Submitted:
18 November 2024
Posted:
19 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Glioblastoma (GB) remains a major challenge owing to its extremely aggressive nature and resistance to conventional therapies. This review focuses on the intricate roles of progenitor cells, microglia, and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in orchestrating GB pathogenesis and therapy resistance. Glioma stem cells (GSCs), derived from progenitor cells, are important drivers of tumor initiation and recurrence and exhibit remarkable plasticity and resistance to treatment. Microglia, the immune cells of the brain, are hijacked by GB cells to create an immunosuppressive microenvironment that supports tumor growth and resistance to therapy. ncRNAs, including microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), regulate multiple resistance mechanisms by modulating gene expression and influencing the interactions between progenitor cells and microglia. This review highlights new insights into these interconnected signaling pathways and explores potential therapeutic strategies targeting these molecular players to overcome treatment resistance and improve outcomes in patients with GB. Keywords: Microglia; Non-coding RNA; Glioblastoma; Progenitors Cells, Glioma, Stem Cells.
Keywords:
- Glioma Stem-like Cells (GSCs), derived from progenitor cells, are crucial in initiating and sustaining glioblastoma (GB), contributing to tumor recurrence and resistance due to their plasticity and self-renewal.
- Genetic mutations and epigenetic modifications convert progenitor cells into tumor-initiating GSCs, forming a therapy-resistant cell population.
- GB cells recruit microglia to create an immunosuppressive microenvironment, which promotes tumor growth and complicates therapeutic response.
- Cytokines and growth factors facilitate communication between microglia and GSCs, supporting GSC survival and enhancing resistance to treatment.
- miRNAs and lncRNAs regulate genes that impact tumor progression, cellular interactions, and immune responses, supporting the maintenance of the stem-like phenotype in GSCs.
- Due to the diversity of cellular and molecular interactions, effective GB treatment requires strategies that target multiple pathways and cell types.
- Tailoring therapies to individual tumor profiles, specifically ncRNA expression patterns, could improve treatment outcomes.
- Combining therapies to address GSCs, microglia, and ncRNAs may help overcome resistance mechanisms and improve therapeutic efficacy.
- Novel drug delivery systems, such as nanoparticles and exosomes, are needed to cross the blood-brain barrier and deliver targeted treatments effectively.
- Targeting this axis with pathway inhibitors, immunomodulatory agents, and ncRNA-based therapies is a promising approach to disrupt tumor growth, reduce resistance, and extend patient survival.
1. Introduction
2. Progenitor Cells in GB: Drivers of Tumorigenesis and Resistance
2.1. Progenitor Cells in the Central Nervous System
2.2. Transformation of Progenitor Cells into GSCs
2.3. Progenitor Cells and Tumor Growth
2.4. Progenitor Cells and Therapy Resistance
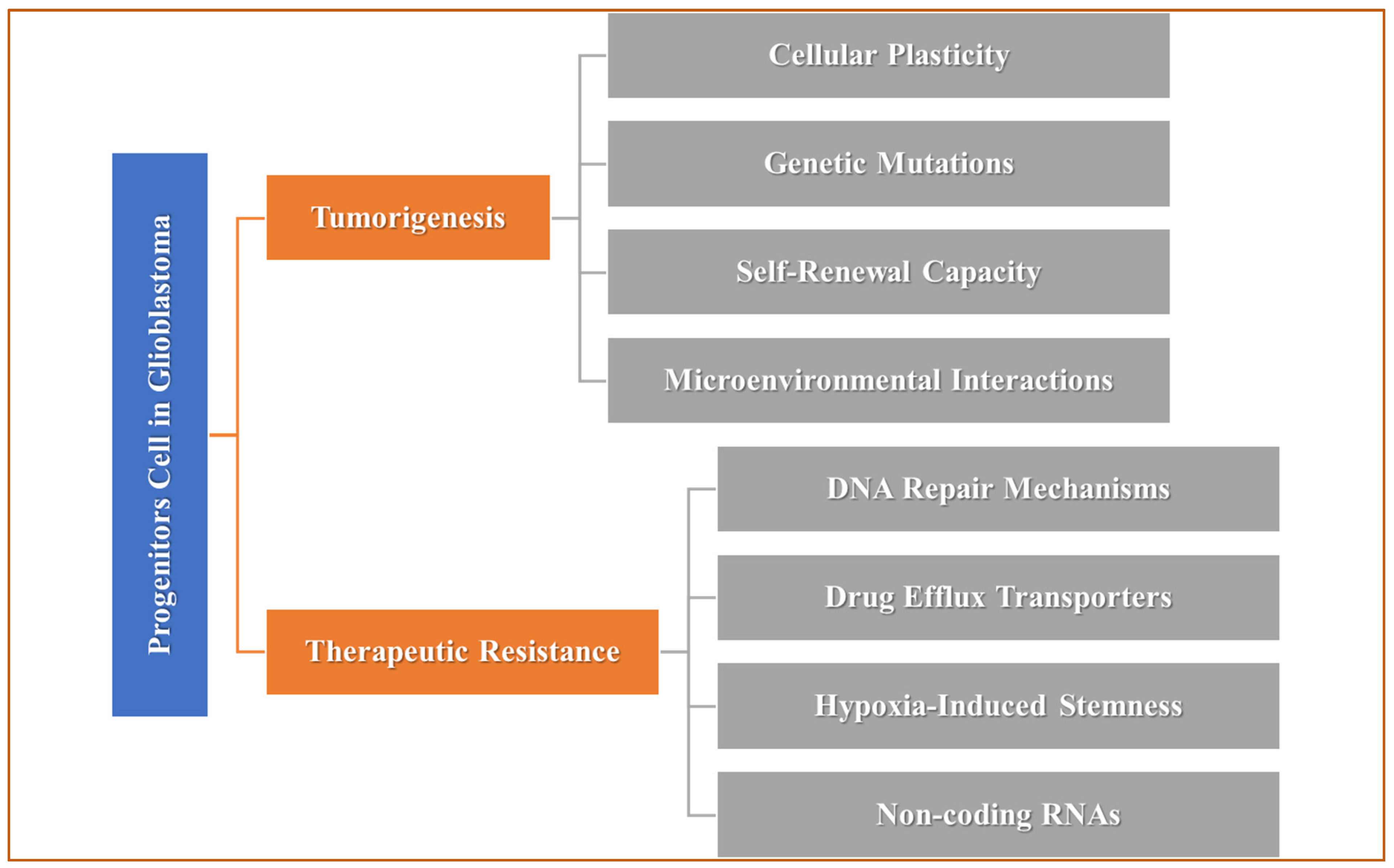
3. Microglia in GB: Tumor-Associated Immune Cells
3.1. Microglia and Their Role in Brain Homeostasis
3.2. Microglial Infiltration into the GB Microenvironment
3.3. Microglial Polarization and GB Progression
M1 Microglia: Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype
M2 Microglia: Tumor-Promoting Phenotype
3.4. Microglia and Therapeutic Resistance
4. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in GB: Key Regulators of Pathogenesis and Resistance
4.1. NcRNAs
- Drug Efflux Mechanisms: miRNAs influence the expression of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, which are responsible for drug efflux. The overexpression of specific miRNAs can enhance the expression of these transporters, leading to decreased intracellular concentrations of chemotherapeutic agents and reduced drug efficacy.
- Evasion of Apoptosis: By down-regulating pro-apoptotic factors and up-regulating anti-apoptotic factors, miRNAs enable GB cells to evade programmed cell death. This mechanism is particularly important in the context of chemotherapy and radiation, where the induction of apoptosis is a primary therapeutic goal [60,63].
- LncRNAs and Their Role in GB: Defined as ncRNAs longer than 200 nucleotides, lncRNAs exhibit a wide range of biological activities. They can interact with chromatin, transcription factors, and other RNA molecules, influencing gene expression at multiple levels. LncRNAs are involved in regulating cellular processes such as cell cycle progression, differentiation, and responses to stress [53,54,55]. LncRNAs are increasingly recognized for their roles in GB pathogenesis. Key lncRNAs involved in GB include:
4.5. NcRNAs in Therapeutic Resistance
5. Interplay Between Progenitor Cells, Microglia, and NcRNAs in GB [AH]
5.1. Progenitor Cell-Microglia Cross-talk
5.2. ncRNAs as Mediators of Cellular Interactions
5.3. Implications for Tumor Progression and Resistance
| Progenitor Cells | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Types | Role in GB Pathogenesis | Mechanism of Resistance | Ref |
| Neural Progenitor Cells (NPCs) | Provide cells with self-renewal and differentiation potential; Mutations can trigger tumorigenic transformation. | High drug-efflux pump activity, enhanced DNA repair, and maintenance of stemness properties. | [87] |
| Glioma Stem-Like Cells (GSCs) | Promote tumor growth and recurrence with stem-like properties and contribute to GB heterogeneity. | Quiescence, increased DNA repair, hypoxic niche protection | [88] |
| Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells (OPCs) | Potential cell of origin in the proneural GB; Dysregulation of OPCs promotes tumor progression | Activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways; Adaptation to microenvironmental stressors | [89,90] |
| Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells (MPCs) | Differentiation into tumor-associated stromal cells; supports aggressive growth of the mesenchymal subtype. | Enhance invasion, angiogenesis, and immune evasion | [91] |
| Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) | Support neovascularization, increase blood supply to the tumor, and facilitate invasion. | Maintain a hypoxic environment, protect from radiotherapy, and support angiogenesis. | [92] |
| Microglia | |||
| Tumor-Associated Microglia/Macrophages (TAMs) | Support tumor growth through secretion of growth factors and cytokines; promote GB invasion and vascularization. | Immunosuppressive environment, increased secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines | [93] |
| M1 Microglia (Pro-inflammatory) | Transiently suppress GB progression by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β) | Reduced activity due to tumor-derived immunosuppressive signaling and metabolic reprogramming | [94] |
| M2 Microglia (Anti-inflammatory) | Promote tumor growth by enhancing angiogenesis, immunosuppression, and extracellular matrix remodeling. | High resistance through secretion of growth factors (e.g. TGF-β) and anti-inflammatory cytokines | [33,95] |
| Reactive Microglia | Activated in response to GB-induced inflammation; secrete factors promoting GB proliferation and matrix remodeling. | Secrete matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that support tumor invasion | [96] |
| Perivascular Microglia | Facilitate the invasion of GB cells along blood vessels and contribute to the formation of the perivascular niche. | Protect tumor cells by promoting a supportive niche and maintaining BBB integrity. | [97] |
| Glioma-Associated Microglia (GAMs) | Specialized microglia in GB; interact closely with GSCs and tumor cells to promote proliferation and invasion | Promote therapeutic resistance by maintaining stemness and supporting immune evasion. | [98] |
| Non-Coding RNAs | |||
| miR-21 (microRNA-21) | Promotes GB cell proliferation, and invasion, and inhibits apoptosis by targeting tumor suppressor genes (e.g., PTEN, PDCD4). | Increases resistance by activating anti-apoptotic signaling pathways and reduces sensitivity to chemotherapy | [99,100] |
| miR-10b | Facilitates tumor cell invasion and promotes stem cell-like properties | Induces therapeutic resistance through upregulation of pro-survival pathways and inhibition of apoptosis | [101] |
| lncRNA HOTAIR | Enhances GB cell migration, invasion, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) | Contributes to radioresistance by promoting DNA damage repair and enhancing stemness properties | [102,103,104] |
| lncRNA MALAT1 | Supports tumor growth and angiogenesis through modulation of gene expression | Enhances resistance by modulating autophagy and promoting anti-apoptotic mechanisms | [105,106,107] |
| circRNA circHIPK3 | Promotes GB proliferation and invasiveness by sponging tumor-suppressive miRNAs (e.g., miR-124) | Mediates chemoresistance through PI3K/AKT signaling activation | [75,108] |
| SNHG12 (Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 12) | Enhances GB proliferation, migration, and immune evasion | Increases resistance by modulating immune checkpoints and enhancing anti-apoptotic signaling | [109,110] |
| miR-155 | Promotes tumor progression by targeting tumor suppressor genes and facilitating immunosuppression | Contributes to radioresistance and chemoresistance by improving DNA repair mechanisms | [111,112] |
6. Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
6.1. Current Therapeutic Strategies
6.2. Challenges in Targeting the Progenitor Cells-Microglia-ncRNA Axis
6.3. Emerging Therapeutic Approaches
7. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Approval
Data Availability Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2016—2020. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 25, iv1–iv99. [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.G.; Fine, H.A. Diffuse Glioma Heterogeneity and Its Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Discov 2021, 11, 575–590. [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Weller, M.; Belanger, K.; Bogdahn, U.; Ludwin, S.K.; Lacombe, D.; Mirimanoff, R.O. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. The New England Journal of Medicine 2005, 10.
- Stupp, R.; Brada, M.; van den Bent, M.J.; Tonn, J.C.; Pentheroudakis, G. High-Grade Glioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Annals of Oncology 2014, 25, 93–101. [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma Stem Cells Promote Radioresistance by Preferential Activation of the DNA Damage Response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cerdeño, V.; Noctor, S.C. Neural Progenitor Cell Terminology. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy 2018, 12, 104. [CrossRef]
- Finkel, Z.; Esteban, F.; Rodriguez, B.; Fu, T.; Ai, X.; Cai, L. Diversity of Adult Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells in Physiology and Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 2045. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xiao, X.; Yi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Shen, Y.; Lin, D.; Wu, C. Tumor Initiation and Early Tumorigenesis: Molecular Mechanisms and Interventional Targets. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 1–36. [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [CrossRef]
- Avsar, T.; Kose, T.B.; Oksal, M.D.; Turan, G.; Kilic, T. IDH1 Mutation Activates mTOR Signaling Pathway, Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion in Glioma Cells. Molecular Biology Reports 2022, 49, 9241–9249. [CrossRef]
- Bhavya, B.; Anand, C.R.; Madhusoodanan, U.K.; Rajalakshmi, P.; Krishnakumar, K.; Easwer, H.V.; Deepti, A.N.; Gopala, S. To Be Wild or Mutant: Role of Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and 2-Hydroxy Glutarate (2-HG) in Gliomagenesis and Treatment Outcome in Glioma. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology 2020, 40, 53–63. [CrossRef]
- Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.C.-H.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Siu, I.-M.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. An Integrated Genomic Analysis of Human Glioblastoma Multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807. [CrossRef]
- Kreth, S.; Thon, N.; Kreth, F.W. Epigenetics in Human Gliomas. Cancer Letters 2014, 342, 185–192. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Singh, R.; Habib, N.; Tripathi, R.; Kushwaha, R.; Mahdi, A. Regulation of Hypoxia Dependent Reprogramming of Cancer Metabolism: Role of HIF-1 and Its Potential Therapeutic Implications in Leukemia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2024, 25, 1121–1134. [CrossRef]
- Bikfalvi, A.; Da Costa, C.A.; Avril, T.; Barnier, J.-V.; Bauchet, L.; Brisson, L.; Cartron, P.F.; Castel, H.; Chevet, E.; Chneiweiss, H.; et al. Challenges in Glioblastoma Research: Focus on the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends in Cancer 2023, 9, 9–27. [CrossRef]
- El-Tanani, M.; Rabbani, S.A.; Babiker, R.; Rangraze, I.; Kapre, S.; Palakurthi, S.S.; Alnuqaydan, A.M.; Aljabali, A.A.; Rizzo, M.; El-Tanani, Y.; et al. Unraveling the Tumor Microenvironment: Insights into Cancer Metastasis and Therapeutic Strategies. Cancer Letters 2024, 591, 216894. [CrossRef]
- Emami Nejad, A.; Najafgholian, S.; Rostami, A.; Sistani, A.; Shojaeifar, S.; Esparvarinha, M.; Nedaeinia, R.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Taherian, M.; Ahmadlou, M.; et al. The Role of Hypoxia in the Tumor Microenvironment and Development of Cancer Stem Cell: A Novel Approach to Developing Treatment. Cancer Cell International 2021, 21, 62. [CrossRef]
- Prager, B.C.; Bhargava, S.; Mahadev, V.; Hubert, C.G.; Rich, J.N. Glioblastoma Stem Cells: Driving Resiliency through Chaos. Trends in cancer 2020, 6, 223. [CrossRef]
- Gimple, R.C.; Bhargava, S.; Dixit, D.; Rich, J.N. Glioblastoma Stem Cells: Lessons from the Tumor Hierarchy in a Lethal Cancer. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 591–609. [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.L.V.; Gomes, I.N.F.; Carloni, A.C.; Rosa, M.N.; Da Silva, L.S.; Evangelista, A.F.; Reis, R.M.; Silva, V.A.O. Role of Glioblastoma Stem Cells in Cancer Therapeutic Resistance: A Perspective on Antineoplastic Agents from Natural Sources and Chemical Derivatives. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 206. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, S.-R.; Lv, S.-Q.; Qin, J.; Yu, S.-C. Models for Evaluating Glioblastoma Invasion along White Matter Tracts. Trends in Biotechnology 2024, 42, 293–309. [CrossRef]
- Eckerdt, F.; Platanias, L.C. Emerging Role of Glioma Stem Cells in Mechanisms of Therapy Resistance. Cancers 2023, 15, 3458. [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Mu, N.; Jia, B.; Guo, Q.; Pan, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Li, W.; Li, M.; et al. Targeting Radiation-Tolerant Persister Cells as a Strategy for Inhibiting Radioresistance and Recurrence in Glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 1056–1070. [CrossRef]
- Dymova, M.A.; Kuligina, E.V.; Richter, V.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Glioblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 6385. [CrossRef]
- Auffinger, B.; Spencer, D.; Pytel, P.; Ahmed, A.U.; Lesniak, M.S. The Role of Glioma Stem Cells in Chemotherapy Resistance and Glioblastoma Multiforme Recurrence. Expert review of neurotherapeutics 2015, 15, 741. [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.; Kim, B.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Youn, H.; Youn, B. Targeting Glioblastoma Stem Cells to Overcome Chemoresistance: An Overview of Current Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1308. [CrossRef]
- da Silva-Diz, V.; Lorenzo-Sanz, L.; Bernat-Peguera, A.; Lopez-Cerda, M.; Muñoz, P. Cancer Cell Plasticity: Impact on Tumor Progression and Therapy Response. Seminars in Cancer Biology 2018, 53, 48–58. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Norgard, R.J.; Stanger, B.Z. Cellular Plasticity in Cancer. Cancer Discov 2019, 9, 837–851. [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Grigore, F.; Chen, C.C.; Li, M. Self-renewal Signaling Pathways and Differentiation Therapies of Glioblastoma Stem Cells (Review). Int J Oncol 2021, 59, 45. [CrossRef]
- Safa, A.R.; Saadatzadeh, M.R.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Pollok, K.E.; Bijangi-Vishehsaraei, K. Emerging Targets for Glioblastoma Stem Cell Therapy. J Biomed Res 2016, 30, 19–31. [CrossRef]
- Cherry, A.E.; Stella, N. G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Oncogenic Signals in Glioma: Emerging Therapeutic Avenues. Neuroscience 2014, 0, 222. [CrossRef]
- Da, M.; D, G.-N. Microglial Dynamics During Human Brain Development. Frontiers in immunology 2018, 9. [CrossRef]
- Orihuela, R.; McPherson, C.A.; Harry, G.J. Microglial M1/M2 Polarization and Metabolic States. British Journal of Pharmacology 2015, 173, 649. [CrossRef]
- Kuntzel, T.; Bagnard, D. Manipulating Macrophage/Microglia Polarization to Treat Glioblastoma or Multiple Sclerosis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 344. [CrossRef]
- D, H.; Dh, G.; H, K. The Role of Microglia and Macrophages in Glioma Maintenance and Progression. Nature neuroscience 2016, 19. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Graeber, M.B. The Molecular Profile of Microglia under the Influence of Glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 958. [CrossRef]
- Ling, E.A.; Wong, W.C. The Origin and Nature of Ramified and Amoeboid Microglia: A Historical Review and Current Concepts. Glia 1993, 7, 9–18. [CrossRef]
- Szulzewsky, F.; Pelz, A.; Feng, X.; Synowitz, M.; Markovic, D.; Langmann, T.; Holtman, I.R.; Wang, X.; Eggen, B.J.L.; Boddeke, H.W.G.M.; et al. Glioma-Associated Microglia/Macrophages Display an Expression Profile Different from M1 and M2 Polarization and Highly Express Gpnmb and Spp1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116644. [CrossRef]
- Zeiner, P.S.; Preusse, C.; Blank, A.-E.; Zachskorn, C.; Baumgarten, P.; Caspary, L.; Braczynski, A.K.; Weissenberger, J.; Bratzke, H.; Reiß, S.; et al. MIF Receptor CD74 Is Restricted to Microglia/Macrophages, Associated with a M1-Polarized Immune Milieu and Prolonged Patient Survival in Gliomas. Brain Pathology 2014, 25, 491. [CrossRef]
- Sj, C.; E, E.; K, D.; Er, S.; Bl, W.; Mh, S.; Je, S. Microglial Stimulation of Glioblastoma Invasion Involves Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor (CSF-1R) Signaling. Molecular medicine (Cambridge, Mass.) 2012, 18. [CrossRef]
- I, B.; S, T.; W, P. Microglia Promote Glioma Migration. Acta neuropathologica 2002, 103. [CrossRef]
- Markovic, D.S.; Glass, R.; Synowitz, M.; Rooijen, N. van; Kettenmann, H. Microglia Stimulate the Invasiveness of Glioma Cells by Increasing the Activity of Metalloprotease-2. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2005, 64, 754–762. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sarkar, S.; Cua, R.; Zhou, Y.; Hader, W.; Yong, V.W. A Dialog between Glioma and Microglia That Promotes Tumor Invasiveness through the CCL2/CCR2/Interleukin-6 Axis. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 312–319. [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; A Dzaye, O.D.; Hahn, A.; Yu, Y.; Scavetta, R.J.; Dittmar, G.; Kaczmarek, A.K.; Dunning, K.R.; Ricciardelli, C.; Rinnenthal, J.L.; et al. Glioma-Derived Versican Promotes Tumor Expansion via Glioma-Associated Microglial/Macrophages Toll-like Receptor 2 Signaling. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 200–210. [CrossRef]
- Wick, W.; Platten, M.; Weller, M. [No Title Found]. Journal of Neuro-Oncology 2001, 53, 177–185. [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, R.; Liu, D. CSF1R Inhibitors Are Emerging Immunotherapeutic Drugs for Cancer Treatment. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2023, 245, 114884. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Tan, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, R.; Zuo, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Ruan, W.; et al. Neutralizing IL-8 Potentiates Immune Checkpoint Blockade Efficacy for Glioma. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 693-710.e8. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Ai, X.; Yang, K.; Yang, Z.; Fei, F.; Liao, X.; Qiu, Z.; Gimple, R.C.; Yuan, H.; Huang, H.; et al. Targeting Microglial Metabolic Rewiring Synergizes with Immune-Checkpoint Blockade Therapy for Glioblastoma. Cancer Discovery 2023, 13, 974–1001. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, Y.; Duan, H.; Guo, X.; Chang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Fu, Z.; Gao, Y.; et al. PERK-Mediated Cholesterol Excretion from IDH Mutant Glioma Determines Anti-Tumoral Polarization of Microglia. Advanced Science 2023, 10, 2205949. [CrossRef]
- Chandran, M.; Candolfi, M.; Shah, D.; Mineharu, Y.; Yadav, V.N.; Koschmann, C.; Asad, A.S.; Lowenstein, P.R.; Castro, M.G. Single vs. Combination Immunotherapeutic Strategies for Glioma. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy 2017, 17, 543–554. [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.S.; Routkevitch, D.; Jackson, C.; Lim, M. Targeting Myeloid Cells in Combination Treatments for Glioma and Other Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1715. [CrossRef]
- Balandeh, E.; Mohammadshafie, K.; Mahmoudi, Y.; Hossein Pourhanifeh, M.; Rajabi, A.; Bahabadi, Z.R.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Rahimian, N.; Hamblin, M.R.; Mirzaei, H. Roles of Non-Coding RNAs and Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 716462. [CrossRef]
- Mahinfar, P.; Baradaran, B.; Davoudian, S.; Vahidian, F.; Cho, W.C.-S.; Mansoori, B. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Multidrug Resistance of Glioblastoma. Genes 2021, 12, 455. [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Derakhshan, M.; Baharloii, F.; Dashti, F.; Mirazimi, S.M.A.; Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Hosseindoost, S.; Goleij, P.; Rahimian, N.; Hamblin, M.R.; et al. Non-Coding RNAs and Glioblastoma: Insight into Their Roles in Metastasis. Molecular Therapy - Oncolytics 2022, 24, 262–287. [CrossRef]
- Subaiea, G.M.; Syed, R.U.; Afsar, S.; Alhaidan, T.M.S.; Alzammay, S.A.; Alrashidi, A.A.; Alrowaili, S.F.; Alshelaly, D.A.; Alenezi, A.M.S.R.A. Non-Coding RNAs (ncRNAs) and Multidrug Resistance in Glioblastoma: Therapeutic Challenges and Opportunities. Pathology - Research and Practice 2024, 253, 155022. [CrossRef]
- Brower, J.V.; Clark, P.A.; Lyon, W.; Kuo, J.S. MicroRNAs in Cancer: Glioblastoma and Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells. Neurochemistry International 2014, 77, 68–77. [CrossRef]
- Sati, I.S.E.E.; Parhar, I. MicroRNAs Regulate Cell Cycle and Cell Death Pathways in Glioblastoma. IJMS 2021, 22, 13550. [CrossRef]
- D’Asti, E.; Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Lee, T.H.; Rak, J. Extracellular Vesicles in Brain Tumor Progression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2016, 36, 383–407. [CrossRef]
- Turra, L.P.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Lizarte Neto, F.S.; Novais, P.C.; Nunes, M.J.; Tirapelli, V.C.; Peria, F.M.; Carneiro, V.M.; Cirino, M.L.D.A.; Carlotti Jr, C.G.; et al. Expression of microRNAs miR-21 and miR-326 Associated with HIF-1α Regulation in Neurospheres of Glioblastoma Submitted to Ionizing Radiation Treatment. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022, 27, 215–225. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Ruggieri, R.; Jamil, E.; Tran, N.L.; Gonzalez, C.; Mugridge, N.; Gao, S.; MacDiarmid, J.; Brahmbhatt, H.; Sarkaria, J.N.; et al. Nanocell-Mediated Delivery of miR-34a Counteracts Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma. Mol Med 2021, 27, 28. [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, A.; Nikitović, M.; Stanojković, T.P.; Grujičić, D.; Bukumirić, Z.; Srbljak, I.; Ilić, R.; Milošević, S.; Arsenijević, T.; Petrović, N. Association between microRNAs 10b/21/34a and Acute Toxicity in Glioblastoma Patients Treated with Radiotherapy and Temozolomide. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 7505. [CrossRef]
- Jesionek-Kupnicka, D.; Braun, M.; Trąbska-Kluch, B.; Czech, J.; Szybka, M.; Szymańska, B.; Kulczycka-Wojdala, D.; Bieńkowski, M.; Kordek, R.; Zawlik, I. MiR-21, miR-34a, miR-125b, miR-181d and miR-648 Levels Inversely Correlate with MGMT and TP53 Expression in Primary Glioblastoma Patients. aoms 2019, 15, 504–512. [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Yan, W.; You, Y. Exosomal Transfer of miR-1238 Contributes to Temozolomide-Resistance in Glioblastoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 238–251. [CrossRef]
- Goenka, A.; Tiek, D.M.; Song, X.; Iglesia, R.P.; Lu, M.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.-Y. The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Glioma. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2031. [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, O.; Tamizkar, K.H.; Sharifi, G.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Emerging Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathobiology of Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 625884. [CrossRef]
- Vecera, M.; Sana, J.; Lipina, R.; Smrcka, M.; Slaby, O. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Gliomas: From Molecular Pathology to Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. IJMS 2018, 19, 2754. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, G.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Niu, J.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle lncRNA Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 Released From Glioma Stem Cells Modulates the Inflammatory Response of Microglia After Lipopolysaccharide Stimulation Through Regulating miR-129-5p/High Mobility Group Box-1 Protein Axis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3161. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Niu, W.; Deng, C.; Zhou, M. LncRNA NEAT1 Enhances Glioma Progression via Regulating the miR-128-3p/ITGA5 Axis. Mol Neurobiol 2021, 58, 5163–5177. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, A.; Wu, B.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z. Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Promotes Progression of Glioma as a ceRNA by Sponging miR-185-5p to Stimulate DNMT1/mTOR Signaling. Journal Cellular Physiology 2021, 236, 121–130. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Dang, H.X.; Lim, D.A.; Feng, F.Y.; Maher, C.A. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2021, 21, 446–460. [CrossRef]
- Molavand, M.; Ebrahimnezhade, N.; Kiani, A.; Yousefi, B.; Nazari, A.; Majidinia, M. Regulation of Autophagy by Non-Coding RNAs in Human Glioblastoma. Med Oncol 2024, 41, 260. [CrossRef]
- Sandhanam, K.; Tamilanban, T. Unraveling the Noncoding RNA Landscape in Glioblastoma: From Pathogenesis to Precision Therapeutics. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 2024. [CrossRef]
- Ghadami, E.; Gorji, A.; Pour-Rashidi, A.; Noorbakhsh, F.; Kabuli, M.; Razipour, M.; Choobineh, H.; Maghsudlu, M.; Damavandi, E.; Ghadami, M. CircZNF609 and circNFIX as Possible Regulators of Glioblastoma Pathogenesis via miR-145-5p/EGFR Axis. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 13551. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yan, S.; Sun, C.; Xiao, F.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis. JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2018, 110, 304–315. [CrossRef]
- Stella, M.; Falzone, L.; Caponnetto, A.; Gattuso, G.; Barbagallo, C.; Battaglia, R.; Mirabella, F.; Broggi, G.; Altieri, R.; Certo, F.; et al. Serum Extracellular Vesicle-Derived circHIPK3 and circSMARCA5 Are Two Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Glioblastoma Multiforme. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 618. [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, M.; Alamdari-palangi, V.; Rahimi Jaberi, K.; Ehtiati, S.; Ojaghi, S.; Rahimi-Jaberi, A.; Samavarchi Tehrani, S.; Dang, P.; Movahedpour, A.; Hossein Khatami, S. Exosomal Long Non-Coding RNAs in Glioblastoma. Clinica Chimica Acta 2024, 553, 117705. [CrossRef]
- Bouzari, B.; Mohammadi, S.; Bokov, D.O.; Krasnyuk, I.I.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Hajibaba, M.; Mirzaei, R.; Karampoor, S. Angioregulatory Role of miRNAs and Exosomal miRNAs in Glioblastoma Pathogenesis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 148, 112760. [CrossRef]
- Crivii, C.-B.; Boșca, A.B.; Melincovici, C.S.; Constantin, A.-M.; Mărginean, M.; Dronca, E.; Suflețel, R.; Gonciar, D.; Bungărdean, M.; Șovrea, A. Glioblastoma Microenvironment and Cellular Interactions. Cancers 2022, 14, 1092. [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Lu, X.; Liao, Y.; Ouyang, P.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G.; Qi, S.; Li, Y. Crosstalk between Glioblastoma and Tumor Microenvironment Drives Proneural–Mesenchymal Transition through Ligand-Receptor Interactions. Genes & Diseases 2024, 11, 874–889. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tao, W. Current Perspectives on Microglia-Neuron Communication in the Central Nervous System: Direct and Indirect Modes of Interaction. Journal of Advanced Research 2024. [CrossRef]
- Ramón Y Cajal, S.; Segura, M.F.; Hümmer, S. Interplay Between ncRNAs and Cellular Communication: A Proposal for Understanding Cell-Specific Signaling Pathways. Front Genet 2019, 10, 281. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Marín, D.; Trujano-Camacho, S.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; De León, D.C.; Campos-Parra, A.D. LncRNAs Driving Feedback Loops to Boost Drug Resistance: Sinuous Pathways in Cancer. Cancer Letters 2022, 543, 215763. [CrossRef]
- Slack, F.J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Oncology. Cell 2019, 179, 1033–1055. [CrossRef]
- Yabo, Y.A.; Niclou, S.P.; Golebiewska, A. Cancer Cell Heterogeneity and Plasticity: A Paradigm Shift in Glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 669–682. [CrossRef]
- Mosher, K.I.; Andres, R.H.; Fukuhara, T.; Bieri, G.; Hasegawa-Moriyama, M.; He, Y.; Guzman, R.; Wyss-Coray, T. Neural Progenitor Cells Regulate Microglia Functions and Activity. Nat Neurosci 2012, 15, 1485–1487. [CrossRef]
- Noch, E.K.; Ramakrishna, R.; Magge, R. Challenges in the Treatment of Glioblastoma: Multisystem Mechanisms of Therapeutic Resistance. World Neurosurgery 2018, 116, 505–517. [CrossRef]
- Llaguno, S.R.A.; Parada, L.F. Cell of Origin of Glioma: Biological and Clinical Implications. British Journal of Cancer 2016, 115, 1445. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of Human Brain Tumour Initiating Cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.W.; Mulholland, S.A.; Pearson, D.M.; Malley, D.S.; Openshaw, S.W.S.; Lambert, S.R.; Liu, L.; Bäcklund, L.M.; Ichimura, K.; Collins, V.P. Adult Grade II Diffuse Astrocytomas Are Genetically Distinct from and More Aggressive than Their Paediatric Counterparts. Acta Neuropathol 2011, 121, 753–761. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sage, J.C.; Miller, M.R.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Hippenmeyer, S.; Vogel, H.; Foreman, O.; Bronson, R.T.; Nishiyama, A.; Luo, L.; et al. Mosaic Analysis with Double Markers Reveals Tumor Cell of Origin in Glioma. Cell 2011, 146, 209–221. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Hu, X.; Kim, H.; Squatrito, M.; Scarpace, L.; deCarvalho, A.C.; Lyu, S.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; et al. Tumor Evolution of Glioma-Intrinsic Gene Expression Subtypes Associates with Immunological Changes in the Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 42-56.e6. [CrossRef]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Pallini, R.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Invernici, G.; Cenci, T.; Maira, G.; Parati, E.A.; Stassi, G.; Larocca, L.M.; et al. Tumour Vascularization via Endothelial Differentiation of Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells. Nature 2010, 468, 824–828. [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.C.; Sarkar, S.; Yong, V.W.; Kelly, J.J.P. Glioblastoma-Associated Microglia and Macrophages: Targets for Therapies to Improve Prognosis. Brain 2017, 140, 1548–1560. [CrossRef]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Bergers, G. Glioblastoma: Defining Tumor Niches. Trends in cancer 2015, 1, 252. [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Pan, C.; Komohara, Y.; Yamada, R.; Yano, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kai, K.; Mukasa, A. The Roles of Glioma-Associated Macrophages/Microglia and Potential Targets for Anti-Glioma Therapy. Immunological Medicine 0, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Martuza, R.L.; Rabkin, S.D. Macrophage Polarization Contributes to Glioblastoma Eradication by Combination Immunovirotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 253-267.e5. [CrossRef]
- Matias, D.; Balça-Silva, J.; Graça, G.C. da; Wanjiru, C.M.; Macharia, L.W.; Nascimento, C.P.; Roque, N.R.; Coelho-Aguiar, J.M.; Pereira, C.M.; Santos, M.F.D.; et al. Microglia/Astrocytes–Glioblastoma Crosstalk: Crucial Molecular Mechanisms and Microenvironmental Factors. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 2018, 12, 235. [CrossRef]
- Roesch, S.; Rapp, C.; Dettling, S.; Herold-Mende, C. When Immune Cells Turn Bad—Tumor-Associated Microglia/Macrophages in Glioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 436. [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, M.S.; Mehrabian, E.; Mirzaei, H. MiR-21: A Key Player in Glioblastoma Pathogenesis. J Cell Biochem 2018, 119, 1285–1290. [CrossRef]
- Ivo D’Urso, P.; Fernando D’Urso, O.; Damiano Gianfreda, C.; Mezzolla, V.; Storelli, C.; Marsigliante, S. miR-15b and miR-21 as Circulating Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Glioma. Curr Genomics 2015, 16, 304–311. [CrossRef]
- Teplyuk, N.M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Gabriely, G.; Giese, A.; Kim, E.; Smolsky, M.; Kim, R.Y.; Saria, M.G.; Pastorino, S.; Kesari, S.; et al. MicroRNAs in Cerebrospinal Fluid Identify Glioblastoma and Metastatic Brain Cancers and Reflect Disease Activity. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 689–700. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadov, U.; Picard, D.; Bartl, J.; Silginer, M.; Trajkovic-Arsic, M.; Qin, N.; Blümel, L.; Wolter, M.; Lim, J.K.M.; Pauck, D.; et al. The Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIRM1 Promotes Tumor Aggressiveness and Radiotherapy Resistance in Glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 885. [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Yao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. Knockdown of Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Inhibits Malignant Biological Behaviors of Human Glioma Cells via Modulation of miR-326. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21934. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y. LncRNA HOTAIR Participates in Microglia Activation and Inflammatory Factor Release by Regulating the Ubiquitination of MYD88 in Traumatic Brain Injury. J Mol Neurosci 2021, 71, 169–177. [CrossRef]
- Baspinar, Y.; Elmaci, I.; Ozpinar, A.; Altinoz, M.A. Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 as a Key Target in Pathogenesis of Glioblastoma. Janus Faces or Achilles’ Heal? Gene 2020, 739, 144518. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xu, X.-K.; Li, J.-L.; Kong, K.-K.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; He, J.; Wang, F.; Li, P.; Ge, X.-S.; et al. MALAT1 Is a Prognostic Factor in Glioblastoma Multiforme and Induces Chemoresistance to Temozolomide through Suppressing miR-203 and Promoting Thymidylate Synthase Expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22783–22799. [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q. Regulatory Networks of LncRNA MALAT-1 in Cancer. CMAR 2020, Volume 12, 10181–10198. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Sun, H. Biogenesis, Cellular Effects, and Biomarker Value of circHIPK3. Cancer Cell Int 2021, 21, 256. [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Bhushan, A.; Shukla, U.; Pundir, A.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, T. Downregulation of lncRNA SNHG1 in Hypoxia and Stem Cells Is Associated with Poor Disease Prognosis in Gliomas. Cell Cycle 2023, 22, 1135–1153. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Zou, X.; Zeng, X. Long Noncoding RNA SNHG5 Knockdown Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Targeting the miR-154-5p/CXCL13 Axis. Neurochem Res 2020, 45, 1566–1575. [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.K.; Panda, L.P.; Biswal, S.; Barhwal, K. Insights into the Glioblastoma Tumor Microenvironment: Current and Emerging Therapeutic Approaches. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2024, 15, 1355242. [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H. MicroRNA-155-3p Promotes Glioma Progression and Temozolomide Resistance by Targeting Six1. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 2020, 24, 5363. [CrossRef]
- Yalamarty, S.S.K.; Filipczak, N.; Li, X.; Subhan, M.A.; Parveen, F.; Ataide, J.A.; Rajmalani, B.A.; Torchilin, V.P. Mechanisms of Resistance and Current Treatment Options for Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM). Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 2116. [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.; Bhat, K.P.; Olar, A. Current Clinical Management of Patients with Glioblastoma. Cancer Rep (Hoboken) 2019, 2, e1216. [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Blanco, J.; Sanz-Arriazu, L.; Lorenzoni, R.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. Glioblastoma Chemotherapeutic Agents Used in the Clinical Setting and in Clinical Trials: Nanomedicine Approaches to Improve Their Efficacy. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2020, 581, 119283. [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, D.T.; Gorlia, T.; Gilbert, M.R.; Kim, M.M.; Burt Nabors, L.; Mason, W.P.; Hegi, M.E.; Zhang, P.; Golfinopoulos, V.; Perry, J.R.; et al. Is More Better? The Impact of Extended Adjuvant Temozolomide in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Secondary Analysis of EORTC and NRG Oncology/RTOG. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 1119–1126. [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zuo, C.; Fang, P.; Liu, G.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tang, R. Targeting Glioblastoma Stem Cells: A Review on Biomarkers, Signal Pathways and Targeted Therapy. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 701291. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Q. The Adaptive Transition of Glioblastoma Stem Cells and Its Implications on Treatments. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.; Wan, F.; Farhadi, M.; Ernst, A.; Zeppernick, F.; Tagscherer, K.E.; Ahmadi, R.; Lohr, J.; Dictus, C.; Gdynia, G.; et al. Differentiation Therapy Exerts Antitumor Effects on Stem-like Glioma Cells. Clin Cancer Res 2010, 16, 2715–2728. [CrossRef]
- Arima, Y.; Nobusue, H.; Saya, H. Targeting of Cancer Stem Cells by Differentiation Therapy. Cancer Science 2020, 111, 2689. [CrossRef]
- Takebe, N.; Miele, L.; Harris, P.J.; Jeong, W.; Bando, H.; Kahn, M.; Yang, S.X.; Ivy, S.P. Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt Pathways in Cancer Stem Cells: Clinical Update. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2015, 12, 445–464. [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Xu, M.; Yang, J.; Ma, X. The Role of Hedgehog and Notch Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Molecular Biomedicine 2022, 3, 44. [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.S.; Anand, A.; Harwood, D.S.L.; Kristensen, B.W. Tumor-Associated Microglia and Macrophages in the Glioblastoma Microenvironment and Their Implications for Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4255. [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-Coding RNAs in Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Nat Rev Genet 2024, 25, 211–232. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Liu, B.; Fan, Z. Noncoding RNAs in Tumorigenesis and Tumor Therapy. Fundamental Research 2023, 3, 692–706. [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA: Trends in Clinical Trials of Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy Strategies. Exp Mol Med 2023, 55, 1314–1321. [CrossRef]
- Toden, S.; Zumwalt, T.J.; Goel, A. Non-Coding RNAs and Potential Therapeutic Targeting in Cancer. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Reviews on cancer 2020, 1875, 188491. [CrossRef]
- Saenz-Pipaon, G.; Dichek, D.A. Targeting and Delivery of microRNA-Targeting Antisense Oligonucleotides in Cardiovascular Diseases. Atherosclerosis 2023, 374, 44–54. [CrossRef]
- Valerius, A.R.; Webb, L.M.; Thomsen, A.; Lehrer, E.J.; Breen, W.G.; Campian, J.L.; Riviere-Cazaux, C.; Burns, T.C.; Sener, U. Review of Novel Surgical, Radiation, and Systemic Therapies and Clinical Trials in Glioblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 10570. [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z. Emerging Therapies for Glioblastoma: Current State and Future Directions. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2022, 41, 142. [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Miyata, Y.; Okada, M. Current Clinical Trials with Non-Coding RNA-Based Therapeutics in Malignant Diseases: A Systematic Review. Translational Oncology 2023, 31, 101634. [CrossRef]
- Shergalis, A.; Armand Bankhead, I.I.I.; Luesakul, U.; Muangsin, N.; Neamati, N. Current Challenges and Opportunities in Treating Glioblastoma. Pharmacological Reviews 2018, 70, 412. [CrossRef]
- Benmelouka, A.Y.; Munir, M.; Sayed, A.; Attia, M.S.; Ali, M.M.; Negida, A.; Alghamdi, B.S.; Kamal, M.A.; Barreto, G.E.; Ashraf, G.M.; et al. Neural Stem Cell-Based Therapies and Glioblastoma Management: Current Evidence and Clinical Challenges. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 2258. [CrossRef]
- Achar, A.; Myers, R.; Ghosh, C. Drug Delivery Challenges in Brain Disorders across the Blood–Brain Barrier: Novel Methods and Future Considerations for Improved Therapy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1834. [CrossRef]
- Husain, A.; Pandey, N.; Singh, D.; Ahmad, F.; Sharma, R.; Siddiqui, M.H. Drug Discovery in Glioblastoma: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Cha, G.D.; Kang, T.; Baik, S.; Kim, D.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Advances in Drug Delivery Technology for the Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Journal of Controlled Release 2020, 328, 350–367. [CrossRef]
- Qazi, M.A.; Vora, P.; Venugopal, C.; Sidhu, S.S.; Moffat, J.; Swanton, C.; Singh, S.K. Intratumoral Heterogeneity: Pathways to Treatment Resistance and Relapse in Human Glioblastoma. Annals of Oncology 2017, 28, 1448–1456. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Kim, L.J.Y.; Wu, Q.; Wallace, L.C.; Prager, B.C.; Sanvoranart, T.; Gimple, R.C.; Wang, X.; Mack, S.C.; Miller, T.E.; et al. Targeting Glioma Stem Cells through Combined BMI1 and EZH2 Inhibition. Nat Med 2017, 23, 1352–1361. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Vashishta, M.; Kong, L.; Wu, X.; Lu, J.J.; Guha, C.; Dwarakanath, B.S. The Role of Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt Signaling Pathways in the Resistance of Tumors to Anticancer Therapies. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2021, 9, 650772. [CrossRef]
- Adewunmi, O.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.H.-F.; Rosen, J.M. Targeted Inhibition of lncRNA Malat1 Alters the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Preclinical Syngeneic Mouse Models of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunology Research 2023, 11, 1462–1479. [CrossRef]
- Rončević, A.; Koruga, N.; Soldo Koruga, A.; Rončević, R.; Rotim, T.; Šimundić, T.; Kretić, D.; Perić, M.; Turk, T.; Štimac, D. Personalized Treatment of Glioblastoma: Current State and Future Perspective. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1579. [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.; Saini, S.; Bhadra, S.; Kulavi, S.; Bandyopadhyay, J. Precision Medicine Advancements in Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review. BioMedicine 2023, 13, 1. [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Sani, I.; Molavi, Z.; Naderi, S.; Mirmajidi, S.-H.; Zare, I.; Naeimzadeh, Y.; Mansouri, A.; Tajbakhsh, A.; Savardashtaki, A.; Sahebkar, A. Personalized mRNA Vaccines in Glioblastoma Therapy: From Rational Design to Clinical Trials. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 601. [CrossRef]
- Hersh, A.M.; Bhimreddy, M.; Weber-Levine, C.; Jiang, K.; Alomari, S.; Theodore, N.; Manbachi, A.; Tyler, B.M. Applications of Focused Ultrasound for the Treatment of Glioblastoma: A New Frontier. Cancers 2022, 14, 4920. [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, K.; Srinivasan, S.; Shanmugam, A. Review of the Efficacy of Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment. Biomedical Technology 2024, 5, 109–122. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Ye, Y.; Lei, Y.; Islam, R.; Tan, S.; Tong, R.; Miao, Y.-B.; Cai, L. Smart Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-C.; Gao, J.-Q. Exosomes as Novel Bio-Carriers for Gene and Drug Delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2017, 521, 167–175. [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Sasso, J.M.; Wang, X.; Liaw, W.-S.; Chen, C.-A.; Zhou, Q.A. Exosomes─Nature’s Lipid Nanoparticles, a Rising Star in Drug Delivery and Diagnostics. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 17802–17846. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Rehman, K.; Mahmood, A.; Shabbir, M.; Liang, Y.; Duan, L.; Zeng, H. Exosome for mRNA Delivery: Strategies and Therapeutic Applications. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 395. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





