Submitted:
02 January 2025
Posted:
03 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
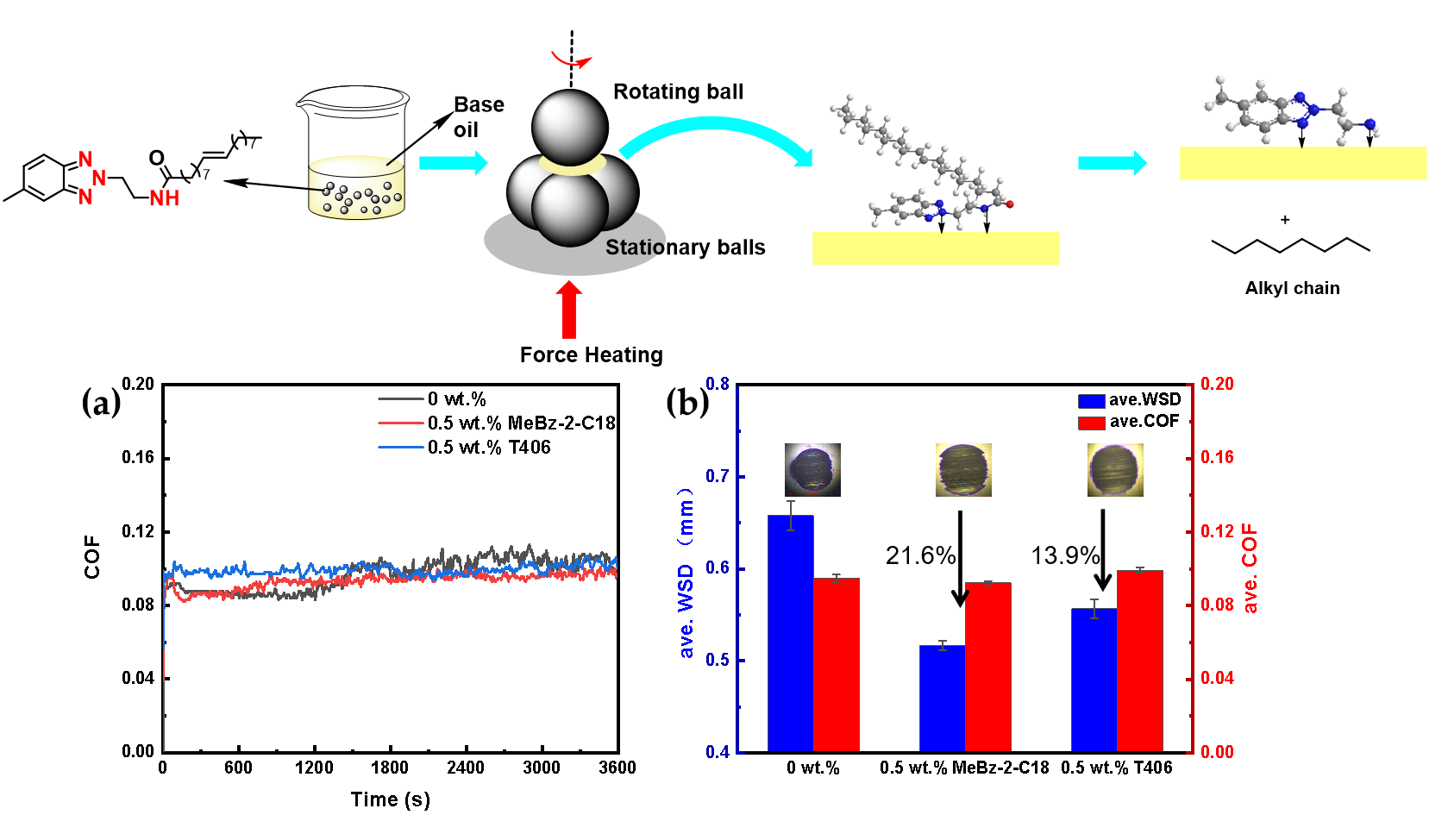
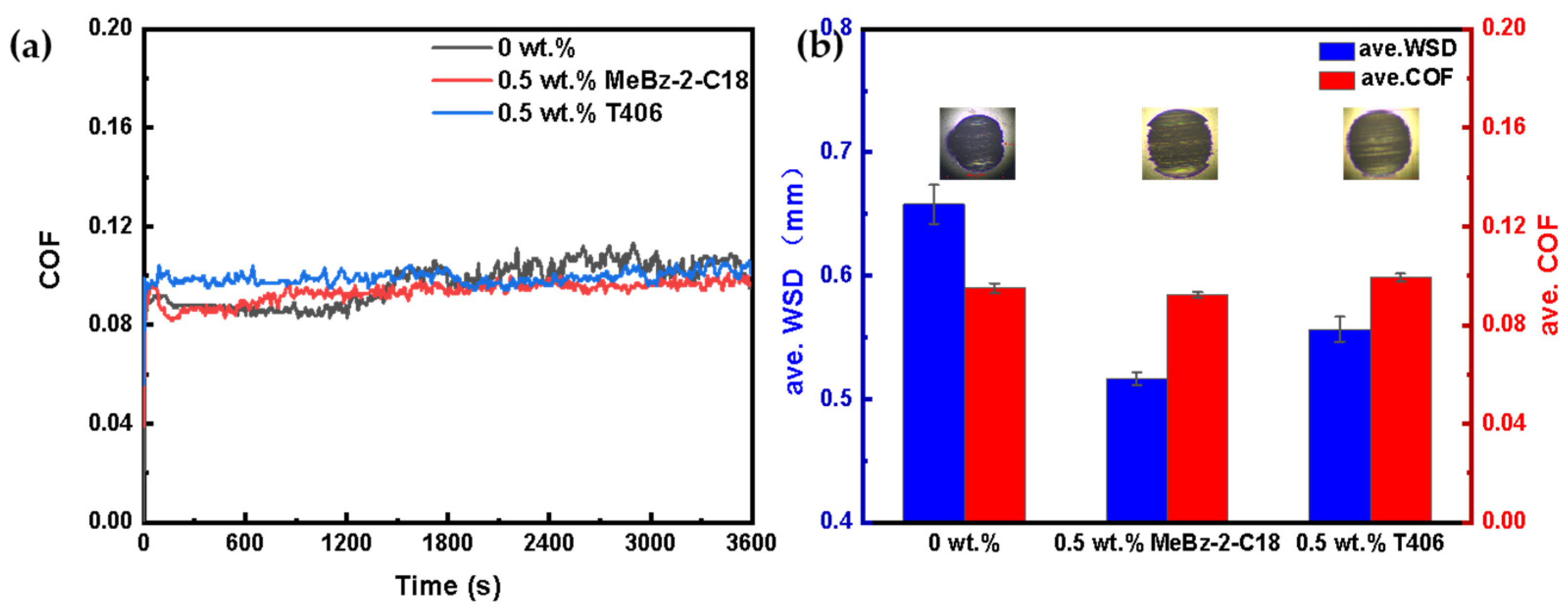
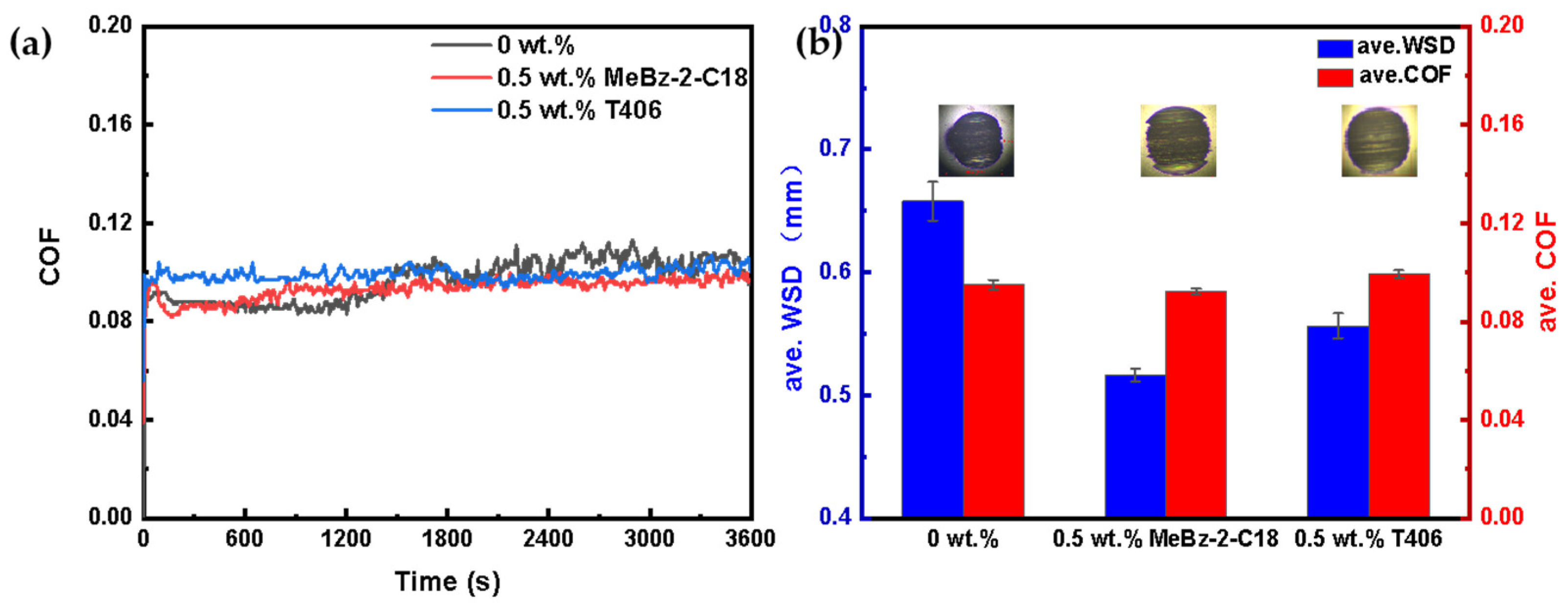
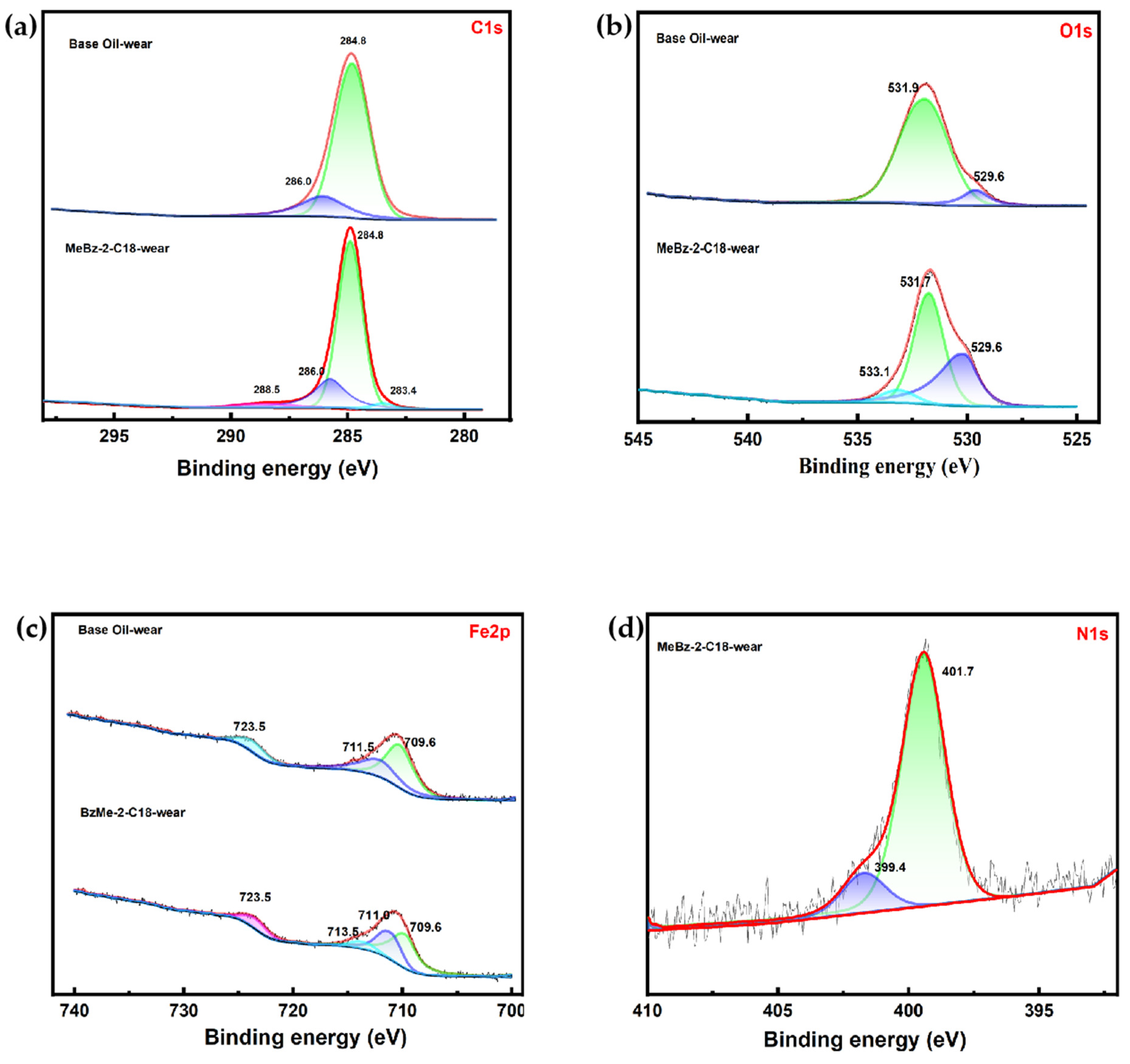
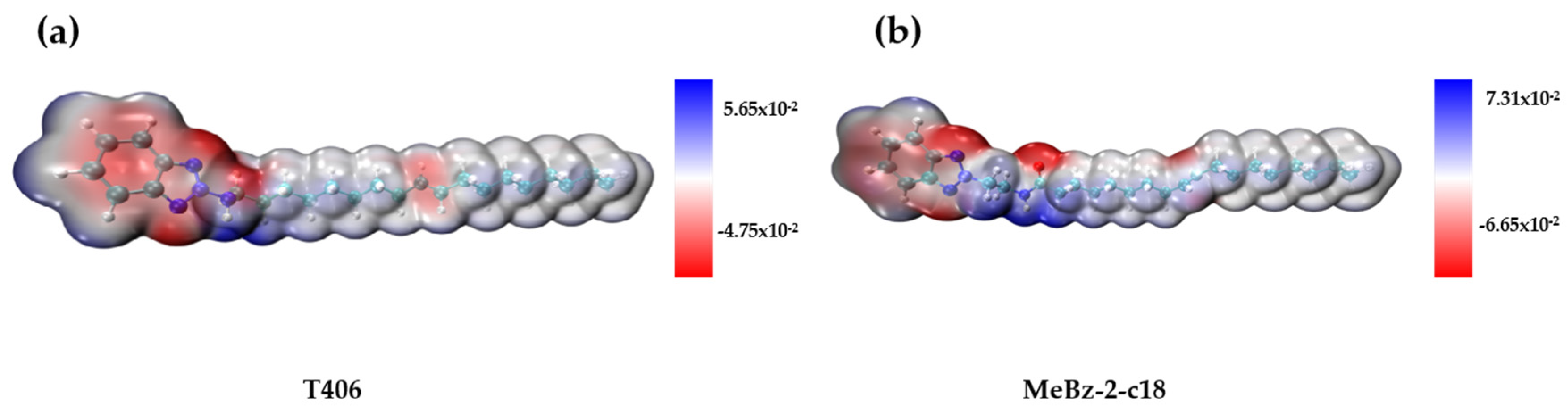
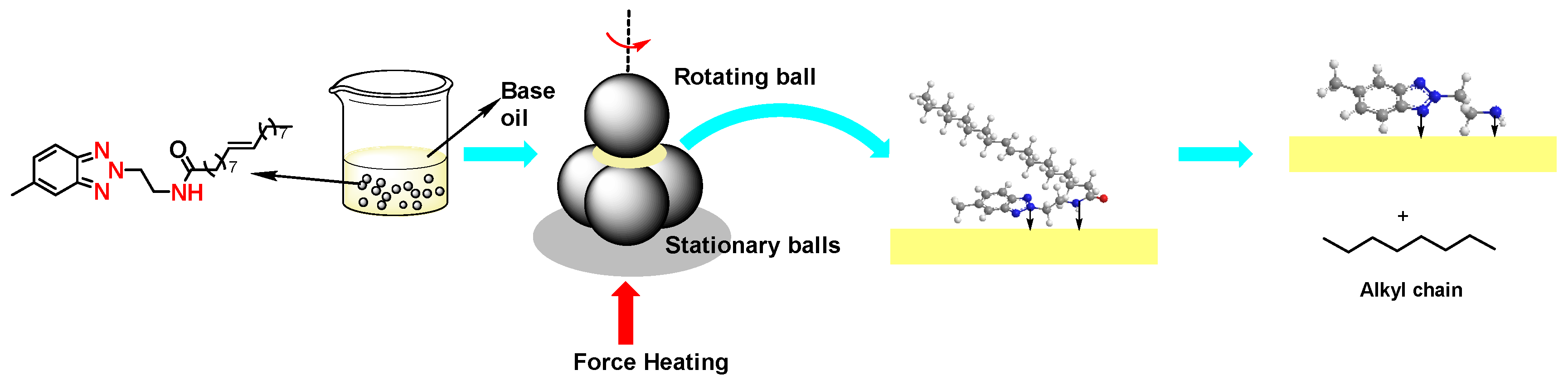
Benzotriazole and its derivatives show good tribological properties, anti-oxidation, anti-corrosion, rust prevention and dispersion capabilities as lubricating additives, becoming the common multifunctional additives. And how to avoid sulfur- or phosphorus-introduction to improve their functionality and the compatibility with hydrocarbons is the forefront research. In this study, methylbenzotriazole and oleic acid were applied to synthesize a new methylbenzotriazole-amide that with long alkyl-chain (E)-N-(2-(5-methyl-2H-benzodiazole-2-yl)ethyl)octadec-9-enamide (MeBz-2-C18), which was characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), high-resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS), FT-IR and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The thermal stability and tribological properties of MeBz-2-C18 were compared with the commercially available benzotriazole oleamide (T406). The results show that MeBz-2-C18 has better thermal stability and base oil compatibility than that of T406, and 0.5 wt.% addition of MeBz-2-C18 could decrease the average wear scar diameter (ave. WSD) by 21.6%. The wear surface analysis and DFT calculation show that the amide group in MeBz-2-C18 is preferentially broken during friction, which would reduce the interfacial shear force and easily react with the metal surface to form iron oxide film, thus demonstrating a better anti-wear and friction reducing performance, indicating its potential application as an environmental friendly multifunctional additive.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
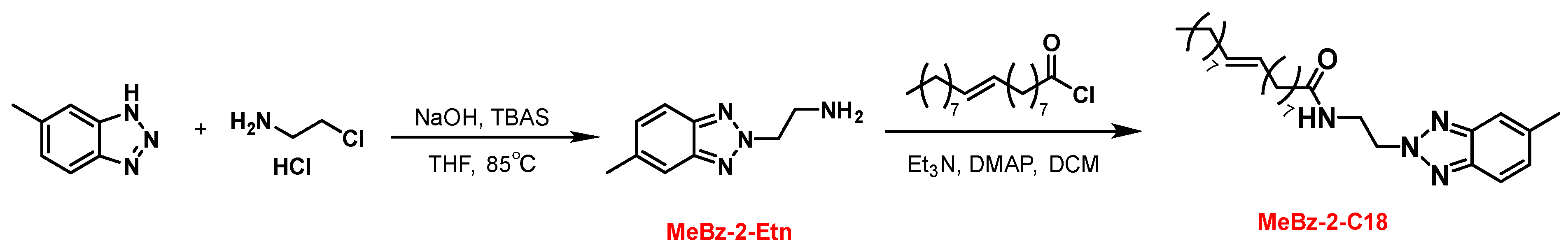
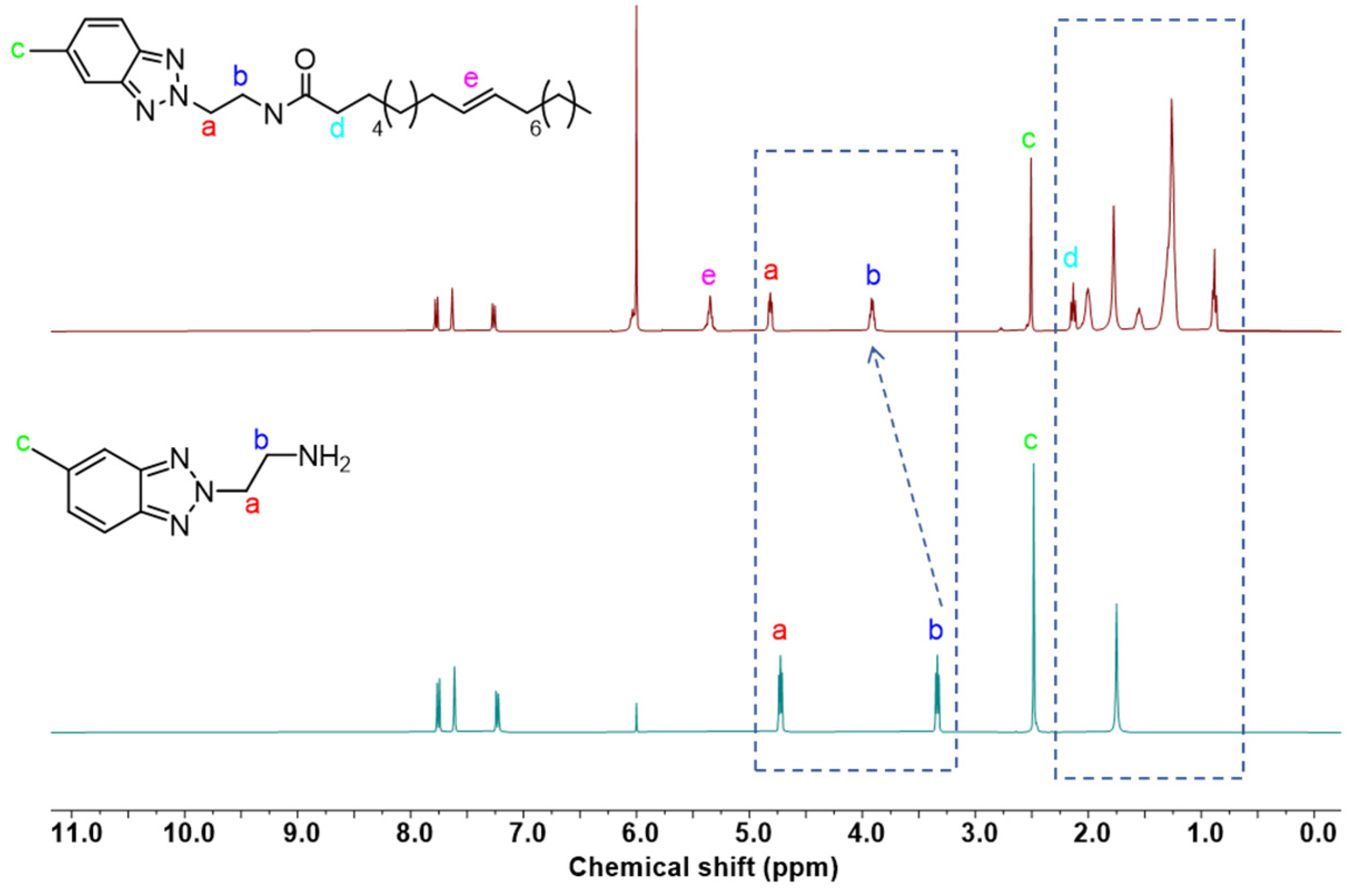
2.1. Synthesis of MeBz-2-C18
2.2. Stability Characterization
2.2.1. Thermal Stability
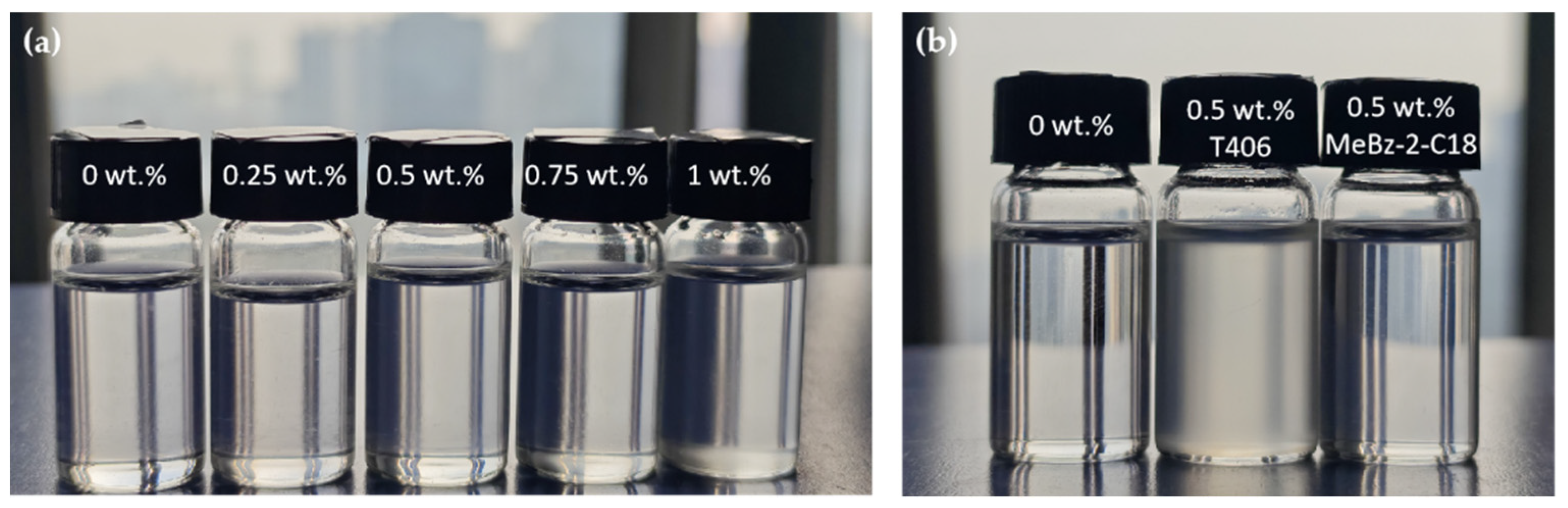
2.2.2. Storage Stability in Base Oil
2.3. Tribological Behaviors
2.3.1. Different Additions of MeBz-2-C18
2.3.2. Comparison with Commercial Additive
2.4. Lubrication Mechanism
2.4.1. Wear Surface Analysis
2.4.2. DFT Calculations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of MeBz-2-C18
3.3. Characterizations
3.4. Preparation of Oil Samples
3.5. Tribological Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jackson, M. Environmentally Compatible Lubricants: Focusing on the Long-Term. NLGI Spokesman 1995, 59, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T.; Xue, Q. Research and development status of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds and their derivatives as multifunctional lubricating oil additives. Tribology 1994, 4, 370–381. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, P.K.; Dpatel, P.D. Metal Complexation Studies of 1-(4-Carboxy-3-hydroxy-4-phenyl Amino Methyl) Benzotriazole. Journal of Chemistry 2009, 6(2), 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; He, Z.; Han, S.; Tang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, X. Tribological Properties Study of N-Containing Heterocyclic Imidazoline Derivatives as Lubricant Additives in Water-Glycol. Tribology International 2016, 104, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Ren, T.; Zeng, X.; van der Heide, E. Hydrolytic Stability and Tribological Properties of N-Containing Heterocyclic Borate Esters as Lubricant Additives in Rapeseed Oil. Tribology International 2014, 73, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, X.; Huang, X. Synthesis and tribological properties of biodegradable lubricating oil additives. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals 2011, 42(7), 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Yu, L. The Effect of Tribenyl Phosphate and Dibutyl Phosphite as- Additives on the Tribological Behaviors of Rapeseed Oil. Tribology 2000, 2, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Fan, B.; Ren, T.; Zhao, Y. Tribological Study and Mechanism of B–N and B–S–N Triazine Borate Esters as Lubricant Additives in Mineral Oil. Tribology International 2015, 88, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashry, E.-S.H.; El-Rafey, M.E.; El-Nagdi, M.H.; Abou-Elnaga, H.H.; Bakry, W.M.A.; Boghdady, Y.M. Synthesis of Benzotriazole Derivatives as Antioxidants for Industrial Lubricating Oils. Lubrication Science 2006, 18(2), 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Hua, X.; Zhang, L. Study on properties and application of T581 multifunctional metal passivator. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals 2008, 3, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Yan, H.; Yang, H. Preparation of highly dispersed silver powder with benzotriazole as dispersant. Electronic Components and Materials 2020, 39(10), 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Niu, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhan, N.; Zou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, J. Corrosion Inhibition Mechanisms of Triazole Derivatives on Copper Chemical Mechanical Polishing: Combined Experiment and DFT Study. Applied Surface Science 2024, 654, 159469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rao, W.; Liu, W. Tribologcal Behavior of an S-P Containing Benzotriazole Derivative as an Additive in Rapeseed Oil. Tribology 2002, 2, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; He, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S. Tribological Synergy Study of a Benzotrizole Derivative and Tricresyl Phosphate. Lubrication Engineering 2009, 34(5), 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, S. Tribological Properties of Benzotrizole Alcohol Derivative. Journal of East China Jiaotong University 2009, 26(1), 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yan, F.; Guo, Y. Characterization of methylphenyltriazole fatty amine salt. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals 2016, 47(7), 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Yang, F.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Tang, Y. Preparation and Tribological Behaviors of Sulfur- and Phosphorus-Free Organic Friction Modifier of Amide–Ester Type. Lubricants 2024, 12(6), 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros, M.I.; Bouchet, J.; Raoult, I.; Le Mogne, Th.; Martin, J.M.; Kasrai, M.; Yamada, Y. Friction Reduction by Metal Sulfides in Boundary Lubrication Studied by XPS and XANES Analyses. Wear 2003, 254(9), 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, L. High-Performance Lubricant Additives Based on Modified Graphene Oxide by Ionic Liquids. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2015, 452, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Cai, M.; Shi, L. Effective Sugar-Derived Organic Gelator for Three Different Types of Lubricant Oils to Improve Tribological Performance. Friction 2020, 8(6), 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Song, H. Preparation and Tribological Properties of Core-Shell Fe3O4@C Microspheres. Tribology International 2019, 129, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Gao, C.; Song, N.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P. In-Situ Formed Carbon Based Composite Tribo-Film with Ultra-High Load Bearing Capacity. Tribology International 2020, 152, 106577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Blakeslee, D.M.; Powell, C.J.; John R Rumble, J. Development of the Web-Based NIST X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Database. Data Science Journal 2006, 1(1), 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, I.; López, E. R.; Reichelt, M.; Fernández, J. Tribo-Chemical Reactions of Anion in Pyrrolidinium Salts for Steel–Steel Contact. Tribology International 2014, 77, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, H.; Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Xue, Q. Room Temperature Ionic Liquid 1-Ethyl-3-Hexylimidazolium-Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-Imide as Lubricant for Steel–Steel Contact. Tribology International 2004, 37(7), 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item | MeBz-2-Etn | MeBz-2-C18 | T406 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decomposition temperature (°C) | Initial | 19.7 | 185.5 | 76.8 |
| Max. | 217.4 | 374.4 | 221.1 | |
| Terminal | 236.0 | 434.7 | 420.3 | |
| Residual mass (%) | @ Max. decomposition | 15.1 | 22.4 | 39.2 |
| @200 ℃ | 44.8 | 99.9 | 71.9 | |
| @300 ℃ | 1.8 | 89.3 | 11.0 | |
| @400 ℃ | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




