Submitted:
21 November 2024
Posted:
21 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Background and Objectives: This study aims to assess the bone implant osseointegration after the healing process of machined, reabsorbable blast material (RBM) and sandblasted and large acid grid (SLA) surface titanium implants placed simultaneously using graft material in rat tibias. Materials and Methods: The study involved 30 Sprague Dawley rats that were divided into three groups: machined surfaced (MS) (n = 10), resorbable blast material (RBM) (n = 10), and sandblasted and large acid grid (SLA) surfaced (n = 10). The titanium implants were inserted into the bone sockets along with the graft, and the rats were euthanized after a 4-week experimental period. The implants and the bone tissue surrounding them were extracted for reverse torque analysis (Newton’s). Results: The biomechanical bone implant contact rate was greater in SLA-surfaced implants than in RBM and machined surface implants (P<0.05). Conclusions: The application of graft material may be more effective in implants with SLA and RBM surfaces when used locally, as per the biomechanical parameters.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Study Design
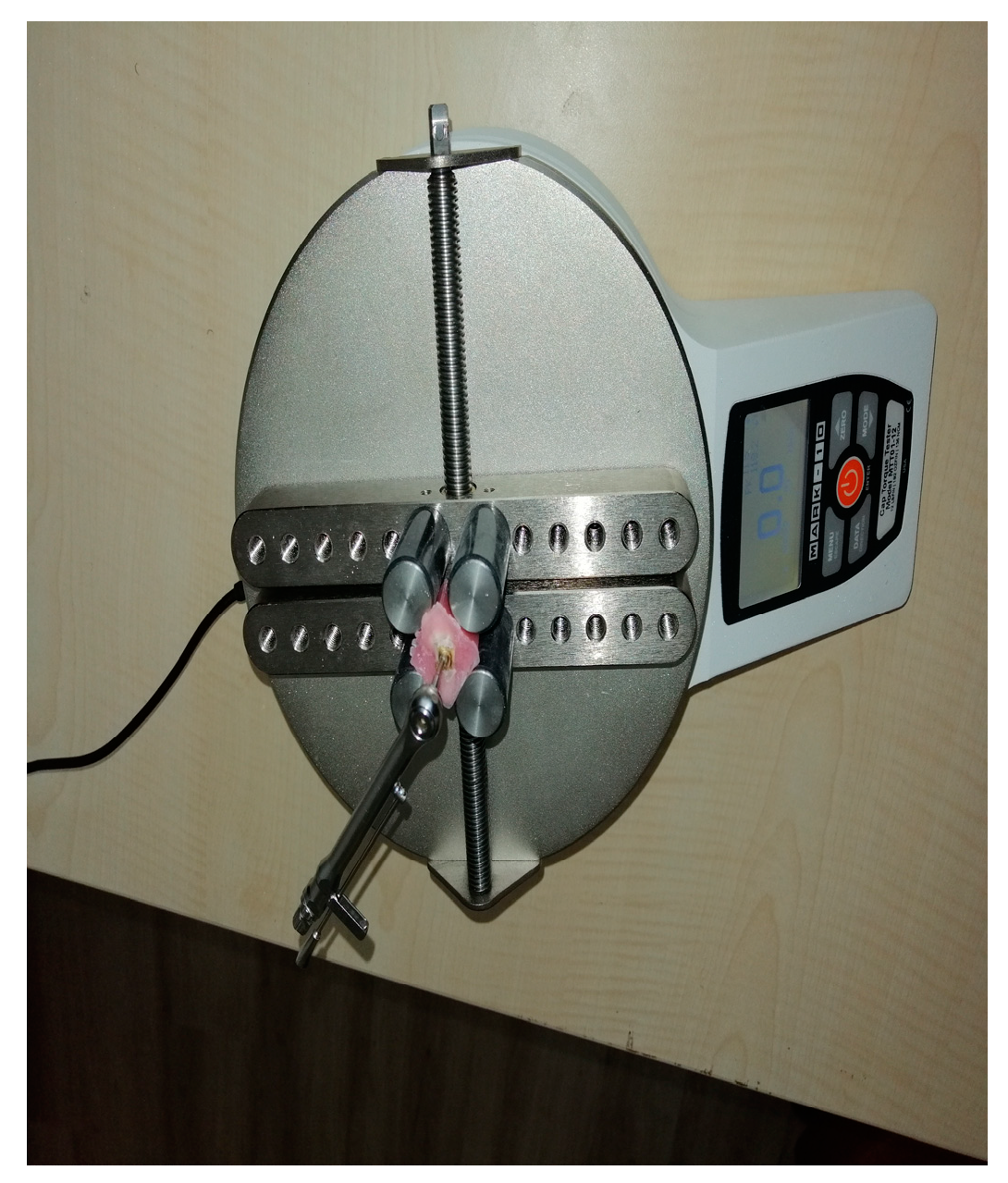
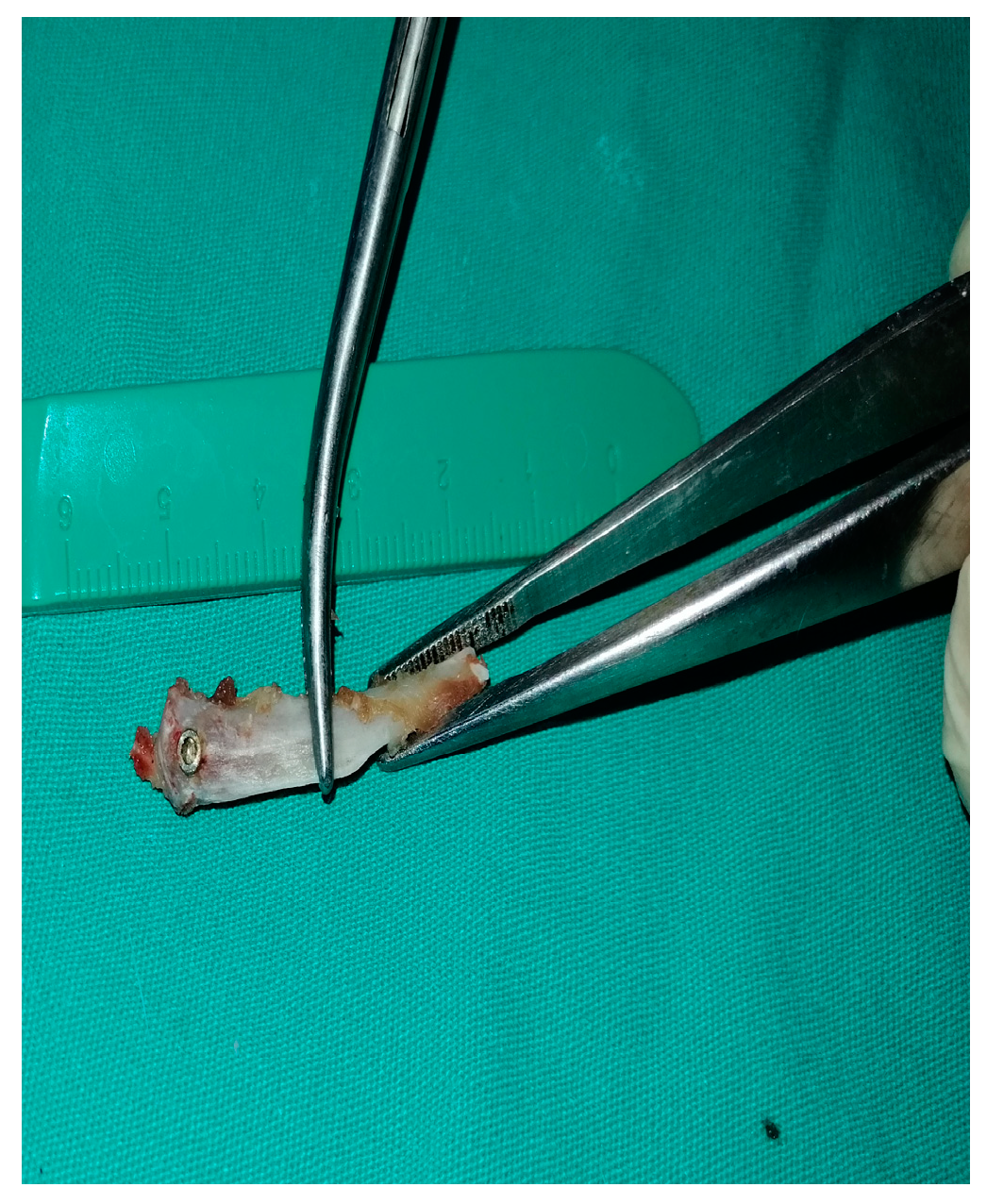
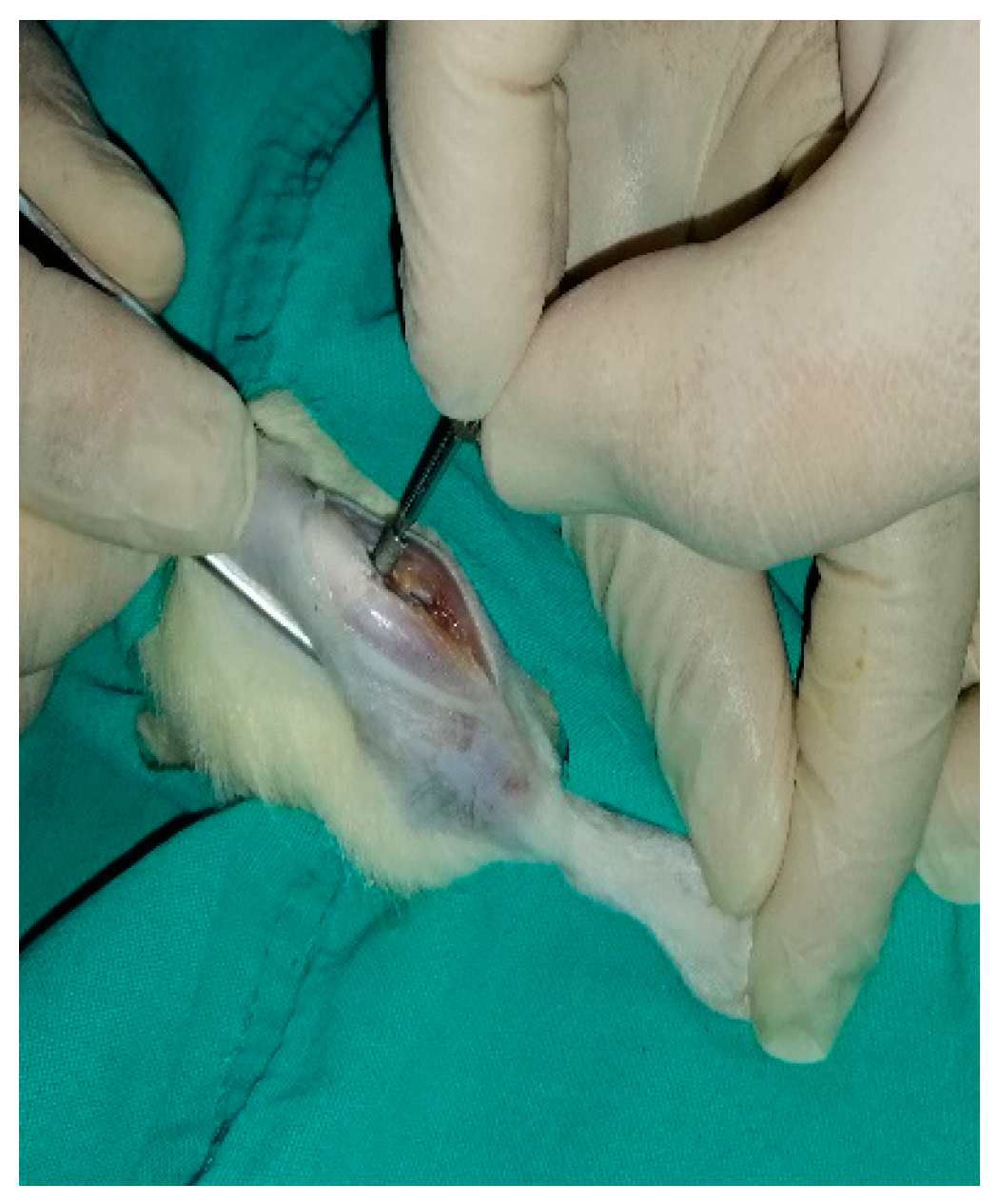
2.2. Surgical Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Topkaya T, Solmaz M, Dündar S, et al. Numerical analysis of the effect of implant geometry to stress distributions of dental implant system. Cumhuriyet Dent J. 2014;18(1):17-24.
- Buser D, Mericske-stern R, Pierre Bernard JP, et al. Long-term evaluation of non-submerged ITI implants. Part 1: 8-year life table analysis of a prospective multi-center study with 2359 implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997;8(3):161-72.
- Ezirganli Ş, Polat S, Barış E, et al. Comparative investigation of the effects of different materials used with a titanium barrier on new bone formation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24(3):312-9.
- Le Guehennec L, Goyenvalle E, Lopez-Heredia MA, et al. Histomorphometric analysis of the osseointegration of four different implant surfaces in the femoral epiphyses of rabbits. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19(11):1103-10.
- Junker R, Dimakis A, Thoneick M, et al. Effects of implant surface coatings and composition on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20:185-206.
- Le Guéhennec L, Soueidan A, Layrolle P, et al. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent Mater J. 2007;23(7):844-54.
- Coelho PG, Jimbo R, Tovar N, et al.. Osseointegration: hierarchical designing encompassing the macrometer, micrometer, and nanometer length scales. Dent Mater J. 2015;31(1):37-52.
- Ehrenfest DMD, Coelho PG, Kang B-S, et al. Classification of osseointegrated implant surfaces: materials, chemistry and topography. Trends Biotechnol. 2010;28(4):198-206.
- Shibata Y, Tanimoto Y. A review of improved fixation methods for dental implants. Part I: Surface optimization for rapid osseointegration. J Prosthodont Res. 2015;59(1):20-33.
- Mendonça G, Mendonça DB, Aragao FJ, et al. Advancing dental implant surface technology–from micron-to nanotopography. Biomaterials. 2008;29(28):3822-35.
- Anil S, Anand P, Alghamdi H, et al. Dental implant surface enhancement and osseointegration. Implant Dent—a rapidly evolving practice. 2011:83-108.
- Zhu L, Luo D, Liu Y. Effect of the nano/microscale structure of biomaterial scaffolds on bone regeneration. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):1-15.
- Jokstad A, Braegger U, Brunski JB, et al. Quality of dental implants. Int Dent J. 2003;53(S6P2):409-43.
- Sanz A, Oyarzún A, Farias D, et al. Experimental study of bone response to a new surface treatment of endosseous titanium implants. Implant Dent. 2001;10(2):126-31.
- Demetoglu U, Ocak H, Songur T, et al. Which dental implant surface is more effective in osteointegration: RBM surface versus SLA surface. Ann Clin Anal Med. 2021;12:736–739.
- Dundar S, Yaman F, Bozoglan A, et al. Comparison of osseointegration of five different surfaced titanium implants. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(7):1991-5.
- Lee J, Lee J-B, Yun J, et al. The impact of surface treatment in 3-dimensional printed implants for early osseointegration: a comparison study of three different surfaces. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1-10.
- Ozcan EC, Gul M, Dundar S, et al. Effects of local application of the ankaferd blood stopper on osseointegration in three different surface titanium implants. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11(4):524-8.
- El Chaar E, Zhang L, Zhou Y, et al. Osseointegration of Superhydrophilic Implants Placed in Defect Grafted Bones. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019;34(2).
- Hao C-P, Cao N-J, Zhu Y-H, et al. The osseointegration and stability of dental implants with different surface treatments in animal models: a network meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1-12.
- Zhang T, Zhang T, Cai X. The application of a newly designed L-shaped titanium mesh for GBR with simultaneous implant placement in the esthetic zone: a retrospective case series study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(5):862-72.

| Groups | N | Mean (N) | Minimum (N) | Maximum | P* Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machined | 9 | 4.04 | 3.2 | 5.2 | <0.005 | ||
| RBMa1 | 8 | 6.88 | 4.3 | 11.2 | <0.005 | ||
| SLAa2, b | 9 | 11.11 | 5.9 | 19.2 | <0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





