Submitted:
18 November 2024
Posted:
19 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
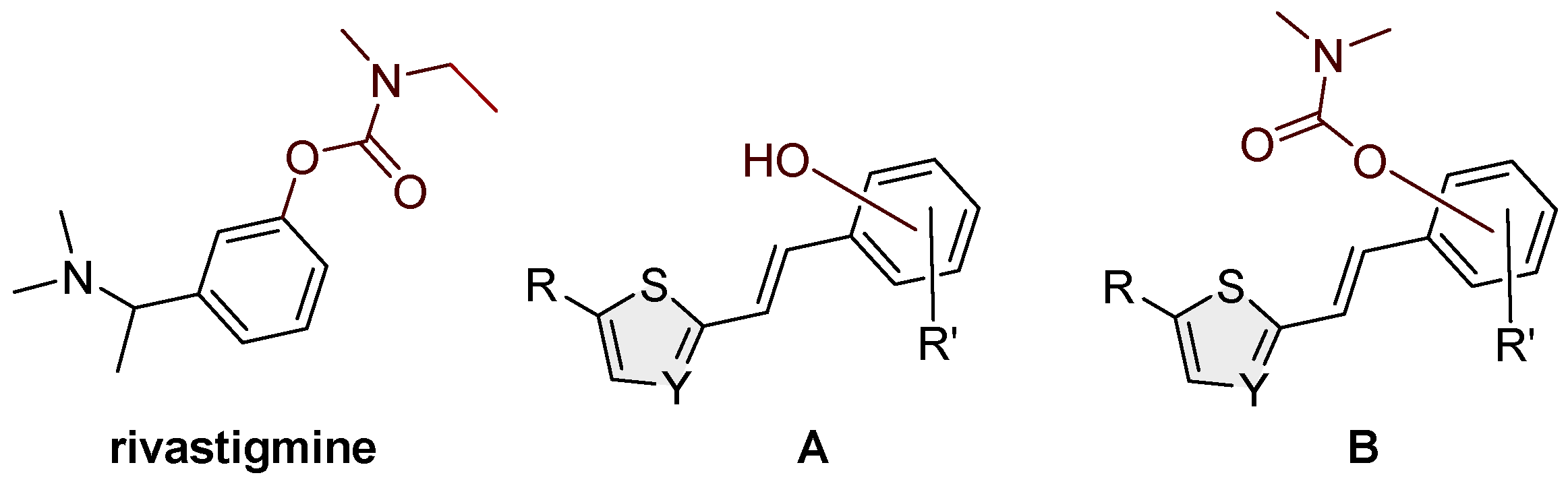
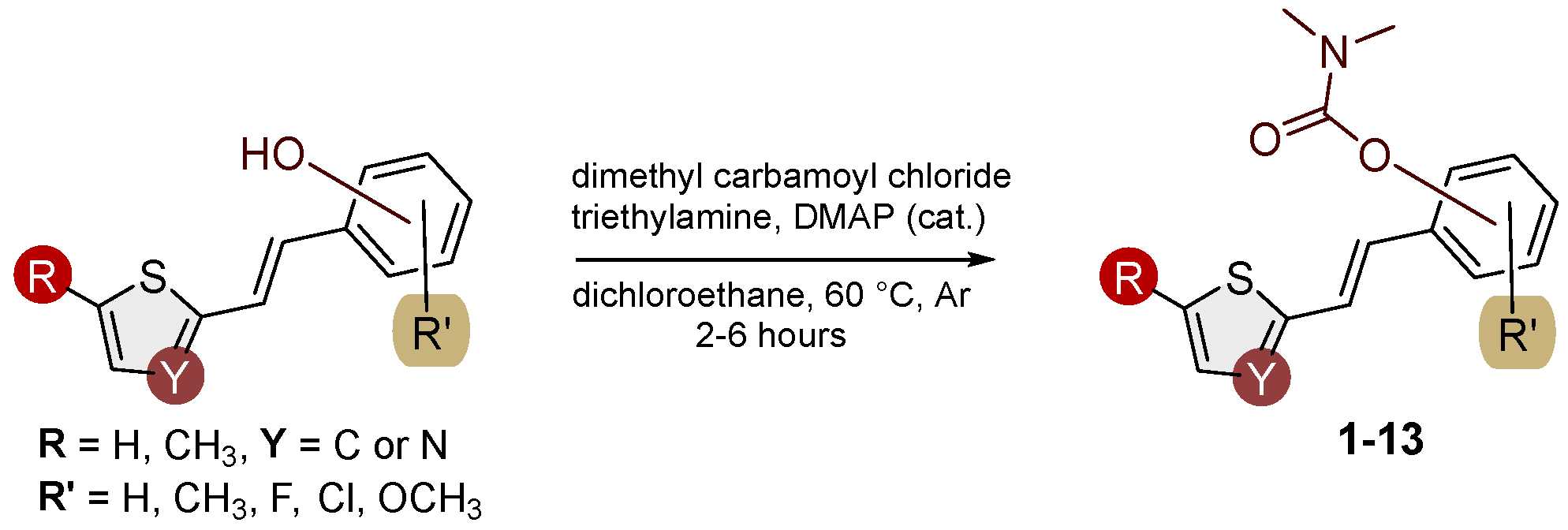
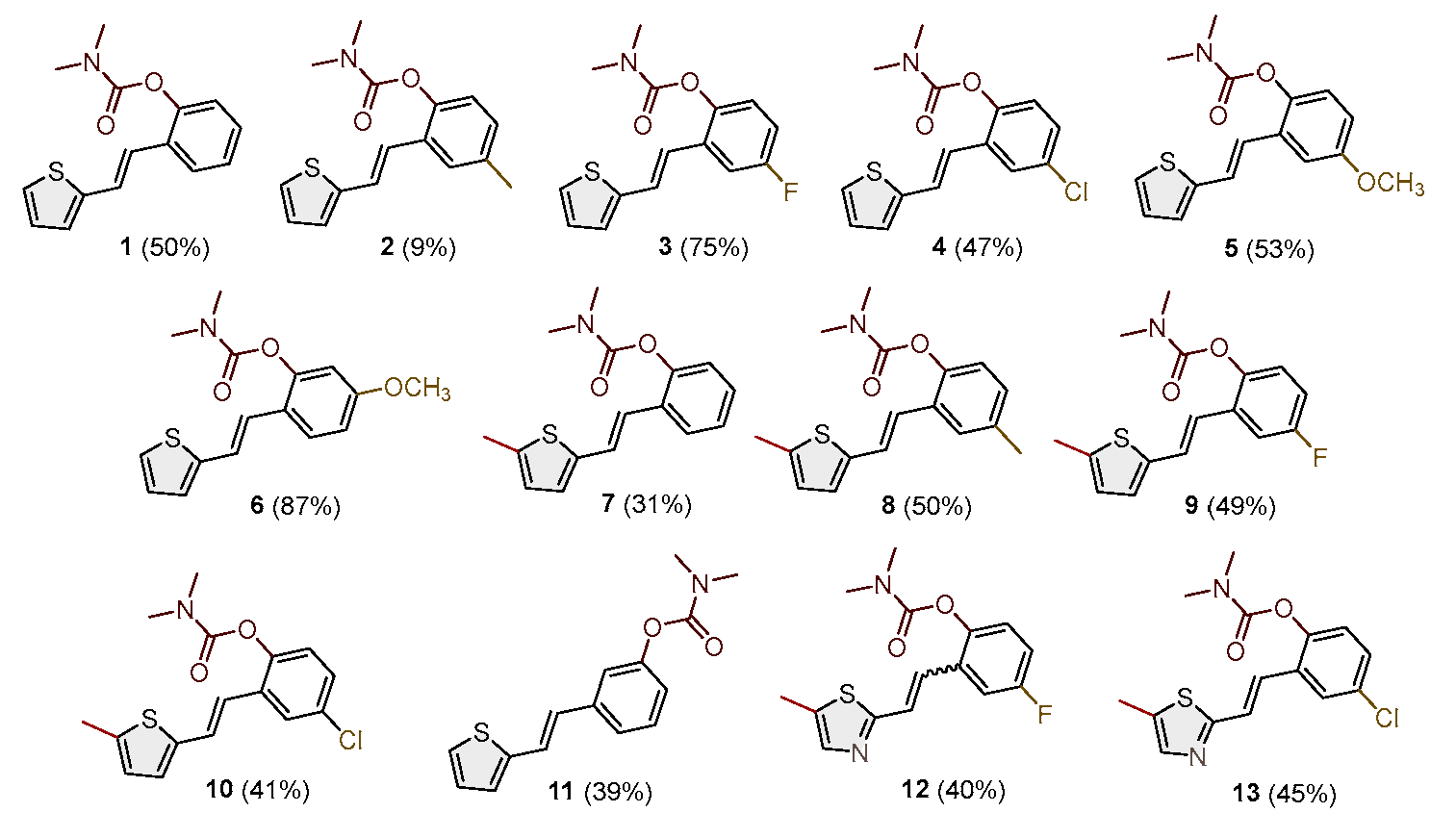
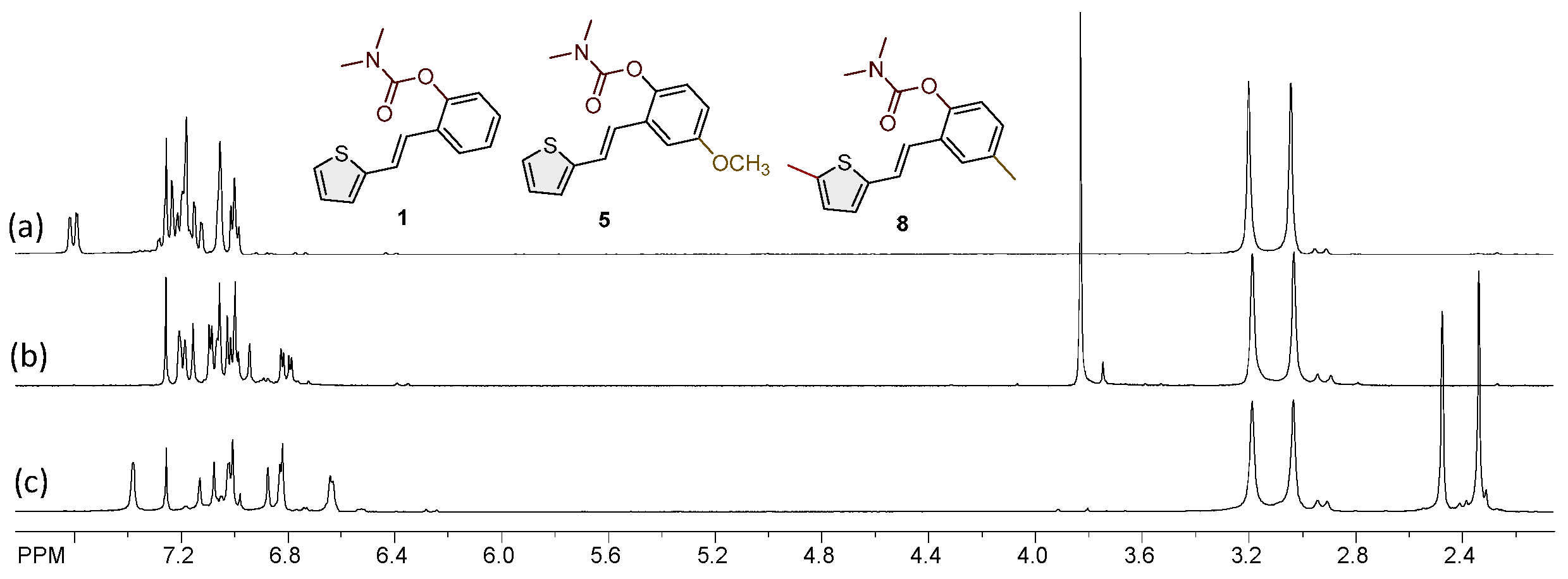
2.1. Design, Synthesis and Characterization of New Carbamates 1–13
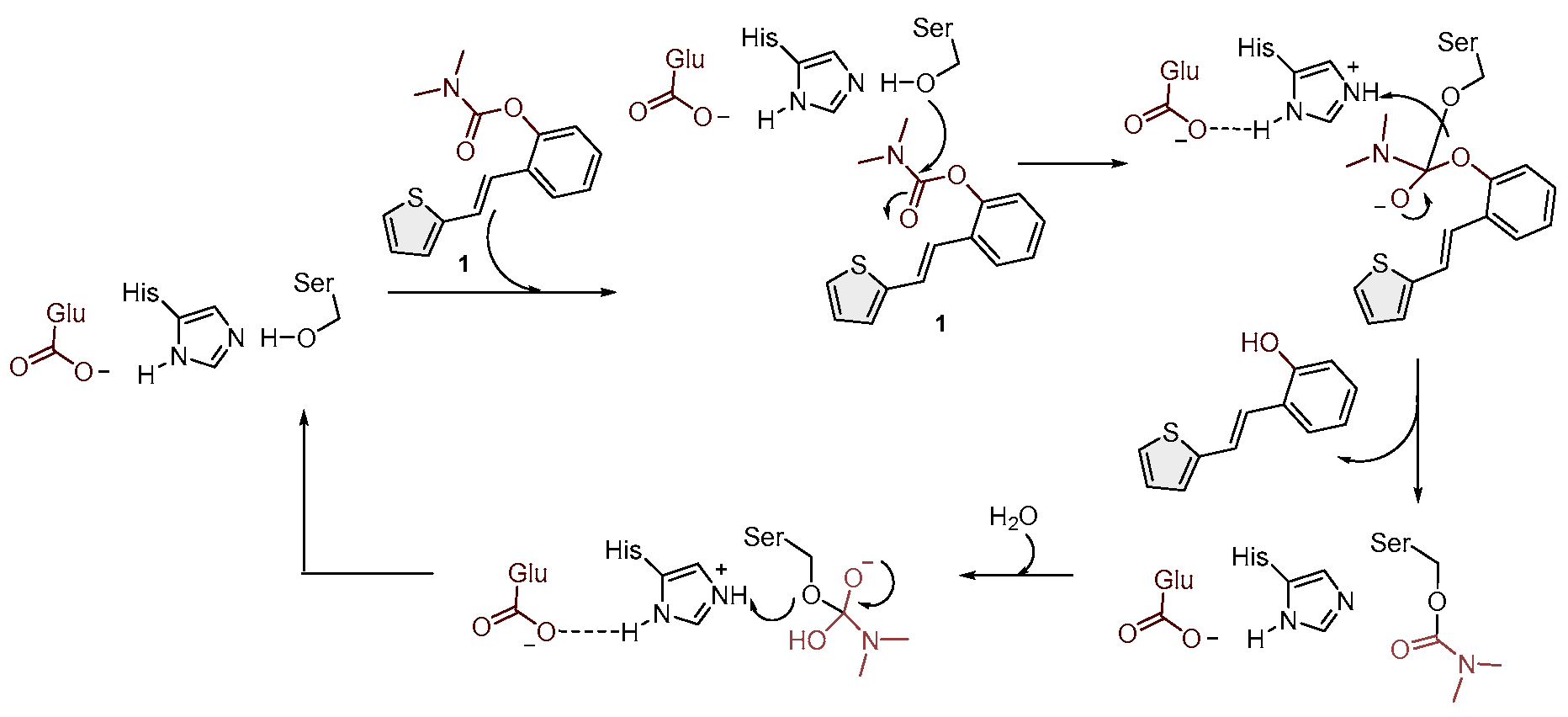
2.2. Cholinesterases Inhibitory Activity of Carbamate Derivatives
2.3. In Silico Evaluation of ADME(T) Properties and In Silico Assessment of the Possibility of a Compound Passing Through the Blood-Brain Barrier by Passive Transport
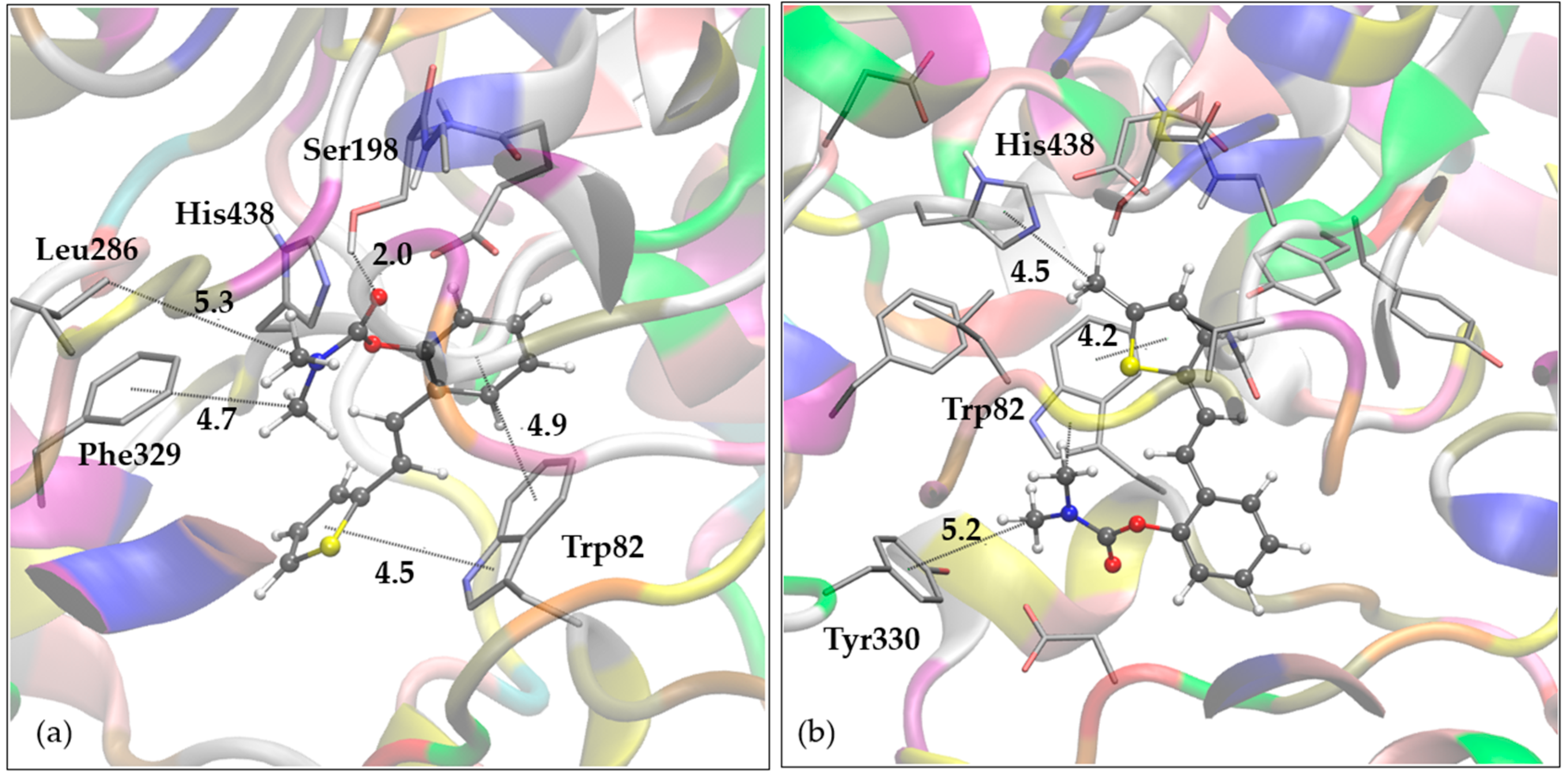
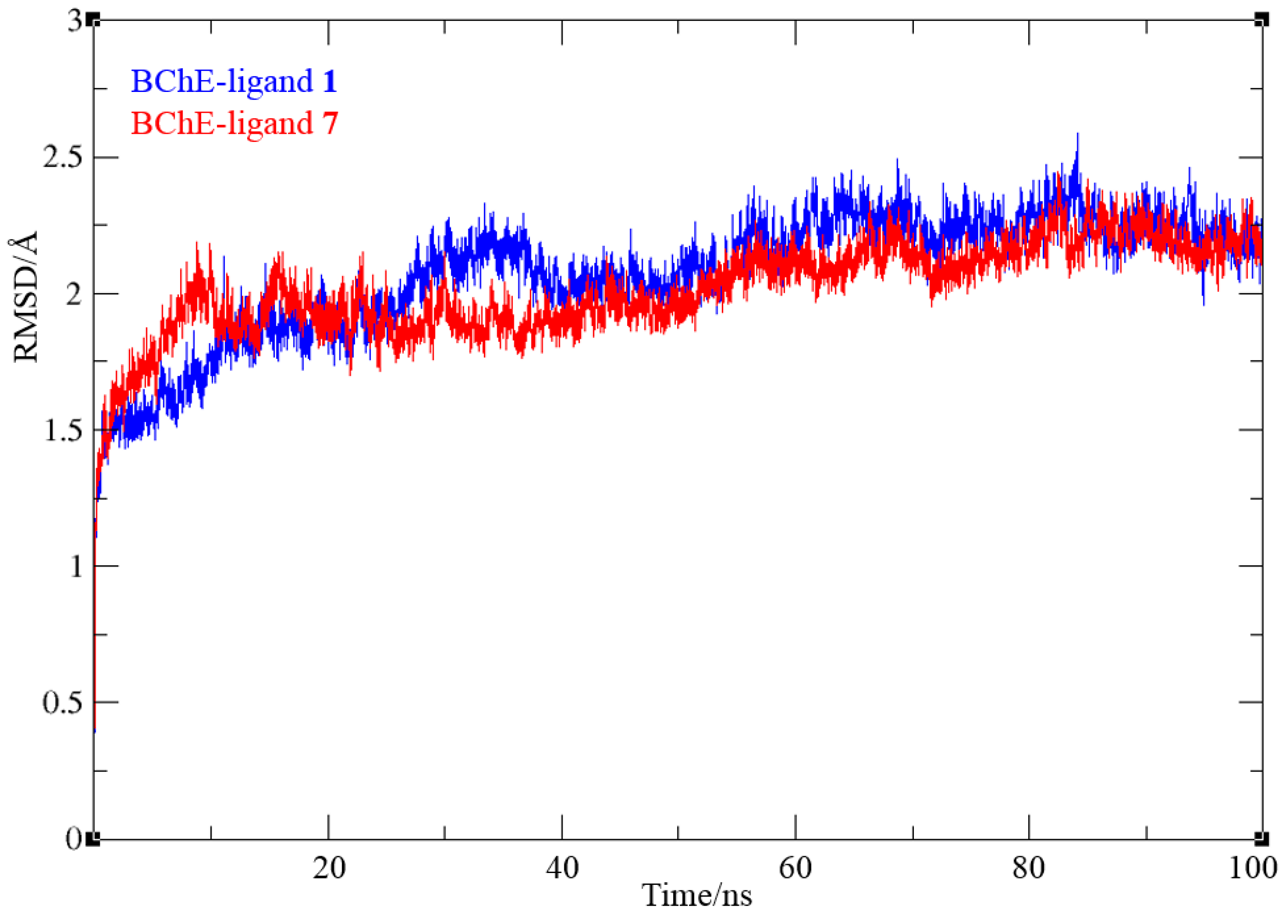
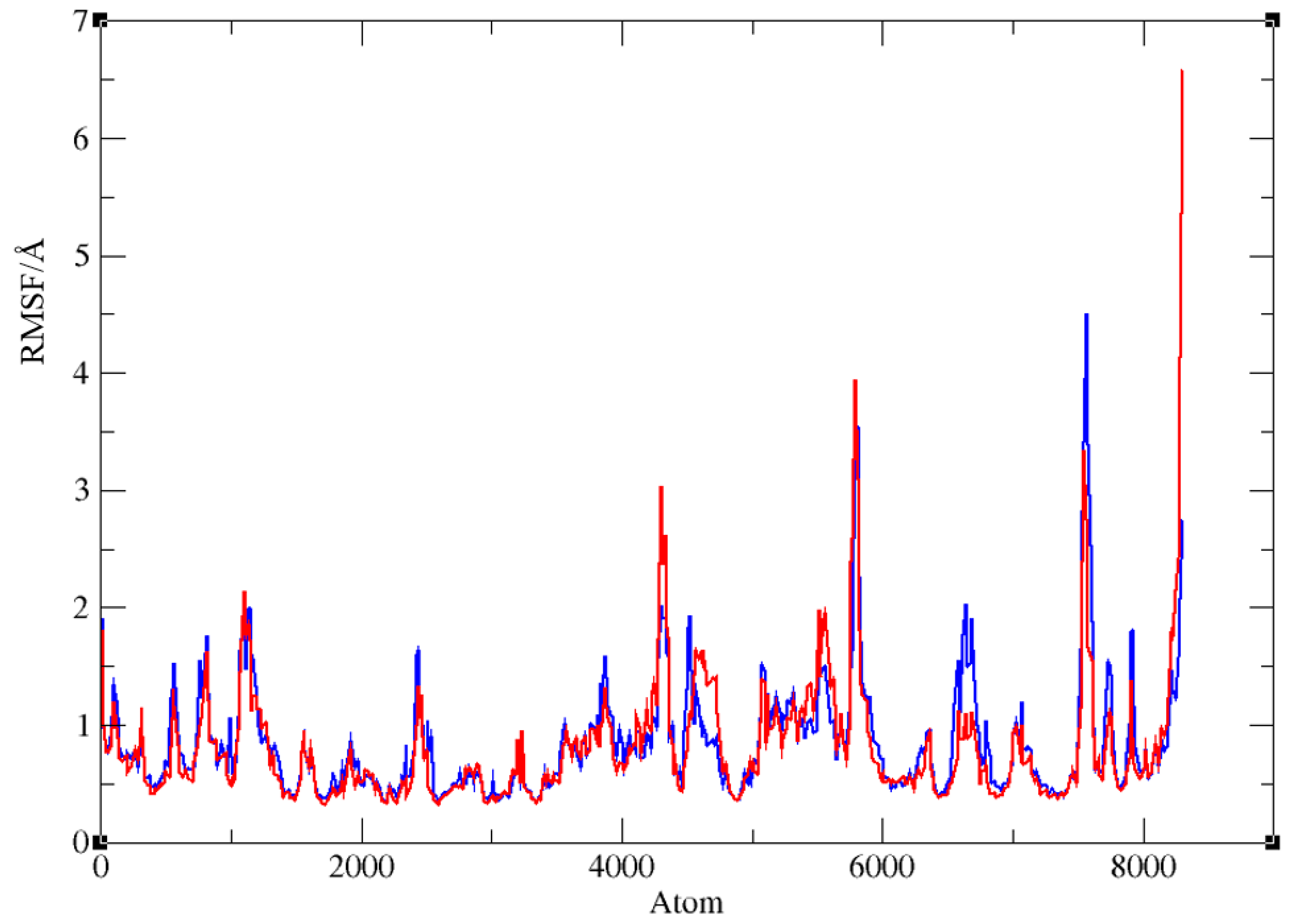
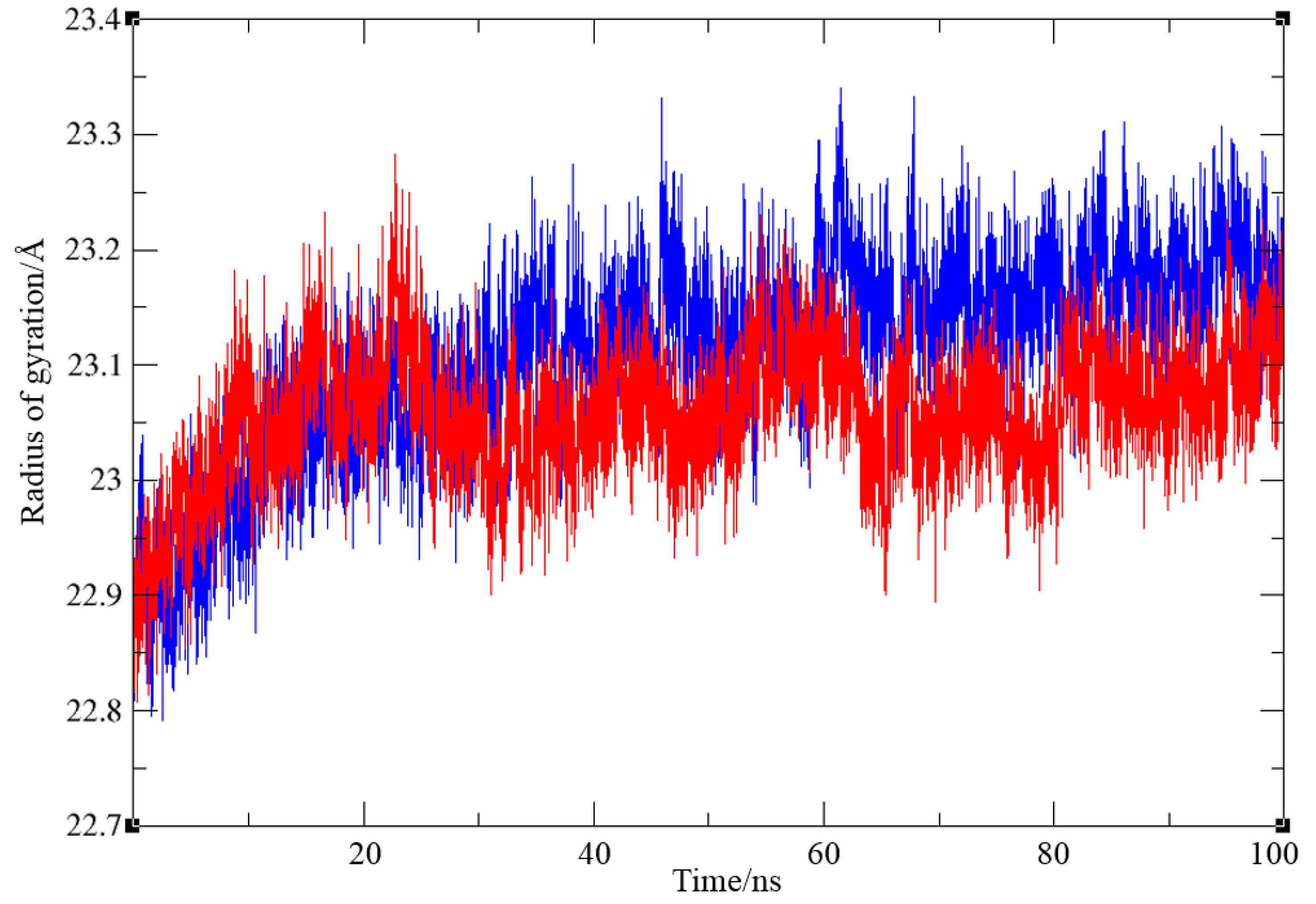
2.4. Docking Study and Molecular Dynamics
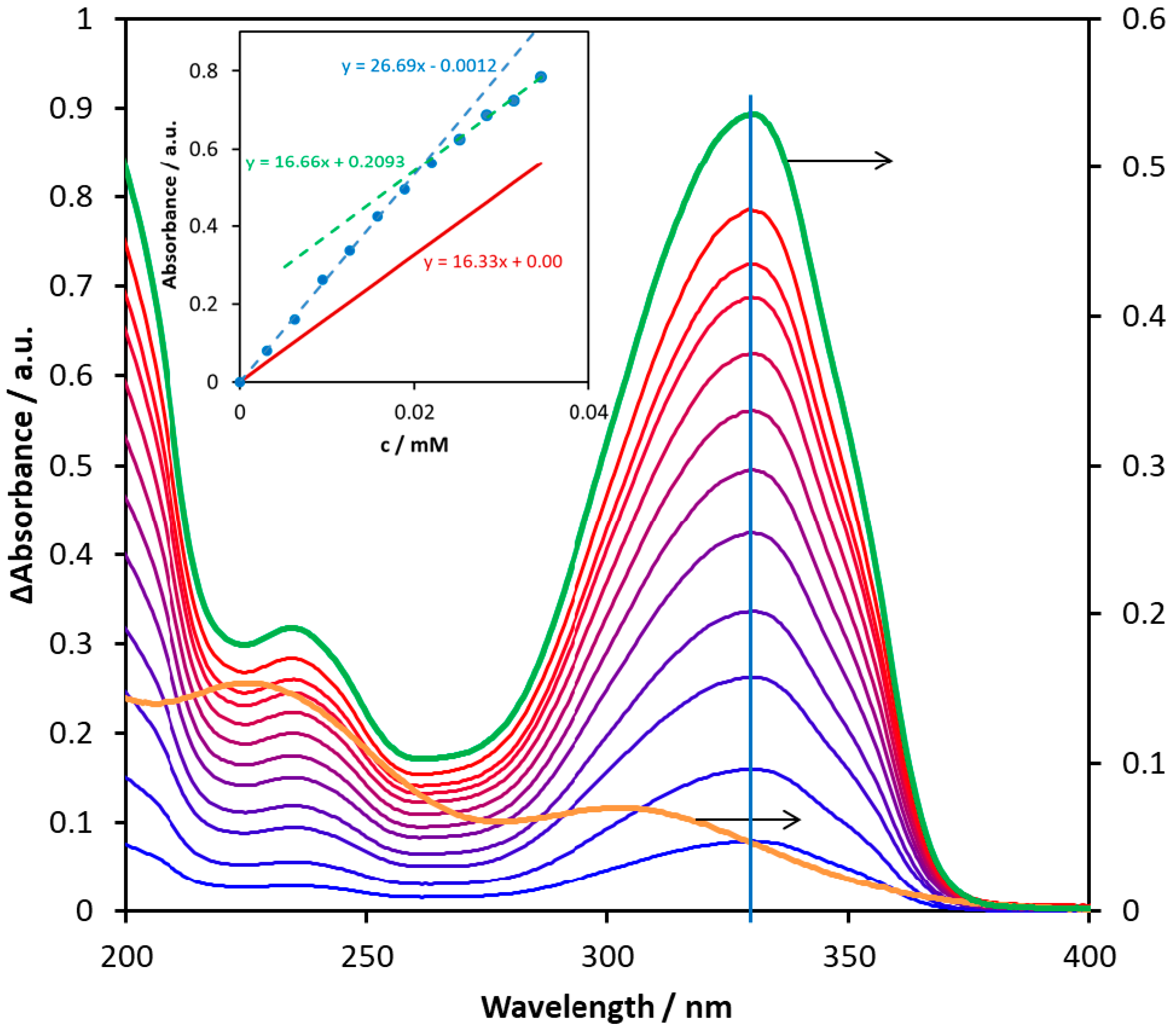
2.5. Complex Formation of Biometals with Bioactive Carbamates
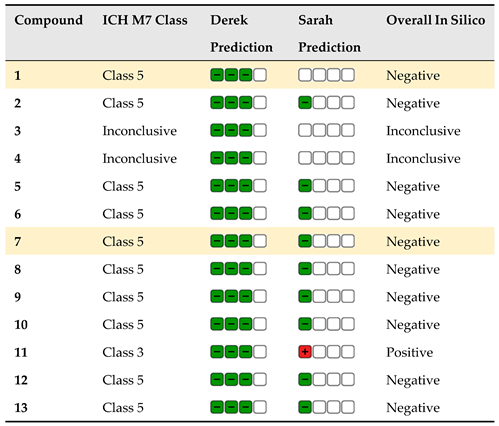
2.6. In-Silico Genotoxicity Evaluation
 |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedure
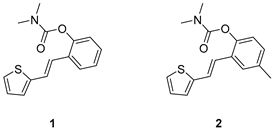
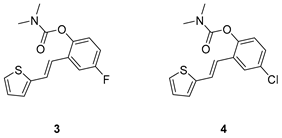
3.2. Synthesis of Carbamates 1–13
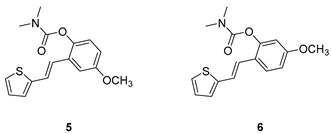
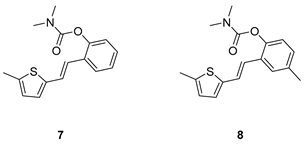
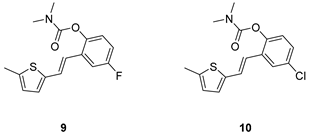
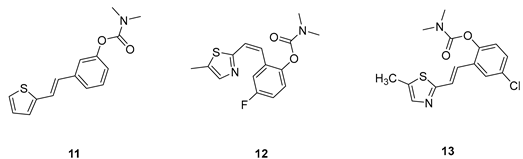
3.2. Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity
3.3. Metal-Chelate or -Associate Formation
3.4. Computational Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive review on Alzheimer's disease: causes and treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, e5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyness, S.A.; Zarow, C.; Chui, H.C. Neuron loss in key cholinergic and aminergic nuclei in Alzheimer disease: a meta-analysis. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer's Association, 2021 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer. Dement. 2021, 17, 321–387. [CrossRef]
- Szeto, J.Y.Y.; Lewis, S.J.G. Current treatment options for Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M. Preventing Alzheimer's disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1924–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Y.L.; Liu, X.Z.; Shen, P.; Zheng, Y.G.; Lan, X.R.; Lu, C.B.; Wang, J.Z. Current understanding of metal ions in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Picançoa, L.C.; Ozelaa, P.F.; de Brito Brito, M.d.F.; Pinheiroa, A.A.; Padilhab, E.C.; Bragac, F.S.; Tomich de Paula da Silvad, C.D.; Dos Santos, C.B.; Rosad, J.M.C.; da Silva Hage-Melim, L.I. Alzheimer's disease: a review from the pathophysiology to diagnosis, new perspectives for pharmacological treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3141–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey-Bloom, J.; Anand, R.; Veach, J. A randomized trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of ENA 713 (rivastigmine tartrate), a new acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, in patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychopharmacol. 1998, 1, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, T. Rivastigmine in the treatment of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotenberg, M.; Almog, S. Evaluation of the decarbamylation process of cholinesterase during assay of enzyme activity. Clin. Chim. Acta 1995, 240, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, P.; Fringeli, U.P. Acetylcholinesterase kinetics. Biophys. Struct. Mech. 1981, 8, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, E. Spontaneous reactivation of phosphorylated and carbamaylated cholinesterases. Bull. Wld. Hlth. Org. 1971, 44, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mahase, E. Aducanumab: European agency rejects Alzheimer's drug over efficacy and safety concerns. BMJ 2021, 375, e3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvesh, S.; Darvesh, K.V.; McDonald, R.S.; Mataija, D.; Walsh, R.; Mothana, S.; Lockridge, O.; Martin, E. Carbamates with differential mechanism of inhibition toward acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4200–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Singh, B. A review on cholinesterase inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.L.; Bartolini, M.; Cavalli, A.; Andrisano, V.; Rosini, M.; Minarini, A.; Melchiorre, C. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of conformationally restricted rivastigmine analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5945–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, J.; Herzig, Y.; Goren, T.; Finkelstein, N.; Lerner, D.; Goldenberg, W.; Miskolczi, I.; Molnar, S.; Rantal, F.; Tamas, T.; Toth, G.; Zagyva, A.; Zekany, A.; Finberg, J.; Lavian, G.; Gross, A.; Friedman, R.; Razin, M.; Huang, W.; Krais, B.; Chorev, M.; Youdim, M.B.; Weinstock, M. Novel dual inhibitors of AChE and MAO derived from hydroxy aminoindan and henethylamine as potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 5260–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, G.; Gokhan, N.; Yesilada, A.; Bilgin, A.A. 1-N-Substituted thiocarbamoyl-3-phenyl-5-thienyl-2-pyrazolines: a novel cholinesterase and selective monoamine oxidase B nhibitors for the treatment of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 38, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, N.; Tago, K.; Marumoto, S.; Takami, K.; Ori, M.; Yamada, N.; Koyama, K.; Naruto, S.; Abe, K.; Yamazaki, R.; Hara, T.; Aoyagi, A.; Abe, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Kogen, H. A conformational restriction approach to the development of dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and serotonin transporter as potential agents for Alzheimer's disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 4389–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krátký, M.; Štěpánková, Š.; Vorčáková, K.; Švarcová, M.; Vinšová, J. Novel cholinesterase inhibitors based on O-aromatic N,N-disubstituted carbamates and thiocarbamates. Molecules 2016, 21, e21020191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groner, E.; Ashani, Y.; Schorer-Apelbaum, D.; Sterling, J.; Herzig, Y.; Weinstock, M. The kinetics of inhibition of human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase by two series of novel carbamates. Molec. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košak, U.; Strašek, N.; Knez, D.; Jukič, M.; Žakelj, S.; Zahirović, A.; Pišlar, A.; Brazzolotto, X.; Nachon, F.; Kos, J.; Gobec, S. N-alkylpiperidine carbamate as potential anti- Alzheimer`s agensts. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 197, 112282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlakić, M.; Đurčević, E.; Odak, I.; Barić, D.; Juričević, I.; Šagud, I.; Burčul, F.; Lasić, Z.; Marinić, Ž.; Škorić, I. Thieno-thiazolostilbenes, thienobenzo-thiazoles, and naphtho-oxazoles: Computational study and cholinesterase inhibitory activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlakić, M.; Faraho, I.; Odak, I.; Kovačević, B.; Raspudić, A.; Šagud, I.; Bosnar, M.; Škorić, I.; Barić, D. Cholinesterase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activity of the naphtho- and thienobenzo-triazole photoproducts: Experimental and computational study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Selec, I.; Ćaleta, I.; Odak, I.; Barić, D.; Ratković, A.; Molčanov, K.; Škorić, I. New thienobenzo/naphtho-triazoles as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. Design, synthesis and computational study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlakić, M.; Odak, I.; Faraho, I.; Talić, S.; Bosnar, M.; Lasić, K.; Barić, D.; Škorić, I. New naphtho/thienobenzo-triazoles with interconnected anti-inflammatory and cholinesterase inhibitory activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 241, 114616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Faraho, I.; Odak, I.; Talić, S.; Vukovinski, A.; Raspudić, A.; Bosnar, M.; Zadravec, R.; Ratković, A.; Lasić, K.; Marinić, Ž.; Barić, D.; Škorić, I. Synthesis, photochemistry and computational study of novel 1,2,3-triazole heterostilbenes: Expressed biological activity of their electrocyclization photoproducts. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 121, 105701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modrić, M.; Božičević, M.; Faraho, I.; Bosnar, M.; Škorić, I. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new 1,3-thiazole derivatives as potential anti-inflammatory agents. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1239, 130526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Odak, I.; Barić, D.; Talić, S.; Šagud, I.; Štefanić, Z.; Molčanov, K.; Lasić, Z.; Kovačević, B.; Škorić, I. New resveratrol analogs as improved biologically active structures: design, synthesis and computational modeling. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 143, 106965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Rajić, L.; Ljubić, A.; Vušak, V.; Zelić, B.; Gojun, M.; Odak, I.; Čule, I.; Šagud, I.; Šalić, A.; Škorić, I. Synthesis of new heterocyclic resveratrol analogues in milli- and microreactors: Intensification of the Wittig reaction. J. Flow Chem. 2022, 12, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, M.; Talić, S.; Odak, I.; Barić, D.; Šagud, I.; Škorić, I. Cholinesterase Inhibition and Antioxidative Capacity of New Heteroaromatic Resveratrol Analogs: Synthesis and Physico—Chemical Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E. Giacobini, R. Spiegel, A. Enz, A. E. Veroff i N. R. Cutler, Inhibition of acetyl- and butyryl-cholinesterase in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease by rivastigmine: correlation with cognitive benefit. J. Neural. Transm. 2002, 109, 1053–1065. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Y. Zhou, S. Wang i Y. Zhang, Catalytic reaction mechanism of acetylcholinesterase determined by Born-Oppenheimer ab initio QM/MM molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2010, 114, 8817–8825. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtnex, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matošević, A.; Knežević, A.; Zandona, A.; Maraković, N.; Kovarik, Z.; Bosak, A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of biscarbamates as potential selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matošević, A.; Radman Kastelic, A.; Mikelić, A.; Zandona, A.; Katalinić, M.; Primožič, I.; Bosak, A.; Hrenar, T. Quinuclidine-Based Carbamates as Potential CNS Active Compounds. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
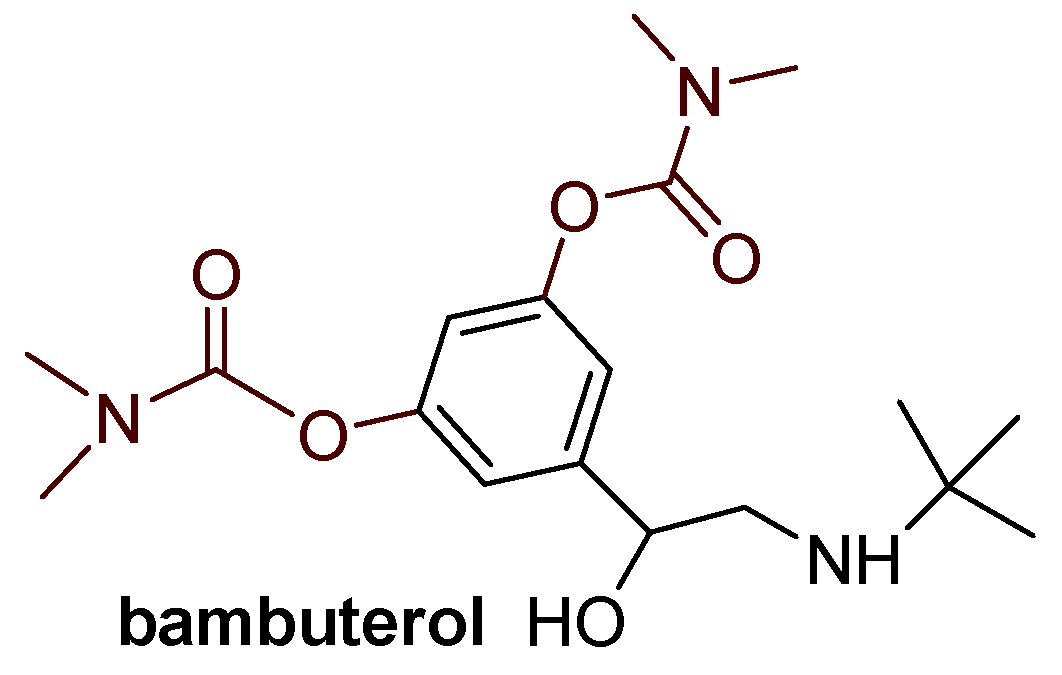
- Tunek, A.; Svensson, L.A. Bambuterol, a carbamate ester prodrug of terbutaline, as inhibitor of cholinesterases in human blood. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1988, 16, 759–764. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, M.A.; Qu, X.; Yu, Q.S.; Tweedie, D.; Halloway, H.W.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Greig, N.H. Tetrahydrofurobenzofuran cymserine, a potent butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor and experimental Alzheimer drug candidate, enzyme kinetic analysis. J. Neural. Transm. 2008, 115, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbanac, J.; Slauter, R. ADME in Drug Discovery. In A Comprehensive Guide to Toxicology in Nonclinical Drug Development, 2nd Ed.; Faqi, A.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, USA, 2017; pp. 39–67. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic properties using graph-based signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://ai-druglab.smu.edu/admetresult (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Mlakić, M.; Fodor, L.; Odak, I.; Horváth, O.; Lovrić, M.J.; Barić, D.; Milašinović, V.; Molčanov, K.; Marinić, Ž.; Lasić, Z.; et al. Resveratrol–Maltol and Resveratrol–Thiophene Hybrids as Cholinesterase Inhibitors and Antioxidants: Synthesis, Biometal Chelating Capability and Crystal Structure. Molecules 2022, 27, 6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselgren, C.; Bercu, J.; Cayley, A.; Cross, K.; Glowienke, S.; Kruhlak, N.; Muster, W.; Nicolette, J.; Reddy, M.V.; Saiakhov, R.; Dobo, K. Management of pharmaceutical ICH M7 (Q)SAR predictions – The impact of model updates. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2020, 118, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision, C01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carletti, E.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Ekstrom, F.; Nicolet, Y.; Loiodice, M.; Gillon, E.; Froment, M.T.; Lockridge, O.; Schopfer, L.M.; Masson, P.; Nachon, F. Nonaged Form of Human Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibited by Tabun. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16011–16020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDock-823 Tools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 16, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D. A.; Ben-Shalom, I. Y.; Brozell, S. R.; Cerutti, D. S.; Cheatham, III; T. E.; Cruzeiro, V. W. D.; Darden, T. A.; Duke, R. E.; Ghoreishi, D.; Gilson, M. Ket al. (2016), AMBER 2016, University of California, San Francisco.
- Maier, J. A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K. E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R. M.; Caldwell, J. W.; Kollman, P. A.; Case, D. A. Development and Testing of a General Amber Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Carbamate derivative | AChE Inhibition* (%) |
AChE IC50 (μM) |
BChE Inhibition* (%) |
BChE IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30.0 (100) | - | 85.0 (50) | 0.12 ± 0.09 |
| 2 | 16.7 (100) | - | 85.0 (10) | 1.05 ± 0.09 |
| 3 | 12.6 (100) | - | 85.0 (100) | 1.48 ± 0.36 |
| 4 | 35.0 (100) | - | 85.3 (25) | 2.83 ± 0.03 |
| 5 | 11.0 (100) | - | 84.0 (100) | 11.59 ± 0.18 |
| 6 | 1.0 (100) | - | 84.4 (25) | 0.90 ± 0.14 |
| 7 | 17.7 (100) | - | 86.3 (25) | 0.38 ± 0.01 |
| 8 | 25.2 (100) | - | 72.5 (100) | 25.50 ± 0.21 |
| 9 | 23.6 (100) | - | 85.2 (100) | 15.05 ± 2.32 |
| 10 | 27.0 (100) | - | 85.7 (100) | 23.17 ± 3.78 |
| 11 | 19.0 (100) | - | 83.4 (100) | 11.37 ± 2.48 |
| 12 | 23.9 (100) | - | 81.4 (100) | 23.39 ± 2.43 |
| 13 | 37.5 (100) | - | 84.1 (50) | 4.03 ± 0.50 |
| Galantamine | 90.0 (4.5) | 0.15 ± 0.07 | 90.1 (25) | 7.54 ± 1.64 |
| Property | Model Name | 1 | 7 | bambuterol | rivastigmine | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption | Water solubility | -4.1 | -4.43 | log mol/L | ||
| Caco2 permeability | 1.911 | 1.843 | log Papp in 10-6 cm/s | |||
| Intestinal absorption | 90.749 | 91.133 | % Absorbed | |||
| Skin Permeability | -2.687 | -2.689 | log Kp | |||
| P-glycoprotein substrate | No | No | ||||
| P-glycoprotein I inhibitor | No | No | ||||
| P-glycoprotein II inhibitor |
No | No | ||||
| Distribution | VDss (human) | 0.313 | 0.412 | 0.401 | 0.451 | log L/kg |
| Fraction unbound (human) |
0.033 | 0.023 | - | - | Fu | |
| BBB permeability | 0.31 | 0.322 | 0.707 | 0.968 | log BB | |
| CNS permeability | -0.941 | -0.955 | -1.95 | -0.801 | log PS | |
| Metabolism | CYP2D6 substrate | No | No | |||
| CYP3A4 substrate | Yes | Yes | ||||
| CYP1A2 inhibitior | Yes | Yes | ||||
| CYP2C19 inhibitior | Yes | Yes | ||||
| CYP2C9 inhibitior | Yes | No | ||||
| CYP2D6 inhibitior | No | No | ||||
| CYP3A4 inhibitior | No | No | ||||
| Excretion | Total Clearance | 0.167 | 0.111 | log ml/min/kg | ||
| Renal OCT2 substrate | No | No | Yes/No | |||
| Toxicity | AMES toxicity | No | No | Yes/No | ||
| Max. tolerated dose (human) |
0.245 | 0.166 | log mg/kg/day | |||
| hERG I inhibitor | No | No | ||||
| hERG II inhibitor | No | Yes | ||||
| Oral Rat Acute Toxicity (LD50) | 2.579 | 2.618 | mol/kg | |||
| Oral Rat Chronic Toxicity (LOAEL) | 1.874 | 1.855 | log mg/kg_bw/day | |||
| Hepatotoxicity | No | Yes | ||||
| Skin Sensitisation | No | No | ||||
| T.Pyriformis toxicity | 1.785 | 1.927 | log ug/L | |||
| Minnow toxicity | 0.379 | -0.096 | log mM |
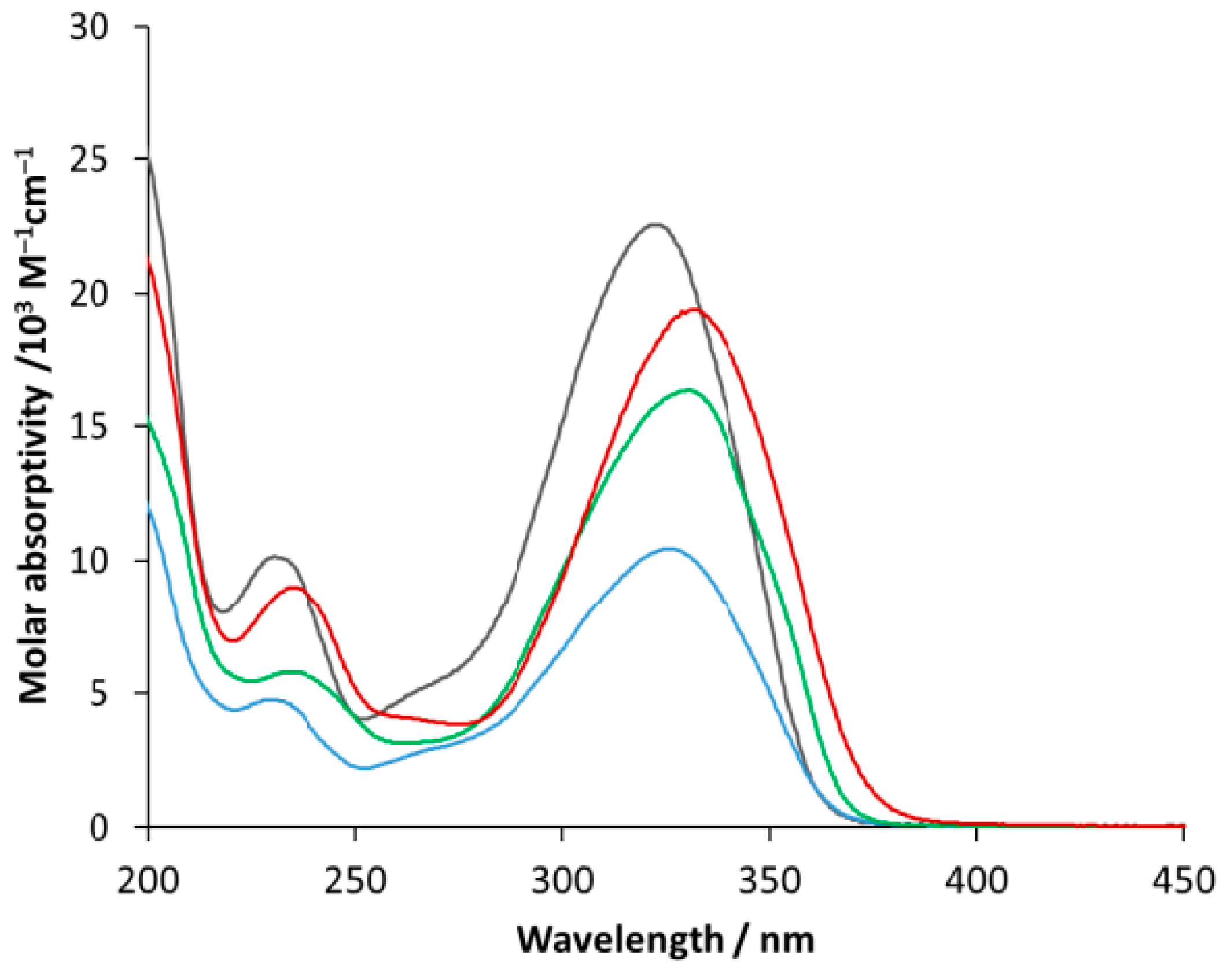
| Compound | λ / nm | ε / M–1cm–1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 322 | 22570 |
| 3 | 325 | 10440 |
| 6 | 330 | 16330 |
| 7 | 331 | 19410 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).