Introduction
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes encode for cell-surface glycoproteins that present antigenic peptides to T cell receptors and play key roles in the induction of adaptive immune responses. HLA genes are located at the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) locus on human chromosome 6p21.3. The MHC locus is among the most polymorphic genetic loci in the human genome (1999). The extreme polymorphism of HLA genes combined with the codominant expression of chromosomal alleles constitutes the basis for the extensive diversity in antigen presentation. This diversity enables the presentation of a broad range of epitopes to T cells, thus potentially maximizing the repertoire of immune responses to non-self antigenic challenges.
Maximum diversity in antigen presentation is attained through HLA heterozygosity. An antigen-presenting cell (APC) from a heterozygous individual at each of the six classical HLA-class I or HLA-class II loci could theoretically present over 1012 different peptides (Sewell 2012). Studies suggest that MHC heterozygosity provides an advantage against infectious diseases both in mice (Penn et al. 2002) and humans (Carrington et al. 1999). This heterozygote advantage is one of the main mechanisms postulated to favor the maintenance of HLA diversity in a population over time (Dendrou et al. 2018). Furthermore, in animal models, restriction of the MHC-peptide repertoire has been shown to predispose to autoimmunity (Logunova et al. 2005).
While the MHC locus is the single genomic region associated with the greatest number of human diseases (Shiina et al. 2009), including autoimmune diseases, the mechanisms by which HLA genes affect the risk of autoimmunity have not been fully elucidated. Historically, the contribution of HLA genes to the development of autoimmunity has been examined predominantly from the standpoint of specific HLA allele and/or haplotype associations with particular disease phenotypes (Miyadera and Tokunaga 2015). Furthermore, the presence of HLA homozygosity of specific high-risk alleles such as HLA-B27 (Arnett et al. 1977; Jaakkola et al. 2006; Khan et al. 1978; Kim et al. 2009; Kim et al. 2013; Kvien et al. 1985; Lauter et al. 1977; Prakash et al. 1983; Spencer et al. 1979; Vannas and Karjalainen 1984) has been postulated to worsen the clinical manifestations of autoimmunity by means of a “gene dosage effect”. We propose that the documented effect of HLA homozygosity in autoimmunity may be alternatively explained by the limitation of HLA diversity and the resulting constraint of the heterozygote advantage.
To our knowledge, the potential role of the limitation of HLA diversity in human autoimmunity has not been characterized. Thus, we tested the hypothesis that the limitation of HLA diversity across multiple loci is a distinct risk factor for autoimmune disease independent of allele specificity. We conducted a proof-of-concept case-control study examining the limitation of HLA diversity across multiple loci (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DQB1, HLA- DRB1, HLA- DRB3/4/5) as an allele-independent risk factor for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. In this context, we introduced the novel metric of “Limitation of HLA Diversity” (LoHLAD) which, for the purpose of our study, was defined as 1) homozygosity at any of the 5 examined loci, and/or 2) the presence of either a single allele or the complete lack of an allele at the HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus. As the results of our study indicate, LoHLAD is a significant risk factor for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease.
Patients and Methods
Study Population
Retrospective review of electronic medical records of all patients evaluated at the University of New Mexico pediatric rheumatology clinic between November 2016 and January 2021 was performed. HLA typing was obtained during laboratory evaluation of children referred to the pediatric rheumatology clinic. Inclusion criteria consisted of 1) availability of data for all 5 HLA loci (see “HLA typing” below), and 2) diagnosis of pediatric-onset (prior to 16 years of age) autoimmune rheumatic disease (“cases”) or non-autoimmune common musculoskeletal conditions (“controls”). Cases consisted of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), chronic idiopathic uveitis, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), undifferentiated connective tissue disease (UCTD), localized scleroderma (LoS), vasculitis, juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM), Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), and systemic sclerosis (SSc). Controls did not satisfy the diagnostic criteria for any autoimmune rheumatic disease, and consisted of patients with benign hypermobility, orthopedic conditions, and pain amplification syndromes. Patients with isolated (primary) Raynaud’s phenomenon or autoinflammatory conditions such as periodic fever syndromes were excluded because our study focus is autoimmune rheumatic disease. Race and ethnicity were self-reported from a fixed set of categories. The diagnostic criteria used to identify cases along with an overview of the study design (Supplementary Figure 1) are detailed in the online supplementary material.
HLA Typing
Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood samples using the Qiagen EZ1 Blood Kit and the EZ1 Advanced or EZ1 Advanced XL automated purification instrument (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA). HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB3/4/5, and HLA-DQB1 genotyping was performed using a microarray bead-based reverse sequence specific oligonucleotide (SSO) typing methodology (LABTypeTM [rSSO], One Lambda, A Thermal Fisher Scientific Brand, West Hills, CA, USA) and the LABScan3D™ instrumentation with Luminex® xPONENT® software for data acquisition (One Lambda, A Thermal Fisher Scientific Brand, West Hills, CA, USA). Genotype data was analyzed using HLA FusionTM software 4.2 (One Lambda, A Thermal Fisher Scientific Brand, West Hills, CA, USA).
Statistical Analysis
We examined 5 HLA loci (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DQB1, HLA- DRB1, HLA- DRB3/4/5). The term “Limitation of HLA Diversity” (LoHLAD) was defined as 1) homozygosity at any of the 5 examined loci, and/or 2) the presence of a single allele or the complete lack of an allele at the HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus. The HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus is in linkage disequilibrium with the HLA-DRB1 locus; DRB1*01, DRB1*08 and DRB1*10 are associated with the lack of an allele at the HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus (Kotsch and Blasczyk 2000). Descriptive statistics for demographics were summarized as means, standard deviations, standard error of means, medians, inter-quartile ranges, odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), counts, and percentages. The distributions of patient characteristics between controls and cases, and the association of LoHLAD or specific alleles with pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases were examined using Fisher’s exact test. Risk estimates are presented as OR. Cochran-Armitage trend test was used to determine the cumulative effect of LoHLAD by comparing the distribution of the number of loci with LoHLAD (“hits”) between cases and controls. The OR of the number of “hits” were calculated in conjunction with cumulative outcomes to demonstrate quantifiable effects of LoHLAD. Logistic regression modeling evaluated the ability of LoHLAD or alleles to predict autoimmune rheumatic disease. The concordance between observed and predicted outcomes (“c-statistic”) from univariate and multivariate logistic regression models was used to identify the best fitted models. P values were adjusted using the “False Discovery Rate” (FDR) correction for multiple comparisons. Missing values were excluded from all analyses. A P value < 0.05 was considered significant. SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC) was used for all analyses.
Results
Study Population Demographics and Clinical Parameters
To identify patients with pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases and controls, the electronic medical records of 516 individuals were reviewed. We excluded 103 individuals from the analysis: 81 were excluded due to lack of
HLA typing data, and 22 were excluded due to their diagnosis of an autoinflammatory condition or primary Raynaud’s phenomenon (Supplementary Figure 1). A total of 413 individuals (279 cases and 134 controls) satisfied the inclusion criteria (see Methods and Patients). No statistically significant differences were noted between cases and controls regarding sex, race, or ethnicity (
Table 1). We observed significantly higher frequency of positive family history of autoimmunity in cases compared to controls (
Table 1; OR 2.00 [1.30-3.10];
P = 0.002). The age of cases (mean 12.7 years, median 13.1 years) was significantly lower than the age of controls (mean 13.5 years, median 14.6 years) (
Table 1;
P = 0.029). The distribution of specific pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease diagnoses in our cohort is presented in Supplementary Table 1.
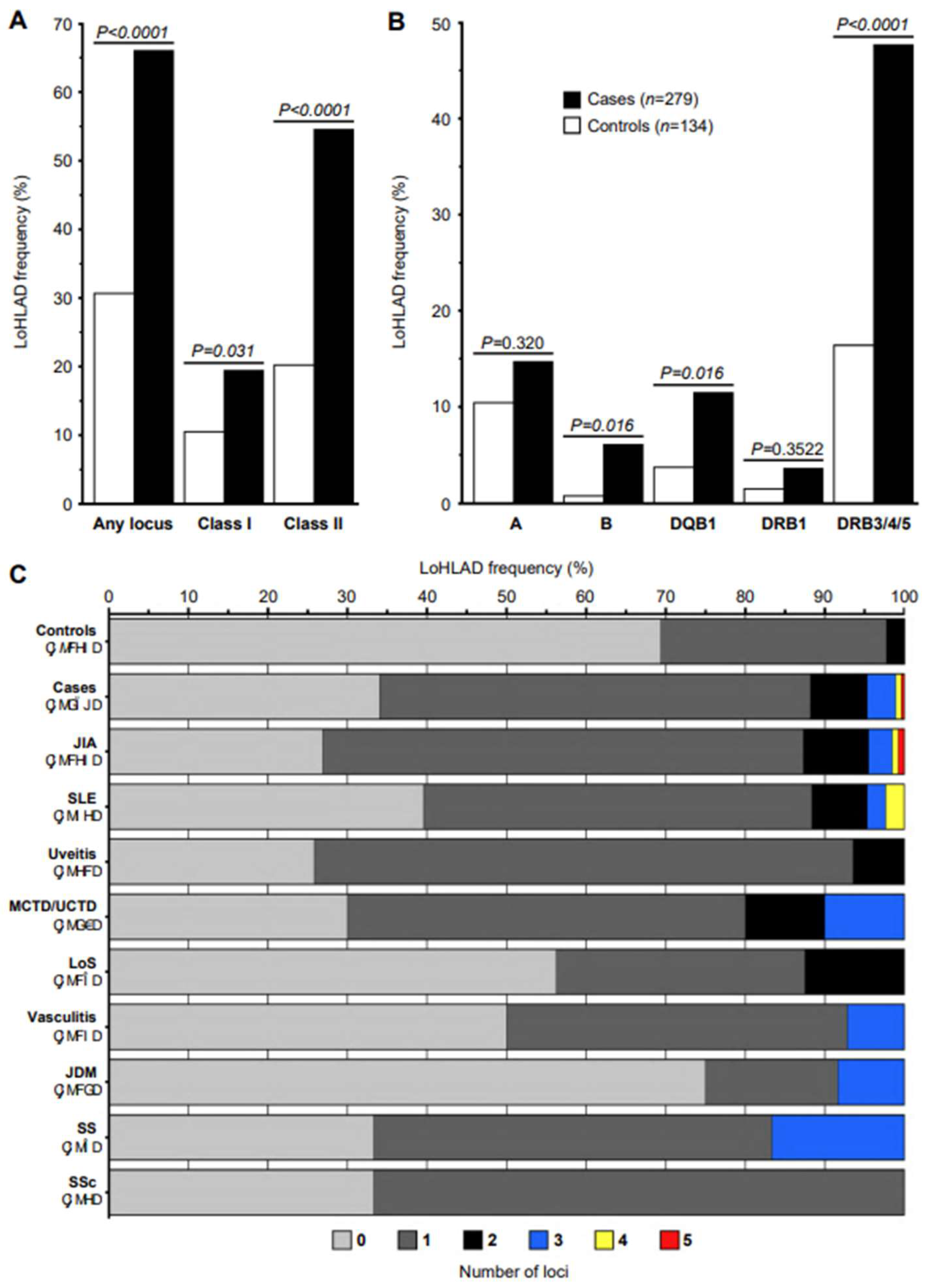
Figure 1.
Limitation of HLA Diversity (LoHLAD) frequency distributions. (A, B) LoHLAD frequency distributions of cases (black bars, n=279) and controls (white bars, n=134) exhibited as grouped bar plots; LoHLAD frequencies displayed as the percentage of subjects that LoHLAD was present; P values calculated by Fisher’s exact test (corrected for multiple comparisons by False Discovery Rate). (A) Collective frequencies of LoHLAD at any of the 5 examined HLA loci (“Any locus”), HLA-class I loci, and HLA-class II loci in cases vs controls. (B) Frequencies of LoHLAD at individual loci (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB3/4/5) in cases vs controls. (C) The cumulative effect of LoHLAD (number of loci with LoHLAD, range 0-5) is presented by displaying the frequency distributions (horizontal axis) of the number of loci with LoHLAD (colors) in controls, all cases, and specific pediatric-onset autoimmune disease diagnoses (vertical axis) as stacked bars. Bar colors correspond to the number of loci with LoHLAD (0: light gray, 1: dark gray, 2: black, 3: blue, 4: yellow, 5: red). JIA, Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis; SLE, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus; MCTD, Mixed Connective Tissue Disease; UCTD, Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease; LoS, Localized Scleroderma; JDM, Juvenile Dermatomyositis; SS, Sjögren’s Syndrome; SSc, Systemic Sclerosis.
Figure 1.
Limitation of HLA Diversity (LoHLAD) frequency distributions. (A, B) LoHLAD frequency distributions of cases (black bars, n=279) and controls (white bars, n=134) exhibited as grouped bar plots; LoHLAD frequencies displayed as the percentage of subjects that LoHLAD was present; P values calculated by Fisher’s exact test (corrected for multiple comparisons by False Discovery Rate). (A) Collective frequencies of LoHLAD at any of the 5 examined HLA loci (“Any locus”), HLA-class I loci, and HLA-class II loci in cases vs controls. (B) Frequencies of LoHLAD at individual loci (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB3/4/5) in cases vs controls. (C) The cumulative effect of LoHLAD (number of loci with LoHLAD, range 0-5) is presented by displaying the frequency distributions (horizontal axis) of the number of loci with LoHLAD (colors) in controls, all cases, and specific pediatric-onset autoimmune disease diagnoses (vertical axis) as stacked bars. Bar colors correspond to the number of loci with LoHLAD (0: light gray, 1: dark gray, 2: black, 3: blue, 4: yellow, 5: red). JIA, Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis; SLE, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus; MCTD, Mixed Connective Tissue Disease; UCTD, Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease; LoS, Localized Scleroderma; JDM, Juvenile Dermatomyositis; SS, Sjögren’s Syndrome; SSc, Systemic Sclerosis.
LoHLAD in Cases vs Controls
We assessed the effect of LoHLAD as a risk factor for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease by comparing the frequency of LoHLAD between cases and controls as a binary event (present vs non-present) (
Table 2). First, we examined whether LoHLAD was present at any of the 5 examined loci (
HLA-A,
HLA-B, HLA-DQB1, HLA- DRB1, HLA- DRB3/4/5), and compared the frequency of LoHLAD between cases and controls. The frequency of LoHLAD at any locus was significantly higher in cases compared to controls (65.95% vs 30.60%, OR 4.39 [2.82-6.84],
P < 0.0001) (
Figure 1A and
Table 2). We then evaluated LoHLAD at the
HLA-class I and
HLA-class II level, and at the level of individual loci. Although the frequency of LoHLAD was significantly higher in cases compared to controls at both the
HLA-class I and
HLA-class II level, the difference was more prominent at
HLA-class II (54.48% vs 20.15%, OR 4.74 [2.92-7.69],
P < 0.0001) compared to
HLA-class I (19.35% vs 10.45%, OR 2.06 [1.10-3.86],
P = 0.031) loci (
Figure 1A and
Table 2). Examination of individual loci revealed significantly higher frequencies of LoHLAD in cases compared to controls at the
HLA-B (6.09% vs 0.75%; OR 8.63 [1.14-65.55],
P = 0.016),
HLA-DQB1 (11.47% vs 3.73%, OR 3.34 [1.27-8.78],
P = 0.016), and
HLA-DRB3/4/5 (47.67% vs 16.42%, OR 4.64 [2.77-7.75],
P < 0.0001) loci (
Figure 1B and
Table 2). The association of LoHLAD with pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease at the
HLA-A and
HLA-DRB1 loci was not statistically significant.
Cumulative Effect of LoHLAD (“Dose-Response Effect”)
We next examined the cumulative effect of LoHLAD as a risk factor for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease by comparing the distribution of the number of “hits” (defined as the number of
HLA loci with LoHLAD, range: 0-5) between cases and controls. The observed difference was significant (Cohran-Armitage trend test,
P < 0.0001). Specifically, 0 “hits” were observed in 34.05% of cases vs 69.40% of controls, 1 “hit” in 54.12% of cases vs 28.36% of controls (OR 3.89 [2.47, 6.14],
P < 0.0001), and 2 “hits” in 7.17% of cases vs 2.24% of controls (OR 6.53 [1.88, 22.70],
P = 0.0007) and 2 or more “hits” in 11.83% of cases vs 2.23% of controls (OR 10.77 [3.19-36.33],
P < 0.0001) (
Table 3). Notably, 3 or more “hits” were observed exclusively in cases although at low frequency (4.66%). A graphic representation of the cumulative effect of LoHLAD as a risk factor for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease is illustrated in
Figure 1C.\
LoHLAD in specific Pediatric-Onset Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
After determining the differences in the frequency of LoHLAD between all cases and controls, we evaluated the association of LoHLAD with specific pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease diagnoses (
Table 4) by comparing the frequency of LoHLAD between groups of cases with specific diagnoses and controls. Significantly higher frequencies of LoHLAD were observed in all specific disease diagnosis groups with 20 or more cases (JIA, SLE, chronic idiopathic uveitis, MCTD/UCTD) compared to controls. The strongest associations were observed in JIA (OR 6.18 [3.63-10.49],
P < 0.0001) and chronic idiopathic uveitis (OR 6.52 [2.69-15.79],
P < 0.0001). Furthermore, the distribution of the number of “hits” was significantly different between all specific disease diagnosis groups with 20 or more cases and controls (
P < 0.0001, Supplementary Table 2). Within cases, we examined whether earlier symptom onset and shorter time to diagnosis is associated with LoHLAD. Cases with LoHLAD compared to cases without LoHLAD had significantly earlier symptom onset and shorter time to diagnosis (Supplementary Table 3).
LoHLAD-Based Models
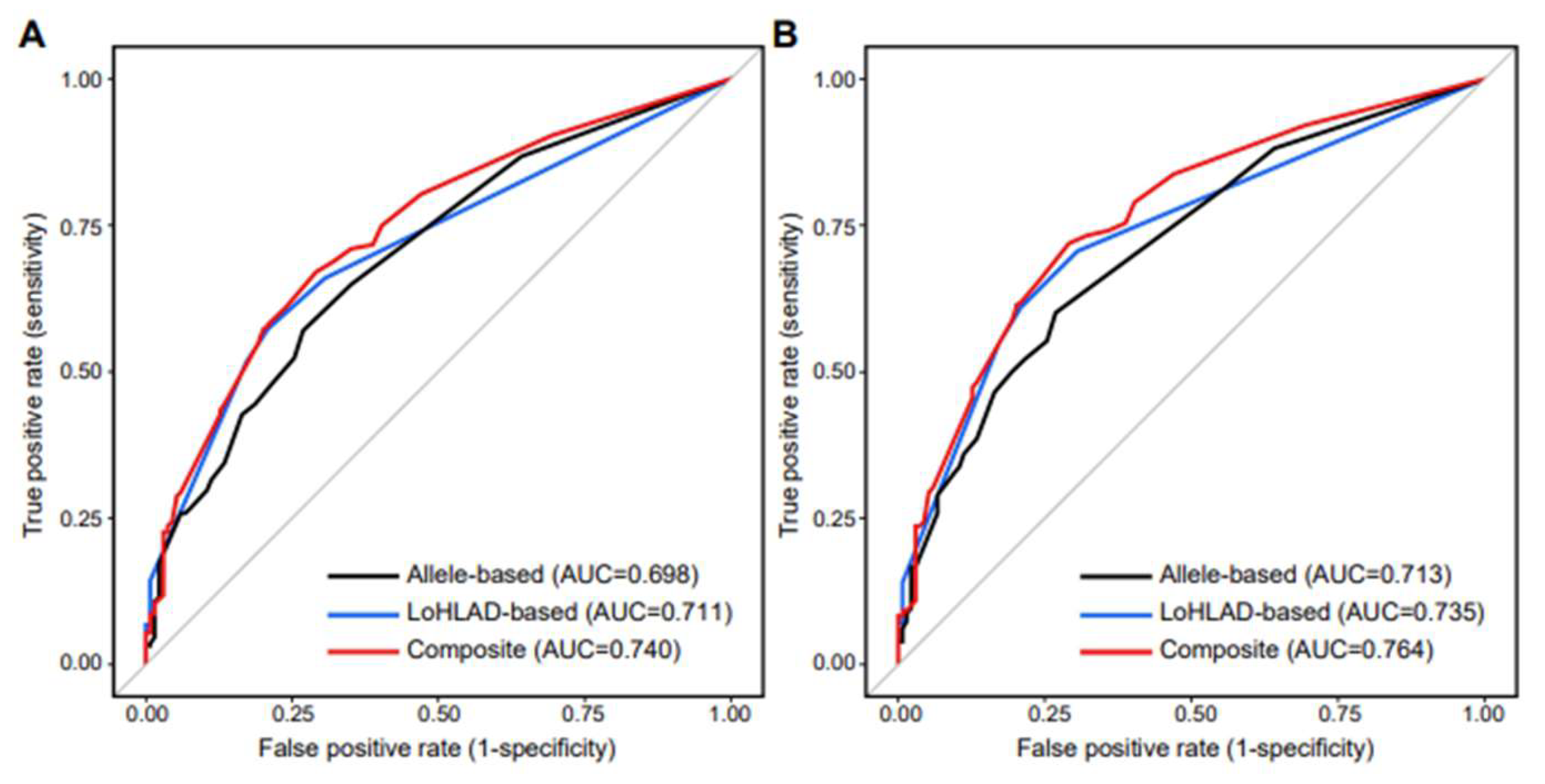
Logistic regression models were constructed to evaluate LoHLAD as a positive predictor of pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. The best fitted model included LoHLAD of 4 out of the 5 examined HLA loci (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB3/4/5) as separate binary variables (present vs non-present). LoHLAD at the HLA-DRB1 locus correlated significantly with LoHLAD at the HLA-DQB1 locus and thus was excluded from the best fitted model to limit multicollinearity (Supplementary Table 4); the HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 loci are in linkage disequilibrium (Fernandez-Vina et al. 1991). The c-statistic of the best fitted model was 0.711 for predicting any pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease, and 0.735 for predicting any of the 4 most common specific disease diagnoses in our cohort (JIA, SLE, chronic idiopathic uveitis, MCTD/UCTD) (Supplementary Table 5). The ability of the best fitted LoHLAD-based model to predict specific disease diagnoses was highest for JIA and chronic idiopathic uveitis, with c-statistic values of 0.749 and 0.769 respectively (Supplementary Table 5). Detailed evaluation of the best fitted LoHLAD-based model is presented in Supplementary Table 6.
Allele-Based Models
Logistic regression models were constructed to evaluate allele specificity as a positive predictor of pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. Six alleles were identified as positive predictors for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease: HLA-A02, HLA-A24, HLA-B27, HLA-DRB1*01, HLA-DRB1*08, and HLA-DQB1*04 (Supplementary Table 8). The best fitted allele-based model included 5 out of 6 alleles (HLA-A02, HLA-A24, HLA-B27, HLA-DRB1*01, HLA-DRB1*08). HLA-DQB1*04 strongly correlated with HLA-DRB1*08 (Supplementary Table 4); 73 out of 81 HLA-DRB1*08 positive individuals were HLA-DQB1*04 positive, and 73 out of 89 HLA-DQB1*04 positive individuals were HLA-DRB1*08 positive (P < 0.0001). Therefore, HLA-DQB1*04 was excluded from the best fitted model to limit multicollinearity (Supplementary Table 5). The linkage disequilibrium between HLA-DRB1*08 and HLA-DQB1*04 is well-established (Smerdel et al. 2002). The c-statistic of the best fitted allele-based model was 0.698 for predicting any pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease, and 0.713 for predicting any of the 4 most common specific disease diagnoses in our cohort (JIA, SLE, chronic idiopathic uveitis, MCTD/UCTD) (Supplementary Table 5). The ability of the best fitted allele-based model to predict specific disease diagnoses was highest for JIA and chronic idiopathic uveitis, with c-statistic values of 0.753 and 0.780 respectively (Supplementary Table 5).
Composite Models
We constructed composite models by utilizing both LoHLAD and allele specificity as positive predictors of pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease (Supplementary Table 5). The best fitted composite model included 4 LoHLAD-based variables (
HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DBQ1, HLA-DRB3/4/5) and 3 allele-based variables (
HLA-A02, HLA-A24, HLA-B27).
HLA-DRB1*01,
HLA-DRB1*08 and
HLA-DQB1*04 significantly correlated with LoHLAD at the
HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus and thus were excluded to limit multicollinearity (Supplementary Table 4). The c-statistic of the best fitted composite model was 0.740 for predicting any pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease, and 0.764 for predicting any of the 4 most common diagnoses in our cohort (JIA, SLE, chronic idiopathic uveitis, MCTD/UCTD) (Supplementary Table 5). The ability of the best fitted composite model to predict specific disease diagnoses was highest for JIA and chronic idiopathic uveitis, with c-statistic values of 0.796 and 0.822 respectively (Supplementary Table 5). The Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves of the best fitted LoHLAD-based, allele-based, and composite models are illustrated in
Figure 2.
Discussion
In this proof-of-concept case-control study, we documented a 4-fold increased risk for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases associated with LoHLAD at any of the 5 examined loci. In addition, the risk for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease increased as the number of loci with LoHLAD increased. Our findings indicate that LoHLAD is a significant genetic risk factor for the development of early-onset autoimmunity in humans. The assessment of the LoHLAD introduces a novel approach in the investigation of HLA-related genetic determinants of autoimmunity, extending beyond the well-established role of specific HLA alleles and haplotypes in autoimmune disease immunopathogenesis. The identification of LoHLAD as a risk factor for autoimmune rheumatic disease highlights the potentially beneficial role of the “heterozygote advantage” (Dendrou et al. 2018) outside of the realm of infectious diseases (Carrington et al. 1999; Penn et al. 2002). We theorize that LoHLAD increases the risk for autoimmunity by limiting the diversity of the MHC-peptide repertoire and thus restricting antigen-specific immune responses; in animal models, restriction of the MHC-peptide repertoire has been shown to predispose to autoimmunity (Logunova et al. 2005). The risk effect of LoHLAD on autoimmunity is further amplified in individuals with high-risk HLA alleles. Our theory proposes that the combination of high-risk HLA alleles and a restricted antigen presentation repertoire through LoHLAD results in the potential enrichment of adaptive immune responses for autoreactive T cells.
The detrimental effects of HLA homozygosity have been described in a variety of autoimmune diseases. For example, HLA-B27 homozygosity is associated with increased phenotypic severity in ankylosing spondylitis (Arnett et al. 1977; Jaakkola et al. 2006; Khan et al. 1978; Kvien et al. 1985; Lauter et al. 1977; Prakash et al. 1983; Spencer et al. 1979). The effects of HLA homozygosity in autoimmunity are not limited to HLA-B27. Patients homozygous for the HLA-Cw*06 allele have increased risk for developing psoriasis compared to heterozygotes (Gudjonsson et al. 2003). HLA-DRB1*04 homozygosity is associated with severe extra-articular disease in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (Turesson et al. 2000; Turesson et al. 2005; Weyand et al. 1992). Runs of homozygosity (ROH) at the human MHC locus are associated with RA (Yang et al. 2012). HLA-DQ2.5 heterodimer (HLA-DQA1*05-DQB1*02) homozygosity increases the risk for celiac disease (CD) (Lopes et al. 2019). Children homozygous for the haplotype DR3-DQ2 are at high risk for early-onset CD (Liu et al. 2014). The effects of HLA homozygosity have also been documented in immune thrombocytopenia (Ho et al. 2012), autoimmune liver disease (Ma et al. 2021), pemphigus vulgaris (Bhanusali et al. 2013), and multiple sclerosis (Sadovnick 2012).
The mechanisms mediating the effects of HLA homozygosity on autoimmunity are complex. Homozygosity for specific HLA alleles does not uniformly increase the risk of disease or alter the clinical phenotype. HLA-B27 homozygosity in Korean patients with ankylosing spondylitis has no effect on clinical manifestations, functional disability, or radiographic damage (Kim et al. 2009; Kim et al. 2013). HLA-B27 homozygosity is not associated with increased risk for acute anterior uveitis (Derhaag et al. 1989). Homozygosity for HLA-DQB1 has no effect on CD clinical outcomes but is associated with anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies (Bajor et al. 2019). Therefore, additional HLA-related factors are involved in the development of clinical phenotypes including specific allele variants (“suballeles”) and extended haplotypes.
The complex interaction of HLA homozygosity with specific alleles and haplotypes is demonstrated in a different CD study where the highest risk for developing CD was conferred by the combination of the HLA-DQ2.5 heterodimer with HLA-DQB1*02 in homozygosity (Ruiz-Ortiz et al. 2014). The interaction of homozygosity with extended haplotypes is further complicated by cis/trans configuration effects in CD (van Belzen et al. 2004). Studies in type 1 diabetes examining homozygous HLA-DR3 (DRB1*03:01-DQA1*05:01-DQB1*02:01) individuals (Aydemir et al. 2019), HLA-DQ8 (HLA-DQA1*03:01-HLA-DQB1*03:02) homozygosity (Eerligh et al. 2011), or individual DRB1*03-DQB1*02 and DRB1*04:01-DQB1*03:02 homozygous genotypes (Koeleman et al. 2004) also highlight the complexity of the interaction of HLA homozygosity with extended haplotypes and the important effects of genotypic epistasis. Finally, the variation of linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks of the human MHC loci in a haplotype-specific manner (Blomhoff et al. 2006) further complicates the interpretation of HLA associations with human disease, including the potential effects of homozygosity.
In our study, we introduced and explored the novel concept of LoHLAD which includes
HLA homozygosity but also encompasses the presence of a single allele or the complete lack of an allele at the
HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus. This unique feature of the
HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus is based on its distinctive linkage disequilibrium with the
HLA-DRB1 locus; specific
HLA-DRB1 alleles (
DRB1*01, DRB1*08, DRB1*10) are associated with the lack of an allele at the
HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus (Kotsch and Blasczyk 2000).
HLA-DRB3/4/5 genes belong to the
HLA class II beta chain paralogues that are postulated to have formed as the result of evolutionary duplication of
HLA-DRB1 (Doxiadis et al. 2012). In our cohort, the complete lack of an allele at the
HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus was observed exclusively in cases (4 cases with JIA, 2 cases with chronic idiopathic uveitis, and 1 case with SLE); there were no controls with complete lack of an allele at the
HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus. Furthermore, LoHLAD at the
HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus had the strongest association with pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases compared to any of the other 4 examined loci (
Table 2). This finding may suggest a unique role of the
HLA-DRB3/4/5 locus in pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases that is independent of allele specificity.
Our study demonstrates that, across multiple loci, LoHLAD is significantly associated with pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases, specifically with JIA, SLE, chronic idiopathic uveitis, and MCTD/UCTD. The lack of association of LoHLAD with LoS, vasculitis, JDM, SS, and SSc relates either to factors inherent to those specific diagnoses or to the small number of such cases in our cohort. The association LoHLAD with pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases was observed in all diagnoses with 20 or more cases in our cohort, suggesting that the small number of cases in the remaining diagnoses may account for the lack of association (
Table 4). The association of LoHLAD with pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease was observed in both
HLA-class I and
HLA-class II loci but was most notable in class II loci highlighting the prominent role of CD4+ T cells in autoimmunity. Differences between cases and controls were noted at each of the 5 examined loci but were statistically significant only at the
HLA-B, HLA-DRB3/4/5, and
HLA-DQB1 loci. The observed “dose-response effect” (
Figure 1C and
Table 3) further supports LoHLAD as a positive predictor for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. Remarkably, LoHLAD at 3 or more loci was observed exclusively in cases. Thus, our findings indicate that the higher the number of loci with LoHLAD, the higher the risk for autoimmunity. Additionally, in our study, cases with LoHLAD compared to cases without LoHLAD had significantly earlier symptom onset and shorter time to diagnosis (Supplementary
Table 3) suggesting that LoHLAD may be associated with increased phenotypic severity.
Regression models provide additional insight into the significance of LoHLAD as a positive predictor for pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. In our study, the comparison of LoHLAD-based models with allele-based models demonstrated that LoHLAD is not inferior to allele specificity as a positive predictor of pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. The c-statistics of the best fitted LoHLAD-based model for predicting the presence of either any pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease or the 4 most common diagnoses in our cohort were higher than the respective c-statistics of the best fitted allele-based model. Most importantly, composite models utilizing both LoHLAD and specific alleles as variables had the best ability in predicting pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. Therefore, our data suggest that the combination of LoHLAD and allele specificity provides a novel approach in the assessment of positive autoimmunity risk that may be superior to either LoHLAD-based or allele-based approaches. The results of composite modeling suggest that LoHLAD may have a synergistic effect with allele specificity in increasing the risk for pediatric-onset rheumatic autoimmune disease. The underlying mechanism mediating this synergy is unknown. We postulate that high-risk HLA alleles present potentially autoreactive peptides and LoHLAD limits the overall diversity of presented peptides thus skewing antigen presentation towards epitopes enriched for autoreactivity.
Our study has strengths as well as limitations. The strengths of our study include the pediatric population, the large sample size, the matching of cases and controls, and the age of cases and controls. The pediatric population may demonstrate the contribution of genetic factors to autoimmunity more clearly than its adult counterpart because, generally, studies in children are less confounded by factors such as environmental exposures and common adult comorbid conditions. The sample size of 413 participants is adequate to provide sufficient data for the study of rare conditions such as pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Furthermore, cases and controls were evenly matched regarding sex, race, and ethnicity, thus limiting potential bias related to demographic factors. Finally, cases were younger than controls; this difference limits possible bias related to the age of onset of autoimmune rheumatic disease in our cohort.
The limitations of our study include the single center retrospective cohort, the “convenience” control population, and the HLA typing approach. The University of New Mexico pediatric rheumatology clinic is the only clinic in the state of New Mexico providing care to children with rheumatic diseases; therefore, our cohort is at least representative of the pediatric population of the entire state of New Mexico. To provide some form of indirect validation of the HLA data in our cohort, we performed a secondary analysis examining the association of specific alleles with pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic diseases (Supplementary Table 7). This secondary analysis confirmed several known associations such as the associations of JIA with HLA-A02, HLA-B27, HLA-DRB1*01, HLA-DRB1*08, and HLA-DQB1*04 (Berntson et al. 2008; Burgos-Vargas et al. 1997; De Silvestri et al. 2017; Hollenbach et al. 2010; Silva-Ramirez et al. 2010; Smerdel et al. 2003; Thomson et al. 2002; Yanagimachi et al. 2011; Zuber et al. 2015). The greatest limitation of our study is the use of “convenience” controls instead of healthy children. Nonetheless, the individuals in our control group were formally evaluated by experts from a variety of pediatric subspecialties, and the presence of autoimmune rheumatic disease was ruled out by thorough clinical assessment including, but not limited to, laboratory and imaging studies. The final limitation of our study relates to the HLA typing approach that examined only 5 HLA loci and was performed by means of low-to-medium resolution sequencing. Although our typing approach provides adequate information to evaluate LoHLAD as a risk factor for autoimmune rheumatic disease, it did not examine all HLA loci nor provided potentially important information on the specificity of suballeles and haplotypes.
Conclusion
To conclude, in this proof-of-concept case-control study on autoimmunity risk conferred by the MHC locus, we introduced the novel concept of LoHLAD, utilized LoHLAD as an innovative data analysis framework to investigate HLA associations with autoimmunity, and demonstrated that LoHLAD is a significant positive risk factor for the development of pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. Analytical approaches utilizing the concept of LoHLAD need to be studied in greater depth, as they can potentially provide new insights into the role of HLA genes in autoimmune disease immunopathogenesis, especially when combined with allele specificity. Future clinical studies will combine data from genetically distinct populations, include healthy individuals as controls, perform typing of all HLA loci by means of high-resolution sequencing, and further elucidate the role of LoHLAD in the development of pediatric-onset autoimmune rheumatic disease. Our findings should prompt researchers to consider LoHLAD when analyzing and interpreting the role of HLA genes in autoimmunity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Funding
The study received internal funding from the Department of Pediatrics at the University of New Mexico and was supported by the University of New Mexico Clinical Translational Science Center (UL1TR001449).
Data availability
De-identified data are available upon reasonable request with a transfer agreement.
Declarations
Ethics approval statement
This research study involves human participants and was approved by the institutional review board of the University of New Mexico (20-054). The study was performed according to the medical research ethical principles of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki and was compliant with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations. Consent was waived because only de-identified data were used.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and staff at the University of New Mexico pediatric rheumatology clinic. We are also grateful to the laboratory technicians at Tricore Reference Laboratories for their technical analyses.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- (1999) Complete sequence and gene map of a human major histocompatibility complex. The MHC sequencing consortium. Nature 401:921-3 . [CrossRef]
- Arnett FC, Jr., Schacter BZ, Hochberg MC, Hsu SH, Bias WB (1977) Homozygosity for HLA-B27. Impact on rheumatic disease expression in two families. Arthritis Rheum 20:797-804.
- Aydemir O, Noble JA, Bailey JA, Lernmark A, Marsh P, Andersson Svard A, Bearoff F, Blankenhorn EP, Mordes JP, Better Diabetes Diagnosis Study G (2019) Genetic Variation Within the HLA-DRA1 Gene Modulates Susceptibility to Type 1 Diabetes in HLA-DR3 Homozygotes. Diabetes 68:1523-1527 . [CrossRef]
- Bajor J, Szakacs Z, Juhasz M, Papp M, Kocsis D, Szegedi E, Foldi I, Farkas N, Hegyi P, Vincze A (2019) HLA-DQ2 homozygosis increases tTGA levels at diagnosis but does not influence the clinical phenotype of coeliac disease: A multicentre study. Int J Immunogenet 46:74-81 . [CrossRef]
- Berntson L, Damgard M, Andersson-Gare B, Herlin T, Nielsen S, Nordal E, Rygg M, Zak M, Fasth A, Nordic Paediatric Rheumatology Study G (2008) HLA-B27 predicts a more extended disease with increasing age at onset in boys with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 35:2055-61.
- Bhanusali DG, Sachdev A, Rahmanian A, Gerlach JA, Tong JC, Seiffert-Sinha K, Sinha AA (2013) HLA-E*0103X is associated with susceptibility to Pemphigus vulgaris. Exp Dermatol 22:108-12 . [CrossRef]
- Blomhoff A, Olsson M, Johansson S, Akselsen HE, Pociot F, Nerup J, Kockum I, Cambon-Thomsen A, Thorsby E, Undlien DE, Lie BA (2006) Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks in the MHC vary in an HLA haplotype specific manner assessed mainly by DRB1*03 and DRB1*04 haplotypes. Genes Immun 7:130-40.
- Burgos-Vargas R, Pacheco-Tena C, Vazquez-Mellado J (1997) Juvenile-onset spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 23:569-98.
- Carrington M, Nelson GW, Martin MP, Kissner T, Vlahov D, Goedert JJ, Kaslow R, Buchbinder S, Hoots K, O'Brien SJ (1999) HLA and HIV-1: heterozygote advantage and B*35-Cw*04 disadvantage. Science 283:1748-52.
- De Silvestri A, Capittini C, Poddighe D, Marseglia GL, Mascaretti L, Bevilacqua E, Scotti V, Rebuffi C, Pasi A, Martinetti M, Tinelli C (2017) HLA-DRB1 alleles and juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Diagnostic clues emerging from a meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev 16:1230-1236.
- Dendrou CA, Petersen J, Rossjohn J, Fugger L (2018) HLA variation and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 18:325-339.
- Derhaag PJ, van der Horst AR, de Waal LP, Feltkamp TE (1989) HLA-B27+ acute anterior uveitis and other antigens of the major histocompatibility complex. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 30:2160-4.
- Doxiadis GG, Hoof I, de Groot N, Bontrop RE (2012) Evolution of HLA-DRB genes. Mol Biol Evol 29:3843-53.
- Eerligh P, van Lummel M, Zaldumbide A, Moustakas AK, Duinkerken G, Bondinas G, Koeleman BP, Papadopoulos GK, Roep BO (2011) Functional consequences of HLA-DQ8 homozygosity versus heterozygosity for islet autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. Genes Immun 12:415-27.
- Fernandez-Vina MA, Gao XJ, Moraes ME, Moraes JR, Salatiel I, Miller S, Tsai J, Sun YP, An JB, Layrisse Z, et al. (1991) Alleles at four HLA class II loci determined by oligonucleotide hybridization and their associations in five ethnic groups. Immunogenetics 34:299-312.
- Gudjonsson JE, Karason A, Antonsdottir A, Runarsdottir EH, Hauksson VB, Upmanyu R, Gulcher J, Stefansson K, Valdimarsson H (2003) Psoriasis patients who are homozygous for the HLA-Cw*0602 allele have a 2.5-fold increased risk of developing psoriasis compared with Cw6 heterozygotes. Br J Dermatol 148:233-5.
- Ho WL, Lu MY, Hu FC, Lee CC, Huang LM, Jou ST, Lin DT, Lin KH (2012) Clinical features and major histocompatibility complex genes as potential susceptibility factors in pediatric immune thrombocytopenia. J Formos Med Assoc 111:370-9.
- Hollenbach JA, Thompson SD, Bugawan TL, Ryan M, Sudman M, Marion M, Langefeld CD, Thomson G, Erlich HA, Glass DN (2010) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis and HLA class I and class II interactions and age-at-onset effects. Arthritis Rheum 62:1781-91.
- Jaakkola E, Herzberg I, Laiho K, Barnardo MC, Pointon JJ, Kauppi M, Kaarela K, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Tuomilehto J, Wordsworth BP, Brown MA (2006) Finnish HLA studies confirm the increased risk conferred by HLA-B27 homozygosity in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:775-80.
- Khan MA, Kushner I, Braun WE, Zachary AA, Steinberg AG (1978) HLA--B27 homozygosity in ankylosing spondylitis: relationship to risk and severity. Tissue Antigens 11:434-8.
- Kim TJ, Na KS, Lee HJ, Lee B, Kim TH (2009) HLA-B27 homozygosity has no influence on clinical manifestations and functional disability in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27:574-9.
- Kim TJ, Sung IH, Lee S, Joo KB, Choi JH, Park DJ, Park YW, Lee SS, Kim TH (2013) HLA-B27 homozygosity has no influence on radiographic damage in ankylosing spondylitis: Observation Study of Korean spondyloArthropathy Registry (OSKAR) data. Joint Bone Spine 80:488-91.
- Koeleman BP, Lie BA, Undlien DE, Dudbridge F, Thorsby E, de Vries RR, Cucca F, Roep BO, Giphart MJ, Todd JA (2004) Genotype effects and epistasis in type 1 diabetes and HLA-DQ trans dimer associations with disease. Genes Immun 5:381-8.
- Kotsch K, Blasczyk R (2000) The noncoding regions of HLA-DRB uncover interlineage recombinations as a mechanism of HLA diversification. J Immunol 165:5664-70.
- Kvien TK, Moller P, Dale K (1985) Juvenile ankylosing spondylitis and HLA B27 homozygosity. Scand J Rheumatol 14:47-50.
- Lauter SA, Vasey FB, Espinoza LR, Bombardier C, Osterland CK (1977) Homozygosity for HLA-B27 in psoriatic arthritis and spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 20:1569-70.
- Liu E, Lee HS, Aronsson CA, Hagopian WA, Koletzko S, Rewers MJ, Eisenbarth GS, Bingley PJ, Bonifacio E, Simell V, Agardh D, Group TS (2014) Risk of pediatric celiac disease according to HLA haplotype and country. N Engl J Med 371:42-9.
- Logunova NN, Viret C, Pobezinsky LA, Miller SA, Kazansky DB, Sundberg JP, Chervonsky AV (2005) Restricted MHC-peptide repertoire predisposes to autoimmunity. J Exp Med 202:73-84.
- Lopes LHC, Muniz JG, Oliveira RP, Sdepanian VL (2019) Celiac Disease in Brazilian First-degree Relatives: The Odds Are Five Times Greater for HLA DQ2 Homozygous. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 68:e77-e80.
- Ma Y, Su H, Yuksel M, Longhi MS, McPhail MJ, Wang P, Bansal S, Wong GW, Graham J, Yang L, R JT, Doherty DG, Hadzic N, Zen Y, Quaglia A, Heneghan MA, Samyn M, Vergani D, Mieli-Vergani G (2021) Human Leukocyte Antigen Profile Predicts Severity of Autoimmune Liver Disease in Children of European Ancestry. Hepatology 74:2032-2046.
- Miyadera H, Tokunaga K (2015) Associations of human leukocyte antigens with autoimmune diseases: challenges in identifying the mechanism. J Hum Genet 60:697-702.
- Penn DJ, Damjanovich K, Potts WK (2002) MHC heterozygosity confers a selective advantage against multiple-strain infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:11260-4.
- Prakash S, Mehra NK, Malaviya AN (1983) HLA-B27 homozygosity in seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Ann Intern Med 98:676.
- Ruiz-Ortiz E, Montraveta M, Cabre E, Herrero-Mata MJ, Pujol-Borrell R, Palou E, Faner R (2014) HLA-DQ2/DQ8 and HLA-DQB1*02 homozygosity typing by real-time polymerase chain reaction for the assessment of celiac disease genetic risk: evaluation of a Spanish celiac population. Tissue Antigens 84:545-53.
- Sadovnick AD (2012) Genetic background of multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 11:163-6.
- Sewell AK (2012) Why must T cells be cross-reactive? Nat Rev Immunol 12:669-77.
- Shiina T, Hosomichi K, Inoko H, Kulski JK (2009) The HLA genomic loci map: expression, interaction, diversity and disease. J Hum Genet 54:15-39.
- Silva-Ramirez B, Cerda-Flores RM, Rubio-Perez N, Vargas-Alarcon G, Perez-Hernandez N, Granados-Arriola J, Burgos-Vargas R (2010) Association of HLA DRB1 alleles with juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Mexicans. Clin Exp Rheumatol 28:124-7.
- Smerdel A, Lie BA, Finholt C, Ploski R, Forre O, Undlien DE, Thorsby E (2003) An additional susceptibility gene for juvenile idiopathic arthritis in the HLA class I region on several DR-DQ haplotypes. Tissue Antigens 61:80-4.
- Smerdel A, Ploski R, Flato B, Musiej-Nowakowska E, Thorsby E, Forre O (2002) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is primarily associated with HLA-DR8 but not DQ4 on the DR8-DQ4 haplotype. Ann Rheum Dis 61:354-7.
- Spencer DG, Hick HM, Dick WC (1979) Ankylosing spondylitis--the role of HLA-B27 homozygosity. Tissue Antigens 14:379-84.
- Thomson W, Barrett JH, Donn R, Pepper L, Kennedy LJ, Ollier WE, Silman AJ, Woo P, Southwood T, British Paediatric Rheumatology Study G (2002) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis classified by the ILAR criteria: HLA associations in UK patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:1183-9.
- Turesson C, Jacobsson L, Bergstrom U, Truedsson L, Sturfelt G (2000) Predictors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 29:358-64.
- Turesson C, Schaid DJ, Weyand CM, Jacobsson LT, Goronzy JJ, Petersson IF, Sturfelt G, Nyhall-Wahlin BM, Truedsson L, Dechant SA, Matteson EL (2005) The impact of HLA-DRB1 genes on extra-articular disease manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R1386-93.
- van Belzen MJ, Koeleman BP, Crusius JB, Meijer JW, Bardoel AF, Pearson PL, Sandkuijl LA, Houwen RH, Wijmenga C (2004) Defining the contribution of the HLA region to cis DQ2-positive coeliac disease patients. Genes Immun 5:215-20.
- Vannas A, Karjalainen K (1984) Homozygosity of HLA-B27 antigen in the recipient and susceptibility to the corneal allograft reaction. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 221:272-5.
- Weyand CM, Xie C, Goronzy JJ (1992) Homozygosity for the HLA-DRB1 allele selects for extraarticular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 89:2033-9.
- Yanagimachi M, Miyamae T, Naruto T, Hara T, Kikuchi M, Hara R, Imagawa T, Mori M, Kaneko T, Goto H, Morita S, Mizuki N, Kimura A, Yokota S (2011) Association of HLA-A*02:06 and HLA-DRB1*04:05 with clinical subtypes of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Hum Genet 56:196-9.
- Yang HC, Chang LC, Liang YJ, Lin CH, Wang PL (2012) A genome-wide homozygosity association study identifies runs of homozygosity associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the human major histocompatibility complex. PLoS One 7:e34840.
- Zuber Z, Turowska-Heydel D, Sobczyk M, Chudek J (2015) Prevalence of HLA-B27 antigen in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Reumatologia 53:125-30.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).