Submitted:
29 November 2024
Posted:
02 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
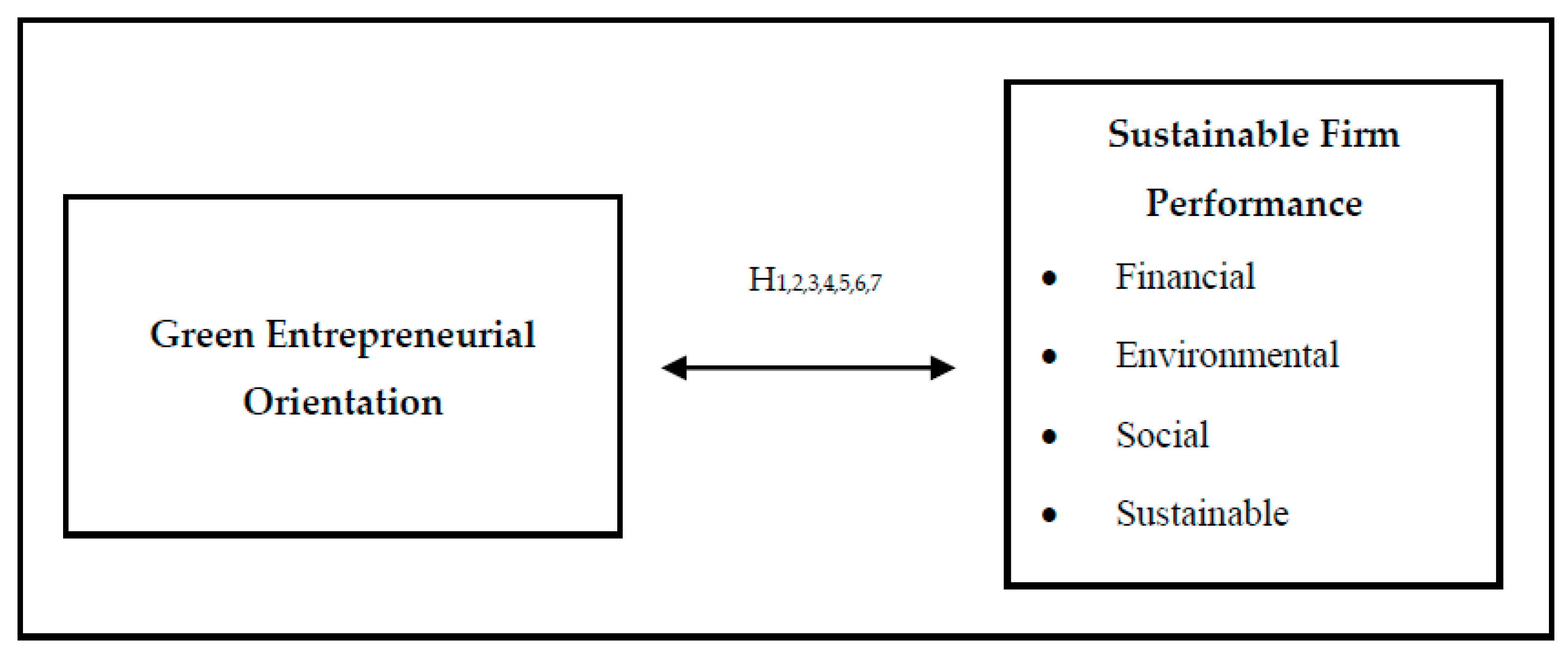
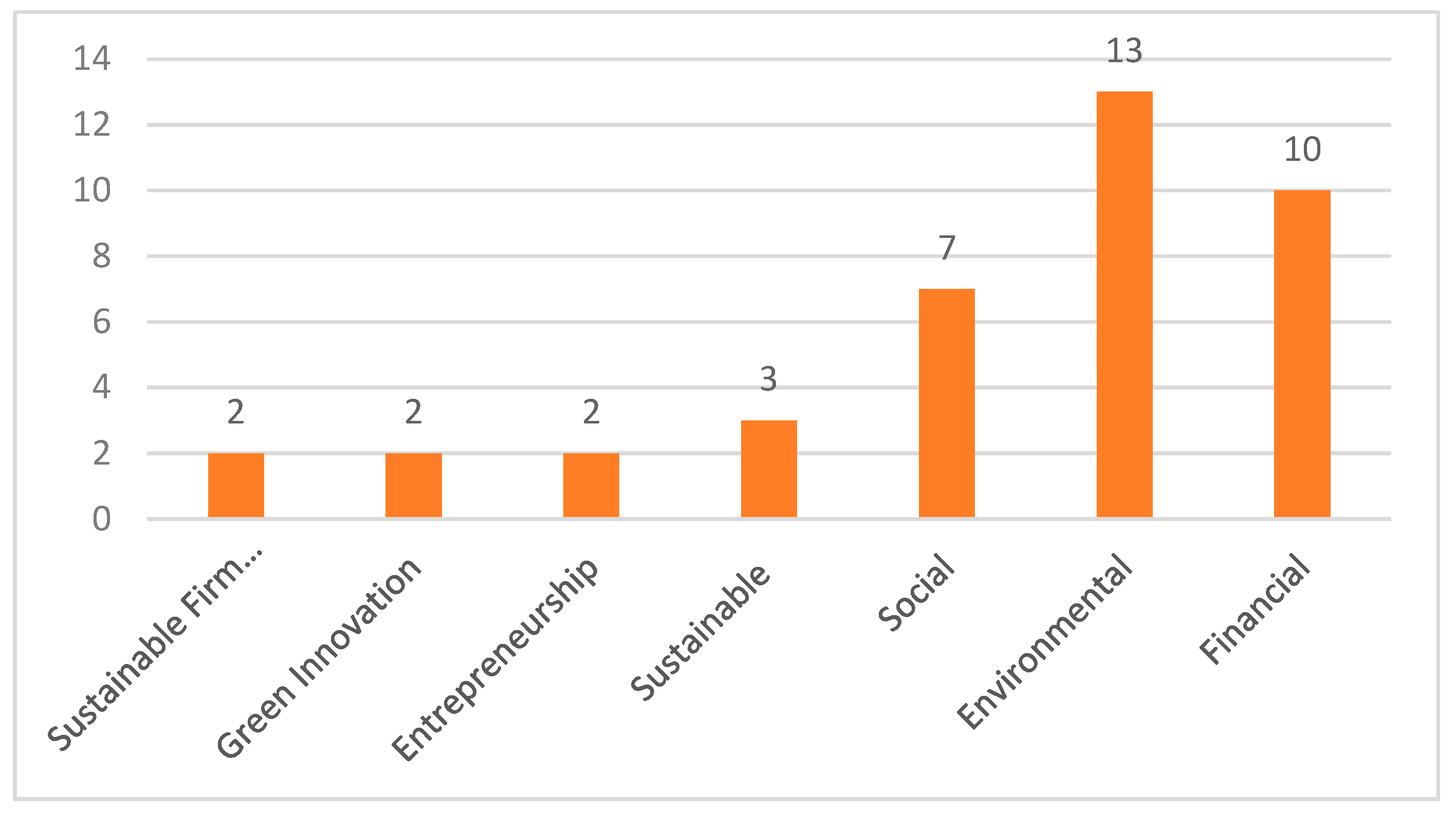
The purpose of this study is to examine the relationship between green entrepreneurial orientation and sustainable firm performance. In order to examine this relationship, meta-analysis method was used and analyses were carried out with Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Software (CMA) v4 package programme. In the study, a sample of 23 articles, 42 effect sizes and 6666 enterprises was reached through a systematic literature review. The studies included in the research were accessed by searching the keywords "green entrepreneurial orientation" and "sustainable firm performance" from Web of Science, EBSCO Host, Scopus and Google Scholar databases and only articles were included without any year limit. Throughout the study, statistical analyses were performed on Fisher z values and conducted under the random effects model. The effect size, heterogeneity and publication bias analyses of green entrepreneurial orientation and sustainable firm performance and its sub-dimensions were tested separately, and the findings were interpreted by converting them into correlation coefficients. As a result of the analyses, it was found that the relationship between green entrepreneurial orientation and sustainable firm performance is positive and highly significant. In addition, the relationship between financial, environmental, social, sustainable and entrepreneurial performance, which are the sub-dimensions of sustainable firm performance, and green entrepreneurial orientation was found to be high and significant. However, it was concluded that there is no significant relationship between green innovation performance, which is another dimension of sustainable firm performance, and green entrepreneurial orientation.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Green Entrepreneur Orientation
2.2. Sustainable Firm Performance
3. Methodology
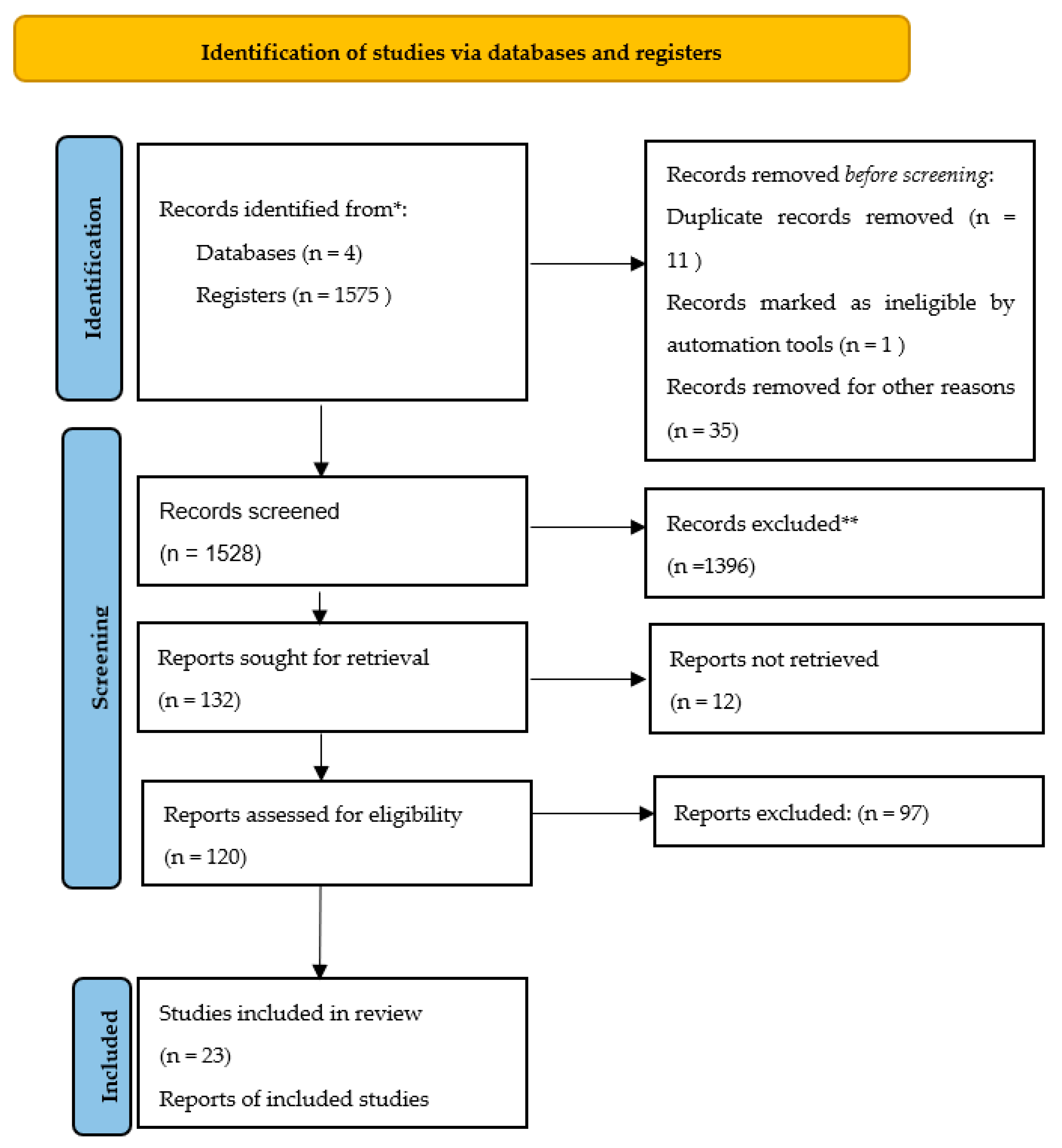
3.1. Scope of the Study and Selection Criteria
3.2. Data Coding
3.3. Data Analysis
3.4. Results
4. Conclusion and Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Implication
4.2. Practical Implication
4.3. Limitations and Further Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- *References marked with a single asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analysis.
- Ullah, S.; Qaiser Danish, R. The impact of green entrepreneurial orientation on firm performance through green innovation: The moderating role of strategic green marketing orientation. European Online Journal of Natural and Social Sciences 2020, 9, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, L. Environmental entrepreneurial orientation and firm performance: The role of environmental innovation and stakeholder pressure. Sage Open 2022, 12, 21582440211061354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Le, Y.; Meng, Q.; Teng, X. Green entrepreneurial orientation and financial performance in Chinese firms: The role of stakeholder engagement and green absorptive capacity. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management 2023, 30, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majali, T.E.; Alkaraki, M.; Asad, M.; Aladwan, N.; Aledeinat, M. Green transformational leadership, green entrepreneurial orientation and performance of SMEs: The mediating role of green product innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 2022, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoki, O. Green entrepreneurial orientation and firm performance in South Africa. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues 2019, 7, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Swidi, A.K.; Al-Hâkimi, M.A.; Al-Sarraf, J.; Al Koliby, I.S. Innovate or perish: can green entrepreneurial orientation foster green innovation by leveraging green manufacturing practices under different levels of green technology turbulence? Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management 2024, 35, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, W.J.; Gupta, V.K.; Mousa, F.T. Empirical research on entrepreneurial orientation: An assessment and suggestions for future research. International Small Business Journal 2013, 31, 357–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, G.A.; Anghel, M.A. Green Entrepreneurship among Students-Social and Behavioural Motivation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, A. Linking green entrepreneurial orientation and ambidextrous green innovation to stimulate green performance: a moderated mediation approach. Business Process Management Journal 2024, 30(8), 71–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, B.; Korchagina, E. A systematic literature review and conceptual framework on green entrepreneurial orientation. Administrative Sciences 2024, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhloufi, L.; Laghouag, A.A.; Meirun, T.; Belaid, F. Impact of green entrepreneurship orientation on environmental performance: The natural resource-based view and environmental policy perspective. Business Strategy and the Environment 2022, 31, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Feng, T.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, Y. Enabling green supply chain integration via green entrepreneurial orientation: Does environmental leadership matter? Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management 2023, 30, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y. Green entrepreneurial orientation and green innovation: The mediating effect of supply chain learning. Sage Open 2020, 10, 2158244019898798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chai, H.; Shao, J.; Feng, T. Green entrepreneurial orientation for enhancing firm performance: A dynamic capability perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 198, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowar-Sulej, K.; Krzywonos, M.; Kwil, I. Environmental entrepreneurship-Bibliometric and content analysis of the subject literature based on H-Core. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 295, 126277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, M.; Aledeinat, M.; Majali, T.E.; Almajali, D.A.; Shrafat, F.D. Mediating role of green innovation and moderating role of resource acquisition with firm age between green entrepreneurial orientation and performance of entrepreneurial firms. Cogent Business & Management 2024, 11, 2291850. [Google Scholar]
- Teece, D.J. Dynamic capabilities and entrepreneurial management in large organisations: Toward a theory of the (entrepreneurial) firm. European Economic Review 2016, 86, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, G.; Zainurrafiqi, Z. The effect of green entrepreneur orientation on network resource acquisition and small and medium enterprises' business performance with knowledge transfer and integration and green technology dynamism as moderator variables. Indonesian Interdisciplinary Journal of Sharia Economics (IIJSE) 2023, 6, 136–153. [Google Scholar]
- Shafique, I.; Kalyar, M.N.; Mehwish, N. Organisational ambidexterity, green entrepreneurial orientation, and environmental performance in SMEs context: Examining the moderating role of perceived CSR. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management 2021, 28, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Abbas, Q.; Khan, M.A. Entrepreneurial orientation and innovative performance: the moderating effect of market orientation. Global Management Journal for Academic & Corporate Studies 2018, 7, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Hu, H.; Wang, Z. The relationship between institutional pressure, green entrepreneurial orientation, and entrepreneurial performance-The moderating effect of network centrality. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhloufi, L.; Meirun, T.; Belaid, F.; Yaacob, N.A. Impact of green entrepreneurship orientation on environmental performance: The natural resource-based view perspective. 2021.
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, H.C. Critical factors for enhancing green service innovation: Linking green relationship quality and green entrepreneurial orientation. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology 2018, 9, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taouab, O.; Issor, Z. Firm performance: Definition and measurement models. European Scientific Journal 2019, 15, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chet Miller, C.; Washburn, N.T.; Glick, W.H. The myth of firm performance. Organization Science 2013, 24, 948–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Pan, Y.; Sensoy, A.; Uddin, G.S.; Cheng, F. Green credit policy and firm performance: What we learn from China. Energy Economics 2021, 101, 105415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriastuti, M.; Chariri, A. The role of green investment and corporate social responsibility investment on sustainable performance. Cogent Business & Management 2021, 8, 1960120. [Google Scholar]
- Civelek, M.E.; Çemberci, M.; Artar, O.K.; Uca, N. Key factors of sustainable firm performance: A strategic approach; Zea Books: Lincoln, Nebraska, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Golicic, S.L.; Smith, C.D. A meta-analysis of environmentally sustainable supply chain management practices and firm performance. Journal of Supply Chain Management 2013, 49, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T. How do corporate social responsibility and green innovation transform corporate green strategy into sustainable firm performance? Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 362, 132228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, J. Impact of total quality management on corporate green performance through the mediating role of corporate social responsibility. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.E.; Li, Q. Does green proactiveness orientation improve the performance of agricultural new ventures in China? The mediating effect of sustainable opportunity recognition. Sage Open 2021, 11, 21582440211067224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afum, E.; Issau, K.; Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Baah, C.; Dacosta, E.; Essandoh, E.; Agyenim Boateng, E. The missing links of sustainable supply chain management and green radical product innovation between sustainable entrepreneurship orientation and sustainability performance. Design and Technology 2023, 21, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangmee, C.; Dacko-Pikiewicz, Z.; Meekaewkunchorn, N.; Kassakorn, N.; Khalid, B. Green entrepreneurial orientation and green innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Social Sciences 2021, 10(4), 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz Baig, M.; Yadegaridehkordi, E. Exploring moderating effects of industry 4.0 adoption on sustainable performance of Malaysian manufacturing organisations. Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering 2023, 40, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.A.; Bao, Y.; Ilmudeen, A. The impact of green entrepreneurial orientation, market orientation and green supply chain management practices on sustainable firm performance. Cogent Business & Management 2020, 7, 1743616. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Yildirim, I. Meta-analysis applications with cma. Anı Publishing: Ankara, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 1(36), 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frare, A.B.; Beuren, I.M. The role of green process innovation translating green entrepreneurial orientation and proactive sustainability strategy into environmental performance. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development 2022, 29, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Yang, Y.; Xia, H.; Shao, Y.; Gu, X.; Shen, J. Green entrepreneurial orientation, boundary-spanning search and enterprise sustainable performance: The moderating role of environmental dynamism. Frontiers in Psychology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, M.; Majali, T.E.; Aledeinat, M.; Abdelkarim Almajali, D.; Akhorshaideh, A.H.O. Green entrepreneurial orientation for enhancing SMEs financial and environmental performance: Synergetic moderation of green technology dynamism and knowledge transfer and integration. Cogent Business & Management 2023, 10, 2278842. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaq, M.I.; Sarwar, H.; Aftab, J.; Franzoni, S.; Raza, A. Accomplishing sustainable performance through leaders' competencies, green entrepreneurial orientation, and innovation in an emerging economy: Moderating role of institutional support. Business Strategy and the Environment 2024, 33, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.; Ferreira, J.; Proença, C. The impact of green entrepreneurial orientation on sustainability performance through the effects of green product and process innovation: The moderating role of ambidexterity. Business Strategy and the Environment 2024, 33, 3184–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, H.; Xu, J.; Andrianarivo Andriandafiarisoa Ralison, N.A. Green entrepreneurial orientation and knowledge creation process as enablers of green innovation performance: the moderating role of resource orchestration capability. European Journal of Innovation Management 2023. [CrossRef]
- Aftab, J.; Veneziani, M.; Sarwar, H.; Abid, N. Do green practices drive business excellence in SMEs? Investigating how green entrepreneurial orientation improves firm's performance. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence 2024, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Su, Y.Y.; Khan, A.; Hishan, S.S.; Ahmad Lone, S. The investigation of sustainable environmental performance of manufacturing companies: mediating role of organisational support and moderating role of CSR. Economic research-Ekonomska istraživanja 2022, 35, 4128–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, J.; El Ebrashi, R. The interplay among green absorptive capacity, green entrepreneurial, and learning orientations and their effect on triple bottom line performance. Business Strategy and the Environment 2024, 33, 1962–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Khan, R.U.; Dagar, V.; Qian, F. Do international resources configure SMEs' sustainable performance in the digital era? Evidence from Pakistan. Resources Policy 2023, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tze San, O.; Latif, B.; Di Vaio, A. GEO and sustainable performance: the moderating role of GTD and environmental consciousness. Journal of Intellectual Capital 2022, 23, 38–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, S.M.; Al Mamun, A.; Wu, M.; Naznen, F.; Kanwal, S.; Makhbul, Z.K.M. Modelling the significance of green orientation and culture on green innovation performance: moderating effect of firm size and green implementation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2023, 30, 99855–99874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankgele, K. Green entrepreneurial orientation and environmental performance of SMEs in Johannesburg municipality in the Gauteng province: the role of green competitive advantage and green innovation. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science 2023, 12, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinçer, S. Introduction to meta-analysis. 2019: Ankara: Anı Publishing.
- Cohen, J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences (2nd Edition) ed. 1988: Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates.
- Guerrero, M.; Liñán, F.; Cáceres-Carrasco, F.R. The influence of ecosystems on the entrepreneurship process: a comparison across developed and developing economies. Small Business Economics 2021, 57, 1733–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, F.; Khan, N.R. Green entrepreneurial orientation and corporate environmental performance: A systematic literature review. European Management Journal 2023, 41(5), 755–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrick, D.C.; Mason, A. Upper echelons: The organisation as a reflection of its top managers. Academy of Management Review 1984, 9, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
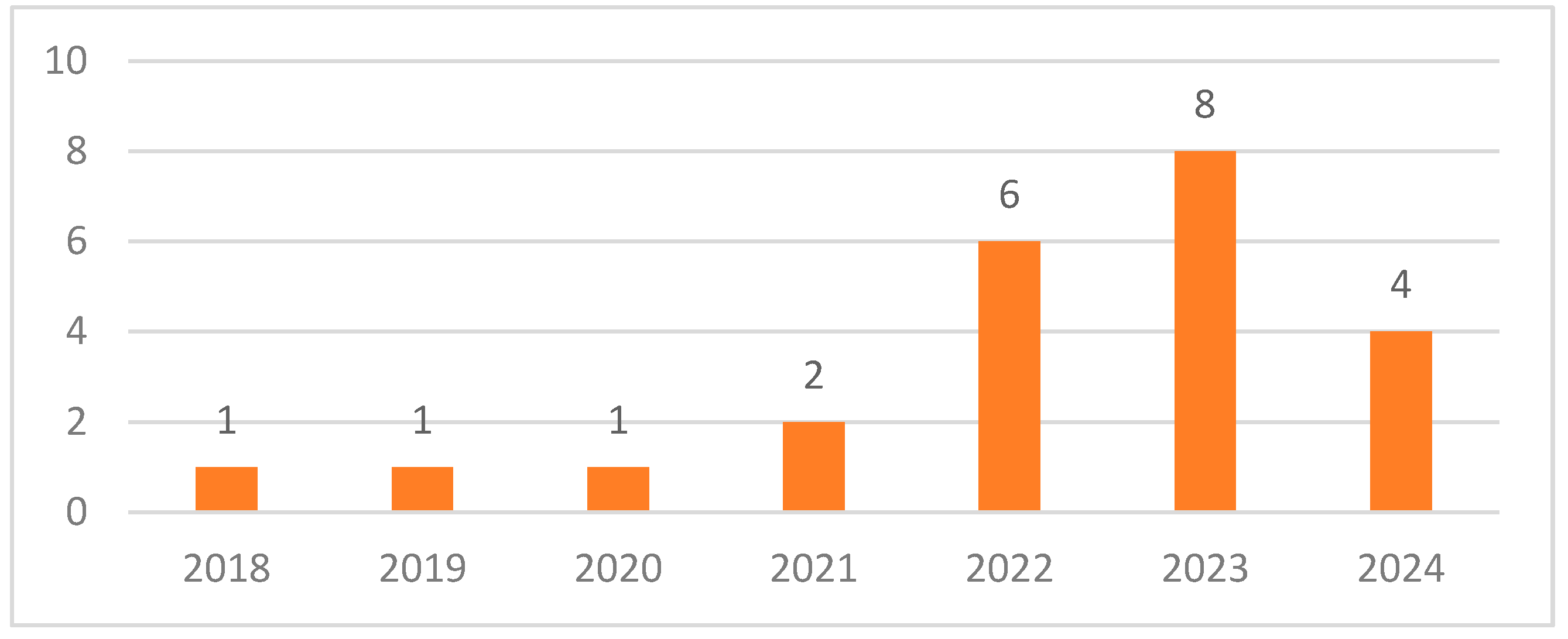
| S.N. | Sources | N | SFP | FP | EP | SP | Sus.P. | Ent. P | GIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [14] | 264 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 2 | [5] | 192 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 3 | [39] | 81 | ✓ | ||||||
| 4 | [40] | 202 | ✓ | ||||||
| 5 | [34] | 226 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 6 | [19] | 307 | ✓ | ||||||
| 7 | [36] | 246 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 8 | [41] | 384 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 9 | [3] | 230 | ✓ | ||||||
| 10 | [16] | 384 | ✓ | ||||||
| 11 | [42] | 329 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 12 | [43] | 369 | ✓ | ||||||
| 13 | [44] | 424 | ✓ | ||||||
| 14 | [45] | 576 | ✓ | ||||||
| 15 | [46] | 510 | ✓ | ||||||
| 16 | [47] | 211 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 17 | [48] | 380 | ✓ | ||||||
| 18 | [49] | 160/136 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 19 | [50] | 293 | ✓ | ||||||
| 20 | [51] | 424 | ✓ | ||||||
| 21 | [21] | 288 | ✓ | ||||||
| 22 | [2] | 416 | ✓ | ||||||
| 23 | [33] | 248 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 95% CI of r | Fail safe N | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RANDOM Model | Total studies | Total effect | Sample size | Effect size (r) | Standard error | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Q-statistic | Z value | P value | Rosenthal | Orwin |
| H1->SFP | 23 | 42 | 11.424 | 0.577 | 0.054 | 0.502 | 0.642 | 1341.949 | 12.164 | 0.000 | 2084 | 7883 |
| H2->FP | 10 | 11 | 2.626 | 0.569 | 0.109 | 0.408 | 0.696 | 304.533 | 5.940 | 0.000 | 3138 | 7350 |
| H3->EP | 13 | 14 | 3.818 | 0.605 | 0.099 | 0.467 | 0.713 | 454.876 | 7.107 | 0.000 | 6280 | 9782 |
| H4->SP | 7 | 8 | 1.748 | 0.574 | 0107 | 0.416 | 0.697 | 136.698 | 6.102 | 0.000 | 1522 | 5288 |
| H5->SusP | 3 | 3 | 951 | 0.665 | 0.348 | 0.121 | 1.450 | 220.118 | 2.310 | 0.021 | 488 | 2531 |
| H6->EntP | 2 | 2 | 672 | 0.537 | 0.105 | 0.373 | 0.667 | 7.212 | 5.702 | 0.000 | 124 | 1832 |
| H7->GIP | 2 | 2 | 717 | 0.465 | 0.441 | -0.346 | 0.878 | 133.522 | 1.142 | 0.253 | 108 | 1748 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




