |
0 |
2 |
| |
IVa |
40 (61.54%) |
27 |
13 |
| |
IVb |
18 (27.69%) |
12 |
6 |
| Chemotherapy regimen |
|
| |
Carboplatin + paclitaxel |
4 (6.15%) |
0 |
4 |
0.001 |
| |
Cisplatin + paclitaxel |
58 (89.24%) |
40 |
18 |
| |
Carboplatin + gemsitabine |
3 (4.61%) |
3 |
0 |
Table 2.
The Mean SII for One Year Survival.
Table 2.
The Mean SII for One Year Survival.
| |
|
Mean SII (±SD) |
p
(95% CI) |
| Survival |
<1 Year |
3414.95 (±3300.18) |
0.01 (455.63-3338.36) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).