1. Introduction
The quest to reconcile quantum mechanics (QM) with the general theory of relativity (GR) is among the most profound and long-standing challenges in theoretical physics. While quantum field theory (QFT) and the Standard Model of particle physics have led to precise and empirically verified descriptions of three of the four known fundamental forces—electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction—gravity continues to elude a fully satisfactory quantum description. Various approaches to quantum gravity, including loop quantum gravity [
1,
2,
3,
4], string theory [
5,
6,
7], and asymptotic safety scenarios [
8,
9], have yielded important insights, yet a consistent, experimentally testable quantum theory of gravity remains out of reach. A central difficulty in constructing such a theory is encapsulated by the black hole information paradox [
10,
11,
12,
13], which arises at the intersection of unitarity in quantum mechanics and classical gravitational descriptions of horizons and singularities. As black holes evaporate via Hawking radiation—predicted by the QFT in curved space–time—they appear to radiate away information in a nearly thermal, featureless spectrum. This seems to contradict the unitarity of quantum evolution, fueling a host of proposals aiming to restore information conservation. Ideas such as the holographic principle [
14,
15], firewalls [
16], fuzzballs [
17], and the ER=EPR conjecture [
18] have offered conceptual resolutions, yet a universally accepted solution remains elusive.
Recently, the
Quantum Memory Matrix (QMM) hypothesis [
19] introduced a distinct perspective: it treats space–time itself as a dynamic quantum information repository. In the QMM framework, the continuum space–time manifold is replaced at the Planck scale by a discretized structure composed of space–time quanta, each associated with a finite-dimensional Hilbert space. Interactions of quantum fields at these discrete cells produce
quantum imprints, local records that encode information about quantum states and events into the fabric of space–time. Initial investigations focused on incorporating gravitational degrees of freedom, suggesting that black hole evaporation need not lead to permanent information loss. Instead, information may be stored in and later retrieved from the QMM, providing a local and unitary resolution of the paradox that does not hinge on nonlocal or topological features.
This paper extends the QMM approach to electromagnetism. Electromagnetic interactions, governed by a local U(1) gauge symmetry, offer a stringent test: the theory of quantum electrodynamics (QED) is highly constrained, quantitatively accurate, and extremely well-tested [
20,
21,
22,
23]. Incorporating electromagnetism into QMM is thus not merely adding a known interaction but ensuring that gauge invariance, locality, and unitarity persist at the Planck scale. It also demands carefully constructing gauge-invariant imprint operators that reflect how photons—massless spin-1 quanta—interact with space–time quanta. Crucially, we aim to move beyond heuristic arguments and provide a more structured, operator-level treatment. By defining imprint operators in terms of gauge-invariant field strengths and matter currents and by formulating the interaction Hamiltonian on a discretized lattice-like framework, we set the stage for a more rigorous unification that can, in principle, be extended to other gauge fields.
This approach diverges from attempts that rely on additional spatial dimensions or asymptotic boundary conditions. Instead, it embraces a fundamentally discrete picture that is background-independent and manifestly local, resonating with the spirit of causal sets and loop quantum gravity, yet differing by focusing on the quantum informational aspect of space–time quanta as memory units [
24,
25]. In doing so, we provide a setting where the interplay of geometry, quantum fields, and gauge invariance can be analyzed more explicitly. The promise is that by embedding electromagnetism into QMM, one obtains a finite, gauge-invariant discretization scheme that could, in principle, tame ultraviolet divergences and shed light on the high-energy behavior of QED in a quantum gravitational regime.
To elucidate the QMM framework and its integration with electromagnetism, this manuscript is organized as follows. In
Section 2, we review the foundational principles of the QMM hypothesis, clarifying the discretization scheme and the introduction of quantum imprints. We also discuss how fundamental principles such as unitarity and covariance are preserved. In
Section 3, we incorporate the electromagnetic field, constructing gauge-invariant imprint operators and deriving the corresponding interaction Hamiltonian. We ensure that the resulting theory respects local U(1) symmetry and maintains physical consistency. In
Section 4, we apply the extended framework to analyze charged black holes and investigate how electromagnetic imprints stored in the QMM influence Hawking radiation and information retrieval. We further consider how vacuum polarization and the structure of QED at trans-Planckian scales might be affected.
Section 5 provides a critical comparison with other unification attempts, highlighting the advantages of a local, discretized, quantum informational approach.
Section 6 examines potential indirect observational signatures and suggests strategies to differentiate QMM predictions from other speculative ideas. Finally, in
Section 7, we summarize our results and discuss future steps, including incorporating non-Abelian gauge symmetries and the path toward a comprehensive unified framework.
Unless otherwise stated, we work with the metric signature
and set
. Greek indices
run over space–time coordinates
. Standard references in QFT, general relativity, and gauge theories [
20,
21] will be invoked as needed to ground our approach in established theory.
To promote intuition, let us consider a simplified scenario where a charged scalar field interacts with the QMM. In this case, the field’s configuration at each discrete space-time cell x interacts with the corresponding QMM quanta, imprinting information about the local charge density and electromagnetic field strength. These imprints are encoded in the finite-dimensional Hilbert space associated with each cell, ensuring that the information is preserved and can be later retrieved through interactions with outgoing radiation or other probes. This example stresses how QMM can maintain information continuity without resorting to nonlocal mechanisms or altering the underlying space-time geometry.
The QMM framework shares similarities with lattice gauge theories, where space–time is discretized, and gauge fields are defined on lattice links [
26]. However, QMM introduces an additional layer of quantum information storage, treating each discrete cell not just as a geometric entity but as a dynamic repository of quantum imprints. This dual role facilitates the preservation of unitarity and information flow in a manner that is inherently local, distinguishing QMM from traditional lattice approaches.
Furthermore, by focusing on quantum information aspects, QMM aligns with recent developments in quantum information theory applied to quantum gravity, such as entanglement entropy calculations and tensor network approaches. This synergy suggests that QMM could serve as a bridge between discrete quantum gravity models and quantum information frameworks, potentially offering new tools and insights for tackling longstanding problems like the black hole information paradox.
In summary, this paper makes the following key advances:
Integration of Electromagnetism into QMM. We extend the QMM framework to include electromagnetic interactions, ensuring gauge invariance, locality, and unitarity are maintained at the Planck scale.
Construction of Gauge-Invariant Imprint Operators. We develop explicit constructions for imprint operators based on gauge-invariant field strengths and matter currents, providing a concrete mechanism for information encoding.
Analysis of Charged Black Hole Evaporation. We apply the extended QMM framework to charged black holes, demonstrating how electromagnetic imprints facilitate information retrieval from Hawking radiation.
Exploration of Vacuum Polarization and UV Behavior. We investigate how the QMM-induced discretization affects vacuum polarization processes and the running of electromagnetic couplings at high energies.
Identification of Cosmological Signatures. We outline potential cosmological implications of QMM-electromagnetism coupling, suggesting observable signatures in the cosmic microwave background and large-scale structures.
Comparison with Existing Quantum Gravity Theories. We critically compare the QMM approach with other unification attempts, highlighting its unique advantages in providing a locally defined information reservoir.
Proposed Experimental and Observational Tests. We propose strategies for indirectly testing QMM predictions through astrophysical observations, cosmological measurements, and laboratory analog experiments.
By addressing these areas, our work advances the QMM hypothesis towards a more comprehensive and unified framework that encompasses both gravitational and electromagnetic interactions, laying the groundwork for future extensions to other fundamental forces.
2. Foundations of the Quantum Memory Matrix
In this section, we provide a comprehensive review of the QMM hypothesis, laying the groundwork required for incorporating electromagnetism within a discretized space–time framework. We begin by introducing the fundamental principles and mathematical structures that define QMM, wherein space–time at the Planck scale is treated as a discrete reservoir of quantum information. We then discuss the concept of quantum imprints, which capture and store local quantum data. Finally, we examine how the QMM preserves key physical principles such as unitarity, locality, and covariance, thereby preparing the stage for the extension to electromagnetic gauge fields in subsequent sections.
2.1. Discretization of Space–Time and Finite-Dimensional Hilbert Spaces
A pivotal assumption of QMM is that the continuum of classical space-time ceases to be valid at the Planck scale (), yielding discrete, finite-sized cells referred to as space-time quanta. These quanta not only serve as the smallest geometric building blocks but also actively record quantum information.
Let us label each space–time quantum by an index
, where
denotes the set of all discrete cells in space–time. Each cell
x is associated with a finite-dimensional Hilbert space
. The total Hilbert space representing the QMM is then the tensor product
Each local Hilbert space
may be visualized as containing a finite basis of states that encode both geometric and quantum informational degrees of freedom pertinent to that cell. Operators acting on
correspond to local quantum observables, including discrete measures of length, area, and volume, analogous to the spectra encountered in loop quantum gravity or spin foam models.
By endowing each with finite dimension, QMM naturally imposes an ultraviolet (UV) cutoff at the Planck scale. Normally, continuum quantum field theories encounter divergences at high momenta. Here, however, discretization yields discrete spectra for geometric operators (e.g., area and volume), preventing integrals from diverging and offering a built-in regularization scheme. This approach parallels the logic of lattice gauge theory, though QMM not only discretizes geometry but also treats each discrete cell as an active repository of quantum information.
Though space-time is discretized at Planckian resolutions, continuum physics must re-emerge at scales . In this regime, the collective behavior of many space–time quanta approximates smooth geometry, recovering the familiar predictions of general relativity and quantum field theory. Demonstrating how Lorentz invariance and classical geometry arise from an underlying discrete structure is an active area of research. In QMM, this is accomplished by constructing imprint operators and interactions that respect local symmetries in the continuum limit, ensuring consistency with low-energy effective field theories.
2.2. Quantum Imprints and Local Encoding of Information
A central element of QMM is the notion of quantum imprints, which encode local quantum data into space–time quanta. If a quantum field interacts at cell x, that interaction leaves a record—an imprint—in the Hilbert space . This mechanism transforms space–time from a passive background into an information-active substrate.
Imprint operators
act jointly on the field Hilbert space and the QMM cell’s Hilbert space. For a generic matter field
, the minimal coupling to the QMM can be captured by an interaction Hamiltonian of the form:
The operator
encodes how the field’s local configuration (e.g., amplitude, phase, internal quantum numbers) modifies the QMM state. Conversely, the QMM can affect the field’s evolution if
appears in the total Hamiltonian, facilitating a bidirectional information flow.
Because these imprint operators are incorporated into an overall unitary evolution, no net information is lost; the QMM Hilbert space retains quantum coherence data from all interactions that occur at cell x. This local record-keeping structure provides a natural resolution to scenarios, like black hole evaporation, where naive semiclassical arguments suggest irretrievable information loss. In QMM, the apparent loss is merely a matter of accessibility: the information is encoded in the QMM degrees of freedom and may later be retrieved through suitable interactions.
2.3. Physical Requirements: Unitarity, Locality, and Covariance
For QMM to serve as a physically consistent framework bridging quantum field theory and gravity, it must satisfy three foundational pillars:
Unitarity: The global evolution operator must be unitary. If includes both the QMM and field Hamiltonians (plus interaction terms), the combined system evolves without violating probability conservation or quantum coherence.
Locality: Interactions must be confined to individual cells. The imprinting process acts only at the cell x where the field is defined, preventing any acausal influence. This ensures compatibility with the causal structure inherent in relativistic quantum field theory and general relativity.
Covariance: Although QMM discretizes space–time, the construction must remain coordinate-independent at scales larger than the cell size. Covariance can be preserved by building the imprint operators and Hamiltonians from tensorial or scalar combinations of field operators and geometric variables, ensuring that the form of the interactions is preserved under changes of coordinates.
The Hermiticity of implies that and appear symmetrically in the interaction. This symmetry guarantees that information flow is bidirectional: not only do fields imprint on QMM cells, but QMM cells can, in principle, feed back information into the field evolution, preserving overall unitarity.
2.4. Retrieval Mechanisms and Information Restoration
QMM posits that information once embedded in space–time quanta remains in the global Hilbert space, even if conventional semiclassical reasoning suggests irretrievability.
Consider a black hole forming from collapsing matter described by . As matter crosses the event horizon, imprint operators at horizon cells encode the infalling state into QMM degrees of freedom. During Hawking radiation, the outgoing modes interact again with these QMM quanta, gradually revealing correlations that appear as subtle non-thermal features in the radiation spectrum. Over the entire evaporation period, the final state (radiation + QMM) retains unitarity, thus offering a resolution to the black hole information paradox.
While black hole evaporation provides a striking application, the retrieval mechanism is generic. Any quantum process happening at cell x leaves a footprint in , which subsequent interactions can probe. For instance, in cosmological settings, quantum fluctuations at the early universe scale could leave imprints that might be detected in relic radiation or large-scale structure.
2.5. Comparison with Other Discrete Quantum Gravity Approaches
Loop quantum gravity (LQG) discretizes space–time via spin networks, focusing on the geometric quantization of the gravitational field. QMM shares the concept of discrete geometry but extends beyond pure geometry by framing each quantum cell as an active information unit. The imprint operator structure provides a mechanism for matter and gauge fields to exchange information with the space–time quanta, an aspect not typically highlighted in LQG.
Causal set theory posits that space–time is a partially ordered set of events, capturing causal relations at the fundamental level. QMM, while discrete, differs by explicitly associating each cell x with a finite Hilbert space and implementing local unitarity via imprint operators. This emphasis on quantum informational capacity offers a more direct path for coupling to quantum fields and ensures gauge invariance can be built into the discretized framework.
2.6. Implications and Transition to Electromagnetism
By embedding quantum information directly into a discretized space–time, QMM addresses longstanding issues at the intersection of general relativity and quantum theory. However, the approach so far has been primarily examined with scalar or gravitational fields. Incorporating electromagnetism, governed by local U(1) gauge symmetry, raises essential questions:
Gauge Invariance: How do we construct imprint operators that remain invariant under local U(1) transformations?
Photon Imprints: What operators encode photon states and electromagnetic field strengths at each cell?
Charge and Current Interactions: How does charged matter leave gauge-invariant imprints that reflect electric and magnetic fields?
In the upcoming section, we extend the QMM framework to encompass electromagnetism. We provide explicit constructions of gauge-invariant imprint operators, show how U(1) gauge fields couple to space–time quanta, and demonstrate that the pillars of unitarity, locality, and covariance persist. This extension lays the foundation for a more comprehensive unified approach that may eventually include non-Abelian gauge fields and full Standard Model interactions.
3. Incorporation of Electromagnetism into QMM
In this section, we extend the QMM framework to include the electromagnetic field. Our aim is to formulate quantum electrodynamics (QED) on a discretized space-time such that local U(1) gauge symmetry, unitarity, and locality remain intact. We begin by introducing the U(1) gauge potential and its discretization, then develop imprint operators specifically suited for electromagnetic interactions, and finally derive the interaction Hamiltonian that preserves the fundamental QMM principles.
3.1. Gauge Symmetry and the Discretized Electromagnetic Field
In continuum QED, the electromagnetic field is described by a gauge potential
, transforming under local U(1) gauge transformations:
where
is a real function. The field strength tensor,
is gauge-invariant. Upon quantization,
becomes the photon field operator
, with canonical commutation relations satisfying the local U(1) symmetry.
In the QMM framework, space–time is discretized into Planck-scale cells . To preserve gauge invariance in a discrete setting, we adopt a procedure analogous to lattice gauge theory:
Each cell x stores electromagnetic degrees of freedom in a finite-dimensional Hilbert space .
The gauge field is represented by link variables or imprint operators that connect neighboring cells, ensuring local U(1) transformations remain well-defined at the discrete level.
For simplicity, one may represent the gauge field via exponentiated link operators , where a is the lattice spacing (Planck scale), and q is the charge coupling. However, a direct continuum-like operator can also be assigned to each cell, provided imprint operators are constructed to ensure gauge-covariance or gauge-invariance.
3.2. Constructing Gauge-Invariant Electromagnetic Imprint Operators
The key insight for incorporating electromagnetism into QMM is that
imprint operators must be built from gauge-invariant combinations of field variables to preserve local U(1) symmetry.
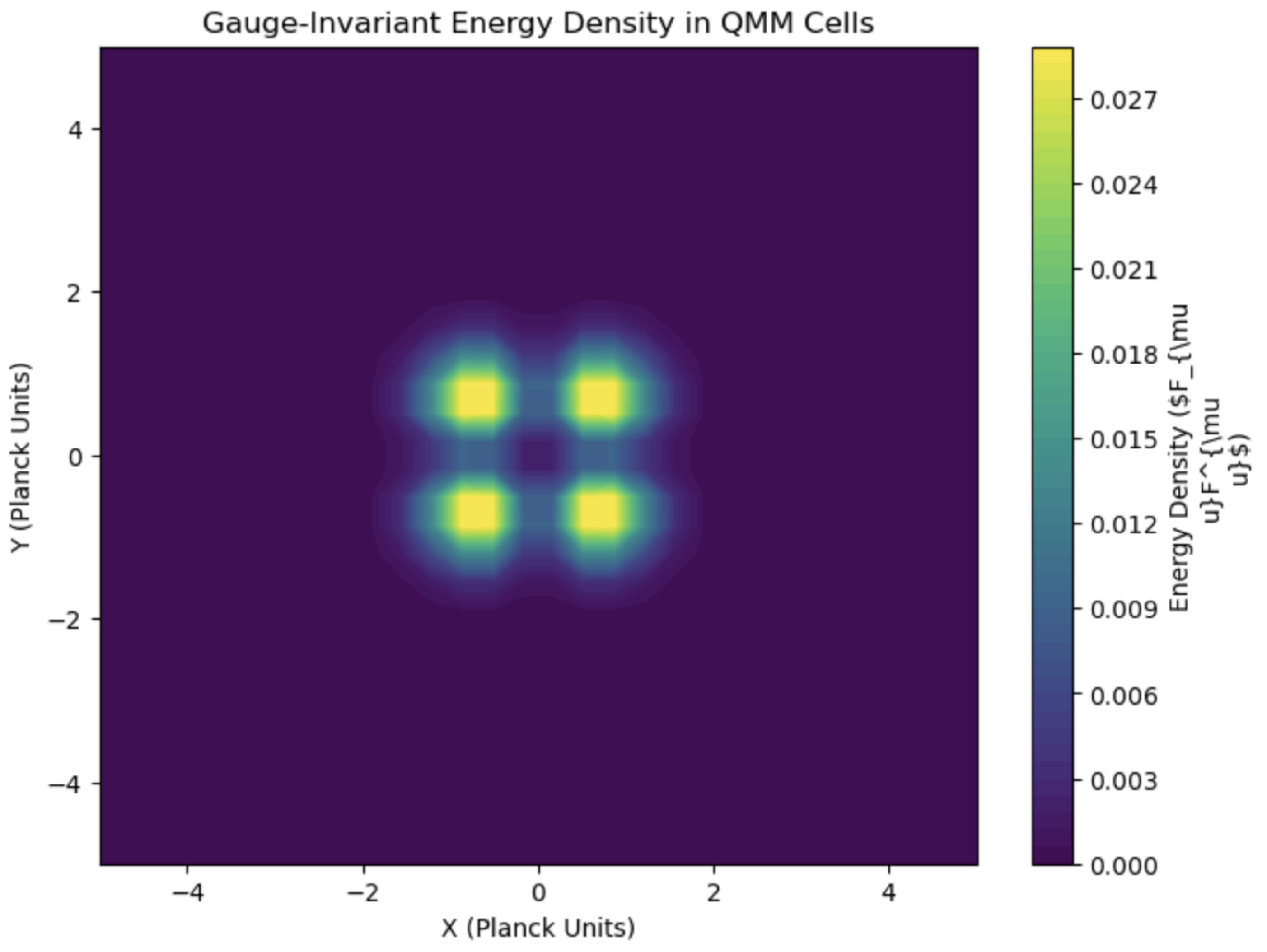
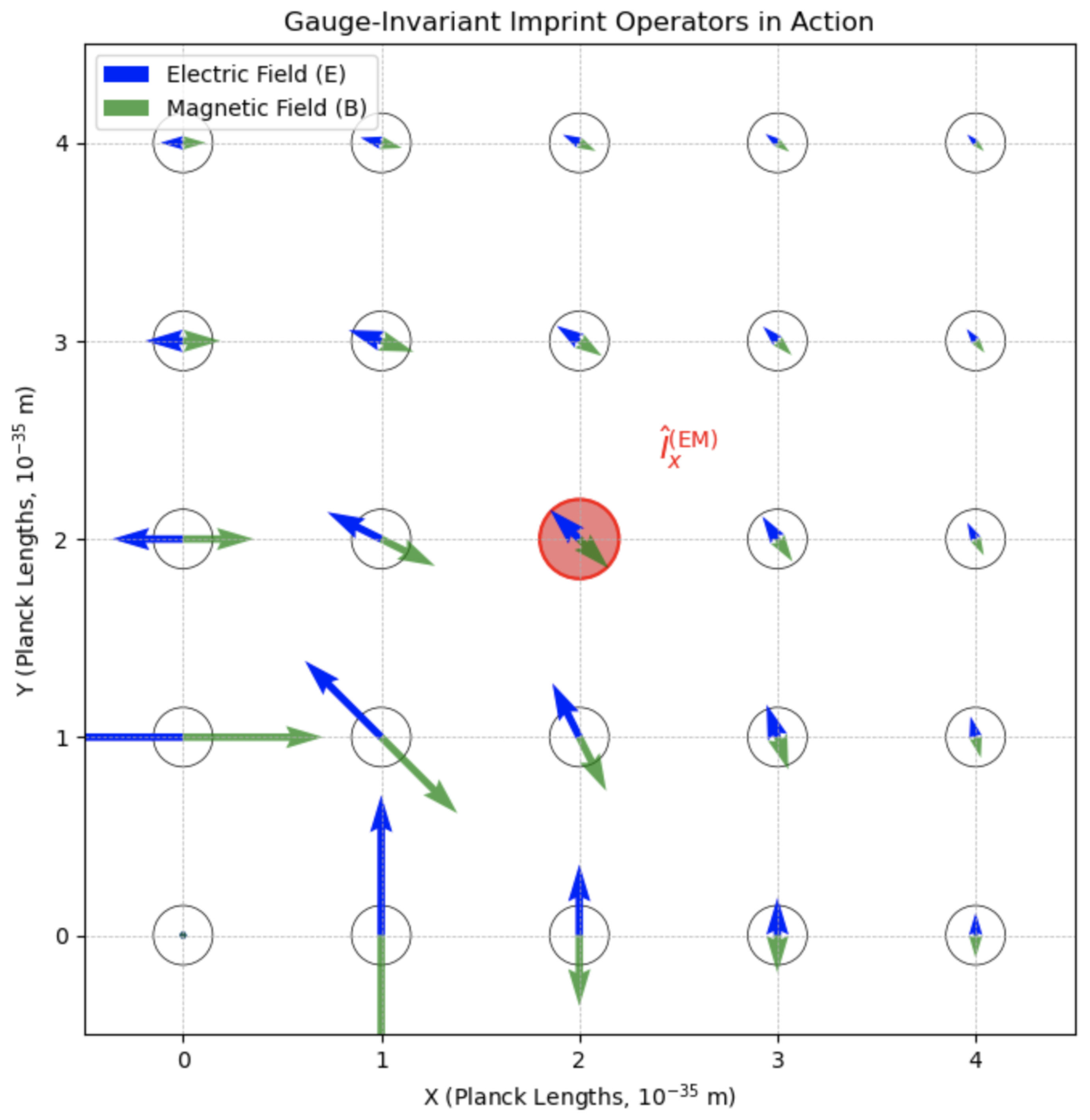
Figure 1 demonstrates the role of gauge-invariant operators in encoding electromagnetic information into QMM cells, ensuring gauge symmetry at the Planck scale. This gauge symmetry ensures that physical observables do not depend on a gauge function
and that the QMM framework does not introduce spurious gauge artifacts.
A straightforward choice for imprint operators encoding the free electromagnetic field is to use the operator-valued field strength tensor
.
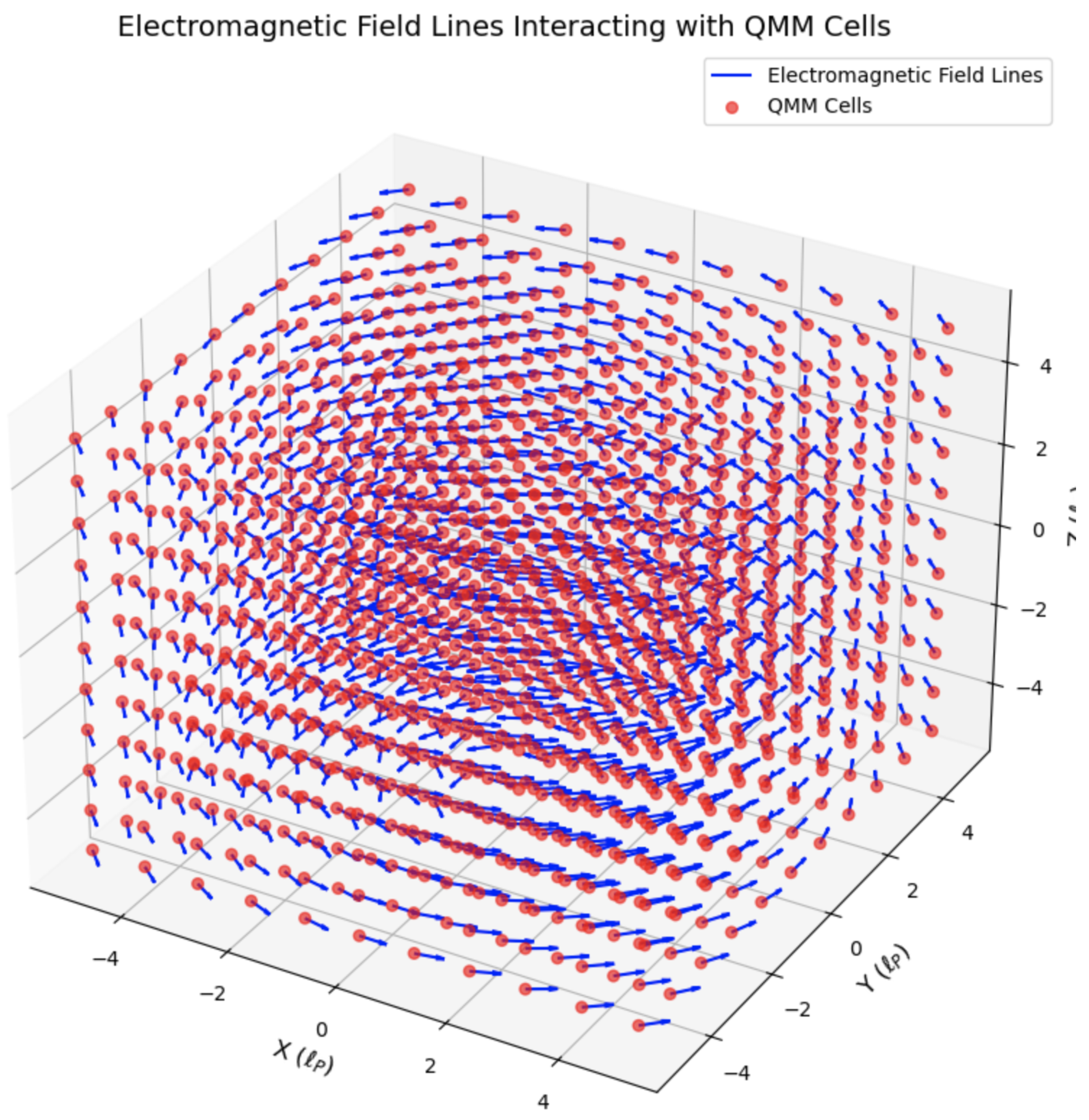
Figure 2 illustrates how electromagnetic field lines interact with QMM cells, emphasizing the role of gauge-invariant imprint operators in preserving information. For instance, a gauge-invariant imprint operator might be
where
is a coupling constant of appropriate dimension. This operator captures the local electromagnetic energy density (electric plus magnetic fields) at the discrete cell
x.
To describe charged matter fields (e.g., a Dirac field
), one needs to encode local charge-current interactions in the imprint operator. The minimal coupling is given by the covariant derivative
. A gauge-invariant combination involving the matter current
can be used:
where
and
are coupling constants. The first term records information about the free field strength; the second term imprints local charge-current data. Although
is gauge-dependent, the full operator
can be constructed in a gauge-covariant manner (for example, using link variables or by enforcing the condition that
appear only in gauge-invariant forms, such as
).
The precise functional form of depends on how is dimensioned. For a small enough dimensional Hilbert space at each cell (e.g., a qudit of dimension d), can be expressed in a truncated polynomial basis of local field operators. Higher-dimensional expansions may be necessary to capture nonlinear interactions or extended field configurations. Regardless of the dimension, the key requirement is that transforms covariantly (or is fully gauge-invariant) so as to preserve local U(1) symmetry.
3.3. Interaction Hamiltonian for QMM–Electromagnetism Coupling
We now assemble the total Hamiltonian, which includes contributions from:
: The standard QED Hamiltonian of the electromagnetic field and charged matter.
: The intrinsic Hamiltonian of space–time quanta, governing the internal dynamics of each cell and possible interactions between neighboring cells.
: The local interaction Hamiltonian coupling the electromagnetic field to the QMM via imprint operators.
Formally,
The Hamiltonian
includes the photon kinetic term
and matter field parts
, suitably discretized.
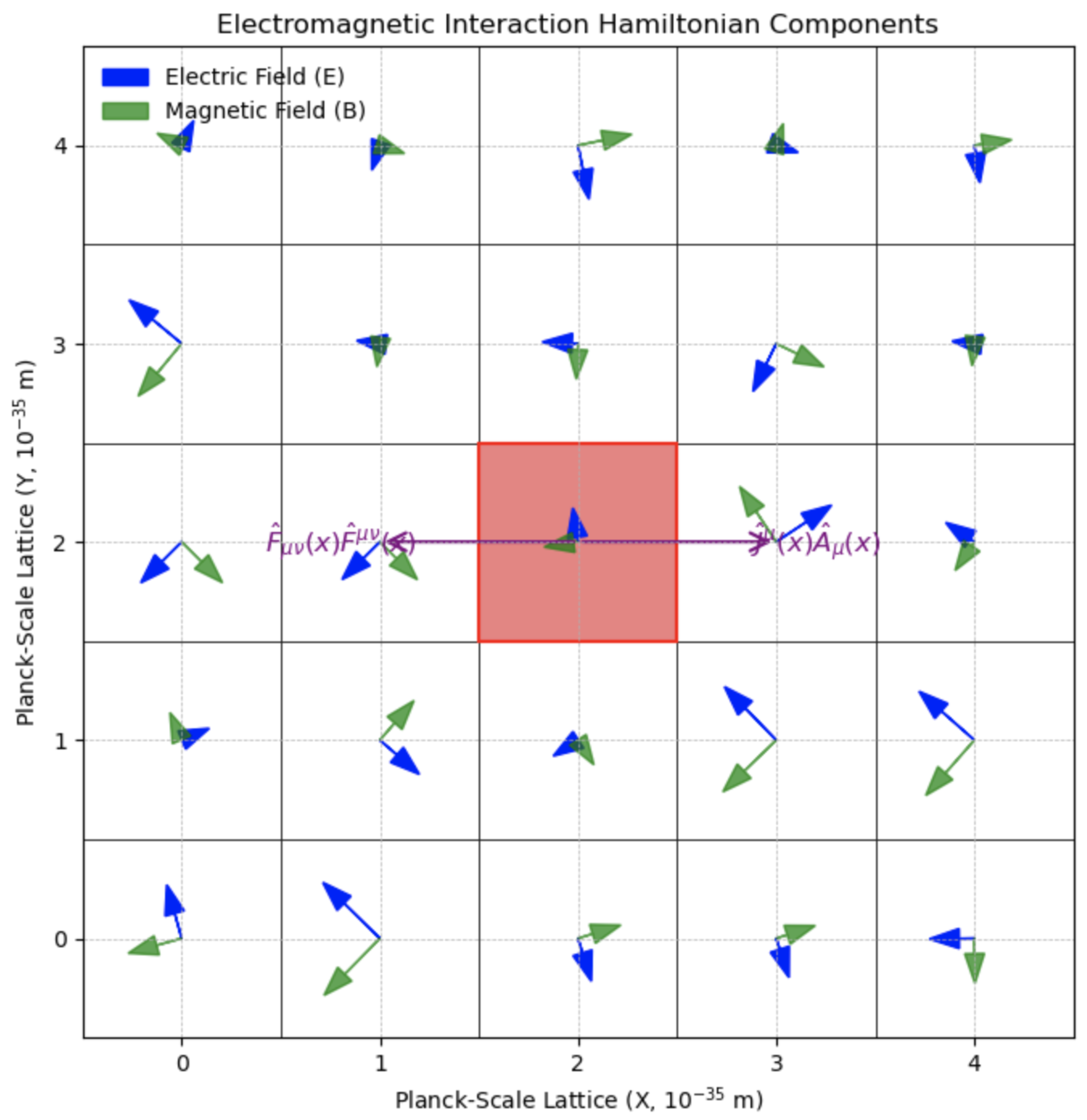
Figure 3 illustrates the interaction Hamiltonian’s role in coupling electromagnetic fields with QMM cells to maintain local gauge invariance.
The electromagnetic interaction Hamiltonian ensures consistency between QMM lattice cells and electromagnetic fields.
Figure 4 shows the decomposition of the electromagnetic interaction Hamiltonian, with contributions from gauge-invariant imprint operators and energy density terms. The electromagnetic interaction Hamiltonian, analogous to the scalar field imprint coupling, can be written as
Here,
and
act on the electromagnetic or matter Hilbert spaces, while
and
act on
. The ellipsis can include higher-order terms (e.g., self-interactions, nonlinear corrections).
Requiring to be Hermitian ensures probability conservation and unitarity of the full QMM–EM system. This typically demands to be self-adjoint or appear in Hermitian-conjugate pairs. Gauge invariance is maintained if and are built from gauge-invariant quantities like and matter currents that transform covariantly.
3.4. Preserving Unitarity, Locality, and Gauge Invariance
Since is Hermitian, the time evolution operator is unitary. Locality is enforced by constructing the Hamiltonian so that imprinting interactions occur only at the same cell x. This ensures that no instantaneous correlations arise between distant cells, thus upholding the principle of causality.
Crucially, to preserve gauge symmetry, the imprint operators should be either strictly gauge-invariant or gauge-covariant in a manner that yields gauge-invariant physics. For instance, using link variables ensures that the imprint operators remain consistent under local transformations . The QMM thus encodes physically meaningful (i.e., gauge-invariant) electromagnetic data.
3.5. Implications for Charged Black Holes and QED Vacuum Structure
Incorporating electromagnetism within QMM enables the study of charged black holes (Reissner–Nordström or Kerr–Newman space–times) at the Planck scale. Imprints of charge distributions and electromagnetic field strengths are stored in QMM degrees of freedom at or just inside the horizon cells. As the black hole radiates, outgoing photons and charged particles interact again with these quanta, retrieving phase information and correlations that would otherwise appear lost. This yields non-thermal Hawking radiation signatures carrying the black hole’s electromagnetic memory, consistent with unitarity.
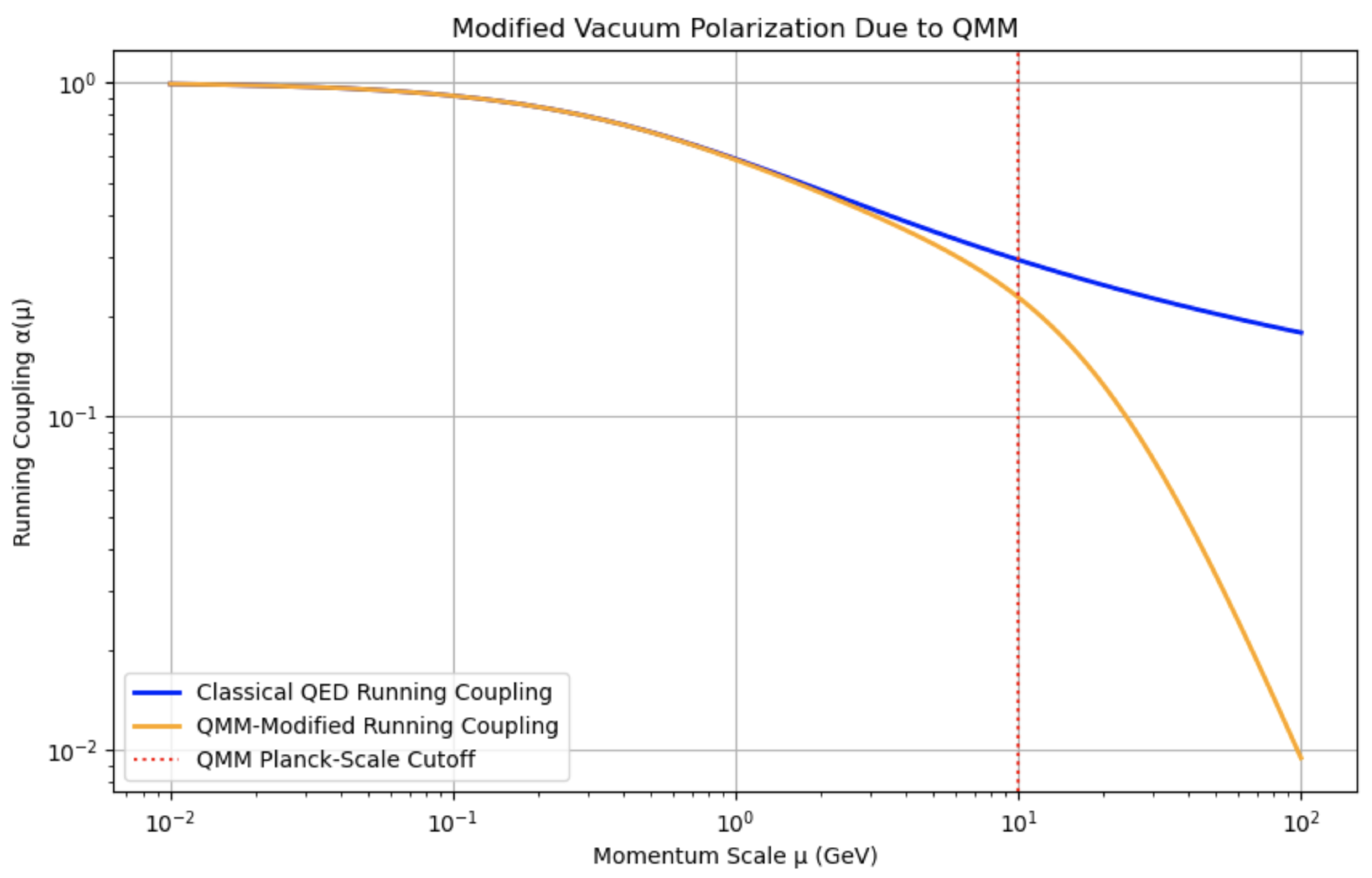
The discrete nature of QMM imposes an intrinsic UV cutoff around the Planck scale, potentially modifying vacuum polarization effects. Loop integrals in QED, which typically diverge in the continuum, become finite sums over discrete modes. This may alter the running of the electromagnetic coupling at trans-Planckian scales. While standard renormalization procedures apply at energies , QMM suggests that the coupling constants may level off or exhibit novel behavior near the Planck scale.
The presence of a QMM-encoded electromagnetic field in the early universe can influence magnetogenesis or reionization, leaving imprints on the cosmic microwave background (CMB) and large-scale structure.
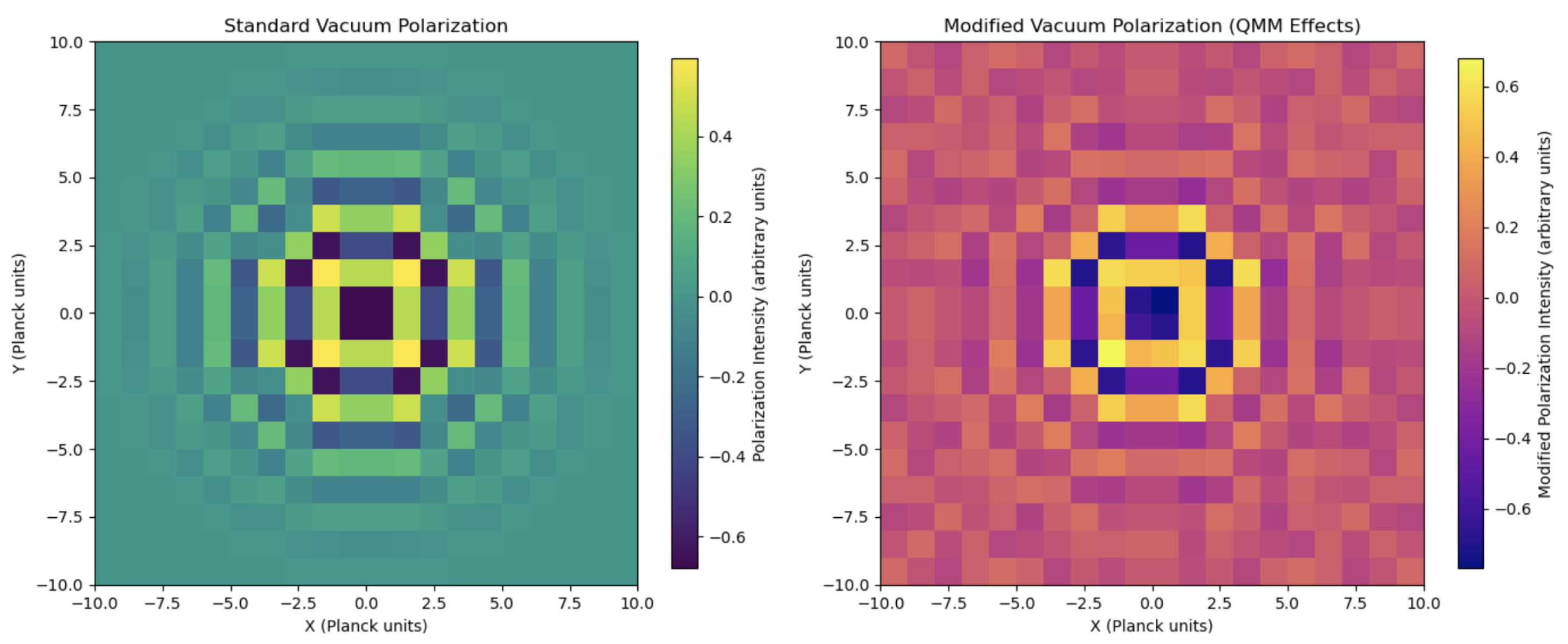
Figure 5 shows modified vacuum polarization patterns due to QMM effects, suggesting observable imprints in the cosmic microwave background. Tiny deviations from standard cosmological predictions (e.g., modified polarization spectra) might arise due to QMM discretization effects at extremely high energies, providing a potential observational window into Planck-scale physics.
Figure 6 expands on modified vacuum polarization patterns, emphasizing QMM’s role in altering small-scale cosmological predictions.
3.6. Towards a Fully Unified Field Theory
By embedding electromagnetism into the QMM, we have demonstrated how local gauge invariance can be preserved in a discretized space–time that serves as an active information reservoir. This achievement sets the stage for further unification endeavors:
Non-Abelian Gauge Fields. Incorporating SU(2) or SU(3) gauge groups (as in the electroweak and strong interactions) requires generalizing imprint operators to handle non-Abelian field strength tensors and link variables.
Full Standard Model Integration. Extending the QMM approach to the entire Standard Model, including quark and lepton fields, Yukawa couplings, and the Higgs mechanism, would move one step closer to a quantum gravity framework describing all fundamental interactions.
Quantum Gravity Coupling. While the original QMM formulation addressed gravitational degrees of freedom, an integrated QMM-based theory of quantum gravity plus all gauge interactions remains the ultimate objective.
We have introduced the electromagnetic field into the Quantum Memory Matrix framework by carefully constructing gauge-invariant imprint operators and embedding local U(1) transformations into discrete space–time quanta. The resulting interaction Hamiltonian preserves unitarity, locality, and gauge invariance, allowing the QMM to store and retrieve information about electromagnetic processes without violating fundamental principles. This development enables QMM-based treatments of charged black hole evaporation, vacuum polarization, and cosmological photon fields, advancing us toward a unified quantum theory of fields and geometry. In the next section, we explore the physical consequences of these constructions, focusing on black hole information retrieval, vacuum structure modifications, and potential observational signatures.
4. Applications to Black Hole Information, Vacuum Structure, and Cosmology
Having extended the QMM framework to incorporate U(1) gauge invariance and electromagnetic fields, we now investigate three key arenas where electromagnetism and gravity intersect: charged black holes, vacuum polarization at trans-Planckian energies, and early-universe cosmology. These applications illustrate how the QMM unifies quantum information encoding with gauge interactions in contexts that probe the Planck scale.
4.1. Charged Black Holes and Information Retrieval
Black holes carrying electric charge are classically described by the Reissner–Nordström or Kerr–Newman solutions, depending on their angular momentum. In classical general relativity, these solutions are labeled solely by mass
M, charge
Q, and angular momentum
J. However, they seemingly reveal no internal quantum structure (the no-hair theorems). In the QMM framework, charged matter fields collapsing into a black hole imprint their quantum information—including charge distributions and electromagnetic field configurations—onto the local QMM degrees of freedom near and inside the horizon.
Figure 7 illustrates the process of charged black hole information retrieval, showing the stepwise interactions between QMM cells and emitted Hawking radiation during evaporation.
As the horizon forms, imprint operators such as
record the electromagnetic field strength and local currents within the relevant horizon cells
x. This record-keeping ensures that the black hole is not truly characterized by just
. Instead, a more detailed quantum memory of the initial charged matter state resides in the QMM Hilbert spaces
.
Semiclassical arguments predict that Hawking radiation is approximately thermal, carrying negligible information about the black hole’s internal microstates. However, once electromagnetic degrees of freedom are coupled to QMM imprint operators, outgoing photons and charged particles continually interact (directly or indirectly) with the QMM quanta encoding the horizon’s memory.
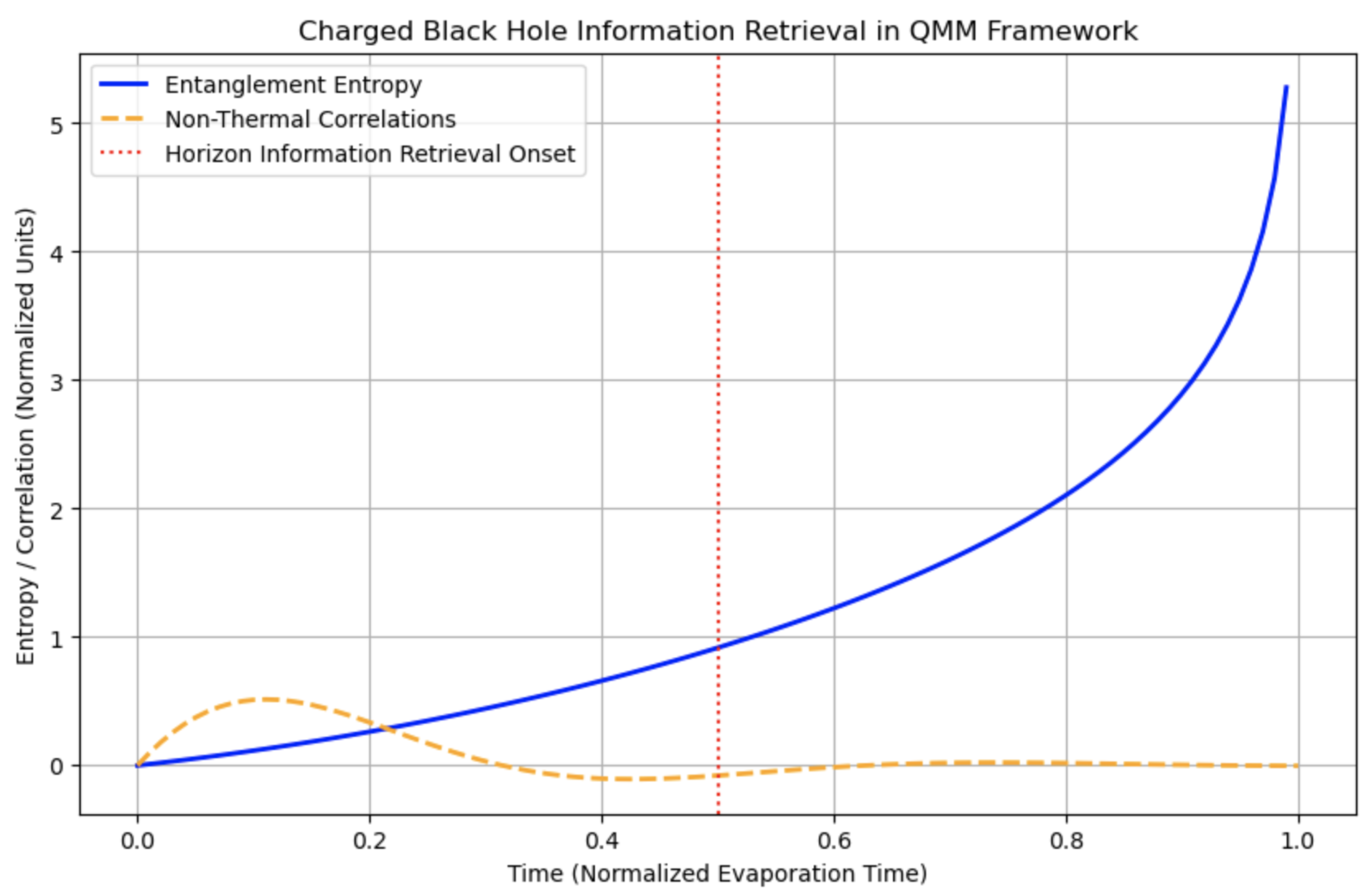
Over the course of evaporation, these subtle interactions introduce non-thermal correlations into Hawking radiation.
Figure 8 highlights the evolution of entanglement entropy and non-thermal correlations during the evaporation process, demonstrating the role of QMM in restoring unitarily. Namely:
The QMM cells near the horizon store local electromagnetic data.
Outgoing radiation modes (photons, charged quanta) interact again with the QMM degrees of freedom, picking up phases and correlations reflective of the black hole’s formation history.
Over many emission events, the radiation accumulates entanglement with the stored QMM states, gradually releasing all the information—including charge distribution details—that initially collapsed into the black hole.
This mechanism alters the Page curve for entanglement entropy, ensuring it returns to zero when the black hole fully evaporates, thus preserving quantum unitarity.
While providing a fully dynamical calculation of QMM-based charged black hole evaporation goes beyond the scope of this paper, one can outline possible observational consequences:
Charge-Dependent Correlations: Hawking radiation may exhibit subtle charge-sensitive correlation functions, measurable in principle if one could detect extremely small deviations from thermality.
Entanglement Entropy Evolution: The entanglement entropy of the outgoing radiation deviates from the standard semiclassical Page curve, reflecting the gauge-invariant information encoded in .
Observing these effects directly is extraordinarily challenging, but analogous features might be testable in laboratory analog systems or through gravitational wave ringdown analyses if charge effects are not overwhelmed by astrophysical environments.
4.2. Vacuum Polarization and UV Behavior
One of the long-standing puzzles in quantum field theory is how to manage the divergences in loop integrals, especially in QED. Conventional renormalization techniques yield finite results at presently accessible energies but leave open questions about behavior at trans-Planckian regimes. In the QMM framework, space–time discretization at the Planck scale provides a physical cutoff:
where
is the Planck length. Loop integrals for vacuum polarization and self-energy diagrams become finite sums over discrete momentum modes or Planck-cell excitations.
In continuum QED, the effective coupling runs with energy scale . In the QMM discretization, the high-energy running may deviate from the standard logarithmic flow due to the natural cutoff. At or near the Planck scale, the coupling might saturate or exhibit novel behavior, suggesting a possible UV-complete scenario for QED without additional degrees of freedom. One could imagine an effective renormalization group (RG) flow that transitions to discrete summations of modes, ensuring no Landau pole arises.
The QMM might also modify zero-point energies and Casimir-like forces at extremely short distances. Normally, these phenomena depend on integrating field modes up to arbitrarily high momenta. With QMM, the Hilbert space dimension at each cell is finite, cutting off infinite mode sums and potentially altering the vacuum energy density. Such effects, if not canceled by gravitational backreaction, may have implications for the cosmological constant problem, though the details require a careful QMM-based renormalization analysis.
4.3. Early-Universe Cosmology and Primordial Fields
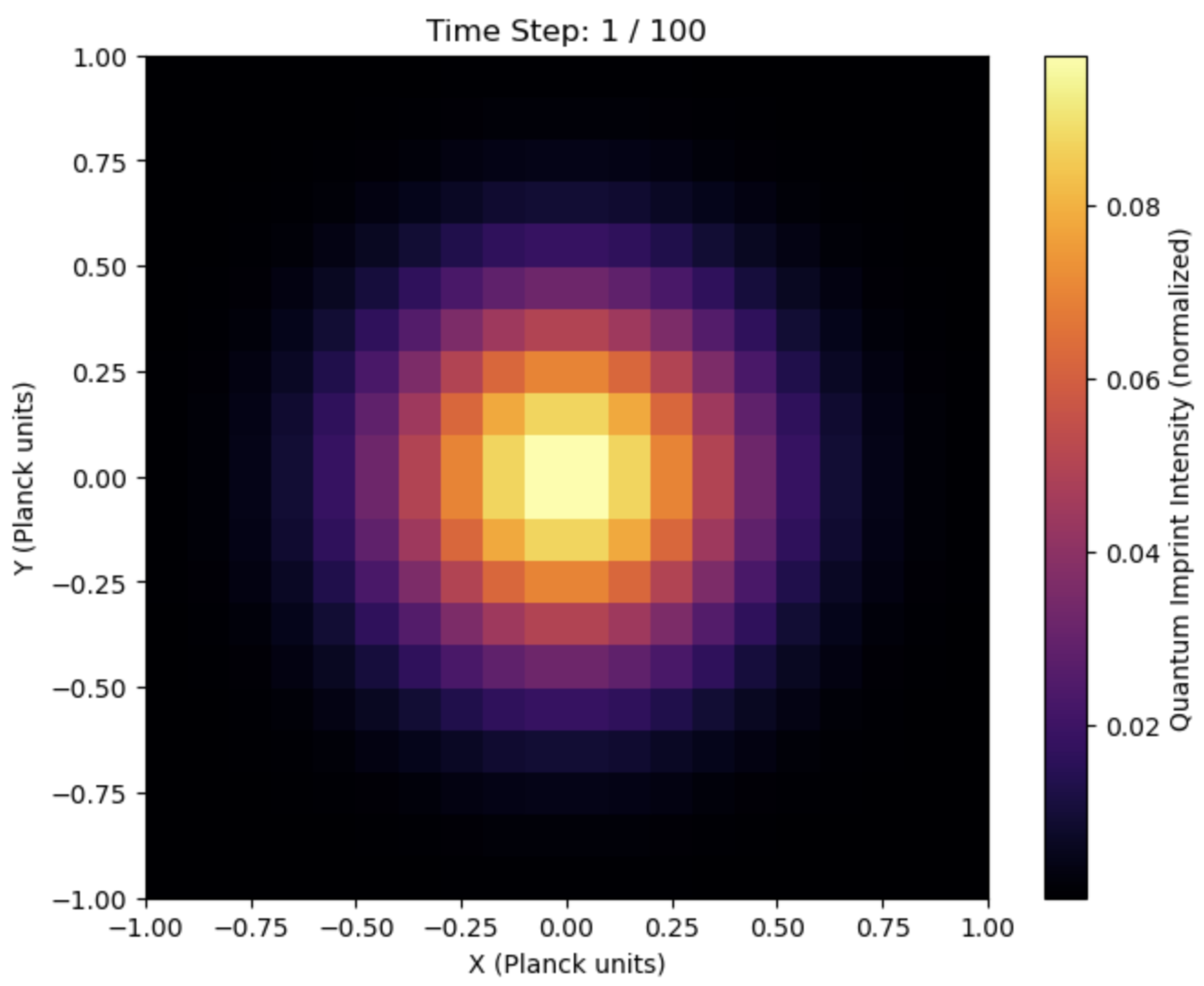
Cosmological magnetogenesis posits that tiny seed magnetic fields generated in the early universe could be amplified to the large-scale magnetic fields observed in galaxies and clusters. Standard magnetogenesis scenarios often rely on inflationary dynamics or phase transitions. In QMM, Planck-scale discretization and local imprint operators could endow the nascent electromagnetic field with quantum imprints that seed primordial magnetism.
Quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field at the Planck epoch, encoded in QMM cells, may evolve into subtle anisotropies or polarization patterns in the cosmic microwave background (CMB).
Figure 9 illustrates QMM-induced effects on early-universe electromagnetic fluctuations, highlighting their potential cosmological imprints. The QMM imprint mechanism could introduce:
Non-Gaussianities: Additional correlations beyond the standard CDM predictions, potentially detectable in high-precision CMB polarization surveys.
Small-Scale Power Modulations: Slight modifications to the power spectrum at scales approaching the horizon at recombination, especially if QMM discretization influences early-universe dynamics.
While observing such tiny signatures directly is difficult, next-generation CMB and 21-cm line experiments might constrain or reveal QMM-induced electromagnetic effects in the early universe.
4.4. Analog Models and Prospects for Experimental Tests
Directly probing Planck-scale physics is beyond current technology. However, quantum simulators (e.g., cold-atom lattices, superconducting qubits) offer controllable environments to mimic certain aspects of QMM discretization and local gauge invariance. By engineering U(1) lattice gauge theories with imprint-like operators,
one can investigate how local information encoding and retrieval might manifest in a discrete quantum system. Observing emergent entanglement patterns or correlation functions in these analog models can validate the QMM approach at an operational level.
Analogs of event horizons—such as sonic horizons in Bose–Einstein condensates (BECs) or optical waveguide arrays—allow investigation of Hawking-like radiation phenomena. Incorporating electromagnetic field analogs in these systems, one might reproduce the imprint-and-retrieval cycle that QMM posits for real black holes. If measured correlation functions deviate from purely thermal predictions in ways consistent with QMM, this could offer partial empirical support for the QMM hypothesis.
4.5. Toward a Unified QMM-Based Field Theory
Extending QMM to non-Abelian gauge fields (SU(2), SU(3)) requires generalizing the gauge-invariant imprint operators to field strength tensors and non-Abelian currents. This step is crucial for merging the electroweak and strong sectors of the Standard Model into the QMM scheme, forming a comprehensive discrete quantum gravity and gauge theory approach.
Ultimately, the QMM approach aims to unify gravitational, gauge, and matter degrees of freedom within a single discretized, information-centric framework. By assigning each space-time quantum a finite-dimensional Hilbert space that can store gravitational and gauge imprints, QMM offers a plausible route to a finite and unitary theory of all fundamental interactions.
By incorporating electromagnetism into the QMM, we have examined charged black hole evaporation, vacuum polarization, and early-universe electromagnetic fields through the lens of Planck-scale quantum information encoding. These applications highlight the potential of QMM to resolve the black hole information paradox for charged holes, provide a UV completion mechanism for QED, and modify cosmological magnetogenesis scenarios. Although experimental verification remains challenging, laboratory analogs and future high-precision cosmological observations may offer indirect probes of QMM predictions. Building upon these insights, the next steps involve extending QMM to non-Abelian gauge fields and seeking a truly unified theory of gravity and all known interactions within a discretized quantum information substrate.
5. Comparison with Existing Approaches and Theoretical Consistency
In the previous sections, we presented the QMM framework as a unifying approach to quantum gravity and electromagnetism, integrating gauge-invariant imprint operators and ensuring that information is stored and retrieved in a manner consistent with unitarity, locality, and gauge invariance. We now compare QMM with other major approaches addressing the black hole information paradox and quantum gravity, highlighting the advantages and distinctions of QMM’s locally defined mechanism for information storage. We also examine theoretical consistency requirements of QMM and discuss open questions that must be addressed to fully realize a Planck-scale unification.
5.1. Holography and the Holographic Principle
One of the most influential modern paradigms for quantum gravity is the holographic principle, particularly realized in the AdS/CFT correspondence. Holography posits that the degrees of freedom in a bulk gravitational system can be mapped onto a lower-dimensional boundary field theory, elegantly resolving many conceptual puzzles related to the black hole information paradox.
Comparison with QMM:
Bulk vs. Boundary Encoding. Unlike holographic approaches, where the fundamental description is relegated to a boundary theory, QMM posits that space–time itself—throughout the bulk—acts as a dynamic quantum information reservoir. This bulk-centric approach is potentially more compatible with realistic cosmologies, which often do not exhibit AdS-like boundary conditions.
Discretized vs. Continuum Boundary Data. AdS/CFT works with a continuum boundary field theory, whereas QMM discretizes the entire four-dimensional geometry at the Planck scale. The QMM discretization avoids reliance on a specific asymptotic geometry and aims to be generally applicable, including de Sitter or other cosmological space–times.
Local Mechanisms vs. Nonlocal Mapping. Holography implements an isomorphism between bulk and boundary Hilbert spaces, often relying on nonlocal transformations. By contrast, QMM encodes information locally in Planck-scale cells, sidestepping the need for nonlocal maps.
While holography has proven remarkably successful in asymptotically AdS space–times, direct applicability to realistic de Sitter cosmology remains uncertain. QMM offers a local resolution to the black hole information paradox that does not require an AdS boundary, making it an attractive alternative in broader cosmological scenarios.
5.2. ER=EPR, Wormholes, and Nonlocal Mechanisms
The ER=EPR conjecture proposes that Einstein–Rosen bridges (wormholes) correspond to entangled pairs of particles. This line of thinking seeks to explain black hole information recovery by hypothesizing that entanglement across a horizon is geometrically manifested via wormholes, potentially allowing nonlocal correlations to transport information.
Comparison with QMM:
Local vs. Nonlocal Resolution. QMM emphasizes a strictly local encoding of information in Planck-scale Hilbert spaces. ER=EPR, in contrast, suggests nontrivial topological connections (wormholes) that could mediate entanglement.
Involving Topology Changes vs. Planck-Scale Memory. ER=EPR implicitly relies on modifications to the global topology of space–time. QMM posits no radical topology change; instead, all quantum information is stored locally in finite-dimensional Hilbert spaces.
Observational Distinctions. If signatures were found that point to genuinely nonlocal correlations or wormhole-mediated phenomena, these would favor ER=EPR-like scenarios. Conversely, strictly local correlations and the absence of wormhole-type connectivity would favor QMM.
Although wormholes may exist within broader theories of quantum gravity, QMM demonstrates that it is at least possible to solve the information paradox without invoking large-scale nonlocal structures.
5.3. Firewalls, Complementarity, and Observer-Dependence
The firewall paradox challenges black hole complementarity by suggesting that an infalling observer encounters a high-energy barrier at the horizon, ostensibly violating the equivalence principle. Proponents of firewalls argue that preserving unitarity and standard quantum field theory in black hole evaporation forces a breakdown of the smooth horizon picture.
Comparison with QMM:
Smooth Horizons vs. Firewalls. QMM sustains smooth horizons for infalling observers, as the quantum imprints are Planck-scale effects embedded in the local Hilbert spaces of horizon cells. No macroscopic firewall forms because the QMM mechanism disperses information throughout the Planck-scale structure of space–time, preserving the equivalence principle.
Observer-Independent Encoding. In QMM, the imprinted information is stored objectively at each cell, irrespective of an observer’s frame. This contrasts with black hole complementarity, where the fate of information can be observer-dependent.
Thus, QMM provides a scenario wherein both the equivalence principle and quantum unitarity hold, obviating the need for radical horizon-scale disruptions like firewalls.
5.4. Loop Quantum Gravity, Spin Foams, and Causal Sets
Loop quantum gravity (LQG) and spin foam models discretize geometry by quantizing the gravitational field, while causal set theory envisions space–time as a partially ordered set reflecting its causal structure. These frameworks highlight the fundamentally discrete nature of geometry, aiming to unify quantum theory and gravity without extra dimensions.
Comparison with QMM:
Emphasis on Quantum Information: While LQG and spin foams focus primarily on geometric quantization, QMM introduces the notion of quantum imprints to encode and retrieve local quantum information. This explicit link to quantum information flow is less central in LQG and causal sets.
Gauge Field Incorporation: Non-Abelian gauge fields and matter couplings pose challenges in LQG and spin foam approaches. QMM takes a direct approach to gauge fields via imprint operators, potentially simplifying the integration of matter and interactions.
Unitarity in Black Hole Evaporation: Demonstrating unitarity in black hole evaporation remains an open issue in LQG/spin foam frameworks. QMM addresses unitarity directly by treating space–time quanta as dynamic Hilbert spaces that store and later release all quantum information.
QMM could be seen as complementary to these geometric discretization programs, adding a specialized quantum informational mechanism that might be grafted onto or combined with LQG/spin foam techniques.
5.5. Minimal Length Scenarios and UV Regularization
Minimal length scenarios assert that the Planck length is the smallest operational scale, effectively introducing a cutoff. Conventional quantum field theories often require ad hoc regularizations (e.g., momentum cutoffs). The QMM discretization naturally encodes this minimal length into the finite dimensionality of local Hilbert spaces.
Comparison with QMM:
Cutoff Interpretation. QMM interprets the Planck-scale cutoff as the maximum resolution of each cell’s Hilbert space, elegantly linking the minimal length concept to quantum information capacity.
Operational Meaning. Rather than simply imposing a momentum cutoff, QMM provides an operational meaning: no physical processes can probe smaller scales than the dimension of allows, preserving unitarity and avoiding divergences.
This viewpoint bridges “minimal length” ideas with discrete quantum gravity, clarifying how fundamental cutoffs might arise from the structure of space–time itself.
5.6. Challenges, Open Questions, and Future Directions
Although QMM presents a coherent pathway toward unifying quantum gravity and gauge fields, several unresolved challenges deserve further exploration:
Non-Abelian Gauge Groups. Extending the QMM approach to SU(2), SU(3), or larger gauge groups remains technically intricate. Gauge-invariant imprint operators for non-Abelian fields must capture local color degrees of freedom, self-interactions, and the phenomenon of confinement.
Dynamical Quantum Geometry. The QMM has so far been formulated on a discretized geometry introduced by hand. A fully dynamical model would endogenously generate the space–time discretization, possibly integrating insights from loop quantum gravity, spin foams, or other covariant approaches.
Renormalization and Low-Energy Effective Theories. The interplay between QMM discretization and standard renormalization group flows in QED or the Standard Model is not fully understood. An in-depth analysis of how discrete Planck-scale Hilbert spaces alter the running of couplings at intermediate energies is vital to connecting QMM with established phenomenology.
Empirical Signatures. Testing Planck-scale effects is notoriously difficult, yet subtle signatures (e.g., deviations in black hole radiation spectra, modifications to cosmic microwave background anisotropies, or anomalies in gravitational wave ringdown) might provide indirect confirmation. Designing observational strategies or analog experiments to isolate QMM-specific predictions is an ongoing challenge.
5.7. Advantages of QMM and the Path Ahead
Despite open questions, QMM stands out as a local, covariant framework that systematically encodes quantum information into space–time quanta. It resolves black hole information paradoxes without requiring exotic boundary geometries, wormholes, or firewalls, and it accommodates gauge fields in a manner consistent with local U(1) invariance.
Key Strengths:
Local Unitary Mechanism. By associating finite-dimensional Hilbert spaces with space–time cells, QMM circumvents nonlocal mechanisms and retains a manifestly local interpretation of information storage and retrieval.
Integration of Gauge Symmetries. QMM’s imprint operators are constructed from gauge-invariant field strengths and matter currents, enabling straightforward incorporation of electromagnetism—and, potentially, other gauge groups.
Natural UV Cutoff. The discrete Hilbert space dimension at each cell enforces a Planck-scale cutoff, rendering loop integrals finite and offering a UV completion approach in principle.
The Road to Full Unification:
Extending QMM to the non-Abelian sector (e.g., SU(3) for QCD) and coupling it with a dynamical quantum geometry remains the ultimate goal. If successful, this line of research could yield a discrete, background-independent, and fully unified quantum gravity theory that is testable through indirect observational and analog experiments.
By situating QMM alongside holography, ER=EPR wormhole proposals, LQG/spin foams, and minimal length scenarios, we see that QMM offers a unique emphasis on local quantum information processing in space–time quanta. It addresses black hole information problems and potential UV completions of gauge theories without necessitating nonlocal effects or specialized boundary conditions. Nevertheless, a full dynamical implementation, including non-Abelian gauge groups and a robust renormalization scheme, remains an open frontier. In the next section, we explore potential observational strategies and experimental analogs that may provide indirect validation or constraints on the QMM framework.
6. Experimental and Observational Perspectives
Extending the QMM framework to electromagnetic fields yields distinctive predictions that subtly depart from standard quantum field theory, general relativity, and semiclassical black hole thermodynamics. Although directly probing Planck-scale physics lies far beyond current technological capabilities, these deviations may still manifest indirectly in astrophysical and cosmological contexts or through suitable laboratory analog experiments. This section surveys potential observational strategies and experimental testbeds for the QMM hypothesis, with particular attention to distinguishing QMM-specific signatures from other new physics scenarios.
6.1. Non-Thermal Features in Black Hole Evaporation
A key prediction of QMM is that Hawking radiation from black holes—charged, rotating, or otherwise—may exhibit non-thermal correlations reflecting Planck-scale imprint operators. While the low temperature of astrophysical black holes and accretion noise obscure such signals, primordial black holes (PBHs) formed in the early universe and now nearing the end of their lifetimes could emit high-energy gamma rays or cosmic rays. If the evaporation spectra of these PBHs deviate from a purely thermal, Planckian distribution and display correlation patterns consistent with QMM encoding, this would constitute a signature of Planck-scale quantum information retention. Future gamma-ray observatories (such as CTA or advanced Fermi instruments) or cosmic-ray detectors could potentially detect anomalous emission features. Although constraints on PBH abundance are stringent, even null results would place upper bounds on the fraction of PBHs that exhibit QMM-like deviations from standard Hawking emission.
Gravitational wave detectors like LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA can already observe the inspiral and merger phases of stellar-mass black hole binaries, but upcoming observatories (including LISA, the Einstein Telescope, and Cosmic Explorer) may capture more subtle ringdown-phase anomalies. QMM-induced modifications to the horizon’s quantum memory could introduce small deviations in the quasi-normal modes predicted by general relativity, with late-time ringdown dynamics exhibiting phase shifts or amplitude modulations indicative of horizon-scale information retrieval. Such signals would be extremely challenging to detect, demanding high signal-to-noise ratios and careful waveform modeling. Nonetheless, suppose ringdown anomalies correlated with black hole parameters are ever identified. In that case, they might bolster the idea that QMM-like processes enable retrieval of quantum information at the horizon, thereby restoring unitarity.
6.2. Cosmic Microwave Background and Large-Scale Structure
When QMM discretization and electromagnetic imprints act in the early universe, subtle signatures could emerge in cosmological observables. For instance, primordial electromagnetic fields, if subject to QMM imprinting, might modify the cosmic microwave background (CMB) polarization patterns or correlation functions. One possible manifestation is the appearance of non-Gaussian correlations or scale-dependent spectral features in the E-mode or B-mode polarization. High-sensitivity polarization campaigns, including LiteBIRD or future CMB-S4 projects, might detect these subtle anomalies if they deviate from the standard inflationary predictions. QMM discretization at the Planck epoch might also influence magnetogenesis, generating slight changes in the coherence scale of primordial magnetic fields. Such changes could affect large-scale intergalactic magnetism and possibly imprint in Faraday rotation measurements or gamma-ray blazar halos. Alterations to small-scale power or matter-radiation coupling may likewise influence structure formation in ways that are broadly consistent with minimal additional assumptions but differ from competing new physics explanations.
6.3. Laboratory Analog Experiments and Quantum Simulators
Direct Planck-scale experimentation remains out of reach, yet laboratory analog systems and quantum simulators offer a means to probe QMM concepts in a controlled environment. Sonic horizons engineered in Bose–Einstein condensates can mimic aspects of Hawking-like radiation, and introducing local imprint-like interactions (akin to artificial QMM cells) might reveal correlations analogous to those predicted by QMM. Similar setups in optical waveguides or superconducting circuit resonators allow effective horizons to be studied; observing non-thermal correlations in emitted excitations could partially validate the QMM’s local memory mechanism for horizon-scale unitarity. Meanwhile, recent advancements in quantum computing—such as Rydberg atom arrays, trapped ions, or superconducting qubits—enable discretized gauge theory simulations. One can define operators on each lattice site to play the role of QMM imprint operators, storing and releasing quantum information as the system evolves. Monitoring entanglement patterns in these simulated gauge theories may confirm the feasibility of QMM’s imprint-and-retrieval cycle. If emergent correlation structures or non-thermal features mimic QMM predictions, these experiments would provide a proof-of-concept demonstration of the QMM hypothesis.
6.4. Distinguishing QMM Effects from Other New Physics
Deviations from standard expectations, if detected, must be distinguished from alternative new physics explanations. The QMM’s approach is rooted in strictly local, gauge-invariant Planck-scale imprint mechanisms, whereas some other scenarios rely on nonlocal phenomena like wormholes or extra dimensions. In principle, QMM-induced modifications to Hawking radiation or cosmological fields exhibit particular correlation structures guided by local imprint operators, a hallmark absent in many competing theories. QMM also does not invoke exotic topological changes or radical symmetry-breaking beyond the discretization at the Planck scale. If the simplest, gauge-consistent explanations match observed anomalies, this would argue in favor of QMM over more elaborate frameworks.
6.5. Long-Term Outlook: Indirect Probes and Future Missions
Direct Planck-scale testing is beyond present technologies, but a synergy of theoretical models, astrophysical observations, precision cosmology, and quantum simulator experiments could place meaningful constraints on or lend indirect support to QMM. High-sensitivity gamma-ray telescopes might detect non-thermal PBH evaporation spectra, and next-generation gravitational wave detectors could reveal ringdown anomalies consistent with horizon-level information retrieval. Advanced CMB or 21-cm line surveys might observe unusual polarization or non-Gaussian signals indicative of Planck-scale discretization in electromagnetic fields. Concurrently, quantum simulator platforms may replicate imprint-and-retrieval processes with engineered local Hilbert spaces. Though each path involves significant challenges, collectively, they can narrow the range of viable discrete quantum gravity theories. If multiple lines of evidence suggest that space–time itself functions as a dynamic information reservoir, the QMM approach would gain significant credibility as a unifying quantum information framework for gravity and gauge fields.
7. Conclusion
We have introduced a framework that extends the QMM hypothesis—originally developed to address the quantum-gravity interface and the black hole information paradox—into the domain of electromagnetism. By quantizing space–time into discrete cells and embedding quantum information directly in this discrete substrate, the QMM framework allows gravitational and electromagnetic fields to leave imprints at the Planck scale, thus acting as dynamic information reservoirs that preserve unitarity and encode the full quantum history of interactions. In doing so, this approach offers a way to integrate the U(1) gauge invariance of electromagnetism without breaking locality or introducing nontrivial topologies such as wormholes, resulting in a mechanism by which even charged black holes can evaporate in a manner that respects unitarity, with the initially hidden information gradually retrieved through non-thermal correlations in the emitted radiation. The implications of this integration are multifaceted. The QMM provides a natural ultraviolet cutoff, potentially altering how vacuum polarization and charge renormalization behave at trans-Planckian energies, and suggests novel perspectives on charged black holes, allowing their detailed quantum microstates to be recorded and later recovered from subtle features in the outgoing quanta. In cosmology, early-universe electromagnetic fields might leave distinct signatures in the cosmic microwave background or large-scale structures, as primordial imprints interact with and are stored in the QMM. These considerations open the possibility of indirect observational tests, such as identifying non-thermal deviations in evaporation spectra of primordial black holes or measuring subtle statistical anomalies in cosmological data. Additionally, laboratory analog experiments and quantum simulators of discretized gauge theories might mimic aspects of QMM imprinting, enabling controlled explorations of QMM-inspired principles and offering a tangible route to understanding how quantum information could be managed by space–time quanta. By refraining from relying on specific geometries, nonlocal processes, or observer-dependent constructions, and by respecting both gauge invariance and the equivalence principle, the QMM scenario presents itself as a robust candidate for unification. Nonetheless, numerous open questions remain. Future steps involve incorporating non-Abelian gauge fields, understanding dynamical quantum geometry within QMM, and developing a comprehensive renormalization scheme that ties the high-energy predictions of QMM to low-energy effective field theories. As research progresses, this framework is expected to contribute to a deeper understanding of how quantum information and geometry coalesce into a unified description of fundamental physics.
Author Contributions
F.N. developed the research concept and prepared the initial manuscript draft. V.V. and E.M. critically reviewed the manuscript, contributed to the formalism, and aided in its revision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. All theoretical results are derived from the proposed Quantum Memory Matrix framework, and no datasets are associated with this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rovelli, C. Loop Quantum Gravity. Living Rev. Relativity 1998, 1, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Lewandowski, J. Background Independent Quantum Gravity: A Status Report. Class. Quantum Gravity 2004, 21, R53–R152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C. Black Hole Entropy from Loop Quantum Gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3288–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Pawlowski, T.; Singh, P. Quantum Nature of the Big Bang: Improved Dynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 084003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polchinski, J. String Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Maldacena, J. The Large-N Limit of Superconformal Field Theories and Supergravity. Adv. Theor. Math. Phys. 1998, 2, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, S.B.; Lippert, M. The Information Paradox and the Black Hole Partition Function. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 024006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Ultraviolet Divergences in Quantum Theories of Gravitation. In General Relativity: An Einstein Centenary Survey; Hawking, S.W., Israel, W., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1979; pp. 790–831. [Google Scholar]
- Reuter, M.; Saueressig, F. Renormalization Group Flow of Quantum Einstein Gravity in the Einstein-Hilbert Truncation. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 65, 065016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W. Breakdown of Predictability in Gravitational Collapse. Phys. Rev. D 1976, 14, 2460–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W. Particle Creation by Black Holes. Commun. Math. Phys. 1975, 43, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unruh, W.G. Notes on Black-Hole Evaporation. Phys. Rev. D 1976, 14, 870–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskill, J. Do Black Holes Destroy Information? Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 1992, 1, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ’t Hooft, G. Dimensional Reduction in Quantum Gravity. Conf. Proc. C 1993, 930308, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susskind, L. The World as a Hologram. J. Math. Phys. 1995, 36, 6377–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almheiri, A.; Marolf, D.; Polchinski, J.; Sully, J. Black Holes: Complementarity or Firewalls? J. High Energy Phys. 2013, 2013, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.D. The Fuzzball Proposal for Black Holes: An Elementary Review. Fortschr. Phys. 2005, 53, 793–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldacena, J.; Susskind, L. Cool Horizons for Entangled Black Holes. Fortschr. Phys. 2013, 61, 781–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukart, F.; Brasher, R.; Marx, E. The Quantum Memory Matrix: A Unified Framework for the Black Hole Information Paradox. Entropy 2024, 26, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peskin, M.E.; Schroeder, D.V. An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, S. The Quantum Theory of Fields, Vol. 1: Foundations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai, J.J.; Napolitano, J. Modern Quantum Mechanics; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dyson, F.J. Divergent Series in Quantum Electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. 1952, 85, 631–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombelli, L.; Koul, R.K.; Lee, J.; Sorkin, R.D. A Quantum Source of Entropy for Black Holes. Phys. Rev. D 1987, 34, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossenfelder, S. Minimal Length Scale Scenarios for Quantum Gravity. Living Rev. Relativity 2013, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.G. Confinement of Quarks. Physical Review D 1974, 10, 2445–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).